P
Parkinson’s Disease Treatment
TYPES OF MEDICATIONS FOR PARKINSON’S DISEASE DOPAMINE PRECURSOR
Levodopa/carbidopa:
Levodopa: Dopamine precursor supplementation to enhance dopaminergic neurotransmission. A small amount of levodopa crosses the blood-brain barrier and is decarboxylated to dopamine, which is then available to stimulate dopaminergic receptors.
Carbidopa: Inhibits peripheral decarboxylation of levodopa, decreasing its conversion to dopamine in peripheral tissues, which results in an increased availability of levodopa for transport across the blood-brain barrier.
COMT INHIBITORS
Entacapone, tolcapone: Reversible inhibitor of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT). COMT is responsible for catalyzing levodopa. In the presence of a decarboxylase inhibitor (carbidopa), COMT becomes the major metabolizing enzyme for levodopa in the brain and periphery. By inhibiting COMT, higher plasma levels of levodopa are attained, resulting in more dopaminergic stimulation in the brain and lessening the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
DOPAMINE RECEPTOR AGONISTS
Bromocriptine: Stimulates postsynaptic dopamine type 2 receptors in the neostriatum of the CNS.
Pramipexole: Stimulates dopamine receptors in the striatum of the CNS.
Ropinirole: Stimulates postsynaptic dopamine D2 type receptors within the caudate putamen in the brain.
MONOAMINE OXIDASE B INHIBITORS
Rasagiline, Selegiline: Increase dopaminergic activity due to irreversible inhibition of monoamine oxidase type B (MAO B). MAO B is involved in the oxidative deamination of dopamine in the brain.
MEDICATIONS FOR TREATMENT OF PARKINSON’S DISEASE
| Name | Type | Availability | Dosage | Side Effects |
| Amantadine | Dopamine agonist |
C: 100 mg Syrup: 10 mg/ml T: 100 mg | 100 mg 2 times/day. May increase up to 400 mg/day in divided doses | Cognitive impairment, confusion, insomnia, hallucinations, levido reticularis |
| Carbidopa/levodopa (Parcopa, Rytary, Sinemet, Sinemet CR) | Dopamine precursor |
OD (Parcopa): 10/100 mg, 25/100 mg, 25/250 mg Immediate-release (Sinemet): 10/100 mg, 25/100 mg, 25/250 mg Extended-release (Sinemet CR): 25/100 mg, 50/200 mg (Rytary): 23.75 mg/95 mg, 36.25 mg/145 mg, 48.75 mg/195 mg, 61.25 mg/245 mg |
Parcopa: 300–1,500 mg levodopa in divided doses Sinemet: 300–1,500 mg levodopa in divided doses Sinemet CR: Initially, 400 mg/day in 2 divided doses. May increase up to 1,600 mg levodopa in divided doses Rytary: Initially, 23.75 mg/95 mg 3 times/day. May increase up to 612.5 mg/2,450 mg per day in divided doses | Anorexia, nausea, orthostatic hypotension initially; hallucinations, confusion, sleep disturbances with chronic use, constipation, dry mouth, headache, dyskinesia |
