SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: GI disturbances (mild diarrhea, nausea, vomiting), headache, oral/vaginal candidiasis. Occasional: Generalized rash, urticaria.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Antibiotic-associated colitis, other superinfections (abdominal cramps, severe watery diarrhea, fever) may result from altered bacterial balance of GI tract. Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, acute interstitial nephritis, occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of allergies, esp. penicillins, cephalosporins, renal impairment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Promptly report rash, diarrhea (fever, abdominal pain, mucus and blood in stool may indicate antibiotic-associated colitis). Be alert for superinfection: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, anal/genital pruritus, black “hairy” tongue, oral mucosal changes (ulceration, pain, erythema). Monitor renal/hepatic function tests.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Continue antibiotic for full length of treatment. • Space doses evenly. • Take with meals if GI upset occurs. • Thoroughly crush or chew the chewable tablets before swallowing. • Report rash, diarrhea, other new symptoms.
amoxicillin/clavulanate
a-mox-i-sil-in/klav-yoo-la-nate
(Amoclan, Apo-Amoxi-Clav
 , Augmentin, Augmentin ES 600, Augmentin XR, Clavulin
, Augmentin, Augmentin ES 600, Augmentin XR, Clavulin
 , Novo-Clavamoxin
, Novo-Clavamoxin
 )
)
Do not confuse Augmentin with amoxicillin or Azulfidine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Penicillin. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of susceptible infections due to streptococci, E. coli, E. faecalis, P. mirabilis, beta-lactamase producing H. influenzae, Klebsiella spp., M. catarrhalis, and S. aureus (not methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [MRSA]) including lower respiratory, skin and skin structure, UTIs, otitis media, sinusitis. OFF-LABEL: Chronic antimicrobial suppression of prosthetic joint infection.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to amoxicillin, clavulanate, any penicillins; history of cholestatic jaundice or hepatic impairment with amoxicillin/clavulanate therapy. Augmentin XR (additional): Severe renal impairment, hemodialysis pt. Cautions: History of allergies, esp. cephalosporins; renal impairment, infectious mononucleosis.
ACTION
Amoxicillin inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. Clavulanate inhibits bacterial beta-lactamase. Therapeutic Effect: Amoxicillin is bactericidal in susceptible microorganisms. Clavulanate protects amoxicillin from enzymatic degradation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 20%. Partially metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 1–1.3 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta, appears in cord blood, amniotic fluid. Distributed in breast milk in low concentrations. May lead to allergic sensitization, diarrhea, candidiasis, skin rash in infant. Children: Immature renal function in neonate/young infant may delay renal excretion. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Allopurinol may increase incidence of rash. Probenecid may increase concentration, toxicity risk. May decrease effect of oral contraceptives. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST. May cause positive Coombs’ test.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Powder for Oral Suspension (Amoclan, Augmentin): 125 mg–31.25 mg/5 ml, 200 mg–28.5 mg/5 ml, 250 mg–62.5 mg/5 ml, 400 mg–57 mg/5 ml, 600 mg–42.9 mg/5 ml. Tablets (Augmentin): 250 mg–125 mg, 500 mg–125 mg, 875 mg–125 mg. Tablets (Chewable [Augmentin]): 200 mg–28.5 mg, 400 mg–57 mg.
 Tablets (Extended-Release [Augmentin XR]): 1,000 mg–62.5 mg.
Tablets (Extended-Release [Augmentin XR]): 1,000 mg–62.5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
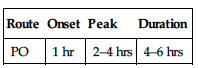
PO
• Store tablets at room temperature. • After reconstitution, oral suspension is stable for 10 days but should be refrigerated. • May mix dose of suspension with milk, formula, or juice and give immediately. • Give without regard to meals. • Give with food to increase absorption, decrease stomach upset. • Instruct pt to chew/crush chewable tablets thoroughly before swallowing. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide extended-release tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Dosage based on amoxicillin component.
Usual Adult Dosage
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 250 mg q8h or 500 mg q8–12h or 875 mg q12h or 2,000 mg q12h.
Usual Pediatric Dosage
PO: CHILDREN OLDER THAN 3 MOS, WEIGHING 40 KG OR MORE: (Mild-Moderate): 500 mg q12h or 250 mg q8h. (Severe): 875 mg q12h or 500 mg q8h. (Extended-Release): 2,000 mg q12h. WEIGHING LESS THAN 40 KG: (Mild-Moderate): 25 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses or 20 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses. (Severe): 45 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses or 40 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses. Maximum Single Dose: 500 mg. LESS THAN 3 MOS: Amoxicillin 30 mg/kg/day divided q12h using 125 mg/5ml suspension only.
Usual Neonate Dosage
PO: NEONATES, CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 3 MOS: 30 mg/kg/day (125 mg/5 ml suspension) in divided doses q12h.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
◀ ALERT ▶ Do not use 875-mg tablet or extended-release tablets for creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min.
Dosage and frequency are modified based on creatinine clearance. Creatinine clearance 10–30 ml/min: 250–500 mg q12h. Creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min: 250–500 mg q24h. HD: 250–500 mg q24h, give dose during and after dialysis. PD: 250 mg q12h.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment (see Contraindications).
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (9%–4%): Diarrhea, loose stools, nausea, skin rashes, urticaria. Rare (less than 3%): Vomiting, vaginitis, abdominal discomfort, flatulence, headache.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Antibiotic-associated colitis, other superinfections (abdominal cramps, severe watery diarrhea, fever) may result from altered bacterial balance. Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, acute interstitial nephritis, occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of allergies, esp. penicillins, cephalosporins, renal impairment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Promptly report rash, diarrhea (fever, abdominal pain, mucus and blood in stool may indicate antibiotic-associated colitis). Be alert for signs of superinfection including fever, vomiting, diarrhea, black “hairy” tongue, ulceration or changes of oral mucosa, anal/genital pruritus. Monitor renal/hepatic tests with prolonged therapy.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Continue antibiotic for full length of treatment. • Space doses evenly. • Take with meals if GI upset occurs. • Thoroughly crush or chew the chewable tablets before swallowing. • Notify physician if rash, diarrhea, other new symptoms occur.
amphotericin B

am-foe-ter-i-sin
(Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec, Fungizone
 )
)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  (Nonliposomal) To be used primarily for pts with progressive, potentially fatal fungal infection. Not to be used for noninvasive forms of fungal disease (oral thrush, vaginal candidiasis).
(Nonliposomal) To be used primarily for pts with progressive, potentially fatal fungal infection. Not to be used for noninvasive forms of fungal disease (oral thrush, vaginal candidiasis).
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Polyene antifungal. CLINICAL: Antifungal, antiprotozoal.
USES
Abelcet: Treatment of aspergillosis or any type of invasive fungal infections refractory or intolerant to Fungizone. AmBisome: Empiric treatment of fungal infection in febrile neutropenic pts. Aspergillus, Candida species, Cryptococcus infections refractory to Fungizone or pt with renal impairment or toxicity with Fungizone. Treatment of cryptococcal meningitis in HIV-infected pts. Treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. Amphotec: Treatment of invasive aspergillosis in pts with renal impairment or toxicity or prior treatment failure with Fungizone. Fungizone: Treatment of life-threatening fungal infections caused by susceptible fungi including Candida spp., Histoplasma, Cryptococcus, Aspergillus, Blastomyces. OFF-LABEL: Abelcet, Amphotec: Serious Candida infections. AmBisome: Treatment of systemic histoplasmosis infection.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to amphotericin B. Cautions: Concomitant use with other nephrotoxic drugs; renal impairment.
ACTION
Generally fungistatic but may become fungicidal with high dosages or very susceptible microorganisms. Binds to sterols in fungal cell membrane. Therapeutic Effect: Alters fungal cell membrane permeability, allowing loss of potassium, other cellular components, resulting in cell death.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Protein binding: 90%. Widely distributed. Metabolic fate unknown. Cleared by nonrenal pathways. Minimal removal by hemodialysis. Amphotec and Abelcet are not dialyzable. Half-life: Fungizone, 24 hrs (increased in neonates and children); Abelcet, 7.2 days; AmBisome, 100–153 hrs; Amphotec, 26–28 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established, but use the least amount for therapeutic regimen. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antineoplastic agents may increase potential for bronchospasm, renal toxicity, hypotension. Steroids may cause severe hypokalemia. May increase digoxin toxity (due to hypokalemia). Nephrotoxic medications (e.g., cyclosporine, IV contrast dye, vancomycin) may increase nephrotoxicity. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, BUN, creatinine. May decrease serum calcium, magnesium, potassium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 50 mg (AmBisome, Amphotec, Fungizone), 100 mg (Amphotec). Injection, Suspension (Abelcet): 5 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
• Use strict aseptic technique; no bacteriostatic agent or preservative is present in diluent.
Reconstitution
ABELCET
• Shake 20-ml (100-mg) vial gently until contents are dissolved. Withdraw required dose using 5-micron filter needle (supplied by manufacturer). • Dilute with D5W to 1–2 mg/ml.
AMBISOME
• Reconstitute each 50-mg vial with 12 ml Sterile Water for Injection to provide concentration of 4 mg/ml. • Shake vial vigorously for 30 sec. Withdraw required dose and inject syringe contents through a 5-micron filter into an infusion of D5W to provide final concentration of 1–2 mg/ml (0.2–0.5 mg/ml for infants and small children).
AMPHOTEC
• Add 10 ml Sterile Water for Injection to each 50-mg vial to provide concentration of 5 mg/ml. Shake gently. • Further dilute only with D5W to a concentration of 0.1–2 mg/ml.
FUNGIZONE
• Add 10 ml Sterile Water for Injection to each 50-mg vial. • Further dilute with 250–500 ml D5W. • Final concentration should not exceed 0.1 mg/ml (0.25 mg/ml for central infusion).
Rate of Administration
• Give by slow IV infusion. Infuse conventional amphotericin over 4–6 hrs; Abelcet over 2 hrs (shake contents if infusion longer than 2 hrs); Amphotec over minimum of 2 hrs (avoid rate faster than 1 mg/kg/hr); AmBisome over 1–2 hrs.
Storage
ABELCET
• Refrigerate unreconstituted solution. Reconstituted solution is stable for 48 hrs if refrigerated, 6 hrs at room temperature.
AMBISOME
• Refrigerate unreconstituted solution. Reconstituted vials are stable for 24 hrs when refrigerated. Concentration of 1–2 mg/ml is stable for 6 hrs.
AMPHOTEC
• Refrigerate unused vials. • Reconstituted solution is stable for 24 hrs if refrigerated.
FUNGIZONE
• Refrigerate unused vials. • Once reconstituted, vials stable for 24 hrs at room temperature, 7 days if refrigerated. • Diluted solutions stable for 24 hrs at room temperature, 2 days if refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Note: Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec: Do not mix with any other drug, diluent, or solution. Fungizone: Allopurinol (Aloprim), aztreonam (Azactam), calcium gluconate, cefepime (Maxipime), cimetidine (Tagamet), ciprofloxacin (Cipro), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dopamine (Intropin), enalapril (Vasotec), filgrastim (Neupogen), fluconazole (Diflucan), foscarnet (Foscavir), magnesium sulfate, meropenem (Merrem IV), ondansetron (Zofran), piperacillin and tazobactam (Zosyn), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
 IV COMPATIBILITY
IV COMPATIBILITY
Lorazepam (Ativan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Abelcet Dose
IV Infusion (Abelcet): ADULTS, CHILDREN: 2.5–5 mg/kg/day at rate of 2.5 mg/kg/hr.
Usual AmBisome Dose
IV Infusion (Ambisome): ADULTS, CHILDREN: 3–6 mg/kg/day over 2 hrs.
Usual Amphotec Dose
IV Infusion (Amphotec): ADULTS, CHILDREN: 3–4 mg/kg/day at rate no faster than 1 mg/kg/hr. Maximum: 6 mg/kg/day.
Fungizone, Usual Dose
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Dosage based on pt tolerance and severity of infection. Initially, 1-mg test dose is given over 20–30 min. If tolerated, usual dose is 0.3–1.5 mg/kg/day or 1–1.5 mg/kg q48h. Maximum: 1.5 mg/kg/day. CHILDREN: Test dose of 0.1 mg/kg/dose (maximum: 1 mg) is infused over 30–60 min. If test dose is tolerated, usual dose is 0.25–1 mg/kg/day or 1–1.5 mg/kg q48h. NEONATES: Initially, 0.5 mg/kg/dose once daily. May gradually increase by 0.25–0.5 mg/kg each day to maximum of 1.5 mg/kg/day. Maintenance dose: 0.25–1 mg/kg/day or 1–1.5 mg/kg/dose every other day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (greater than 10%): Abelcet: Chills, fever, increased serum creatinine, multiple organ failure. AmBisome: Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hyperglycemia, hypocalcemia, edema, abdominal pain, back pain, chills, chest pain, hypotension, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, fever, rigors, insomnia, dyspnea, epistaxis, increased hepatic/renal function test results. Amphotec: Chills, fever, hypotension, tachycardia, increased serum creatinine, hypokalemia, bilirubinemia. Amphocin: Fever, chills, headache, anemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, anorexia, malaise, generalized pain, nephrotoxicity.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Cardiovascular toxicity (hypotension, ventricular fibrillation), anaphylaxis occur rarely. Altered vision/hearing, seizures, hepatic failure, coagulation defects, multiple organ failure, sepsis may occur. Each alternative formulation is less nephrotoxic than conventional amphotericin (Amphocin).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline BMP, LFT, serum magnesium, ionized calcium. Question for history of allergies, esp. to amphotericin B, sulfite. Avoid, if possible, other nephrotoxic medications. Obtain premedication orders to reduce adverse reactions during IV therapy (antipyretics, antihistamines, antiemetics, corticosteroids).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, temperature, pulse, respirations; assess for adverse reactions (fever, tremors, chills, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain) q15min twice, then q30min for 4 hrs of initial infusion. If symptoms occur, slow infusion, administer medication for symptomatic relief. For severe reaction, stop infusion and notify physician. Evaluate IV site for phlebitis. Monitor I&O, renal function tests for nephrotoxicity. Monitor CBC, BMP (esp. potassium), LFT, serum magnesium.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Prolonged therapy (wks or mos) is usually necessary. • Fever reaction may decrease with continued therapy. • Muscle weakness may be noted during therapy (due to hypokalemia).
ampicillin
am-pi-sil-in
(Apo-Ampi
 , Novo-Ampicillin
, Novo-Ampicillin
 , Nu-Ampi
, Nu-Ampi
 )
)
Do not confuse ampicillin with aminophylline.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Penicillin. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of susceptible infections due to streptococci, S. pneumoniae, staphylococci (non–penicillinase producing), meningococci, Listeria, some Klebsiella, E. coli, H. influenzae, Salmonella, Shigella including GI, GU, respiratory infections, meningitis, endocarditis prophylaxis. OFF-LABEL: Surgical prophylaxis for liver transplantation.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ampicillin or any penicillin. Infections caused by penicillinase-producing organisms. Cautions: History of allergies, esp. cephalosporins, renal impairment, asthmatic pts, infectious mononucleosis.
