LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Avoid pregnancy. May cause fetal harm. Contraception should be considered during therapy and for at least 12 wks after discontinuation. Do not initiate therapy until pregnancy status confirmed. Unknown if crosses placenta or distributed in breast milk. Nursing mothers must discontinue either nursing or drug therapy. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Strong CYP3A inhibitors including atazanavir, clarithromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole, ritonavir, saquinavir, voriconazole may increase concentration. Strong CYP3A inducers including carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifabutin, rifampin may decrease concentration. May alter plasma levels of alfentanil, cyclosporine, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, fentanyl, pimozide, sirolimus. Proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers, antacids may decrease solubility. May increase plasma levels of colchicine, dexamethasone, doxorubicin, etoposide, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, protease inhibitors, quinidine, tacrolimus, vinblastine. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease effectiveness. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase concentration/toxicity (potential for torsades, myelotoxicity). LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin. May decrease neutrophils, platelets, lymphocytes.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Capsules: 200 mg, 250 mg.
Capsules: 200 mg, 250 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• May give without regard to meals. • Avoid grapefruit products. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide capsules.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ALK Positive), Metastatic NSCLC, ROS-1 Positive
PO: ADULTS: 250 mg twice daily. Dosage Modification: Interrupt and/or reduce to 200 mg twice daily based on graded protocol, including hematologic toxicity (grade 4), elevated LFT with bilirubin elevation (grade 1), QT prolongation (grade 3). May reduce to 250 mg once daily if indicated. Discontinue treatment for QT prolongation (grade 4), elevated LFT with bilirubin elevation (grades 2, 3, 4), pneumonitis of any grade.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl Less Than 30 ml/min: 250 mg once daily.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment (see dose for hepatotoxicity during treatment).
Dosage Modification for Toxicity
Hematologic
Grade 3 toxicity (WBC 1,000–2,000 cells/mm3, ANC 500–1,000 cells/mm3, platelets 25,000–50,000 cells/mm3), grade 3 anemia: Withhold treatment until recovery to grade 2 or less, then resume at same dosage. Grade 4 toxicity (WBC less than 1,000 cells/mm3, ANC less than 500 cells/mm3, platelets less than 25,000 cells/mm3), grade 4 anemia: Withhold treatment until recovery to grade 2 or less, then resume at 200 mg twice daily. Grade 4 toxicity on 200 mg twice daily: Withhold treatment until recovery to grade 2 or less, then resume at 250 mg once daily. Recurrent grade 4 toxicity on 250 mg once daily: Permanently discontinue.
Cardiac
Grade 3 QTc prolongation on at least 2 separate EKGs: Withhold treatment until recovery to baseline or grade 1 or less. Resume at 200 mg twice daily. Recurrent grade 3 QTc prolongation on 200 mg twice daily: Withhold treatment until recovery to baseline or grade 1 or less. Resume at 250 mg once daily. Recurrent Grade 3 QTc prolongation on 250 mg once daily: Permanently discontinue.
Bradycardia
Grades 2 or 3: Withhold until recovery to asymptomatic bradycardia or heart rate 60 or more beats/min, evaluate concomitant medications, then resume at 200 mg twice daily. Grade 4 due to crizotinib: Permanently discontinue. Grade 4 associated with concurrent medications known to cause bradycardia/hypotension: Withhold until recovery to asymptomatic bradycardia or heart rate 60 or more beats/min, and if concurrent medications can be stopped, resume at 250 mg once daily.
