Suppository, Vaginal Inserts
• Keep frozen (−4°F); bring to room temperature just before use. • Administer only in hospital setting with emergency equipment available. • Warm suppository to room temperature before removing foil wrapper. • Avoid skin contact (risk of absorption). • Insert high into vagina. • Pt should remain supine for 10 min after administration of suppository, 2 hrs after vaginal insert. • Wait at least 30 min after removing insert before initiating oxytocin therapy.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Abortifacient
Intravaginal: ADULTS (VAGINAL SUPPOSITORY): 20 mg (one suppository) high into vagina. May repeat at 3- to 5-hr intervals until abortion occurs. Do not administer for longer than 2 days.
Ripening of Unfavorable Cervix
Intracervical (Prepidil): ADULTS (ENDOCERVICAL GEL): Using catheter supplied, insert 0.5 mg into cervical canal. May repeat 0.5-mg dose q6h prn. Maximum: 1.5 mg (7.5 ml) for a 24-hr period.
Intracervical (Cervidil): ADULTS (VAGINAL INSERT): 10 mg transversely into posterior formix of the vagina (remove upon onset of active labor or 12 hrs after insertion).
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (66%–33%): Vomiting, diarrhea, nausea. Occasional (10%): Headache, chills/shivering, urticaria, bradycardia, increased uterine pain accompanying abortion, peripheral vasoconstriction. Rare: Flushing of skin, vulvar edema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may cause uterine contractions with spasm and tetanic contraction, leading to cervical laceration/perforation, uterine rupture/hemorrhage.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Offer emotional support. Suppository: Obtain orders for antiemetics, antidiarrheals, meperidine, other pain medication for abdominal cramps. Assess any uterine activity, vaginal bleeding. Gel: Assess Bishop score. Assess degree of effacement (determines size of shielded endocervical catheter).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Suppository: Check strength, duration, frequency of contractions. Monitor vital signs q15min until stable, then hourly until abortion complete. Check resting uterine tone. Administer medications for relief of GI effects if indicated or for abdominal cramps. Gel: Monitor uterine activity (onset of uterine contractions), fetal status (heart rate), character of cervix (dilation, effacement). Have pt remain recumbent 12 hrs after application with continuous electronic monitoring of fetal heart rate, uterine activity. Record maternal vital signs at least hourly in presence of uterine activity. Reassess Bishop score.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Suppository: Report promptly fever, chills, foul-smelling/increased vaginal discharge, uterine cramps, pain.
dinutuximab
din-ue-tux-i-mab
(Unituxin)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Life-threatening infusion-related reactions have occurred. Administer required prehydration and premedication, including antihistamines, prior to each infusion. Treatment causes severe neuropathic pain. Administer IV opioids prior to each infusion and for 2 hrs following completion of infusion. Severe peripheral sensory neuropathy occurred in pts with neuroblastoma. Severe motor neuropathy was observed. Discontinue therapy if severe unresponsive pain, severe sensory neuropathy, or moderate to severe peripheral motor neuropathy occurs.
Life-threatening infusion-related reactions have occurred. Administer required prehydration and premedication, including antihistamines, prior to each infusion. Treatment causes severe neuropathic pain. Administer IV opioids prior to each infusion and for 2 hrs following completion of infusion. Severe peripheral sensory neuropathy occurred in pts with neuroblastoma. Severe motor neuropathy was observed. Discontinue therapy if severe unresponsive pain, severe sensory neuropathy, or moderate to severe peripheral motor neuropathy occurs.
Do not confuse dinutuximab with brentuximab, cetuximab, rituximab, or siltuximab.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: GD2-binding monoclonal antibody. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Used in combination with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interleukin-2 (IL-2), and 13-cis-retinoic acid, for the treatment of pediatric pts with high-risk neuroblastoma who achieve at least a partial response to prior fine-line multiagent, multimodality therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: History of anaphylaxis to dinutuximab. Cautions: Active infection; baseline cytopenias; diabetes mellitus, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, hepatic/renal impairment, peripheral or generalized edema; intolerance of opioids, antipyretics, antihistamines; history of arrhythmias, hypotension, neuropathy, optic disorders.
ACTION
Binds to glycolipid GD2 expressed on neuroblastoma cells and on normal cells of neuroectodermal origin, including CNS and peripheral nerves. Induces cell lysis of GD2-expressing cells through antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Metabolism not specified. Protein binding: not specified. Elimination not specified. Half-life: 10 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Avoid pregnancy; may cause fetal harm, esp. in third trimester. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. However, human immunoglobulin G is present in human breast milk. Must either discontinue drug or discontinue breastfeeding. Females of reproductive potential must use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 2 mos following discontinuation. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Safety and efficacy not established.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None known (not studied). HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease Hgb, Hct, lymphocytes, neutrophils, platelets, RBCs; serum albumin, calcium, magnesium, phosphate, potassium, sodium. May increase serum ALT, AST, bilirubin, creatinine, glucose; urine protein.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 17.5 mg/5 ml (3.5 mg/ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Pretreatment Guidelines
IV Hydration • Administer bolus of 0.9% NaCl 10 ml/kg IV over 1 hr prior to initiation. Analgesics • Administer morphine sulfate 50 mcg/kg IV immediately prior to initiation and then continue as morphine sulfate drip at rate of 20–50 mcg/kg/hr during and for 2 hrs following completion of infusion. • Administer additional doses of morphine sulfate 25–50 mcg/kg IV once every 2 hrs as needed for pain, followed by an increase in morphine infusion rate, if clinically stable. • Consider use of fentanyl or hydromorphone if morphine sulfate not tolerated. • If pain is inadequately controlled with opioids, consider use of gabapentin or lidocaine in addition with IV morphine.
Antihistamines and Antipyretics • Administer an antihistamine such as diphenhydramine 0.5–1 mg/kg (maximum dose 50 mg) IV over 10–15 min, starting 20 min prior to initiation and as tolerated every 4–6 hrs during infusion. • Administer acetaminophen 10–15 mg/kg (maximum dose 650 mg) 20 minutes prior to each infusion and every 4–6 hrs as needed for fever/pain. • May administer ibuprofen 5–10 mg/kg every 6 hrs as needed for persistent fever/pain.
Preparation of Infusion • Visually inspect for particulate matter or discoloration. Do not use if solution is cloudy or contains particulate matter. • Withdraw required volume from vial and inject into 100 ml 0.9% NaCl. • Mix by gently inversion. Do not shake or agitate. • Discard unused portions of vial.
Rate of Administration • Initiate infusion rate at 0.875 mg/m2/hr for 30 min via dedicate IV line. May gradually increase rate to maximum rate of 1.75/m2/hr as tolerated. • Do not infuse as IV push or bolus.
Storage • Refrigerate vials. • Protect from light by storing in outer carton. • May refrigerate diluted solution up to 4 hrs. • Discard diluted solution 24 hr after preparation.
 IV INCOMPATABILITIES
IV INCOMPATABILITIES
Do not mix with other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Neuroblastoma
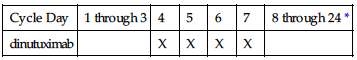
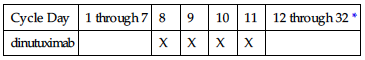
IV: PEDIATRIC: 17.5 mg/m2/day over 10–20 hrs for 4 consecutive days for maximum of 5 cycles (Tables 1 and 2).
TABLE 1
SCHEDULE OF DINUTUXIMAB ADMINISTRATION FOR CYCLES 1, 3, AND 5
| Cycle Day | 1 through 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 through 24 * |
| dinutuximab | | X | X | X | X | |
*Cycles 1, 3, and 5 are 24 days in duration.
TABLE 2
SCHEDULE OF DINUTUXIMAB ADMINISTRATION FOR CYCLES 2 AND 4
| Cycle Day | 1 through 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 through 32 * |
| dinutuximab | | X | X | X | X | |
*Cycles 2 and 4 are 32 days in duration.
Dose Modification
Infusion-Related Reactions
Mild to moderate adverse reactions such as transient rash, fever, rigors, or localized urticaria that respond promptly to symptomatic treatment: Onset of Reaction: Decrease infusion rate to 50% of the previous rate. After Resolution: Gradually increase infusion rate up to maximum rate 1.75 mg/m2/hr. Prolonged or severe adverse reactions such as mild bronchospasm without other symptoms, angioedema that does not affect the airway: Onset of Reaction: Immediately interrupt infusion. After Resolution: If symptoms resolve rapidly, restart infusion at 50% of the previous rate. First Recurrence: Discontinue treatment until the following day. If symptoms resolve and continued treatment is warranted, premedicate with hydrocortisone 1 mg/kg (maximum dose 50 mg) IV and administer dinutuximab infusion at a rate of 0.875 mg/m2/hr in an intensive care unit. Second Recurrence: Permanently discontinue.
Capillary Leak Syndrome
Moderate to severe, non–life-threatening capillary leak syndrome: Onset of Reaction: Interrupt infusion. After Resolution: Resume infusion rate at 50% of previous rate. Life-threatening capillary leak syndrome: Onset of Reaction: Discontinue for the current cycle. After Resolution: In subsequent cycles, administer at 50% of the previous rate. First Recurrence: Permanently discontinue.
Hypotension Requiring Medical Intervention
Onset of Reaction: Interrupt infusion. After Resolution: Resume infusion at 50% of the previous rate. If blood pressure remains stable for at least 2 hrs, increase infusion rate as tolerated up to maximum rate of 1.75 mg/m2/hr.
Severe Systemic Infection or Sepsis
Onset of Reaction: Discontinue treatment until resolution of infection, then proceed with subsequent cycles of therapy.
Neurologic Disorders of the Eye
Onset of Reaction: Discontinue infusion until resolution of disorder. After Resolution: Reduce dose by 50%. First Recurrence or if Accompanied by Visual Impairment: Permanently discontinue.
