D
dabigatran

dab-i-gah-tran
(Pradaxa)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Risk of thrombotic events (e.g., stroke) increased if dabigatran discontinued for a reason other than pathological bleeding. Spinal or epidural hematoma may occur with neuraxial anesthesia.
Risk of thrombotic events (e.g., stroke) increased if dabigatran discontinued for a reason other than pathological bleeding. Spinal or epidural hematoma may occur with neuraxial anesthesia.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Thrombin inhibitor. CLINICAL: Anticoagulant.
USES
Indicated to reduce risk of stroke, systemic embolism in pts with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Treatment and reduction of risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Prophylaxis of DVT and PE in pts who have undergone hip replacement surgery.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Severe hypersensitivity to dabigatran. Active major bleeding, pts with mechanical prosthetic heart valves. Cautions: Renal impairment (CrCl 15–30 ml/min), moderate hepatic impairment, invasive procedures, spinal anesthesia, major surgery, pts with congenital or acquired bleeding disorders, elderly, concurrent use of medication that increases risk of bleeding, valvular heart disease.
ACTION
Direct thrombin inhibitor that inhibits coagulation by preventing thrombin effects (e.g., inhibition of thrombin-induced platelet aggregation). Therapeutic Effect: Produces anticoagulation, preventing development of thrombus.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 35%. Eliminated primarily in urine. Half-life: 12–17 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: Severe renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Rifampin may decrease concentration. Antacids, proton pump inhibitors (e.g., omeprazole, pantoprazole) may decrease level, effect. Antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin, clopidogrel), NSAIDs, other anticoagulants, thrombolytics may increase risk of bleeding. HERBAL: Feverfew, ginkgo biloba, green tea, red clover may increase risk of bleeding. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effect. FOOD: High-fat meal delays absorption approximately 2 hrs. LAB VALUES: May increase aPTT, PT, INR.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Capsules: 75 mg, 110 mg, 150 mg.
Capsules: 75 mg, 110 mg, 150 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May be given without regard to food. Administer with water. • Do not break, cut, open capsules.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Medication should be discontinued prior to invasive or surgical procedures.
Treatment/Prevention of DVT/PE
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 150 mg twice daily (after 5–10 days of treatment with parenteral anticoagulants).
Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 150 mg twice daily.
Prophylaxis following Hip Surgery
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 110 mg on day one (1–4 hr postoperative and established hemostasis), then 220 mg daily up to 35 days’ duration.
Dosage in Renal Impairment (Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation)
CrCl 15–30 ml/min: 75 mg twice daily. CrCl less than 15, or HD: Not recommended (removes ∼60% over 2–3 hrs).
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (less than 16%): Dyspepsia (heartburn, nausea, indigestion), diarrhea, upper abdominal pain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Severe, sometimes fatal, hemorrhagic events including intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke, Gl bleeding may occur. Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, reported in less than 1% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC (esp. platelet count), renal function test, PT, aPTT. Question history of mechanical heart valve, recent surgery; hepatic, renal impairment; recent spinal, epidural procedures.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for any sign of bleeding (hematuria, melena, bleeding from gums, petechiae, bruising). Do not obtain B/P in lower extremities (possible deep vein thrombosis). Assess for decrease in B/P, increase in pulse rate, complaint of abdominal pain, diarrhea. Obtain aPTT, PT, platelet count. Question for increase in discharge during menses. Monitor for hematoma. Use care in removing any dressing, tape.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not chew, crush, open, or divide capsules. • Use electric razor, soft toothbrush to prevent bleeding. • Report any sign of red or dark urine, black or red stool, coffee-ground vomitus, red-speckled mucus from cough. • Keep in original container. • Once bottle is opened, must be used within 60 days. • Open blister pack at time of use.
dabrafenib
da-braf-e-nib
(Tafinlar)
Do not confuse dabrafenib with dasatinib.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Kinase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation as detected by FDA-approved test.
◀ ALERT ▶ Not indicated for treatment of wild-type BRAF melanomas.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dabrafenib. Cautions: Diabetes mellitus, hepatic/renal impairment, dehydration, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, pts at increased risk for arrhythmias.
ACTION
Inhibits BRAF kinase gene mutation, a main cause of tumor cell growth, in the absence of growth factors that are normally required for proliferation. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 99.7%. Peak plasma concentration: 2 hrs. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in feces (71%), urine (23%). Half-life: 8 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Avoid pregnancy. May cause fetal harm. Must use effective nonhormonal contraception during treatment and for at least 4 wks after treatment (intrauterine device, barrier methods). Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Must either discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue therapy. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May have increased risk of adverse effects, skin lesions.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antacids, H2-receptors blockers (e.g., famotidine, ranitidine), proton pump inhibitors (e.g., omeprazole, pantoprazole) may decrease concentration/effect. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effect. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, gemfibrozil, ketoconazole) may increase concentration. May decrease effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives, warfarin. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effect. FOOD: High-fat meals may decrease absorption/effect. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, alkaline phosphatase. May decrease serum phosphate, sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Capsules: 50 mg, 75 mg.
Capsules: 50 mg, 75 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give at least 1 hr before or at least 2 hrs after meal. • Do not break, crush, open, or divide capsule. • Missed dose may be given up to 6 hrs prior to next dose.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Metastatic Melanoma
PO: ADULTS/ELDERLY: 150 mg twice daily (about 12 hrs apart) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dose Modification
Based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) grading 1–4.
| Reduction Levels | Dose |
| 1st dose reduction | 100 mg twice daily |
| 2nd dose reduction | 75 mg twice daily |
| 3rd dose reduction | 50 mg twice daily |
Fever Greater Than 101.3°F or Any Grade 2 or Grade 3 Adverse Event
Withhold until fever or adverse event resolves to grade 1 or less, then reduce dose by one level. May further decrease each dose level based on tolerability.
Recurrent Grade 4 Adverse Event or 50-mg Dose Intolerability or Hemodynamic Instability
Permanently discontinue.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dosage adjustment. Severe impairment: Use with caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (37%–17%): Hyperkeratosis, headache, pyrexia, arthralgia, alopecia, rash. Occasional (12%–10%): Back pain, cough, myalgia, constipation, nasopharyngitis, fatigue.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cuSCC) and keratocanthomas reported in 11% of pts (esp. elderly, prior skin cancer, chronic sun exposure). Skin reactions including palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (PPES), papilloma have occurred. May increase cell proliferation of wild-type BRAF melanoma or new malignant melanomas. Eye conditions including uveitis, iritis reported. Hyperglycemia reported in 6% of pts. Serious febrile drug reactions including hypotension, rigors, dehydration reported in 4% of pts. Pts with G6PD deficiency have increased risk of hemolytic anemia. Pancreatitis, interstitial nephritis, bullous rash reported in less than 10% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain BMP, LFT, serum magnesium, phosphate, blood glucose level. Confirm presence of BRAF V600E mutation, negative urine pregnancy before initiating treatment. Assess skin for moles, lesions, papillomas. Baseline ophthalmologic exam, visual acuity. Question current breastfeeding status. Receive full medication history including herbal products.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Offer emotional support. Monitor serum electrolytes, blood glucose routinely. Obtain CBC if hemolytic anemia suspected. Monitor for signs of hyperglycemia. Assess for skin lesions every 2 mos during treatment and at least 6 mos after discontinuation. Immediately report any vision changes, eye pain/swelling, febrile events, renal impairment.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Treatment may cause hair loss. • Do not breastfeed. • Avoid pregnancy; nonhormonal contraception should be used during treatment and up to 4 wks after last dose. • Take capsule at least 1 hr before or at least 2 hrs after meal. Swallow whole; do not chew, crush, open, or divide. • Report any increased urination, thirst, confusion, vision changes, eye pain, fever, skin changes including moles or lesions.• Minimize exposure to sunlight.• Males may experience a decreased sperm count. • Report any newly prescribed medications.
daclatasvir
dak-lat-as-vir
(Daklinza)
Do not confuse daclatasvir with ombitasvir, or Daklinza with Zolinza.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: NS5A inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiviral.
USES
Treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes 1 or 3 infection, in combination with sofosbuvir with or without riboflavin.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to daclatasvir. Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, St. John’s wort). Cautions: Concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors, moderate CYP3A inducers. Concomitant use of amiodarone is not recommended. History of bradycardia, bradyarrhythmias, cardiovascular disease, severe hepatic disease.
ACTION
Inhibits NS5A, a nonstructural protein encoded by HCV. Binds to N-terminus of NS5A and inhibits both viral RNA replication and virion assembly. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits viral replication of hepatitis C virus.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 99%. Peak plasma concentration: 2 hrs. Eliminated in feces (88%), urine (7%). Half-life: 12–15 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Amiodarone, beta blockers (e.g., metoprolol) may increase risk of symptomatic bradycardia. Strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, itraconazole, saquinavir), moderate CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., ciprofloxacin, diltiazem, fosamprenavir) may increase concentration/effect. Moderate CYP3A inducers (e.g., dexamethasone, efavirenz, nafcillin) may decrease concentration/effect. May increase concentration/effect, anticoagulant effect of dabigatran. May increase concentration/effect of digoxin. May increase risk of myopathy, concentration/effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (e.g., atorvastatin, simvastatin). HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effect; use contraindicated. FOOD: High-fat, high-caloric meal may decrease absorption by 28%. LAB VALUES: May increase serum lipase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 30 mg, 60 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Cirrhotic pts with genotype 1a should undergo testing for presence of virus with NSA5A-resistance–associated polymorphisms.
Chronic HCV Infection (Genotypes 1 and 3)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 60 mg once daily, in combination with sofosbuvir, for 12 wks.
Dose Modification
Concomitant Use of Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
30 mg once daily, in combination with sofosbuvir, with or without riboflavin for 12 wks.
Concomitant Use of Moderate CYP3A Inducers
90 mg once daily, in combination with sofosbuvir, with or without riboflavin for 12 wks.
Discontinuation
If sofosbuvir is permanently discontinued, then daclatasvir should also be discontinued.
Concomitant Use of Digoxin
Consider decreasing digoxin dose by 30%–50% or use lowest dose possible to maintain adequate response.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Safety and efficacy not established in pts with decompensated hepatic cirrhosis or liver transplant pts.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (14%–8%): Headache, fatigue, nausea. Rare (5%): Diarrhea.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Symptomatic bradycardia and some cases requiring pacemaker intervention have been reported when amiodarone is co-administered with sofosbuvir, in combination with another HCV direct-acting antiviral, including daclatasvir. Bradycardia generally occurred within hrs to days, but may extend up to 2 wks after initiation. Pts taking beta blockers (e.g., metoprolol), those with underlying cardiac disease, or pts with advanced hepatic disease are at increased risk of bradycardia when treated with amiodarone. Transient, asymptomatic elevations of serum lipase levels greater than 3 times upper limit of normal reported in 2% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain HCV-RNA level, LFT. Receive full medication history including herbal products and screen for contraindications/interactions, esp. concomitant use of amiodarone or digoxin. Confirm HCV genotype 3. Question history of bradycardia, arrhythmias. Assess hydration status.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor HCV-RNA level, LFT as indicated. Pts requiring treatment with amiodarone should be monitored with a cardiac monitor in an inpatient setting for the first 48 hrs of initiation. Further outpatient monitoring or self-monitoring of the heart rate should occur on a daily basis for at least the first 2 wks of treatment. Due to the amiodarone’s long half-life, pts discontinuing amiodarone just prior to starting sofosbuvir, in combination with daclatasvir, should have similar cardiac monitoring as listed earlier. Immediately report symptoms of bradycardia.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• There is an increased risk of drug interactions with other medications. • Do not take any new medications unless approved by physician. • Treatment with amiodarone, an antiarrhythmic drug, may increase the risk of a slow heartbeat and is not recommended during drug therapy. If taking amiodarone, seek immediate medical attention if chest pain, confusion, dizziness, fainting, lethargy, or shortness of breath occur after starting therapy. • Do not take herbal products, esp. St. John’s wort. • Daclatasvir must be used in combination with sofosbuvir (an antiviral drug) and should not be used alone.
daclizumab
dac-klye-zue-mab
(Zinbryta)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause severe, sometimes life-threatening, hepatic injury including hepatic failure and autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatic injury, including autoimmune hepatitis, may occur at any time during treatment and up to 4 mos after discontinuation. Contraindicated in pts with preexisting hepatic disease or impairment. Immune-mediated disorders including toxic skin reactions, lymphadenopathy, noninfectious colitis were reported.
May cause severe, sometimes life-threatening, hepatic injury including hepatic failure and autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatic injury, including autoimmune hepatitis, may occur at any time during treatment and up to 4 mos after discontinuation. Contraindicated in pts with preexisting hepatic disease or impairment. Immune-mediated disorders including toxic skin reactions, lymphadenopathy, noninfectious colitis were reported.
Do not confuse daclizumab with certolizumab, eculizumab, efalizumab, natalizumab, tocilizumab, vedolizumab.
♦ CLASSFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Interleukin-2 receptor blocking antibody. CLINICAL: Multiple sclerosis agent.
USES
Treatment of adult pts with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). Therapy should generally be reserved for pts who have had an inadequate response to 2 or more medications indicated for the treatment of MS.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to daclizumab; preexisting hepatic disease or impairment, including serum ALT or AST at least 2 times upper limit of normal (ULN), history of autoimmune hepatitis or other autoimmune disorders involving the liver. Cautions: History of chronic opportunistic infections (esp. fungal infections, viral infections, tuberculosis); history of autoimmune disorders (demyelinating polyneuropathy, Crohn’s disease, Guillain-Barré syndrome, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, hyperthyroidism, myasthenia gravis, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, type 1 diabetes, vasculitis); concomitant use of other immunosuppressants; conditions predisposing to infection (e.g., diabetes, kidney failure, open wounds), elderly, HIV infection, hematologic cytopenias; history of depression, suicidal ideation. Concomitant use of live vaccines not recommended during treatment and up to 4 mos after treatment. Avoid use during severe active infection.
ACTION
Exact mechanism of action unknown. May involve modulation of interleukin-2 mediated activation of lymphocytes, reducing the number of lymphocytes available to CNS. Therapeutic Effect: May reduce lymphocyte migration into CNS, which reduces central inflammation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Bioavailability: 90%. Degraded into small peptides and amino acids via catabolic pathway. Peak plasma concentration: 5–7 days. Elimination not specified. Half-life: 21 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Monoclonal antibodies are known to cross the placenta. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 17 yrs. Elderly: Not specified; use caution.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None known. Note: Use caution with other hepatotoxic medications/supplements. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, bilirubin. May decrease absolute neutrophil count, Hgb, Hct, lymphocytes, RBC.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 150 mg/ml in prefilled syringe.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Subcutaneous
• 30 mins prior to injection, remove syringe from the refrigerator to allow to warm to room temperature. • Do not use external heat sources (e.g., hot water, heating plate). • Visually inspect for particulate matter or discoloration. • Solution should appear colorless to slightly yellow, clear to slightly opalescent in color. Discard if solution is cloudy or discolored or visible particles are observed. • If a dose is missed, inject missed dose as soon as possible if no more than 2 wks have passed. If more than 2 wks have passed, skip missed dose and administer the next dose on schedule.
Administration
• Insert needle subcutaneously into upper arms, outer thigh, or abdomen and inject solution. • Do not inject into areas of active skin disease or injury such as sunburns, rashes, inflammation, skin infections, or active psoriasis. • Rotate injection sites.
Storage
• Refrigerate until time of use. • If unable to refrigerate, may store protected from light at room temperature (no more than 30°C [86°F]) up to 30 days. • Do not place syringe back in refrigerator after allowing it to warm to room temperature. • Do not freeze.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Multiple Sclerosis, Relapsing
SQ: ADULTS: 150 mg once monthly.
Dose Modification
Hepatic Impairment
Serum ALT or AST greater than 5 times ULN; total serum bilirubin greater than 2 times ULN; serum ALT or AST 3 to less than 5 times ULN with total serum bilirubin 1.5 to less than 2 times ULN: Withhold treatment and investigate for other etiologies of abnormal LFT values. If none are identified, discontinue treatment. If other etiologies are identified, use clinical judgment and consider if it is appropriate to resume treatment when both serum ALT or AST are less than 2 times ULN and total serum bilirubin is less than or equal to ULN.
Suspected autoimmune hepatitis: Permanently discontinue.
Immune-Mediated Disorders
Dermatologic toxicity, serious diffuse or inflammatory rashes; lymphadenopathy, lymphadenitis; noninfectious colitis; other single-organ or multiorgan inflammatory events: Consider interrupting treatment or permanent discontinuation.
Other Toxicities
Allergic reaction, anaphylaxis: Permanently discontinue. Severe depression, suicidal ideation: Consider permanent discontinuation. Infection: Withhold treatment until infection fully resolved.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Not specified; use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (11%–5%): Rash, oropharyngeal pain, eczema. Rare (3%–2%): Acne, pyrexia, diarrhea, dry skin, erythema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Serious, sometimes life-threatening, hepatic injury including autoimmune hepatitis may occur (less than 1% of pts). Serum ALT or AST elevation reported in 6% of pts. Infections occurred in up to 60% of pts. Respiratory tract infections including nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, influenza, bronchitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, rhinitis, laryngitis, pneumonia reported in 29%–4% of pts. Dermatitis, folliculitis, skin exfoliation, toxic skin eruption may occur. Lymphadenopathy, lymphadenitis reported in 5%–2% of pts. Other immune-mediated disorders may include immune hemolytic anemia, glomerulonephritis, noninfectious colitis, pancreatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoidosis, sialadenitis thyroiditis. Depression occurred in 7% of pts. Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema may occur any time during treatment. Immunogenicity (auto-daclizumab antibodies) reported in 8%–19% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline LFT, vital signs. Screen for hepatitis B and C virus infection; active infection. Pts should be evaluated for active tuberculosis and tested for latent infection prior to initiating treatment and periodically during therapy. Induration of 5 mm or greater with tuberculin skin testing should be considered a positive test result when assessing for latent tuberculosis infection. Antifungal therapy should be considered for pts who reside in or travel to regions where mycoses are endemic. Question history of autoimmune diseases (as listed in Precautions), depression or suicidal ideation, demyelinating disorders, HIV infection, prior hypersensitivity reactions. Conduct neurologic and dermatologic exam.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor LFT monthly during treatment and for at least 6 mos after discontinuation. If autoimmune hepatitis is suspected or severe immune-mediated disorder occurs, consider referral to specialist; may require treatment with corticosteroids and other immunosuppressant agents. Monitor for symptoms of tuberculosis, including those who tested negative for latent tuberculosis infection at baseline. Interrupt or discontinue treatment if serious infection, opportunistic infection, or sepsis occurs and initiate appropriate antimicrobial therapy. Diligently monitor for depression or suicidal ideation, hepatotoxicity, hypersensitivity reaction (esp. anaphylaxis, angioedema), lymphadenopathy, noninfectious colitis, other immune-mediated disorders, reactivation of latent infection, toxic skin reactions. Assess neurologic status for symptom improvement. Assess skin for rash, lesions.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Treatment may depress immune system and reduce ability to fight infection. Report symptoms of infection such as body aches, chills, cough, fatigue, fever. Avoid those with active infection. • Report travel plans to possible endemic areas. • Do not receive live vaccines during treatment and up to 4 mos following last dose. • Expect frequent tuberculosis screening. • Treatment may cause signs of a common cold or flu-like symptoms. • Allergic reactions such as difficulty breathing, hives, rash, swelling of the face or tongue, wheezing can happen at any time. If allergic reaction occurs, seek immediate medical attention. • Treatment may cause worsening of chronic autoimmune disorders; inflammatory disorders such as toxic skin reactions, inflammation of the lymph nodes or colon, or life-threatening inflammation of the liver. • Report abdominal pain, diarrhea, easy bruising, clay-colored stools, dark-amber urine, fatigue, loss of appetite, yellowing of skin or eyes; swelling or pain of lymph nodes. • Immediately report thoughts of suicide or worsening of depression.
dalbavancin
dal-ba-van-sin
(Dalvance)
Do not confuse dalbavancin with oritavancin or telavancin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Glycopeptide. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of adult pts with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by susceptible strains of gram-positive microorganisms including Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, and Streptococcus anginosus group (including S. anginosus, S. intermedius, S. constellatus).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Known hypersensitivity reaction to dalbavancin. Cautions: Hepatic/renal impairment, chronic hepatitis, hx alcohol abuse, hx hypersensitivity reaction to glycopeptides (e.g., vancomycin), recent Clostridium difficile infection or antibiotic-associated colitis.