ACTION
Inhibits cell wall synthesis in susceptible microorganisms. Therapeutic Effect: Bactericidal in susceptible microorganisms.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Moderately absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 15%–25%. Widely distributed. Partially metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 1–1.5 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; appears in cord blood, amniotic fluid. Distributed in breast milk in low concentrations. May lead to allergic sensitization, diarrhea, candidiasis, skin rash in infant. Children: Immature renal function in neonates/young infants may delay renal excretion. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Allopurinol may increase incidence of rash. Probenecid may increase concentration, toxicity risk. May decrease effects of oral contraceptives. May increase level/effect of methotrexate. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST. May cause positive Coombs’ test.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 250 mg, 500 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconsitution: 125 mg, 250 mg, 500 mg, 1 g, 2 g. Powder for Oral Suspension: 125 mg/5 ml, 250 mg/5 ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
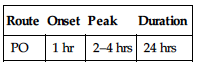
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • For IV injection, dilute each vial with 5 ml Sterile Water for Injection or 0.9% NaCl (10 ml for 1- and 2-g vials). Maximum concentration: 100 mg/ml for IV push. • For intermittent IV infusion (piggyback), further dilute with 50–100 ml 0.9% NaCl. Maximum concentration: 30 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • For IV injection, give over 3–5 min (125–500 mg) or over 10–15 min (1–2 g). For intermittent IV infusion (piggyback), infuse over 15–30 min. • Due to potential for hypersensitivity/anaphylaxis, start initial dose at few drops per min, increase slowly to ordered rate; stay with pt first 10–15 min, then check q10min.
Storage • IV solution, diluted with 0.9% NaCl, is stable for 8 hrs at room temperature or 2 days if refrigerated. • If diluted with D5W, is stable for 2 hrs at room temperature or 3 hrs if refrigerated. • Discard if precipitate forms.
IM
• Reconstitute each vial with Sterile Water for Injection or Bacteriostatic Water for Injection (consult individual vial for specific volume of diluent). • Stable for 1 hr. • Give deeply in large muscle mass.
PO
• Oral suspension, after reconstitution, is stable for 7 days at room temperature, 14 days if refrigerated. • Shake oral suspension well before using. • Give orally 1–2 hrs before meals for maximum absorption.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Diltiazem (Cardizem), midazolam (Versed), ondansetron (Zofran).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Calcium gluconate, cefepime (Maxipime), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), dopamine (Intropin), famotidine (Pepcid), furosemide (Lasix), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), insulin (regular), levofloxacin (Levaquin), lipids, magnesium sulfate, morphine, multivitamins, potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 250–500 mg q6h. CHILDREN: 50–100 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6h. Maximum: 2–4 g/day.
IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1–2 g q4–6h or 50–250 mg/kg/day in divided doses. Maximum: 12 g/day. CHILDREN: 25–200 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6h. Maximum: 12 g/day. NEONATES: 50 mg/kg/dose q6–12h.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 10–50 ml/min | Administer q6–12h |
| Less than 10 ml/min | Administer q12–24h |
| Hemodialysis | 1–2 g q12–24h |
| Peritoneal dialysis | 250 mg q12h |
| Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) | 2g, then 1–2 g q6–8h |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Pain at IM injection site, GI disturbances (mild diarrhea, nausea, vomiting), oral or vaginal candidiasis. Occasional: Generalized rash, urticaria, phlebitis, thrombophlebitis (with IV administration), headache. Rare: Dizziness, seizures (esp. with IV therapy).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Antibiotic-associated colitis, other superinfections (abdominal cramps, severe watery diarrhea, fever) may result from altered bacterial balance in GI tract. Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, acute interstitial nephritis occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of allergies, esp. penicillins, cephalosporins; renal impairment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Promptly report rash (although common with ampicillin, may indicate hypersensitivity) or diarrhea (fever, abdominal pain, mucus and blood in stool may indicate antibiotic-associated colitis). Evaluate IV site for phlebitis. Check IM injection site for pain, induration. Monitor I&O, urinalysis, renal function tests. Be alert for superinfection: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, anal/genital pruritus, oral mucosal changes (ulceration, pain, erythema).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Continue antibiotic for full length of treatment. • Space doses evenly. • More effective if taken 1 hr before or 2 hrs after food/beverages. • Discomfort may occur with IM injection. • Report rash, diarrhea, or other new symptoms.
ampicillin/sulbactam
amp-i-sil-in/sul-bak-tam
(Unasyn)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Penicillin. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of susceptible infections, including intra-abdominal, skin/skin structure, gynecologic infections, due to beta-lactamase-producing organisms including H. influenzae, E. coli, Klebsiella, Acinetobacter, Enterobacter, S. aureus, and Bacteroides spp. OFF-LABEL: Endocarditis, community-acquired pneumonia, surgical prophylaxis, pelvic inflammatory disease.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ampicillin, any penicillins, or sulbactam. Hx of cholestatic jaundice, hepatic impairment associated with ampicillin/sulbactam. Cautions: History of allergies, esp. cephalosporins, renal impairment, infectious mononucleosis, asthmatic pts.
ACTION
Ampicillin inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. Sulbactam inhibits bacterial beta-lactamase. Therapeutic Effect: Ampicillin is bactericidal in susceptible microorganisms. Sulbactam protects ampicillin from enzymatic degradation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Protein binding: 28%–38%. Widely distributed. Partially metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 1–1.3 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; appears in cord blood, amniotic fluid. Distributed in breast milk in low concentrations. May lead to allergic sensitization, diarrhea, candidiasis, skin rash in infant. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 1 yr. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Allopurinol may increase incidence of rash. Probenecid may increase concentration, toxicity risk. May decrease effect of oral contraceptives. May increase level/effect of methotrexate. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, LDH, creatinine. May cause positive Coombs’ test.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconsitution: 1.5 g (ampicillin 1 g/sulbactam 500 g), 3 g (ampicillin 2 g/sulbactam 1 g).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • For IV injection, dilute with Sterile Water for Injection to provide concentration of 375 mg/ml. • For intermittent IV infusion (piggyback), further dilute with 50–100 ml 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • For IV injection, give slowly over minimum of 10–15 min. • For intermittent IV infusion (piggyback), infuse over 15–30 min. • Due to potential for hypersensitivity/anaphylaxis, start initial dose at few drops per min, increase slowly to ordered rate; stay with pt first 10–15 min, then check q10min.
Storage • IV solution, diluted with 0.9% NaCl, is stable for up to 72 hrs if refrigerated (4 hrs if diluted with D5W). • Discard if precipitate forms.
IM
• Reconstitute each 1.5-g vial with 3.2 ml Sterile Water for Injection or lidocaine to provide concentration of 250 mg ampicillin/125 mg sulbactam/ml. • Give deeply into large muscle mass within 1 hr after preparation.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), diltiazem (Cardizem), idarubicin (Idamycin), ondansetron (Zofran).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Famotidine (Pepcid), heparin, insulin (regular), morphine.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage Range
IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 13 YRS AND OLDER: 1.5–3 g q6h. Maximum: 12 g/day. IV: CHILDREN 12 YRS AND YOUNGER: 100–200 mg ampicillin/kg/day in divided doses q6h. Maximum: 12 g/day (Unasyn). 8 g/day (ampicillin). NEONATES: 100 mg (ampicillin)/kg/day in divided doses q8–12h.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage and frequency are modified based on creatinine clearance and severity of infection.
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| Greater than 30 ml/min | No dose adjustment |
| 15–30 ml/min | 1.5–3 g q12h |
| 5–14 ml/min | 1.5–3 g q24h |
| Hemodialysis | 1.5–3 g q12–24h (after HD on dialysis days) |
| Peritoneal dialysis | 1.5-3 g q12–24h |
| Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) | 3 g, then 1.5–3 g q6–12h |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Diarrhea, rash (most common), urticaria, pain at IM injection site, thrombophlebitis with IV administration, oral or vaginal candidiasis. Occasional: Nausea, vomiting, headache, malaise, urinary retention.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Antibiotic-associated colitis, other superinfections (abdominal cramps; severe, watery diarrhea; fever) may result from altered bacterial balance in GI tract. Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, acute interstitial nephritis, blood dyscrasias may occur. High dosage may produce seizures.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of allergies, esp. penicillins, cephalosporins; renal impairment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Promptly report rash (although common with ampicillin, may indicate hypersensitivity) or diarrhea (fever, abdominal pain, mucus and blood in stool may indicate antibiotic-associated colitis). Evaluate IV site for phlebitis. Check IM injection site for pain, induration. Monitor I&O, urinalysis, renal function tests. Be alert for superinfection: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, anal/genital pruritus, oral mucosal changes (ulceration, pain, erythema).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take antibiotic for full length of treatment. • Space doses evenly. • Discomfort may occur with IM injection. • Report rash, diarrhea, or other new symptoms.
anastrozole

an-as-troe-zole
Apo-Anastrozole
 (Arimidex)
(Arimidex)
Do not confuse anastrozole with letrozole, or Arimidex with Imitrex.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Aromatase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic hormone.
USES
Treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women who have developed progressive disease while receiving tamoxifen therapy. First-line therapy in advanced or metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Adjuvant treatment in early hormone receptor–positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of recurrent or metastatic endometrial or uterine cancers; treatment of ovarian cancer.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to anastrazole. Pregnancy, women who may become pregnant. Cautions: Preexisting ischemic cardiac disease, osteopenia (higher risk of developing osteoporosis), hyperlipidemia.
ACTION
Decreases circulating estrogen level by inhibiting aromatase, the enzyme that catalyzes the final step in estrogen production. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits growth of breast cancers that are stimulated by estrogens by lowering serum estradiol concentration.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed into systemic circulation (absorption not affected by food). Protein binding: 40%. Extensively metabolized in liver. Eliminated by biliary system and, to a lesser extent, kidneys. Mean half-life: 50 hrs in postmenopausal women. Steady-state plasma levels reached in about 7 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; may cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Estrogen therapies may reduce concentration/effects. Tamoxifen may reduce plasma concentration. HERBAL: Avoid black cohosh, dong quai, licorice, red clover. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May elevate serum GGT level in pts with liver metastases. May increase serum ALT, AST, alkaline phosphate, total cholesterol, LDL.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 1 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Breast Cancer (Advanced)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1 mg once daily (continue until tumor progresses).
Breast Cancer (Early, Adjuvant)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (16%–8%): Asthenia, nausea, headache, hot flashes, back pain, vomiting, cough, diarrhea. Occasional (6%–4%): Constipation, abdominal pain, anorexia, bone pain, pharyngitis, dizziness, rash, dry mouth, peripheral edema, pelvic pain, depression, chest pain, paresthesia. Rare (2%–1%): Weight gain, diaphoresis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Thrombophlebitis, anemia, leukopenia occur rarely. Vaginal hemorrhage occurs rarely (2%).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for asthenia, dizziness; assist with ambulation if needed. Assess for headache, pain. Offer antiemetic for nausea, vomiting. Monitor for onset of diarrhea; offer antidiarrheal medication.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Notify physician if nausea, asthenia (loss of strength, energy), hot flashes become unmanageable.
anidulafungin
a-nid-ue-la-fun-jin
(Eraxis)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Echinocandin. CLINICAL: Antifungal.
USES
Treatment of candidemia, other forms of Candida infections (e.g., intra-abdominal abscess, peritonitis), esophageal candidiasis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to anidulafungin, other echinocandins. Cautions: Hepatic impairment.
ACTION
Inhibits synthesis of the enzyme glucan, (vital component of fungal cell formation), preventing fungal cell wall formation. Therapeutic Effect: Fungistatic.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Distributed in tissue. Moderately bound to albumin. Protein binding: 84%–99%. Slow chemical degradation; 30% excreted in feces over 9 days. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 40–50 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May be embryotoxic. Crosses placental barrier. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, amylase, ALT, AST, bilirubin, calcium, creatinine, CPK, LDH, lipase. May decrease serum albumin, bicarbonate, magnesium, protein, potassium, Hgb, Hct, WBCs, neutrophils, platelet count. May prolong prothrombin time (PT).
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconsitution: 50-mg vial, 100-mg vial.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute each 50-mg vial with 15 ml Sterile Water for Injection (100 mg with 30 ml). Swirl, do not shake. • Further dilute 50 mg with 50 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl (100 mg with 100 ml, 200 mg with 200 ml).
Rate of Administration • Do not exceed infusion rate of 1.1 mg/min. Not for IV bolus injection.
Storage • Refrigerate unreconstituted vials. Reconstituted vials are stable for 24 hrs at room temperature. Infusion solution is stable for 48 hrs at room temperature.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B (Abelcet, AmBisome), ertapenem (Invanz), sodium bicarbonate.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Dexamethasone (Decadron), famotidine (Pepcid), furosemide (Lasix), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lorazepam (Ativan), methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), morphine. Refer to IV Compatibility Chart in front of book.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Duration of treatment based on pt’s clinical response. In general, treatment is continued for at least 14 days after last positive culture.
Candidemia, Other Candida Infections
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Give single 200-mg loading dose on day 1, followed by 100 mg/day thereafter for at least 14 days after last positive culture.
Esophageal Candidiasis
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Give single 100-mg loading dose on day 1, followed by 50 mg/day thereafter for a minimum of 14 days and for at least 7 days following resolution of symptoms.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Rare (3%–1%): Diarrhea, nausea, headache, rigors, peripheral edema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hypokalemia occurs in 4% of pts. Hypersensitivity reaction characterized by facial flushing, hypotension, pruritus, urticaria, rash occurs rarely. Hepatitis, elevated LFT, hepatic failure was reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, BMP, LFT. Obtain specimens for fungal culture prior to therapy. Treatment may be instituted before results are known.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for evidence of hepatic dysfunction, hypokalemia. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess for rash, urticaria.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• For esophageal candidiasis, maintain diligent oral hygiene.
antihemophilic factor (factor VIII, AHF)
an-tee-hee-moe-fil-ik fak-tor
(Antihemophilic Factor/von Willebrand Factor Complex: Alphanate, Humate-P, Wilate. Human: Hemofil M, Koate-DVI, Monoclate-P. Recombinant: Advate, Eloctate, Kogenate FS, Recombinate, Xyntha)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antihemophilic agent. CLINICAL: Hemostatic.
USES
Human: Prevention/treatment of hemorrhagic episodes, perioperative management of hemophilia A. Alphanate, Humate-P, Wilate: Prevention/treatment of hemorrhagic episodes in pts with hemophilia A. Prophylaxis with surgical/invasive procedures, treatment of bleeding in pts with von Willebrand disease (vWD) when desmopressin is known or suspected to be inadequate. Recombinant: Management of hemophilia A, prevention and control of bleeding episodes, perioperative management of hemophilia A, prophylaxis of joint bleeding and reduce risk of joint damage in children with hemophilia A.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to any component of product. Cautions: Hepatic disease, pts with blood types A, B, AB (progressive anemia, intravascular hemolysis may occur).
ACTION
Assists in conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, essential for blood coagulation. Replaces missing clotting factor VIII. Therapeutic Effect: Produces hemostasis; corrects or prevents bleeding episodes.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Half-life: 8–27 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Human: Injection, Powder for Reconsitution (Hemofil M, Koate-DVI, Monoclate-P): Actual number of units listed on each vial. Alphanate: 250 units, 500 units, 1,000 units, 1,500 units. Eloctate: 250 units, 500 units, 750 units, 1,000 units, 1,500 units, 2,000 units, 3,000 units. Humate-P: 250 units, 500 units, 1,000 units. Recombinant: Injection, Powder for Reconsitution: Advate: 250 units, 500 units, 1,000 units, 1,500 units, 2,000 units, 3,000 units. Kogenate, Recombinate: 250 units, 500 units, 1,000 units. Xyntha: 250 units, 500 units, 1,000 units, 2,000 units.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Warm concentrate and diluent to room temperature. • Using needle supplied by the manufacturer, add diluent to powder to dissolve, gently agitate or rotate. Do not shake vigorously. Complete dissolution may take 5–10 min. • Use second filtered needle supplied by the manufacturer, and add to infusion bag.
Rate of Administration • Advate: Over 5 min or less. Maximum: 10 ml/min. • Hexilate FS, Kogenate FS: Over 1–15 min based on pt tolerance. • Xyntha: Over several min. • Hemofil M, Koate-DVI: Over 5–10 min. Maximum: 10 ml/min. • Monoclate-P: Infuse at 2 ml/min. • Alphanate: 10 ml/min. Humate-P: 4 ml/min.