Adverse Reactions Requiring Permanent Discontinuation (using CTCAE Grading 1–5)
Grade 3 or 4 anaphylaxis, serum sickness; grade 3 pain unresponsive to maximum supportive measures; grade 4 sensory neuropathy or grade 3 sensory neuropathy that interferes with daily activities for more than 2 wks; grade 2 peripheral motor neuropathy, subtotal or total vision loss; grade 4 hyponatremia despite appropriate fluid management.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Not specified; use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (85%–24%): Pain (abdominal, back, bladder, bone, chest, neck, facial, gingival, musculoskeletal, oropharyngeal, extremity), arthralgia, myalgia, neuralgia, proctalgia, pyrexia, hypotension, vomiting, diarrhea, urticaria, hypoxia. Occasional (19%–10%): Tachycardia, edema, hypertension, peripheral neuropathy, weight gain, nausea.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Anemia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia are expected results of therapy. Severe bone marrow suppression occurred in up to 39% of pts. Serious infusion-related reactions, such as bronchospasm, dyspnea, facial and upper airway edema, hypotension, stridor, and urticaria, may require urgent interventions including bronchodilator therapy, blood pressure support, corticosteroids, infusion interruption, infusion rate reduction, or permanent treatment discontinuation. Severe infusion-related reactions were reported in 26% of pts. Infusion-related reactions usually occurred during or within 24 hrs of infusion completion. Other serious adverse effects may include: severe urticaria (13% of pts); anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest (1% or less of pts); pain despite pretreatment with analgesics including morphine sulfate infusion (85% of pts); grade 3 pain (51% of pts); grade 3 peripheral sensory/motor neuropathy (1% of pts); grade 3–5 capillary leak syndrome (23% of pts); grade 3 hypotension (16% of pts); grade 3 or 4 bacteremia requiring IV antibiotics or other urgent interventions (13% of pts); sepsis (18% of pts); neurologic disorders of the eye including blurred vision, photophobia, mydriasis, fixed or unequal pupils, optic nerve disorder, eyelid ptosis, papilledema (2%–13% of pts); grade 3 or 4 electrolyte abnormalities including hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia (37%–23% of pts); atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome resulting in anemia, electrolyte imbalance, hypertension, renal insufficiency. Bleeding events including GI/rectal/renal/respiratory/urinary tract/catheter site hemorrhage; disseminated intravascular coagulation, epistaxis, hematemesis, hematochezia, hematuria were reported. Immunogenicity (anti-dinutuximab antibodies) reported in 18% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, BMP, LFT; serum magnesium, ionized calcium, prealbumin, phosphate triglyceride level; capillary blood glucose, urinalysis, urine protein, urine pregnancy test, vital signs. Verify pts have adequate hematologic/hepatic/ophthalmic/respiratory/renal function; proper hydration status prior to start of each infusion. Ensure proper resuscitative equipment/medications are readily available. Obtain baseline visual acuity, pupillary response, neurologic status. Question history of anaphylaxis; intolerance of opioids, antipyretics, antihistamines. Screen for active infection.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Frequently monitor CBC, BMP, LFT, other serum electrolytes, vital signs. Monitor I&Os. Administer required prehydration and premedication with antihistamine, antipyretics, opioids prior to each infusion and during infusion as indicated. Diligently monitor for infusion-related reactions as listed in Adverse Effects/Toxic Reactions and institute medical support as needed. Monitor for bleeding events of any kind. Consider administration of naloxone if narcotic overdose is suspected. Routinely assess visual acuity, hydration status. Offer emotional support. Initiate fall precautions.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Serious infusion reactions including anaphylaxis, difficulty breathing, facial swelling, itching, rash, and wheezing may occur during or within 24 hrs of each infusion. • Immediately report any allergic reactions; bleeding of any kind; decreased urine output or dark urine; disorders of the eye including blurry vision, double vision, unequal pupil size, sensitivity to light, eyelid drooping; fever; palpitations; seizures (related to electrolyte imbalance); severe nerve pain or loss of motor function; signs of low blood pressure such as confusion, fainting, pallor; swelling of face, arms, or legs. • Moderate to severe generalized pain is an expected side effect. Medications for pain, fever, and mild allergic reactions will need to be provided before or during each infusion; report any intolerance to such medications. • Therapy is expected to lower blood counts/immune system and may increase risk of bleeding or infection. • Drink plenty of fluids. • Treatment may be harmful to fetuses. Contraception is recommended during therapy and for at least 2 mos after discontinuation in female of childbearing potential.
*diphenhydrAMINE
dye-fen-hye-dra-meen
(Allerdryl
 , Banophen, Benadryl, Benadryl Children’s Allergy, Diphen, Diphenhist, Dytan, Genahist, Nytol
, Banophen, Benadryl, Benadryl Children’s Allergy, Diphen, Diphenhist, Dytan, Genahist, Nytol
 )
)
Do not confuse Benadryl with benazepril, Bentyl, or Benylin, or diphenhydramine with desipramine, dicyclomine, or dimenhydrinate.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Advil PM: diphenhydramine/ibuprofen (NSAID): 38 mg/200 mg. With calamine, an astringent, and camphor, a counterirritant (Caladryl).
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Ethanolamine. CLINICAL: Antihistamine, anticholinergic, antipruritic, antitussive, antiemetic, antidyskinetic.
USES
Treatment of allergic reactions including nasal allergies and allergic dermatoses; parkinsonism, including drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms; prevention/treatment of nausea, vomiting, or vertigo due to motion sickness; antitussive; short-term management of insomnia; adjunct to epinephrine in treatment of anaphylaxis. Topical form used for relief of pruritus from insect bites, skin irritations.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to diphenhydrAMINE. Acute exacerbation of asthma, neonates or premature infants, breastfeeding. Cautions: Narrow-angle glaucoma, stenotic peptic ulcer, prostatic hypertrophy, pyloroduodenal/bladder neck obstruction, asthma, COPD, increased IOP, cardiovascular disease, hyperthyroidism, elderly.
ACTION
Competes with histamine for receptor site on effector cells in GI tract, blood vessels, respiratory tract. Therapeutic Effect: Produces anticholinergic, antipruritic, antitussive, antiemetic, antidyskinetic, sedative effects.
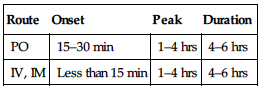
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 15–30 min | 1–4 hrs | 4–6 hrs |
| IV, IM | Less than 15 min | 1–4 hrs | 4–6 hrs |
Well absorbed after PO, parenteral administration. Protein binding: 98%–99%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 1–4 hrs. Adults: 7–12 hrs, elderly: 9–18 hrs, children: 4–7 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Detected in breast milk (may produce irritability in breastfed infants). Increased risk of seizures in neonates, premature infants if used during third trimester of pregnancy. May prohibit lactation. Children: Not recommended in newborns, premature infants (increased risk of paradoxical reaction, seizures). Elderly: Increased risk for dizziness, sedation, confusion, hypotension, hyperexcitability.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants may increase CNS depressant effects. Anticholinergics may increase anticholinergic effects. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May suppress wheal/flare reactions to antigen skin testing unless drug is discontinued 4 days before testing.
AVAILABILITY (OTC)
Capsules: 25 mg, 50 mg. Cream: 1%, 2%. Injection Solution: 50 mg/ml. Syrup: 12.5 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 25 mg, 50 mg. Tablets, Chewable: 12.5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
• May be given undiluted. • Give IV injection over at least 1 min. Maximum rate: 25 mg/min.
IM
• Give deep IM into large muscle mass.
PO
• Give with food to decrease GI distress. • Scored tablets may be crushed.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Allopurinol (Aloprim), cefepime (Maxipime), dexamethasone (Decadron), foscarnet (Foscavir).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Atropine, cisplatin (Platinol), cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), cytarabine (Ara-C), fentanyl, glycopyrrolate (Robinul), heparin, hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), hydroxyzine (Vistaril), lidocaine, metoclopramide (Reglan), ondansetron (Zofran), potassium chloride, promethazine (Phenergan), propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Allergic Reaction
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 25–50 mg q4–8h. Maximum: 300 mg/day. IM, IV: 10–50 mg/dose. Maximum: 400 mg/day. PO, IV, IM: CHILDREN: 5 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6–8h. Maximum: 300 mg/day.
Motion Sickness
Note: When used for prophylaxis, give 30 min before motion.
PO:(Prophylaxis/treatment): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 25–50 mg q6–8h. CHILDREN: 5 mg/kg/day in 3–4 divided doses. Maximum: 300 mg/day. IV/IM: (Treatment): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 10–50 mg/dose. Maximum: 400 mg/day. CHILDREN: 5 mg/kg/day in 4 divided doses. Maximum: 300 mg/day.
Antitussive
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 25 mg q4h. Maximum: 150 mg/day.
Nighttime Sleep Aid
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 25–50 mg at bedtime. CHILDREN 2–11 YRS: 1 mg/kg/dose. Maximum: 50 mg.
Pruritus
Topical: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: Apply 1% or 2% cream or spray 3–4 times/day. CHILDREN 2–11 YRS: Apply 1% cream or spray 3–4 times/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Drowsiness, dizziness, muscle weakness, hypotension, urinary retention, thickening of bronchial secretions, dry mouth, nose, throat, lips; in elderly: sedation, dizziness, hypotension. Occasional: Epigastric distress, flushing, visual/hearing disturbances, paresthesia, diaphoresis, chills.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hypersensitivity reactions (eczema, pruritus, rash, cardiac disturbances, photosensitivity) may occur. Overdose symptoms may vary from CNS depression (sedation, apnea, hypotension, cardiovascular collapse, death) to severe paradoxical reactions (hallucinations, tremors, seizures). Children, infants, neonates may experience paradoxical reactions (restlessness, insomnia, euphoria, nervousness, tremors). Overdosage in children may result in hallucinations, seizures, death.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
If pt is having acute allergic reaction, obtain history of recently ingested foods, drugs, environmental exposure, emotional stress. Monitor B/P rate; depth, rhythm, type of respiration; quality, rate of pulse. Assess lung sounds for rhonchi, wheezing, rales.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, esp. in elderly (increased risk of hypotension). Monitor children closely for paradoxical reaction.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Tolerance to antihistaminic effect generally does not occur; tolerance to sedative effect may occur. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Dry mouth, drowsiness, dizziness may be an expected response to drug. • Avoid alcohol.
diphenoxylate with atropine
dye-fen-ox-i-late at-roe-peen
(Lomotil)
Do not confuse Lomotil with Lamictal, Lamisil, or Lasix, or Lonox with Lanoxin, Loprox, or Lovenox.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Lomotil: diphenoxylate/atropine (anticholinergic, antispasmodic): 2.5 mg/0.025 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Meperidine derivative. CLINICAL: Antidiarrheal.
USES
Adjunctive treatment of acute, chronic diarrhea.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to diphenoxylate, atropine. Children younger than 2 yrs, obstructive jaundice, diarrhea associated with pseudomembranous colitis or enterotoxin-producing bacteria. Cautions: Children, acute ulcerative colitis, renal/hepatic impairment.
ACTION
Acts locally and centrally on gastric mucosa. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces excessive GI motility and GI propulsion.