Pulmonary
Pulmonary toxicity: Permanently discontinue.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (62%–27%): Diplopia, photopsia, photophobia, blurry vision, visual field defect, vitreous floaters, reduced visual acuity, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, peripheral/localized edema, constipation. Occasional (20%–4%): Fatigue, decreased appetite, dizziness, neuropathy, paresthesia, dysgeusia, dyspepsia, dysphagia, esophageal obstruction/pain/spasm/ulcer, odynophagia, reflux esophagitis, rash, abdominal pain/tenderness, stomatitis, glossodynia, glossitis, cheilitis, mucosal inflammation, oropharyngeal pain/discomfort, bradycardia, headache, cough. Rare (3%–1%): Musculoskeletal chest pain, insomnia, dyspnea, arthralgia, nasopharyngitis, rhinitis, pharyngitis, URI, back pain, complex renal cysts, chest pain/tightness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Severe, sometimes fatal treatment-related pneumonitis, pneumonia, dyspnea, pulmonary embolism in less than 2% of pts was noted. Grades 3–4 elevation of hepatic enzymes, increased QT prolongation may require discontinuation. May cause thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, lymphopenia. Severe/worsening vitreous floaters, photopsia may indicate retinal hole, retinal detachment.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess vital signs, O2 saturation. Obtain baseline CBC with differential, serum chemistries, LFT, PT/INR, EKG. Question possibility of pregnancy or plans for breastfeeding. Obtain full medication history including vitamins, herbal products. Detection of ALK-positive NSCLC test needed prior to treatment. Assess history of tuberculosis, HIV, HF, bradyarrhythmias, electrolyte imbalance, medications that prolong QT interval. Assess visual acuity, history of vitreous floaters.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess vital signs, O2 saturation routinely. Monitor CBC with differential monthly, LFT, monthly; increase testing for grades 2, 3, 4 adverse effects. Obtain EKG for bradycardia, electrolyte imbalance, chest pain, difficulty breathing. Monitor for bruising, hematuria, jaundice, right upper abdominal pain, weight loss, or acute infection (fever, diaphoresis, lethargy, oral mucosal changes, productive cough). Report decrease in RBC, Hgb, Hct, platelets, neutrophils, lymphocytes. Worsening cough, fever, or shortness of breath may indicate pneumonitis. Consider ophthalmological evaluation for vision changes. Reinforce birth control compliance.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Blood levels will be drawn routinely. • Report urine changes, bloody or clay-colored stools, upper abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, bruising, fever, cough, difficulty breathing. • Report history of liver abnormalities or heart problems including long QT syndrome, syncope, palpitations, extremity swelling. • Immediately report any newly prescribed medications, suspected pregnancy, or vision changes including light flashes, blurred vision, photophobia, or new or increased floaters. • Contraception recommended during treatment and for at least 3 mos after treatment. • Avoid alcohol, grapefruit products.
cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12)
sye-an-oh-koe-bal-a-min
(Nascobal)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Coenzyme. CLINICAL: Vitamin, antianemic.
USES
Treatment of pernicious anemia, vitamin B12 deficiency due to malabsorption diseases, increased B12 requirement due to pregnancy, thyrotoxicosis, hemorrhage, malignancy, hepatic/renal disease.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to cyanocobalamin. Hereditary optic nerve atrophy. Cautions: Folic acid deficiency, anemia, premature neonates.
ACTION
Coenzyme for metabolic functions (fat, carbohydrate metabolism, protein synthesis). Therapeutic Effect: Necessary for cell growth and replication, hematopoiesis, myelin synthesis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
In presence of calcium, absorbed systemically in lower half of ileum. Initially, bound to intrinsic factor; this complex passes down intestine, binding to receptor sites on ileal mucosa. Protein binding: High. Metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated unchanged in urine. Half-life: 6 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 1,000 mcg/ml. Nasal Spray (Nascobal): 500 mcg/spray. Tablets: 50 mcg, 100 mcg, 250 mcg, 500 mcg, 1,000 mcg. Tablets (Extended-Release): 1,000 mcg. Tablets (Sublingual): 2,500 mcg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
IM, Subcutaneous
• Avoid IV route.
PO
• May give without regard to food.
