E
edoxaban
e-dox-a-ban
(Savaysa)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Avoid use in pts with creatinine clearance (CrCl) greater than 95 ml/min (increased risk of ischemic stroke). Premature discontinuation of oral anticoagulant in the absence of alternative anticoagulation may increase risk of ischemic events. If treatment is discontinued for any reason other than pathologic bleeding or completion of course of therapy, consider coverage with another anticoagulant as described in transition guideline. Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in pts who are receiving neuraxial anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture, which may result in long-term or permanent paralysis.
Avoid use in pts with creatinine clearance (CrCl) greater than 95 ml/min (increased risk of ischemic stroke). Premature discontinuation of oral anticoagulant in the absence of alternative anticoagulation may increase risk of ischemic events. If treatment is discontinued for any reason other than pathologic bleeding or completion of course of therapy, consider coverage with another anticoagulant as described in transition guideline. Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in pts who are receiving neuraxial anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture, which may result in long-term or permanent paralysis.
Do not confuse edoxaban with apixaban or rivaroxaban.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Factor Xa inhibitor. CLINICAL: Anticoagulant.
USES
To reduce risk of stroke and systemic embolism (SE) in pts with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF). Treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) following 5–10 days of initial therapy with a parenteral anticoagulant.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to edoxaban. Major active bleeding. Cautions: Elderly, pts at increased risk of bleeding (e.g., prior CVA, thrombocytopenia, severe uncontrolled hypertension; history of bleeding ulcers, upper or lower GI bleeding), recent surgery, renal/hepatic impairment. Avoid concomitant use with aspirin, heparin, low molecular weight heparin (LMWH), NSAIDs, P-gp Inducers (e.g., rifampin). Not recommended in pts with CrCl greater than 95 ml/min (increased risk of ischemic stroke); mechanical heart valves; moderate to severe mitral stenosis.
ACTION
Selectively blocks active site of factor Xa, a key factor in the intrinsic and extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation cascade. Inhibits platelet activation and fibrin clot formation. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits blood coagulation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed after PO administration. Peak plasma concentration: 1–2 hrs. Steady state reached within 3 days. Protein binding: 55%. Primarily eliminated in urine (50%), biliary/intestinal excretion (remaining %). Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 10–14 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if excreted in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May have increased risk of bleeding due to age-related renal impairment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelets (e.g., clopidogrel), NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen), fibrinolytic therapy (e.g., TPA) may increase concentration/effect; may increase risk of bleeding. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase AST, ALT. May prolong aPTT, PT/INR.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets: 15 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg.
Tablets: 15 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Do not administer within 2 hrs of removal of epidural or intrathecal catheters.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
DVT/PE
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 60 mg once daily following 5–10 days of initial therapy with a parenteral anticoagulant.
Dose Modification
Body weight less than or equal to 60 kg or concomitant use of certain P-gp inhibitors: 30 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
DVT/PE
CrCl 15–50 ml/min: 30 mg once daily. CrCl less than 15 ml/min: Not recommended.
NVAF
CrCl greater than 95 ml/min: Not recommended. CrCl 51–95 ml/min: No dose adjustment. CrCl 15–50 ml/min: 30 mg once daily. CrCl less than 15 ml/min: Not recommended.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment: Not recommended.
Discontinuation for Surgery or Other Interventions
Discontinue at least 24 hrs before invasive surgical procedures. May restart as soon as adequate hemostasis is achieved, noting that the time of onset of pharmacodynamic effect is 1–2 hrs.
Transition Guideline to Edoxaban
From warfarin or other vitamin K antagonists: Discontinue warfarin and start edoxaban when INR is less than or equal to 2.5. From oral anticoagulants other than warfarin or other vitamin K antagonists: Discontinue current oral anticoagulant and start edoxaban at the time of the next scheduled dose of the other oral anticoagulant. From LMWH: Discontinue LMWH and start edoxaban at the time of the next scheduled dose of LMWH. From low unfractionated heparin: Discontinue infusion and start edoxaban 4 hrs later.
Transition Guideline from Edoxaban to Other Anticoagulant
To Warfarin: Oral option: For pts taking edoxaban 60 mg, reduce to 30 mg and begin warfarin concomitantly. For pts taking edoxaban 30 mg, reduce dose to 15 mg and begin warfarin concomitantly. Once stable INR greater than or equal to 2, discontinue edoxaban and continue warfarin. Parenteral option: Discontinue edoxaban and administer parenteral anticoagulant and warfarin at the time of next scheduled edoxaban dose. Once stable INR greater than or equal to 2, discontinue parenteral anticoagulant and continue warfarin. To non–vitamin K-dependent oral anticoagulant or parenteral anticoagulant: Discontinue edoxaban and start other oral anticoagulant at the time of the next scheduled dose.
SIDE EFFECTS
Rare (4%): Rash.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hemorrhagic events including intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke, cutaneous/GI/GU/oral/pharyngeal/urethral/vaginal bleeding, epistaxis, epidural/spinal hematoma (esp. with epidural catheters, spinal trauma) were reported. Discontinuation in the absence of other adequate anticoagulants may increase the risk of ischemic events, stroke. May increase risk of epidural or spinal hematomas, which can lead to long-term or permanent paralysis. Protamine sulfate, vitamin K, tranexamic acid are not expected to reverse anticoagulant effect. Interstitial lung disease was reported in less than 1% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline renal function test, esp. creatinine clearance; PT/INR in pts transitioning on or off warfarin therapy. Do not initiate if CrCl greater than 95 ml/min. Question history of bleeding disorders, recent surgery, spinal procedures, intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding ulcers, open wounds, anemia, renal/hepatic impairment. Receive full medication history including herbal products.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor renal function test; occult urine/stool, urine output. Monitor for symptoms of hemorrhage: abdominal/back pain, headache, altered mental status, weakness, paresthesia, aphasia, vision changes, GI bleeding. Question for increase in menstrual bleeding/discharge. Assess peripheral pulses; skin for ecchymosis, petechiae. Assess urine output for hematuria.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not discontinue current blood thinning regimen or take any newly prescribed medication unless approved by physician who started anticoagulant therapy. • Suddenly stopping therapy may increase risk of stroke or blood clots. Refill prescriptions so next scheduled dose is not missed. • Immediately report bleeding of any kind. • Avoid alcohol, aspirin, NSAIDs. • Consult physician before surgery/dental work. • Use electric razor, soft toothbrush to prevent bleeding. • Report any numbness, muscular weakness, signs of stroke (confusion, headache, one-sided weakness, trouble speaking), bloody stool or urine, nosebleeds. • Monitor changes in urine output.
efavirenz
e-fav-ir-enz
(Sustiva)
FIXED COMBINATION(S)
Atripla: efavirenz/emtricitabine (an antiretroviral)/tenofovir (an antiretroviral): 600 mg/200 mg/300 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiretroviral.
USES
Treatment of HIV infection, in combination with at least two other appropriate antiretroviral agents, in adults and children 3 mos and older weighing at least 3.5 kg.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to efavirenz. Concurrent use with bepridil, ergot derivatives, midazolam, St. John’s wort, triazolam. Cautions: History of mental illness, seizures, suspected hepatitis B or C infection, history of substance abuse, hepatic impairment (class A). Avoid pregnancy.
ACTION
Binds to reverse transcriptase, blocking RNA and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity including HIV-1 replication. Therapeutic Effect: Interrupts HIV replication, slowing progression of HIV infection.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated in feces (16%–61%), urine (14%–34%). Half-life: 40–55 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 3 yrs; may have increased incidence of rash. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Ergot derivatives, midazolam, triazolam may cause serious or life-threatening reactions (cardiac arrhythmias, prolonged sedation, respiratory depression). Decreases plasma concentrations of amprenavir, atazanavir, boceprevir, telaprevir, indinavir, saquinavir. Increases plasma concentrations of ritonavir. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., phenobarbital, rifabutin, rifampin) decrease concentration/effects. May alter warfarin plasma concentration. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: High-fat meals may increase drug absorption. LAB VALUES: May produce false-positive urine test results for cannabinoid. May increase serum ALT, AST, GGT, amylase, glucose, triglycerides, cholesterol. May decrease neutrophils.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 50 mg, 200 mg.
![]() Tablets: 600 mg.
Tablets: 600 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with water at bedtime (decreases CNS adverse effects). • Avoid high-fat meals (may increase absorption) • Capsules may be opened and added to small amount of food/liquid. Administer within 30 min. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
HIV Infection
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN WEIGHING 40 KG OR MORE: 600 mg once daily at bedtime. CHILDREN WEIGHING 32.5 KG–LESS THAN 40 KG: 400 mg once daily. CHILDREN WEIGHING 25 KG–LESS THAN 32.5 KG: 350 mg once daily. CHILDREN WEIGHING 20 KG–LESS THAN 25 KG: 300 mg once daily. CHILDREN WEIGHING 15 KG–LESS THAN 20 KG: 250 mg once daily. CHILDREN WEIGHING 7.5 KG–LESS THAN 15 KG: 200 mg once daily. CHILDREN WEIGHING 5 KG–LESS THAN 7.5 KG: 150 mg once daily. CHILDREN WEIGHING 3.5 KG–LESS THAN 5 KG: 100 mg once daily.
Dosage: Concurrent Rifampin
PO: ONLY IF PT WEIGHS 50 KG OR GREATER: 800 mg once daily.