ACTION
Inhibits cell wall synthesis by binding to bacterial cell membrane. Therapeutic Effect: Bactericidal.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Metabolism not defined. Protein binding: 93%. Primarily eliminated in urine. Half-life: 14.4 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk; use caution. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None known. HERBAL: None known. FOOD: None significant. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, bilirubin.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 500 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
◀ ALERT ▶ Must be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection and subsequently diluted with 5% Dextrose Injection only.
Reconstitution • Reconstitute each 500 mg vial with 25 ml of Sterile Water for Injection for final concentration of 20 mg/ml. • To avoid foaming, alternate between gentle swirling and inversion of vial until completely dissolved. Do not shake. • Visually inspect for particulate matter. Solution should appear clear, colorless to yellow. Do not use if particulate matter observed. • Aseptically transfer required dose into 5% dextrose to a final concentration of 1–5 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 30 min.
Storage • Store unused vials at room temperature. • Reconstituted vials/diluted bag may be refrigerated or stored at room temperature for up to 48 hrs. • Do not freeze.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not infuse with other medications or electrolytes. Saline-based solutions may cause precipitate formation. If using single IV access, flush IV with 5% dextrose before and after each use.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infection
IV: ADULTS/ELDERLY: (Two-Dose Regimen): 1,000 mg once, followed by 500 mg once 7 days later. (Single-Dose Regimen): 1,500 mg.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl less than 30 ml/min who are not receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis: (Two-Dose Regimen): 750 mg once, followed by 375 mg once 7 days later. (Single-Dose Regimen): 1,125 mg. Pts receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis: No dose adjustment necessary.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment: Not defined; use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (6%–4%): Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache. Rare (3%–2%): Rash, pruritus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis or severe skin reactions have been reported with glycopeptide antibacterial agents. Too-rapid infusion may cause “red-man syndrome” reaction, characterizing by flushing of upper body, urticaria, pruritus, rash. C. difficile–associated diarrhea with severity ranging from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis has occurred. Drug-induced hepatotoxicity with hepatic enzymes greater than 3 times upper limit normal has been reported. Treatment in the absence of proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection may increase risk of drug-resistant bacteria.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, BMP, LFT, wound culture and sensitivity, vital signs. Question history of recent C. difficile infection, hepatic/renal impairment, hypersensitivity reaction. Assess skin wound characteristics; hydration status. Question pt’s usual stool characteristics (color, frequency, consistency).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess skin infection/wound for improvement. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency; increasing severity may indicate antibiotic-associated colitis. If frequent diarrhea occurs, obtain C. difficile toxin screen and initiate isolation precautions until result confirmed. Encourage PO intake. Monitor I&O. Monitor for “red-man syndrome” during infusion; stopping or slowing infusion may decrease reaction.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• It is essential to complete drug therapy despite symptom improvement. Early discontinuation may result in antibacterial resistance or increased risk of recurrent infection. • Report any episodes of diarrhea, esp. following weeks after treatment completion. Frequent diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain, blood-streaked stool may indicate C. difficile infection, which may be contagious to others. • Report abdominal pain, black/tarry stools, bruising, yellowing of skin or eyes, dark urine, decreased urine output. • Do not breastfeed. • Drink plenty of fluids.
dalfampridine
dal-fam-pri-deen
(Ampyra, Fampyra
![]() )
)
Do not confuse Ampyra with anakinra, or dalfampridine with desipramine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Potassium channel blocker. CLINICAL: Multiple sclerosis agent.
USES
Indicated to improve ambulation in pts with MS.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dalfampridine. History of seizures, moderate to severe renal impairment (CrCl equal to or less than 50 ml/min). Cautions: Mild renal impairment (CrCl equal to 51–80 ml/min).
ACTION
Increases conduction of action potentials in demyelinated axons, inhibiting potassium channels. Therapeutic Effect: Improves ambulation in those with multiple sclerosis (MS).
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed from GI tract. Minimally metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 5.2–6.5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase creatinine clearance.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablet, Film-Coated, Extended-Release: 10 mg.
Tablet, Film-Coated, Extended-Release: 10 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May give without regard to food. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Multiple Sclerosis
PO: ADULTS 18 YRS AND OLDER, ELDERLY: 10 mg twice daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl 50 ml/min or less: Contraindicated.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (9%–5%): Insomnia, dizziness, headache, nausea, asthenia, back pain.
Rare (4%–2%): Paresthesia, nasopharyngitis, constipation, dyspepsia, pharyngolaryngeal pain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Urinary tract infection occurs in 12% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC, BUN, creatinine clearance, serum chemistries prior to treatment and routinely thereafter. Offer emotional support.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, serum chemistries, renal function tests, particularly creatinine clearance. Monitor for urinary, respiratory infection. Assess for therapeutic response (improvement in walking as demonstrated by increase in walking speed).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Report difficulty in sleeping, dizziness, headache, nausea, back pain, loss of strength or energy. • Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets.
dalteparin

dal-te-par-in
(Fragmin)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Epidural or spinal anesthesia greatly increases potential for spinal or epidural hematoma, subsequent long-term or permanent paralysis.
Epidural or spinal anesthesia greatly increases potential for spinal or epidural hematoma, subsequent long-term or permanent paralysis.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Low molecular weight heparin. CLINICAL: Anticoagulant.
USES
Prevention of ischemic complications in pts with unstable angina or non–Q-wave MI. Prevention of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in pts undergoing hip replacement surgery, or abdominal surgery who are at risk for thromboembolic complications (e.g., pts older than 40 yrs, obese, pts with malignancy, history of DVT or PE, surgery requiring general anesthesia and lasting more than 30 min). Extended treatment of symptomatic venous thromboembolism (VTE) to reduce recurrence of VTE in cancer pts. Prevention of DVT or pulmonary embolism in acutely ill pts with severely restricted mobility.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Active major bleeding; concurrent heparin therapy; hypersensitivity to dalteparin, heparin, pork products; unstable angina; history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia; non–Q-wave MI; prolonged venous thromboembolism undergoing epidural/neuraxial anesthesia. Cautions: Conditions with increased risk for hemorrhage, bacterial endocarditis, renal/hepatic impairment, uncontrolled hypertension, history of recent GI ulceration/hemorrhage, peptic ulcer disease, pericarditis, preexisting thrombocytopenia, recent childbirth, concurrent use of aspirin.
ACTION
Antithrombin in presence of low molecular weight heparin inhibits factor Xa, thrombin. Only slightly influences platelet aggregation, PT, aPTT. Therapeutic Effect: Produces anticoagulation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| Subcutaneous | N/A | 4 hrs | N/A |
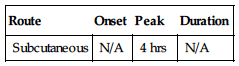
Protein binding: less than 10%. Half-life: 3–5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Use with caution, particularly during last trimester, immediate postpartum period (increased risk of maternal hemorrhage). Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anticoagulants, NSAIDs, platelet inhibitors (e.g., clopidogrel), thrombolytic agents may increase risk of bleeding. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, garlic, ginseng, other herbs with anticoagulant/antiplatelet activity may increase antiplatelet activity. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST. May decrease serum triglycerides.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution: 2,500 units/0.2 ml, 5,000 units/0.2 ml, 7,500 units/0.3 ml, 10,000 units/ml, 25,000 units/ml, 12,500 units/0.5 ml, 15,000 units/0.6 ml, 18,000 units/0.72 ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Subcutaneous
• Visually inspect for particulate matter or discoloration. • Subcutaneously insert needle into abdomen, outer thigh, or upper arm region and inject solution. • Do not inject into areas of active skin disease or injury such as sunburns, rashes, inflammation, or infection. Rotate injection sites.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Abdominal Surgery, Low to Moderate DVT Risk
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2,500 units 1–2 hrs before surgery, then daily for 5–10 days.
Abdominal Surgery
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Low DVT Risk): 2,500 units 1–2 hrs before surgery, then daily for 5–10 days. (High DVT Risk): 5,000 units evening before surgery or 2,500 units 1–2 hrs before surgery, 2,500 units 12 hrs later, then 5,000 units daily for 5–10 days.
Total Hip Surgery
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2,500 units 1–2 hrs before surgery, then 2,500 units 4–8 hrs after surgery, then 5,000 units/day (starting at least 6 hrs after postsurgical dose) for 7–10 days.
Unstable Angina, Non–Q-Wave MI
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 120 units/kg q12h for up to 5–8 days (maximum: 10,000 units/dose) given with aspirin. Discontinue dalteparin once clinically stable.
Venous Thromboembolism (Cancer Pts)
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially (1 mo), 200 units/kg (maximum: 18,000 units) daily for 30 days. Maintenance (2–6 mos): 150 units/kg once daily (maximum: 18,000 units). If platelet count 50,000–100,000/mm3, reduce dose by 2,500 units until platelet count recovers to 100,000/mm3 or more. If platelet count less than 50,000/mm3, discontinue until platelet count recovers to more than 50,000/mm3.
Prevention of DVT, Acutely Ill Pt, Immobile Pt
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5,000 units once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
For CrCl less than 30 ml/min, monitor anti-Xa levels to determine appropriate dose.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (7%–3%): Hematoma at injection site. Rare (less than 1%): Hypersensitivity reaction (chills, fever, pruritus, urticaria, asthma, rhinitis, lacrimation, headache); mild, local skin irritation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may lead to bleeding complications ranging from local ecchymoses to major hemorrhage. Thrombocytopenia occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline coagulation studies, CBC, esp. platelet count. Determine baseline B/P.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Periodically monitor CBC, stool for occult blood (no need for daily monitoring in pts with normal presurgical coagulation parameters). Assess for any sign of bleeding (bleeding at surgical site, hematuria, blood in stool, bleeding from gums, petechiae, bruising/bleeding at injection sites).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Usual length of therapy is 5–10 days. • Do not take any OTC medication (esp. aspirin) without consulting physician. • Report bleeding, bruising, dizziness, light-headedness, rash, itching, fever, swelling, breathing difficulty. • Rotate injection sites daily. • Teach proper injection technique. • Excessive bruising at injection site may be lessened by ice massage before injection.
dantrolene
dan-troe-leen
(Dantrium, Revonto, Ryanodex)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Potential for hepatotoxicity.
Potential for hepatotoxicity.
Do not confuse Dantrium with danazol or Daraprim, Revontro with Revatio.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
CLINICAL: Skeletal muscle relaxant.
USES
PO: Relief of symptoms of spasticity due to spinal cord injuries, stroke, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, esp. flexor spasms, concomitant pain, clonus, muscular rigidity. Management of malignant hyperthermia (MH), prevention of MH in susceptible individuals. Parenteral: Management of malignant hyperthermia. Prevention of malignant hyperthermia (preoperative/postoperative administration). Ryanodex: Treatment of malignant hyperthermia; prevention of malignant hyperthermia in pts at high risk. OFF-LABEL: Neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dantrolene. IV: None known. PO: When spasticity used to maintain posture/balance during locomotion or to obtain increased motor function. Active hepatic disease. Cautions: Cardiac/pulmonary impairment, history of previous hepatic disease.
ACTION
Acts directly on skeletal muscle by interfering with release of calcium ion. Reduces calcium ion concentration. Therapeutic Effect: Dissociates excitation-contraction coupling. Interferes with catabolic process associated with malignant hyperthermia.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Poorly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: High. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: IV: 4–8 hrs; PO: 8.7 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Readily crosses placenta. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: No age-related precautions noted in pts 5 yrs and older. Elderly: No precautions specified.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CNS depressants may increase CNS depression with short-term use. Hepatotoxic medications may increase risk of hepatic toxicity with chronic use. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin) may increase concentration. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May alter serum ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules (Dantrium): 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Dantrium, Revontro): 20-mg vial. Injection Suspension (Ryanodex): 250 mg powder.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute 20-mg vial with 60 ml Sterile Water for Injection (not Bacteriostatic Water for Injection). (Ryanodex): 250 mg vial with 5 ml Sterile Water for Injection.
Rate of Administration • For therapeutic or emergency dose, give IV over 2–3 min. • For IV infusion, administer over 1 hr. • Diligently monitor for extravasation (high pH of IV preparation). May produce severe complications. (Ryanodex): Do not dilute; infuse into IV catheter or indwelling catheter.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Use within 6 hrs after reconstitution. • Solution is clear, colorless. Discard if cloudy, precipitate forms.
PO
• Give without regard to food.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
D5W, 0.9% NaCl.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Spasticity
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 25 mg once daily for 7 days; then 25 mg 3 times/day for 7 days; then 50 mg 3 times/day for 7 days; then 100 mg 3 times/day. Maximum: 400 mg/day. CHILDREN: Initially, 0.5 mg/kg/dose once daily for 7 days; then 0.5 mg/kg/dose 3 times/day for 7 days; then 1 mg/kg/dose 3 times/day for 7 days; then 2 mg/kg/dose 3 times/day. Maximum: 400 mg/day.
Perioperative Prophylaxis for Malignant Hyperthermic Crisis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 4–8 mg/kg/day in 3–4 divided doses beginning 1–2 days before surgery; give last dose 3–4 hrs before surgery.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 2.5 mg/kg about 1.25 hrs before surgery with additional doses as needed.
Management of Malignant Hyperthermic Crisis
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: Initially, a minimum of 2.5 mg/kg rapid IV; may repeat up to total cumulative dose of 10 mg/kg. May follow with 4–8 mg/kg/day PO in 4 divided doses up to 3 days after crisis. (Ryanodex): Minimum dose of 1 mg/kg. Maximum: 10 mg/kg (cumulative).
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Contraindicated with active hepatic disease.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, general malaise, diarrhea (mild). Occasional: Confusion, diarrhea (severe), headache, insomnia, constipation, urinary frequency. Rare: Paradoxical CNS excitement or restlessness, paresthesia, tinnitus, slurred speech, tremor, blurred vision, dry mouth, nocturia, impotence, rash, pruritus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Risk of hepatotoxicity, most notably in females, pts 35 yrs and older, pts taking other hepatotoxic medications concurrently. Overt hepatitis noted most frequently between 3rd and 12th mo of therapy. Overdose results in vomiting, muscular hypotonia, muscle twitching, respiratory depression, seizures.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline LFT. Record onset, type, location, duration of muscular spasm. Check for immobility, stiffness, swelling.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation. For pts on long-term therapy, hepatic/renal function tests, CBC should be performed periodically. Assess for therapeutic response: relief of pain, stiffness, spasm.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Drowsiness usually diminishes with continued therapy. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol/other depressants. • Report continued weakness, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, skin rash, itching, bloody/tarry stools.
dapagliflozin
dap-a-gli-floe-zin
(Farxiga)
Do not confuse dapagliflozin with canagliflozin or empagliflozin.
FIXED COMBINATION(S)
Xigduo XR: dapagliflozin/metformin (an antidiabetic): 5 mg/500 mg, 5 mg/1,000 mg, 10 mg/500 mg, 10 mg/1,000 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antidiabetic agent.
USES
Adjunctive treatment to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in pts with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dapagliflozin, other SGLT2 inhibitors; severe renal impairment, dialysis, end-stage renal disease. Cautions: Baseline hypotension, mild to moderate renal impairment, elderly, hypovolemia/dehydration (correct before initiating treatment), hx of genital mycotic infection. Not recommended in pts with active bladder cancer, diabetic ketoacidosis, type 1 diabetes mellitus. May be associated with ketoacidosis. Concurrent use of loop diuretics.
ACTION
Increases excretion of urinary glucose by inhibiting reabsorption of glucose in kidneys by inhibiting SGLT2 in proximal renal tubule. Therapeutic Effect: Lowers serum glucose levels, Hgb A1c.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed following PO administration. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 91%. Peak plasma concentration: 2 hrs. Eliminated in urine (75%), feces (21%). Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 12.9 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Must either discontinue drug or discontinue breastfeeding. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: May have increased adverse effects related to renal impairment/volume depletion.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: Fenugreek, garlic, ginkgo, ginger, ginseng may increase hypoglycemic effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase Hct, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels; serum creatinine, phosphate. May decrease eGFR. Expected to decrease Hgb A1c; may yield positive urine glucose test.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets: 5 mg, 10 mg.
Tablets: 5 mg, 10 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May give without regard to meals.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
PO: ADULTS/ELDERLY: Initially, 5 mg once daily in the morning. May increase to 10 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment (eGFR greater than 60 ml/min): No dose adjustment necessary; use caution. Severe impairment (eGFR less than 60 ml/min): Avoid use. Development of renal impairment during treatment: Discontinue if eGFR is persistently less than 60 ml/min.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Concomitant Use of Insulin or Insulin Secretagogue
Consider lowering dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to reduce risk of hypoglycemia.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (6%–3%): Nasopharyngitis, back pain, increased urination, nausea. Rare (2%): Constipation, extremity pain, discomfort with urination.