Intranasal
• Clear both nostrils. • Pull clear cover off top of pump. • Press down firmly and quickly on pump’s finger grips until a droplet of gel appears at top. Then press down on finger grips two more times. • Place the tip halfway into nostril, pointing tip toward back of nose. • Press down firmly and quickly on finger grips to release medication into one nostril while pressing other nostril closed. • Massage medicated nostril for a few seconds. • Administer nasal preparation at least 1 hr before or 1 hr after hot foods or liquids are consumed (hot foods can cause nasal secretion, resulting in loss of medication).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Pernicious Anemia
IM, Subcutaneous: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100 mcg/day for 7 days, then every other day for 7 doses, then every 3–4 days for 2–3 wks. Maintenance: 100 mcg/mo (PO 1,000–2,000 mcg/day). CHILDREN: 30–50 mcg/day for 2 or more wks (to a total dose of 1,000–5,000 mcg). Maintenance: 100 mcg/mo. NEONATES: 0.2 mcg/kg for 2 days, then 1,000 mcg/day for 2–7 days. Maintenance: 100 mcg/mo.
Vitamin Deficiency
IM, Subcutaneous: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100 mcg daily for 6–7 days; if improvement, 100 mcg q other day for 7 doses, then q3–4 days for 2–3 wks. Maintenance: 100 mcg monthly.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1,000–2,000 mcg daily for 1–2 wks. Maintenance: 1,000 mcg daily.
Intranasal: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (NASCOBAL): 500 mcg in one nostril once wkly.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Diarrhea, pruritus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Impurities in preparation may cause rare allergic reaction. Peripheral vascular thrombosis, pulmonary edema, hypokalemia, HF occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess for signs, symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency (anorexia, ataxia, fatigue, hyporeflexia, insomnia, irritability, loss of positional sense, pallor, palpitations on exertion).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for HF, pulmonary edema, hypokalemia in cardiac pts receiving subcutaneous/IM therapy. Monitor serum potassium, serum B12, rise in reticulocyte count (peaks in 5–8 days). Assess for reversal of deficiency symptoms (hyporeflexia, loss of positional sense, ataxia, fatigue, irritability, insomnia, anorexia, pallor, palpitations on exertion). Therapeutic response usually dramatic within 48 hrs.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Lifetime treatment may be necessary with pernicious anemia. • Report symptoms of infection. • Foods rich in vitamin B12 include clams, oysters, herring, red snapper, muscle meats, fermented cheese, dairy products, egg yolks. • Use nasal preparation at least 1 hr before or 1 hr after consuming hot foods, liquids.
cyclobenzaprine
sye-kloe-ben-za-preen
(Amrix, Apo-Cyclobenzaprine
 , Fexmid, Novo-Cycloprine
, Fexmid, Novo-Cycloprine
 )
)
Do not confuse cyclobenzaprine with cycloserine or cyproheptadine, or Flexeril with Floxin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
CLINICAL: Skeletal muscle relaxant.
USES
Treatment of muscle spasm associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of muscle spasms associated with temporomandibular joint pain (TMJ).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to cyclobenzaprine. Acute recovery phase of MI, arrhythmias, HF, heart block, conduction disturbances, hyperthyroidism, use within 14 days of MAOIs. Cautions: Hepatic impairment, history of urinary hesitancy or retention, angle-closure glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure (IOP), elderly.
ACTION
Centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant that reduces tonic somatic muscle activity at level of brainstem. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves local skeletal muscle spasm.
PHARMACOKINETICS
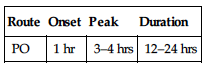
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 1 hr | 3–4 hrs | 12–24 hrs |
Well but slowly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 93%. Metabolized in GI tract and liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 8–37 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Increased sensitivity to anticholinergic effects (e.g., confusion, urinary retention).
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressant medications may increase CNS depression. MAOIs may increase risk of hypertensive crisis, seizures. Tramadol may increase risk of seizures. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, SAMe, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 5 mg, 7.5 mg (Flexmid), 10 mg.
 Capsules (Extended-Release [Amrix]): 15 mg, 30 mg.
Capsules (Extended-Release [Amrix]): 15 mg, 30 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide extended-release capsule. • Give extended-release capsule at same time each day.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Do not use longer than 2–3 wks.