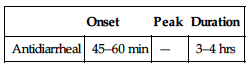
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Onset | Peak | Duration |
| Antidiarrheal | 45–60 min | — | 3–4 hrs |
Well absorbed from GI tract. Metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated in feces. Half-life: 2.5 hrs; metabolite: 12–24 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Not recommended (increased susceptibility to toxicity, including respiratory depression). Elderly: More susceptible to anticholinergic effects, confusion, respiratory depression.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants may increase CNS depressant effects. Anticholinergics may increase effects of atropine. MAOIs may precipitate hypertensive crisis. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum amylase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Liquid (Lomotil): 2.5 mg diphenoxylate/ 0.025 mg atropine/5 ml. Tablets (Lomotil): 2.5 mg diphenoxylate/0.025 mg atropine.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals. If GI irritation occurs, give with food. • Use liquid for children 2–12 yrs (use graduated dropper for administration of liquid medication).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Diarrhea
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 5 mg (2 tabs or 10 ml) 3–4 times/day. Maximum: 20 mg/day. Then reduce dose as needed. CHILDREN: 0.3–0.4 mg/kg/day in 4 divided doses (maximum: 10 mg/day); then reduce dose as needed.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Use with caution with severe renal/hepatic disease.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Drowsiness, light-headedness, dizziness, nausea. Occasional: Headache, dry mouth. Rare: Flushing, tachycardia, urinary retention, constipation, paradoxical reaction (marked by restlessness, agitation), blurred vision.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Dehydration may predispose pt to diphenoxylate toxicity. Paralytic ileus, toxic megacolon (constipation, decreased appetite, abdominal pain with nausea/vomiting) occur rarely. Severe anticholinergic reaction (severe lethargy, hypotonic reflexes, hyperthermia) may result in severe respiratory depression, coma.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Check baseline hydration status: skin turgor, mucous membranes for dryness, urinary status.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Encourage adequate fluid intake. Assess bowel sounds for peristalsis. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Record time of evacuation. Assess for abdominal disturbances. Discontinue medication if abdominal distention occurs.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol. • Report persistent fever, palpitations, diarrhea. • Report abdominal distention.
*DOBUTamine

doe-bue-ta-meen
(Dobutrex
 )
)
Do not confuse dobutamine with dopamine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Sympathomimetic. CLINICAL: Cardiac stimulant.
USES
Short-term management of cardiac decompensation.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dobutamine. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with outflow obstruction. Cautions: Atrial fibrillation, hypovolemia, post-MI, concurrent use of MAOIs, elderly.
ACTION
Direct-action inotropic agent acting primarily on beta1-adrenergic receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Enhances myocardial contractility, increases heart rate.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| IV | 1–2 min | 10 min | Length of infusion |
Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Sympathomimetics may increase effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum potassium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Infusion (Ready-to-Use): 1 mg/ml (250 ml), 2 mg/ml (250 ml), 4 mg/ml (250 ml). Injection Solution: 12.5-mg/ml vial.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Correct hypovolemia with volume expanders before dobutamine infusion. Those with atrial fibrillation should be digitalized before infusion. Administer by IV infusion only.
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Dilute vial in 0.9% NaCl or D5W to maximum concentration of 5,000 mcg/ml (5 mg/ml).
Rate of Administration • Use infusion pump to control flow rate. • Titrate dosage to individual response. • Infiltration causes local inflammatory changes. • Extravasation may cause dermal necrosis.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Pink discoloration of solution (due to oxidation) does not indicate significant loss of potency if used within recommended time period. • Further diluted solution for infusion is stable for 48 hrs at room temperature, 7 days if refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Acyclovir (Zovirax), alteplase (Activase), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), bumetanide (Bumex), cefepime (Maxipime), foscarnet (Foscavir), furosemide (Lasix), heparin, piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn), sodium bicarbonate.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, diltiazem (Cardizem), dopamine (Intropin), enalapril (Vasotec), epinephrine, famotidine (Pepcid), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), insulin (regular), lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, nitroglycerin, nitroprusside (Nipride), norepinephrine (Levophed), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Dosage determined by severity of decompensation.
Cardiac Decompensation
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: Initially, 0.5–2.5 mcg/kg/min. Maintenance: 2–20 mcg/kg/min titrated to desired response. May be infused at a rate of up to 40 mcg/kg/min to increase cardiac output. NEONATES: 2–20 mcg/kg/min titrated to desired response.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (greater than 5%): Increased heart rate, B/P. Occasional (5%–3%): Pain at injection site. Rare (3%–1%): Nausea, headache, anginal pain, shortness of breath, fever.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may produce marked increase in heart rate (30 beats/min or higher), marked increase in B/P (50 mm Hg or higher), anginal pain, premature ventricular contractions (PVCs).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Pt must be on continuous cardiac monitoring. Determine weight (for dosage calculation). Obtain initial B/P, heart rate, respirations. Correct hypovolemia before drug therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Continuously monitor for cardiac rate, arrhythmias. Maintain accurate I&O; measure urinary output frequently. Assess serum potassium, plasma dobutamine (therapeutic range: 40–190 ng/ml). Monitor B/P continuously (hypertension risk greater in pts with preexisting hypertension). Check cardiac output, pulmonary wedge pressure/central venous pressure (CVP) frequently. Immediately notify physician of decreased urinary output, cardiac arrhythmias, significant increase in B/P, heart rate, or less commonly, hypotension.
*DOCEtaxel

doe-se-tax-el
(Docefrez, Taxotere)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Avoid use with bilirubin more than upper limit of normal (ULN) or serum ALT, AST more than 1.5 times ULN in conjunction with serum alkaline phosphatase more than 2.5 times ULN. Severe hypersensitivity reaction (rash, hypotension, bronchospasm, anaphylaxis) may occur. Fluid retention syndrome (pleural effusions, ascites, edema, dyspnea at rest) has been reported. Pts with abnormal hepatic function, receiving higher doses, and pts with non–small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) and history of prior platinum treatment receiving docetaxel dose of 100 mg/m2 at higher risk for mortality. Avoid use with ANC more than 1,500/mm3.
Avoid use with bilirubin more than upper limit of normal (ULN) or serum ALT, AST more than 1.5 times ULN in conjunction with serum alkaline phosphatase more than 2.5 times ULN. Severe hypersensitivity reaction (rash, hypotension, bronchospasm, anaphylaxis) may occur. Fluid retention syndrome (pleural effusions, ascites, edema, dyspnea at rest) has been reported. Pts with abnormal hepatic function, receiving higher doses, and pts with non–small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) and history of prior platinum treatment receiving docetaxel dose of 100 mg/m2 at higher risk for mortality. Avoid use with ANC more than 1,500/mm3.
Do not confuse docetaxel with paclitaxel or Taxotere with Taxol.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antimitotic agent, taxoid. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of locally advanced or metastatic breast carcinoma after failure of prior chemotherapy. Treatment of metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer. Treatment of metastatic prostate cancer, head and neck cancer (with prednisone). Treatment of advanced gastric adenocarcinoma. OFF-LABEL: Bladder, esophageal, ovarian, small-cell lung carcinoma; soft tissue carcinoma, cervical cancer, Ewing’s sarcoma, osteosarcoma.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to docetaxel. History of severe hypersensitivity to drugs formulated with polysorbate 80, neutrophil count less than 1,500 cells/mm3. Cautions: Hepatic impairment, myelosuppression, concomitant CYP3A4 inhibitors/inducers, fluid retention, pulmonary disease, HF, active infection.
ACTION
Disrupts microtubular cell network, essential for cellular function. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits cellular mitosis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Protein binding: 94%. Extensively metabolized in liver. Excreted in feces (75%), urine (6%). Half-life: 11.1 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 16 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin, ketoconazole) may increase concentration/toxicity. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin) may decrease concentration/effects. Live virus vaccines may potentiate replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease concentration. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, ALT, AST. Reduces neutrophil, platelet count, Hgb, Hct.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 20 mg, 80 mg. Injection Solution: 10 mg/ml, 20 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution (Solution) • Withdraw dose and add to 250–500 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W in glass or polyolefin container to provide a final concentration of 0.3–0.74 mg/ml. (Powder) Add 1 ml diluent provided to 20-mg vial to provide a concentration of 20 mg/0.8 ml (4 ml to 80-mg vial to provide a concentration of 24 mg/ml). Shake well. Further dilute in 250 ml NaCl or D5W to a final concentration of 0.3–0.74 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • Administer as a 1-hr infusion. • Monitor closely for hypersensitivity reaction (flushing, localized skin reaction, bronchospasm [may occur within a few min after beginning infusion]).
Storage • Store vials between 36°F–77°F. • Protect from bright light. • If refrigerated, stand vial at room temperature for 5 min before administering (do not store in PVC bags). • Diluted solution should be used within 4 hrs (including infusion time).
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B (Fungizone), methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), nalbuphine (Nubain).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Bumetanide (Bumex), calcium gluconate, dexamethasone (Decadron), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), furosemide (Lasix), granisetron (Kytril), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, mannitol, morphine, ondansetron (Zofran), palonosetron (Aloxi), potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Pt should be premedicated with oral corticosteroids (e.g., dexamethasone 16 mg/day for 5 days beginning day 1 before docetaxel therapy); reduces severity of fluid retention, hypersensitivity reaction.
Breast Carcinoma
IV: ADULTS: 60–100 mg/m2 given over 1 hr q3wks as a single agent. Operable, node positive: 75 mg/m2 q3wks for 6 courses (in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide).
Non–Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma
IV: ADULTS: 75 mg/m2 q3wks (as monotherapy or in combination with cisplatin).
Prostate Cancer
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 75 mg/m2 q3wks with concurrent administration of prednisone.
Head/Neck Cancer
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 75 mg/m2 q3wks (in combination with cisplatin and fluorouracil) for 3–4 cycles, followed by radiation therapy.
Gastric Adenocarcinoma
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 75 mg/m2 q3wks (in combination with cisplatin and fluorouracil).
Dose Modification for Gastric or Head/Neck Cancer
| ALT, AST 2.5 to 5 times ULN and alkaline phosphatase less than or equal to 2.5 times ULN | 80% of dose |
| ALT, AST 1.5 to 5 times ULN and alkaline phosphatase 2.5 to 5 times ULN | 80% of dose |
| ALT, AST greater than 5 times ULN and/or alkaline phosphatase greater than 5 times ULN | Discontinue docetaxel |
Note: Toxicity includes febrile neutropenia, neutrophils less than 500/mm3 for longer than 1 wk, severe cutaneous reactions. Also, for NSCLC, platelet nadir less than 25,000/mm3, any CTCAE Grade 3 or 4 nonhematologic toxicity.
Breast Cancer
Reduce dose to 75 mg/mm3; if toxicity persists, reduce to 55 mg/mm3.
Breast Cancer Adjuvant
Administer when neutrophils are less than 1,500/mm3. If toxicity persists, or grade 3 or 4 stomatitis, reduce dose to 60 mg/mm3.
Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Monotherapy
Hold dose until toxicity resolves, then reduce dose to 55 mg/mm3. Discontinue if Grade 3 or 4 neuropathy occurs.
Combination Therapy
Reduce dose to 65 mg/mm3; may further reduce to 50 mg/mm3 if needed.
Prostate Cancer
Reduce dose to 60 mg/mm3; discontinue if toxicity persists.