Administration Precautions • Check pulse rate prior to and following administration. If pulse rate increases, reduce or stop administration. • After administration, apply prolonged pressure on venipuncture site. • Monitor IV site for oozing q5–15min for 1–2 hrs following administration.
Storage • May refrigerate or store at room temperature. • See individual products for specific storage durations.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with other IV solutions or medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hemophilia A, Von Willebrand Disease
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: Dosage is highly individualized and is based on pt’s weight, severity of bleeding, coagulation studies.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Allergic reaction, including fever, chills, urticaria, wheezing, hypotension, nausea, feeling of chest tightness, stinging at injection site, dizziness, dry mouth, headache, altered taste.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Risk of transmitting viral hepatitis. Intravascular hemolysis may occur if large or frequent doses are used with blood group A, B, or AB.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question history of hepatic disease, prior hypersensitivity reaction. When monitoring B/P, avoid overinflation of cuff to prevent trauma, bleeding. Remove adhesive tape from any pressure dressing carefully and slowly.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Following IV administration, apply prolonged pressure on venipuncture site. Monitor IV site for oozing q5–15 min for 1–2 hrs following administration. Assess for allergic reaction. Immediately report any evidence of hematuria or change in vital signs. Assess for decreases in B/P, increased pulse rate, complaint of abdominal or back pain, severe headache (may be evidence of hemorrhage). Question for increased discharge during menses. Assess skin for bruises, petechiae. Check for excessive bleeding from minor cuts, scratches. Assess gums for erythema, gingival bleeding. Assess urine for hematuria. Evaluate for therapeutic relief of pain, reduction of swelling, restricted joint movement.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Use electric razor, soft toothbrush to prevent bleeding. • Report any sign of bleeding, including red or dark urine, black/red stool, coffee-ground vomitus, blood-tinged mucus from cough. • Wear identification indicating a hemolytic condition. • Bring adequate supply of agent when traveling.
apixaban
a-pix-a-ban
(Eliquis)
Do not confuse apixaban with rivaroxaban, argatroban, or dabigatran.
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Discontinuation in absence of alternative anticoagulation increases risk for thrombotic events. Spinal or epidural hematoma resulting in paralysis may occur with neuraxial anesthesia or spinal/epidural puncture.
Discontinuation in absence of alternative anticoagulation increases risk for thrombotic events. Spinal or epidural hematoma resulting in paralysis may occur with neuraxial anesthesia or spinal/epidural puncture.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Factor Xa inhibitor. CLINICAL: Anticoagulant.
USES
Reduces risk for stroke, systemic embolism in pts with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Prophylaxis of DVT following hip or knee replacement surgery. Treatment of DVT and PE. Reduces risk of recurrent DVT/PE following initial therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Severe hypersensitivity to apixaban. Active pathologic bleeding. Cautions: Mild to moderate hepatic impairment, severe renal impairment (may increase bleeding risk). Avoid use in pts with severe hepatic impairment, prosthetic heart valve, significant rheumatic heart disease.
ACTION
Selectively blocks active site of factor Xa, a key factor in the intrinsic and extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation cascade. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits clot-induced platelet aggregation, fibrin clot formation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed after PO administration. Peak plasma concentration: 3–4 hrs. Protein binding: 87%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted primarily in urine, feces. Half-life: 12 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin) may decrease level/effect. Aspirin, NSAIDs, warfarin, heparin, antiplatelet agents, CYP3A4 inhibitors, (e.g., ketoconazole, clarithromycin) may increase concentration, bleeding risk. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease level/effect. Flaxseed, garlic, ginger, ginko biloba, ginseng, Omega-3 may increase risk of bleeding. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase level/adverse effects. LAB VALUES: May decrease platelet count, Hgb, LFT.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 2.5 mg, 5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Discontinuation in absence of alternative anticoagulation increases risk for thrombotic events.
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • If elective surgery or invasive procedures with moderate or high risk for bleeding, discontinue apixaban at least 24–48 hrs prior to procedure.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5 mg twice daily. In pts with at least 2 of the following characteristics: age 80 yrs or older, body weight 60 kg or less, serum creatinine 1.5 mg/dL or greater, concurrent use with CYP3A4, or P-gp inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, ritonavir), reduce dose to 2.5 mg twice daily.
DVT/PE Treatment
PO: ADULTS/ELDERLY: 10 mg twice daily for 7 days, then 5 mg twice daily.
DVT Prophylaxis (Hip/Knee Replacement)
Note: Begin 12–24 hrs postoperatively.
ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2.5 mg twice daily (35 days for hip; 12 days for knee).
DVT Prophylaxis, Reduce Risk Recurrent DVT/PE
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2.5 mg twice daily (after at least 6 mos of treatment).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
DVT/PE/Reduce Risk Recurrent DVT, Postoperative: No adjustment. Nonvalvular A-fib, HD: SCr < 1.5: No adjustment. SCr 1.5 or greater, age older than 80 yrs, weight 60 kg or less: 2.5 mg 2 times/day.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild Impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate Impairment: Use caution. Severe Impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Rare (3%–1%): Nausea, ecchymosis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Increased risk for bleeding/hemorrhagic events. May cause serious, potentially fatal, bleeding, accompanied by one or more of the following: a decrease in Hgb of 2 g/dL or more; a need for 2 or more units of packed RBCs; bleeding occurring at one of the following sites: intracranial, intraspinal, intraocular, pericardial, intra-articular, intramuscular with compartment syndrome, retroperitoneal. Serious reactions include jaundice, cholestasis, cytolytic hepatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, hypersensitivity reaction, anaphylaxis.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC. Question history of bleeding disorders, recent surgery, spinal punctures, intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding ulcers, open wounds, anemia, hepatic impairment. Obtain full medication history including herbal products.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Periodically monitor CBC, stool for occult blood. Be alert for complaints of abdominal/back pain, headache, confusion, weakness, vision change (may indicate hemorrhage). Question for increased menstrual bleeding/discharge. Assess for any sign of bleeding: bleeding at surgical site, hematuria, blood in stool, bleeding from gums, petechiae, ecchymosis.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not take/discontinue any medication except on advice from physician. • Avoid alcohol, aspirin, NSAIDs. • Consult physician before surgery, dental work. • Use electric razor, soft toothbrush to prevent bleeding. • Report blood-tinged mucus from coughing, heavy menstrual bleeding, headache, vision problems, weakness, abdominal pain, frequent bruising, bloody urine or stool, joint pain or swelling.
apremilast
a-pre-mi-last
(Otezla)
Do not confuse apremilast with roflumilast.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor. CLINICAL: Anti–psoriatic arthritis agent.
USES
Treatment of adult pts with active psoriatic arthritis, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to apremilast. Cautions: History of depression, severe renal impairment, suicidal ideation. Pts with latent infections (e.g., TB, viral hepatitis).
ACTION
Selectively inhibits PDE4, increasing cyclic AMP (cAMP) and inflammatory mediators. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces psoriatic arthritis exacerbations.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 68%. Peak plasma concentration: 2.5 hrs. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated in urine (58%), feces (39%). Half-life: 6–9 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Not recommended for nursing mothers. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Strong CYP450 inducers (carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effect. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effect. FOOD: None significant. LAB VALUES: None known.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg.
Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meal. Administer whole; do not crush, cut, dissolve, or divide.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Psoriatic Arthritis, Plaque Psoriasis
PO: ADULTS/ELDERLY: Initially, titrate dose from day 1–day 5. Day 1: 10 mg in am only. Day 2: 10 mg in am; 10 mg in pm. Day 3: 10 mg in am; 20 mg in pm. Day 4: 20 mg in am; 20 mg in pm. Day 5: 20 mg in am; 30 mg in pm. Day 6/Maintenance: 30 mg twice daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment (CrCl less than 30 ml/min)
Days 1–3: 10 mg in am. Days 4–5: 20 mg in am, using only am schedule. Day 6/Maintenance: 30 mg once daily.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (9%–4%): Nausea, diarrhea, headache, upper respiratory tract infection. Rare (3% or less): Vomiting, nasopharyngitis, upper abdominal pain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Increased risk of depression reported in less than 1% of pts. Weight decrease of 5%–10% of body weight occurred in 10% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline weight, vital signs. Question history of depression, severe renal impairment, suicidal ideations. Screen for prior allergic reactions to drug class. Receive full medication history including herbal products. Assess degree of joint pain, range of motion, mobility.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Be alert for worsening depression, suicidal ideation. Monitor for weight loss.
Assess for dehydration if diarrhea occurs. Assess improvement of joint pain, range of motion, mobility.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report changes in mood or behavior, thoughts of suicide, self-destructive behavior. Report weight loss of any kind. • Increase fluid intake if dehydration suspected. • Immediately notify physician if pregnancy suspected. • Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets.
aprepitant/fosaprepitant
a-prep-i-tant/fos-a-prep-i-tant
(Emend)
Do not confuse fosaprepitant with aprepitant, fosamprenavir, or fospropofol.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Selective receptor antagonist. CLINICAL: Antinausea, antiemetic.
USES
PO/IV: Prevention of nausea, vomiting associated with repeat courses of moderate to high emetogenic cancer chemotherapy. PO: Prevention of postop nausea, vomiting.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to aprepitant or fosaprepitant. Concurrent use with pimozide. Cautions: Severe hepatic impairment. Concurrent use of medications metabolized through CYP3A4 (e.g., docetaxol, etoposide, ifosfamide, imatinib, irinotecan, paclitaxel, vinbastine, vincristine, vinorelbine).
ACTION
Inhibits substance P receptor, augments antiemetic activity of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents acute and delayed phases of chemotherapy-induced emesis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Moderately absorbed from GI tract. Crosses blood-brain barrier. Extensively metabolized in liver. Protein binding: greater than 95%. Eliminated primarily by liver metabolism (not excreted renally). Half-life: 9–13 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, clarithromycin) may increase concentration. Strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin) may decrease concentration. May decrease effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives, warfarin. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease plasma concentration. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase plasma concentration. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, creatinine, glucose, alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST. May produce proteinuria.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules (Emend): 40 mg, 80 mg, 125 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Fosaprepitant): 150 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food.
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute each vial with 5 ml 0.9% NaCl. • Add to 145 ml 0.9% NaCl to provide a final concentration of 1 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 20–30 min 30 min prior to chemotherapy.
Storage • Refrigerate unreconstituted vials. • After reconstitution, solution is stable at room temperature for 24 hrs.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not infuse with any solutions containing calcium or magnesium.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea, Vomiting
Note: Administer in combination with a 5-HT3 antagonist and dexamethasone.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS OR YOUNGER WEIGHING 30 KG OR MORE: 125 mg 1 hr before chemotherapy on day 1 and 80 mg once daily in the morning on days 2 and 3.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY (SINGLE-DOSE REGIMEN): 150 mg over 20–30 min 30 min prior to chemotherapy.
Prevention of Postop Nausea, Vomiting
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 40 mg once within 3 hrs prior to induction of anesthesia.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Caution in severe hepatic impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (17%–10%): Fatigue, nausea, hiccups, diarrhea, constipation, anorexia. Occasional (8%–4%): Headache, vomiting, dizziness, dehydration, heartburn. Rare (3% or less): Abdominal pain, epigastric discomfort, gastritis, tinnitus, insomnia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Neutropenia, mucous membrane disorders occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess for dehydration (poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, longitudinal furrows in tongue).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor hydration, nutritional status, I&O. Assess bowel sounds for peristalsis. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Provide supportive measures. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Relief from nausea/vomiting generally occurs shortly after drug administration. • Report persistent vomiting, headache. • May decrease effectiveness of oral contraceptives.
argatroban

ar-gat-roe-ban
Do not confuse argatroban with Aggrestat.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Thrombin inhibitor. CLINICAL: Anticoagulant.
USES
Prophylaxis or treatment of thrombosis in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) in pts with HIT or at risk of developing HIT. percutaneous coronary procedures. OFF-LABEL: Maintain extracorporeal circuit patency of continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) in pts with HIT.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to argatroban, active major bleeding. Cautions: Severe hypertension, immediately following lumbar puncture, spinal anesthesia, major surgery, pts with congenital or acquired bleeding disorders, gastrointestinal ulcerations, hepatic impairment, critically ill pts.
ACTION
Direct thrombin inhibitor that reversibly binds to thrombin-active sites. Inhibits thrombin-catalyzed or thrombin-induced reactions, including fibrin formation, activation of coagulant factors V, VIII, and XIII; inhibits protein C formation, platelet aggregation. Therapeutic Effect: Produces anticoagulation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Distributed primarily in extracellular fluid. Protein binding: 54%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in the feces, presumably through biliary secretion. Half-life: 39–51 min (prolonged in hepatic failure).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if excreted in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antiplatelet agents, other anticoagulants, thrombolytics, NSAIDs may increase the risk of bleeding. HERBAL: Dong quai, evening primrose oil, ginkgo, policosanol, willow bark may increase risk of bleeding. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Prolongs prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), international normalized ratio (INR). May decrease Hgb, Hct.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Infusion (Pre-Mix): 125 mg/125 ml, 250 mg/250 ml. Injection Solution: 250 mg/2.5 ml vial.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Dilute each 250-mg vial with 250 ml 0.9% NaCl, D5W to provide a final concentration of 1 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • Initial rate of administration is based on body weight at 2 mcg/kg/min (e.g., 50-kg pt infuse at 6 ml/hr). Dosage should not exceed 10 mcg/kg/min.
Storage • Discard if solution appears cloudy or an insoluble precipitate is noted. • Following reconstitution, stable for 96 hrs at room temperature or refrigerated. • Avoid direct sunlight.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITY
IV INCOMPATIBILITY
Amiodarone (Cardarone).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), furosemide (Lasix), midazolam (Versed), morphine, vasopressin (Pitressin). Refer to IV Compatibility Chart in front of book.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT)
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 2 mcg/kg/min administered as a continuous infusion. After initial infusion, dose may be adjusted until steady-state aPTT is 1.5–3 times initial baseline value, not to exceed 100 sec. Dosage should not exceed 10 mcg/kg/min.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, administer bolus of 350 mcg/kg over 3–5 min, then infuse at 25 mcg/kg/min. Check ACT (activated clotting time) 5–10 min following bolus. If ACT is less than 300 sec, give additional bolus 150 mcg/kg, increase infusion to 30 mcg/kg/min. If ACT is greater than 450 sec, decrease infusion to 15 mcg/kg/min. Once ACT of 300–450 sec achieved, continue dose through duration of procedure.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Moderate to Severe Impairment: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 0.5 mcg/kg/min. CHILDREN: Initially, 0.2 mcg/kg/min. Adjust dose in increments of 0.05 mcg/kg/min or less.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (8%–3%): Dyspnea, hypotension, fever, diarrhea, nausea, pain, vomiting, infection, cough.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Ventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation occur occasionally. Major bleeding, sepsis occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC, PT, aPTT. Determine initial B/P. Minimize need for multiple injection sites, blood draws, catheters.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for any sign of bleeding: bleeding at surgical site, hematuria, melena, bleeding from gums, petechiae, ecchymoses, bleeding from injection sites. Handle pt carefully and infrequently to prevent bleeding. Assess for decreased B/P, increased pulse rate, complaint of abdominal/back pain, severe headache (may indicate hemorrhage). Monitor ACT, PT, aPTT, platelet count, Hgb, Hct. Question for increase in discharge during menses. Assess for hematuria. Observe skin for any occurring ecchymoses, petechiae, hematoma. Use care in removing any dressing, tape.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Use electric razor, soft toothbrush to prevent cuts, gingival trauma. • Report any sign of bleeding, including red/dark urine, black/red stool, coffee-ground vomitus, blood-tinged mucus from cough.