Acute, Painful Musculoskeletal Conditions
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 15 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 5 mg 3 times/day. May increase to 7.5–10 mg 3 times/day.
PO (Extended-Release): ADULTS: 15–30 mg once daily. Not recommended in elderly.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Note: Extended-release capsule not recommended in hepatic impairment. Mild impairment: 5 mg 3 times/day. Moderate to severe impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (39%–11%): Drowsiness, dry mouth, dizziness. Rare (3%–1%): Fatigue, asthenia, blurred vision, headache, anxiety, confusion, nausea, constipation, dyspepsia, unpleasant taste.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may result in visual hallucinations, hyperactive reflexes, muscle rigidity, vomiting, hyperpyrexia.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Record onset, type, location, duration of muscular spasm. Check for immobility, stiffness, swelling.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation. Assess for therapeutic response: relief of pain; decreased stiffness, swelling; increased joint mobility; reduced joint tenderness; improved grip strength.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Drowsiness usually diminishes with continued therapy. • Avoid alcohol, other depressants while taking medication. • Avoid sudden changes in posture. • Sugarless gum, sips of water may relieve dry mouth.
cyclophosphamide

sye-kloe-foss-fa-mide
(Procytox
 )
)
Do not confuse cyclophosphamide with cyclosporine or ifosfamide.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Alkylating agent. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of acute lymphocytic, acute nonlymphocytic, chronic myelocytic, chronic lymphocytic leukemias; ovarian, breast carcinomas; neuroblastoma; retinoblastoma; Hodgkin’s, non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas; multiple myeloma; mycosis fungoides; nephrotic syndrome in children. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of adrenocortical, bladder, cervical, endometrial, prostatic, testicular carcinomas; Ewing’s sarcoma; multiple sclerosis; non–small-cell, small-cell lung cancer; organ transplant rejection; osteosarcoma; ovarian germ cell, primary brain, trophoblastic tumors; rheumatoid arthritis; soft-tissue sarcomas; systemic dermatomyositis; systemic lupus erythematosus; Wilms’ tumor.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to cyclophosphamide. Urinary outflow obstruction. Cautions: Severe leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, tumor infiltration of bone marrow, previous therapy with other antineoplastic agents, radiation, renal/hepatic/cardiac impairment, active UTI.
ACTION
Inhibits DNA, RNA protein synthesis by cross-linking with DNA, RNA strands. Cell cycle–phase nonspecific. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents cell growth. Potent immunosuppressant.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 10%–60%. Crosses blood-brain barrier. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 3–12 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy. May cause fetal malformations (limb abnormalities, cardiac anomalies, hernias). Distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP2D6 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenobarbital) may decrease concentration; CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g., paroxetine, amiodarone) may increase concentration. Anthracycline agents (e.g., doxorubicin, epirubicin) may increase risk of cardiomyopathy. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) may increase concentration, risk of adverse effects. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: Pts with an estrogen-dependent tumor should avoid black cohosh, dong quai. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum uric acid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Capsules: 25 mg, 50 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 500 mg, 1 g, 2 g.
Capsules: 25 mg, 50 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 500 mg, 1 g, 2 g.
Tablets: 25 mg, 50 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ May be carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic. Handle with extreme care during preparation/administration.
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute each 100 mg with 5 ml Sterile Water for Injection, 0.9% NaCl, or D5W to provide concentration of 20 mg/ml. • Shake to dissolve. • Allow to stand until clear.
Rate of Administration • Infusion rates vary based on protocol. May give by direct IV injection, IV piggyback, or continuous IV infusion.
Storage • Reconstituted solution in 0.9% NaCl is stable for 24 hrs at room temperature or up to 6 days if refrigerated.
PO
• Give on an empty stomach. If GI upset occurs, give with food. • Do not cut or crush. • To minimize risk of bladder irritation, do not give at bedtime.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITY
IV INCOMPATIBILITY
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Granisetron (Kytril), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lorazepam (Ativan), morphine, ondansetron (Zofran), propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Hematologic toxicity may require dose reduction.