Gastric or Head and Neck Cancer
Reduce dose to 60 mg/mm3; if neutropenic toxicity persists, further reduce to 45 mg/mm3. For Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia, reduce dose from 75 mg/mm3 to 60 mg/mm3; discontinue if toxicity persists.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Total bilirubin more than ULN, or ALT, AST more than 1.5 times ULN with Alkaline Phosphatase more than 2.5 times ULN: Use not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (80%–19%:) Alopecia, asthenia, hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., dermatitis), which is decreased in pts pretreated with oral corticosteroids; fluid retention, stomatitis, nausea, diarrhea, fever, nail changes, vomiting, myalgia. Occasional: Hypotension, edema, anorexia, headache, weight gain, infection (urinary tract, injection site, indwelling catheter tip), dizziness. Rare: Dry skin, sensory disorders (vision, speech, taste), arthralgia, weight loss, conjunctivitis, hematuria, proteinuria.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
In pts with normal hepatic function, neutropenia (ANC count less than 1,500 cells/mm3), leukopenia (WBC count less than 4,000 cells/mm3) occur in 96% of pts; anemia (hemoglobin level less than 11 g/dL) occurs in 90% of pts; thrombocytopenia (platelet count less than 100,000 cells/mm3) occurs in 8% of pts; infection occurs in 28% of pts. Neurosensory, neuromotor disturbances (distal paresthesia, weakness) occur in 54% and 13% of pts, respectively.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline ANC, CBC, serum chemistries. Offer emotional support to pt, family. Antiemetics may be effective in preventing, treating nausea/vomiting. Pt should be pretreated with corticosteroids to reduce fluid retention, hypersensitivity reaction.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Frequently monitor blood counts, particularly ANC count (less than 1,500 cells/mm3 requires discontinuation of therapy). Monitor LFT, serum uric acid levels. Observe for cutaneous reactions (rash with eruptions, mainly on hands, feet). Assess for extravascular fluid accumulation: rales in lungs, dependent edema, dyspnea at rest, pronounced abdominal distention (due to ascites).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Hair loss is reversible, but new hair growth may have different color or texture. • New hair growth resumes 2–3 mos after last therapy dose. • Maintain strict oral hygiene. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance). • Avoid those who have recently taken any live virus vaccine. • Report persistent nausea, diarrhea, respiratory difficulty, chest pain, fever, chills, unusual bleeding, bruising.
docusate
dok-ue-sate
(Apo-Docusate
 , Colace, Diocto, Novo-Docusate
, Colace, Diocto, Novo-Docusate
 , Selax
, Selax
 , Soflax
, Soflax
 )
)
Do not confuse Colace with Calan or Cozaar, or Surfak with Surbex.
FIXED COMBINATION(S)
Peri-Colace, Senokot-S: colace/senna (a laxative): 50 mg/8.6 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Bulk-producing laxative. CLINICAL: Stool softener.
USES
Prevention of straining during defecation; constipation associated with hard, dry stools. Relief of occasional constipation.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to docusate. Acute abdominal pain, concomitant use of mineral oil, intestinal obstruction, nausea, vomiting. Cautions: Do not use for longer than 1 wk.
ACTION
Decreases surface film tension by mixing liquid with bowel contents. Therapeutic Effect: Increases infiltration of liquid to form softer stool.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Minimal absorption from GI tract. Acts in small and large intestines. Results usually occur 1–2 days after first dose but may take 3–5 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Children: Not recommended in pts younger than 6 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (OTC)
Capsules: 50 mg, 100 mg, 250 mg. Liquid: 50 mg/5 ml. Syrup: 60 mg/15 ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• Drink 6–8 glasses of water a day (aids stool softening). • Give each dose with full glass of water, fruit juice. • Administer docusate liquid with milk, fruit juice, infant formula (masks bitter taste).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Stool Softener
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 50–500 mg/day once daily or in divided doses. CHILDREN 2–11 YRS: 50–150 mg/day once daily or in divided doses.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Mild GI cramping, throat irritation (with liquid preparation). Rare: Rash.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
None known.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Encourage adequate fluid intake. Assess bowel sounds for peristalsis. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Record time of evacuation.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Institute measures to promote defecation: increase fluid intake, exercise, high-fiber diet. • Do not use for longer than 1 wk.
dofetilide
doe-fet-i-lide
(Tikosyn)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Pt must be placed in a setting with continuous cardiac monitoring for minimum of 3 days and monitored by staff familiar with treatment of life-threatening arrhythmias.
Pt must be placed in a setting with continuous cardiac monitoring for minimum of 3 days and monitored by staff familiar with treatment of life-threatening arrhythmias.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Potassium channel blocker. CLINICAL: Antiarrhythmic: Class III.
USES
Maintenance of normal sinus rhythm (NSR) in pts with chronic atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter of longer than 1-wk duration who have been converted to NSR. Conversion of atrial fibrillation/flutter to NSR.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dofetilide. Congenital or acquired prolonged QT syndrome (do not use if baseline QT interval or QTc is greater than 440 msec), severe renal impairment, concurrent use of drugs that may prolong QT interval, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, concurrent use with verapamil, dolutegravir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, prochlorperazine, megestrol, cimetidine, hydrochlorothiazide, trimethoprim. Severe renal impairment (CrCl less than 20 ml/min). Cautions: Severe hepatic impairment, renal impairment, pts previously taking amiodarone, elderly. Concurrent use of other agents that prolong QT interval. Pts with sick sinus syndrome or second- or third-degree heart block unless functional pacemaker in place.
ACTION
Prolongs repolarization without affecting conduction velocity by blocking one or more time-dependent potassium currents. No effect on sodium channels, alpha-adrenergic, beta-adrenergic receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Terminates reentrant tachyarrhythmias, preventing reinduction.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following PO administration. 80% eliminated in urine as unchanged drug, 20% excreted as minimally active metabolites. Protein binding: 60%–70%. Half-life: 2–3 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Cimetidine, verapamil, itracanazole, ketoconazole, trimethoprim, hydrochlorothiazide may increase concentration, toxicity. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Ephedra may worsen arrhythmias. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 125 mcg, 250 mcg, 500 mcg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Do not break, crush, or open capsules.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ EKG interval measurements, esp. QTc interval, must be determined prior to first dose.
Antiarrhythmias
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 500 mcg twice daily. Modify dose in response to QTc interval.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| Greater than 60 ml/min | 500 mcg twice daily |
| 40–60 ml/min | 250 mcg twice daily |
| 20–39 ml/min | 125 mcg twice daily |
| Less than 20 ml/min | Contraindicated |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Rare (less than 2%): Headache, chest pain, dizziness, dyspnea, nausea, insomnia, back/abdominal pain, diarrhea, rash.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Angioedema, bradycardia, cerebral ischemia, facial paralysis, serious arrhythmias (ventricular, various forms of block) have been noted.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Prior to initiating treatment, QTc intervals must be determined. Do not use if heart rate less than 50 beats/min. Provide continuous EKG monitoring, calculation of creatinine clearance, equipment for resuscitation available for minimum of 3 days. Anticipate proarrhythmic events.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for conversion of cardiac dysrhythmias and absence of new arrhythmias. Constantly monitor EKG. Provide emotional support. Monitor renal function for electrolyte imbalance (prolonged or excessive diarrhea, sweating, vomiting, thirst).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Instruct pt on need for compliance and requirement for periodic monitoring of EKG and renal function. • Do not break, crush, or open capsule.
donepezil
doe-nep-e-zil
(Apo-Donepezil
 , Aricept, Aricept ODT)
, Aricept, Aricept ODT)
Do not confuse Aricept with Aciphex, Ascriptin, or Azilect.
FIXED COMBINATION(S)
Namzaric: donepezil/memantine (NMDA receptor antagonist): 10 mg/14 mg, 10 mg/28 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Cholinesterase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Cholinergic.
USES
Treatment of dementia of Alzheimer’s disease. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of behavioral syndromes in dementia, dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease, Lewy body dementia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: History of hypersensitivity to donepezil, other piperidine derivatives. Cautions: Asthma, COPD, bradycardia, bladder outflow obstruction, history of ulcer disease, those taking concurrent NSAIDs, supraventricular cardiac conduction disturbances (e.g., “sick sinus syndrome,” Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome), seizures.
ACTION
Inhibits enzyme acetylcholinesterase, increasing concentration of acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses, enhancing cholinergic function in CNS. Therapeutic Effect: Slows progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 96%. Extensively metabolized. Eliminated in urine, feces. Half-life: 70 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effect of anticholinergic medications. May increase synergistic effects of cholinergic agonists, neuromuscular blockers, succinylcholine. Ketoconazole may inhibit metabolism. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effects. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Ginkgo may increase adverse effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets (Aricept): 5 mg, 10 mg, 23 mg. Tablets (Orally Disintegrating [Aricept ODT]): 5 mg, 10 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May be given at bedtime without regard to meals. • Swallow tablets whole; do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide. • ODT: Allow to dissolve completely on tongue. • Follow dose with water.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Alzheimer’s Disease
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially 5 mg/day at bedtime. May increase at 4- to 6-wk intervals to 10 mg/day at bedtime. For moderate to severe Alzheimer’s, a dose of 23 mg once daily can be administered once pt has been taking 10 mg once daily for at least 3 mos.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (11%–8%): Nausea, diarrhea, headache, insomnia, nonspecific pain, dizziness. Occasional (6%–3%): Mild muscle cramps, fatigue, vomiting, anorexia, ecchymosis. Rare (3%–2%): Depression, abnormal dreams, weight loss, arthritis, drowsiness, syncope, frequent urination.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may result in cholinergic crisis (severe nausea, increased salivation, diaphoresis, bradycardia, hypotension, flushed skin, abdominal pain, respiratory depression, seizures, cardiorespiratory collapse). Increasing muscle weakness may occur, resulting in death if muscles of respiration become involved. Antidote: Atropine sulfate 1–2 mg IV with subsequent doses based on therapeutic response.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess cognitive function (e.g., memory, attention, reasoning). Obtain baseline vital signs. Assess history for peptic ulcer, urinary obstruction, asthma, COPD, seizure disorder, cardiac conduction disturbances.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor behavior, mood/cognitive function, activities of daily living. Monitor for cholinergic reaction (GI discomfort/cramping, feeling of facial warmth, excessive salivation/diaphoresis), lacrimation, pallor, urinary urgency, dizziness. Monitor for nausea, diarrhea, headache, insomnia.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, diaphoresis, increased salivary secretions, severe abdominal pain, dizziness. • May take without regard to food (best taken at bedtime). • Not a cure for Alzheimer’s disease but may slow progression of symptoms.
*DOPamine

dope-a-meen
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  If extravasation occurs, infiltrate area with phentolamine (5–10 ml 0.9% NaCl) as soon as possible, no later than 12 hrs after extravasation.
If extravasation occurs, infiltrate area with phentolamine (5–10 ml 0.9% NaCl) as soon as possible, no later than 12 hrs after extravasation.
Do not confuse dopamine with dobutamine or Dopram.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Sympathomimetic (adrenergic agonist). CLINICAL: Cardiac stimulant, vaso-pressor.
USES
Adjunct in treatment of shock (e.g., MI, trauma, renal failure, cardiac decompensation, open heart surgery, persisting after adequate fluid volume replacement). OFF-LABEL: Symptomatic bradycardia or heart block unresponsive to atropine or cardiac pacing.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dopamine, sulfites. Pheochromocytoma, ventricular fibrillation. Uncorrected tachyarrhythmias. Cautions: Ischemic heart disease, occlusive vascular disease, hypovolemia, recent use of MAOIs (within 2–3 weeks), ventricular arrhythmias, post-MI.