ADVERSE REACTIONS/TOXIC EFFECTS
Orthostatic hypotension, postural dizziness, symptomatic hypotension, syncope, volume depletion may occur; pts who are elderly, use loop diuretics, or have baseline renal impairment have increased risk. Genital mycotic (yeast) infections occurred in 6% of pts; most reported cases were vulvovaginal infections in women and balanitis in men. Hypoglycemic events reported in 1.5% of pts (5% in elderly). Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema (tongue/lip swelling), erythema, rash, pruritus, urticaria have occurred. Newly diagnosed bladder cancer occur rarely. Genitourinary infections including cystitis, kidney infection, prostatitis, pyelonephritis, trigonitis, urethritis, UTI occurred in 5.7% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain capillary blood glucose, Hgb A1c, LDL-C, renal function test, urinalysis. Assess hydration status. Correct volume depletion prior to initiating treatment. Assess pt’s understanding of diabetes management, routine home glucose monitoring. Receive full medication history including herbal products. Question history of co-morbidities, esp. hypersensitivity reaction, renal impairment, type 1 diabetes. Assess breastfeeding status.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor capillary blood glucose, Hgb A1c, renal function tests. Assess for hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, mycotic infections. Screen for glucose-altering conditions: fever, increased activity or stress, trauma, surgery. Obtain dietary consult for nutritional education. Encourage PO intake. Monitor for hypotension. Monitor for hypersensitivity reaction such as dyspnea, urticaria, angioedema, dizziness.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Diabetes mellitus requires lifelong control. Diet and exercise are principal parts of treatment; do not skip or delay meals. • Test blood sugar regularly. • When taking combination drug therapy or when glucose demands are altered (fever, infection, trauma, stress), have low blood sugar treatment available (glucagon, oral dextrose). • Monitor daily calorie intake. • Report suspected pregnancy. Do not breastfeed. • Genital itching or discharge may indicate yeast infection. • Therapy may increase risk for dehydration/low blood pressure, esp. in pts who are elderly, on low-salt diet, have low blood pressure, or take water pills (diuretics). Drink plenty of fluids. • Report any decrease in urine output, dark-colored urine, painful urination, or flank pain. • Therapy may increase risk of bladder cancer; report any blood in urine or painful urination. • May rarely cause allergic reaction; report itching, hives, difficulty breathing, wheezing.
*DAPTOmycin
dap-toe-mye-sin
(Cubicin)
Do not confuse Cubicin with Cleocin, or daptomycin with dactinomycin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Lipopeptide antibacterial agent. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of complicated skin/skin structure infections caused by susceptible strains of gram-positive pathogens, including Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin susceptible and methicillin resistant) [MRSA], Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae. Treatment of S. aureus systemic infections caused by methicillin-susceptible and -resistant S. aureus. OFF-LABEL: Severe infections caused by MRSA or Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE); treatment of prosthetic joint infection caused by staphylococci or Enterococcus.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to daptomycin. Cautions: Severe renal impairment (CrCl less than 30 ml/min), concurrent use of other medications associated with myopathy (e.g., statins).
ACTION
Binds to bacterial membranes and causes rapid depolarization of membrane potential. Inhibits protein, DNA, RNA synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Bactericidal.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Protein binding: 90%. Primarily excreted unchanged in urine. Moderately removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 7–8 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Concurrent use with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (e.g., simvastatin) may cause myopathy. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase CPK, serum potassium. May alter LFT results.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 500 mg/vial.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute 500-mg vial with 10 ml 0.9% NaCl to provide a concentration of 50 mg/ml. May further dilute in 0.9% NaCl. • Do not shake or agitate vial.
Rate of Administration • For IV injection, give over 2 min (concentration: 50 mg/ml). • For intermittent IV infusion (piggyback), infuse over 30 min.
Storage • Refrigerate. • Appears as pale yellow to light brown lyophilized cake. • Reconstituted solution is stable for 12 hrs at room temperature or up to 48 hrs if refrigerated. • Discard if particulate forms.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Diluents containing dextrose. If same IV line is used to administer different drugs, flush line with 0.9% NaCl.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
0.9% NaCl, Lactated Ringer’s, aztreonam (Azactam), dopamine, fluconazole (Diflucan), gentamicin, heparin, levofloxacin (Levaquin).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Complicated Skin/Skin Structure Infections
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 4 mg/kg every 24 hrs for 7–14 days.
Systemic Infections
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 6 mg/kg once daily for 2–6 wks.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl less than 30 ml/min, hemodialysis (HD), peritoneal dialysis (PD): Dosage is 4 mg/kg q48h for skin and soft tissue infections; 6 mg/kg q48h for staphylococcal bacteremia. Hemodialysis (HD): Give dose after dialysis. Continuous renal replacement therapy: Continuous Venovenous Hemodialysis (CVVHD): 8 mg/kg q48h, Continuous Venovenous Hemofiltration (CVVH) or Continuous Venovenous Hemodiafiltration (CVVHDF): 8 mg/kg q48h or 4–6 mg/kg q24h.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (6%–5%): Constipation, nausea, peripheral injection site reactions, headache, diarrhea. Occasional (4%–3%): Insomnia, rash, vomiting. Rare (less than 3%): Pruritus, dizziness, hypotension.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Skeletal muscle myopathy (muscle pain/weakness, particularly of distal extremities) occurs rarely. Antibiotic-associated colitis, other superinfections (abdominal cramps, severe diarrhea, fever) may result from altered bacterial balance in GI tract.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CPK, blood cultures before first dose (therapy may begin before results are known).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess oral cavity for white patches on mucous membranes, tongue (thrush). Monitor for myopathy (muscle pain, weakness), CPK levels, renal function tests. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Mild GI effects may be tolerable, but increasing severity may indicate onset of antibiotic-associated colitis. Be alert for superinfection: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, anal/genital pruritus, oral mucosal changes (ulceration, pain, erythema). Monitor for dizziness, institute appropriate measures.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report rash, headache, nausea, dizziness, constipation, diarrhea, muscle pain, or any other new symptom.
daratumumab
dar-a-toom-ue-mab
(Darzalex)
Do not confuse daratumumab with adalimumab, ofatumumab, panitumumab, or necitumumab.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Monoclonal antibody. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Monotherapy for the treatment of pts with multiple myeloma who have received at least three prior lines of therapy including a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent or who are double-refractory to a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent. In combination for treatment of multiple myeloma in pts who have received at least one prior therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to daratumumab. Cautions: Obstructive pulmonary disorders (e.g., COPD, emphysema), baseline cytopenias, herpes zoster infection, elderly.
ACTION
Binds to cell surface glycoprotein CD38 on CD38-expressing tumor cells. Inhibits tumor cell proliferation and induces apoptosis. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis. Promotes tumor cell death.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Metabolism not specified. Steady state reached approx. 5 mos into the q4wk dosing period (by 21st infusion). Elimination not specified. Half-life: 18 ± 9 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Avoid pregnancy; may cause fetal harm/malformations. Monoclonal antibodies are known to cross the placenta. Females of reproductive potential should use effective contraception during treatment and up to 3 mos after discontinuation. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. However, human immunoglobulin G is present in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None known. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Drug may be detected on both serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation assays used to monitor multiple myeloma endogenous M protein. May affect the determination of complete response and disease progression of some pts with immunoglobulin G kappa myeloma protein. May cause positive Coombs’ test. Expected to decrease Hgb, Hct, lymphocytes, neutrophils, platelets, RBCs.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 100 mg/5 ml, 400 mg/20 ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Preparation for Administration • Calculate the dose and number of vials required based on weight in kg. • Solution should appear colorless to pale yellow. Do not use if opaque particles, discoloration, or foreign particles are observed. • Remove a volume from the 0.9% NaCl infusion bag that is equal to the required volume of the dose solution. • Dilute in 1000 ml (first infusion) or 500 ml (subsequent infusions) 0.9% NaCl bag. • Mix by gentle inversion. Do not shake or agitate. • Infusion bags must be made of polyvinylchloride, polypropylene, polyethylene, or polyolefin blend. • Diluted solution may develop very small translucent to white proteinaceous particles; do not use if diluted solution is discolored or if visibly opaque or foreign particles are observed. • Discard used portions of vials.
Infusion Guidelines • Prior to administration, premedicate with an IV corticosteroid, acetaminophen, and an IV or oral antihistamine approx. 60 mins before each infusion (see manufacturer guidelines). • Infuse using an inline, sterile, nonpyrogenic, low-protein-binding polyethersulfone filter (0.22 or 0.2 μm). • Infuse via dedicated line using infusion pump. • Do not administer as IV push or bolus. • Infusion should be completed within 15 hrs. • If infusion cannot be completed for any reason, do not save unused portions for reuse. • Postinfusion, administer an oral corticosteroid on the first and second day after each infusion to reduce risk of delayed infusion reactions (see manufacturer guidelines). • In pts with a history of obstructive pulmonary disease, consider short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators and an inhaled corticosteroid postinfusion (may discontinue if no infusion reaction occurs after the first four infusions).
Rate of Administration • First infusion (1000 ml volume): Infuse at 50 ml/hr for the first 60 mins. Increase in increments of 50 ml/hr q1hr if no infusion reactions occur. Maximum: 200 ml/hr. • Second infusion (500 ml volume): Infuse at 50 ml/hr for the first 60 mins. Increase in increments of 50 ml/hr q1hr if there were no Grade 1 or greater infusion reactions during the first 3 hrs of first infusion. Maximum: 200 ml/hr. • Subsequent infusions (500 ml volume): Infuse at 100 ml/hr if there were no Grade 1 or greater infusion reactions during a final infusion rate of greater than or equal to 100 ml/hr in the first two infusions. Increase in increments of 50 ml/hr q1hr if tolerated. Maximum: 200 ml/hr.
Storage • Refrigerate unused vials. • Do not shake. • May refrigerate diluted solution up to 24 hr. • If diluted solution is refrigerated, allow solution to warm to room temperature before use. • Protect from light.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Multiple Myeloma
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Monotherapy or combination with Lenalidomide/dexamethasone) Wks 1–8: 16 mg/kg once wkly. Wks 9–24: 16 mg/kg once q2wks. Wk 25 and beyond: 16 mg/kg once q4wks. (Combination with bortezomib/dexamethasone) Wks 1–9): 16 mg/kg once wkly. Wks 10–24): 16 mg/kg q3wks. Wk 25 and beyond: 16 mg/kg q4wks.
Dose Modification
Infusion Reactions
Promptly interrupt infusion if any reaction occurs.
Grade 1 or 2 reaction: Once symptoms resolve, resume infusion at a decreased rate that is 50% (or less) of previous rate. If no further reactions are observed, may increase infusion rate as appropriate.
Grade 3 reaction: If symptoms resolve to grade 2 or less, consider resuming infusion at a decreased rate that is 50% (or less) of previous rate. If no further reactions are observed, may increase rate as appropriate. If a grade 3 reaction recurs, decrease rate as outlined earlier. If grade 3 reaction occurs for a third time, permanently discontinue.
Grade 4 reaction: Permanently discontinue.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment.
Moderate to severe impairment: Not specified; use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (37%–14%): Fatigue, back pain, nausea, pyrexia, cough, nasal congestion, arthralgia, diarrhea, dyspnea, decreased appetite, extremity pain, constipation, vomiting. Occasional (12%–10%): Headache, musculoskeletal chest pain, chills, hypertension.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia is an expected response to therapy. Infusion reactions occurred in approx. 50% of pts (mostly during first infusion). Infusion reactions can also occur with subsequent infusions (mainly during the infusion or within 4 hrs of completion). Severe infusion reactions may include cough, dyspnea, bronchospasm, hypertension, hypoxia, laryngeal edema, pulmonary edema, wheezing. Less common reactions may include chills, headache, hypotension, rash, nausea pruritus urticaria, vomiting. Infections including pneumonia, upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis reported in 20%–11% of pts. Herpes zoster reported in 3% of pts. Thrombocytopenia may increase risk of bleeding.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC, blood type and screen; vital signs. Obtain pregnancy test in female pts of reproductive potential. Question history of COPD, emphysema, herpes infection; prior hypersensitivity reaction to any drug in treatment regimen; prior infusion reaction. Assess nutritional status. Screen for active infection. Offer emotional support.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC; vital signs periodically. Administer in an environment equipped to monitor for and manage infusion reactions. If infusion reaction of any grade/severity occurs, immediately interrupt infusion and manage symptoms. Accurately record characteristics of infusion reactions (severity, type, time of onset). Reactions may affect future infusion rates. To prevent herpes zoster reactivation in pts with prior history, consider antiviral prophylaxis within 1 wk of starting treatment and continue for 3 mos following discontinuation. Monitor for infection. Monitor daily pattern bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Blood levels will be monitored periodically. • Treatment may depress your immune system and reduce your ability to fight infection. Report symptoms of infection such as body aches, chills, cough, fatigue, fever. Avoid those with active infection. • Avoid pregnancy. Do not breastfeed. • Severe infusion reactions can occur at any time. Immediately report symptoms of infusion reactions such as chills, cough, difficulty breathing, headache, hives, itching, nausea, rash, stuffy or runny nose, throat tightness, vomiting, wheezing.
darbepoetin alfa

dar-be-poe-e-tin al-fa
(Aranesp)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of serious cardiovascular events, thromboembolic events, mortality, time-to-tumor progression when administered to a target hemoglobin greater than 11 g/dL. Shortened overall survival and/or increased risk of tumor progression has been reported with breast, cervical, head/neck, NSCL cancers.
Increased risk of serious cardiovascular events, thromboembolic events, mortality, time-to-tumor progression when administered to a target hemoglobin greater than 11 g/dL. Shortened overall survival and/or increased risk of tumor progression has been reported with breast, cervical, head/neck, NSCL cancers.
Do not confuse Aranesp with Aricept, or darbepoetin with dalteparin or epoetin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Glycoprotein. CLINICAL: Hematopoietic agent.
USES
Treatment of anemia associated with chronic renal failure (including pts on dialysis and pts not on dialysis), treatment of anemia caused by concurrent myelosuppressive chemotherapy in pts planned to receive chemotherapy for minimum of 2 additional months. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of symptomatic anemia in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to darbepoetin. Pure red cell aplasia, uncontrolled hypertension. Cautions: History of seizures, hypertension. Not recommended in pts with mild to moderate anemia and HF or CAD.
ACTION
Stimulates formation of RBCs in bone marrow. Therapeutic Effect: Induces erythropoiesis, release of reticulocytes from bone marrow into bloodstream.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after subcutaneous administration. Half-life: 48.5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum ferritin, serum transferrin saturation.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 25 mcg/ml, 40 mcg/ml, 60 mcg/ml, 100 mcg/ml, 150 mcg/0.75 ml, 200 mcg/ml, 300 mcg/ml. Prefilled Syringe: 25 mcg/0.42 ml, 40 mcg/0.4 ml, 60 mcg/0.3 ml, 100 mcg/0.5 ml, 150 mcg/0.3 ml, 200 mcg/0.4 ml, 300 mcg/0.6 ml, 500 mcg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Avoid excessive agitation of vial; do not shake (will cause foaming).
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • No reconstitution necessary. Do not dilute.
Rate of Administration • May be given as IV bolus.
Storage • Refrigerate. • Do not shake. Vigorous shaking may denature medication, rendering it inactive.
Subcutaneous
• Use 1 dose per vial; do not reenter vial. Discard unused portion.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Anemia in Chronic Renal Failure
◀ ALERT ▶ Individualize dosing and use lowest dose to reduce need for RBC transfusions. ON DIALYSIS: Initiate when Hgb less than 10 g/dL; reduce or stop dose when Hgb approaches or exceeds 11 g/dL. NOT ON DIALYSIS: Initiate when Hgb less than 10 g/dL and Hgb decline would likely result in RBC transfusion; reduce dose or stop if Hgb exceeds 10 g/dL.
IV, SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: ON DIALYSIS: Initially, 0.45 mcg/kg once wkly or 0.75 mcg/kg once q2wks. NOT ON DIALYSIS: 0.45 mcg/kg q4wks.
Decrease dose by 25%: If Hgb approaches 12 g/dL or increases greater than 1 g/dL in any 2-wk period.
Increase dose by 25%: If Hgb does not increase by 1 g/dL after 4 wks of therapy and Hgb is below target range (with adequate iron stores), do not increase dose more frequently than every 4 wks.
Note: If pt does not attain Hgb range of 10–12 g/dL after appropriate dosing over 12 wks, do not increase dose and use minimum effective dose to maintain Hgb level that will avoid red blood cell transfusions. Discontinue treatment if responsiveness does not improve.
Anemia Associated with Chemotherapy
◀ ALERT ▶ Initiate only if Hgb less than 10 g/dL and anticipated duration of myelosuppression is 2 months or longer. Titrate dose to maintain Hgb level and avoid RBC transfusions. Discontinue upon completion of chemotherapy.
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2.25 mcg/kg once wkly or 500 mcg every 3 wks.
Increase dose: If Hgb does not increase by 1 g/dL after 6 wks and Hgb is below target range, increase dose to 4.5 mcg/kg once wkly. No dose adjustment if using q3wk dosing.
Decrease dose: Decrease dose by 40% if Hgb increases greater than 1 g/dL in any 2-wk period or Hgb reaches level that will avoid red blood cell transfusions. Note: Withhold dose when Hgb exceeds a level needed to avoid RBC transfusions, resume at dose 40% lower when Hgb approaches a level where transfusions may be required.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Myalgia, hypertension/hypotension, headache, diarrhea. Occasional: Fatigue, edema, vomiting, reaction at injection site, asthenia, dizziness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Vascular access thrombosis, HF, sepsis, arrhythmias, anaphylactic reaction occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Establish baseline CBC (esp. note Hgb, Hct). Assess B/P before drug administration. B/P often rises during early therapy in pts with history of hypertension. Assess serum iron (transferrin saturation should be greater than 20%), serum ferritin (greater than 100 ng/ml) before and during therapy. Consider supplemental iron therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum ferritin, CBC, serum creatinine, BUN, potassium, phosphorus; reticulocyte count. Monitor B/P aggressively for increase (25% of pts taking medication require antihypertension therapy, dietary restrictions).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Frequent blood tests needed to determine correct dose. • Report swollen extremities, breathing difficulty, extreme fatigue, or severe headache. • Avoid tasks requiring alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established.
darifenacin
dare-i-fen-a-sin
(Enablex)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Muscarinic receptor antagonist. CLINICAL: Urinary antispasmodic.
USES
Management of symptoms of bladder overactivity (urge incontinence, urinary urgency/frequency).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to darifenacin. Uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma, paralytic ileus, GI/GU obstruction, urine retention. Cautions: Bladder outflow obstruction, hepatic impairment, nonobstructive prostatic hyperplasia, decreased GI motility, constipation, hiatal hernia, reflux esophagitis, ulcerative colitis, controlled narrow-angle glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Hot weather and/or exercise.
ACTION
Acts as a direct antagonist at muscarinic receptor sites in cholinergically innervated organs; limits bladder contractions. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces symptoms of bladder irritability/overactivity (urge incontinence, urinary urgency/frequency), improves bladder capacity.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 98%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine (60%), feces (40%). Half-life: 13–19 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (clarithromycin, erythromycin, protease inhibitors) may increase concentration/effects. Anticholinergics may increase side effects (e.g., dry mouth, constipation). HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None known.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets (Extended-Release): 7.5 mg, 15 mg.
