O
Obesity Management
ANOREXIANTS
| Name | Availability | Dosage | Side Effects |
| Diethylpropion (Tenuate, Tenuate Dospan) |
T: 25 mg, T (CR): 75 mg | 25 mg 3–4 times/day or 75 mg once daily in midmorning | Headaches, euphoria, palpitations, hypertension, pulmonary hypertension, valvular heart disease, seizures, bone marrow depression, dependence, withdrawal psychosis |
| Liraglutide (Victoza) | I: 18 mg/3 ml | SQ: Initially, 0.6 mg/day. May increase by 0.6 mg/day weekly up to 3 mg/day | Diarrhea, constipation, dyspepsia, fatigue, vomiting, increased heart rate, renal impairment |
| Lorcaserin (BelViq, Belviq XR) |
C: 10 mg T: 20 mg |
(Belviq) 10 mg 2 times/day (Belviq XR): 20 mg once daily | Nausea, headache, dizziness, fatigue, dry mouth, diarrhea, constipation, hypoglycemia, hallucinations, decreased white/red blood cells, euphoria, cognitive impairment |
| Naltrexone/bupropion (Contrave) | T: 8 mg/90 mg | Titrate weekly up to 2 tablets 2 times/day (1 tablet once daily, then 1 tablet 2 times/day, then 2 tablets in am and 1 in pm, then 2 tablets 2 times/day) | Suicidal ideation, mood changes, seizures, increased HR with or without B/P, allergic reactions, hepatic toxicity, nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, dry mouth, angle closure glaucoma |
| Orlistat (Alli, Xenical) | C: 60 mg, 120 mg |
Alli: 60 mg up to tid with meals Xenical: 120 mg tid with each meal containing fat | Flatulence, rectal incontinence, oily stools, cholelithiasis, abdominal/rectal pain, hepatitis, pancreatitis, nausea |
| Phenteramine (Apidex-P, Suprenza) |
C: 15 mg, 30 mg, 37.5 mg T: 37.5 mg T (ODT): 15 mg, 30 mg, 37.5 mg |
15–37.5 mg/day in 1 or 2 divided doses ODT: 15–37.5 mg once daily in morning | Headaches, euphoria, palpitations, hypertension, pulmonary hypertension, valvular heart disease, tremor, dependence, withdrawal psychosis, CNS stimulation, GI complaints |
| Phenteramine/topiramate (Qsymia) | C: 13.75 mg/23 mg | 3.75 mg/23 mg to 15 mg/92 mg once daily in the morning | Paresthesia, dizziness, insomnia, depression, tachycardia, cognitive impairment, angle-closure glaucoma, hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis, constipation, dry mouth, suicidal ideation, kidney stones |
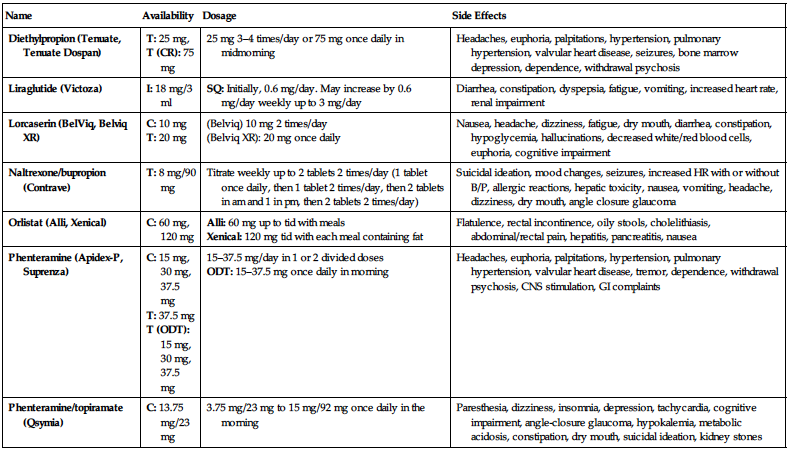
AS, Appetite suppressant; B/P, blood pressure; C, capsules; CNS, central nervous system; CR, controlled-release; DI, digestion inhibitor; GI, gastrointestinal; HR, heart rate; I, injection; ODT, orally disintegrating tablets; SQ, subcutaneously; T, tablets.
Osteoporosis
BISPHOSPHONATES
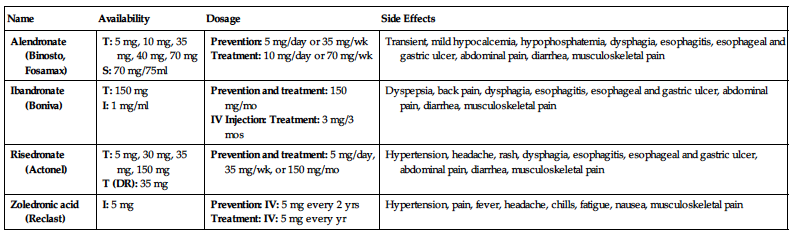
| Name | Availability | Dosage | Side Effects |
| Alendronate (Binosto, Fosamax) |
T: 5 mg, 10 mg, 35 mg, 40 mg, 70 mg S: 70 mg/75ml |
Prevention: 5 mg/day or 35 mg/wk Treatment: 10 mg/day or 70 mg/wk | Transient, mild hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, dysphagia, esophagitis, esophageal and gastric ulcer, abdominal pain, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain |
| Ibandronate (Boniva) |
T: 150 mg I: 1 mg/ml |
Prevention and treatment: 150 mg/mo IV Injection: Treatment: 3 mg/3 mos | Dyspepsia, back pain, dysphagia, esophagitis, esophageal and gastric ulcer, abdominal pain, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain |
| Risedronate (Actonel) |
T: 5 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg, 150 mg T (DR): 35 mg | Prevention and treatment: 5 mg/day, 35 mg/wk, or 150 mg/mo | Hypertension, headache, rash, dysphagia, esophagitis, esophageal and gastric ulcer, abdominal pain, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain |
| Zoledronic acid (Reclast) | I: 5 mg |
Prevention: IV: 5 mg every 2 yrs Treatment: IV: 5 mg every yr | Hypertension, pain, fever, headache, chills, fatigue, nausea, musculoskeletal pain |
SERM
| Name | Availability | Dosage | Side Effects |
| Raloxifene (Evista) | T: 60 mg | Prevention and treatment: 60 mg/day | Peripheral edema, hot flashes, arthralgia, leg cramps, muscle spasms, flu syndrome, infection |

PARATHYROID HORMONE
| Name | Availability | Dosage | Side Effects |
| Teriparatide (Forteo) | I: 250 mcg/ml syringe delivers 20 mcg/dose | Treatment: 20 mcg subcutaneously once daily | Hypercalcemia, muscle cramps, nausea, dizziness, headache |

CALCITONIN
| Name | Availability | Dosage | Side Effects |
| Calcitonin (Fortical, Miacalcin) |
I (Miacalcin): 200 units/ml Nasal (Fortical, Miacalcin): 200 units/activation |
Treatment: IM/Subcutaneous (Miacalcin): 100 units every other day Nasal: 200 units in 1 nostril daily | Rhinitis, local nasal irritation. Injection: nausea, local inflammation, flushing of face, hands |