*ARIPiprazole

ar-i-pip-ra-zole
(Abilify, Abilify Maintena, Aristada)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Increased risk of mortality in elderly pts with dementia-related psychosis, mainly due to pneumonia, HF. Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Increased risk of mortality in elderly pts with dementia-related psychosis, mainly due to pneumonia, HF. Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Do not confuse Abilify with Ambien, or aripiprazole with esomeprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole, or rabeprazole (proton pump inhibitors).
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Dopamine agonist. CLINICAL: Antipsychotic agent.
USES
PO: Treatment of schizophrenia. Treatment of bipolar disorder. Adjunct treatment in major depressive disorder. Treatment of irritability associated with autistic disorder in children 6–17 yrs of age. Treatment of Tourette disorder. IM: (Immediate-Release): Agitation associated with schizophrenia/bipolar disorder. (Extended-Release): Treatment of schizophrenia in adults. Aristada: Treatment of schizophrenia. OFF-LABEL: Schizoaffective disorder, depression with psychotic features, aggression, bipolar disorder (children), conduct disorder (children), psychosis/agitation related to Alzheimer’s dementia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to aripiprazole. Cautions: Concurrent use of CNS depressants (including alcohol), disorders in which CNS depression is a feature, cardiovascular or cerebrovascular diseases (may induce hypotension), Parkinson’s disease (potential for exacerbation), history of seizures or conditions that may lower seizure threshold (Alzheimer’s disease), diabetes mellitus. Pts at risk for pneumonia. Elderly with dementia.
ACTION
Provides partial agonist activity at dopamine and serotonin (5-HT1A) receptors and antagonist activity at serotonin (5-HT2A) receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Improves symptoms associated with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, autism, depression.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed through GI tract. Protein binding: 99% (primarily albumin). Reaches steady levels in 2 wks. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated in feces (55%), urine (25%). Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 75 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta. May be distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May increase serum glucose. May decrease neutrophils, leukocytes.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol may potentiate cognitive and motor effects. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine) may decrease concentration. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., itraconazole, ketoconazole) may increase concentration. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease levels. Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Prefilled Syringe (Aristada): 441 mg/1.6 ml, 662 mg/2.4 ml, 882 mg/3.2 ml. Injection, Solution (Abilify): 9.75 mg/1.3 ml (7.5 mg/ml). Solution, Oral: 1 mg/ml. Tablets: 2 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg. Tablets, Orally Disintegrating: 10 mg, 15 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Abilify Maintena): 300 mg, 400 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
IM (Abilify)
• For IM use only (inject slowly into deep muscle mass). Do not administer IV or subcutaneous.
IM (Abilify Maintena)
• Reconstitute 400-mg vial with 1.9 ml Sterile Water for Injection (300-mg vial with 1.5 ml) to provide a concentration of 100 mg/0.5 ml. Once reconstituted, administer in gluteal muscle. Do not administer via IV or subcutaneously.
PO
• Give without regard to food.
Orally Disintegrating Tablet
• Remove tablet, place entire tablet on tongue. • Do not break, split tablet. • May give without liquid.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: May substitute oral solution/tablet mg per mg up to 25 mg. For 30-mg tablets, give 25 mg oral solution.
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers: Aripiprazole dose should be doubled. Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Aripiprazole dose should be reduced by 50%.
Schizophrenia
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10–15 mg once daily. May increase up to 30 mg/day. Titrate dose at minimum of 2-wk intervals. CHILDREN 13–17 YRS: Initially, 2 mg/day for 2 days, then 5 mg/day for 2 days. May further increase to target dose of 10 mg/day. May then increase in increments of 5 mg up to maximum of 30 mg/day. IM: (Abilify Maintena): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 400 mg monthly (separate doses by at least 26 days). (Aristada): Oral aripiprazole 10 mg/day: initially 441 mg/mos; oral aripiprazole 15 mg/day: initially, 662 mg/mos; oral aripiprazole 20 mg/day, initially, 882 mg q4–6 wks.
Bipolar Disorder
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Monotherapy: Initially, 15 mg once daily. May increase to 30 mg/day. Adjunct to lithium or valproic acid: Initially, 10–15 mg. May increase to 30 mg/day based on pt tolerance. CHILDREN 10–17 YRS: Initially, 2 mg/day for 2 days, then 5 mg/day for 2 days. May further increase to a target of 10 mg/day. Give subsequent dose increases of 5 mg/day. Maximum: 30 mg/day.
Major Depressive Disorder (Adjunct to Antidepressants)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Abilify): Initially, 2–5 mg/day. May increase up to 15 mg/day. Titrate dose in 5-mg increments of at least 1-wk intervals.
Agitation with Schizophrenia/Bipolar Disorder
IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY (Abilify): 5.25–15 mg as a single dose. May repeat after 2 hrs. Maximum: 30 mg/day.
Irritability with Autistic Disorder
PO: CHILDREN 6–17 YRS: Initially, 2 mg/day for 7 days followed by increase to 5 mg/day. Subsequent increases made in 5-mg increments at intervals of at least 1 wk. Maximum: 15 mg/day.
Tourette Disorder
PO: CHILDREN 6–17 YRS WEIGHING 50 KG OR MORE: 2 mg/day for 2 days; then 5 mg/day for 5 days with target dose of 10 mg on day 8. Maximum: 20 mg/day. LESS THAN 50 KG: 2 mg/day for 2 days, then 5 mg/day. Maximum: 10 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (11%–5%): Weight gain, headache, insomnia, vomiting. Occasional (4%–3%): Light-headedness, nausea, akathisia, drowsiness. Rare (2% or less): Blurred vision, constipation, asthenia (loss of strength, energy), anxiety, fever, rash, cough, rhinitis, orthostatic hypotension.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Extrapyramidal symptoms, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, tardive dyskinesia, hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar coma, CVA, TIA occur rarely. Prolonged QT interval occurs rarely. May cause leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess behavior, appearance, emotional status, response to environment, speech pattern, thought content. Correct dehydration, hypovolemia. Assess for suicidal tendencies.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Periodically monitor weight. Monitor for extrapyramidal symptoms (abnormal movement), tardive dyskinesia (protrusion of tongue, puffing of cheeks, chewing/puckering of the mouth). Periodically monitor B/P, pulse (particularly in pts with preexisting cardiovascular disease). Assess for therapeutic response (greater interest in surroundings, improved self-care, increased ability to concentrate, relaxed facial expression).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid alcohol. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Report worsening depression, suicidal ideation, unusual changes in behavior, extrapyramidal effects.
armodafinil

ar-moe-daf-i-nil
(Nuvigil)
Do not confuse armodafinil with modafinil.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Alpha1 agonist. CLINICAL: CNS stimulant.
USES
Treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness associated with obstructive sleep apnea–hypopnea syndrome, narcolepsy, shift-work sleep disorder.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: History of sensitivity to armodafinil or modafinil. Cautions: History of mitral valve prolapse, left ventricular hypertrophy, hepatic impairment, recent history of MI, unstable angina, cardiac ischemia, drug abuse, psychosis, depression, mania, renal impairment, elderly.
ACTION
Exact mechanism unknown. May bind to dopamine reuptake carrier sites in the brain, increasing alpha activity, decreasing delta, theta, and beta activity. Therapeutic Effect: Improves wakefulness.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed. Widely distributed. Mainly eliminated by hepatic metabolism with less than 10% excreted by kidneys. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 15 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Use caution in pregnant women. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 17 yrs. Elderly: Age-related renal/hepatic impairment may require decreased dosage.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Carbamazine, erythromycin, ketoconazole, phenobarbital, rifampin may alter concentration/effect. May reduce effects of cyclosporine, oral contraceptives. May increase concentrations of diazepam, omeprazole, phenytoin, propanolol, tricyclic antidepressants, warfarin. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: Food slows peak concentration by 2–4 hrs; may affect time of onset, length of drug action. LAB VALUES: May increase alkaline phosphatase, GGT. May decrease serum uric acid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 50 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 250 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May give without regard to food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Narcolepsy, Obstructive Sleep Apnea–Hypopnea Syndrome
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 150 or 250 mg/day given as a single dose in the morning.
Shift-Work Sleep Disorder
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 150 mg given daily approximately 1 hr prior to the start of work shift.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Severe Hepatic Impairment: May decrease dose.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (17%–7%): Headache, nausea. Occasional (5%–4%): Dizziness, insomnia, dry mouth, diarrhea, anxiety. Rare (2%): Depression, fatigue, palpitations, dyspepsia, rash, upper abdominal pain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Small risk of serious rash, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline evidence of narcolepsy or other sleep disorders, including pattern, environmental situations, lengths of time of sleep episodes. Question for sudden loss of muscle tone (cataplexy) precipitated by strong emotional responses before sleep episode. Assess frequency/severity of sleep episodes prior to drug therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor sleep pattern, evidence of restlessness during sleep, length of insomnia episodes at night. Assess for dizziness, anxiety; initiate fall precautions.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid or limit alcohol. • Use alternative contraceptives during therapy and 1 mo after discontinuing drug (reduces effectiveness of oral contraceptives). Report rash, depression, diarrhea, insomnia. • Sips of water may relieve dry mouth.
arsenic trioxide

ar-sen-ik tri-ox-ide
(Trisenox)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  May prolong QT interval. May lead to multiform ventricular tachycardia (torsade de pointes) or complete AV block. May cause retinoic acid–acute promyelocytic leukemia (RA-APL) syndrome or acute promyelocytic leukemia.
May prolong QT interval. May lead to multiform ventricular tachycardia (torsade de pointes) or complete AV block. May cause retinoic acid–acute promyelocytic leukemia (RA-APL) syndrome or acute promyelocytic leukemia.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antineoplastic. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Induction of remission and consolidations in pts with relapsed or refractory acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). OFF-LABEL: Treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome; initial treatment of APL.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to arsenic. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, preexisting QT-interval prolongation, concomitant medications that prolong QT interval. HF, history of torsades de pointes, conditions causing hypokalemia/hypomagnesemia.
ACTION
Produces morphologic changes and DNA fragmentation in promyelocytic leukemia cells. Therapeutic Effect: Induces apoptosis is in APL cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Distributed in liver, kidneys, heart, lungs, hair, and nails. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated by kidneys. Half-life: Not available.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. May cause fetal harm. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 5 yrs. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May prolong QT interval in pts taking antiarrhythmics, moxifloxacin, thioridazine. Amphotericin B, cyclosporine, diuretics may produce electrolyte abnormalities. HERBAL: Bilberry, fenugreek, garlic, ginger, ginseng may worsen hypoglycemia. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease WBC count, Hgb, platelet count, serum magnesium, calcium. May increase serum ALT, AST. Higher risk of hypokalemia than hyperkalemia, hyperglycemia than hypoglycemia.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 1 mg/ml (10 ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
◀ ALERT ▶ Central venous line is not required for drug administration.
Reconstitution • After withdrawing drug from ampule, dilute with 100–250 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 1–2 hrs. • Duration of infusion may be extended up to 4 hrs if acute vasomotor reactions occur.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Diluted solution is stable for 24 hrs at room temperature, 48 hrs if refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with any other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Obtain baseline 12-lead EKG, electrolytes, creatinine prior to treatment.
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 5 YRS AND OLDER: Induction: 0.15 mg/kg/day until bone marrow remission. Do not exceed 60 induction doses. Consolidation: Beginning 3–6 wks after completion of induction therapy, 0.15 mg/kg/day for maximum 25 doses over a period of up to 5 wks.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild to Moderate Impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe Impairment: Use caution.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution. Monitor for toxicity.
SIDE EFFECTS
Expected (75%–50%): Nausea, cough, fatigue, fever, headache, vomiting, abdominal pain, tachycardia, diarrhea, dyspnea. Frequent (43%–30%): Dermatitis, insomnia, edema, rigors, prolonged QT interval, sore throat, pruritus, arthralgia, paresthesia, anxiety. Occasional (28%–20%): Constipation, myalgia, hypotension, epistaxis, anorexia, dizziness, sinusitis. (15%–8%): Ecchymosis, nonspecific pain, weight gain, herpes simplex infections, wheezing, flushing, diaphoresis, tremor, hypertension, palpitations, dyspepsia, eye irritation, blurred vision, asthenia (loss of strength, energy), adventitious or diminished breath sounds (crackles). Rare: Confusion, petechiae, dry mouth, oral candidiasis, incontinence, pulmonary rhonchi.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Seizures, GI hemorrhage, renal impairment or failure, pleural or pericardial effusion, hemoptysis, sepsis occur rarely. Prolonged QT interval, complete AV block, unexplained fever, dyspnea, weight gain, effusion are evidence of arsenic toxicity. Treatment should be halted, steroid therapy instituted.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess CBC, BMP, LFT, coagulation profiles before and frequently during treatment. Ask if pt is breast-feeding.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, BMP, LFT. Monitor for arsenic toxicity syndrome (fever, dyspnea, weight gain, confusion, muscle weakness, seizures).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid crowds, those with known infection. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Report high fever, vomiting, difficulty breathing, or rapid heart rate.
asparaginase

as-par-a-jin-ace
(Erwinaze, Kidrolase
 )
)
Do not confuse asparaginase with pegaspargase.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Enzyme. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of ALL in pts with hypersensitivity to E. coli–derived asparaginase. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of chronic lymphoblastic leukemia (CLL).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: History of hypersensitivity to asparaginase. History of serious thrombosis, pancreatitis, or hemorrhagic events with prior asparaginase therapy. Cautions: Underlying coagulopathy, preexisting hepatic impairment.
ACTION
Inhibits DNA, RNA, protein synthesis by breaking down asparagine, depriving tumor cells of this essential amino acid. Cell cycle–specific for G1 phase of cell division. Therapeutic Effect: Toxic to leukemic cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Metabolized by reticuloendothelial system through slow sequestration. Half-life: IM: 39–49 hrs; IV: 8–30 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy, esp. first trimester. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase level of dexamethasone. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ammonia, BUN, uric acid, glucose, partial thromboplastin time (PTT), platelet count, prothrombin time (PT), thrombin time (TT), ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin. May decrease blood clotting factors (plasma fibrinogen, antithrombin, plasminogen), serum albumin, calcium, cholesterol.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 10,000 international units.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ May be carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic. Handle with extreme care during preparation/administration. Handle voided urine as infectious waste. Powder, solution may irritate skin on contact. Wash area for 15 min if contact occurs.
 IV
IV
Reconstitute 10,000 international units vial with 5 ml Sterile Water for Injection or 0.9% NaCl to provide a concentration of 2,000 international units/ml. • Shake gently to ensure complete dissolution (vigorous shaking produces foam, some loss of potency). Further dilute in 50–250 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over at least 30 min.
Storage • Refrigerate powder for reconstitution. • Reconstituted solution stable for 8 hrs if refrigerated. • Gelatinous fiber-like particles may develop (remove via 5-micron filter during administration).