Tablets (Extended-Release): 7.5 mg, 15 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Administer extended-release tablets whole; do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablet.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Overactive Bladder
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 7.5 mg once daily. If response is not adequate after at least 2 wks, may increase to 15 mg once daily. Do not exceed 7.5 mg once daily in moderate hepatic impairment or concurrent use with CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, fluconazole, protease inhibitors).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage Hepatic Impairment
Moderate impairment: Maximum dose: 7.5 mg. Severe impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (35%–21%): Dry mouth, constipation. Occasional (8%–4%): Dyspepsia, headache, nausea, abdominal pain. Rare (3%–2%): Asthenia, diarrhea, dizziness, ocular dryness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
UTI occurs occasionally.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Monitor voiding pattern, assess signs/symptoms of overactive bladder prior to therapy as baseline.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor I&O. Palpate bladder for urine retention. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency for evidence of constipation. Dry mouth may be relieved with sips of water. Assess for relief of symptoms of overactive bladder (urge incontinence, urinary frequency/urgency).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Swallow tablet whole; do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide. • Increase fluid intake to reduce risk of constipation. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established.
darunavir

dar-ue-na-veer
(Prezista)
FIXED COMBINATION(S)
Prezcobix: Darunavir/cobicistat (antiretroviral booster): 800 mg/150 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Protease inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiretroviral.
USES
Treatment of HIV infection in combination with ritonavir and other antiretroviral agents in adults and children 3 yrs and older.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to darunavir. Concurrent therapy with alfuzosin, colchicine, dihydroergotamine, ergonovine, ergotamine, lovastatin, methylergonovine, oral midazolam, pimozide, ranolazine, rifampin, sildenafil (for treatment of PAH), simvastatin, St. John’s wort, triazolam. Cautions: Diabetes mellitus, hemophilia, known sulfonamide allergy, hepatic impairment.
ACTION
Binds to site of HIV-I protease activity, inhibiting cleavage of viral precursors into functional proteins required for infectious HIV. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents formation of mature viral cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 95%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated in feces (79.5%), urine (13.9%). Not significantly removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 15 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration/effects of amiodarone, bepridil, lidocaine, desipramine, colchicine, beta blockers, midazolam, paroxetine, sertraline, atorvastatin, clarithromycin, cyclosporine, felodipine, inhaled fluticasone, lovastatin, nicardipine, nifedipine, pravastatin, simvastatin, sirolimus, tacrolimus, trazodone, sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., itraconazole, ketoconazole, voriconazole) may increase concentration. May decrease effects of methadone, oral contraceptives. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may lead to loss of virologic response, potential resistance to darunavir. FOOD: Food increases plasma concentration. LAB VALUES: May increase aPTT, PT, serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, amylase, lipase, cholesterol, triglycerides, uric acid. May decrease lymphocytes/neutrophil count, platelets, WBC count; serum bicarbonate, albumin, calcium. May alter serum glucose, sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Suspension, oral (Prezista): 100 mg/ml
![]() Tablets (Prezista): 75 mg, 150 mg, 400 mg, 600 mg, 800 mg.
Tablets (Prezista): 75 mg, 150 mg, 400 mg, 600 mg, 800 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with food (increases plasma concentration). • Coadministration with ritonavir required. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide film-coated tablets. • Shake suspension prior to each dose. Use provided oral dosing syringe.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Genotypic testing recommended in therapy-experienced pts.
HIV Infection, Treatment Experienced
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (With 1 or more darunavir resistance–associated substitution): 600 mg administered twice daily with 100 mg ritonavir twice daily. (With no darunavir resistance–associated substitutions): 800 mg with 100 mg ritonavir or 150 mg cobicistat once daily.
HIV Infection, Treatment Naive
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 800 mg administered with 100 mg ritonavir or 150 mg cobicistat once daily.
Usual Dosage During Pregnancy
PO: ADULTS: 600 mg administered twice daily with 100 mg ritonavir twice daily.
Usual Pediatric Dose
Treatment naive or treatment experienced with no darunavir resistance–associated substitutions:(Once daily dosing) (Suspension only): 14 kg: 490 mg with 96 mg ritonavir. 13 kg: 455 mg with 80 mg ritonavir. 12 kg: 420 mg with 80 mg ritonavir. 11 kg: 385 mg with 64 mg ritonavir. 10 kg: 350 mg with 64 mg ritonavir.
(Suspension or Tablets): 40 kg or greater: 800 mg with 100 mg ritonavir. 30–39 kg: 675 mg with 100 mg ritonavir. 15–29 kg: 600 mg with 100 mg ritonavir.
Treatment Experienced with 1 or More Darunavir Resistance–Associated Substitution
Use Tablet or Suspension
PO: CHILDREN WEIGHING 40 KG OR MORE: 600 mg twice daily with 100 mg ritonavir. WEIGHING 30–39 KG: 450 mg twice daily with 60 mg ritonavir. WEIGHING 15–29 KG: 375 mg twice daily with 50 mg ritonavir.
Use Oral Suspension Only
14 KG TO LESS THAN 15 KG: 280 mg (48 mg ritonavir) twice daily. 13 KG TO LESS THAN 14 KG: 260 mg (40 mg ritonavir) twice daily. 12 KG TO LESS THAN 13 KG: 240 mg (40 mg ritonavir) twice daily. 11 KG TO LESS THAN 12 KG: 220 mg (32 mg ritonavir) twice daily. 10 KG TO LESS THAN 11 KG: 200 mg (32 mg ritonavir) twice daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Not recommended in severe impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (19%–13%): Diarrhea, nausea, headache, nasopharyngitis. Occasional (3%–2%): Constipation, abdominal pain, vomiting. Rare (less than 2%): Allergic dermatitis, dyspepsia, flatulence, abdominal distention, anorexia, arthralgia, myalgia, paresthesia, memory impairment.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hypertension, MI, transient ischemic attack occur in less than 2% of pts. Acute renal failure, diabetes mellitus, dyspnea, worsening of hepatic impairment, skin reactions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline LFT before beginning therapy and at periodic intervals during therapy. Offer emotional support. Obtain full medication history.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Closely monitor for GI discomfort. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess skin for rash, other skin reactions, chemistries, laboratory abnormalities, particularly hepatic profile, glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides. Assess for opportunistic infections (onset of fever, oral mucosa changes, cough, other respiratory symptoms).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take medication with food. • Continue therapy for full length of treatment. • Doses should be evenly spaced. • Darunavir is not a cure for HIV infection, nor does it reduce risk of transmission to others. • Pt may continue to experience illnesses, including opportunistic infections. • Diarrhea can be controlled with OTC medication. • Report any skin reactions.
dasatinib

da-sa-ti-nib
(Sprycel)
Do not confuse dasatinib with erlotinib, imatinib, or lapatinib.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): Treatment of adults with chronic, accelerated, myeloid or lymphoid blast phase of CML with resistance, intolerance to prior therapy, including imatinib. Treatment of Ph+ CML in chronic phase of newly diagnosed pt. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Treatment of adults with Philadelphia chromosome–positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy including imatinib. OFF-LABEL: Post–stem cell transplant follow-up treatment of CML. Treatment of GI stromal tumor.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dasatinib. Cautions: Hepatic impairment, myelosuppression (particularly thrombocytopenia), pts prone to fluid retention, those with prolonged QT interval, cardiovascular/pulmonary disease. Concomitant use of anticoagulants, CYP3A4 inducers/inhibitors may increase risk of pulmonary arterial hypertension.
ACTION
Reduces activity of proteins responsible for uncontrolled growth of leukemia cells by binding to most imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL mutations of pts with CML or ALL. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits proliferation, tumor growth of CML and ALL cancer cell lines.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Extensively distributed in extravascular space. Protein binding: 96%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated primarily in feces. Half-life: 3–5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Has potential for severe teratogenic effects, fertility impairment. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., atazanavir, clarithromycin, erythromycin, indinavir, ketoconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir) may increase concentration. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease concentration. Antacids alter pH-dependent solubility of dasatinib. Famotidine, omeprazole may reduce dasatinib absorption. HERBAL: St. John’s wort, echinacea may decrease concentration. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase concentration/toxicity (increased risk of torsades, myelotoxicity). LAB VALUES: May decrease WBC, platelets, Hgb, Hct, RBC; serum calcium, phosphates. May increase serum ALT, AST, bilirubin, creatinine.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets (Film-Coated): 20 mg, 50 mg, 70 mg, 80 mg, 100 mg, 140 mg.
Tablets (Film-Coated): 20 mg, 50 mg, 70 mg, 80 mg, 100 mg, 140 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Take with food or large glass of water if GI upset occurs. • Avoid grapefruit products. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide film-coated tablets. • Store at room temperature. • Do not give antacids either 2 hrs prior to or within 2 hrs after dasatinib administration.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Consider decreasing dose from 100 mg to 20 mg or 140 mg to 40 mg.
CYP3A4 Inducers: Consider increasing dose with monitoring.
CML (Resistant or Intolerant)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Chronic phase): 100 mg once daily. May increase to 140 mg once daily in pts not achieving cytogenetic response. (Accelerated or blast phase): 140 mg once daily. May increase to 180 mg once daily in pts not achieving cytogenetic response.
CML (Newly Diagnosed in Chronic Phase)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100 mg once daily. May increase to 140 mg/day in pts not achieving cytogenetic response.
Ph+ ALL
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 140 mg once daily. May increase to 180 mg once daily in pts not achieving cytogenetic response.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (50%–32%): Fluid retention, diarrhea, headache, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, fever, rash, nausea, dyspnea. Occasional (28%–12%): Cough, abdominal pain, vomiting, anorexia, asthenia, arthralgia, stomatitis, dizziness, constipation, peripheral neuropathy, myalgia. Rare (less than 12%): Abdominal distention, chills, weight increase, pruritus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Pleural effusion occurred in 8% of pts, febrile neutropenia in 7%, GI bleeding, pneumonia in 6%, thrombocytopenia in 5%, dyspnea in 4%; anemia, cardiac failure in 3%.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC weekly for first mo, biweekly for second mo, and periodically thereafter. Monitor LFT before treatment begins and monthly thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess lower extremities for pedal edema, early evidence of fluid retention. Weigh daily, monitor for unexpected rapid weight gain. Offer antiemetics to control nausea, vomiting. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess oral mucous membranes for evidence of stomatitis. Monitor CBC for neutropenia, thrombocytopenia; monitor hepatic function tests for hepatotoxicity.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid crowds, those with known infection. • Avoid contact with anyone who recently received live virus vaccine; do not receive vaccinations. • Antacids may be taken up to 2 hrs before or 2 hrs after taking dasatinib. • Avoid grapefruit products. Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets.
*DAUNOrubicin

daw-noe-roo-bi-sin
(Cerubidine, DaunoXome)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Irreversible cardiotoxicity may occur. Myelosuppresant. Lipid component may cause infusion-related effects (back pain, flushing, chest tightness) within first 5 min of infusion. Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. Caution in renal impairment or hepatic dysfunction. Potent vesicant.
Irreversible cardiotoxicity may occur. Myelosuppresant. Lipid component may cause infusion-related effects (back pain, flushing, chest tightness) within first 5 min of infusion. Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. Caution in renal impairment or hepatic dysfunction. Potent vesicant.
Do not confuse daunorubicin with dactinomycin, doxorubicin, epirubicin, idarubicin, or valrubicin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Anthracycline antibiotic. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Cerubidine: Treatment of leukemias (acute lymphocytic [ALL], acute myeloid [AML]) in combination with other agents. DaunoXome: Advanced HIV-related Kaposi’s sarcoma.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to daunorubicin. Cautions: Preexisting heart disease or bone marrow suppression, hypertension, concurrent chemotherapeutic agents, elderly, infants, radiation therapy.
ACTION
Inhibits DNA, DNA-dependent RNA synthesis by binding with DNA strands. Cell cycle–phase nonspecific. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents cell division.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Protein binding: High. Does not cross blood-brain barrier. Metabolized in liver to active metabolite. Excreted in urine (40%); biliary excretion (40%). Half-life: 18.5 hrs; metabolite: 26.7 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy, esp. first trimester. May cause fetal harm. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Cardiotoxicity may be more frequent; reduced bone marrow reserves require caution. Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Previous use of doxorubicin, concurrent use of cyclophosphamide increases risk of cardiotoxicity. Hepatotoxic medications increase risk of hepatotoxicity. Bone marrow depressants may enhance myelosuppression. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease level/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, uric acid, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution (Cerubidine): 5 mg/ml. Injection Solution (DaunoXome): 2 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
◀ ALERT ▶ Cerubidine: Give by IV push or IV infusion. DaunoXome: Give by IV infusion. May be carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic. Handle with extreme care during preparation/administration.
Reconstitution
Cerubidine • May further dilute with 100 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl.
DaunoXome • Must dilute with equal part D5W to provide concentration of 1 mg/ml. • Do not use any other diluent.
Rate of Administration
Cerubidine • For IV push, withdraw desired dose into syringe containing 10–15 ml 0.9% NaCl. Inject over 1–5 min into tubing of rapidly infusing IV solution of D5W or 0.9% NaCl. • For IV infusion, further dilute with 100 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl. Infuse over 15–30 min. • Extravasation produces immediate pain, severe local tissue damage. Aspirate as much infiltrated drug as possible, then infiltrate area with hydrocortisone sodium succinate injection (50–100 mg hydrocortisone) and/or isotonic sodium thiosulfate injection or ascorbic acid injection (1 ml of 5% injection). Apply cold compresses.
DaunoXome • Infuse over 60 min. • Do not use in-line filter.
Storage
Cerubidine • Refrigerate intact vials. Protect from light. Solutions prepared for infusion stable for 24 hrs at room temperature.
DaunoXome • Refrigerate unopened vials • Reconstituted solution is stable for 6 hrs if refrigerated. • Do not use if opaque.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Allopurinol (Aloprim), aztreonam (Azactam), cefepime (Maxipime), dexamethasone (Decadron), heparin, piperacillin and tazobactam (Zosyn). DaunoXome: Do not mix with any other solution, esp. NaCl or bacteriostatic agents (e.g., benzyl alcohol).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Granisetron (Kytril), ondansetron (Zofran).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Refer to individual protocols. Cerubidine: Cumulative dose should not exceed 550 mg/m2 in adults (increased risk of cardiotoxicity) or 400 mg/m2 in those receiving chest irradiation.
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
IV (Cerubidine): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 45 mg/m2 on days 1, 2, and 3 (in combination with vincristine, prednisone, asparaginase). CHILDREN 2 YRS AND OLDER, BODY SURFACE AREA 0.5 m2 OR GREATER: 25 mg/m2 on day 1 of every wk for up to 4–6 cycles (in combination with vincristine, prednisone). Cumulative dose not to exceed 300 mg/m2. CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 2 YRS, BODY SURFACE AREA LESS THAN 0.5 m2: 1 mg/kg/dose per protocol (in combination with vincristine, prednisone). Cumulative dose not to exceed 10 mg/kg.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
IV (Cerubidine): ADULTS YOUNGER THAN 60 YRS: 45 mg/m2 on days 1, 2, and 3 of induction course, then on days 1 and 2 of subsequent courses (in combination with cytarabine). ADULTS 60 YRS AND OLDER: 30 mg/m2 on days 1, 2, and 3 of induction course, then on days 1 and 2 of subsequent courses (in combination with cytarabine).
Kaposi’s Sarcoma
IV (Daunoxome): ADULTS: 40 mg/m2 over 1 hr repeated q2wks until disease progression.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Cerubidine: Serum creatinine greater than 3 mg/dL: 50% of normal dose.
Daunoxome: Serum creatinine greater than 3 mg/dL: 50% of normal dose.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Cerubidine: Bilirubin 1.2–3 mg/dL: 75% of normal dose. Bilirubin 3.1–5 mg/dL: 50% of normal dose. Bilirubin Greater than 5 mg/dL: Daunorubicin is not recommended for use in this pt population.
Daunoxome: Bilirubin 1.2–3 mg/dL: 75% of normal dose. Bilirubin greater than 3 mg/dL: 50% of normal dose.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Complete alopecia (scalp, axillary, pubic), nausea, vomiting (beginning a few hrs after administration and lasting 24–48 hrs). DaunoXome: Mild to moderate nausea, fatigue, fever. Occasional: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, esophagitis, stomatitis, transverse pigmentation of fingernails, toenails. Rare: Transient fever, chills.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Myelosuppression manifested as hematologic toxicity (severe leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia). Decrease in platelet count, WBC count occurs in 10–14 days, returns to normal level by third week. Cardiotoxicity noted as either acute, transient, abnormal. EKG findings and/or cardiomyopathy manifested as HF (risk increases when cumulative dose exceeds 550 mg/m2 in adults, 300 mg/m2 in children 2 yrs and older, or total dosage greater than 10 mg/kg in children younger than 2 yrs).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain WBC, platelet, erythrocyte counts before and at frequent intervals during therapy. EKG should be obtained before therapy. Antiemetics may be effective in preventing, treating nausea.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for stomatitis. May lead to ulceration within 2–3 days. Assess skin, nailbeds for hyperpigmentation. Monitor hematologic status, renal/hepatic function, serum uric acid. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor for hematologic toxicity (fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site), symptoms of anemia (excessive fatigue, weakness).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Urine may turn reddish color for 1–2 days after beginning therapy. • Hair loss is reversible, but new hair growth may have different color, texture. • New hair growth resumes about 5 wks after last therapy dose. • Maintain strict oral hygiene. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance). • Avoid contact with those who have recently received live virus vaccine. • Promptly report fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site, yellowing of whites of eyes/skin, difficulty breathing. • Increase fluid intake (may protect against hyperuricemia). • Report for persistent nausea, vomiting.
deferasirox
dee-fur-a-sir-ox
(Exjade, Jadenu)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause renal/hepatic failure, hepatotoxicity, gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
May cause renal/hepatic failure, hepatotoxicity, gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
Do not confuse deferasirox with deferoxamine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Iron-chelating agent. CLINICAL: Iron reduction agent.
USES
Treatment of chronic iron overload due to blood transfusions (transfusional hemosiderosis) or due to non–transfusion-dependent thalassemia syndrome.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to deferasirox. Platelet counts less than 50,000/mm3; poor performance status, high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes or advanced malignancies; CrCl less than 40 ml/min or serum creatinine greater than 2 times the upper limit of normal. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, elderly, concurrent medications that may increase GI effects (e.g., NSAIDs).