Dosage: Concurrent Voriconazole
PO: Reduce efavirenz to 300 mg once daily; increase voriconazole to 400 mg q12h.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: Use caution. Moderate to severe impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (52%): Mild to severe: Dizziness, vivid dreams, insomnia, confusion, impaired concentration, amnesia, agitation, depersonalization, hallucinations, euphoria. Occasional: Mild to moderate: Maculopapular rash (27%); nausea, fatigue, headache, diarrhea, fever, cough (less than 26%).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Serious adverse psychiatric experiences (aggressive reactions, agitation, delusions, emotional lability, mania, neurosis, paranoia, psychosis, suicide) have been reported. Grade 4 rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme occurs rarely. Hepatotoxicity with serum ALT, AST elevation greater than 5 times upper limit of normal reported in 5% of pts. May induce immune reconstitution syndrome (inflammatory response to dormant opportunistic infections or acceleration of autoimmune disorders).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Offer emotional support. Obtain baseline ALT, AST in pts with history of hepatitis B or C virus infection; serum cholesterol or triglycerides before initiating therapy and at intervals during therapy. Receive full medication history including herbal products (high risk of drug interaction).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for CNS, psychological symptoms: severe acute depression (including suicidal ideation or attempts), dizziness, impaired concentration, drowsiness, abnormal dreams, insomnia (begins during first or second day of therapy, generally resolves in 2–4 wks). Assess for evidence of rash (common side effect). Monitor LFT for abnormalities. Assess for headache, nausea, diarrhea.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid high-fat meals during therapy. • Report appearance of skin rash immediately. • CNS, psychological symptoms occur in more than half of pts (dizziness, impaired concentration, delusions, depression). • Take medication every day as prescribed. • Do not alter dose or discontinue medication without informing physician. • Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol. • Efavirenz is not a cure for HIV infection, nor does it reduce risk of transmission to others.
elbasvir/grazoprevir
el-bas-vir/graz-oh-pre-vir
(Zepatier)
Do not confuse elbasvir with daclatasvir, ombitasvir or grazoprevir with boceprevir or simeprevir.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: NS5A inhibitor/protease inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiviral.
USES
Treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus genotypes 1 or 4 infection in adults, with or without ribavirin.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to elbasvir or grazoprevir, decompensated hepatic cirrhosis, moderate or severe hepatic impairment; concomitant use of organic anion transporting polypeptides 1B1/3 (OATP1B1/3) inhibitors, strong CYP3A inducers. Concomitant use of atazanavir, carbamazepine, cyclosporine, darunavir, efavirenz, lopinavir, phenytoin, rifampin, saquinavir, St. John’s wort, tipranavir. Any contraindications or hypersensitivity to ribavirin (if used with treatment regimen). Cautions: HIV infection, mild hepatic impairment. Safety and efficacy not established in pts with hepatitis B virus coinfection, liver transplant recipients.
ACTION
Elbasvir inhibits hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A protein, which is essential for viral RNA replication and virion assembly. Grazoprevir inhibits HCV NS3/4A protease needed for processing HCV-encoded polyproteins, which is essential for viral replication. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits viral replication of hepatitis C virus.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: elbasvir (99.9%), grazoprevir (98.8%). Peak plasma concentration: 3 hrs. Steady state reached in approx. 6 days. Eliminated in feces (greater than 90%), urine (less than 1%). Half-life: elbasvir: 24 hrs; grazoprevir: 31 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Use caution in pregnancy. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. When used with ribavirin, breastfeeding and pregnancy are contraindicated during treatment and up to 6 mos after discontinuation. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: May have increased risk of hepatotoxicity.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anticonvulsants (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin), antimycobacterials (e.g., rifabutin, rifampin), efavirenz may significantly decrease concentration/effect; use contraindicated. Atazanavir, darunavir, lopinavir, tipranavir, cyclosporine may significantly increase risk of hepatotoxicity; use contraindicated. Moderate CYP3A inducers (e.g., etravirine, modafinil, nafcillin) may decrease concentration/effect. Elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir (disoproxil or alafenamide), ketoconazole may increase concentration/effect. May increase concentration/effect of atorvastatin, fluvastatin, hydrocodone, lovastatin, nimodipine, rosuvastatin, simvastatin, tacrolimus. Acetaminophen may increase risk of hepatotoxicity. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effect; use contraindicated. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase grazoprevir concentration/effect. LAB VALUES: May decrease Hgb. May increase serum ALT, bilirubin.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Fixed-Dose Combination Tablets: elbasvir 50 mg/grazoprevir 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: NS5A resistance testing recommended in HCV genotype 1a infected pts prior to initiating treatment with Zepatier.
Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1 tablet once daily (with or without ribavirin).
Treatment Regimen and Duration
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Genotype 1a: Treatment-naïve or peginterferon alfa (PegIFN)/ribavirin (RBV)–experienced without baseline NS5A polymorphisms: 1 tablet once daily for 12 wks. Genotype 1a: Treatment-naïve or PegIFN/RBV–experienced with baseline NS5A polymorphisms: 1 tablet once daily with ribavirin for 16 wks. Genotype 1b: Treatment-naïve or PegIFV/RBV–experienced: 1 tablet once daily for 12 wks. Genotype 1a or 1b: PegIFV/RBV/protease inhibitor–experienced: 1 tablet once daily with ribavirin for 12 wks. Genotype 4: Treatment-naïve: 1 tablet once daily for 12 wks. Genotype 4: PegIFN/RBV–experienced: 1 tablet once daily with ribavirin for 16 wks.
Treatment-Induced Hepatotoxicity
Consider discontinuation in pts with persistent serum ALT elevation greater than 10 times upper limit of normal (ULN). Permanently discontinue if serum ALT elevation is accompanied with elevated alkaline phosphatase, conjugated bilirubin, prolonged INR, or signs of acute hepatic inflammation.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment: Contraindicated.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (11%–3%): Fatigue, headache, diarrhea, nausea, insomnia, dyspnea, rash, pruritus, irritability. Rare (2%): Abdominal pain, arthralgia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Serum ALT elevation up to 5 times ULN reported in 1% of pts. Serum bilirubin elevation greater than 2.5 times ULN occurred in 6% of pts. Serum ALT elevation occurred more frequently in the elderly, female pts, and pts of Asian ancestry.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC, LFT, HCV-RNA level; pregnancy test in female pts of reproductive potential. Confirm hepatitis C genotype. In pts with HCV genotype 1a, recommend testing for the presence of NS5A resistance-associated polymorphisms prior to initiation. Receive full medication history including herbal products; screen for contraindications. Question history of chronic anemia, hepatitis B virus infection, HIV infection, liver transplantation.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Obtain LFT at wk 8, then as clinically indicated. For pts receiving 16 wks of therapy, obtain additional LFT at wk 12. Monitor CBC periodically; HCV-RNA levels at wks 4, 8, 12, 16 and as clinically indicated. Monitor for hepatotoxicity. Assess for anemia-related dizziness, exertional dyspnea, fatigue, weakness, syncope. Encourage nutritional intake. Assess for decreased appetite, weight loss. Obtain monthly pregnancy tests in females of reproductive potential if treated with ribavirin.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Blood levels will be drawn routinely. • Treatment may be used in combination with ribavirin (inform pt of side effects/toxic reactions). If therapy includes ribavirin, female pts of reproductive potential should avoid pregnancy during treatment and up to 6 mos after last dose. • Do not take newly prescribed medication unless approved by the doctor who originally started treatment. • Do not take herbal products, esp. St. John’s wort. • Avoid alcohol, grapefruit products. • Report signs of treatment-induced liver injury such as abdominal pain, clay-colored stool, dark amber urine, decreased appetite, fatigue, weakness, yellowing of the skin or eyes. • Maintain proper nutritional intake.
eletriptan
el-e-trip-tan
(Relpax)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Serotonin receptor agonist. CLINICAL: Antimigraine.
USES
Treatment of acute migraine headache with or without aura.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to eletriptan. Arrhythmias associated with conduction disorders, cerebrovascular syndrome including strokes and transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), coronary artery disease, hemiplegic or basilar migraine, ischemic heart disease, peripheral vascular disease including ischemic bowel disease, severe hepatic impairment, uncontrolled hypertension; use within 24 hrs of treatment with another 5-HT1 agonist, an ergotamine-containing or ergot-type medication such as dihydroergotamine (DHE) or methysergide. Recent use (within 72 hrs) of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir). Cautions: Mild to moderate renal/hepatic impairment, controlled hypertension, history of CVA.
ACTION
Binds selectively to serotonin receptors, producing vasoconstrictive effect on cranial blood vessels. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves migraine headache.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after PO administration. Metabolized by liver. Eliminated in urine. Half-life: 4.4 hrs (increased in hepatic impairment, elderly [older than 65 yrs]).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May decrease possibility of ovulation. Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: Increased risk of hypertension in those older than 65 yrs.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir) may decrease metabolism. Ergotamine-containing medications may produce vasospastic reaction. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets: 20 mg, 40 mg.
Tablets: 20 mg, 40 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May take without regard to food. Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide film-coated tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Acute Migraine Headache
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20–40 mg. Maximum: 40 mg. If headache improves but then returns, dose may be repeated after 2 hrs. Maximum: 80 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Not recommended in severe hepatic impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (6%–5%): Dizziness, drowsiness, asthenia, nausea. Rare (3%–2%): Paresthesia, headache, dry mouth, warm or hot sensation, dyspepsia, dysphagia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Cardiac reactions (ischemia, coronary artery vasospasm, MI), noncardiac vasospasm-related reactions (hemorrhage, CVA) occur rarely, particularly in pts with hypertension, obesity, diabetes, strong family history of coronary artery disease; smokers; males older than 40 yrs; postmenopausal women.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question pt regarding onset, location, duration of migraine, possible precipitating symptoms. Obtain baseline B/P for evidence of uncontrolled hypertension (contraindication).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for relief of migraine headache, potential for photophobia, phonophobia (sound sensitivity), nausea, vomiting.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take a single dose as soon as symptoms of an actual migraine attack appear. • Medication is intended to relieve migraine headaches, not to prevent or reduce number of attacks. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Immediately report palpitations, pain/tightness in chest/throat, sudden or severe abdominal pain, pain/weakness of extremities.
elotuzumab
el-oh-tooz-ue-mab
(Empliciti)
Do not confuse elotuzumab with alemtuzumab, eculizumab, evolocumab, pertuzumab, gemtuzumab, trastuzumab.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Monoclonal antibody. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of multiple myeloma (in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone) in pts who have received one to three prior therapies.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to elotuzumab. Cautions: Diabetes, baseline cytopenias, hypertension; history of chronic opportunistic infections (esp. viral infections, fungal infections), conditions predisposing to infection (e.g., diabetes, kidney failure, open wounds). Concomitant use of medications known to cause bradycardia (e.g., antiarrhythmics, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers). Concomitant use of live vaccines not recommended during treatment and up to 3 mos after discontinuation. Avoid use during severe active infection.