IM
• Add 2 ml 0.9% NaCl injection to 10,000 international units vial to provide a concentration of 5,000 international units/ml. • Administer no more than 2 ml into large muscle mass.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Methotrexate, sodium bicarbonate.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage
IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: As a substitute for pegaspargase: 25,000 units/m2 3 times/wk for 6 doses. As a substitute for pegaspargase (E. coli): 25,000 units/m2 for each planned dose.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Allergic reaction (rash, urticaria, arthralgia, facial edema, hypotension, respiratory distress), pancreatitis (severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting). Occasional: CNS effects (confusion, drowsiness, depression, anxiety, fatigue), stomatitis, hypoalbuminemia or uric acid nephropathy (manifested as pedal or lower extremity edema), hyperglycemia. Rare: Hyperthermia (including fever or chills), thrombosis, seizures.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hepatotoxicity usually occurs within 2 wks of initial treatment. Risk of allergic reaction, including anaphylaxis, increases after repeated therapy. Myelosuppression may be severe.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
CBC, BMP, LFT should be performed before therapy begins and when 1 or more wks have elapsed between doses. Before giving medication, agents for adequate airway and allergic reaction (antihistamine, epinephrine, O2, IV corticosteroid) should be readily available. Assess baseline CNS functions.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor vital signs, CBC, urinalysis, serum amylase, BMP, LFT, coagulation profile, glucose, uric acid. Discontinue medication at first sign of renal dysfunction (oliguria, anuria), pancreatitis. Monitor for hematologic toxicity (fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding), symptoms of anemia, hypersensitivity reaction.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Increase fluid intake (protects against renal impairment). • Nausea may decrease during therapy. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers body’s resistance). • Avoid contact with those who have recently received a live virus vaccine. • Notify physician if abdominal pain, rash, nausea, vomiting occurs.
aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid, ASA)


as-pir-in
(Asaphen E.C.
 , Ascriptin, Bayer, Bufferin, Durlaza, Ecotrin, Entrophen
, Ascriptin, Bayer, Bufferin, Durlaza, Ecotrin, Entrophen
 , Halfprin, Novasen
, Halfprin, Novasen
 )
)
Do not confuse aspirin or Ascriptin with Afrin, Aricept, or Ecotrin with Epogen.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Aggrenox: aspirin/dipyridamole (an antiplatelet agent): 25 mg/200 mg. Fiorinal: aspirin/butalbital/caffeine (a barbiturate): 325 mg/50 mg/40 mg. Lortab/ASA: aspirin/hydrocodone (an analgesic): 325 mg/5 mg. Percodan: aspirin/oxycodone (an analgesic): 325 mg/2.25 mg, 325 mg/4.5 mg. Pravigard: aspirin/pravastatin (a cholesterol-lowering agent): 81 mg/20 mg, 81 mg/40 mg, 81 mg/80 mg, 325 mg/20 mg, 325 mg/40 mg, 325 mg/80 mg. Yosprala: aspirin/omeprazole (a proton pump inhibitor [PPI]) 325 mg/40 mg, 81 mg/40 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Nonsteroidal salicylate. CLINICAL: Anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, anticoagulant.
USES
Treatment of mild to moderate pain, fever. Reduces inflammation related to rheumatoid arthritis (RA), juvenile arthritis, osteoarthritis, rheumatic fever. Used as platelet aggregation inhibitor in the prevention of transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), cerebral thromboembolism, MI or reinfarction. Durlaza: Reduce risk of MI in pts with CAD or stroke in pts who have had TIA or ischemic stroke. OFF-LABEL: Prevention of pre-eclampsia; alternative therapy for preventing thromboembolism associated with atrial fibrillation when warfarin cannot be used; pericarditis associated with MI; prosthetic valve thromboprophylaxis. Adjunctive treatment of Kawasaki’s disease. Complications associated with autoimmune disorders; colorectal cancer.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to salicylates, NSAIDs. Aspirin triad (asthma, rhinitis [with or without nasal polyps], aspirin intolerance). Asthma, rhinitis, nasal polyps; inherited or acquired bleeding disorders; use in children (younger than 16 yrs) for viral infections. Do not use for at least 7 days after tonsillectomy or oral surgery. Cautions: Platelet/bleeding disorders, severe renal/hepatic impairment, dehydration, erosive gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, sensitivity to tartrazine dyes, elderly (chronic use of doses 325 mg or greater). Avoid use in pregnancy, especially third trimester.
ACTION
Inhibits cyclo-oxygenase enzyme via acetylation. Inhibits formation of prostaglandin derivative thromboxane A. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces inflammatory response, intensity of pain; decreases fever; inhibits platelet aggregation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 1 hr | 2–4 hrs | 4–6 hrs |
Rapidly and completely absorbed from GI tract; enteric-coated absorption delayed; rectal absorption delayed and incomplete. Protein binding: High. Widely distributed. Rapidly hydrolyzed to salicylate. Half-life: 15–20 min (aspirin); 2–3 hrs (salicylate at low dose); more than 20 hrs (salicylate at high dose).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Readily crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. May prolong gestation and labor; decrease fetal birth weight; increase incidence of stillbirths, neonatal mortality, hemorrhage. Avoid use during last trimester (may adversely affect fetal cardiovascular system: premature closure of ductus arteriosus). Children: Caution in pts with acute febrile illness (Reye’s syndrome). Elderly: May be more susceptible to toxicity; lower dosages recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, NSAIDs may increase risk of GI effects (e.g., ulceration). Antacids, urinary alkalinizers increase excretion. Anticoagulants, heparin, thrombolytics, rivaroxaban, ticagrelor increase risk of bleeding. HERBAL: Avoid cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo, ginseng, green tea, horse chestnut, red clover (possess antiplatelet activity). FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May alter serum ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, uric acid; prolongs prothrombin time (PT), bleeding time. May decrease serum cholesterol, potassium, T3, T4.
AVAILABILITY (OTC)
Caplets (Bayer): 81 mg, 325 mg, 500 mg. Suppositories: 300 mg, 600 mg. Tablets: 325 mg. Tablets (Chewable [Bayer, St. Joseph]): 81 mg.
 Capsule, Extended-Release: (Durlaza) 162.5 mg. Tablets (Enteric-Coated [Bayer, Ecotrin, St. Joseph]): 81 mg, 325 mg, 500 mg, 650 mg.
Capsule, Extended-Release: (Durlaza) 162.5 mg. Tablets (Enteric-Coated [Bayer, Ecotrin, St. Joseph]): 81 mg, 325 mg, 500 mg, 650 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide enteric-coated tablets or extended-release capsule. • May give with water, milk, meals if GI distress occurs.
Rectal
• Refrigerate suppositories; do not freeze. • If suppository is too soft, chill for 30 min in refrigerator or run cold water over foil wrapper. • Moisten suppository with cold water before inserting well into rectum.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Analgesia, Fever
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER AND 50 KG OR MORE: 325–650 mg q4–6h or 975 mg q6h prn or 500–1,000 mg q4–6h prn. Maximum: 4 g/day. RECTAL: 300–600 mg q4h prn. INFANTS, CHILDREN LESS THAN 50 KG: 10–15 mg/kg/dose q4–6h. Maximum: 4 g/day or 90 mg/kg/day.
Revascularization
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 80–325 mg/day.
Kawasaki’s Disease
PO: CHILDREN: 80–100 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6h up to 14 days (until fever resolves for at least 48 hrs). After fever resolves, 1–5 mg/kg once daily for at least 6–8 wks.
Mi, Stroke (Risk Reduction)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Durlaza: 162.5 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use in severe impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: GI distress (including abdominal distention, cramping, heartburn, mild nausea); allergic reaction (including bronchospasm, pruritus, urticaria).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
High doses of aspirin may produce GI bleeding and/or gastric mucosal lesions. Dehydrated, febrile children may experience aspirin toxicity quickly. Reye’s syndrome, characterized by persistent vomiting, signs of brain dysfunction, may occur in children taking aspirin with recent viral infection (chickenpox, common cold, or flu). Low-grade aspirin toxicity characterized by tinnitus, generalized pruritus (may be severe), headache, dizziness, flushing, tachycardia, hyperventilation, diaphoresis, thirst. Marked toxicity characterized by hyperthermia, restlessness, seizures, abnormal breathing patterns, respiratory failure, coma.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Do not give to children or teenagers who have or recently had viral infections (increases risk of Reye’s syndrome). Do not use if vinegar-like odor is noted (indicates chemical breakdown). Assess type, location, duration of pain, inflammation. Inspect appearance of affected joints for immobility, deformities, skin condition. Therapeutic serum level for antiarthritic effect: 20–30 mg/dL (toxicity occurs if level is greater than 30 mg/dL).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor urinary pH (sudden acidification, pH from 6.5 to 5.5, may result in toxicity). Assess skin for evidence of ecchymosis. If given as antipyretic, assess temperature directly before and 1 hr after giving medication. Evaluate for therapeutic response: relief of pain, stiffness, swelling; increased joint mobility; reduced joint tenderness; improved grip strength.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not, chew, crush, dissolve, or divide enteric-coated tablets. • Avoid alcohol. • Report tinnitus or persistent abdominal GI pain, bleeding. • Therapeutic anti-inflammatory effect noted in 1–3 wks. • Behavioral changes, persistent vomiting may be early signs of Reye’s syndrome; contact physician.
atazanavir

a-ta-zan-a-veer
(Reyataz)
Do not confuse Reyataz with Retavase.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Evotaz: atazanavir/cobicistat (antiretroviral booster): 300 mg/150 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antiretroviral. CLINICAL: Protease inhibitor.
USES
Treatment of HIV-1 infection in combination with at least two other antiretroviral agents in pts 3 mos and older, weighing 5 kg or more.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to atazanavir. Concurrent use with alfuzosin, ergot derivatives, indinavir, lovastatin, midazolam (oral), pimozide, rifampin, sildenafil (for pulmonary arterial hypertension), St. John’s wort, simvastatin, triazolam. Cautions: Preexisting conduction system defects (first-, second-, or third-degree AV block), diabetes mellitus, elderly, renal impairment (not recommended in end-stage renal disease or pts on hemodialysis), hemophilia A or B, hepatitis B or C. Do not use in pts younger than 3 mos (potential for kernicterus). Pts with increased transaminase levels prior to use or underlying hepatic disease.
ACTION
Binds to HIV-1 protease, inhibiting cleavage of viral precursors into functional proteins. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents formation of mature HIV viral cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 86%. Extensively metabolized in liver. Eliminated in feces (79%), urine (13%). Half-life: 5–8 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or distributed in breast milk. Lactic acidosis syndrome, hyperbilirubinemia, kernicterus have been reported. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 3 mos. Elderly: Age-related hepatic impairment may require dose reduction.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration, toxicity of amiodarone, atorvastatin, bepridil, clarithromycin, cyclosporine, diltiazem, felodipine, lidocaine, lovastatin, nicardipine, nifedipine, rosuvastatin, sildenafil, simvastatin, sirolimus, tacrolimus, tadalafil, tricyclic antidepressants, vardenafil, verapamil, warfarin. H2-receptor antagonists, proton pump inhibitors, rifampin may decrease concentration/effects. Ritonavir, voriconazole may increase concentration. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: High-fat meals may decrease absorption. LAB VALUES: May increase serum bilirubin, ALT, AST, amylase, lipase. May decrease Hgb, neutrophil count, platelets. May alter LDL, triglycerides.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 150 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg. Packet, Oral: 50 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with food. • Swallow whole; do not break or open capsules. • Administer at least 2 hrs before or 10 hrs after H2 antagonist, 12 hrs after proton pump inhibitor.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Dosage adjustment may be necessary with colchicine, bosentin, H2 antagonists, proton pump inhibitors, PDE5 inhibitors.
HIV-1 Infection
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY (ANTIRETROVIRAL-NAIVE): 300 mg and ritonavir 100 mg, or cobicistat 150 mg, once daily, or 400 mg (2 capsules) once daily with food in pts unable to tolerate ritonavir. CHILDREN 6–17 YRS (NAIVE OR EXPERIENCED) WEIGHING 40 KG OR MORE: Capsules: 300 mg once daily (with ritonavir 100 mg). WEIGHING 20–39 KG: 200 mg once daily (with ritonavir 100 mg). WEIGHING 15–19 KG: 150 mg once daily (with ritonavir 100 mg). ADULTS, ELDERLY (ANTIRETROVIRAL-EXPERIENCED), PREGNANT PTS, CHILDREN WEIGHING 40 KG OR MORE: (Capsule): 300 mg and ritonavir (Norvir) 100 mg once daily. WEIGHING 20–39 KG: 200 mg and ritonavir 100 mg once daily. WEIGHING 15–19 KG: 150 mg and ritonavir 100 mg once daily.
Powder (Naive and Experienced)
CHILDREN WEIGHING 25 KG OR MORE: 300 mg plus ritonavir 100 mg once daily. WEIGHING 15–24 KG: 250 mg plus ritonavir 80 mg once daily. WEIGHING 5–14 KG: 200 mg plus ritonavir 80 mg once daily.
HIV-1 Infection (Concurrent Therapy with Efavirenz)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg atazanavir, 100 mg ritonavir (as a single dose given with food), and 600 mg efavirenz as a single daily dose on an empty stomach (preferably at bedtime).
HIV-1 Infection (Concurrent Therapy with Didanosine)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Give atazanavir with food 2 hrs before or 1 hr after didanosine.
HIV-1 Infection (Concurrent Therapy with Tenofovir)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 300 mg atazanavir, 100 mg ritonavir, and 300 mg tenofovir given as a single daily dose with food. FOR TREATMENT-EXPERIENCED PREGNANT WOMEN DURING SECOND OR THIRD TRIMESTER: 400 mg with ritonavir 100 mg once daily.
HIV-1 Infection in Pts with Mild to Moderate Hepatic Impairment
◀ ALERT ▶ Avoid use in pts with severe hepatic impairment.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 300 mg once daily with food.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
HD (Naive): 300 mg with ritonavir. (Experienced): Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (16%–14%): Nausea, headache. Occasional (9%–4%): Rash, vomiting, depression, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever. Rare (3% or less): Dizziness, insomnia, cough, fatigue, back pain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Severe hypersensitivity reaction (angioedema, chest pain), jaundice may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, BMP, LFT before beginning therapy and at periodic intervals during therapy. Offer emotional support.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor lab results. Assess for nausea, vomiting; assess eating pattern. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess skin for rash. Question for evidence of headache. Assess mood for evidence of depression.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take with food. • Small, frequent meals may offset nausea, vomiting. • Swallow whole; do not break or open capsules. • Pt must continue practices to prevent HIV transmission. • Atazanavir is not a cure for HIV infection, nor does it reduce risk of transmission to others. • Report dizziness, light-headedness, yellowing of skin or whites of eyes, flank pain or when urinating, blood in urine, skin rash.
atenolol

a-ten-oh-lol
(Apo-Atenol
 , Tenormin)
, Tenormin)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Do not abruptly discontinue; taper gradually to avoid acute tachycardia, hypertension, ischemia.
Do not abruptly discontinue; taper gradually to avoid acute tachycardia, hypertension, ischemia.
Do not confuse atenolol with albuterol, timolol, or Tylenol, or Tenormin with Imuran, Norpramin, or thiamine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Beta1-adrenergic blocker. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive, antianginal, antiarrhythmic.
USES
Treatment of hypertension, alone or in combination with other agents; management of angina; secondary prevention of post-MI. OFF-LABEL: Arrhythmia (esp. supraventricular and ventricular tachycardia), thyrotoxicosis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to atenolol. Cardiogenic shock, uncompensated HF, second- or third-degree heart block (except with functioning pacemaker), sinus bradycardia, sinus node dysfunction, pulmonary edema, pregnancy. Cautions: Renal impairment, peripheral vascular disease, diabetes, thyroid disease, bronchospastic disease, compensated HF, concurrent use with digoxin, verapamil, or diltiazem; myasthenia gravis, psychiatric disease. History of anaphylaxis to allergens, elderly.
ACTION
Blocks beta1-adrenergic receptors in cardiac tissue. Therapeutic Effect: Slows sinus node heart rate, decreasing cardiac output, B/P. Decreases myocardial oxygen demand.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 1 hr | 2–4 hrs | 24 hrs |
Incompletely absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 6%–16%. Minimal liver metabolism. Primarily excreted unchanged in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 6–9 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Readily crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Avoid use during first trimester. May produce bradycardia, apnea, hypoglycemia, hypothermia during delivery; low birth-weight infants. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Age-related peripheral vascular disease, renal impairment require caution.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Diuretics, other antihypertensives may increase hypotensive effect. Sympathomimetics, xanthines may mutually inhibit effects. May mask symptoms of hypoglycemia, prolong hypoglycemic effect of insulin, oral antidiabetic medications. NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive effect. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Garlic may increase antihypertensive effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ANA titer, serum BUN, creatinine, potassium, uric acid, lipoprotein, triglycerides.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Tablets may be crushed.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 25–50 mg once daily. May increase dose up to 100 mg once daily. ELDERLY: Usual initial dose, 25 mg/day. CHILDREN: Initially, 0.5–1 mg/kg/dose given once daily. Range: 0.5–1.5 mg/kg/day. Maximum: 2 mg/kg/day up to 100 mg/day.