| Entacapone (Comtan) | COMT inhibitor | T: 200 mg | 200 mg 3–4 times/day up to maximum of 8 times/day (1,600 mg) | Dyskinesias, nausea, diarrhea, urine discoloration |
| Pramipexole (Mirapex, Mirapex ER) | Dopamine agonist |
T: 0.125 mg, 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 0.75 mg, 1 mg, 1.5 mg ER: 0.375 mg, 0.75 mg, 1.5 mg, 2.25 mg, 3 mg, 3.75 mg, 4.5 mg |
T: Initially, 0.125 mg 3 times/day. May increase q5–7 days. Usual dose: 0.5–1.5 mg 3 times/day ER: Initially, 0.375 mg once daily. May increase q5–7 days by 0.75 mg/dose up to 4.5 mg once daily | Nausea, drowsiness, lower extremity edema, postural hypotension, confusion, toxic psychosis (avoid use in pts with dementia) |
| Rasagiline (Azilect) | MAO B inhibitors | T: 0.5 mg, 1 mg | 0.5–1 mg once daily | Nausea, orthostatic hypotension |
| Ropinirole (Requip, Requip XL) | Dopamine agonist |
T: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, 4 mg, 5 mg XL: 2 mg, 4 mg, 6 mg, 8 mg, 12 mg |
T: Initially, 0.25 mg 3 times/day. May increase at weekly intervals to 0.5 mg 3 times/day, then 0.75 mg 3 times/day, then 1 mg 3 times/day. May then increase by 1.5 mg/day up to 9 mg/day, then by 3 mg/day up to total dose of 24 mg/day in divided doses XL: Initially, 2 mg/day for 1–2 wks, then increase by 2 mg/day at weekly intervals | Nausea, drowsiness, lower extremity edema, postural hypotension, confusion, toxic psychosis (avoid use in pts with dementia) |
| Rotigotine (Neupro) | Dopamine agonist | Transdermal patch: 1 mg/24 hrs, 2 mg/24 hrs, 3 mg/24 hrs, 4 mg/24 hrs, 6 mg/24 hrs, 8 mg/24 hrs |
Early stage: Initially, 2 mg/24 hrs up to 6 mg/24 hrs Advanced stage: Initially, 4 mg/24 hrs up to 8 mg/24 hrs | Peripheral edema, dizziness, fatigue, application site reactions, sleep disturbances, dyskinesia, nausea, arthralgia |
| Selegiline (Eldepryl, Zelapar) | MAO B inhibitor |
C (Eldepryl): 5 mg OD (Zelapar): 1.25 mg |
C: 5 mg with breakfast and lunch OD: 1.25–2.5 mg daily in the morning | Nausea, orthostatic hypotension |
| Tolcapone (Tasmar) | COMT inhibitor | T: 100 mg | Initially, 100 mg 3 times/day. May increase to 200 mg 3 times/day | Dyskinesias, nausea, diarrhea, urine discoloration |
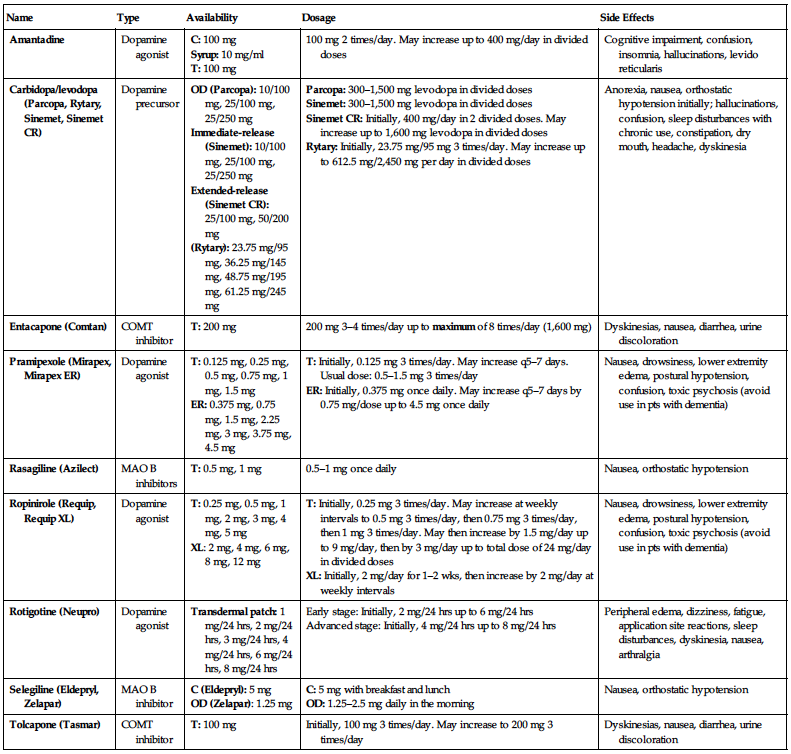
C, Capsules; COMT, catechol-O-methyltransferase; ER, extended-release; I, injection; MAO B, monoamine oxidase B; OD, orally disintegrating; T, tablets; XL, extended-release.