ACTION
Binds to and specifically targets signaling lymphocytic activation molecule family member 7 (SLAMF7), a protein that is expressed on most myeloma and natural killer cells. Directly activates natural killer cells and facilitates cellular death. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Metabolism not specified. Elimination not specified. Half-life: Not specified; 97% of steady-state concentration is expected to be eliminated within 82 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Avoid pregnancy; may cause fetal harm/malformations when used with lenalidomide. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. However, immunoglobulin G (IgG) is present in breast milk. Breastfeeding contraindicated when used with concomitant lenalidomide treatment. Men: Lenalidomide is present in semen. Recommend use of barrier methods during sexual activity. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None known (not studied). HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May be detected on both serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation assays used to monitor multiple myeloma endogenous M protein. May affect the determination of complete response and disease progression of some pts with IgG kappa myeloma protein. Expected to decrease lymphocytes, leukocytes, platelets. May decrease serum albumin, bicarbonate, calcium. May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, glucose, potassium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 300 mg, 400 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Calculate the dose and number of vials required based on weight in kg. • Reconstitute the 300-mg vial with 13 ml of Sterile Water for Injection or the 400-mg vial with 17 ml of Sterile Water for Injection using an 18-g or lower (e.g., 17, 16, or 15) needle. • Gently roll vial upright to mix. To dissolve any powder left on top of vial or stopper, gently invert vial several times. • Do not shake or agitate. • The powder should dissolve in less than 10 mins. • After dissolution, allow vials to stand for 5–10 mins. • Visually inspect solution for particulate matter of discoloration. Solution should appear clear, colorless to slightly yellow. Discard if solution is cloudy or discolored or if foreign particles are observed. Each vial contains an overfill volume to allow for a specific withdraw of 12 ml (300-mg vial) or 16 ml (400-mg vial). • Final concentration of withdrawn volume (without overfill) will equal 25 mg/ml. • Dilute in 230 ml of 0.9% NaCl or 5% Dextrose injection in polyvinyl chloride or polyolefin infusion bag. • Mix by gentle inversion; do not shake or agitate. • The volume may be adjusted in order to not exceed 5 ml/kg of pt weight at any given dose.
Infusion Guidelines • Prior to administration, premedicate with dexamethasone, acetaminophen, antihistamine (H1 blocker, plus H2 blocker) approx. 45–90 mins before each infusion (see manufacturer guidelines). • Use an inline, sterile, nonpyrogenic, low-protein-binding filter (0.2–1.2 mm). • Infuse via dedicated line using an infusion pump.
Rate of Administration • First Infusion (Cycle 1, Dose 1): Infuse at 0.5 ml/min for the first 30 mins. If no infusion reactions occur, may increase to 1 ml/min for next 30 mins. If tolerated, may increase to 2 ml/min. Maximum rate: 2 ml/min. • Second Infusion (Cycle 1, Dose 2): Initiate at 1 ml/min for first 30 mins if no infusion reactions occurred during first infusion. If tolerated, may increase to 2 ml/min until infusion completed. Maximum rate: 2 ml/min. • Subsequent Infusions (Cycle 1, Dose 3 and 4, All Subsequent Infusions): Initiate at 2 ml/min until completion if no infusion reactions occurred during prior infusion. Maximum rate: 2 ml/min. In pts who have received four cycles of treatment, infusion rate may be increased to maximum rate of 5 ml/min.
Storage • Refrigerate intact vials until time of use. • Do not freeze or shake. • Refrigerate diluted solution up to 24 hrs • May store at room temperature up to 8 hrs (of the total 24 hrs). • Diluted solution must be administered within 24 hrs of reconstitution. • Protect from light.
 IV INCOMPATABILITIES
IV INCOMPATABILITIES
Do not mix with other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Multiple Myeloma
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Cycles 1 and 2: 10 mg/kg once wkly on days 1, 8, 15, 22 of 28-day cycle (in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone).
Cycles 3 and beyond: 10 mg/kg once q2wks on days 1 and 15 of 28-day cycle (in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone). Continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dose Modification
Infusion Reactions
Grade 2 or higher reaction: Interrupt infusion until symptoms improve. Once resolved to Grade 1 or 0, resume infusion at 0.5 ml/min. If tolerated, increase in increments of 0.5 ml/min q30mins back to previous rate. May further increase rate as indicated if no reaction recurs. If infusion reaction recurs, stop infusion and do not restart for that day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Not specified; use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (61%–20%): Fatigue, diarrhea, pyrexia, constipation, cough, peripheral neuropathy, decreased appetite. Occasional (16%–10%): Extremity pain, headache, vomiting, decreased weight, oropharyngeal pain, hypoesthesia, mood change, night sweats.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
All cases were reported in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone. Infusion reactions reported in 10% of pts. Most infusion reactions were Grade 3 and lower. Lymphopenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia are expected responses to therapy. Infections were reported in 81% of pts. Grade 3 or 4 infections occurred in 28% of pts. Nasopharyngitis (25% of pts), upper respiratory tract infection (23% of pts), opportunistic infection (22% of pts), herpes zoster (14% of pts), fungal infection (10% of pts), influenza; second primary malignancies, skin malignancies, solid tumors, malignant neoplasms; tachycardia, bradycardia, systolic or diastolic hypertension, hypotension; pulmonary embolism may occur. Hepatotoxicity with elevation of serum alkaline phosphatase greater than 2 times upper limit of normal (ULN), serum ALT/AST greater than 3 times ULN, total bilirubin greater than 2 times ULN reported in 3% of pts. Other adverse effects may include cataracts (12% of pts), hyperglycemia (89% of pts), hypersensitivity reaction (greater than 5% of pts). Immunogenicity (auto-elotuzumab antibodies) occurred in 19% of pts. Thrombocytopenia may increase risk of bleeding.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC, BMP, LFT; serum ionized calcium; capillary blood glucose, vital signs; pregnancy test in female pts of reproductive potential. Obtain baseline EKG in pts concurrently using of medications known to cause bradycardia. Question history of chronic opportunistic infections, diabetes, hepatic impairment, pulmonary embolism; prior infusion or hypersensitivity reactions. Screen for medications known to cause bradycardia, hyperglycemia. Screen for active infection. Offer emotional support.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Obtain CBC, BMP, LFT, ionized calcium periodically. Administer in an environment equipped to monitor for and manage infusion reactions. If infusion reaction of any grade/severity occurs, immediately interrupt infusion and manage symptoms. Accurately record characteristics of infusion reactions (severity, type, time of onset). Infusion reactions may affect future infusion rates. Monitor HR, BP q30mins during infusion and for at least 2 hrs after completion in pts with prior hemodynamic reactions. Cough, dyspnea, hypoxia, tachycardia may indicate pulmonary embolism. Monitor for bradycardia, cataracts, hyperglycemia, hyperkalemia, hypersensitivity reaction, hepatotoxicity, neuropathy, tachycardia. Assess for new primary malignancies (solid tumors, skin cancers); skin for new lesions, moles. Monitor daily pattern bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Blood levels, EKGs will be monitored routinely. • Treatment may depress your immune system and reduce your ability to fight infection. Report symptoms of infection such as body aches, chills, cough, fatigue, fever. Avoid those with active infection. • Therapy may decrease your heart rate, esp. in those taking medications that lower heart rate; report dizziness, chest pain, palpitations, or fainting. • Avoid pregnancy. Do not breastfeed. • Male pts should use condoms during sexual activity. • Treatment includes a steroid that may raise blood sugar levels; report dehydration, blurry vision, confusion, frequent urination, increased thirst, fruity breath. • Report allergic reactions of any kind. • Abdominal pain, easy bruising, clay-colored stools, dark-amber urine, fatigue, loss of appetite, yellowing of skin or eyes may indicate liver problem.
eltrombopag
el-trom-boe-pag
(Promacta, Revolade
![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause hepatotoxicity. Measure serum ALT, AST, and bilirubin prior to initiation of eltrombopag, every 2 wks during dose adjustment phase, and monthly following establishment of a stable dose. If bilirubin is elevated, perform fractionation. Discontinue eltrombopag if ALT levels increase to 3 times or greater upper limit of normal and are progressive, persistent for 4 or more wks, accompanied by increased direct bilirubin, clinical symptoms of hepatic injury, or evidence of hepatic decompensation.
May cause hepatotoxicity. Measure serum ALT, AST, and bilirubin prior to initiation of eltrombopag, every 2 wks during dose adjustment phase, and monthly following establishment of a stable dose. If bilirubin is elevated, perform fractionation. Discontinue eltrombopag if ALT levels increase to 3 times or greater upper limit of normal and are progressive, persistent for 4 or more wks, accompanied by increased direct bilirubin, clinical symptoms of hepatic injury, or evidence of hepatic decompensation.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Thrombopoietin receptor agonist. CLINICAL: Prevents thrombocytopenia.
USES
Treatment of thrombocytopenia in pts with chronic immune (idiopathic) thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) with insufficient response with corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy. Use only in pts who are at increased risk for bleeding; should not be used to normalize platelet counts. Treatment of thrombocytopenia in pts with chronic hepatitis C infection to allow the initiation and maintenance of interferon-based therapy. Treatment of severe aplastic anemia in pts having an insufficient response to immunosuppressive therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to eltrombopag. Cautions: Preexisting hepatic impairment, renal impairment (any degree), myelodysplastic syndrome (may increase risk for hematologic malignancies). Pts with known risk for thromboembolism, risk for cataracts.