Angina Pectoris
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 50 mg once daily. May increase dose up to 200 mg once daily. ELDERLY: Usual initial dose, 25 mg/day.
Post-MI
PO: ADULTS: 100 mg once daily or 50 mg twice daily for 6–9 days post-MI.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage interval is modified based on creatinine clearance.
| Creatinine Clearance | Maximum Dosage |
| 15–35 ml/min | 50 mg/day |
| Less than 15 ml/min | 25 mg/day |
| Hemodialysis (HD) | Give dose post-HD or give 25–50 mg supplemental dose |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Atenolol is generally well tolerated, with mild and transient side effects. Frequent: Hypotension manifested as cold extremities, constipation or diarrhea, diaphoresis, dizziness, fatigue, headache, nausea. Occasional: Insomnia, flatulence, urinary frequency, impotence or decreased libido, depression. Rare: Rash, arthralgia, myalgia, confusion (esp. in the elderly), altered taste.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may produce profound bradycardia, hypotension. Abrupt withdrawal may result in diaphoresis, palpitations, headache, tremors. May precipitate HF, MI in pts with cardiac disease; thyroid storm in pts with thyrotoxicosis; peripheral ischemia in pts with existing peripheral vascular disease. Hypoglycemia may occur in previously controlled diabetes. Thrombocytopenia (unusual bruising, bleeding) occurs rarely. Antidote: Glucagon (see Appendix J for dosage).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess B/P, apical pulse immediately before drug is administered (if pulse is 60/min or less, or systolic B/P is less than 90 mm Hg, withhold medication, contact physician). Antianginal: Record onset, quality (sharp, dull, squeezing), radiation, location, intensity, duration of anginal pain, precipitating factors (exertion, emotional stress). Assess baseline renal/hepatic function tests.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P for hypotension, pulse for bradycardia, respiration for difficulty in breathing, EKG. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess for evidence of HF: dyspnea (particularly on exertion or lying down), nocturnal cough, peripheral edema, distended neck veins. Monitor I&O (increased weight, decreased urinary output may indicate HF). Assess extremities for pulse quality, changes in temperature (may indicate worsening peripheral vascular disease). Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not abruptly discontinue medication. • Compliance with therapy essential to control hypertension, angina. • To reduce hypotensive effect, go from lying to standing slowly. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Advise diabetic pts to monitor blood glucose carefully (may mask signs of hypoglycemia). • Report dizziness, depression, confusion, rash, unusual bruising/bleeding. • Outpatients should monitor B/P, pulse before taking medication, following correct technique. • Restrict salt, alcohol intake. • Therapeutic antihypertensive effect noted in 1–2 wks.
atezolizumab
a-te-zoe-liz-ue-mab
(Tecentriq)
Do not confuse atezolizumab with daclizumab, certolizumab, eculizumab, omalizumab, or tocilizumab.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) blocking antibody. Monoclonal antibody. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of pts with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who have disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy or have disease progression within 12 mos of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to atezolizumab. Cautions: Active infection; baseline anemia, lymphopenia; diabetes; pts at risk for dehydration, electrolyte imbalance; hepatic impairment, peripheral or generalized edema, neuropathy, optic disorders, interstitial lung disease; history of venous thromboembolism, intestinal obstruction, pancreatitis.
ACTION
Binds to PD-L1 and blocks interaction with both PD-L1 and B7.1 receptors. Releases the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway-mediated inhibition of the immune response (including antitumor immune response). Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits T-cell proliferation and cytokine production. Inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Metabolization not specified. Steady state reached in 6–9 wks. Elimination not specified. Half-life: 27 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Avoid pregnancy; may cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk; however, human immunoglobulin G is present in break milk. Breastfeeding not recommended during treatment and for at least 5 mos after discontinuation. Females of reproductive potential should use effective contraception during treatment and up to 5 mos after discontinuation. May impair fertility in females. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None known. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, creatinine, glucose. May decrease serum albumin, sodium; lymphocytes, Hgb, Hct, RBCs.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 1,200 mg/20 ml (60 mg/ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Visually inspect solution for particulate matter or discoloration. Solution should appear clear to slightly yellow. Discard if solution is cloudy or discolored or if visible particles are present. • Do not shake vial. • Withdraw 20 ml of solution from vial and dilute into a 250-ml polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene, or polyolefin infusion bag containing 0.9% NaCl. Dilute with 0.9% NaCl only. • Mix by gentle inversion. • Do not shake. • Discard partially used or empty vials.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 60 min using sterile, nonpyrogenic, low-protein binding, 0.2–0.22 micron in-line filter. • If first infusion is tolerated, all subsequent infusions may be delivered over 30 mins. • Do not administer as IV bolus.
Storage • Refrigerate diluted solution up to 24 hrs or store at room temperature for no more than 6 hrs (includes time of preparation and infusion). • Do not freeze. • Do not shake.
 IV INCOMPATABILITIES
IV INCOMPATABILITIES
Do not administer with other medications. Infuse via dedicated line.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Urothelial Carcinoma
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1,200 mg q3wks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs. No dose reductions are recommended.
Dose Modification
Based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE). Withhold treatment for any of the following toxic reactions: Grade 2 or 3 diarrhea or colitis; grade 2 pneumonitis; serum AST or ALT elevation 3–5 times upper limit of normal (ULN) or serum bilirubin elevation 1.5–3 times ULN; symptomatic hypophysitis, adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism; grade 3 or 4 hyperglycemia; grade 3 rash; grade 2 ocular inflammatory toxicity, grade 2 or 3 pancreatitis, grade 3 or 4 infection, grade 2 infusion-related reactions. Restarting treatment after interruption of therapy: Resume treatment when adverse effects return to grade 0 or 1. Permanently discontinue for any of the following toxic reactions: Grade 3 or 4 diarrhea or colitis; grade 3 or 4 pneumonitis; serum AST or ALT elevation greater than 5 times UNL or serum bilirubin elevation 3 times UNL; grade 4 hypophysitis; grade 4 rash; grade 3 or 4 ocular inflammatory toxicity; grade 4 or any grade recurrent pancreatitis; grade 3 or 4 infusion-related reactions; any occurrence of encephalitis, Guillain-Barré, meningitis, meningoencephalitis, myasthenic syndrome/myasthenia gravis.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment: Not specified; use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (52%–18%): Fatigue, decreased appetite, nausea, pyrexia, constipation, diarrhea, peripheral edema. Occasional (17%–13%): Abdominal pain, vomiting, dyspnea, back/neck pain, rash, arthralgia, cough, pruritus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
May cause severe immune-mediated events including adrenal insufficiency (0.4% of pts), interstitial lung disease or pneumonitis (3% of pts), colitis or diarrhea (20% of pts), hepatitis (2%–3% of pts), hypophysitis (0.2% of pts), hyperthyroidism (1% of pts), hypothyroidism (4% of pts), rash (up to 37% of pts), new-onset diabetes with ketoacidosis (0.2% of pts), pancreatitis (0.1% of pts); meningoencephalitis, myasthenic syndrome/myasthenia gravis, Guillain-Barré, ocular inflammatory toxicity (less than 1% of pts). Severe, sometimes fatal, infections including sepsis, herpes encephalitis, mycobacterial infection occurred in 38% of pts. Urinary tract infections were there the most common cause of grade 3 or higher infection, occurring in 7% of pts. Severe infusion-related reactions reported in less than 1% of pts. Other adverse events including acute kidney injury, dehydration, dyspnea, encephalitis, hematuria, intestinal obstruction, meningitis, neuropathy, pneumonia, urinary obstruction, venous thromboembolism were reported. Immunogenicity (auto-atezolizumab antibodies) occurred in 42% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, BMP, LFT, thyroid panel, urine pregnancy, urinalysis; vital signs. Screen for history of pituitary/pulmonary/thyroid disease, autoimmune disorders, diabetes, hepatic impairment, venous thromboembolism. Conduct full dermatologic/neurologic/ophthalmologic exam. Verify use of effective contraception in females of reproductive potential. Screen for active infection. Assess hydration status.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, BMP, LFT, thyroid panel, vital signs. Diligently monitor for immune-mediated adverse events as listed in Adverse Effects/Toxic Reactions. Notify physician if any CTCAE toxicities occur and initiate proper treatment. Obtain chest X-ray if interstitial lung disease, pneumonitis suspected. Due to high risk for dehydration/diarrhea, strictly monitor I&O. Encourage PO intake. If corticosteroid therapy is initiated for immune-mediated events, monitor capillary blood glucose and screen for corticosteroid side effects. Report any changes in neurologic status including nuchal rigidity with fever, positive Kernig’s sign, positive Brudzinski’s sign, altered mental status, seizures. Diligently monitor for infection.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Blood levels will be routinely monitored. • Avoid pregnancy; treatment may cause birth defects. Do not breastfeed. Females of childbearing potential should use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 5 mos after final dose • Treatment may cause serious or life-threatening inflammatory reactions. Report signs and symptoms of treatment-related inflammatory events in the following body systems: colon (severe abdominal pain or diarrhea); eye (blurry vision, double vision, unequal pupil size, sensitivity to light, eyelid drooping); lung (chest pain, cough, shortness of breath); liver (bruising easily, amber-colored urine, clay-colored/tarry stools, yellowing of skin or eyes); pituitary (persistent or unusual headache, dizziness, extreme weakness, fainting, vision changes); thyroid (trouble sleeping, high blood pressure, fast heart rate [overactive thyroid]), (fatigue, goiter, weight gain [underactive thyroid]), neurologic (confusion, headache, seizures, neck rigidity with fever, severe nerve pain or loss of motor function). • Immediately report allergic reactions, bleeding of any kind, signs of infection. • Treatment may cause severe diarrhea. Drink plenty of fluids.
*atoMOXetine
at-oh-mox-e-teen
Apo-Atomoxetine
 (Strattera)
(Strattera)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Do not confuse atomoxetine with atorvastatin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. CLINICAL: Psychotherapeutic agent.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to atomoxetine. Narrow-angle glaucoma, use within 14 days of MAOIs. Pheochromocytoma or history of pheochromocytoma. Severe cardiovascular disease. Cautions: Hypertension, tachycardia, cardiovascular disease (e.g., structural abnormalities, cardiomyopathy), urinary retention, moderate or severe hepatic impairment, suicidal ideation, emergent psychotic or manic symptoms, comorbid bipolar disorder, renal impairment, poor metabolizers of CYP2D6 metabolized drugs (e.g., fluoxetine, paroxetine). Pts predisposed to hypotension.
ACTION
Inhibits reuptake of norepinephrine. Therapeutic Effect: Improves symptoms of ADHD.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 98% (primarily to albumin). Eliminated in urine (80%), feces (17%). Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 4–5 hrs (increased in moderate to severe hepatic insufficiency).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 6 yrs. May produce suicidal thoughts in children and adolescents. Elderly: Age-related hepatic/renal impairment, cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease may increase risk of adverse effects.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: MAOIs may increase concentration/effect. Fluoxetine, paroxetine may increase concentration/effect. Avoid concurrent use of medications that can increase heart rate or B/P. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase hepatic enzymes, serum bilirubin.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 10 mg, 18 mg, 25 mg, 40 mg, 60 mg, 80 mg, 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Swallow capsules whole, do not break or open (powder in capsule is ocular irritant). Give as single daily dose in the morning or 2 evenly divided doses in morning and late afternoon/early evening.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
PO: ADULTS, CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER WEIGHING 70 KG OR MORE: 40 mg once daily. May increase after at least 3 days to 80 mg daily. Maximum: 100 mg. Concurrent CYP2D6 Inhibitors: Initially, 40 mg/day. May increase to 80 mg/day after 4 wks. CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER WEIGHING LESS THAN 70 KG: Initially, 0.5 mg/kg/day. May increase after at least 3 days to 1.2 mg/kg/day. Maximum: 1.4 mg/kg/day or 100 mg, whichever is less. Concurrent CYP2D6 Inhibitors: Initially, 0.5 mg/kg. May increase to 1.2 mg/kg/day after 4 wks.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Expect to administer 50% of normal atomoxetine dosage to pts with moderate hepatic impairment and 25% of normal dosage to pts with severe hepatic impairment.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage with Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors
ADULTS: Initially, 40 mg/day. May increase to 80 mg/day after minimum of 4 wks. CHILDREN: Initially, 0.5 mg/kg/day. May increase to 1.2 mg/kg/day only after minimum 4-wk interval.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Headache, dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, decreased appetite, dizziness, altered mood. Occasional: Tachycardia, hypertension, weight loss, delayed growth in children, irritability. Rare: Insomnia, sexual dysfunction in adults, fever.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Urinary retention, urinary hesitancy may occur. In overdose, gastric lavage, activated charcoal may prevent systemic absorption. Severe hepatic injury occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess pulse, B/P before therapy, following dose increases, and periodically during therapy. Assess attention span, interactions with others.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor urinary output; complaints of urinary retention/hesitancy may be a related adverse reaction. Monitor B/P, pulse periodically and following dose increases. Monitor for growth, attention span, hyperactivity, unusual changes in behavior, suicidal ideation. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Be alert to mood changes. Monitor fluid and electrolyte status in pts with significant vomiting.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Take last dose early in evening to avoid insomnia. • Report palpitations, fever, vomiting, irritability. • Monitor growth rate, weight. • Report changes in behavior, suicidal ideation, chest pain, palpitations, dyspnea.
*atorvaSTATin

a-tor-va-sta-tin
(Apo-Atorvastatin
 , Lipitor, Novo-Atorvastatin
, Lipitor, Novo-Atorvastatin
 )
)
Do not confuse atorvastatin with atomoxetine, lovastatin, nystatin, pitavastatin, pravastatin, or simvastatin, or Lipitor with Levatol, lisinopril, or Zocor.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Caduet: atorvastatin/amlodipine (calcium channel blocker): 10 mg/2.5 mg, 10 mg/5 mg, 10 mg/10 mg, 20 mg/2.5 mg, 20 mg/5 mg, 20 mg/10 mg, 40 mg/2.5 mg, 40 mg/5 mg, 40 mg/10 mg, 80 mg/5 mg, 80 mg/10 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antihyperlipidemic.
USES
Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in high-risk pts. Reduces risk of stroke and heart attack in pts with type 2 diabetes with or without evidence of heart disease. Reduces risk of stroke in pts with or without evidence of heart disease with multiple risk factors other than diabetes. Adjunct to diet therapy in management of hyperlipidemias (reduces elevations in total cholesterol, LDL-C, apolipoprotein B triglycerides in pts with primary hypercholesterolemia), homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in pts 10–17 yrs of age, females more than 1 yr postmenarche. OFF-LABEL: Secondary prevention in pts who have experienced a noncardioembolic stroke/TIA or following an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) event.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to atorvastatin. Active hepatic disease, breastfeeding, pregnancy, unexplained elevated LFT results. Cautions: Anticoagulant therapy; history of hepatic disease; substantial alcohol consumption; pts with prior stroke/TIA; concomitant use of potent CYP3A4 inhibitors; elderly (predisposed to myopathy).