Proton Pump Inhibitors
PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS
| Name | Availability | Indications | Usual Dosage | Side Effects |
| Dexlansoprazole (Dexilant) | C: 30 mg, 60 mg | Erosive esophagitis, heartburn associated with nonerosive GERD | 30–60 mg/day | Diarrhea, abominal pain, nausea, upper respiratory tract infection, vomiting, flatulence |
| Esomeprazole (Nexium) |
C: 20 mg, 40 mg I: 20 mg, 40 mg | Helicobacter pylori eradication, GERD, erosive esophagitis | 20–40 mg/day | Headaches, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea |
| Lansoprazole (Prevacid) |
C: 15 mg, 30 mg T (ODT): 15 mg, 30 mg | Duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer, NSAID-associated gastric ulcer, hypersecretory conditions, H. pylori eradication, GERD, erosive esophagitis | 15–30 mg/day | Diarrhea, skin rash, pruritus, headaches |
| Omeprazole (Prilosec) | C: 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg | Duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer, hypersecretory conditions, H. pylori eradication, GERD, erosive esophagitis | 20–40 mg/day | Headaches, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea |
| Omeprazole and Sodium Bicarbonate (Zegerid) | P: 20 mg, 40 mg | Duodenal ulcer, benign gastric ulcer, GERD, erosive esophagitis | 20–40 mg/day | Headaches, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea |
| Pantoprazole (Protonix) |
T: 20 mg, 40 mg I: 40 mg | Erosive esophagitis, hypersecretory conditions | 40 mg/day | Diarrhea, headaches |
| Rabeprazole (Aciphex) |
T: 20 mg S: 5 mg, 10 mg | Duodenal ulcer, hypersecretory conditions, H. pylori eradication, GERD, erosive esophagitis | 20 mg/day | Headaches |
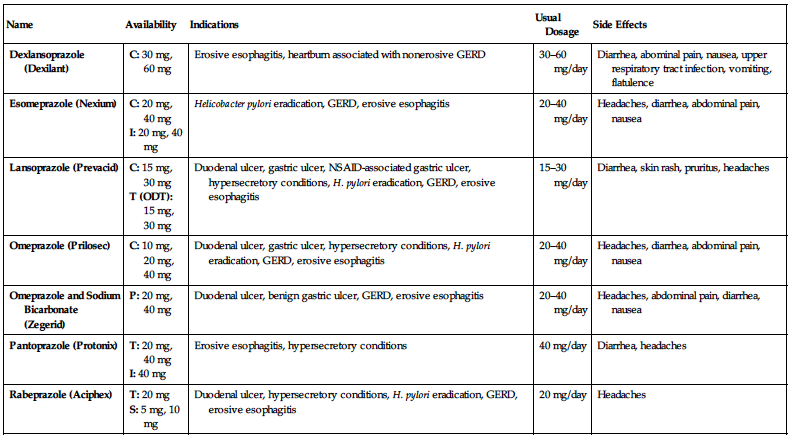
C, Capsules; GERD, gastroesophageal reflux disease; I, injection; NSAID, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug; ODT, orally disintegrating tablets; P, powder for suspension; S, sprinkles; T, tablets.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease associated with progressive disability, systemic complications, early death, and socioeconomic costs. RA affects most joints and their surrounding tissues. RA is characterized by synovial inflammation and hyperplasia, autoantibody production (e.g., rheumatoid factor), cartilage and bone destruction, and systemic features (e.g., cardiovascular, pulmonary, psychological, skeletal disorders). The clinical hallmark of RA is polyarticular synovial inflammation of peripheral joints (typically in the hands, resulting in pain, stiffness, and some degree of irreversible joint damage; deformity; and disability).
Medications used in RA include disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDS) and biologic agents, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors.