ACTION
Interacts with the human thrombopoietin receptor and initiates signaling cascades. Therapeutic Effect: Induces proliferation and differentiation of megakaryocytes from bone marrow progenitor cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed from gastrointestinal tract. Primarily distributed in blood cells. Protein binding: 99%. Extensively metabolized including oxidation, conjugation with glucuronic acid or cysteine. Excreted primarily in feces. Half-life: 26–35 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Use caution due to increased frequency of hepatic, renal, cardiac dysfunction.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration/toxicity of atorvastatin, fluvastatin, methotrexate, nateglinide, pravastatin, repaglinide, rifampin, rosuvastatin. Aluminum, antacids, calcium, iron, magnesium may decrease concentration/effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: Dairy products may decrease concentration/effects. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg. Oral Suspension: 25 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give on an empty stomach, either 1 hr before or 2 hrs after meal. • Give at least 4 hrs before or 4 hrs after ingestion of antacids, food high in calcium or minerals, or calcium-fortified juices.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Aplastic Anemia
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 50 mg once daily (25 mg for pts of East Asian ancestry or hepatic impairment). Titrate dose based on platelet response. Adjust dose to maintain platelets more than 50,000/mm3. Maximum: 150 mg/day.
ITP
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 50 mg once daily (25 mg for pts of East Asian ancestry or moderate to severe hepatic insufficiency or children 1 to 5 yrs of age). Then, adjust dose (25 mg to 75 mg once daily) to achieve and maintain platelet count of 50,000 mm3 or greater as necessary to reduce risk of bleeding. Maximum: 75 mg once daily.
Chronic Hepatitis C–associated Thrombocytopenia
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 25 mg once daily. Titrate dose based on platelet response. Maximum: 100 mg once daily.
Dosage Adjustment Based on Platelet Response
| Less than 50,000/mm3 (after at least 2 wks) | Increase by 25 mg q2 wks up to 100 mg/day |
| 200,000/mm3 or more and 400,000/mm3 or less | Decrease by 25 mg |
| More than 400,000/mm3 | Withhold; when less than 150,000/mm3, resume with dose reduced by 25 mg |
| More than 400,000/mm3 after 2 wks at lowest dose | Discontinue |
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
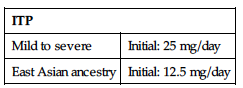
| ITP | |
| Mild to severe | Initial: 25 mg/day |
| East Asian ancestry | Initial: 12.5 mg/day |
Chronic Hepatitis C
No dose adjustment.
Aplastic Anemia
Initial dose 25 mg once daily.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (6%–4%): Nausea, vomiting, menorrhagia. Occasional (3%–2%): Myalgia, paresthesia, dyspepsia, ecchymosis, cataract, conjunctival hemorrhage.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
May cause hepatotoxicity. Increases risk of reticulin fiber deposits within bone marrow (may lead to bone marrow fibrosis). May produce hematologic malignancies. May cause excessive increase in platelets, leading to thrombotic complications.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess CBC and peripheral blood smears, LFT. Examine peripheral blood smear to establish extent of RBC and WBC abnormalities. Conduct ocular examination.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, platelet counts, peripheral blood smears, LFT throughout and following discontinuation. Monitor for cataracts during therapy.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Lab values will be closely monitored throughout therapy and for at least 4 wks after last dose. • Report any yellowing of the skin or eyes, unusual darkening of the urine, unusual tiredness, pain in right upper stomach area. • Report changes in vision.
eluxadoline
el-ux-ad-oh-leen
(Viberzi)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Mu-opioid receptor agonist. CLINICAL: Antidiarrheal.
USES
Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea in adults.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to eluxadoline. Known or suspected biliary duct obstruction, sphincter of Oddi disease or dysfunction; severe hepatic impairment; severe constipation or sequelae from constipation, or known or suspected mechanical GI obstruction. History of alcoholism, alcohol abuse, alcohol addiction, or consumption of more than 3 alcoholic beverages/day. History of pancreatitis; structural disease of the pancreas, including known or suspected ancreatic duct obstruction. Cautions: Pts without a gallbladder, mild to moderate hepatic impairment, respiratory disease.
ACTION
Affects mu-opioid receptors involved with gut motility, pain sensations, and secretion of liquids within the digestive tract. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces abdominal pain and diarrhea (without causing constipation).
PHARMACOKINETICS
Metabolism not specified. Protein binding: 81%. Peak plasma concentration: 1.5 hrs. Primarily eliminated in feces (82%), urine (less than 1%). Half-life: 3.7–6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: OATP1B1 inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine, atazanavir, ritonavir, rifampin), strong CYP inhibitors (e.g., ciprofloxacin, gemfibrozil, fluconazole, clarithromycin) may increase concentration/effect. Drugs that cause constipation (e.g., alosetron, anticholinergics [e.g., diphenhydramine], loperamide, opioids [e.g., morphine] may increase risk of serious constipation-associated adverse effects. May increase concentration of rosuvastatin, increasing risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis. May increase effects of CYP3A substrates with narrow therapeutic index (e.g., cyclosporine, sirolimus, tacrolimus). HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: High-fat meals may decrease absorption. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, lipase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets: 75 mg, 100 mg.
Tablets: 75 mg, 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Administer with food. • If scheduled dose is missed, give next dose at the regular time; do not give 2 doses at once.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Irritable Bowel Syndrome–Associated Diarrhea
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100 mg twice daily. May decrease to 75 mg twice daily if unable to tolerate 100 mg dose.
Dose Modification
Pts without a gallbladder, or are unable to tolerate 100-mg dose, or are receiving concomitant OATP1B1 inhibitors: 75 mg twice daily.
Pts who develop severe constipation for more than 4 days: Permanently discontinue.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Not specified; use caution.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: 75 mg twice daily. Severe impairment: Contraindicated.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (8%–4%): Constipation, nausea, abdominal pain (upper or lower), upper respiratory tract infection, vomiting. Rare (3%–1%): Abdominal distention, dizziness, flatulence, rash, urticaria, fatigue, sedation, somnolence, euphoric mood.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
May increase risk of sphincter of Oddi spasm (esp. in pts without a gallbladder), resulting in pancreatitis or hepatic enzyme elevation that may be associated with or without acute abdominal pain, or nausea/vomiting; 80% of pts reported sphincter of Oddi spasm within the first week of treatment. May also increase risk of pancreatitis that is not associated with sphincter of Oddi spasm. Infectious processes including upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, nasopharyngitis, viral gastroenteritis were reported. May cause hypersensitivity reaction including asthma, bronchospasm, respiratory failure, wheezing.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline LFT in pts with baseline hepatic impairment. Receive full medication history and screen for interactions requiring lower dosage. Question pt’s usual stool characteristics (color, frequency, consistency). Question history of alcoholism, biliary duct obstruction, mechanical GI obstruction, hepatic impairment, hypersensitivity reaction, pancreatic disease, respiratory disease, sphincter of Oddi disease or spasm. Assess hydration status.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for abdominal pain that radiates to the back or shoulder, with or without nausea or vomiting (esp. during first few weeks of treatment). Obtain LFT, serum lipase level if acute pancreatitis, sphincter of Oddi spasm, biliary tract obstruction suspected. Monitor for hypersensitivity reaction including dyspnea, rash, wheezing. Observe and record daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Encourage PO intake. If an acute overdose occurs, a narcotic mu-opioid antagonist such as naloxone may be considered if reversal of overdose-related adverse effects is needed.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Therapy may cause inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis) or elevated liver-associated abdominal pain, esp. during the first few weeks of treatment. Report any new or worsening abdominal pain that radiates to the back or shoulder, with or without nausea/vomiting. • Avoid chronic or acute excessive use of alcohol; may increase risk of liver or pancreas injury. • If a dose is missed, take the next dose at the regular time; do not take 2 doses at once. • Report constipation lasting longer than 4 days. • Avoid medications that cause constipation (e.g., antidiarrheals, narcotics). • Report signs of allergic reaction; respiratory problems such as worsening of asthma, bronchitis, wheezing. • Drink plenty of fluids.
elvitegravir
el-vi-teg-ra-vir
(Vitekta)
Do not confuse elvitegravir with dolutegravir or raltegravir.
FIXED COMBINATION(S)
Genvoya, Stribild: elvitegravir (an integrase inhibitor)/cobicistat (an antiretroviral booster)/emtricitabine/tenofovir (antiretroviral agents): 150 mg/150 mg/200 mg/300 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Integrase strand transfer inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiretroviral agent.
USES
Used in combination with an HIV protease inhibitor, co-administered with ritonavir and other antiretroviral medications for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in antiretroviral treatment–experienced adults.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to elvitegravir. Cautions: Diabetes, hepatic impairment, hypercholesterolemia. Not recommended with a HIV protease inhibitor and cobicistat combination; co-administration of HIV-1 protease inhibitors other than atazanavir, darunavir, fosamprenavir, lopinavir, and tipranavir.
ACTION
Inhibits HIV integrase by preventing integration of HIV-1 DNA into host DNA, blocking formation of HIV-1 provirus. Therapeutic Effect: Interferes with HIV replication, slowing progression of HIV infection.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed after PO administration. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 98%–99%. Peak plasma concentration: 4 hrs. Eliminated in feces (95%), urine (7%). Half-life: 8.7 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommend due to risk of postnatal HIV transmission. Unknown if distributed in human breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: Safety and efficacy not established in pts older than 65 yrs. May have increased risk of adverse reactions, hepatic impairment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antacids, aluminum/calcium/magnesium/iron supplements, antiretrovirals (e.g., efavirenz, nevirapine), corticosteroids (e.g., dexamethasone), anticonvulsants (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin), rifampin may decrease concentration/effect. May increase concentrations/effects of ketoconazole, rifampin. Antifungals (e.g., ketoconazole), atazanavir, lopinavir may increase concentration/effect. May decrease concentration/effect of hormonal contraceptives. HERBAL: St John’s wort may decrease effectiveness. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, amylase bilirubin, cholesterol, creatine kinase (CK), GGT, glucose, lipase, triglycerides, urine glucose, urine RBC. May decrease neutrophils.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets: 85 mg, 150 mg.