ACTION
Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the early step in cholesterol synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases LDL and VLDL, plasma triglyceride levels; increases HDL concentration.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Poorly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: greater than 98%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated in feces (biliary). Half-life: 14 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. Contraindicated during pregnancy. May produce fetal skeletal malformation. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, protease inhibitors, itraconazole) may increase concentration, risk of rhabdomyolysis. Cyclosporine may increase concentration. Gemfibrozil, fibrates, niacin, colchicine may increase risk of myopathy, rhabdomyolysis. Strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, efavirenz) may decrease concentration. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease level. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase serum concentrations. Red yeast rice may increase serum levels (2.4 mg lovastatin per 600 mg rice). LAB VALUES: May increase serum transaminase, creatinine kinase concentrations.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, 80 mg.
Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, 80 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food or time of day. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide film-coated tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Do not use in pts with active hepatic disease.
Note: Individualize dosage based on baseline LDL/cholesterol, goal of therapy, pt response. Maximum dose with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors: 20 mg/day.
Dyslipidemias
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10–20 mg/day (40 mg in pts requiring greater than 45% reduction in LDL-C). Range: 10–80 mg/day.
Heterozygous Hypercholesterolemia
PO: CHILDREN 10–17 YRS: Initially, 10 mg/day. Maximum: 20 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
See contraindications.
SIDE EFFECTS
Common: Atorvastatin is generally well tolerated. Side effects are usually mild and transient. Frequent (16%): Headache. Occasional (5%–2%): Myalgia, rash, pruritus, allergy. Rare (less than 2%–1%): Flatulence, dyspepsia, depression.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Potential for cataracts, photosensitivity, myalgia, rhabdomyolysis.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline cholesterol, triglycerides, LFT. Question for possibility of pregnancy before initiating therapy. Obtain dietary history.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for headache. Assess for rash, pruritus, malaise. Monitor cholesterol, triglyceride lab values for therapeutic response. Monitor LFTs, CPK.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Follow special diet (important part of treatment). • Periodic lab tests are essential part of therapy. • Do not take other medications without consulting physician. • Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets. • Report dark urine, muscle fatigue, bone pain. • Avoid excessive alcohol intake, large quantities of grapefruit products.
atovaquone
a-toe-va-kwone
(Mepron)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Systemic anti-infective. CLINICAL: Antiprotozoal.
USES
Treatment or prevention of mild to moderate Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP) in pts intolerant to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMZ). OFF-LABEL: Treatment of babesiosis. Prophylaxis in HIV pts at high risk for developing Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Development or history of potentially life-threatening allergic reaction to the drug. Cautions: Elderly, pts with severe PCP, chronic diarrhea, malabsorption syndromes, severe hepatic impairment.
ACTION
Inhibits mitochondrial electron transport system at the cytochrome bc1 complex (Complex III) interrupting nucleic acid, adenosine triphosphate synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Antiprotozoal, antipneumocystic activity.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Rifabutin, rifampin may decrease concentration. May increase rifampin concentration. HERBAL: Bilberry, fenugreek, garlic, ginger, ginseng may enhance risk of hypoglycemia. FOOD: High-fat meals increase absorption. LAB VALUES: May elevate serum ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, amylase. May decrease serum sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Suspension, Oral: 750 mg/5 ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Must give with food or high-fat meals. Shake gently prior to using.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonia (PCP)
PO: ADULTS, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 12 YRS: 750 mg twice daily with food for 21 days. CHILDREN 4–24 MOS: 45 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses with food. Maximum: 1,500 mg/day. CHILDREN 1–3 MOS OR OLDER THAN 24 MOS: 30–40 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses with food. Maximum: 1,500 mg/day. NEONATES: 30–40 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses.
Prevention of PCP
PO: ADULTS, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 12 YRS: 1,500 mg once daily with food. CHILDREN 4–24 MOS: 45 mg/kg/day as single dose. Maximum: 1,500 mg/day. CHILDREN 1–3 MOS OR OLDER THAN 24 MOS: 30 mg/kg/day as single dose. Maximum: 1,500 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (greater than 10%): Rash, nausea, diarrhea, headache, vomiting, fever, insomnia, cough. Occasional (less than 10%): Abdominal discomfort, thrush, asthenia, anemia, neutropenia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
None known.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline lab studies, esp. LFT.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, BMP, LFT, serum amylase. Assess for GI discomfort, nausea, vomiting. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess skin for rash. Monitor elderly closely for decreased hepatic, renal, cardiac function. Monitor I&O.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Continue therapy for full length of treatment. • Do not take any other medications unless approved by physician. • Report rash, diarrhea, or other new symptoms. • Must be taken with high-fat meal or food.
atropine
at-roe-peen
Lomotil: atropine/diphenoxylate (peristaltic inhibitor): 0.025 mg/2.5 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Acetylcholine antagonist. CLINICAL: Antiarrhythmic, antispasmodic, antidote, cycloplegic, antisecretory, anticholinergic.
USES
Injection: Preop to inhibit salivation/secretions; treatment of symptomatic sinus bradycardia; AV block; ventricular asystole; antidote for organophosphate pesticide poisoning. Adjuvant to decrease side effects during reversal of neuromuscular blockage.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to atropine. Narrow-angle glaucoma, pyloric stenosis, prostatic hypertrophy. Cautions: Autonomic neuropathy, paralytic ileus, intestinal atony, severe ulcerative colitis, toxic megacolon, renal/hepatic impairment, myocardial ischemia, hyperthyroidism, hypertension, tachyarrhythmias, HF, coronary artery disease, esophageal reflux or hiatal hernia associated with reflux esophagitis; infants, children with spastic paralysis or brain damage; elderly; biliary tract disease, chronic pulmonary disease.
ACTION
Competes with acetylcholine for common binding sites on muscarinic receptors located on exocrine glands, cardiac and smooth muscle ganglia, intramural neurons. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases GI motility, secretory activity, GU muscle tone (ureter, bladder); abolishes various types of reflex vagal cardiac slowing or asystole.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly and well absorbed after IM administration. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine (30%–50% as unchanged drug). Half-life: 2–3 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: Increased susceptibility to atropine effects.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anticholinergics may increase effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection (AtroPen): 0.25 mg/0.3 ml, 0.5 mg/0.7 ml, 1 mg/0.7 ml, 2 mg/0.7 ml. Injection, Solution: 0.4 mg/ml, 1 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
• Must be given rapidly (prevents paradoxical slowing of heart rate).
IM
• May be given subcutaneously or IM.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
None known.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl), droperidol (Inapsine), fentanyl (Sublimaze), glycopyrrolate (Robinul), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), midazolam (Versed), morphine, potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Preanesthetic
IV, IM, Subcutaneous: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.4–0.6 mg 30–60 min preop. CHILDREN WEIGHING 5 KG OR MORE: 0.01–0.02 mg/kg/dose to maximum of 0.4 mg/dose. Minimum dose: 0.1 mg. CHILDREN WEIGHING LESS THAN 5 KG: 0.02 mg/kg/dose 30–60 min preop.
Bradycardia
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.5–1 mg q5min, not to exceed total of 3 mg or 0.04 mg/kg. CHILDREN: 0.02 mg/kg with a minimum of 0.1 mg to a maximum of 0.5 mg as a single dose. May repeat in 5 min. Maximum total dose: 1 mg.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Dry mouth, nose, throat (may be severe); decreased sweating; constipation; irritation at subcutaneous or IM injection site. Occasional: Dysphagia, blurred vision, bloated feeling, impotence, urinary hesitancy. Ophthalmic: Mydriasis, blurred vision, photophobia, decreased visual acuity, tearing, dry eyes or dry conjunctiva, eye irritation, crusting of eyelid. Rare: Allergic reaction, including rash, urticaria; mental confusion or excitement, particularly in children; fatigue.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may produce tachycardia, palpitations, hot/dry/flushed skin, absence of bowel sounds, increased respiratory rate, nausea, vomiting, confusion, drowsiness, slurred speech, dizziness, CNS stimulation. Overdose may also produce psychosis as evidenced by agitation, restlessness, rambling speech, visual hallucinations, paranoid behavior, delusions, followed by depression. Ophthalmic form may rarely produce increased IOP.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Determine if pt is sensitive to atropine, homatropine, scopolamine.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor changes in B/P, pulse, temperature. Observe for tachycardia if pt has cardiac abnormalities. Assess skin turgor, mucous membranes to evaluate hydration status (encourage adequate fluid intake unless NPO for surgery), bowel sounds for peristalsis. Be alert for fever (increased risk of hyperthermia). Monitor I&O, palpate bladder for urinary retention. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/ FAMILY TEACHING
• For preop use, explain that warm flushing feeling may occur.
axitinib
ax-i-ti-nib
(Inlyta)
Do not confuse axitinib with afatinib, ibrutinib, or imatinib.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Tyrosine kinase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma after failure of one prior systemic chemotherapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to axitinib. Cautions: Pts with increased risk or history of thrombotic events, GI perforation or fistula formation, renal/hepatic impairment, hypertension, HF. Do not use in pts with untreated brain metastasis or recent active GI bleeding.
ACTION
Inhibits vascular endothilial growth factor receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Blocks tumor growth, inhibits angiogenesis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism. Protein binding: greater than 99%. Eliminated primarily in feces with a lesser amount excreted in urine. Half-life: 2.5–6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Unknown whether distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole, ritonavir) may significantly increase concentration; do not use concurrently. If used, reduce dose by 50%. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4/5 inducers (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital) may significantly decrease concentration; do not use concurrently. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase concentration. LAB VALUES: May decrease Hgb, WBC count, platelets, lymphocytes, serum calcium, alkaline phosphatase, albumin, sodium, phosphate, bicarbonate. May increase serum ALT, AST, bilirubin, BUN, creatinine, serum potassium, lipase, amylase; urine protein. May alter serum glucose.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets, film-coated: 1 mg, 5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Swallow tablets whole with full glass of water.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Renal Cell Carcinoma
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 5 mg twice daily, given approximately 12 hrs apart. If tolerated (no adverse events above grade 2, BP normal and no antihypertension use for at least 2 consecutive wks), may increase to 7 mg twice daily, then 10 mg twice daily. For adverse effects, may decrease to 3 mg twice daily, then 2 mg twice daily if adverse effects persist.
Dose Modification
Dosage with concomitant strong CYP3A4 inhibitors: Reduce dose by 50%.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment. Use caution in ESRD.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate Impairment: Reduce initial dose by 50%. Severe Impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (55%–20%): Diarrhea, hypertension, fatigue, decreased appetite, nausea, dysphonia, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (hand-foot) syndrome, weight loss, vomiting, asthenia, constipation. Occasional (19%–11%): Hypothyroidism, cough, stomatitis, arthralgia, dyspnea, abdominal pain, headache, peripheral pain, rash, proteinuria, dysgeusia. Rare (10%–2%): Dry skin, dyspepsia, dizziness, myalgia, pruritus, epistaxis, alopecia, hemorrhoids, tinnitus, erythema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Arterial and venous thrombotic events (MI, CVA), GI perforation, fistula, hemorrhagic events (including cerebral hemorrhage, hematuria, hemoptysis, GI bleeding), hypertensive crisis, cardiac failure have been observed and can be fatal. Hypothyroidism requiring thyroid hormone replacement has been noted. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) has been observed.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline BMP, LFT, renal function test, urine protein, serum amylase, lipase, phosphate before initiation of, and periodically throughout, treatment. Offer emotional support. Assess medical history, esp. hepatic function abnormalities. B/P should be well controlled prior to initiating treatment. Stop medication at least 24 hrs prior to scheduled surgery. Monitor thyroid function before and periodically throughout treatment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, BMP, LFT, renal function test, urine protein, serum amylase, lipase, phosphate, thyroid tests. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess for evidence of bleeding or hemorrhage. Assess for hypertension. For persistent hypertension despite use of antihypertensive medications, dose should be reduced. Permanently discontinue if signs or symptoms of RPLS occur (extreme lethargy, increased B/P from pt baseline, pyuria). Contact physician if changes in voice, redness of skin, or rash is noted.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid crowds, those with known infection. • Avoid contact with anyone who recently received live virus vaccine; do not receive vaccinations. • Swallow tablet whole; do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide. • Avoid grapefruit products. • Report persistent diarrhea, extreme fatigue, abdominal pain, yellowing of skin or eyes, bruising easily; bleeding of any kind, esp. bloody stool or urine; confusion, seizure activity, vision loss, trouble speaking, chest pain; difficulty breathing, leg pain or swelling.
*azaTHIOprine
a-za-thy-o-preen
(Apo-Azathioprine
 , Azasan, Imuran)
, Azasan, Imuran)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Chronic immunosuppression increases risk of developing malignancy.
Chronic immunosuppression increases risk of developing malignancy.
Do not confuse azathioprine with Azulfidine, azacitidine, or azithromycin, or Imuran with Elmiron, Imdur, or Inderal.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Immunologic agent. CLINICAL: Immunosuppressant.
USES
Adjunct in prevention of rejection in kidney transplantation. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in pts unresponsive to conventional therapy. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of dermatomyositis, polymyositis. Maintenance, remission, or reduction of steroid use in Crohn’s disease, lupus nephritis, chronic refractory immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to azathioprine. Pregnant women with RA, pts previously treated for RA with alkylating agents (cyclophosphamide, chlorambucil, melphalan). Cautions: Immunosuppressed pts, pts with hepatic/renal impairment, active infection. Testing for genetic deficiency of thiopurine methyltransferase should be obtained. (Absence or reduced levels increase risk of myelosuppression.)
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Peak levels: 1–2 hrs. Protein binding: 30%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 2 hrs.
ACTION
Antagonizes purine metabolism, inhibits DNA, protein, and RNA synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Suppresses cell-mediated hypersensitivities; alters antibody production, immune response in transplant recipients. Reduces symptoms of arthritis severity.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May depress spermatogenesis, reduction of sperm viability, count. May cause fetal harm. Do not breastfeed. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Allopurinol, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim may increase activity, toxicity. Bone marrow depressants may increase myelosuppression. Other immunosuppressants may increase risk of infection or development of neoplasms. May increase effects of live virus vaccines. HERBAL: Avoid cat’s claw, echinacea (immunostimulant properties). FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease Hgb, serum albumin, uric acid, leukocytes, platelet count. May increase serum ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, amylase, bilirubin.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 50 mg (Imuran), 75 mg (Azasan), 100 mg (Azasan).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with food or in divided doses to reduce potential for GI disturbances. • Store oral form at room temperature.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Reduce dose to 1/3 or 1/4 usual dose when used with allopurinol or in low/absent thiopurine methyltransfurase genetic deficiency.
Prevention of Renal Allograft Rejection
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 3–5 mg/kg/day on day of transplant (or 1–3 days prior to transplant), then 1–3 mg/kg/day as maintenance dose.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 1 mg/kg/day (50–100 mg) as a single dose or in 2 divided doses for 6–8 wks. May increase by 0.5 mg/kg/day after 6–8 wks at 4-wk intervals. Maximum: 2.5 mg/kg/day. Maintenance: Lowest effective dosage. May decrease dose by 0.5 mg/kg or 25 mg/day q4wks (while other therapies, such as rest, physiotherapy, and salicylates, are maintained).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage is modified based on creatinine clearance.