ACTION
Selective for iron. Binds iron with high affinity in a 2:1 ratio. Therapeutic Effect: Induces iron excretion.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in feces (84%), urine (8%). Half-life: 8–16 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Not recommended for pts younger than 2 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antacids containing aluminium, cholestyramine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin, ritonavir decrease concentration/effects. May decrease effects of cyclosporine, simvastatin, oral contraceptives. May increase concentration of cyclobenzaprine, olanzapine, tizanidine. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: Bioavailability is variably increased when given with food. LAB VALUES: Decreases serum ferritin. May increase serum ALT, AST, creatinine, urine protein.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets (Jadenu): 90 mg, 180 mg, 360 mg. Tablets, Soluble (Exjade): 125 mg, 250 mg, 500 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give on empty stomach 30 min before food. • Do not give simultaneously with aluminum-containing antacids, cholestyramine. • Tablets should not be chewed or swallowed whole. • Disperse tablet by stirring in water, apple juice, orange juice until fine suspension is achieved. • Dosage less than 1 g should be dispersed in 3.5 oz of liquid, dosage more than 1 g should be dispersed in 7 oz of liquid. If any residue remains in glass, resuspend with a small amount of liquid.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Iron Overload Due to Transfusions
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 2 YRS AND OLDER: (Exjade): Initially, 20 mg/kg once daily. Maintenance: (Titrate to individual response and goals.) Adjust dosage by 5 or 10 mg/kg/day every 3–6 mos based on serum ferritin levels. Consider holding for serum ferritin less than 500 mcg/L. Maximum: 40 mg/kg once daily. (Jadenu): Initially, 14 mg/kg once daily. Maintenance: (Titrate to individual response and goals.) Adjust dosage by 3.5 or 7 mg/kg/day based on serum ferritin levels. Consider holding for serum ferritin less than 500 mcg/L. Maximum: 28 mcg/kg once daily.
Thalassemia Syndromes
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 10 YRS AND OLDER: (Exjade): Initially, 10 mg/kg once daily. May increase to 20 mg/kg once daily after 4 wks if baseline iron is greater than 15 mg Fe/g dry wgt. (Jadenu): Initially, 7 mg/kg once daily. May increase to 14 mg/kg/day after 4 wks if baseline iron greater than 15 mg Fe/g dry wgt. Maintenance: (Exjade/Jadenu): Dose adjustments based on serum ferritin and hepatic iron concentrations.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Note: See Contraindications.
ADULTS: For increase in serum creatinine greater than 33% on 2 consecutive measures, reduce daily dose by 10 mg/kg. CHILDREN: For increase in serum creatinine above age-appropriate upper limit of normal on 2 consecutive measures, reduce daily dose by 10 mg/kg. (Jadenu): CrCl 40–60 ml/min: Reduce starting dose by 50%.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
For severe or persistent elevations in hepatic function tests, consider dose reduction or discontinuation. Moderate impairment: (Jadenu): Reduce initial dose by 50%.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (19%–10%): Fever, headache, abdominal pain, cough, nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. Occasional (9%–4%): Rash, arthralgia, fatigue, back pain, urticaria. Rare (1%): Edema, sleep disorder, dizziness, anxiety.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Bronchitis, pharyngitis, acute tonsillitis, ear infection occur occasionally. Hepatitis, auditory disturbances, ocular abnormalities occur rarely. Acute renal failure, cytopenias (e.g., agranulocytosis, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia) may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline serum CBC, ferritin, iron, creatinine, ALT, AST, urine protein, then monthly thereafter. Auditory, ophthalmic testing should be obtained before therapy and annually thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Treatment should be interrupted if serum ferritin levels are consistently less than 500 mcg/L. Suspend treatment if severe rash occurs.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take on empty stomach 30 min before food. • Do not chew or swallow tablet whole; disperse tablet completely in water, apple juice, orange juice; drink resulting suspension immediately. • Do not take aluminum-containing antacids concurrently. • Report severe skin rash, changes in vision/hearing, or yellowing of skin/eyes.
denosumab

den-oh-sue-mab
(Prolia, Xgeva)
Do not confuse denosumab with daclizumab, or Prolia with Avandia or Zebeta.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Monoclonal antibody. CLINICAL: Bone resorption inhibitor.
USES
Prolia: Treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at high risk for fracture. Treatment to increase bone mass in men at high risk for fractures; treatment of bone loss in men receiving androgen deprivation therapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer and in women at high risk for fractures receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer. Xgeva: Prevention of skeletal-related events (e.g., fracture, spinal cord compression) in pts with bone metastases from solid tumor. Treatment of giant cell tumor of bone in adults and skeletally mature adolescents. Treatment of hypercalcemia of malignancy refractory to biphosphonate therapy. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of bone destruction caused by rheumatoid arthritis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to denosumab. Prolia: Preexisting hypocalcemia, pregnancy. Cautions: History of hypoparathyroidism, thyroid/parathyroid surgery, malabsorption syndromes, excision of small intestine, immunocompromised pts. Pts with severe renal impairment or receiving dialysis (greater risk for developing hypocalcemia). Pts with impaired immune system or immunosuppressive therapy.
ACTION
Binds to RANK ligand (transmembrane protein), preventing osteoclast formation. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases bone resorption; increases bone mass in osteoporosis; decreases skeletal-related events and tumor-induced bone destruction in solid tumors. Inhibits tumor growth.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Serum level detected 1 hr after administration. Half-life: 32 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Approved for use only in postmenopausal women. Children: Approved for use only in postmenopausal women. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum calcium. May increase serum cholesterol.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution (Prolia): 60 mg/ml. (Xgeva): 120 mg/1.7 ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Subcutaneous
• Administer in upper arm, upper thigh, or abdomen.
Storage • Refrigerate. Use within 14 days once at room temperature. • Solution appears as clear, colorless to pale yellow.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Administer calcium and vitamin D to prevent/treat hypocalcemia.
Prolia
Treatment of androgen deprivation–induced bone loss in men with prostate cancer; treatment of aromatase inhibitor–induced bone loss in women with breast cancer; treatment of osteoporosis in men or postmenopausal women.
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 60 mg every 6 mos.
Xgeva Prevention of Skeletal-Related Events from Solid Tumors
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 120 mg q4wks.
Xgeva Giant Cell Tumor of Bone, Hypercalcemia of Malignancy
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY, MATURE ADOLESCENTS: 120 mg q4wks with additional doses on days 8 and 15 of first mo of therapy.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (35%–12%): Back pain, extremity pain. Occasional (8%–5%): Musculoskeletal pain, vertigo, peripheral edema, sciatica. Rare (4%–2%): Bone pain, upper abdominal pain, rash, insomnia, flatulence, pruritus, myalgia, asthenia, GI reflux.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Increases risk of infection, specifically cystitis, upper respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, pharyngitis, herpes zoster (shingles) occur in 2%–6% of pts. Osteonecrosis of the jaw (OJN) was reported. Suppression of bone turnover, pancreatitis have been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Hypocalcemia must be corrected prior to treatment. Calcium 1,000 mg/day and vitamin D at least 400 international units/day should be given. Dental exam should be provided prior to treatment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum magnesium, calcium, ionized calcium, phosphate. In pts predisposed with hypocalcemia and disturbances of mineral metabolism, clinical monitoring of calcium, mineral levels is highly recommended. Adequately supplement all pts with calcium and vitamin D. Monitor for delayed fracture healing.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report rash, new-onset eczema. • Seek prompt medical attention if signs, symptoms of severe infection (rash, itching, reddened skin, cellulitis) occur. • Report muscle stiffness, numbness, cramps, spasms (signs of hypocalcemia); swelling or drainage from jaw, mouth, or teeth.
desloratadine
des-lor-a-ta-deen
(Aerius
![]() , Clarinex, Clarinex Redi-Tabs)
, Clarinex, Clarinex Redi-Tabs)
Do not confuse Clarinex with Celebrex or Claritin.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Clarinex-D 24 Hour: desloratadine/pseudoephedrine (a sympathomimetic): 5 mg/240 mg. Clarinex-D 12 Hour: desloratadine/pseudoephedrine: 2.5 mg/120 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: H1 antagonist. CLINICAL: Nonsedating antihistamine.
USES
Relief of nasal/non-nasal symptoms of seasonal and perennial rhinitis (sneezing, rhinorrhea, itching/tearing of eyes, stuffiness), chronic idiopathic urticaria (hives).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to desloratadine or loratidine. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, breastfeeding.
ACTION
Exhibits selective peripheral histamine H1 receptor blocking action. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents allergic response mediated by histamine (rhinitis, urticaria).
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed from GI tract. Distributed mainly in liver, lungs, GI tract, bile. Protein binding: 82%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated in urine, feces. Half-life: 27 hrs (increased in elderly, renal/hepatic impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Excreted in breast milk. Children/Elderly: More sensitive to anticholinergic effects (e.g., dry mouth, nose, throat).
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Erythromycin, ketoconazole, fluconazole, clarithromycin may increase concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May suppress wheal, flare reactions to antigen skin testing unless antihistamines are discontinued 4 days before testing.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Syrup (Clarinex): 2.5 mg/5 ml. Tablets (Clarinex): 5 mg. Tablet, Oral Dispersable: 2.5 mg, 5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May give with or without food. • Oral dispersable tablet: Place directly on tongue (disintegrates immediately). • May take with or without water.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Allergic Rhinitis, Urticaria
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 12 YRS: 5 mg once daily. CHILDREN 6–12 YRS: 2.5 mg once daily.
CHILDREN 1–5 YRS: 1.25 mg once daily. CHILDREN 6–11 MOS: 1 mg once daily.
Dosage in Hepatic/Renal Impairment
Dosage is decreased to 5 mg every other day.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (12%): Headache. Occasional (3%): Dry mouth, drowsiness. Rare (less than 3%): Fatigue, dizziness, diarrhea, nausea.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
None known.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess lung sounds for wheezing; skin for urticaria, hives.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
For upper respiratory allergies, increase fluids to decrease viscosity of secretions, offset thirst, replace any loss of fluids. Monitor symptoms for therapeutic response.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Drink plenty of water (may cause dry mouth). • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established (may cause drowsiness). • Avoid alcohol.
desmopressin
des-moe-press-in
(Apo-Desmopressin
![]() , DDAVP, DDAVP Rhinal Tube, Stimate)
, DDAVP, DDAVP Rhinal Tube, Stimate)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Synthetic pituitary hormone. CLINICAL: Antidiuretic.
USES
DDAVP Nasal: (DDAVP Rhinal Tube): Antidiuretic replacement therapy in managing central cranial diabetes insipidus. Parenteral: Antidiuretic replacement therapy in managing central cranial diabetes insipidus. Manage polyuria and polydipsia following head trauma or surgery in pituitary region. Maintain hemostasis and control bleeding in hemophilia A, von Willebrand’s disease (type I). Stimate intranasal: Maintain hemostasis and control bleeding due to spontaneous or trauma-induced injuries in hemophilia A, von Willebrand’s disease (type I). PO: Antidiuretic replacement therapy in managing central cranial diabetes insipidus, primary management of nocturnal enuresis, management of temporary polyuria, polydipsia following pituitary surgery or head trauma. OFF-LABEL: Uremic bleeding occurring with acute/chronic renal failure; prevent surgical bleeding in pts with uremia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to desmopressin. Hyponatremia, history of hyponatremia, moderate to severe renal impairment. Cautions: Predisposition to thrombus formation; conditions with fluid, electrolyte imbalance; coronary artery disease; hypertensive cardiovascular disease, elderly, cystic fibrosis, HF, renal impairment, polydipsia. Avoid use in hemophilia A with factor VIII levels less than 5%; hemophilia B; severe type I, type IIB, platelet-type von Willebrand’s disease.
ACTION
Increases CAMP in renal tubular cells, which increases water permeability, decreasing urine volume. Increases levels of von Willebrand factor, factor VIII, tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). Therapeutic Effect: Shortens activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), bleeding time. Decreases urinary output.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 1 hr | 2–7 hrs | 8–12 hrs |
| IV | 15–30 min | 1.5–3 hrs | 8–12 hrs |
| Intranasal | 15 min–1 hr | 1–5 hrs | 8–12 hrs |
Poorly absorbed after PO, nasal administration. Metabolism: Unknown. Half-life: PO: 1.5–2.5 hrs. Intranasal: 3.3–3.5 hrs. IV: 0.4–4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Caution in neonates, pts younger than 3 mos (increased risk of fluid balance problems). Careful fluid restrictions recommended in infants. Elderly: Increased risk of hyponatremia, water intoxication.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Carbamazepine, lamotrigine, NSAIDs, SSRIs, tricyclic antidepressants may increase effect. Demeclocycline, lithium may decrease effect. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution (DDAVP): 4 mcg/ml. Nasal Solution (DDAVP Rhinal Tube 0.01%): 100 mcg/ml (10 mcg/spray). Nasal Spray (Stimate): 1.5 mg/ml (150 mcg/spray). Tablets (DDAVP): 0.1 mg, 0.2 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • For IV infusion, dilute in 10–50 ml 0.9% NaCl (10 ml for children 10 kg or less; 50 ml for adults, children greater than 10 kg).
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 15–30 min.
Storage • Refrigerate.
Subcutaneous
• Withdraw dose from vial. Further dilution not required.
Intranasal
• Refrigerate DDAVP Rhinal Tube solution, Stimate nasal spray. • Rhinal Tube solution, Stimate nasal spray are stable for 3 wks at room temperature. • DDAVP nasal spray is stable at room temperature. • Calibrated catheter (rhinyle) is used to draw up measured quantity of desmopressin; with one end inserted in nose, pt blows on other end to deposit solution deep in nasal cavity. • For infants, young children, obtunded pts, air-filled syringe may be attached to catheter to deposit solution.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Primary Nocturnal Enuresis
PO: CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER: 0.2–0.6 mg once before bedtime. Limit fluid intake 1 hr prior and at least 8 hrs after dose.
Central Cranial Diabetes Insipidus
◀ ALERT ▶ Fluid restriction should be observed.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 4 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 0.05 mg twice daily. Titrate to desired response. Range: 0.1–1.2 mg/day in 2–3 divided doses.
IV, SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 2–4 mcg/day in 2 divided doses or
![]() of maintenance intranasal dose.
of maintenance intranasal dose.
Intranasal (Use 100 mcg/ml Concentration): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 12 YRS: 10–40 mcg (0.1–0.4 ml) in 1–3 doses/day. Usual dose: 10 mcg 2 times/day. CHILDREN 3 MOS–12 YRS: Initially, 5 mcg (0.05 ml)/day. Range: 5–30 mcg (0.05–0.3 ml)/day as a single or 2 divided doses.
Hemophilia A, Von Willebrand’s Disease (Type I)
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 0.3 mcg/kg as slow infusion.
Intranasal (Use 1.5 mg/ml Concentration Providing 150 mcg/Spray): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN WEIGHING MORE THAN 50 KG: 300 mcg; use 1 spray in each nostril. ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN WEIGHING 50 KG OR LESS: 150 mcg as a single spray. Repeat use based on clinical conditions/laboratory work.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl less than 50 ml/min: Not recommended.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: IV: Pain, redness, swelling at injection site; headache, abdominal cramps, vulvular pain, flushed skin, mild B/P elevation, nausea with high dosages. Nasal: Rhinorrhea, nasal congestion, slight B/P elevation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Water intoxication, hyponatremia (headache, drowsiness, confusion, decreased urination, rapid weight gain, seizures, coma) may occur in overhydration. Children, elderly pts, infants are esp. at risk.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Establish baselines for B/P, pulse, weight, serum electrolytes, urine specific gravity. Check lab values for factor VIII coagulant concentration for hemophilia A, von Willebrand’s disease; bleeding times.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Check B/P, pulse with IV infusion. Monitor pt weight, fluid intake; urine volume, urine specific gravity, osmolality, serum electrolytes for diabetes insipidus. Assess factor VIII antigen levels, aPTT, factor VIII activity level for hemophilia.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid overhydration. • Follow guidelines for proper intranasal administration. • Report headache, shortness of breath, heartburn, nausea, abdominal cramps.
desvenlafaxine
des-ven-la-fax-een
(Khedezia, Pristiq)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Phenethylamine derivative. CLINICAL: Antidepressant.
USES
Treatment of major depression disorder (MDD).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to desvenlafaxine or venlafaxine. Use of MAOIs within 14 days or in those currently taking MAOIs (may cause neuroleptic malignant syndrome). Allow at least 7 days after discontinuation before starting an MAOI. Initiation in pts taking linezolid or methylene blue. Cautions: Renal impairment, history of seizures, bipolar disorder, pts with suicidal ideation and behavior, increased intraocular pressure, narrow-angle glaucoma, cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease, elderly.
ACTION
Appears to inhibit serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake at CNS neuronal presynaptic membranes (weakly inhibits dopamine reuptake). Therapeutic Effect: Produces antidepressant effect.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 30%. Excreted primarily in urine. Steady-state plasma levels occur in 4–5 days. Half-life: 9–11 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Concurrent use of MAOIs (e.g., phenelzine, selegiline) may cause neuroleptic malignant syndrome: hyperthermia, rigidity, myoclonus, autonomic instability (including rapid fluctuations of vital signs), mental status changes, coma, extreme agitation. Alcohol may increase CNS depressant effects. May decrease midazolam concentration. May increase desipramine concentration. Aspirin, NSAIDs, warfarin increase risk of bleeding. Ketoconazole may increase concentration/effect. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depressant effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase total serum cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, ALT, AST, prolactin level.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets (Extended-Release): 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg.
Tablets (Extended-Release): 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Give with food or milk if GI distress occurs. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets. • Must be swallowed whole, with fluid.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Major Depressive Disorder
PO: ADULTS: 50 mg once daily. Maximum: 400 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl 30–50 ml/min: 50 mg once daily (Maximum). CrCl less than 30 ml/min: 25 mg once daily or 50 mg every other day (Maximum). HD: 25 mg once daily or 50 mg every other day (Maximum).
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dosage adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment: 50 mg once daily. Maximum: 100 mg/day.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (22%–20%): Nausea, headache. Occasional (13%–7%): Dizziness, dry mouth, diarrhea, sweating, constipation, insomnia, fatigue. Rare (5%–2%): Anorexia, drowsiness, decreased libido, erectile dysfunction in men, anxiety, blurred vision, vomiting, decreased weight, tremor, paresthesia, irritability, abnormal dreams, blurred vision, tinnitus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Seizures, syncope, extrapyramidal disorder, depersonalization, hypomania, epistaxis occur rarely. Ischemic cardiac events, including myocardial ischemia, MI, coronary occlusion requiring revascularization, may occur. Sustained increase in diastolic B/P (10–15 mm Hg) occurs occasionally.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain initial weight, B/P. Assess appearance, behavior, speech pattern, level of interest, mood, sleep pattern.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
For pts on long-term therapy, LFT should be performed periodically. Assess sleep pattern for evidence of insomnia. Monitor for suicidal ideation (esp. at initiation of therapy or changes in dosage). Assess appearance, behavior, speech pattern, level of interest, mood for therapeutic response.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take with food to minimize GI distress. • Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets. • Do not increase, decrease, or suddenly discontinue medication. • Therapeutic effect may be noted within 1–4 wks. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol. • Report worsening depression, suicidal ideation, unusual changes in behavior.
dexamethasone
dex-a-meth-a-sone
(Apo-Dexamethasone
![]() , Dexamethasone Intensol, DexPak, Maxidex)
, Dexamethasone Intensol, DexPak, Maxidex)
Do not confuse Decadron with Percodan, or dexamethasone with dextroamphetamine, or Maxidex with Maxzide.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Ciprodex Otic: dexamethasone/ciprofloxacin (antibiotic): 0.1%/0.3%.