DMARDS
| Name | Dosage | Side Effects/Comments |
| Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) |
Induction: 400–600 mg/day for 4–12 wks Maintenance: 200–400 mg/day | Side Effects: nausea, epigastric pain, hemolysis may occur in pts with G6PD deficiency, retinal toxicity with long-term use |
| Leflunomide (Arava) |
Induction: 100 mg/day × 3 days Maintenance: 10–20 mg/day |
Side Effects: diarrhea, respiratory tract infection, hypertension, headache, reversible alopecia, rash, myelosuppression, and/or elevated hepatic enzymes Comments: contraindicated for use during pregnancy |
|
Methotrexate (oral) (Rheumatrex, Trexall) Methotrexate (injectable) Otrexup, Rasuvo) |
Induction: 7.5–10 mg PO once/wk Maintenance: 7.5–25 mg PO once wkly Induction: 7.5 PO once wkly Maintenance: 10–25 mg IM or SQ once wkly |
Side Effects: stomatitis, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, hepatic enzyme elevations, thrombocytopenia Comments: not recommended in pts with CrCl <30 ml/min; should not be prescribed for women who are or may become pregnant |
| Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) |
Induction: 3–4 g/day in divided doses Maintenance: 2 g/day in divided doses | Side Effect: headache, nausea, anorexia, rash, hemolysis may occur in pts with G6PD deficiency |
BIOLOGIC AGENTS
TNF Inhibitors
| Name | Dosage | Side Effects/Comments |
| Adalimumab (Humira) | 40 mg SQ once wkly or q2wks |
Side Effects: headache, skin rash, positive ANA titer, antibody development, injection site reaction (erythema, itching, pain, swelling), upper respiratory tract infection Comments: increased risk for serious infections (e.g., tuberculosis, invasive fungal infections), avoid use in pts with recent history of malignancy or pre-existing demyelinating disorders |
| Certolizumab (Cimzia) |
Induction: 400 mg SQ at 0, 2, 4 wks Maintenance: 200 mg SQ every other week or 400 mg q4wks |
Side Effects: nausea, infection, upper respiratory tract infection, skin rash Comments: see adalimumab |
| Etanercept (Enbrel) | 25 mg SQ 2 times/wk or 50 mg SQ once/wk |
Side Effects: headache, skin rash, diarrhea, injection site reactions (e.g., erythema, swelling), upper respiratory tract infection, rhinitis Comments: see adalimumab |
| Golimumab (Simponi, Simponi Aria) |
Simponi: 50 mg SQ once monthly Simponi Aria: Induction: 2 mg/kg IV at 0 and 4 wks Maintenance: 2 mg/kg IV q8wks |
Side Effects: positive ANA titer, upper respiratory tract infection (e.g., nasopharyngitis, rhinitis) Comments: see adalimumab |
| Infliximab (Remicade) |
Induction: 3 mg/kg IV at 0, 2, and 6 wks Maintenance: 3 mg/kg IV q8wks |
Side Effects: nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, increased ANA titer, upper respiratory tract infection, sinusitis, cough, pharyngitis Comments: see adalimumab |
OTHER BIOLOGIC AGENTS
| Name | Dosage | Side Effects/Comments |
| Abatacept (Orencia) |
IV: 500 mg, 750 mg, or 1,000 mg IV at 0, 2, and 4 wks, then q4wks SQ: 125 mg SQ once/wk |
Side Effects: nausea, UTIs, acute exacerbation of COPD, hypertension, headache, dizziness Comments: may increase risk of serious infections (e.g., pneumonia, pyelonephritis, cellulitis, diverticulitis) |
| Rituximab (Rituxan) | 1,000 mg IV twice, 2 wks apart |
Side Effects: hypotension, peripheral edema, abdominal pair anemia, arthralgia, infusion site reactions Comments: Pts at high risk for hepatitis B virus infection should be screened before beginning therapy |
| Tocilizumab (Actemra) |
IV: Induction: 4 mg/kg IV q4wks Maintenance: 8 mg/kg q4 wks SQ: Induction: 162 mg SQ every other week Maintenance: 162 mg once wkly |
Side Effects: hypertension, upper abdominal pain, increased ALT/AST, injection site reactions, neutropenia, dyslipidemia Comments: severe complications including GI perforation and hypersensitivity with anaphylaxis have been reported |
| Tofacitinib (Xeljanz) | 5 mg PO bid |
Side Effects: diarrhea, nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory infections, headache hypertension, increased LFT, dyslipidemia, cytopenias have been reported Comments: screening for tuberculosis recommended, increased incidence of solid cancers detected |
ANA, Antinuclear antibodies; CNS, central nervous system; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; GI, gastrointestinal; UTI, urinary tract infection.