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 10–50 ml/min | 75% of normal |
| Less than 10 ml/min | 50% of normal |
| Hemodialysis | 50% of normal (Adults: additional 0.25 mg/kg) |
| Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) | 75% of normal |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Nausea, vomiting, anorexia (particularly during early treatment and with large doses). Occasional: Rash. Rare: Severe nausea/vomiting with diarrhea, abdominal pain, hypersensitivity reaction.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Increases risk of neoplasia (new abnormal-growth tumors). Significant leukopenia and thrombocytopenia may occur, particularly in pts undergoing renal transplant rejection. Hepatotoxicity occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Arthritis: Assess onset, type, location, and duration of pain, fever, inflammation. Inspect appearance of affected joints for immobility, deformities, skin condition.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
CBC, LFT should be performed weekly during first mo of therapy, twice monthly during second and third mos of treatment, then monthly thereafter. If WBC falls rapidly, dosage should be reduced or discontinued. Assess particularly for delayed myelosuppression. Routinely watch for any change from baseline. Arthritis: Assess for therapeutic response: relief of pain, stiffness, swelling; increased joint mobility; reduced joint tenderness; improved grip strength.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Contact physician if unusual bleeding/bruising, sore throat, mouth sores, abdominal pain, fever occurs. • Therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis may take up to 12 wks. • Women of childbearing age must avoid pregnancy.
azilsartan
a-zil-sar-tan
(Edarbi)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
Do not confuse azilsartan with losartan, irbesartan, or valsartan.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Edarbyclor: azilsartan/chlorthalidone, a diuretic: 40 mg/12.5 mg, 40 mg/25 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). CLINICAL: Antihypertensive.
USES
Treatment of hypertension alone or in combination with other antihypertensives.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to azilsartan. Concomitant use with aliskiren in pts with diabetes mellitus. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, unstented renal artery stenosis, significant aortic/mitral stenosis, severe HF, volume depletion/salt-depleted pts, history of angioedema.
ACTION
Inhibits vasoconstriction, aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotension II, blocking the binding of angiotension II to AT1 receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Produces vasodilation, decreases peripheral resistance, decreases B/P.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Hydrolyzed to active metabolite in GI tract. Moderately absorbed (60%). Peak plasma concentration: 1.5–3 hrs. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: greater than 99%. Eliminated in feces (55%), urine (42%). Half-life: 11 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm when administered during third trimester. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Elevated creatinine levels may occur in pts older than 75 yrs.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: ACE inhibitors, potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements may increase risk of hyperkalemia. NSAIDs, COX-2 inhibitors (e.g., celecoxib) may decrease effect. Hypotensive agents may increase hypotensive effects. HERBAL: Yohimbe, ephedra, licorice, ginseng may increase B/P. Garlic may enhance antihypertensive effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum creatinine. May decrease Hgb, Hct.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 40 mg, 80 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May give without regard to food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 80 mg once daily. Reduce to 40 mg once daily if giving high-dose diuretic concurrently.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (2%–0.4%): Diarrhea, orthostatic hypotension. Rare (0.3%): Nausea, fatigue, muscle spasm, cough.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Oliguria, acute renal failure may occur in pts with history of renal artery stenosis, severe HF, volume depletion.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline Hgb, Hct, BMP, LFT. Obtain B/P, apical pulse immediately before each dose, in addition to regular monitoring (be alert to fluctuations). Question for possibility of pregnancy. Assess medication history (esp. diuretics). Question history of hepatic/renal impairment, renal artery stenosis, severe HF.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Maintain hydration (offer fluids frequently). Monitor serum electrolytes, B/P, pulse, hepatic/renal function. Observe for symptoms of hypotension. If excessive reduction in B/P occurs, place pt in supine position, feet slightly elevated. Correct volume or salt depletion prior to treatment.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take measures to avoid pregnancy. If pregnancy occurs, inform physician immediately. • Low blood pressure is more likely to occur if pt takes diuretics or other medications to control hypertension, consumes low-salt diet, experiences vomiting or diarrhea, or becomes dehydrated. • Change positions slowly, particularly from lying to standing position. • Report light-headedness or dizziness; lie down immediately. • Report swollen extremities or decreased urine output despite fluid intake.
azithromycin
a-zith-roe-mye-sin
(Apo-Azithromycin
 , AzaSite, Novo-Azithromycin
, AzaSite, Novo-Azithromycin
 , Zithromax, Zithromax TRI-PAK, Zithromax Z-PAK, Zmax)
, Zithromax, Zithromax TRI-PAK, Zithromax Z-PAK, Zmax)
Do not confuse azithromycin with azathioprine or erythromycin, or Zithromax with Fosamax or Zovirax.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Macrolide. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
IV/PO: Treatment of susceptible infections due to Chlamydia pneumoniae, C. trachomatis, H. influenzae, Legionella, M. catarrhalis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, N. gonorrhoeae, S. aureus., S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, including mild to moderate infections of upper respiratory tract (pharyngitis, tonsillitis), lower respiratory tract (acute bacterial exacerbations, COPD, pneumonia), uncomplicated skin and skin-structure infections, sexually transmitted diseases (nongonococcal urethritis, cervicitis due to C. trachomatis), chancroid. Prevents disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). Treatment of mycoplasma pneumonia, community-acquired pneumonia, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Prevention/treatment of MAC in pts with advanced HIV infection. OFF-LABEL: Prophylaxis of endocarditis. Prevention of pulmonary exacerbations in pts with cystic fibrosis. Ophthalmic: Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis caused by susceptible infections due to H. influenzae, S. aureus, S. mitis, S. pneumoniae. Prevention of pulmonary exacerbations in pts with cystic fibrosis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to azithromycin or other macrolide antibiotics. History of cholestatic jaundice/hepatic impairment associated with prior azithromycin therapy. Cautions: Hepatic/renal impairment; myasthenia gravis. Hepatocellular and/or cholestatic hepatitis (with or without jaundice), hepatic necrosis. May prolong QT interval.
ACTION
Binds to ribosomal receptor sites of susceptible organisms, inhibiting RNA-dependent protein synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Bacteriostatic or bactericidal, depending on drug dosage.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 7%–50%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated primarily by biliary excretion. Half-life: 68 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 16 yrs for IV use and younger than 6 mos for oral use. Elderly: No age-related precautions in those with normal renal function.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Aluminum/magnesium-containing antacids may decrease concentration (give 1 hr before or 2 hrs after antacid). May increase levels of amiodarone, cyclosporine, dronedarone, QT-prolonging medications, thioridazine, toremifene, ziprasidone. Quetiapine may increase concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK), ALT, AST, bilirubin, LDH, potassium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Zithromax): 500 mg. Ophthalmic Solution (AzaSite): 1%. Suspension, Oral (Zithromax): 100 mg/5 ml, 200 mg/5 ml. Suspension, Oral (Extended-Release [Zmax]): 2-g single-dose packet. Tablets: 250 mg, 500 mg, 600 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute each 500-mg vial with 4.8 ml Sterile Water for Injection to provide concentration of 100 mg/ml. • Shake well to ensure dissolution. • Further dilute with 250 or 500 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W to provide final concentration of 2 mg/ml with 250 ml diluent or 1 mg/ml with 500 ml diluent.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 60 min (2 mg/ml). Infuse over 3 hrs (1 mg/ml).
Storage • Store vials at room temperature. • Following reconstitution, diluted solution is stable for 24 hrs at room temperature or 7 days if refrigerated.
PO (Immediate-Release Suspension)
• Give tablets without regard to food. • May store suspension at room temperature. Stable for 10 days after reconstitution.
PO (Extended-Release Suspension)
• Do not administer oral suspension with food. Give at least 1 hr before or 2 hrs after meals. • Give Zmax within 12 hrs of reconstitution. • Give tablets with food to decrease GI effects.
PO
• Tablets: May give with food to decrease GI effects.
Ophthalmic
• Place gloved finger on lower eyelid and pull out until a pocket is formed between eye and lower lid. • Place prescribed number of drops into pocket.• Instruct pt to close eye gently for 1 to 2 min (so medication will not be squeezed out of sac) and to apply digital pressure to lacrimal sac at inner canthus for 1 min to minimize systemic absorption.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Ceftriaxone (Rocephin), ciprofloxacin (Cipro), famotidine (Pepcid), furosemide (Lasix), ketorolac (Toradol), levofloxacin (Levaquin), morphine, piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn), potassium chloride.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Ceftaroline (Teflaro), doripenem (Doribax), ondansetron (Zofran), tigecycline (Tygacil), diphenhydramine (Benadryl).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage Range
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 250–600 mg once daily or 1–2 g as single dose. (Zmax): 2 g as a single dose. CHILDREN 6 MOS AND OLDER: 5–12 mg/kg (maximum: 500 mg) once daily or 30 mg/kg (maximum: 1,500 mg) as single dose. (Zmax): 60 mg/kg as a single dose. NEONATES: 10–20 mg/kg once daily.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 250–500 mg once daily CHILDREN, NEONATES: 10 mg/kg once daily.
Mild to Moderate Respiratory Tract, Skin, Soft Tissue Infections
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 500 mg day 1, then 250 mg days 2–5.
MAC Prevention
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1,200 mg once weekly. CHILDREN: 20 mg/kg once weekly. Maximum: 1,200 mg/dose.
MAC Treatment
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 600 mg/day with ethambutol. CHILDREN: 10–12 mg/kg/day (maximum: 500 mg) with ethambutol.
Otitis Media
PO: CHILDREN 6 MOS AND OLDER: 30 mg/kg as single dose (maximum: 1,500 mg) or 10 mg/kg/day for 3 days (maximum: 500 mg) or 10 mg/kg on day 1 (maximum: 500 mg), then 5 mg/kg on days 2–5 (maximum: 250 mg).
Pharyngitis, Tonsillitis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 16 YRS AND OLDER: 500 mg on day 1, then 250 mg on days 2–5. CHILDREN 2–15 YRS: 12 mg/kg daily for 5 days (maximum: 500 mg).
Pneumonia, Community-Acquired
PO (Zmax): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2 g as single dose.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 16 YRS AND OLDER: 500 mg on day 1, then 250 mg on days 2–5 or 500 mg/day IV for 2 days, then 500 mg/day PO to complete course of therapy. CHILDREN 6 MOS–15 YRS: 10 mg/kg on day 1 (maximum: 500 mg), then 5 mg/kg (maximum: 250 mg) on days 2–5.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Ophthalmic: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1 drop in affected eye twice daily for 2 days, then 1 drop once daily for 5 days.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Systemic: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain. Ophthalmic: Eye irritation. Rare: Systemic: Headache, dizziness, allergic reaction.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Antibiotic-associated colitis, other superinfections may result from altered bacterial balance in GI tract. Acute interstitial nephritis, hepatotoxicity occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of hepatitis, allergies to azithromycin, erythromycins. Assess for infection (WBC count, appearance of wound, evidence of fever).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Check for GI discomfort, nausea, vomiting. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity and stool consistency. Monitor hepatic function tests, CBC. Assess for hepatotoxicity: malaise, fever, abdominal pain, GI disturbances. Be alert for superinfection: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, anal/genital pruritus, oral mucosal changes (ulceration, pain, erythema).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Continue therapy for full length of treatment. • Avoid concurrent administration of aluminum- or magnesium-containing antacids. • Bacterial conjunctivitis: Do not wear contact lenses.
aztreonam
az-tree-o-nam
(Azactam, Cayston)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Mono-bactam. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Injection: Treatment of infections caused by susceptible gram-negative microorganisms P. aeruginosa, E. coli, S. marcescens, K. pneumoniae, P. mirabilis, H. influenzae, Enterobacter, Citrobacter spp. including lower respiratory tract, skin/skin structure, intraabdominal, gynecologic, complicated/uncomplicated UTIs; septicemia; cystic fibrosis. Cayston: Improve respiratory symptoms in cystic fibrosis pts with P. aeruginosa. OFF-LABEL: Surgical prophylaxis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to aztreonam. Cautions: History of allergy, esp. cephalosporins, penicillins; renal impairment; bone marrow transplant pts with risk factors for toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).
ACTION
Binds to penicillin-binding proteins, which inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Bactericidal.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Completely absorbed after IM administration. Protein binding: 56%–60%. Partially metabolized by hydrolysis. Primarily excreted unchanged in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 1.4–2.2 hrs (increased in renal/hepatic impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta, distributed in amniotic fluid; low concentration in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 9 mos. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, creatinine, LDH, ALT, AST levels. Produces a positive Coombs’ test. May prolong partial thromboplastin time (PTT), prothrombin time (PT).
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Infusion Solution (Azactam): Premix 1 g/50 ml, 2 g/50 ml. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Azactam): 1 g, 2 g. Oral Inhalation, Powder for Reconstitution (Cayston): 75 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • For IV push, dilute each gram with 6–10 ml Sterile Water for Injection. • For intermittent IV infusion, further dilute with 50–100 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl. Final concentration not to exceed 20 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • For IV push, give over 3–5 min. • For IV infusion, administer over 20–60 min.
Storage • Store vials at room temperature. • Solution appears colorless to light yellow. • Following reconstitution, solution is stable for 48 hrs at room temperature or 7 days if refrigerated. • Discard if precipitate forms. Discard unused portions.
IM
• Reconstitute with at least 3 ml diluent per gram of aztreonam. • Shake immediately, vigorously after adding diluent. • Inject deeply into large muscle mass. • Following reconstitution, solution is stable for 48 hrs at room temperature or 7 days if refrigerated.
Inhalation
• Administer only with an Altera nebulizer system. • Nebulize over 2–3 min. • Give bronchodilator 15 min–4 hrs (short-acting) or 30 min–12 hrs (long-acting) before administration. • Reconstituted solution must be used immediately.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Acyclovir (Zovirax), amphotericin (Fungizone), lorazepam (Ativan), metronidazole (Flagyl), vancomycin (Vancocin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Bumetanide (Bumex), calcium gluconate, cimetidine (Tagamet), diltiazem (Cardizem), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), famotidine (Pepcid), furosemide (Lasix), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), insulin (regular), magnesium sulfate, morphine, potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Severe Infections
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2 g q6–8h. Maximum: 8 g/day. CHILDREN: 30 mg/kg q6–8h. Maximum: 8 g/day.
Mild to Moderate Infections
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1–2 g q8–12h. Maximum: 8 g/day. CHILDREN: 30 mg/kg q8h. Maximum: 8 g/day.
Usual Neonatal Dosage
IV: 30 mg/kg/dose q6–12h.
Cystic Fibrosis
IV: CHILDREN: 50 mg/kg/dose q6–8h up to 200 mg/kg/day. Maximum: 8 g/day. Inhalation (Nebulizer): ADULTS, CHILDREN 7 YRS OR OLDER: 75 mg 3 times/day (at least 4 hrs apart) for 28 days, then off for 28-day cycle.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage and frequency are modified based on creatinine clearance and severity of infection:
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 10–30 ml/min | 50% usual dose at usual intervals |
| Less than 10 ml/min | 25% usual dose at usual intervals |
| Hemodialysis | 500 mg–2 g, then 25% of initial dose at usual interval |
| Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) | 2 g, then 1 g q8–12h or 2g q12h |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use with caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (greater than 5%): Cayston: Cough, nasal congestion, wheezing, pharyngolaryngeal pain, pyrexia, chest discomfort, abdominal pain, vomiting.
Occasional (less than 3%): Discomfort and swelling at IM injection site, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash. Rare (less than 1%): Phlebitis or thrombophlebitis at IV injection site, abdominal cramps, headache, hypotension.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Antibiotic-associated colitis, other superinfections may result from altered bacterial balance. Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of allergies, esp. to aztreonam, other antibiotics.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Evaluate for phlebitis, pain at IM injection site. Assess for GI discomfort, nausea, vomiting. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess skin for rash. Be alert for superinfection: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, anal/genital pruritus, oral mucosal changes (ulceration, pain, erythema). Monitor renal/hepatic function.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash.
![]() , Augmentin, Augmentin ES 600, Augmentin XR, Clavulin
, Augmentin, Augmentin ES 600, Augmentin XR, Clavulin
![]() , Novo-Clavamoxin
, Novo-Clavamoxin
![]() )
) LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS![]() Tablets (Extended-Release [Augmentin XR]): 1,000 mg–62.5 mg.
Tablets (Extended-Release [Augmentin XR]): 1,000 mg–62.5 mg.