Usual Dosage (Refer to Individual Protocols)
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: (Single agent): 40–50 mg/kg in divided doses over 2–5 days or 10–15 mg/kg q7–10 days or 3–5 mg/kg twice wkly.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 1–5 mg/kg/day.
Nephrotic Syndrome
PO: ADULTS, CHILDREN: 2 mg/kg/day for 60–90 days. Maximum cumulative dose: 168 mg/kg.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Expected: Marked leukopenia 8–15 days after initiation. Frequent: Nausea, vomiting (beginning about 6 hrs after administration and lasting about 4 hrs); alopecia (33%). Occasional: Diarrhea, darkening of skin/fingernails, stomatitis, headache, diaphoresis. Rare: Pain/redness at injection site.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Myelosuppression resulting in blood dyscrasias (leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, hypoprothrombinemia) has been noted. Expect leukopenia to resolve in 17–28 days. Anemia generally occurs after large doses or prolonged therapy. Thrombocytopenia may occur 10–15 days after drug initiation. Hemorrhagic cystitis occurs commonly in long-term therapy (esp. in children). Pulmonary fibrosis, cardiotoxicity noted with high doses. Amenorrhea, azoospermia, hyperkalemia may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC wkly during therapy or until maintenance dose is established, then at 2- to 3-wk intervals.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, serum BUN, creatinine, electrolytes; urine output. Monitor WBC counts closely during initial therapy. Monitor for hematologic toxicity (fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site), symptoms of anemia (excessive fatigue, weakness). Recovery from marked leukopenia due to myelosuppression can be expected in 17–28 days.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Encourage copious fluid intake, frequent voiding (assists in preventing cystitis) at least 24 hrs before, during, after therapy. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance). • Avoid contact with those who have recently received live virus vaccine. • Promptly report fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, difficulty or pain with urination, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site. • Hair loss is reversible, but new hair growth may have different color, texture.
*cycloSPORINE
sye-kloe-spor-in
(Apo-Cyclosporine
 , Gengraf, Neoral, Restasis, Sandimmune)
, Gengraf, Neoral, Restasis, Sandimmune)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Only physicians experienced in management of immunosuppressive therapy and organ transplant pts should prescribe. Renal impairment may occur with high dosage. Increased risk of neoplasia, susceptibility to infections. May cause hypertension, nephrotoxicity. Psoriasis pts: Increased risk of developing skin malignancies.
Only physicians experienced in management of immunosuppressive therapy and organ transplant pts should prescribe. Renal impairment may occur with high dosage. Increased risk of neoplasia, susceptibility to infections. May cause hypertension, nephrotoxicity. Psoriasis pts: Increased risk of developing skin malignancies.
Do not confuse cyclosporine with cycloserine or cyclophosphamide, Gengraf with ProGraf, Neoral with Neurontin or Nizoral, or Sandimmune with Sandostatin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Cyclic polypeptide. CLINICAL: Immunosuppressant.
USES
Prevents organ rejection of kidney, liver, heart in combination with steroid therapy and/or azathioprine. Treatment of chronic allograft rejection in those previously treated with other immunosuppressives. Capsules/solution: Treatment of severe, active rheumatoid arthritis, severe recalcitrant plaque psoriasis in nonimmunocompromised adults. Ophthalmic: Chronic dry eyes. OFF-LABEL: Allogenic stem cell transplants for prevention/treatment of graft-vs-host disease; focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, lupus nephritis, severe ulcerative colitis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: History of hypersensitivity to cyclosporine, polyoxyethylated castor oil; uncontrolled hypertension, renal impairment, or malignancies in treatment of psoriasis or rheumatoid arthritis. Cautions: Hepatic/renal, impairment. History of seizures. Avoid live vaccines.