ACTION
Stimulates adrenergic and dopaminergic receptors. Effects are dose dependent. Lower dosage stimulates dopaminergic receptors, causing renal vasodilation. Higher doses stimulate both dopaminergic and beta1-adrenergic receptors, causing cardiac stimulation and renal vasodilation. Therapeutic Effect: Low dosage (1–3 mcg/kg/min): Increases renal blood flow, urinary flow, sodium excretion. Low to moderate dosage (4–10 mcg/kg/min): Increases myocardial contractility, stroke volume, cardiac output. High dosage (greater than 10 mcg/kg/min): Increases peripheral resistance, vasoconstriction, B/P.
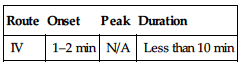
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| IV | 1–2 min | N/A | Less than 10 min |
Widely distributed. Does not cross blood-brain barrier. Metabolized in liver, kidneys, plasma. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Recommended close hemodynamic monitoring (gangrene due to extravasation reported). Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May have increased effects with vasopressors, vasoconstrictive agents. COMT inhibitors (e.g., entacapone, tolcapone) may increase level/effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 40 mg/ml, 80 mg/ml, 160 mg/ml. Injection (Premix with Dextrose): 0.8 mg/ml (250 ml, 500 ml), 1.6 mg/ml (250 ml, 500 ml), 3.2 mg/ml (250 ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Blood volume depletion must be corrected before administering dopamine (may be used concurrently with fluid replacement).
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Available prediluted in 250 or 500 ml D5W or dilute in 250–500 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W, to maximum concentration of 3,200 mcg/ml (3.2 mg/ml).
Rate of Administration • Administer into large vein (antecubital fossa, central line preferred) to prevent extravasation. • Use infusion pump to control flow rate. • Titrate drug to desired hemodynamic, renal response (optimum urinary flow determines dosage).
Storage • Do not use solutions darker than slightly yellow or discolored to yellow, brown, pink to purple (indicates decomposition of drug). • Stable for 24 hrs after dilution.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Acyclovir (Zovirax), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), cefepime (Maxipime), furosemide (Lasix), insulin, sodium bicarbonate.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), calcium chloride, dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), dobutamine (Dobutrex), enalapril (Vasotec), epinephrine, heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), labetalol (Trandate), levofloxacin (Levaquin), lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, nicardipine (Cardene), nitroglycerin, norepinephrine (Levophed), piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Effects of dopamine are dose dependent. Titrate to desired response.
Hemodynamic Support
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: Range: 2–20 mcg/kg/min. Titrate to desired response. May gradually increase by 5–10 mcg/kg/min increments. Maximum: 50 mcg/kg/min. NEONATES: 1–20 mcg/kg/min. Titrate to desired response.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Headache, arrhythmias, tachycardia, anginal pain, palpitations, vasoconstriction, hypotension, nausea, vomiting, dyspnea. Occasional: Piloerection (goose bumps), bradycardia, widening of QRS complex.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
High doses may produce ventricular arrhythmias. Pts with occlusive vascular disease are at high risk for further compromise of circulation to extremities, which may result in gangrene. Tissue necrosis with sloughing may occur with extravasation of IV solution.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Pt must be on continuous cardiac monitoring. Determine weight (for dosage calculation). Obtain initial B/P, heart rate, respirations. Assess potency of IV access.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Continuously monitor for cardiac arrhythmias. Measure urinary output frequently. If extravasation occurs, immediately infiltrate affected tissue with 10–15 ml 0.9% NaCl solution containing 5–10 mg phentolamine mesylate. Monitor B/P, heart rate, respirations q15min during administration (more often if indicated). Assess cardiac output, pulmonary wedge pressure, or central venous pressure (CVP) frequently. Assess peripheral circulation (palpate pulses, note color/temperature of extremities). Immediately notify physician of decreased urinary output, cardiac arrhythmias, significant changes in B/P, heart rate, or failure to respond to increase or decrease in infusion rate, decreased peripheral circulation (cold, pale, mottled extremities). Taper dosage before discontinuing (abrupt cessation of therapy may result in marked hypotension). Be alert to excessive vasoconstriction (decreased urine output, increased heart rate, arrhythmias, disproportionate increase in diastolic B/P, decrease in pulse pressure); slow or temporarily stop infusion, notify physician.
doripenem
dor-i-pen-em
(Doribax)
Do not confuse Doribax with Zovirax, or doripenem with ertapenem, imipenem, or meropenem.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Carbapenem. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections, complicated UTIs (including pyelonephritis) due to susceptible gram-positive, gram-negative (including Pseudomonas aeruginosa), and anaerobic bacteria. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of intravascular catheter-related bloodstream infection due to ESBL producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. Pneumonia, including ventilator-associated.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: History of serious hypersensitivity to doripenem or other carbapenems (meropenem, imipenem-cilastin, ertapenem). Anaphylactic reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics. Cautions: Hypersensitivity to penicillins, cephalosporins. Pts with renal impairment, CNS disorders (e.g., stroke, history of seizures).
ACTION
Inactivates penicillin-binding proteins, resulting in inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Produces bacterial cell death.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Penetrates into body fluids, tissues. Widely distributed. Protein binding: 8%. Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by dialysis. Half-life: 1 hr.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: Advanced renal insufficiency, end-stage renal insufficiency may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Probenecid reduces renal excretion of doripenem. May decrease valproic acid concentration (do not use concurrently). HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST. May decrease Hgb, Hct, platelet count; serum potassium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 250 mg, 500 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute 250-mg or 500-mg vial with 10 ml Sterile Water for Injection or 0.9% NaCl. • Shake well to dissolve. • Further dilute with 100 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W.
Rate of Administration • Give by intermittent IV infusion (piggyback). • Do not give IV push. • Infuse over 60 min.
Storage • Stable for 12 hrs at room temperature, 72 hrs if refrigerated when diluted in 0.9% NaCl; 4 hrs at room temperature, 24 hrs if refrigerated when diluted in D5W.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Diazepam (Valium), potassium phosphate, propofol (Diprivan).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone, bumetanide (Bumex), calcium gluconate, dexamethasone, diltiazem (Cardizem), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), furosemide (Lasix), heparin, hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), insulin, labetalol (Trandate), lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), metoclopramide (Reglan), milrinone, morphine, ondansetron (Zofran), pantoprazole (Protonix), potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Intra-Abdominal Infections
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 500 mg q8h for 5–14 days.
Urinary Tract Infections
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 500 mg q8h for 10–14 days.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| Greater than 50 ml/min | No adjustment |
| 30–50 ml/min | 250 mg q8h |
| 11–29 ml/min | 250 mg q12h |
| Hemodialysis | 250 mg q24h, if treating infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: 500 mg q12h on day 1, then 500 g q24h |
| Continuous renal replacement therapy | 250 mg q12h |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (10%–6%): Diarrhea, nausea, headache. Occasional (5%–2%): Altered mental status, insomnia, rash, abdominal pain, constipation, vomiting, edema, fever. Rare (less than 2%): Dizziness, cough, oral candidiasis, anxiety, tachycardia, phlebitis at IV site.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Antibiotic-associated colitis, other superinfections (abdominal cramps, severe watery diarrhea, fever) may occur. Anaphylactic reactions in pts receiving beta-lactams have occurred. Seizures may occur in those with CNS disorders (brain lesions, history of seizures) or with bacterial meningitis or severe impaired renal function.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question pt for history of allergies, particularly to beta-lactams, penicillins, cephalosporins. Inquire about history of seizures.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for signs of hypersensitivity reaction during first dose. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor for nausea, vomiting. Evaluate hydration status. Evaluate for inflammation at IV injection site. Assess skin for rash. Check mental status; be alert to tremors, possible seizures. Assess sleep pattern for evidence of insomnia.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report tremors, seizures, rash, diarrhea, or other new symptoms.
doxazosin
dox-a-zoe-sin
(Apo-Doxazosin
 , Cardura, Cardura XL)
, Cardura, Cardura XL)
Do not confuse Cardura with Cardene, Cordarone, Coumadin, K-Dur, or Ridaura, or doxazosin with doxapram, doxepin, or doxorubicin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Alpha-adrenergic blocker. CLINICAL: Anti-hypertensive.
USES
Cardura: Treatment of mild to moderate hypertension. Used alone or in combination with other antihypertensives. Treatment of urinary outflow obstruction and/or obstruction and irritation associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): Cardura XL: Treatment of urinary outflow obstruction and/or obstruction and irritation associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. OFF-LABEL: Pediatric hypertension. Facilitate distal ureteral stone expulsion. Erectile dysfunction in pts with BPH.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to doxazosin or other quinazolines (prazosin, terazosin). Cautions: Constipation, ileus, GI obstruction, hepatic impairment.
ACTION
Hypertension: Selectively blocks alphal-adrenergic receptors, decreasing peripheral vascular resistance. BPH: Inhibits postsynaptic alpha-adrenergic receptors in prostatic stromal and bladder neck tissues. Therapeutic Effect: Hypertension: Causes peripheral vasodilation, lowering B/P. BPH: Relaxes smooth muscle of bladder, prostate, reducing BPH symptoms.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO (antihypertensive) | 1–2 hrs | 2–6 hrs | 24 hrs |
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 98%–99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated in feces. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 19–22 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May be more sensitive to hypotensive effects.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: NSAIDs may decrease effect. Hypotension-producing medications (e.g., antihypertensives, diuretics) may increase effect. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., atanazavir, ketoconazole) may increase hypotensive effect. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Garlic may increase antihypertensive effect. Avoid saw palmetto (limited experience with this combination). FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 1 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg, 8 mg.
 Tablets, Extended-Release: 4 mg, 8 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release: 4 mg, 8 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide extended-release tablet. • Immediate-release tablets given morning or evening; extended-release tablets given with morning meal.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 0.5–1 mg once daily. May be increased to 2 mg once daily. Thereafter, may increase upward over several weeks to a maximum of 8 mg/day.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 1 mg/day. May be increased to 2 mg once daily. Thereafter, may increase q1–2wks. Maximum: 8 mg/day. (Extended-Release): Initially, 4 mg/day. May increase to 8 mg in 3–4 wks. Note: When switching to extended-release, omit evening dose prior to starting morning dose.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: Use caution. Severe Impairment: Avoid use.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (20%–10%): Dizziness, asthenia headache, edema. Occasional (9%–3%): Nausea, pharyngitis, rhinitis, pain in extremities, drowsiness. Rare (2%–1%): Palpitations, diarrhea, constipation, dyspnea, myalgia, altered vision, anxiety.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
First-dose syncope (hypotension with sudden loss of consciousness) may occur 30–90 min following initial dose of 2 mg or greater, too-rapid increase in dosage, addition of another antihypertensive agent to therapy. First-dose syncope may be preceded by tachycardia (pulse rate 120–160 beats/min).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Give first dose at bedtime. If initial dose is given during daytime, pt must remain recumbent for 3–4 hrs. Assess B/P, pulse immediately before each dose, and q15–30min until B/P is stabilized (be alert to fluctuations).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, I/O. Monitor pulse diligently (first-dose syncope may be preceded by tachycardia). Assess for edema, headache. Assist with ambulation if dizziness, light-headedness occurs.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Full therapeutic effect may not occur for 3–4 wks. • May cause syncope (fainting); go from lying to standing slowly. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established.
doxepin
dox-e-pin
(Apo-Doxepin
 , Novo-Doxepin
, Novo-Doxepin
 , Prudoxin, Silenor, Sinequan
, Prudoxin, Silenor, Sinequan
 , Zonalon)
, Zonalon)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Do not confuse doxepin with digoxin, doxapram, doxazosin, Doxidan, or doxycycline, or Sinequan with Seroquel, or Singulair.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Tricyclic. CLINICAL: Antidepressant, antianxiety, antineuralgic, antiulcer, antipruritic.