Dexacidin, Maxitrol: dexamethasone/neomycin/polymyxin (anti-infectives): 0.1%/3.5 mg/10,000 units per g or ml.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Long-acting glucocorticoid. CLINICAL: Corticosteroid.
USES
Used primarily as an anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressant agent in a variety of diseases (e.g., allergic, inflammatory autoimmune). OFF-LABEL: Antiemetic, treatment of croup, dexamethasone suppression test (indicator consistent with suicide and/or depression), accelerate fetal lung maturation. Treatment of acute mountain sickness, high-altitude cerebral edema.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dexamethasone. Systemic fungal infections, cerebral malaria. Cautions: Thyroid disease, renal/hepatic impairment, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, glaucoma, cataracts, myasthenia gravis, pts at risk for seizures, osteoporosis, post-MI, elderly.
ACTION
Suppresses neutrophil migration, decreases production of inflammatory mediators, reverses increased capillary permeability. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases inflammation. Suppresses normal immune response.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed from GI tract after PO administration. Widely distributed. Protein binding: High. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Minimally removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 3–4.5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children: Prolonged treatment with high-dose therapy may decrease short-term growth rate, cortisol secretion. Elderly: Higher risk for developing hypertension, osteoporosis.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Amphotericin may increase hypokalemia. May increase digoxin toxicity caused by hypokalemia. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease concentration. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole), macrolide antibiotics may increase concentration. May decrease effects of oral antidiabetic agents. Live virus vaccines may decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine, increase vaccine side effects, potentiate virus replication. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, echinacea may increase immunosuppressant effect. FOOD: Interferes with calcium absorption. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, lipids, sodium levels. May decrease serum calcium, potassium, thyroxine, WBC.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Elixir: 0.5 mg/5 ml. Injection, Solution: 4 mg/ml, 10 mg/ml. Ophthalmic Solution: 0.1%. Ophthalmic Suspension (Maxidex): 0.1%. Solution, Oral: 0.5 mg/5 ml. Solution, Oral Concentrate (Dexamethasone Intensol): 1 mg/ml. Tablets: 0.5 mg, 0.75 mg, 1 mg, 1.5 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg, 6 mg. Tablets (TaperPak [DexPak]): 1.5 mg (35 or 51 tablets on taper dose card).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
◀ ALERT ▶ Dexamethasone sodium phosphate may be given by IV push or IV infusion. Rapid injection may cause genital burning sensation in females.
• For IV push, give over 1–4 min if dose is less than 10 mg. • For IV infusion, mix with 50–100 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W and infuse over 15–30 min. • For neonates, solution must be preservative free. • IV solution must be used within 24 hrs.
IM
• Give deep IM, preferably in gluteus maximus.
PO
• Give with milk, food (to decrease GI effect).
Ophthalmic Solution, Suspension
• Place gloved finger on lower eyelid and pull out until a pocket is formed between eye and lower lid. • Place prescribed number of drops or ¼–½ inch ointment into pocket. • Instruct pt to close eye gently for 1–2 min (so medication will not be squeezed out of the sac). • Instruct pt to apply digital pressure to lacrimal sac at inner canthus for 1–2 min to minimize systemic absorption.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro), daunorubicin (Cerubidine), idarubicin (Idamycin), midazolam (Versed).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Cimetidine (Tagamet), cisplatin (Platinol), cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), cytarabine (Cytosar), docetaxel (Taxotere), doxorubicin (Adriamycin), etoposide (VePesid), furosemide (Lasix), granisetron (Kytril), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lorazepam (Ativan), morphine, ondansetron (Zofran), paclitaxel (Taxol), palonosetron (Aloxi), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Anti-Inflammatory
PO, IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.75–9 mg/day in divided doses q6–12h. CHILDREN: 0.08–0.3 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6–12h.
Cerebral Edema
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10 mg, then 4 mg (IV or IM) q6h.
PO, IV, IM: CHILDREN: Loading dose of 1–2 mg/kg, then 1–1.5 mg/kg/day in divided doses q4–6h.
Nausea/Vomiting in Chemotherapy Pts
Note: Refer to individual protocols and emetogenic potential.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 8–20 mg 15–30 min before treatment. CHILDREN: 10 mg/m2/dose on days of chemotherapy.
Physiologic Replacement
PO, IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 0.03–0.15 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6–12h.
Usual Ophthalmic Dosage, Ocular Inflammatory Conditions
ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: (Solution): Initially, 2 drops q1h while awake and q2h at night for 1 day, then reduce to 3–4 times/day. (Suspension): 1–2 drops up to 4–6 times/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Inhalation: Cough, dry mouth, hoarseness, throat irritation. Intranasal: Burning, mucosal dryness. Ophthalmic: Blurred vision. Systemic: Insomnia, facial edema (cushingoid appearance [“moon face”]), moderate abdominal distention, indigestion, increased appetite, nervousness, facial flushing, diaphoresis. Occasional: Inhalation: Localized fungal infection (thrush). Intranasal: Crusting inside nose, epistaxis, sore throat, ulceration of nasal mucosa. Ophthalmic: Decreased vision; lacrimation; eye pain; burning, stinging, redness of eyes; nausea; vomiting. Systemic: Dizziness, decreased/blurred vision. Rare: Inhalation: Increased bronchospasm, esophageal candidiasis. Intranasal: Nasal/pharyngeal candidiasis, eye pain. Systemic: Generalized allergic reaction (rash, urticaria); pain, redness, swelling at injection site; psychological changes; false sense of well-being; hallucinations; depression.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Long-term therapy: Muscle wasting (esp. arms, legs), osteoporosis, spontaneous fractures, amenorrhea, cataracts, glaucoma, peptic ulcer disease, HF. Ophthalmic: Glaucoma, ocular hypertension, cataracts. Abrupt withdrawal following long-term therapy: Severe joint pain, severe headache, anorexia, nausea, fever, rebound inflammation, fatigue, weakness, lethargy, dizziness, orthostatic hypotension.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for hypersensitivity to any corticosteroids. Obtain baselines for height, weight, B/P, serum glucose, electrolytes.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor I&O, daily weight, serum glucose. Assess for edema. Evaluate food tolerance. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Report hyperacidity promptly. Check vital signs at least twice daily. Be alert to infection (sore throat, fever, vague symptoms). Monitor serum electrolytes, esp. for hypercalcemia, hypokalemia, paresthesia (esp. lower extremities, nausea/vomiting, irritability), Hgb, occult blood loss. Assess emotional status, ability to sleep.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not change dose/schedule or stop taking drug. • Must taper off gradually under medical supervision. • Report fever, sore throat, muscle aches, sudden weight gain, edema, exposure to measles/chickenpox. • Severe stress (serious infection, surgery, trauma) may require increased dosage. • Inform dentist, other physicians of dexamethasone therapy within past 12 mos. • Avoid alcohol, limit caffeine.
dexmedetomidine
dex-med-e-toe-mye-deen
(Precedex)
Do not confuse Precedex with Percocet or Peridex.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Alpha2 agonist. CLINICAL: Nonbarbiturate sedative, hypnotic.
USES
Sedation of initially intubated, mechanically ventilated adults in intensive care setting. Use in nonintubated pts requiring sedation before and/or during surgical and other procedures. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of shivering, use in children. Awake craniotomy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dexmedetomidine. Cautions: Heart block, bradycardia, hepatic impairment, hypovolemia, diabetes, hypotension, chronic hypertension, severe ventricular dysfunction, elderly, use of vasodilators or drugs decreasing heart rate.
ACTION
Selective alpha2-adrenergic agonist. Inhibits norepinephrine release. Therapeutic Effect: Produces analgesic, hypnotic, sedative effects.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Protein binding: 94%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 2 hrs.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Sedatives (e.g., midazolam, lorazepam), opioids (e.g., fentanyl, morphine, hydromorphone), hypnotics (e.g., zolpidem, temazepam) may enhance effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, potassium, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 80 mcg/20 ml, 200 mcg/2 ml vials, 4 mcg/ml solutions (50 ml, 100 ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Dilute 2 ml of dexmedetomidine with 48 ml 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • Individualized, titrated to desired effect. Use controlled infusion pump.
Storage • Store at room temperature.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with any other medications.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), bumetanide (Bumex), calcium gluconate, cisatracurium (Nimbex), dexamethasone, dobutamine, dopamine, magnesium sulfate, norepinephrine (Levophed), propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Sedation
IV: ADULTS: Loading dose of 1 mcg/kg over 10 min followed by maintenance infusion of 0.2–0.7 mcg/kg/hr. ELDERLY: May require decreased dosage.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (30%–11%): Hypotension, nausea. Occasional (3%–2%): Pain, fever, oliguria, thirst.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, hypoxia, anemia, pain, pleural effusion may occur with too-rapid IV infusion.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline B/P, heart rate, LOC prior to initiation.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess cardiac monitor for arrhythmia, pulse for bradycardia, B/P for hypotension, level of sedation. Assess respiratory rate, rhythm. Monitor ventilator settings. Discontinue once pt is extubated.
dexmethylphenidate
dex-meth-il-fen-i-date
(Focalin, Focalin XR)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Chronic use can lead to marked tolerance, psychological dependence. Severe depression may occur during drug withdrawal.
Chronic use can lead to marked tolerance, psychological dependence. Severe depression may occur during drug withdrawal.
Do not confuse dexmethylphenidate with methadone.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Cerebral cortex stimulator (Schedule II). CLINICAL: CNS stimulant.
USES
Treatment of ADHD.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dexmethylphenidate or methylphenidate. Diagnosis or family history of Tourette’s syndrome, glaucoma, history of marked agitation, anxiety, tension, motor tics, use of MAOIs within 14 days. Cautions: Cardiovascular disease (HF, recent MI), seizure disorder, psychosis, emotional instability, acute stress reactions, hyperthyroidism. Avoid use in pts with history of alcohol or substance abuse.
ACTION
Blocks reuptake of norepinephrine, dopamine into presynaptic neurons, increasing release of these neurotransmitters into synaptic cleft. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases motor restlessness, fatigue; increases motor activity, mental alertness, attention span; elevates mood.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed from GI tract. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 2.2 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if excreted in breast milk. Children: May be more susceptible to developing anorexia, insomnia, abdominal pain, weight loss. Chronic use may inhibit growth. In psychotic children, may exacerbate symptoms of behavior disturbance, thought disorder. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May enhance effects of antihypertensives. May inhibit metabolism of phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, tricyclic antidepressants; decreased dosages may be necessary. May alter effects of warfarin. HERBAL: Ephedra may cause hypertension, arrhythmias. Yohimbe may increase CNS stimulation. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None known.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets (Focalin): 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg.
![]() Capsules (Extended-Release [Focalin XR]): 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg, 40 mg.
Capsules (Extended-Release [Focalin XR]): 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg, 40 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Do not give drug in afternoon or evening (causes insomnia). • Tablets may be crushed. • Give without regard to food. • Administer extended-release capsules whole; do not cut or crush. • May sprinkle contents of extended-release capsules on small amount of applesauce. • Give extended-release capsules once each day in the morning, before breakfast.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
NOTE: If pt taking methylphenidate, initially use one half the dose of methylphenidate for conversion to dexmethylphenidate. Maximum immediate-release dose: 20 mg/day. Maximum extended-release dose: 30 mg/day.
ADHD
(Dosage for pts not currently taking methylphenidate)
Capsules (Extended-Release)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10 mg/day. May increase in increments of 10 mg/day at wkly intervals. Maximum: 40 mg/day. CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 5 mg/day. May increase in increments of 5 mg/day at wkly intervals. Maximum: 30 mg/day.
Tablets (Immediate-Release)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 2.5 mg 2 times/day. Doses should be given at least 4 hrs apart. May increase in increments of 2.5–5 mg at wkly intervals. Maximum: 20 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Abdominal pain, nausea, anorexia, fever. Occasional: Tachycardia, arrhythmias, palpitations, insomnia, twitching. Rare: Blurred vision, rash, arthralgia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Withdrawal after prolonged therapy may unmask symptoms of underlying disorder. May lower seizure threshold in pts with history of seizures. Overdose produces excessive sympathomimetic effects (vomiting, tremor, hyperreflexia, seizures, confusion, hallucinations, diaphoresis). Prolonged administration to children may delay growth. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Evaluate pt for cardiac disease, psychiatric conditions. Obtain baseline vital signs, CBC.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
CBC, B/P, heart rate should be performed routinely during therapy. If paradoxical return of ADHD occurs, dosage should be reduced or discontinued. Weigh, measure pediatric pt regularly to detect delayed growth.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report any increase in seizures, chest pain, unexplained syncope. • Avoid caffeine. • Last dose should be given in morning to prevent insomnia. • Report anxiety, fever.
dextroamphetamine and amphetamine

dex-troe-am-fet-ah-meen/am-fet-ah-meen
(Adderall, Adderall-XR)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() High potential for abuse. Prolonged administration may lead to drug dependence. Severe cardiovascular events including stroke/MI reported.
High potential for abuse. Prolonged administration may lead to drug dependence. Severe cardiovascular events including stroke/MI reported.
Do not confuse Adderall with Inderal.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Amphetamine (Schedule II). CLINICAL: CNS stimulant.
USES
Treatment of narcolepsy; treatment of ADHD.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dextroamphetamine, amphetamine, or sympathomimetics. Advanced arteriosclerosis, agitated mental states, glaucoma, history of alcohol or drug abuse, hypersensitivity to sympathomimetic amines, hyperthyroidism, moderate to severe hypertension, symptomatic cardiovascular disease, use of MAOIs within 14 days. Cautions: Elderly, debilitated pts, history of seizures, mild hypertension. Preexisting psychotic or bipolar disorder.
ACTION
Enhances action of dopamine, norepinephrine by blocking reuptake from synapses. Inhibits monoamine oxidase, facilitates release of catecholamines. Therapeutic Effect: Increases motor activity, mental alertness; decreases drowsiness, fatigue; suppresses appetite.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following PO administration. Widely distributed including CNS. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 10–13 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 3 yrs. Elderly: Age-related cardiovascular, cerebrovascular disease, hepatic/renal impairment may increase risk of side effects.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May enhance effects of tricyclic antidepressants, sympathomimetics. MAOIs may prolong, intensify effects. May antagonize effects of hypotensive agents. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase plasma corticosteroid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets (Adderall): 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg, 12.5 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg.
![]() Capsules (Extended-Release [Adderall-XR]): 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, 30 mg.
Capsules (Extended-Release [Adderall-XR]): 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, 30 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give tablets at least 6 hrs before bedtime. • Extended-release capsules should be swallowed whole; do not break, crush, or cut. • Avoid afternoon doses to prevent insomnia. • May open capsules and sprinkle on applesauce. Instruct pt not to chew sprinkled beads; take immediately.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Narcolepsy
PO: ADULTS, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 12 YRS: Initially, 10 mg/day. Increase by 10 mg/day at wkly intervals until therapeutic response is achieved. Maximum: 60 mg/day given in 1–3 divided doses with interval of 4–6 hrs between doses. CHILDREN 6–12 YRS: Initially, 5 mg/day. Increase by 5 mg/day at wkly intervals until therapeutic response is achieved. Maximum: 60 mg/day given in 1–3 divided doses with interval of 4–6 hrs between doses.
ADHD
ADULTS, ELDERLY: (ADDERALL): Initially, 5 mg 1–2 times/day. May increase by 5 mg increments at wkly intervals. Maximum: 40 mg/day in 1–3 divided doses (usual intervals of 4–6 hrs). (ADDERALL-XR): Initially, 20 mg once daily in the morning. May increase up to 60 mg/day. CHILDREN 13–17 YRS: (ADDERALL): Initially, 5 mg 1–2 times/day. May increase by 5 mg at wkly intervals. Maximum: 40 mg/day in 1–3 divided doses (usual intervals of 4–6 hrs). (ADDERALL-XR): Initially, 10 mg once daily in the morning. May increase to 20 mg/day after 1 wk if symptoms are not controlled. May increase up to 60 mg/day. CHILDREN 6–12 YRS: (ADDERALL): Initially, 5 mg 1–2 times/day. May increase in 5-mg increments at wkly intervals until optimal response is obtained. Maximum: 40 mg/day given in 1–3 divided doses (use intervals of 4–6 hrs between additional doses). (ADDERALL-XR): Initially, 5–10 mg once daily in the morning. May increase daily dose in 5- to 10-mg increments at wkly intervals. Maximum: 30 mg/day. CHILDREN 3–5 YRS: (ADDERALL): Initially, 2.5 mg/day given every morning. May increase daily dose in 2.5-mg increments at wkly intervals until optimal response is obtained. Maximum: 40 mg/day given in 1–3 divided doses (use intervals of 4–6 hrs between additional doses). Not recommended in children younger than 3 yrs.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Increased motor activity, talkativeness, nervousness, mild euphoria, insomnia. Occasional: Headache, chills, dry mouth, GI distress, worsening depression in pts who are clinically depressed, tachycardia, palpitations, chest pain, dizziness, decreased appetite.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may produce skin pallor/flushing, arrhythmias, psychosis. Abrupt withdrawal after prolonged use of high doses may produce lethargy (may last for wks). Prolonged administration to children with ADHD may temporarily suppress normal weight/height pattern.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess attention span, impulse control, interaction with others. Screen for drug–seeking behavior, past drug abuse. Obtain baseline B/P.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for CNS overstimulation, increase in B/P, growth rate, change in pulse rate, respirations, weight loss. Narcolepsy: Observe/document frequency of narcoleptic episodes. ADHD: Observe for improved attention span.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Normal dosage levels may produce tolerance to drug’s anorexic mood-elevating effects within a few wks. • Dry mouth may be relieved with sugarless gum, sips of water. • Take early in day. • Do not break, chew, or crush extended-release capsules. • May mask extreme fatigue. • Report pronounced anxiety, dizziness, decreased appetite, dry mouth, new or worsening behavior, chest pain, palpitations. • Avoid alcohol, caffeine.
*diazePAM
dye-az-e-pam
(Apo-Diazepam
![]() , Diastat, Diazepam Intensol, Novo-Dipam
, Diastat, Diazepam Intensol, Novo-Dipam
![]() , Valium)
, Valium)
Do not confuse diazepam with diazoxide, diltiazem, Ditropan, or lorazepam, or Valium with Valcyte.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Benzodiazepine (Schedule IV). CLINICAL: Antianxiety, skeletal muscle relaxant, anticonvulsant.