ACTION
Inhibits cellular, humoral immune responses by inhibiting interleukin-2, a proliferative factor needed for T-cell activity. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents organ rejection, relieves symptoms of psoriasis, arthritis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Variably absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 90%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated primarily by biliary or fecal excretion. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: Adults, 10–27 hrs; children, 7–19 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Readily crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: No age-related precautions noted in transplant pts. Elderly: Increased risk of hypertension, increased serum creatinine.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Allopurinol, bromocriptine, cimetidine, clarithromycin, danazol, diltiazem, oral contraceptives, erythromycin, fluconazole, ketoconazole may increase concentration, risk of hepatic/renal toxicity. Rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin may decrease cyclosporine concentration. ACE inhibitors, potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements may cause hyperkalemia. Immunosuppressants may increase risk of infection, lymphoproliferative disorders. Lovastatin, simvastatin, atorvastatin, pravastatin may increase risk of rhabdomyolysis. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s response to vaccine. May increase concentration/toxicity of digoxin, colchicine. HERBAL: Avoid cat’s claw, echinacea (possess immunostimulant properties). St. John’s wort may decrease plasma concentration. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase absorption/immunosuppression, risk of toxicity. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, alkaline phosphatase, amylase, bilirubin, creatinine, potassium, uric acid, ALT, AST. May decrease serum magnesium. Therapeutic peak serum level: 50–400 ng/ml; toxic serum level: greater than 400 ng/ml.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Capsules (Gengraf, Neoral [Modified], Sandimmune [Nonmodified]): 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg. Injection, Solution (Sandimmune): 50 mg/ml. Ophthalmic Emulsion (Restasis): 0.05%. Oral Solution (Gengraf, Neoral [Modified], Sandimmune [Nonmodified]): 100 mg/ml.
Capsules (Gengraf, Neoral [Modified], Sandimmune [Nonmodified]): 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg. Injection, Solution (Sandimmune): 50 mg/ml. Ophthalmic Emulsion (Restasis): 0.05%. Oral Solution (Gengraf, Neoral [Modified], Sandimmune [Nonmodified]): 100 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Oral solution available in bottle form with calibrated liquid measuring device. Oral form should replace IV administration as soon as possible.
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Dilute each ml (50 mg) concentrate with 20–100 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W (maximum concentration: 2.5 mg/ml).
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 2–6 hrs. • Monitor pt continuously for hypersensitivity reaction (facial flushing, dyspnea).
Storage • Store parenteral form at room temperature. • Protect IV solution from light. • After diluted, stable for 6 hrs in PVC; 24 hrs in Excel or glass.
PO
• Administer consistently with relation to time of day and meals. • Oral solution may be mixed in glass container with milk, chocolate milk, orange juice, or apple juice (preferably at room temperature). Stir well. • Drink immediately. • Add more diluent to glass container. Mix with remaining solution to ensure total amount is given. • Dry outside of calibrated liquid measuring device before replacing cover. • Do not rinse with water. • Avoid refrigeration of oral solution (solution may separate). • Discard oral solution after 2 mos once bottle is opened.
Ophthalmic
• Invert vial several times to obtain uniform suspension. • Instruct pt to remove contact lenses before administration (may reinsert 15 min after administration). • May use with artificial tears.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Acyclovir (Zovirax), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), magnesium.
 IV COMPATIBILITY
IV COMPATIBILITY
Propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Transplantation, Prevention of Organ Rejection
NOTE: Initial dose given 4–12 hrs prior to transplant or postoperatively.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: NOT MODIFIED: Initially, 10–14 mg/kg daily for 1–2 wks, then taper by 5% each wk to maintenance dose of 5–10 mg/kg daily. MODIFIED: (dose dependent upon type of transplant): Renal: 6–12 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses. Hepatic: 4–12 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses. Heart: 4–10 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: Initially, 5–6 mg/kg/dose daily. Switch to oral as soon as possible.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: MODIFIED:Initially, 2.5 mg/kg a day in 2 divided doses. May increase by 0.5–0.75 mg/kg/day after 8 wks with additional increases made at 12 wks. Maximum: 4 mg/kg/day.