USES
Treatment of depression and/or anxiety. Silenor (only): Treatment of insomnia in pts with difficulty staying asleep. Topical: Treatment of pruritus associated with atopic dermatitis. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of neurogenic pain, treatment of anxiety.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to doxepin. Narrow-angle glaucoma, hypersensitivity to other tricyclic antidepressants, urinary retention, use of MAOIs within 14 days. Cautions: Cardiac/hepatic/renal disease, pts at risk for suicidal ideation, respiratory compromise, sleep apnea, history of bowel obstruction, increased IOP, glaucoma, history of seizures, history of urinary retention/obstruction, hyperthyroidism, prostatic hypertrophy, hiatal hernia, elderly.
ACTION
Increases synaptic concentrations of norepinephrine, serotonin. Therapeutic Effect: Produces antidepressant, anxiolytic effects.
PHARMACOKINETICS
PO: Rapidly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 80%–85%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 6–8 hrs. Topical: Absorbed through skin. Distributed to body tissues. Metabolized to active metabolite. Excreted in urine.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 12 yrs. Elderly: Increased risk of toxicity (lower dosages recommended).
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants may increase CNS, respiratory depression, hypotensive effects. Cimetidine may increase concentration, risk of toxicity. MAOIs may increase risk of seizures, hyperpyrexia, hypertensive crisis (discontinue at least 2 wks prior to starting doxepin). Phenothiazines may increase anticholinergic, sedative effects. HERBAL: Kava kava, SAMe, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase sedation, risk of serotonin syndrome. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May alter serum glucose, EKG readings. Therapeutic serum level: 110–250 ng/ml; toxic serum level: greater than 300 ng/ml.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg. Cream (Prudoxin, Zonalon): 5%. Oral Concentrate: 10 mg/ml. Tablets (Silenor): 3 mg, 6 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with food, milk if GI distress occurs. • Dilute concentrate in 4-oz glass of water, milk, orange, tomato, prune, pineapple juice. Incompatible with carbonated drinks. • Give larger portion of daily dose at bedtime. • Silenor: Give within 30 min of bedtime but not within 3 hrs of a meal.
Topical
• Apply thin film of cream on affected areas of skin. • Do not use for more than 8 days. • Do not use occlusive dressing.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Depression, Anxiety
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 25–50 mg/day at bedtime or in 2–3 divided doses. May increase gradually to usual dose of 150 mg–300 mg/day (single dose should not exceed 150 mg). ELDERLY: Initially, 10–25 mg at bedtime. May increase by 10–25 mg/day every 3–7 days.
Insomnia (Silenor only)
PO: ADULTS: 3–6 mg. ELDERLY: 3 mg (give within 30 min of bedtime). May increase to 6 mg once daily.
Pruritus Associated with Atopic Dermatitis
Topical: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Apply thin film 4 times/day at 3- to 4-hr intervals. Not recommended for more than 8 days.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use lower initial dose; adjust gradually. Silenor: Initially, 3 mg once daily.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: PO: Orthostatic hypotension, drowsiness, dry mouth, headache, increased appetite, weight gain, nausea, unusual fatigue, unpleasant taste. Topical: Edema, increased pruritus, eczema, burning, tingling, stinging at application site, altered taste, dizziness, drowsiness, dry skin, dry mouth, fatigue, headache, thirst. Occasional: PO: Blurred vision, confusion, constipation, hallucinations, difficult urination, eye pain, irregular heartbeat, fine muscle tremors, nervousness, impaired sexual function, diarrhea, diaphoresis, heartburn, insomnia. Silenor: Nausea, upper respiratory infection. Topical: Anxiety, skin irritation/cracking, nausea. Rare: PO: Allergic reaction, alopecia, tinnitus, breast enlargement. Topical: Fever, photosensitivity.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Abrupt or too-rapid withdrawal may result in headache, malaise, nausea, vomiting, vivid dreams. Overdose may produce confusion, severe drowsiness, agitation, tachycardia, arrhythmias, shortness of breath, vomiting.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess B/P, pulse, EKG (those with history of cardiovascular disease). Perform CBC, serum electrolyte tests before long-term therapy. Assess pt’s appearance, behavior, level of interest, mood, suicidal ideation, sleep pattern.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, pulse, weight. Perform CBC, serum electrolyte tests periodically to assess renal/hepatic function. Monitor mental status, suicidal ideation. Supervise suicidal-risk pt closely during early therapy (as depression lessens, energy level improves, increasing suicide potential). Assess appearance, behavior, speech pattern, level of interest, mood. Therapeutic serum level: 110–250 ng/ml; toxic serum level: greater than 300 ng/ml.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not discontinue abruptly. • Change positions slowly to avoid dizziness. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Do not cover affected area with occlusive dressing after applying cream. • May cause dry mouth. • Avoid alcohol, limit caffeine. • May increase appetite. • Avoid exposure to sunlight/artificial light source. • Therapeutic effect may be noted within 2–5 days, maximum effect within 2–3 wks. • Report worsening depression, suicidal ideation, unusual changes in behavior (esp. at initiation of therapy or with changes in dosage).
*DOXOrubicin

dox-o-rue-bi-sin
(Adriamycin, Caelyx
 , Doxil, Lipodox)
, Doxil, Lipodox)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  May cause concurrent or cumulative myocardial toxicity. Acute allergic or anaphylaxis-like infusion reaction may be life-threatening. Severe myelosuppresion may occur. Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. Secondary acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome have been reported. Potent vesicant.
May cause concurrent or cumulative myocardial toxicity. Acute allergic or anaphylaxis-like infusion reaction may be life-threatening. Severe myelosuppresion may occur. Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. Secondary acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome have been reported. Potent vesicant.
Do not confuse doxorubicin with dactinoycin, daunorubicin, doxazosin, epirubicin, idarubicin, or valrubicin, or Adriamycin with Aredia or idamycin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Anthracycline antibiotic. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Adriamycin: Treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), Hodgkin’s lymphoma, malignant lymphoma; breast, gastric, small-cell lung, ovarian, epithelial, thyroid, bladder carcinomas; neuroblastoma, Wilms tumor, osteosarcoma, soft tissue sarcoma. Doxil, Lipodox: Treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma, advanced ovarian cancer. Used with bortezomib to treat multiple myeloma in pts who have not previously received bortezomib and have received at least one previous treatment. OFF-LABEL: Adriamycin: Multiple myeloma, endometrial carcinoma, uterine sarcoma; head and neck cancer, liver, kidney cancer. Doxil: Metastatic breast cancer, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, advanced soft tissue sarcomas, recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer, advanced or metastatic uterine sarcoma.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to doxorubicin. Adriamycin: Severe hepatic impairment, severe myocardial insufficiency, recent MI (within 4–6 wks), severe arrhythmias. Previous or concomitant treatment with high accumulative doses of doxorubicin, daunorubicin, idarubicin, or other anthracyclines or anthracenediones; severe, persistent drug-induced myelosuppression or baseline ANC count less than 1,500/mm3. Doxil: Breastfeeding (Canada). Cautions: Hepatic impairment. Cardiomyopathy, preexisting myelosuppression, severe HF. Pts who received radiation therapy.
ACTION
Inhibits DNA, DNA-dependent RNA synthesis by binding with DNA strands. Liposomal encapsulation increases uptake by tumors, prolongs drug action, may decrease toxicity. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents cell division.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Protein binding: 74%–76%. Does not cross blood-brain barrier. Metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated by biliary system. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 20–48 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy, esp. first trimester. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children/Elderly: Cardiotoxicity may be more frequent in pts younger than 2 yrs or older than 70 yrs.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Cyclosporine may increase risk of hematologic toxicity. Bone marrow depressants may increase myelosuppression. Daunorubicin may increase risk of cardiotoxicity. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Avoid black cohosh, dong quai in estrogen-dependent tumors. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May cause EKG changes, increase serum uric acid. May reduce neutrophil, RBC counts.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 10 mg, 20 mg, 50 mg. Injection Solution (Adriamycin): 2 mg/ml (5-ml, 10-ml, 25-ml, 100-ml vial). Lipid Complex (Doxil, Lipodox): 2 mg/ml (10 ml, 25 ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Wear gloves. If powder or solution comes in contact with skin, wash thoroughly. Avoid small veins; swollen/edematous extremities; areas overlying joints, tendons. Doxil: Do not use with in-line filter or mix with any diluent except D5W. May be carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic. Handle with extreme care during preparation/administration.
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute vials of powder with 0.9% NaCl to provide concentration of 2 mg/ml. • Shake vial; allow contents to dissolve. • Withdraw appropriate volume of air from vial during reconstitution (avoids excessive pressure buildup). • May be further diluted with 50–1,000 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl and given as continuous infusion. Doxil: Dilute each dose in 250 ml D5W (doses greater than 90 mg in 500 ml D5W).
Rate of Administration (Adriamycin): • For IV push, administer into tubing of freely running IV infusion of D5W or 0.9% NaCl, preferably via butterfly needle over 3–5 min (avoids local erythematous streaking along vein and facial flushing). • Must test for flashback q30sec to be certain needle remains in vein during injection. IV piggyback over 15–60 min or continuous infusion. • Extravasation produces immediate pain, severe local tissue damage. Terminate administration immediately; withdraw as much medication as possible, obtain extravasation kit, follow protocol. Doxil: Give as infusion over 60 min. Do not use in-line filter.
Storage • Adriamycin powder: Store at room temperature. • Reconstituted vials stable for 7 days at room temperature, 15 days if refrigerated. Infusions stable for 48 hrs at room temperature. • Protect from prolonged exposure to sunlight; discard unused solution. • Adriamycin solution: Refrigerate vials. Solutions diluted in D5W or 0.9% NaCl stable for 48 hrs at room temperature. • Doxil: Refrigerate unopened vials. After solution is diluted, use within 24 hrs.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Doxorubicin: Allopurinol (Aloprim), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), cefepime (Maxipime), furosemide (Lasix), ganciclovir (Cytovene), heparin, piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn), propofol (Diprivan). Doxil: Do not mix with any other medications.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Dexamethasone (Decadron), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), granisetron (Kytril), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lorazepam (Ativan), morphine, ondansetron (Zofran).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Refer to individual protocols.