Tablets: 85 mg, 150 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Must be taken with food. • Must be administered with a protease inhibitor, in combination with ritonavir and another antiretroviral drug. • If pt receiving antacid, do not give aluminum- or magnesium-containing antacids within 2 hrs of dose.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
HIV Infection
ADULTS, ELDERLY: 150 mg once daily. (Co-administered with atazanavir/ritonavir or lopinavir/ritonavir): PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 85 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (7%–4%): Diarrhea, nausea. Rare (3%): Headache.
ADVERSE REACTIONS/TOXIC EFFECTS
May induce immune recovery syndrome (inflammatory response to dormant opportunistic infections such as Mycobacterium avium, cytomegalovirus, Pneomocystis carinii pneumonia [PCP], tuberculosis, or acceleration of autoimmune disorders such as Graves’ disease, polymyositis, Guillain-Barré). Pts co-infected with hepatitis B or C virus have increased risk for viral reactivation and worsening of hepatic function and may experience hepatic decompensation and/or failure if therapy is discontinued. Elevation of hepatic enzymes greater than 5 times upper limit of normal reported in 2% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain BMP, CBC, lipid panel, LFT, urine glucose, vital signs; CD4+ count, viral load level. Screen for hepatitis B or C co-infection, hypercholesterolemia. Receive full medication history including herbal products. Question possibility of pregnancy; history of diabetes, hypercholesterolemia.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, hepatic function, lipid levels. Monitor CD4+ count, viral load for treatment effectiveness. Cough, dyspnea, fever, excess of band cells on CBC may indicate acute infection (WBC count may be unreliable in pts with uncontrolled HIV infection). Screen for immune reconstitution syndrome.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Offer emotional support. • Take elvitegravir with a HIV protease inhibitor, combined with ritonavir at the same time each day with food (optimizes absorption). • Antacids may decrease drug effectiveness; do not take within 2 hrs of dose • Treatment regimen does not cure HIV infection, nor reduce risk of transmission. • Drug resistance can form if therapy is interrupted; do not run out of supply. • As immune system strengthens, it may respond to dormant infections hidden within the body. Report body aches, chills, cough, fever, night sweats, shortness of breath. • Treatment may cause liver dysfunction; report abdominal pain, darkened urine, clay-colored stools, significant weight loss, or yellowing of skin or eyes.• Do not take any new medications, including over-the-counter drugs or herbal products, unless approved by your doctor.
empagliflozin
em-pa-gli-floe-zin
(Jardiance)
Do not confuse empagliflozin with canagliflozin or dapagliflozin.
FIXED COMBINATION(S)
Glyxambi: empagliflozin/linagliptin (an antidiabetic): 10 mg/5 mg, 25 mg/5 mg. Synjardy: Empagliflozin/metformin (an antidiabetic): 5 mg/500 mg, 5 mg/1000 mg, 12.5 mg/500 mg, 12.5 mg/1000 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antidiabetic.
USES
Adjunctive treatment to diet and exercise to improve glycemic controls in pts with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Reduce risk of cardiovascular death in pts with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: History of hypersensitivity to empagliflozin, other SGLT2 inhibitors, severe renal impairment, end-stage renal disease, dialysis. Cautions: Not recommended in type 1 diabetes, diabetic ketoacidosis. Concurrent use of diuretics, other hypoglycemic medications, mild to moderate renal impairment, hypovolemia (dehydration/anemia), elderly, those with low systolic B/P, hyperlipidemia, pts with history of genital mycotic infection. May cause ketoacidosis.
ACTION
Increases excretion of urinary glucose by inhibiting reabsorption of filtered glucose in kidney. Inhibits SGLT2 in proximal renal tubule. Therapeutic Effect: Lowers serum glucose levels.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed following PO administration. Metabolized in liver by glucuronidation. Peak plasma concentration: 1.5 hrs. Protein binding: 86%. Excreted in urine (54%) and feces (41%). Half-life: 12.4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Must either discontinue drug or discontinue breastfeeding. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: May have increased risk for adverse reactions (e.g., hypotension, syncope, dehydration).
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Diuretics (e.g., HCTZ, furosemide) may increase risk of hypotension/volume depletion. Insulin, insulin secretagogues (e.g., glyburide) may increase risk of hypoglycemia. May increase concentration/effect of digoxin. HERBAL: Herbs with hypoglycemic properties (e.g., fenugreek, garlic, ginger, ginseng, gotu) may increase risk of hypoglycemia. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), serum creatinine. May decrease glomerular filtration rate.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
May give without regard to food in the morning.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Reduce Risk of Cardiovascular Death
PO: ADULTS/ELDERLY: Initially, 10 mg once daily in the morning. May increase to 25 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
GFR 45 ml/min or greater: No dose adjustment. GFR less than 45 ml/min: Discontinue. Do not initiate.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (9.3%–5.4%): UTI, female genital mycotic infection. Rare (4 %–1.1%): Upper respiratory tract infection, increased urination, dyslipidemia, arthralgia, male genital mycotic infections, nausea.
ADVERSE REACTIONS/TOXIC EFFECTS
Symptomatic hypotension (postural dizziness, orthostatic hypotension, syncope) may occur. Genital myocotic (yeast) infections reported in 6.5% of pts. Hypoglycemic events reported (concomitant use of hypoglycemic medications may increase hypoglycemic risk).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess hydration status. Obtain serum chemistries, capillary blood glucose, hemoglobin A1c, LDL-C. Assess pt’s understanding of diabetes management, routine home glucose monitoring. Receive full medication history including minerals, herbal products. Question history of co-morbidities, esp. renal or hepatic impairment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum cholesterol, blood glucose, renal function, LFT. Assess for hypoglycemia (diaphoresis, tremors, dizziness, anxiety, headache, tachycardia, perioral numbness, hunger, diplopia, difficulty concentrating), hyperglycemia (polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, Kussmaul respirations), hypersensitivity reaction. Screen for glucose-altering conditions: fever, increased activity or stress, surgical procedures. Obtain dietary consult for nutritional education. Encourage PO intake.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Diabetes mellitus requires lifelong control. • Diet and exercise are principal parts of treatment; do not skip or delay meals. • Test blood sugar regularly. When taking combination drug therapy or when glucose demands are altered (fever, infection, trauma, stress), have low blood sugar treatment available (glucagon, oral dextrose). • Report suspected pregnancy or plans of breastfeeding. • Monitor daily calorie intake. • Slowly go from lying to standing to prevent dizziness. • Therapy may increase risk for dehydration/low blood pressure. • Genital itching may indicate yeast infection. Report any signs of UTI (e.g., burning while urinating, cloudy urine, pelvic pain, back pain).
emtricitabine

em-tri-sye-ta-bine
(Emtriva)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Serious, sometimes fatal, hypersensitivity reaction, lactic acidosis, severe hepatomegaly with steatosis (fatty liver) have occurred. May exacerbate hepatitis B virus infection after completing treatment.
Serious, sometimes fatal, hypersensitivity reaction, lactic acidosis, severe hepatomegaly with steatosis (fatty liver) have occurred. May exacerbate hepatitis B virus infection after completing treatment.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Descovy: emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) (a nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor): 200 mg/25 mg.
Atripla: emtricitabine/efavirenz (an antiretroviral)/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) (an antiretroviral): 200 mg/600 mg/300 mg. Complera: emtricitabine/rilpivirine (an antiretroviral)/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) (an antiretroviral): 200 mg/25 mg/300 mg. Genvoya: emtricitabine/elvitegravir (an integrase inhibitor)/cobicistat (a pharmacokinetic enhancer)/tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) (a nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor): 200 mg/150 mg/150 mg/10 mg. Truvada: emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) (an antiretroviral): 200 mg/300 mg. Stribild: emtricitabine/elvitegravir (an integrase inhibitor)/cobicistat (a pharmacokinetic enhancer)/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) (a nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor): 200 mg/150 mg/150 mg/300 mg.
Odefsey: emtricitabine/rilpivirine (non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor [NNRTI])/tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) (a nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor): 200 mg/25 mg/25 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiretroviral agent.
USES
Used in combination with at least two other antiretroviral agents for treatment of HIV-1 infection.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to emtricitabine. Cautions: Renal impairment, history of hepatitis, diabetes.
ACTION
Inhibits HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by incorporating itself into viral DNA, resulting in chain termination. Therapeutic Effect: Impairs HIV replication, slowing progression of HIV infection.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly, extensively absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: less than 4%. Excreted primarily in urine. Half-life: 10 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum amylase, lipase, ALT, AST, triglycerides. May alter serum glucose.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 200 mg. Oral Solution: 10 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
HIV
Capsules
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 3 MOS–17 YRS, WEIGHING MORE THAN 33 KG: 200 mg once daily.
Oral Solution
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 240 mg once daily. CHILDREN 3 MOS–17 YRS WEIGHING MORE THAN 33 KG: 6 mg/kg once daily. Maximum: 240 mg once daily. CHILDREN 0–3 MOS: 3 mg/kg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Capsule | Oral Solution |
| 30–49 ml/min | 200 mg q48h | 120 mg q24h |
| 15–29 ml/min | 200 mg q72h | 80 mg q24h |
| Less than 15 ml/min; hemodialysis pts | 200 mg q96h | 60 mg q24h (administer after dialysis) |
Administer after dialysis on dialysis days.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (23%–13%): Headache, rhinitis, rash, diarrhea, nausea. Occasional (14%–4%): Cough, vomiting, abdominal pain, insomnia, depression, paresthesia, dizziness, peripheral neuropathy, dyspepsia, myalgia. Rare (3%–2%): Arthralgia, abnormal dreams.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Lactic acidosis, hepatomegaly with steatosis (excess fat in liver) occur rarely; may be severe.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain LFT, serum triglycerides before beginning and at periodic intervals during therapy. Offer emotional support.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Question for evidence of nausea, pruritus. Assess skin for rash, urticaria. Monitor serum chemistry tests, LFT for marked abnormalities; signs/symptoms of lactic acidosis.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• May cause redistribution of body fat. • Continue therapy for full length of treatment. • Emtricitabine is not a cure for HIV infection, nor does it reduce risk of transmission to others. • Pts may continue to acquire illnesses associated with advanced HIV infection. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Report persistent or severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, numbness.
enalapril
en-al-a-pril
(Apo-Enalapril
![]() , Epaned, Novo-Enalapril
, Epaned, Novo-Enalapril
![]() , Vasotec)
, Vasotec)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause fetal injury. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
May cause fetal injury. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
Do not confuse enalapril with Anafranil, Elavil, Eldepryl, or ramipril.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Lexxel: enalapril/felodipine (calcium channel blocker): 5 mg/2.5 mg, 5 mg/5 mg. Teczem: enalapril/diltiazem (calcium channel blocker): 5 mg/180 mg. Vaseretic: enalapril/hydrochlorothiazide (diuretic): 5 mg/12.5 mg, 10 mg/25 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive, vasodilator.