Psoriasis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: MODIFIED:Initially, 2.5 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses. May increase by 0.5 mg/kg/day after 4 wks; additional increases may be made q2wks. Maximum: 4 mg/kg/day.
Dry Eye
Ophthalmic: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Instill 1 drop in each affected eye q12h.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Modify dose if serum creatinine levels 25% or above pretreatment levels.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (26%–12%): Mild to moderate hypertension, hirsutism, tremor. Occasional (4%–2%): Acne, leg cramps, gingival hyperplasia (red, bleeding, tender gums), paresthesia, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache. Rare (less than 1%): Hypersensitivity reaction, abdominal discomfort, gynecomastia, sinusitis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Mild nephrotoxicity occurs in 25% of renal transplants, 38% of cardiac transplants, 37% of liver transplants, generally 2–3 mos after transplantation (more severe toxicity may occur soon after transplantation). Hepatotoxicity occurs in 4% of renal, 7% of cardiac, and 4% of liver transplants, generally within first mo after transplantation. Both toxicities usually respond to dosage reduction. Severe hyperkalemia, hyperuricemia occur occasionally.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline serum chemistries, esp. renal function, LFT. If nephrotoxicity occurs, mild toxicity is generally noted 2–3 mos after transplantation; more severe toxicity noted early after transplantation; hepatotoxicity may be noted during first mo after transplantation.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Diligently monitor serum BUN, creatinine, bilirubin, ALT, AST, LDH levels for evidence of hepatotoxicity/nephrotoxicity (mild toxicity noted by slow rise in serum levels; more overt toxicity noted by rapid rise in levels; hematuria also noted in nephrotoxicity). Monitor serum potassium for evidence of hyperkalemia. Encourage diligent oral hygiene (gingival hyperplasia). Monitor B/P for evidence of hypertension. Note: Reference ranges dependent on organ transplanted, organ function, cyclosporine toxicity. Trough levels should be obtained immediately prior to next dose. Therapeutic serum level: 50–400 ng/ml; toxic serum level: greater than 400 ng/ml.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Blood levels will be drawn routinely. • Report severe headache, persistent nausea/vomiting, unusual swelling of extremities, chest pain. • Avoid grapefruit products (increases concentration/effects), St. John’s wort (decreases concentration).
cytarabine

sye-tar-a-bine
(Ara-C, Cytosar-U
 , Depo-Cyt)
, Depo-Cyt)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. Conventional: Potent myelosuppressant. High risk of multiple toxicities (GI, CNS, pulmonary, cardiac). Liposomal: Chemical arachnoiditis, manifested by profound nausea, vomiting, fever, may be fatal if untreated.
Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. Conventional: Potent myelosuppressant. High risk of multiple toxicities (GI, CNS, pulmonary, cardiac). Liposomal: Chemical arachnoiditis, manifested by profound nausea, vomiting, fever, may be fatal if untreated.
Do not confuse cytarabine with Cytoxan or vidarabine, or Cytosar with Cytoxan or Neosar.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antimetabolite. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Ara-C: Remission induction in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and chronic myelocytic leukemia (CML), prophylaxis and treatment of meningeal leukemia. Depo-Cyt: Treatment of lymphomatous meningitis. OFF-LABEL: Ara-C: Carcinomatous meningitis, Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, myelodysplastic syndrome.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to cytarabine. (Liposomal): Active meningeal infection. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, prior drug-induced bone marrow suppression.
ACTION
Inhibits DNA polymerase. Cell cycle–specific for S phase of cell division. Therapeutic Effect: Appears to inhibit DNA synthesis. Potent immunosuppressive activity.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed; moderate amount crosses blood-brain barrier. Protein binding: 15%. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 1–3 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy. May cause fetal malformations. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease concentration of digoxin, flucytosine. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s response to vaccine. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease therapeutic effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, uric acid, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Ara-C): 100 mg, 500 mg, 1 g. Injection, Solution (Ara-C): 20 mg/ml, 100 mg/ml. Injection, Suspension (Depo-Cyt): 10 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ May give by subcutaneous, IV push, IV infusion, intrathecal routes at concentration not to exceed 100 mg/ml. May be carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic (embryonic deformity). Handle with extreme care during preparation/administration. Depo-Cyt for intrathecal use only.