USES
Short-term relief of anxiety symptoms, relief of acute alcohol withdrawal. Adjunct for relief of acute musculoskeletal conditions, treatment of seizures (IV route used for termination of status epilepticus). Gel: Control of increased seizure activity in refractory epilepsy in pts on stable regimens. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of panic disorder. Short-term treatment of spasticity in children with cerebral palsy. Sedation for mechanically vented pts in ICU.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to diazepam. Acute narrow-angle glaucoma, untreated open-angle glaucoma, severe respiratory depression, severe hepatic insufficiency, sleep apnea syndrome, myasthenia gravis. Children younger than 6 mos (oral). Cautions: Pts receiving other CNS depressants or psychoactive agents, depression, history of drug and alcohol abuse, renal/hepatic impairment, respiratory disease, impaired gag reflex, concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers.
ACTION
Depresses all levels of CNS by enhancing action of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Therapeutic Effect: Produces anxiolytic effect, elevates seizure threshold, produces skeletal muscle relaxation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Widely distributed. Protein binding: 98%. Excreted in urine. Minimally removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 20–70 hrs (increased in hepatic dysfunction, elderly).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. May increase risk of fetal abnormalities if administered during first trimester of pregnancy. Chronic ingestion during pregnancy may produce withdrawal symptoms, CNS depression in neonates. Children/Elderly: Use small initial doses with gradual increases to avoid ataxia, excessive sedation.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, CNS depressants may increase CNS depression. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin) may decrease concentration. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., itraconazole, ketoconazole) may increase concentration. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase concentration/effects. LAB VALUES: None significant. Therapeutic serum level: 0.5–2 mcg/ml; toxic serum level: greater than 3 mcg/ml.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution: 5 mg/ml. Oral Concentrate (Diazepam Intensol): 5 mg/ml. Oral Solution: 5 mg/5 ml. Rectal Gel (Diastat): 2.5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg. Tablet (Valium): 2 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Rate of Administration • Give by IV push into tubing of flowing IV solution as close as possible to vein insertion point. • Administer directly into large vein (reduces risk of thrombosis/phlebitis). Do not use small veins (e.g., wrist/dorsum of hand). • Administer IV at rate not exceeding 5 mg/min for adults. For children, give 1–2 mg/min (too-rapid IV may result in hypotension, respiratory depression). • Monitor respirations q5–15min for 2 hrs.
Storage • Store at room temperature.
IM
• Injection may be painful. Inject deeply into large muscle mass.
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Dilute oral concentrate with water, juice, carbonated beverages; may be mixed in semisolid food (applesauce, pudding). • Tablets may be crushed.
GEL
• Insert rectal tip and gently push plunger over 3 sec. Remove tip after 3 additional sec. • Buttocks should be held together for 3 sec after removal.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), cefepime (Maxipime), diltiazem (Cardizem), fluconazole (Diflucan), foscarnet (Foscavir), furosemide (Lasix), heparin, hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), meropenem (Merrem IV), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan), vitamins.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Dobutamine (Dobutrex), fentanyl, morphine.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Anxiety
PO: ADULTS: 2–10 mg 2–4 times/day. ELDERLY: Initially, 1–2 mg 1–2 times/day. CHILDREN: 0.12–0.8 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6–8h.
IV, IM: ADULTS: 2–10 mg; may repeat in 3–4 hrs if needed. CHILDREN: 0.04–0.3 mg/kg/dose q2–4h. Maximum: 0.6 mg/kg within 8-hr period.
Skeletal Muscle Relaxation
PO: ADULTS: 2–10 mg 2–4 times/day. ELDERLY: Initially, 1–2 mg 1–2 times/day. CHILDREN: 0.12–0.8 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6–8h.
Alcohol Withdrawal
IM, IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10 mg, then 5–10 mg 3–4 hrs later. PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 10 mg 3–4 times during first 24 hrs, then reduce to 5 mg 3–4 times/day as needed.
Status Epilepticus
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–10 mg q5–10 min. Maximum: 30 mg. May repeat in 2–4 hrs. INFANTS, CHILDREN: 0.1–0.3 mg/kg over 2 min; may repeat after 5–10 min. Maximum: 10 mg/dose.
Control of Increased Seizure Activity (Breakthrough Seizures) in Pts with Refractory Epilepsy Who Are on Stable Regimens of Anticonvulsants
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2–10 mg 2–4 times/day. Note: Do not use gel for more than 5 episodes/mo or more than 1 episode q5days. Rectal Gel: ADULTS, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 0.2 mg/kg; may be repeated in 4–12 hrs. CHILDREN 6–11 YRS: 0.3 mg/kg; may be repeated in 4–12 hrs. CHILDREN 2–5 YRS: 0.5 mg/kg; may be repeated in 4–12 hrs.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Use caution.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution. Oral tablets contraindicated in severe hepatic impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Pain with IM injection, drowsiness, fatigue, ataxia. Occasional: Slurred speech, orthostatic hypotension, headache, hypoactivity, constipation, nausea, blurred vision. Rare: Paradoxical CNS reactions (hyperactivity/nervousness in children, excitement/restlessness in elderly/debilitated) generally noted during first 2 wks of therapy, particularly in presence of uncontrolled pain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
IV route may produce pain, swelling, thrombophlebitis, carpal tunnel syndrome. Abrupt or too-rapid withdrawal may result in pronounced restlessness, irritability, insomnia, hand tremor, abdominal/muscle cramps, diaphoresis, vomiting, seizures. Abrupt withdrawal in pts with epilepsy may produce increase in frequency/severity of seizures. Overdose results in drowsiness, confusion, diminished reflexes, CNS depression, coma. Antidote: Flumazenil (see Appendix J for dosage).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess B/P, pulse, respirations immediately before administration. Anxiety: Assess autonomic response (cold, clammy hands, diaphoresis), motor response (agitation, trembling, tension). Musculoskeletal spasm: Record onset, type, location, duration of pain. Check for immobility, stiffness, swelling. Seizures: Review history of seizure disorder (length, intensity, frequency, duration, LOC). Observe frequently for recurrence of seizure activity. Initiate seizure precautions.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor heart rate, respiratory rate, B/P, mental status. Assess children, elderly for paradoxical reaction, particularly during early therapy. Evaluate for therapeutic response (decrease in intensity/frequency of seizures; calm facial expression, decreased restlessness; decreased intensity of skeletal muscle pain). Therapeutic serum level: 0.5–2 mcg/ml; toxic serum level: greater than 3 mcg/ml.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid alcohol. • Limit caffeine. • May cause drowsiness, avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • May be habit forming. • Avoid abrupt discontinuation after prolonged use.
diclofenac
dye-kloe-fen-ak
(Apo-Diclo
![]() , Cambia, Dyloject, Flector, Pennsaid, Solaraze, Voltaren, Voltaren Gel, Zipsor, Zorvolex)
, Cambia, Dyloject, Flector, Pennsaid, Solaraze, Voltaren, Voltaren Gel, Zipsor, Zorvolex)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction, CVA. Increased risk of severe GI reactions, including ulceration, bleeding, perforation of stomach, intestines. Contraindicated for treatment of perioperative pain in setting of CABG surgery.
Increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction, CVA. Increased risk of severe GI reactions, including ulceration, bleeding, perforation of stomach, intestines. Contraindicated for treatment of perioperative pain in setting of CABG surgery.
Do not confuse Cataflam with Catapres, diclofenac with Diflucan or Duphalac, or Voltaren with tramadol, Ultram, or Verelan.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Arthrotec: diclofenac/misoprostol (an antisecretory gastric protectant): 50 mg/200 mcg, 75 mg/200 mcg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: NSAID. CLINICAL: Analgesic, anti-inflammatory.
USES
PO: (Immediate-release): Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, mild to moderate pain, primary dysmenorrhea. (Zipsor): Mild to moderate pain. (Zorvolex): Mild to moderate pain, osteoarthritic pain. (Delayed-release): Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis. (Extended-release): Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis. Oral Solution (Cambia): Treatment of migraine. Injection: Treatment of mild to moderate acute pain and moderate to severe acute pain in adults. Topical Patch: Treatment of acute pain due to minor strains, sprains, contusions. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to diclofenac. Pts experiencing asthma, urticaria after taking aspirin, other NSAIDs. Pts with moderate to severe renal impairment in perioperative period who are at risk for volume depletion (injection only); perioperative pain in setting of CABG surgery. Cautions: HF, hypertension, renal/hepatic impairment, hepatic porphyria, history of GI disease (e.g., bleeding, ulcers), concomitant use of aspirin or anticoagulants, elderly, debilitated.
ACTION
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, intensity of pain stimulus reaching sensory nerve endings. Therapeutic Effect: Produces analgesic, anti-inflammatory effects.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 30 min | 2–3 hrs | Up to 8 hrs |
Completely absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: greater than 99%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Minimally removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 1.2–2 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Avoid use during third trimester (may adversely affect fetal cardiovascular system: premature closure of ductus arteriosus). Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: GI bleeding, ulceration more likely to cause serious adverse effects. Age-related renal impairment may increase risk of hepatic/renal toxicity; reduced dosage recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of acetylcholine, antihypertensives, carbachol, diuretics. Aspirin, other salicylates, warfarin may increase risk of GI side effects/bleeding. CYP2C9 inhibitors (e.g., voriconazole) may increase concentration/risk of toxicity. CYP2C9 inducers (e.g., rifampin) may decrease effect. May increase cyclosporine concentration/toxicity. Ophthalmic: May decrease antiglaucoma effects of antiglaucoma agents, epinephrine. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, garlic, ginseng may increase antiplatelet activity. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase urine protein, serum BUN, alkaline phosphatase, creatinine, LDH, potassium, ALT, AST. May decrease serum uric acid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Adhesive Patch (Flector): 10×14 cm patch containing 180 mg diclofenac. Capsules (Zipsor): 25 mg. (Zorvolex): 18 mg, 35 mg. Intravenous Solution (Dyloject): 37.5 mg/ml. Oral Solution (Cambia): 50-mg packets. Tablets (Cataflam): 50 mg.
![]() Tablets (Delayed-Release [Voltaren]): 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg.
Tablets (Delayed-Release [Voltaren]): 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg.
![]() Tablets (Extended-Release [Voltaren XR]): 100 mg.
Tablets (Extended-Release [Voltaren XR]): 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide enteric-coated tablets. • May give with food, milk, antacids if GI distress occurs. • Cambia: Mix one packet in 1–2 oz water, stir well, and instruct pt to drink immediately.
![]() IV
IV
Administer as IV bolus over 15 sec.
Transdermal Patch
• Apply to intact skin; avoid contact with eyes. • Do not wear when bathing/showering. • Wash hands after handling.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Osteoarthritis
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 50 mg 2–3 times/day.
PO (Extended-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100 mg/day as a single dose. May increase to 200 mg/day in 2 divided doses. (Zorvolex): 35 mg 3 times/day.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 50 mg 3–4 times/day.
PO (Extended-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100 mg once daily. May increase to 200 mg/day in 2 divided doses.
PO (Delayed-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 150–200 mg/day in 2–4 divided doses.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
PO (Delayed-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100–125 mg/day in 4–5 divided doses.
Primary Dysmenorrhea
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 50 mg 3 times/day.
Pain
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate-Release): 100 mg once, then 50 mg 3 times/day. (Zipsor): 25 mg 4 times/day. (Zorvolex): 18–35 mg 3 times/day.
IV: 37.5 mg q6h prn. Maximum: 150 mg/day.
Topical Patch: (Flector): Apply 2 times/day.
Migraine (Oral Solution)
PO ADULTS, ELDERLY: 50 mg (one packet) once.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Not recommended in severe impairment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
May require dose adjustment. Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (9%–4%): PO: Headache, abdominal cramps, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, dyspepsia. Ophthalmic: Burning, stinging on instillation, ocular discomfort. Occasional (3%–1%): PO: Flatulence, dizziness, epigastric pain. Ophthalmic: Ocular itching, tearing. Rare (less than 1%): PO: Rash, peripheral edema, fluid retention, visual disturbances, vomiting, drowsiness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may result in acute renal failure. In pts treated chronically, peptic ulcer, GI bleeding, gastritis, severe hepatic reaction (jaundice), nephrotoxicity (hematuria, dysuria, proteinuria), severe hypersensitivity reaction (bronchospasm, angioedema) occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Anti-inflammatory: Assess onset, type, location, duration of pain, inflammation. Inspect appearance of affected joints for immobility, deformities, skin condition.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, renal function, LFT, urine output, occult blood test. Monitor for headache, dyspepsia. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess for therapeutic response: relief of pain, stiffness, swelling; increased joint mobility; reduced joint tenderness; improved grip strength.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Swallow tablets whole; do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide. • Avoid aspirin, alcohol during therapy (increases risk of GI bleeding). • If GI upset occurs, take with food, milk. • Report skin rash, itching, weight gain, changes in vision, black stools, bleeding, jaundice, upper quadrant pain, persistent headache. • Ophthalmic: Do not use hydrogel soft contact lenses. • Topical: Avoid exposure to sunlight, sunlamps. • Report rash.
digoxin

di-jox-in
(Apo-Digoxin
![]() , Digitek, Digox, Lanoxin)
, Digitek, Digox, Lanoxin)
Do not confuse digoxin with Desoxyn or doxepin, or Lanoxin with Lasix, Levoxyl, Levsinex, Lonox, or Mefoxin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Cardiac glycoside. CLINICAL: Antiarrhythmic, cardiotonic.
USES
Treatment of mild to moderate HF. Control ventricular response rate in pts with chronic atrial fibrillation. OFF-LABEL: Fetal tachycardia with or without hydrops; decrease ventricular rate in supraventricular tachyarrhythmias.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to digoxin. Ventricular fibrillation. Cautions: Renal impairment, sinus nodal disease, acute MI (within 6 mos), second- or third-degree heart block (unless functioning pacemaker), concurrent use of strong inducers or inhibitors of P-glycoprotein (e.g., cyclosporine), hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia.
ACTION
HF: Inhibits sodium/potassium ATPase pump in myocardial cells. Promotes calcium influx. Supraventricular Arrhythmias: Suppresses AV node conduction. Therapeutic Effect: HF: Increases contractility. Supraventricular Arrhythmias: Increases effective refractory period/decreases conduction velocity, decreases heart rate.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 0.5–2 hrs | 2–8 hrs | 3–4 days |
| IV | 5–30 min | 1–4 hrs | 3–4 days |
Readily absorbed from GI tract. Widely distributed. Protein binding: 30%. Partially metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Minimally removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 36–48 hrs (increased in renal impairment, elderly).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children: Premature infants more susceptible to toxicity. Elderly: Age-related hepatic/renal impairment may require dosage adjustment. Increased risk of loss of appetite.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Amiodarone may increase concentration/toxicity. Beta blockers (e.g., metoprolol), calcium channel blockers (e.g., diltiazem) may have additive effect on slowing AV nodal conduction. Potassium-depleting diuretics (e.g., furosemide) may increase toxicity due to hypokalemia. Sympathomimetics (e.g., norepinephrine) may increase risk of arrhythmias. HERBAL: Ephedra may increase risk of arrhythmias. Licorice may cause sodium and water retention, loss of potassium. FOOD: Meals with increased fiber (bran) or high in pectin may decrease absorption. LAB VALUES: None known.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Oral Solution (Lanoxin): 50 mcg/ml. Injection Solution (Lanoxin): 100 mcg/ml, 250 mcg/ml. Tablets (Lanoxin): 62.5 mcg, 125 mcg, 187.5 mcg, 250 mcg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ IM rarely used (produces severe local irritation, erratic absorption). If no other route possible, give deep into muscle followed by massage. Give no more than 2 ml at any one site.
![]() IV
IV
• May give undiluted or dilute with at least a 4-fold volume of Sterile Water for Injection or D5W (less may cause precipitate). • Use immediately. • Give IV slowly over at least 5 min.
PO
• May give without regard to meals. • Tablets may be crushed.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), fluconazole (Diflucan), foscarnet (Foscavir), propofol (Diprivan).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Diltiazem (Cardizem), furosemide (Lasix), heparin, insulin regular, lidocaine, midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Loading dose not recommended in HF.
Loading Dose
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.75–1.5 mg. CHILDREN 10 YRS AND OLDER: 10–15 mcg/kg. CHILDREN 5–9 YRS: 20–35 mcg/kg. CHILDREN 2–4 YRS: 30–40 mcg/kg. CHILDREN 1–23 MOS: 35–60 mcg/kg. NEONATE, FULL-TERM: 25–35 mcg/kg. NEONATE, PREMATURE: 20–30 mcg/kg.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Supraventricular tachyarrhythmias): 0.5–1 mg. CHILDREN 10 YRS AND OLDER: 8–12 mcg/kg. CHILDREN 5–9 YRS: 15–30 mcg/kg. CHILDREN 2–4 YRS: 25–35 mcg/kg. CHILDREN 1–23 MOS: 30–50 mcg/kg. NEONATES, FULL-TERM: 20–30 mcg/kg. NEONATES, PREMATURE: 15–25 mcg/kg.
Maintenance Dosage
| PO | IV/IM | |
| Preterm infant | 5–7.5 mcg/kg | 4–6 mcg/kg |
| Full-term infant | 6–10 mcg/kg | 5–8 mcg/kg |
| 1 mo–2 yrs | 10–15 mcg/kg | 7.5–12 mcg/kg |
| 2–5 yrs | 7.5–10 mcg/kg | 6–9 mcg/kg |
| 5–10 yrs | 5–10 mcg/kg | 4–8 mcg/kg |
HF
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.125–0.25 mg once daily.
Supraventricular Arrhythmias
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Digitalizing dose: 0.75–1.5 mg. Maintenance dose: 0.125–0.5 mg once daily. IV: Digitalizing dose: 0.5–1 mg Maintenance dose: 0.1–0.4 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage adjustment is based on creatinine clearance. Loading dose: decrease by 50% in end-stage renal disease.