Usual Dosage
IV (Adriamycin): ADULTS: (Single-agent Therapy) 60–75 mg/m2 as a single dose every 21 days, 20 mg/m2 once wkly. (Combination Therapy): 40–75 mg/m2 q21–28 days. Because of risk of cardiotoxicity, do not exceed cumulative dose of 550 mg/m2 (400–450 mg/m2 for those previously treated with related compounds or irradiation of cardiac region). CHILDREN: 35–75 mg/m2 as a single dose q3wks or 20–30 mg/m2 wkly, or 60–90 mg/m2 as continuous infusion over 96 hrs q3–4wks.
Kaposi’s Sarcoma
IV (Doxil, Lipodox): ADULTS: 20 mg/m2 q3wks infused over 30 min.
Ovarian Cancer
IV (Doxil, Lipodox): ADULTS: 50 mg/m2 q4wks.
Multiple Myeloma
IV (Doxil, Lipodox): ADULTS: 30 mg/m2/dose on day 4 q3wks (in combination with bortezomib).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dose Modifications
Adriamycin
Neutropenic Fever/Infection: Reduce dose to 75%. ANC less than 1,000/mm3: Delay treatment until ANC 1,000/mm3 or more. Platelets less than 100,000/mm3: Delay treatment until platelets 100,000/mm3 or more.
Doxil
Adjustments for Hand-Foot Syndrome, Stomatitis, Hematologic Toxicities: Refer to manufacturer’s guidelines.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
ADRIAMYCIN
| Hepatic Function | Dosage |
| ALT, AST 2–3 times ULN | 75% of normal dose |
| ALT, AST greater than 3 times ULN or bilirubin 1.2–3 mg/dL | 50% of normal dose |
| Bilirubin 3.1–5 mg/dL | 25% of normal dose |
| Bilirubin greater than 5 mg/dL | Not recommended |
ULN = upper limit of normal.
DOXIL
| Hepatic Function | Dosage |
| Bilirubin 1.2–3 mg/dL | 50% of normal dose |
| Bilirubin greater than 3 mg/dL | 25% of normal dose |
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Complete alopecia (scalp, axillary, pubic hair), nausea, vomiting, stomatitis, esophagitis (esp. if drug is given on several successive days), reddish urine. Doxil: Nausea. Occasional: Anorexia, diarrhea; hyperpigmentation of nailbeds, phalangeal, dermal creases. Rare: Fever, chills, conjunctivitis, lacrimation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Myelosuppression manifested as hematologic toxicity (principally leukopenia and, to lesser extent, anemia, thrombocytopenia) generally occurs within 10–15 days, returns to normal levels by third wk. Cardiotoxicity (either acute, manifested as transient EKG abnormalities, or chronic, manifested as HF) may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain ANC, CBC, erythrocyte counts before and at frequent intervals during therapy. Obtain EKG before therapy, LFT before each dose. Antiemetics may be effective in preventing, treating nausea.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for stomatitis (burning or erythema of oral mucosa at inner margin of lips, difficulty swallowing). Observe IV injection site for infiltration, vein irritation. May lead to ulceration of mucous membranes within 2–3 days. Assess dermal creases, nailbeds for hyperpigmentation. Monitor hematologic status, renal/hepatic function studies, serum uric acid levels. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor for hematologic toxicity (fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site), symptoms of anemia (excessive fatigue, weakness).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Hair loss is reversible, but new hair growth may have different color, texture. New hair growth resumes 2–3 mos after last therapy dose. • Maintain strict oral hygiene. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance). • Avoid contact with those who have recently received live virus vaccine. • Promptly report fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site. • Report persistent nausea/vomiting. • Avoid alcohol (may cause GI irritation, a common side effect with liposomal doxorubicin).
doxycycline

dox-i-sye-kleen
(Actilate, Adoxa, Apo-Doxy
 , Avidoxy, Doryx, Doxy-100, Monodox, Oracea, Vibramycin, Vibra-Tabs
, Avidoxy, Doryx, Doxy-100, Monodox, Oracea, Vibramycin, Vibra-Tabs
 ).
).
Do not confuse doxycycline with dicyclomine or doxepin, Monodox with Maalox, Oracea with Orencia, Vibramycin with Vancomycin or Vibativ, or Vibra-Tabs with Vibativ.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Tetracycline. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of susceptible infections due to H. ducreyi, Pasteurella pestis, P. tularensis, Bacteroides spp., V. cholerae, Brucella spp., Rickettsiae, Y. pestis, Francisella tularensis, M. pneumoniae including brucellosis, chlamydia, cholera, granuloma inguinale, lymphogranuloma venereum, malaria prophylaxis, nongonococcal urethritis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), plague, psittacosis, relapsing fever, rickettsia infections, primary and secondary syphilis, tularemia. (Oracea): Treatment of inflammatory lesions in adults with rosacea. OFF-LABEL: Sclerosing agent for pleural effusion; vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE); alternative for MRSA, treatment of refractory periodontitis, juvenile periodontitis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to doxycycline, other tetracyclines. Cautions: History or predisposition to oral candidiasis (Oracea). Avoid use during pregnancy, during tooth development in children. Avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight.
ACTION
Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to ribosomes. Therapeutic Effect: Bacteriostatic.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 90%. Partially excreted in urine; partially eliminated in bile. Half-life: 15–24 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Children: May cause permanent discoloration of teeth, enamel hypoplasia. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antacids containing aluminum, calcium, magnesium; laxatives containing magnesium, oral iron preparations decrease absorption. Barbiturates, carbamazepine, phenytoin may decrease concentration. Cholestyramine, colestipol may decrease absorption. May decrease effects of oral contraceptives. HERBAL: Dong quai, St. John’s wort may increase photosensitization. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, amylase, bilirubin, ALT, AST. May alter CBC.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 40 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 100 mg. Oral Suspension: 25 mg/5 ml. Syrup: 50 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 20 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Do not administer IM or subcutaneous. Space doses evenly around clock.
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute each 100-mg vial with 10 ml Sterile Water for Injection for concentration of 10 mg/ml.
• Further dilute each 100 mg with at least 100 ml D5W, 0.9% NaCl, lactated Ringer’s.
Rate of Administration • Give by intermittent IV infusion (piggyback). • Infuse over 1–4 hrs.
Storage • After reconstitution, IV infusion (piggyback) is stable for 12 hrs at room temperature or 72 hrs if refrigerated. • Protect from direct sunlight. Discard if precipitate forms.
PO
• Store capsules, tablets at room temperature. • Oral suspension is stable for 2 wks at room temperature. • Give with full glass of fluid. • Instruct pt to sit up for 30 min after taking to reduce risk of esophageal irritation and ulceration. • Give without regard to food. Oracea should be given 1 hr before or 2 hrs after meals. • Avoid concurrent use of antacids, milk; separate by 2 hrs.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Allopurinol (Aloprim), heparin, piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Acyclovir (Zovirax), amiodarone (Cordarone), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), granisetron (Kytril), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), magnesium sulfate, meperidine (Demerol), morphine, ondansetron (Zofran), propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage
IV/PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 8 YRS; WEIGHING MORE THAN 45 KG: 100–200 mg/day in 1–2 divided doses. CHILDREN OLDER THAN 8 YRS; WEIGHING 45 KG OR LESS: 2–5 mg/kg/day (maximum: 200 mg/day) in 1–2 divided doses.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dysphagia, photosensitivity (may be severe). Occasional: Rash, urticaria.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Superinfection (esp. fungal), benign intracranial hypertension (headache, visual changes) may occur. Hepatotoxicity, fatty degeneration of liver, pancreatitis occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of allergies, esp. to tetracyclines, sulfites.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess skin for rash. Monitor LOC due to potential for increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Be alert for superinfection: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, anal/genital pruritus, oral mucosal changes (ulceration, pain, erythema). Monitor CBC, renal/hepatic function tests.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid unnecessary exposure to sunlight. • Do not take with antacids, iron products. • Complete full course of therapy. • After application of dental gel, avoid brushing teeth, flossing the treated areas for 7 days. • Report severe diarrhea.
dronabinol
droe-nab-i-nol
(Marinol, Syndros)
Do not confuse dronabinol with droperidol.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Controlled substance (Schedule III). CLINICAL: Antinausea, antiemetic, appetite stimulant.
USES
Prevention, treatment of nausea/vomiting due to cancer chemotherapy; appetite stimulant in AIDS. OFF-LABEL: Cancer-related anorexia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dronabinol, sesame oil, tetrahydrocannabinol products, marijuana. Cautions: History of psychiatric illness, schizophrenia, history of substance abuse, mania, depression, seizure disorder, hepatic impairment, elderly.
ACTION
Exact mechanism unknown. May inhibit endorphins in brain’s emetic center, suppress prostaglandins synthesis or effect on cannabinoid receptor in CNS. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits nausea/vomiting, stimulates appetite.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after PO administration, only 10%–20% reaches systemic circulation. Protein binding: 97%. Undergoes first-pass metabolism. Highly lipid soluble. Primarily excreted in feces. Half-life: 25–36 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children: Not recommended. Elderly: Monitor carefully during therapy.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS suppressants may increase CNS depression. Sympathomimetics, tricyclic antidepressants may increase risk of hypertension, tachycardia. Anticholinergics may increase drowsiness, tachycardia. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules (Gelatin [Marinol]): 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg. Oral Solution (Syndros): 5 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Store in cool environment. May refrigerate capsules. • May administer without regard to meals. Give before meals if used for appetite stimulant. Oral solution: Always use enclosed calibrated syringe. Take each dose with a full glass of water.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: (Marinol): Initially, 5 mg/m2 1–3 hrs before chemotherapy, then q2–4h after chemotherapy for total of 4–6 doses/day. May increase by 2.5 mg/m2 up to 15 mg/m2 per dose. (Syndros): Initially, 2.1–4.2 mg/m2 1–2 hrs prior to chemotherapy, then q2–4 hrs after chemotherapy for total of 4–6 doses/day. May increase in increments of 2.1 mg/m2. Maximum: 12.6 mg/m2/dose.
Appetite Stimulant
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Marinol): Initially, 2.5 mg twice daily (before lunch and dinner). Range: 2.5–20 mg/day. (Syndros): Initially, 2.1 mg twice daily. May gradually increase dose in 2.1-mg increments. Maximum: 8.4 mg twice daily.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (24%–3%): Euphoria, dizziness, paranoid reaction, drowsiness. Occasional (less than 3%–1%): Asthenia, ataxia, confusion, abnormal thinking, depersonalization. Rare (less than 1%): Diarrhea, depression, nightmares, speech difficulties, headache, anxiety, tinnitus, flushed skin.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Mild intoxication may produce increased sensory awareness (taste, smell, sound), altered time perception, reddened conjunctiva, dry mouth, tachycardia. Moderate intoxication may produce memory impairment, urinary retention. Severe intoxication may produce lethargy, decreased motor coordination, slurred speech, orthostatic hypotension.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess dehydration status if excessive vomiting occurs (skin turgor, mucous membranes, urinary output).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Supervise closely for serious mood, behavior responses, esp. in pts with history of psychiatric illness. Monitor B/P, heart rate.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Change positions slowly to avoid dizziness. • Relief from nausea/vomiting generally occurs within 15 min of drug administration. • Do not take any other medications, including OTC, without physician approval. • Avoid alcohol, barbiturates. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • For appetite stimulation, take before lunch and dinner.
dulaglutide
doo-la-gloo-tide
(Trulicity)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Contraindicated in pts with a personal/family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or in pts with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN2). Unknown if dulaglutide causes thyroid cell tumors in humans.