IV, Subcutaneous, Intrathecal
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Ara-C: Reconstitute with Bacteriostatic Water for Injection. • Dose may be further diluted with 250–1,000 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl for IV infusion. • For intrathecal use, reconstitute vial with preservative-free 0.9% NaCl or pt’s spinal fluid. Dose usually administered in 5–15 ml of solution, after equivalent volume of CSF removed. • Depo-Cyt: No reconstitution required.
Rate of Administration • Ara-C: For IV infusion, give over 1–3 hrs or as continuous infusion.
Storage • Ara-C: Store at room temperature. • Reconstituted solution is stable for 48 hrs at room temperature. • Use diluted solution within 24 hrs. • Discard if slight haze develops. • Depo-Cyt: Refrigerate; use within 4 hrs following withdrawal from vial.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), ganciclovir (Cytovene), heparin, insulin (regular).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Dexamethasone (Decadron), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), filgrastim (Neupogen), granisetron (Kytril), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lorazepam (Ativan), morphine, ondansetron (Zofran), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage for Induction (Refer to Individual Protocols)
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: (Induction): 100 mg/m2/day continuous infusion for 7 days or 200 mg/m2/day continuous infusion (as 100 mg/m2 over 12 hrs q12h) for 7 days.
Intrathecal: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHIDREN: Usual dose: 30 mg/m2 q4 days. Range: 5–75 mg/m2 daily for 4 days or once q4days until CNS findings normalize, followed by one additional treatment.
Usual Maintenance Dosage
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 70–200 mg/m2/day for 2–5 days q mo.
Subcutaneous: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHIDREN: 1–1.5 mg/m2 as single dose q1–4wks.
Usual Dosage for Depo-Cyt
Intrathecal: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Induction): 50 mg q14 days for 2 doses (wks 1, 3). (Consolidation): 50 mg q14 days for 3 doses (wks 5, 7, 9) followed by additional dose at wk 13. (Maintenance): 50 mg q28days for 4 doses (wks 17, 21, 25, 29).
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: IV, Subcutaneous (33%–16%): Asthenia, fever, pain, altered taste/smell, nausea, vomiting (risk greater with IV push than with continuous IV infusion). Intrathecal (28%–11%): Headache, asthenia, altered taste/smell, confusion, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting. Occasional: IV, Subcutaneous (11%–7%): Abnormal gait, drowsiness, constipation, back pain, urinary incontinence, peripheral edema, headache, confusion. Intrathecal (7%–3%): Peripheral edema, back pain, constipation, abnormal gait, urinary incontinence.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Myelosuppression resulting in blood dyscrasias (leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, megaloblastosis, reticulocytopenia) occurring minimally after single IV dose. Leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia should be expected with daily or continuous IV therapy. Cytarabine syndrome (fever, myalgia, rash, conjunctivitis, malaise, chest pain), hyperuricemia may occur. High-dose therapy may produce severe CNS, GI, pulmonary toxicity.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, renal function, LFT. Leukocyte count decreases within 24 hrs after initial dose, continues to decrease for 7–9 days followed by brief rise at 12 days, decreases again at 15–24 days, then rises rapidly for next 10 days. Platelet count decreases 5 days after drug initiation to its lowest count at 12–15 days, then rises rapidly for next 10 days.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor BMP, LFT; serum uric acid. Monitor CBC for evidence of myelosuppression. Monitor for blood dyscrasias (fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site), symptoms of anemia (excessive fatigue, weakness). Monitor for signs of neuropathy (gait disturbances, handwriting difficulties, paresthesia).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Increase fluid intake (may protect against hyperuricemia). • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance). • Avoid contact with those who have recently received live virus vaccine. • Promptly report fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS![]() Capsules: 200 mg, 250 mg.
Capsules: 200 mg, 250 mg.