USES
Treatment of hypertension alone or in combination with other antihypertensives. Adjunctive therapy for symptomatic HF. Treatment of asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. (Epaned): Treatment of hypertension in adults and children older than 1 mo. OFF-LABEL: Proteinuria in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to enalapril. History of angioedema from previous treatment with ACE inhibitors. Idiopathic/hereditary angioedema. Concomitant use of aliskiren in pts with diabetes. Cautions: Renal impairment, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with outflow tract obstruction; severe aortic stenosis; before, during, or immediately after major surgery. Concommitant use of potassium supplement; unstented unilateral or bilateral renal artery stenosis.
ACTION
Suppresses renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (prevents conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor; may inhibit angiotensin II at local vascular, renal sites). Decreases plasma angiotensin II, increases plasma renin activity, decreases aldosterone secretion. Therapeutic Effect: In hypertension, reduces peripheral arterial resistance. In HF, increases cardiac output; decreases peripheral vascular resistance, B/P, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, heart size.
PHARMACOKINETICS
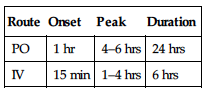
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 1 hr | 4–6 hrs | 24 hrs |
| IV | 15 min | 1–4 hrs | 6 hrs |
Readily absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 50%–60%. Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 11 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. May cause fetal/neonatal mortality, morbidity. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May be more susceptible to hypotensive effects.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, antihypertensive agents (e.g., amlodipine, clonidine, valsartan), diuretics (e.g., furosemide, torsemide) may increase effects. NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive effect, increase risk of possible acute renal failure. Potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., spironolactone, triamterene), potassium supplements may cause hyperkalemia. May increase lithium concentration, toxicity. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Garlic may increase antihypertensive effect. Licorice may cause sodium/water retention, loss of potassium. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, creatinine, potassium, ALT, AST. May decrease serum sodium. May cause positive ANA titer.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 1.25 mg/ml. Powder for Oral Solution (Epaned): 1 mg/ml (after reconstitution). Tablets: 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • May give undiluted or dilute with D5W or 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • For IV push, give undiluted over 5 min. • For IV piggyback, infuse over 10–15 min.
Storage • Store parenteral form at room temperature. • Use only clear, colorless solution. • Diluted IV solution is stable for 24 hrs at room temperature.
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Tablets may be crushed.
Epaned
• Reconstitute with 150 ml Ora-Sweet SF (provided) to produce a 1 mg/ml concentration. Stable for 60 days after reconstitution.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B (Fungizone), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), cefepime (Maxipime), phenytoin (Dilantin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Calcium gluconate, dexmedetomidine (Precedex), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), fentanyl (Sublimaze), heparin, lidocaine, magnesium sulfate, morphine, nitroglycerin, potassium chloride, potassium phosphate, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 2.5–5 mg/day (2.5 mg if pt taking a diuretic). May increase at 1–2 wk intervals. Range: 10–40 mg/day in 1–2 divided doses. CHILDREN 1 MO–16 YRS: Initially, 0.08 mg/kg/day in 1–2 divided doses. Maximum: 5 mg/day. NEONATES: 0.04–0.1 mg/kg/day given q24h. Epaned: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 5 mg once daily. CHILDREN: Initially, 0.08 mg/kg once daily. Maximum: 5 mg.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.625–1.25 mg q6h up to 5 mg q6h.
Adjunctive Therapy for HF
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 2.5 mg twice daily. Titrate slowly at 1–2 wk intervals. Range: 5–40 mg/day in 2 divided doses. Target: 10–20 mg twice daily.
Asymptomatic Left Ventricular Dysfunction
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2.5 mg twice daily. Titrate up to 20 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl greater than 30 ml/min: No dosage adjustment. CrCl 30 ml/min or less: (HTN): Initially, 2.5 mg/day. Titrate until B/P controlled. (HF): Initially, 2.5 mg twice daily. May increase by 2.5 mg/dose at greater than 4-day intervals. Maximum: 40 mg/day.
Hemodialysis: Initially, 2.5 mg on dialysis days, adjust dose on non-dialysis days depending on B/P.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (7%–5%): Headache, dizziness. Occasional (3%–2%): Orthostatic hypotension, fatigue, diarrhea, cough, syncope. Rare (less than 2%): Angina, abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea, rash, asthenia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Excessive hypotension (“first-dose syncope”) may occur in pts with HF, severe salt or volume depletion. Angioedema (facial, lip swelling), hyperkalemia occur rarely. Agranulocytosis, neutropenia may be noted in pts with renal impairment, collagen vascular diseases (scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus). Nephrotic syndrome may be noted in those with history of renal disease.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain B/P immediately before each dose (be alert to fluctuations). In pts with renal impairment, autoimmune disease, or taking drugs that affect leukocytes/immune response, CBC should be performed before beginning therapy, q2wks for 3 mos, then periodically thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Monitor CBC, serum BUN, potassium, creatinine, B/P. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• To reduce hypotensive effect, go from lying to standing slowly. • Several wks may be needed for full therapeutic effect of B/P reduction. • Skipping doses or voluntarily discontinuing drug may produce severe, rebound hypertension. • Limit alcohol intake. • Report vomiting, diarrhea, diaphoresis, persistent cough, difficulty in breathing; swelling of face, lips, tongue.
enoxaparin


en-ox-a-par-in
(Lovenox)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Epidural or spinal anesthesia greatly increases potential for spinal or epidural hematoma, subsequent long-term or permanent paralysis.
Epidural or spinal anesthesia greatly increases potential for spinal or epidural hematoma, subsequent long-term or permanent paralysis.
Do not confuse Lovenox with Lasix, Levaquin, Lotronex, or Protonix.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Low molecular weight heparin. CLINICAL: Anticoagulant.
USES
DVT prophylaxis following hip or knee replacement surgery, abdominal surgery, or pts with severely restricted mobility during acute illness. Treatment of acute coronary syndrome (ACS): unstable angina, non–Q-wave MI, acute ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI). Treatment of DVT with or without pulmonary embolism (PE) (inpatient); without PE (outpatient). OFF-LABEL: DVT prophylaxis following moderate-risk general surgery, gynecologic surgery; management of venous thromboembolism (VTE) during pregnancy. Bariatric surgery, mechanical heart valve to bridge anticoagulation, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) adjunctive therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to enoxaparin. Active major bleeding, concurrent heparin therapy, hypersensitivity to heparin, pork products, thrombocytopenia associated with positive in vitro test for antiplatelet antibodies. Not for IM use. Cautions: Conditions with increased risk of hemorrhage, platelet defects, renal impairment (renal failure), elderly, uncontrolled arterial hypertension, history of recent GI ulceration or hemorrhage. When neuraxial anesthesia (epidural or spinal anesthesia) or spinal puncture is used, pts anticoagulated or scheduled to be anticoagulated with enoxaparin for prevention of thromboembolic complications are at risk for developing an epidural or spinal hematoma that can result in long-term or permanent paralysis. Bacterial endocarditis, hemorrhagic stroke, history HIT, severe hepatic disease.
ACTION
Potentiates action of antithrombin III, inactivates coagulation factor Xa. Therapeutic Effect: Produces anticoagulation. Does not significantly influence PT, aPTT.
PHARMACOKINETICS
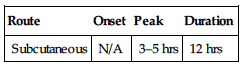
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| Subcutaneous | N/A | 3–5 hrs | 12 hrs |
Well absorbed after subcutaneous administration. Eliminated primarily in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 4.5–7 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Use with caution, particularly during third trimester, immediate postpartum period (increased risk of maternal hemorrhage). Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May be more susceptible to bleeding.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antiplatelet agents, aspirin, NSAIDs, thrombolytics may increase risk of bleeding. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo, ginseng may increase antiplatelet action. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Increases serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST. May decrease Hgb, Hct, RBCs.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 30 mg/0.3 ml, 40 mg/0.4 ml, 60 mg/0.6 ml, 80 mg/0.8 ml, 100 mg/ml, 120 mg/0.8 ml, 150 mg/ml in prefilled syringes.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Do not mix with other injections, infusions. Do not give IM.
Subcutaneous
• Parenteral form appears clear, colorless to pale yellow. • Store at room temperature. • Instruct pt to lie down before administering by deep subcutaneous injection. • Inject between left and right anterolateral and left and right posterolateral abdominal wall. • Introduce entire length of needle (½ inch) into skin fold held between thumb and forefinger, holding skin fold during injection.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Prevention of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) After Hip and Knee Surgery
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 30 mg twice daily, generally for 7–10 days, with initial dose given within 12–24 hrs following surgery. Once-daily dosing following hip surgery: 40 mg with initial dose within 9–15 hrs before surgery.
Prevention of DVT After Abdominal Surgery
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 40 mg/day for 7–10 days, with initial dose given 2 hrs prior to surgery.
Prevention of DVT After Bariatric Surgery
BMI 50 or less (kg/m2): 40 mg q12h. BMI greater than 50 kg/m2: 60 mg q12h.