Contraindicated in pts with a personal/family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or in pts with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN2). Unknown if dulaglutide causes thyroid cell tumors in humans.
Do not confuse dulaglutide with albiglutide or liraglutide.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: GLP-1 receptor agonist. CLINICAL: Antidiabetic.
USES
Adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic controls in pts with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dulaglutide, other GLP-1 receptor agonists. Personal/family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2. Cautions: Pts with increased serum calcitonin, thyroid nodules, hx pancreatitis, renal/hepatic impairment. Not recommended in pts with severe GI disease, diabetic ketoacidosis, or type 1 diabetes.
ACTION
Activates GLP-1 receptors in pancreatic beta cells increasing intracellular cyclic AMP. Therapeutic Effect: Augments glucose-dependent insulin release, slows gastric emptying. Improves glycemic control.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed following subcutaneous administration. Degraded into amino acids by general protein catabolism. Peak plasma concentration: 24–72 hrs. Steady state reached in 2–4 wks. Elimination not specified. Half-life: 5 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Must either discontinue drug or discontinue breastfeeding. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Insulin, insulin secretagogues (e.g., glyburide) may increase risk of hypoglycemia. May reduce rate of absorption of oral medications. HERBAL: Garlic, other herbs with hypooglycemic activity may increase risk of hypoglycemia. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Expected to decrease serum glucose, Hgb A1c. May increase amylase, lipase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Prefilled Injector Pen or Syringe: 0.75 mg/0.5 ml, 1.5 mg/0.5 ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Subcutaneous
• Administer any time of day, without regard to meals, on same day each week. • May change administration day if last dose was given more than 3 days prior. If dose missed, administer within 3 days of missed dose. If more than 3 days have passed after missed dose, wait until next regularly scheduled dose to administer.
Administration • Subcutaneously insert needle into abdomen, thigh, or upper arm region and inject solution. • Do not reuse needle. • Rotate injection sites each week.
Storage • Refrigerate unused pens/syringes; do not freeze. • May store at room temperature for up to 14 days. • Protect from light.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
SQ: ADULTS/ELDERLY: 0.75 mg once wkly. May increase to 1.5 mg once wkly if glycemic response inadequate. Maximum: 1.5 mg wkly.
Dose Modification
Concomitant Use with Insulin Secretagogue (e.g., Sulfonylurea) or Insulin: Consider reduced dose of insulin secretagogue or insulin based on glycemic goal.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (12%–6%): Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain. Rare (4% or less): Decreased appetite, dyspepsia, fatigue, asthenia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
May increase risk of acute renal failure or worsening of chronic renal impairment (esp. with dehydration), severe gastroparesis, pancreatitis, thyroid C-cell tumors. May increase risk of hypoglycemia when used with other hypoglycemic agents or insulin. Dyspnea, pruritus, rash may indicate hypersensitivity reaction. May prolong PR interval by 2–3 msec or may rarely cause first-degree AV block, tachycardia. Immunogenicity (antidulaglutide antibody formation) reported. Some pts with antibody formation also tested positive for antibodies to GLP-1 and human albumin.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline fasting glucose level, Hgb A1c, BMP. Question history of medullary thyroid carcinoma, multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2, pancreatitis, renal impairment; first-degree AV block, PR interval prolongation. Receive full medication history and screen for use of other hypoglycemic agents or insulin. Assess pt’s understanding of diabetes management, routine home glucose monitoring, medication self-administration. Assess hydration status.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor capillary blood glucose levels, Hgb A1c; renal function test in pts with renal impairment reporting severe GI reactions including diarrhea, gastroparesis, vomiting. Screen for thyroid tumors (dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness, neck mass). If tumor suspected, consider endocrinologist consultation. Clinical significance of serum calcitonin level or thyroid ultrasound with GLP-1–associated thyroid tumors is debated/unknown. Assess for hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, hypersensitivity/allergic reaction. Screen for glucose-altering conditions: fever, stress, surgical procedures, trauma. Obtain dietary consult for nutritional education. Encourage PO intake.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Diabetes mellitus requires lifelong control. Diet and exercise are principal parts of treatment; do not skip or delay meals. Test blood sugar regularly. Monitor daily calorie intake. • When taking additional medications to lower blood sugar or when glucose demands are altered (fever, infection, stress trauma), have low blood sugar treatment available (glucagon, oral dextrose). • Report suspected pregnancy or plans for breastfeeding. • Therapy may increase risk of thyroid cancer; report lumps or swelling of the neck; hoarseness, shortness of breath, trouble swallowing. • Persistent, severe abdominal pain that radiates to the back (with or without vomiting) may indicate acute pancreatitis. • Rash, itching, hives may indicate allergic reaction.
*DULoxetine

du-lox-e-teen
(Cymbalta, Irenka)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Do not confuse duloxetine with fluoxetine or paroxetine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). CLINICAL: Antidepressant.
USES
Treatment of major depression. Management of pain associated with diabetic neuropathy, or chronic musculoskeletal pain. Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Cymbalta only: Treatment of fibromyalgia. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of stress incontinence.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to duloxetine. Uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma. Use of MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorder (concurrent or within 14 days of discontinuing MAOI). Initiation of MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorder within 5 days of discontinuing duloxetine. Initiation of duloxetine in pt receiving linezolid or IV methylene blue. Cautions: Renal impairment, history of alcoholism, chronic hepatic disease, history of mania, pts with suicidal ideation or behavior. Concurrent use with inhibitors of CYP1A2 or thioridazine, CNS depressants. Hypertension, controlled narrow-angle glaucoma, pts with impaired GI motility. Concomitant use of NSAIDs (may increase risk of bleeding), history of seizures. Use of medications that lower seizure threshold; elderly; pts at high risk for suicide.
ACTION
Appears to inhibit serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake at CNS neuronal presynaptic membranes; is a less potent inhibitor of dopamine reuptake. Therapeutic Effect: Produces antidepressant effect.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: greater than 90%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine (70%), feces (20%). Half-life: 8–17 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May produce neonatal adverse reactions (constant crying, feeding difficulty, hyperreflexia, irritability). Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Caution required when increasing dosage.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol increases risk of hepatic injury. CYP1A2 and CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g., fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, quinidine, quinolone antimicrobials) may increase plasma concentration. MAOIs may cause serotonin syndrome (autonomic hyperactivity, coma, diaphoresis, excitement, hyperthermia, rigidity). Aspirin, NSAIDs may increase risk of bleeding. May increase concentration, potential toxicity of tricyclic antidepressants. Serotonergic drugs (e.g., triptans, lithium, tramadol) may increase risk of serotonin syndrome. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. St. John’s wort may increase risk of serotonin syndrome. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum bilirubin, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Capsules (Delayed-Release, Enteric-Coated Pellets) (Cymbalta): 20 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg. (Irenka): 40 mg.
Capsules (Delayed-Release, Enteric-Coated Pellets) (Cymbalta): 20 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg. (Irenka): 40 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Allow at least 14 days to elapse between use of MAOIs and duloxetine.
PO
• Give without regard to meals. Give with food, milk if GI distress occurs. • Do not break, crush, cut delayed-release capsules. • Contents of capsule may be sprinkled on applesauce or mixed in apple juice and swallowed (without chewing) immediately.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Fibromyalgia
PO: ADULTS ELDERLY: Initially, 30 mg/day for 1 wk. Increase to 60 mg/day.
Major Depressive Disorder
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 40–60 mg/day in 1 or 2 divided doses. For doses greater than 60 mg/day, titrate in increments of 30 mg/day over 1 wk. Maximum: 120 mg/day.
Diabetic Neuropathy Pain
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 60 mg once daily. Maximum: 60 mg/day.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 30–60 mg once daily. May increase up to 120 mg/day in 30-mg increments wkly. CHILDREN 7–17 YRS: Initially, 30 mg once daily. After 2 wks, may increase to 60 mg once daily. May further increase in increments of 30 mg/day at wkly intervals. Maximum: 120 mg/day.
Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 30 mg once daily for 1 wk, then increase to 60 mg once daily. Maximum: 60 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Renal: Not recommended with CrCl less than 30 ml/min or ESRD. Hepatic: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (20%–11%): Nausea, dry mouth, constipation, insomnia. Occasional (9%–5%): Dizziness, fatigue, diarrhea, drowsiness, anorexia, diaphoresis, vomiting. Rare (4%–2%): Blurred vision, erectile dysfunction, delayed or failed ejaculation, anorgasmia, anxiety, decreased libido, hot flashes.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
May slightly increase heart rate. Colitis, dysphagia, gastritis, irritable bowel syndrome occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess appearance, behavior, speech pattern, level of interest, mood, sleep pattern, suicidal tendencies. Question pain level, intensity, location of pain.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
For pts on long-term therapy, serum chemistry profile to assess hepatic/renal function should be performed periodically. Supervise suicidal-risk pt closely during early therapy (as depression lessens, energy level improves, increasing suicide potential). Monitor B/P, mental status, anxiety, social functioning, serum glucose levels.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Therapeutic effect may be noted within 1–4 wks. • Do not abruptly discontinue medication. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Inform physician of intention of pregnancy or if pregnancy occurs. • Report anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, worsening of depression. • Avoid heavy alcohol intake (associated with severe hepatic injury).
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Life-threatening infusion-related reactions have occurred. Administer required prehydration and premedication, including antihistamines, prior to each infusion. Treatment causes severe neuropathic pain. Administer IV opioids prior to each infusion and for 2 hrs following completion of infusion. Severe peripheral sensory neuropathy occurred in pts with neuroblastoma. Severe motor neuropathy was observed. Discontinue therapy if severe unresponsive pain, severe sensory neuropathy, or moderate to severe peripheral motor neuropathy occurs.
Life-threatening infusion-related reactions have occurred. Administer required prehydration and premedication, including antihistamines, prior to each infusion. Treatment causes severe neuropathic pain. Administer IV opioids prior to each infusion and for 2 hrs following completion of infusion. Severe peripheral sensory neuropathy occurred in pts with neuroblastoma. Severe motor neuropathy was observed. Discontinue therapy if severe unresponsive pain, severe sensory neuropathy, or moderate to severe peripheral motor neuropathy occurs. LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS![]() IV
IV IV INCOMPATABILITIES
IV INCOMPATABILITIES