Maintenance Dose
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 10–50 ml/min | 25%–75% of usual dose or q36h (0.0625 mg q24–36hrs) |
| Less than 10 ml/min (HD, PD, CRRT) | 10%–25% of usual dose or q48h (0.0625 mg q48h) |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Dizziness, headache, diarrhea, rash, visual disturbances.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Most common early manifestations of digoxin toxicity are GI disturbances (anorexia, nausea, vomiting), neurologic abnormalities (fatigue, headache, depression, weakness, drowsiness, confusion, nightmares). Facial pain, personality change, ocular disturbances (photophobia, light flashes, halos around bright objects, yellow or green color perception) may occur. Sinus bradycardia, AV block, ventricular arrhythmias noted. Antidote: Digoxin immune FAB (see Appendix J for dosage).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess apical pulse. If pulse is 60 or less/min (70 or less/min for children), withhold drug, contact physician. Blood samples are best taken 6–8 hrs after dose or just before next dose.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor pulse for bradycardia, EKG for arrhythmias for 1–2 hrs after administration (excessive slowing of pulse may be first clinical sign of toxicity). Assess for GI disturbances, neurologic abnormalities (signs of toxicity) q2–4h during loading dose (daily during maintenance). Monitor serum potassium, magnesium, calcium, renal function. Therapeutic serum level: 0.8–2 ng/ml; toxic serum level: greater than 2 ng/ml.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Follow-up visits, blood tests are an important part of therapy. • Follow guidelines to take apical pulse and report pulse 60 or less/min (or as indicated by physician). • Wear/carry identification of digoxin therapy and inform dentist, other physician of taking digoxin. • Do not increase or skip doses. • Do not take OTC medications without consulting physician. • Report decreased appetite, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, visual changes.
dihydroergotamine
dye-hye-droe-er-got-a-meen
(D.H.E. 45, Migranal)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Concurrent use with CYP3A4 inhibitors (macrolide antibiotics, azole antifungals, protease inhibitors) increases risk of vasospasm, producing ischemia of brain and peripheral extremities.
Concurrent use with CYP3A4 inhibitors (macrolide antibiotics, azole antifungals, protease inhibitors) increases risk of vasospasm, producing ischemia of brain and peripheral extremities.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Cafergot, Wigraine: ergotamine/caffeine (stimulant): 1 mg/100 mg, 2 mg/100 mg.
Do not confuse Cafergot with Carafate.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Ergotamine derivative. CLINICAL: Antimigraine.
USES
Treatment of migraine headache with or without aura. Injection also used to treat cluster headache.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dihydroergotamine. Uncontrolled hypertension, ischemic heart disease, coronary artery vasospasm (including Prinzmetal’s angina), angina pectoris, history of MI following vascular surgery, concurrent use of peripheral and central vasoconstrictors, hemiplegic or basilar migraine, peripheral vascular disease, sepsis, severe renal/hepatic impairment, use of MAOIs within 14 days, use of 5-HTB agonists within 24 hrs, potent CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., azole antifungals, macrolide antibiotics, protease inhibitors), pregnancy, breastfeeding. Cautions: Elderly.
ACTION
Directly stimulates vascular smooth muscle, resulting in peripheral and cerebral vasoconstriction. May have antagonist effects on serotonin. Therapeutic Effect: Suppresses vascular headaches, migraine headaches.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Slowly, incompletely absorbed from GI tract; rapidly and extensively absorbed after rectal administration. Protein binding: greater than 90%. Eliminated in feces by the biliary system. Half-life: 21 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Contraindicated in pregnancy (produces uterine stimulant action, resulting in possible fetal death or retarded fetal growth); increases vasoconstriction of placental vascular bed. Drug distributed in breast milk. May produce diarrhea, vomiting in neonate. May prohibit lactation. Children: No precautions in pts 6 yrs and older, but use only when unresponsive to other medication. Elderly: Age-related occlusive peripheral vascular disease increases risk of peripheral vasoconstriction. Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Beta blockers (e.g., carvedilol, metoprolol), erythromycin may increase risk of peripheral vasoconstriction. Ergot alkaloids, 5-HTB agonists (e.g., sumatriptan), systemic vasoconstrictors may increase vasopressor effect. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: Coffee, cola, tea may increase absorption. Grapefruit products may increase concentration, toxicity. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Dihydroergotamine Injection, Solution: 1 mg/ml. Intranasal Spray, Solution (Migranal): 4 mg/ml (0.5 mg/spray).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Migraine Headache
IM/SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1 mg at onset of headache; repeat hourly. Maximum: 3 mg/day; 6 mg/wk.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Give slowly over 2–3 min) 1 mg at onset of headache; repeat hourly. Maximum: 2 mg/day; 6 mg/wk.
Intranasal: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1 spray (0.5 mg) into each nostril; repeat in 15 min up to a total of 4 sprays (2 mg). Do not exceed 6 sprays (3 mg) in 24-hr period or 8 sprays (4 mg) in a wk.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Contraindicated in severe impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (5%–2%): Cough, dizziness. Rare (less than 2%): Myalgia, fatigue, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, dyspepsia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Prolonged administration, excessive dosage may produce ergotamine poisoning, manifested as nausea, vomiting, paresthesia of extremities, muscle pain/weakness, precordial pain, significant changes in pulse rate and blood pressure. Vasoconstriction of peripheral arteries/arterioles may result in localized edema, pruritus; feet, hands will become cold, pale. Muscle pain will occur when walking and later, even at rest. Other rare effects include confusion, depression, drowsiness, seizures, gangrene.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of peripheral vas-cular disease, renal/hepatic impairment, possibility of pregnancy. Question onset, location, duration of migraine, possible precipitating symptoms.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor closely for evidence of ergotamine overdosage as result of prolonged administration or excessive dosage.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Initiate therapy at first sign of migraine headache. • Report if there is need to progressively increase dose to relieve vascular headaches or if palpitations, nausea, vomiting, paresthesia, pain or weakness of extremities, chest pain. Avoid grapefruit products. • Female pts should avoid pregnancy; if suspected, immediately report.
*dilTIAZem

dil-tye-a-zem
(Apo-Diltiaz
![]() , Cardizem, Cardizem CD, Cardizem LA, Cartia XT, Diltiazem CD, Dilt-XR, Matzim LA, Taztia XT, Tiazac)
, Cardizem, Cardizem CD, Cardizem LA, Cartia XT, Diltiazem CD, Dilt-XR, Matzim LA, Taztia XT, Tiazac)
Do not confuse Cardizem with Cardene or Cardene SR, Cartia XT with Procardia XL, diltiazem with Calan, diazepam, or Dilantin, or Tiazac with Ziac.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Calcium channel blocker. CLINICAL: Antianginal, antihypertensive, antiarrhythmic.
USES
PO: Treatment of angina due to coronary artery spasm (Prinzmetal’s variant angina), chronic stable angina (effort-associated angina). Treatment of hypertension. Parenteral: Temporary control of rapid ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation/flutter. Rapid conversion of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) to normal sinus rhythm.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: PO: Acute MI, pulmonary congestion, hypersensitivity to diltiazem, second- or third-degree AV block (except in presence of pacemaker), severe hypotension (less than 90 mm Hg, systolic), sick sinus syndrome (except in presence of pacemaker). IV: Hypersensitivity to diltiazem. Sick sinus syndrome or second- or third-degree block (except with functioning pacemaker), cardiogenic shock, administration of IV beta blocker within several hours, atrial fibrillation/flutter associated with accessory bypass tract, severe hypotension, ventricular tachycardia. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, HF, concurrent use with beta blocker, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy.
ACTION
Inhibits calcium movement across cardiac, vascular smooth-muscle cell membranes (causes dilation of coronary arteries, peripheral arteries, arterioles). Therapeutic Effect: Relaxes coronary vascular smooth muscle, increases myocardial oxygen delivery in pts with vasospastic angina, decreases heart rate.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 0.5–1 hr | N/A | N/A |
| PO (extended-release) | 2–3 hrs | N/A | N/A |
| IV | 3 min | N/A | N/A |
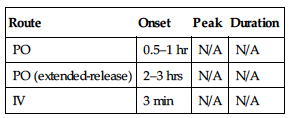
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 70%–80%. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 3–8 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Beta blockers (e.g., carvedilol, metoprolol), digoxin may have additive effect on prolonging AV conduction. May increase concentration, risk of toxicity with carbamazepine, benzodiazepines. May increase serum digoxin concentration. Rifampin may decrease concentration/effects. May increase concentration of statins and risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis. HERBAL: Ephedra may worsen arrhythmias, hypertension. Garlic may increase antihypertensive effect. Ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: EKG: May increase PR interval.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution: 25 mg/5 ml, 50 mg/10 ml, 125 mg/25 ml. Tablets, Immediate-Release: 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg, 120 mg.
![]() Capsules, Extended-Release, 24 Hour: 120 mg, 180 mg, 240 mg, 300 mg, 360 mg, 420 mg.
Capsules, Extended-Release, 24 Hour: 120 mg, 180 mg, 240 mg, 300 mg, 360 mg, 420 mg.
![]() Capsules, Extended-Release, 12 Hour: 60 mg, 90 mg, 120 mg.
Capsules, Extended-Release, 12 Hour: 60 mg, 90 mg, 120 mg.
![]() Tablets, Extended-Release, 24 Hour: 180 mg, 240 mg, 300 mg, 360 mg, 420 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release, 24 Hour: 180 mg, 240 mg, 300 mg, 360 mg, 420 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Add 125 mg to 100 ml D5W, 0.9% NaCl to provide concentration of 1 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • Infuse per dilution/rate chart provided by manufacturer.
Storage • Refrigerate vials. • After dilution, stable for 24 hrs.
PO
• Give immediate-release tablets before meals and at bedtime. • Tablets may be crushed. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide sustained-release capsules or extended-release capsules or tablets. • Taztia XT capsules may be opened and mixed with applesauce; follow with glass of water. • Cardizem CD, Cardizem LA, Cartia XT, Matzim LA may be given without regard to meals. • Dilacor XR, Dilt-XR to be given on empty stomach.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Acetazolamide (Diamox), acyclovir (Zovirax), ampicillin, ampicillin/sulbactam (Unasyn), diazepam (Valium), furosemide (Lasix), heparin, insulin, nafcillin, phenytoin (Dilantin), rifampin (Rifadin), sodium bicarbonate.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Albumin, aztreonam (Azactam), bumetanide (Bumex), cefazolin (Ancef), cefotaxime (Claforan), ceftazidime (Fortaz), ceftriaxone (Rocephin), cefuroxime (Zinacef), ciprofloxacin (Cipro), clindamycin (Cleocin), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), digoxin (Lanoxin), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), gentamicin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), metoclopramide (Reglan), metronidazole (Flagyl), midazolam (Versed), morphine, multivitamins, nitroglycerin, norepinephrine (Levophed), potassium chloride, potassium phosphate, tobramycin (Nebcin), vancomycin (Vancocin).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Angina
PO (Immediate-Release) ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 30 mg 4 times/day. Range: 120–320 mg/day.
PO (Extended-Release) (Cardizem CD, Cartia XT, DILT-XR): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 120–180 mg once daily. May increase at 7–14 day intervals. Range: 120–320 mg. Maximum: 480 mg/day.
(Extended-Release) (Tiazac, Taztia XT): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 120–180 mg once daily. May increase at 7–14 day intervals. Range: 120–320 mg/day. Maximum: 540 mg/day.
(Extended-Release) (Cardizem LA, Matzim LA): Initially, 180 mg/day. May increase at 7–14 day intervals. Range: 120–320 mg. Maximum: 360 mg daily.
Hypertension
PO Capsule Extended-Release (once daily dosing) (Cardizem CD, Cartia XT): Initially, 180–240 mg/day. May increase after 14 days. Usual dose: 240–360 mg/day. Maximum: 480 mg/day. (Dilt-XR): Initially, 180–240 mg/day. May increase after 14 days. Usual dose: 240–360 mg/day. Maximum: 540 mg/day. (Tiazac, Taztia XT): Initially, 120–240 mg/day. Usual dose: 240–360 mg/day. Maximum: 540 mg/day.
PO Capsule Extended-Release (twice daily dosing): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 60–120 mg twice daily. May increase at 14-day intervals. Maintenance: 240–360 mg/day.
PO Tablet Extended-Release (once daily dosing) (Cardizem LA, Matzim LA): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 180–240 mg/day. May increase at 14-day intervals. Range: 120–540 mg/day. 240–360 mg/day. Maximum: 540 mg/day.
Temporary Control of Rapid Ventricular Rate in Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter; Rapid Conversion of Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia to Normal Sinus Rhythm
IV Push: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 0.25 mg/kg (average dose: 20 mg) actual body weight over 2 min. May repeat in 15 min at dose of 0.35 mg/kg (average dose: 25 mg) actual body weight. Subsequent doses individualized.
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: After initial bolus injection, may begin infusion at 5–10 mg/hr; may increase by 5 mg/hr up to a maximum of 15 mg/hr. Infusion duration should not exceed 24 hrs. Attempt conversion to PO therapy as soon as possible.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Use with caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (10%–5%): Peripheral edema, dizziness, light-headedness, headache, bradycardia, asthenia. Occasional (5%–2%): Nausea, constipation, flushing, EKG changes. Rare (less than 2%): Rash, micturition disorder (polyuria, nocturia, dysuria, frequency of urination), abdominal discomfort, drowsiness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Abrupt withdrawal may increase frequency, duration of angina, HF; second- and third-degree AV block occur rarely. Overdose produces nausea, drowsiness, confusion, slurred speech, profound bradycardia. Antidote: Glucagon, insulin drip with continuous calcium infusion (see Appendix J for dosage).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Record onset, type (sharp, dull, squeezing), radiation, location, intensity, duration of anginal pain, precipitating factors (exertion, emotional stress). Assess baseline renal/hepatic function tests. Assess B/P, apical pulse immediately before drug is administered.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Assess for peripheral edema. Monitor pulse rate for bradycardia. Assess B/P, renal function, LFT, EKG with IV therapy. Question for asthenia, headache.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not abruptly discontinue medication. • Compliance with therapy regimen is essential to control anginal pain. • To avoid hypotensive effect, go from lying to standing slowly. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Report palpitations, shortness of breath, pronounced dizziness, nausea, constipation. • Avoid alcohol (may increase risk of hypotension or vasodilation).
dimethyl fumarate

dye-meth-il-fue-ma-rate
(Tecfidera)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Fumaric acid ester. CLINICAL: Multiple sclerosis agent.
USES
Treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dimethyl fumarate. Cautions: Hepatic impairment (may increase hepatic transaminases, lymphopenia (may decrease lymphocyte count).
ACTION
Exact mechanism of action unknown. May include antiinflammatory action and cytoprotective properties. Therapeutic Effect: Modifies disease progression.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Undergoes rapid hydrolysis into active metabolite, monomethyl fumarate. Peak concentration: 2–2½ hrs. Protein binding: 27%–45%. Extensively metabolized by esterases. Primarily eliminated as exhaled carbon dioxide (60%). Half-life: 1 hr.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None known. HERBAL: None known. FOOD: None significant. LAB VALUES: May decrease lymphocytes. May increase serum ALT, AST; eosinophils; urine albumin.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules, Delayed-Release: 120 mg, 240 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give capsule whole; do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide. • May give without regard to meal. May give with food to decrease flushing reaction and GI effects. • Protect from light.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis
PO: ADULTS/ELDERLY: Initially, 120 mg twice daily for 7 days. Then, increase to 240 mg twice daily.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (40%): Flushing. Occasional (18%–5%): Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, pruritus, rash, erythema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Lymphopenia may increase risk for infection. Severe flushing may lead to noncompliance of therapy.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, CMP, urine pregnancy if applicable. Question any plans of breast-feeding. Assess hydration status (urine output, skin turgor). Question history of hepatic impairment, lymphopenia.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, LFT. Encourage PO intake. Offer antiemetics for nausea, vomiting. Question any episodes of noncompliance due to flushing, GI symptoms. Monitor for infectious process (fever, malaise, chills, body aches, cough).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Pts will most likely experience abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and flushing. Side effects may decrease over time. • Take with meals to decrease flushing reaction. • Swallow capsule whole; do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide. • Two dosage strengths will be provided for starting dose and maintenance dose. • Report any yellowing of skin or eyes, upper abdominal pain, bruising, dark-colored urine, fever, body aches, cough, dehydration.
dinoprostone
dye-noe-pros-tone
(Cervidil, Prepidil, Prostin E2)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() To be used only by personnel medically trained in dinoprostone-specific drug effects in a hospital setting.
To be used only by personnel medically trained in dinoprostone-specific drug effects in a hospital setting.
Do not confuse Cervidil or Prepidil with bepridil.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Prostaglandin. CLINICAL: Oxytocic, abortifacient.
USES
Vaginal suppository (Prostin E2): To induce abortion from wk 12 through wk 20 of pregnancy, to evacuate uterine contents in missed abortion or intrauterine fetal death up to 28 wks gestational age (as calculated from first day of last normal menstrual period), benign hydatidiform mole. Gel: (Prepidil) Promote cervical ripening in pregnant women at or near term with medical/obstetric need for labor induction. Vaginal insert: (Cervidil) Initiation and/or continuation of cervical ripening in pts at or near term with medical indication for induction of labor.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dinoprostone. Gel: Active cardiac, hepatic, pulmonary, renal disease; acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID); fetal malpresentation; grand multiparae with 6 or more previous term pregnancy cases with nonvertex presentation; history of cesarean section, major uterine surgery; history of difficult labor, traumatic delivery; hypersensitivity to other prostaglandins; placenta previa, unexplained vaginal bleeding during this pregnancy; pts for whom vaginal delivery is not indicated (vasa previa, active herpes genitalia); significant cephalopelvic disproportion. Vaginal Suppository: Active cardiac, hepatic, pulmonary, renal disease; acute PID. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, asthma, glaucoma, cardiovascular or pulmonary disease, epilepsy. Endocervical gel: With ruptured membrane. Vaginal gel: With ruptured membrane, nonvertex or nonsingleton pregnancy, previous uterine pregnancy. Suppository: History of hypotension/hypertension, anemia, jaundice, diabetes, compromised uteri, cervicitis, endocervical infections or acute vaginitis.
ACTION
Abortifacient: Stimulates uterine contractions. Labor Induction: Relaxes smooth muscle at the cervix.Therapeutic Effect: Stimulates myometrial contractions in gravid uterus.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Onset | Peak | Duration | |
| Uterine stimulation | 10 min (contractions begin) | 1–2 hrs (abortion time) | 2–6 hrs (contractions persist) |
Undergoes rapid enzymatic deactivation primarily in maternal lungs. Protein binding: 73%. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: Less than 5 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Suppository: Teratogenic, therefore abortion must be complete. Gel: Sustained uterine hyperstimulation may affect fetus (e.g., abnormal heart rate). Children/Elderly: Not used in these pt populations.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Oxytocics may cause uterine contractions, possibly resulting in uterine rupture, cervical laceration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May alter B/P, heart rate. May increase body temperature.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Endocervical Gel (Prepidil): 0.5 mg/3 g syringe. Vaginal Inserts (Cervidil): 10 mg. Vaginal Suppositories (Prostin E2): 20 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Gel
• Refrigerate. • Use caution in handling; prevent skin contact. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water following administration. • Bring to room temperature just before use (avoid forcing the warming process). • Assemble dosing apparatus as described in manufacturer’s insert. • Place pt in dorsal position with cervix visualized using a speculum. • Introduce gel into cervical canal just below level of internal os. • Have pt remain in supine position at least 15–30 min (minimizes leakage from cervical canal). • Wait 6–12h after gel administration before initiating oxytocin therapy.