Prevention of Long-Term DVT in Nonsurgical Acute Illness
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 40 mg once daily; continue until risk of DVT has diminished (usually 6–11 days).
Prevention of Ischemic Complications of Unstable Angina, Non–Q-Wave MI (with Oral Aspirin Therapy)
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1 mg/kg q12h (with oral aspirin).
STEMI
SQ: ADULTS YOUNGER THAN 75 YRS: 30 mg IV once plus 1 mg/kg q12h (maximum: 100 mg first 2 doses only). ADULTS 75 YRS OR OLDER: 0.75 mg/kg (maximum: 75 mg first 2 doses only) q12h.
Acute DVT
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Inpatient): 1 mg/kg q12h or 1.5 mg/kg once daily. (Outpatient): 1 mg/kg q12h.
Usual Pediatric Dosage
SQ: CHILDREN 2 MOS AND OLDER: 0.5 mg/kg q12h (prophylaxis); 1 mg/kg q12h (treatment). NEONATES, INFANTS YOUNGER THAN 2 MOS: 0.75/mg/kg/dose q12h (prophylaxis); 1.5 mg/kg/dose q12h (treatment).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Clearance is decreased when CrCl is less than 30 ml/min. Monitor and adjust dosage as necessary.
| Use | Dosage |
| Abdominal surgery, pts with acute illness | 30 mg once/day |
| Hip, knee surgery | 30 mg once/day |
| DVT, angina, MI | 1 mg/kg once/day |
| STEMI: (<75 yrs) | 30 mg IV once plus 1 mg/kg q24h |
| STEMI (75 yrs or greater) | 1 mg/kg q24h |
| NSTEMI | 1 mg/kg q24h |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (4%–1%): Injection site hematoma, nausea, peripheral edema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
May lead to bleeding complications ranging from local ecchymoses to major hemorrhage. May cause heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). Antidote: IV injection of protamine sulfate (1% solution) equal to dose of enoxaparin injected. One mg protamine sulfate neutralizes 1 mg enoxaparin. One additional dose of 0.5 mg protamine sulfate per 1 mg enoxaparin may be given if aPTT tested 2–4 hrs after first injection remains prolonged.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC. Note platelet count. Assess potential risk of bleeding.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Periodically monitor CBC, platelet count, stool for occult blood (no need for daily monitoring in pts with normal presurgical coagulation parameters). Assess for any sign of bleeding (bleeding at surgical site, hematuria, blood in stool, bleeding from gums, petechiae, bruising, bleeding from injection sites).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Usual length of therapy is 7–10 days. • Do not take any OTC medication (esp. aspirin) without consulting physician. • Report unusual bleeding or bruising.
entecavir
en-tek-a-veer
(Baraclude, Apo-Entecavir
![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Serious, sometimes fatal, hypersensitivity reaction, lactic acidosis, severe hepatomegaly with steatosis (fatty liver) have occurred. May cause HIV resistance in chronic hepatitis B pts. Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B virus infection may occur upon discontinuation of entecavir.
Serious, sometimes fatal, hypersensitivity reaction, lactic acidosis, severe hepatomegaly with steatosis (fatty liver) have occurred. May cause HIV resistance in chronic hepatitis B pts. Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B virus infection may occur upon discontinuation of entecavir.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Reverse transcriptase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiretroviral agent.
USES
Treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection with evidence of active viral replication and evidence of either persistent transaminase elevations or histologically active disease or evidence of decompensated hepatic disease. OFF-LABEL: HBV reinfection prophylaxis, post–liver transplant, HIV/HBV coinfection.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to entecavir. Cautions: Renal impairment, pts receiving concurrent therapy that may reduce renal function. Pts at risk for hepatic disease.
ACTION
Inhibits hepatitis B viral polymerase, an enzyme blocking reverse transcriptase activity. Therapeutic Effect: Interferes with viral DNA synthesis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Poorly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 13%. Extensively distributed into tissues. Partially metabolized in liver. Eliminated primarily in urine. Half-life: 5–6 days (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 16 yrs. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Ganciclovir, ribavirin, valganciclovir may increase concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: Food delays absorption, decreases concentration. LAB VALUES: May increase serum amylase, lipase, bilirubin, ALT, AST, creatinine, glucose. May decrease serum albumin; platelets.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Oral Solution: 0.05 mg/ml. Tablets: 0.5 mg, 1 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Administer tablets on an empty stomach (at least 2 hrs after a meal and 2 hrs before the next meal). • Do not dilute, mix oral solution with water or any other liquid. • Each bottle of oral solution is accompanied by a dosing spoon. Before administering, hold spoon in vertical position, fill it gradually to mark corresponding to prescribed dose.
Storage • Store tablets, oral solution at room temperature.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Chronic Hepatitis B (No Previous Nucleoside Treatment)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 16 YRS AND OLDER: 0.5 mg once daily. CHILDREN 2 YRS AND OLDER: (Weighing more than 30 kg): 0.5 mg once daily (tablet or solution). (27–30 kg): 0.45 mg once daily (solution). (24–26 kg): 0.4 mg once daily (solution). (21-23 kg): 0.35 mg once daily (solution). (18–20 kg): 0.3 mg once daily (solution). (15–17 kg): 0.25 mg once daily (solution). (12–14 kg): 0.2 mg once daily (solution). (10–11 kg): 0.15 mg once daily (solution).
Chronic Hepatitis B (Receiving Lamivudine, Known Lamivudine Resistance, Decompensated Liver Disease)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 16 YRS AND OLDER: 1 mg once daily. CHILDREN 2 YRS AND OLDER: (Weighing more than 30 kg): 1 mg once daily (tablet or solution). (27–30 kg): 0.9 mg once daily (solution). (24–26 kg): 0.8 mg once daily (solution). (21–23 kg): 0.7 mg once daily (solution). (18–20 kg): 0.6 mg once daily (solution). (15–17 kg): 0.5 mg once daily (solution). (12–14 kg): 0.4 mg once daily (solution). (10–11 kg): 0.3 mg once daily (solution).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 50 ml/min and greater | 0.5 mg once daily |
| 30–49 ml/min | 0.25 mg once daily |
| 10–29 ml/min | 0.15 mg once daily |
| 9 ml/min and less | 0.05 mg once daily |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (4%–3%): Headache, fatigue. Rare (less than 1%): Diarrhea, dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, insomnia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Lactic acidosis, severe hepatomegaly with steatosis have been reported. Severe, acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in pts who have discontinued therapy; reinitiation of antihepatitis B therapy may be required. Hematuria occurs occasionally. May cause development of HIV resistance if HIV untreated.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline laboratory tests, esp. LFT before beginning therapy and at periodic intervals during therapy. Offer emotional support. Obtain full medication history.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several mos in pts who discontinue antihepatitis B therapy. For pts on therapy, closely monitor serum amylase, lipase, bilirubin, ALT, AST, creatinine, glucose, albumin; platelet count. Assess for evidence of GI discomfort.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take medication at least 2 hrs after a meal and 2 hrs before the next meal. • Avoid transmission of hepatitis B infection to others through sexual contact, blood contamination. • Immediately report unusual muscle pain, abdominal pain with nausea/vomiting, cold feeling in extremities, dizziness (signs and symptoms signaling onset of lactic acidosis).
enzalutamide
en-za-loo-ta-mide
(XTANDI)
Do not confuse enzalutamide with bicalutamide, flutamide, or nilutamide.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antiandrogen renal inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to enzalutamide. Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant (not indicated in female population). Cautions: History of seizure, underlying brain injury with loss of consciousness, transient ischemic attack within past 12 mos, CVA, brain metastases, brain arteriovenous abnormality, use of concurrent medications that may lower seizure threshold.
ACTION
Inhibits androgen binding to androgen receptors in target tissue, and inhibits interaction with DNA. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases proliferation, induces cell death of prostate cancer cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed in GI tract. Maximum plasma concentration achieved in 0.5–3 hrs. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: (97%–98%). Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 5.8 days (Range: 2.8–10.2 days).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Not used in female population. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Strong CYP2C8, CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., gemfibrozil, itraconazole) may increase concentration. Moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: All foods may increase absorption. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, bilirubin. May decrease Hgb, Hct, platelets, WBC count.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Capsules: 40 mg.
Capsules: 40 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO • May give with or without food. Take at same time each day. Swallow whole. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or open capsules.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 160 mg (4 × 40 mg capsules) given once daily.
Dose Modification
If a Grade 3 or greater toxicity or an intolerable side effect occurs, withhold dosing for 1 week or until symptoms improve to Grade 2 or less, then resume at same dose or a reduced dose (120 mg or 80 mg). Concurrent use of strong CYP2C8 inhibitors: Avoid use (if possible). If concurrent use is necessary, reduce the enzalutamide dose to 80 mg once daily. Concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inducers: Increase dose to 240 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Common (51%): Asthenia. Frequent (26%–15%): Back pain, diarrhea, arthralgia, hot flashes, peripheral edema, musculoskeletal pain. Occasional (12%–6%): Headache, dizziness, insomnia, hematuria, paresthesia, anxiety, hypertension. Rare (4%–2%): Mental impairment disorders (includes amnesia, memory impairment, cognitive disorder, attention deficit), hematuria (includes pollakiuria, pruritus, dry skin).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Upper respiratory tract infection occurs in 11% of pts; lower respiratory tract and lung infection (includes pneumonia, bronchitis) occur in slightly less (9% of pts). Spinal cord compression and cauda equina syndrome occurs in 7% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Offer emotional support. Obtain baseline CBC, ALT, AST, bilirubin periodically throughout therapy. Assess bowel activity, stool consistency. If coadministered with warfarin (CYP2C9 substrate), perform additional INR monitoring.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for peripheral edema. Question level of fatigue, weakness. Question presence of back pain, arthralgia, or headache. Assess level of anxiety. Monitor B/P for hypertension. Assess for hematuria. Question pt regarding sleeping pattern.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Sexually active men must wear condom during treatment and for 1 wk after treatment due to potential risks to fetus. • Women who are pregnant or are planning pregnancy may not touch medication without gloves. • Dizziness, headache, muscle weakness, leg swelling/discomfort should be reported. • Immediately report fever or cough. • Routine lab testing will occur during treatment.
*EPINEPHrine

ep-i-nef-rin
(Adrenalin, EpiPen, EpiPen Jr., Twinject)
Do not confuse epinephrine with ephedrine.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
LidoSite: epinephrine/lidocaine (anesthetic): 0.1%/10%.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Sympathomimetic (adrenergic agonist). CLINICAL: Antiglaucoma, bronchodilator, cardiac stimulant, antiallergic, antihemorrhagic, priapism reversal agent.
USES
Treatment of allergic reactions (including anaphylactic reactions). Treatment of hypotension associated with septic shock. Added to local anesthetics to decrease systemic absorption and increase duration of activity of local anesthetic. Decreases superficial hemorrhage. OFF-LABEL: Ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia unresponsive to initial defibrillatory shocks; pulseless electrical activity, asystole, hypotension unresponsive to volume resuscitation; bradycardia/hypotension unresponsive to atropine or pacing; inotropic support.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to epinephrine. Note: There are no absolute contraindications with injectable epinephrine in a life-threatening situation. IV: Narrow-angle glaucoma, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes, hypertension, other cardiovascular disorders. Inhalation: Concurrent use or within 2 wks of MAOIs. Cautions: Elderly, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, Parkinson’s disease, thyroid disease, cerebrovascular or cardiovascular disease, concurrent use of tricyclic antidepressants. History of prostate enlargement, urinary retention.
ACTION
Stimulates alpha-adrenergic receptors (vasoconstriction, pressor effects), beta1-adrenergic receptors (cardiac stimulation), beta2-adrenergic receptors (bronchial dilation, vasodilation). Therapeutic Effect: Relaxes smooth muscle of bronchial tree, produces cardiac stimulation, dilates skeletal muscle vasculature.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| IM | 5–10 min | 20 min | 1–4 hrs |
| Subcutaneous | 5–10 min | 20 min | 1–4 hrs |
| Inhalation | 3–5 min | 20 min | 1–3 hrs |
Well absorbed after parenteral administration; minimally absorbed after inhalation. Metabolized in liver, other tissues, sympathetic nerve endings. Excreted in urine. Ophthalmic form may be systemically absorbed as a result of drainage into nasal pharyngeal passages. Mydriasis occurs within several min and persists several hrs; vasoconstriction occurs within 5 min and lasts less than 1 hr.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of beta blockers (e.g., carvedilol, metoprolol). Digoxin, sympathomimetics may increase risk of arrhythmias. Ergonovine, methergine, oxytocin may increase vasoconstriction. MAOIs, tricyclic antidepressants may increase cardiovascular effects. HERBAL: Ephedra, yohimbe may increase CNS stimulation. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum potassium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution (Prefilled Syringes):
(EpiPen): 0.3 mg/0.3 ml, (EpiPen Jr.): 0.15 mg/0.3 ml, (Twinject): 0.15 mg/0.15 ml. Injection, Solution: 0.1 mg/ml (1:10,000), 1 mg/ml (1:1,000).
Solution for Oral Inhalation
(Adrenalin): 2.25% (0.5 ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • For injection, dilute each 1 mg of 1:1,000 solution with 10 ml 0.9% NaCl to provide 1:10,000 solution and inject each 1 mg or fraction thereof over 1 min or more (except in cardiac arrest). • For infusion, further dilute with 250–500 ml D5W. Maximum concentration 64 mcg/ml.
Rate of Administration • For IV infusion, give at 1–10 mcg/min (titrate to desired response).
Storage • Store parenteral forms at room temperature. • Do not use if solution appears discolored or contains a precipitate.
Subcutaneous
• Shake ampule thoroughly. • Use tuberculin syringe for injection into lateral deltoid region. • Massage injection site (minimizes vasoconstriction effect). Use only 1:1,000 solution.
Nebulizer
• No more than 10 drops Adrenalin Chloride solution 1:100 should be placed in reservoir of nebulizer. • Place nozzle just inside pt’s partially opened mouth. • As bulb is squeezed once or twice, instruct pt to inhale deeply, drawing vaporized solution into lungs. • Rinse mouth with water immediately after inhalation (prevents mouth/throat dryness). • When nebulizer is not in use, replace stopper, keep in upright position.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Ampicillin, pantoprazole (Protonix), sodium bicarbonate.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), fentanyl (Sublimaze), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lorazepam (Ativan), midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, nitroglycerin, norepinephrine (Levophed), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Anaphylaxis
IM, SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.2–0.5 mg (0.2–0.5 ml of 1:1,000 solution). May repeat q5–15 min if anaphylaxis persists. CHILDREN: 0.01 mg/kg (0.01 ml/kg of a 1:1,000 solution) q5–15 min. Maximum single dose: 0.3 mg.
Hypotension (Shock)
IV INFUSION: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.05–2 mcg/kg/min. Titrate to desired mean arterial pressure (MAP). May adjust dose by 0.05–0.2 mcg/kg/min.
Cardiac Arrest
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 1 mg. May repeat q3–5min as needed. CHILDREN: Initially, 0.01 mg/kg (0.1 ml/kg of a 1:10,000 solution). May repeat q3–5min as needed.
Endotracheal: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2–2.5 mg q3–5 min as needed. CHILDREN: 0.1 mg/kg (0.1 ml/kg of a 1:1,000 solution). May repeat q3–5min as needed.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Systemic: Tachycardia, palpitations, anxiety. Ophthalmic: Headache, eye irritation, watering of eyes. Occasional: Systemic: Dizziness, light-headedness, facial flushing, headache, diaphoresis, increased B/P, nausea, trembling, insomnia, vomiting, fatigue. Ophthalmic: Blurred/decreased vision, eye pain. Rare: Systemic: Chest discomfort/pain, arrhythmias, bronchospasm, dry mouth/throat.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Excessive doses may cause acute hypertension, arrhythmias. Prolonged/excessive use may result in metabolic acidosis due to increased serum lactic acid. Metabolic acidosis may cause disorientation, fatigue, hyperventilation, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor changes of B/P, HR. Assess lung sounds for rhonchi, wheezing, rales. Monitor ABGs. In cardiac arrest, adhere to ACLS protocols.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid excessive use of caffeine. • Report any new symptoms (tachycardia, shortness of breath, dizziness) immediately: may be systemic effects.
eplerenone
ep-ler-e-none
(Inspra)
Do not confuse Inspra with Spiriva.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Aldosterone receptor antagonist. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive.
USES
Treatment of hypertension alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents. Treatment of HF following acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to eplerenone. Concurrent use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole), CrCl less than 30 ml/min, serum potassium level greater than 5.5 mEq/L. Hypertension (Additional): Type 2 diabetes with microalbuminuria; CrCl less than 50 ml/min; serum creatinine greater than 2 mg/dL in men, greater than 1.8 mg/dL in women; concomitant use of potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics. Cautions: Hyperkalemia, HF, post-MI, diabetes, mild renal impairment.
ACTION
Binds to mineralocorticoid receptors in kidney, heart, blood vessels, brain, blocking binding of aldosterone. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces B/P.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Absorption unaffected by food. Protein binding: 50%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine (67%), feces (32%). Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 4–6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: ACE inhibitors (e.g., enalapril, lisinopril), angiotensin II antagonists (e.g., losartan, valsartan), potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., spironolactone), potassium supplements increase risk of hyperkalemia. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., itraconazole, ketoconazole) increase concentration five-fold (use is contraindicated). NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive effect. HERBAL: St. John’s wort decreases effectiveness. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase potential for hyperkalemia, arrhythmias. LAB VALUES: May increase serum potassium, ALT, AST, cholesterol, triglycerides, serum creatinine, uric acid. May decrease serum sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets: 25 mg, 50 mg.
Tablets: 25 mg, 50 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide film-coated tablets. • May give without regard to food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 50 mg once daily. If 50 mg once daily produces an inadequate B/P response, may increase dosage to 50 mg twice daily. If pt is concurrently receiving CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin, saquinavir, verapamil, or fluconazole), reduce initial dose to 25 mg once daily.
HF Following MI
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 25 mg once daily. If tolerated, titrate up to 50 mg once daily within 4 wks.
Dosage Adjustment for Serum Potassium Concentrations in HF
Less than 5 mEq/L: Increase dose from 25 mg daily to 50 mg daily or increase dose from 25 mg every other day to 25 mg daily.
5–5.4 mEq/L: No adjustment needed.
5.5–5.9 mEq/L: Decrease dose from 50 mg daily to 25 mg daily. Decrease dose from 25 mg daily to 25 mg every other day. Decrease dose from 25 mg every other day to withhold medication.
6 mEq/L or Greater: Withhold medication until potassium is less than 5.5 mEq/L, then restart at 25 mg every other day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Use is contraindicated in pts with hypertension with CrCl less than 50 ml/min or serum creatinine greater than 2 mg/dL in males or greater than 1.8 mg/dL in females. All other indications, CrCl less than 30 ml/min, use is contraindicated.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Rare (3%–1%): Dizziness, diarrhea, cough, fatigue, flu-like symptoms, abdominal pain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hyperkalemia may occur, particularly in pts with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain B/P, apical pulse immediately before each dose, in addition to regular monitoring (be alert to fluctuations). If excessive reduction in B/P occurs, place pt in supine position, feet slightly elevated.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Monitor serum potassium levels. Assess B/P for hypertension/hypotension. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess for evidence of flu-like symptoms.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established (possible dizziness effect). • Hypertension requires lifelong control. • Avoid exercising during hot weather (risk of dehydration, hypotension). • Do not use salt substitutes containing potassium.
epoetin alfa

e-poe-e-tin al-fa
(Epogen, Eprex
![]() , Procrit)
, Procrit)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of serious cardiovascular events, thromboembolic events, mortality, time-to-tumor progression in pts with head and neck cancer, metastatic breast cancer, non–small-cell lung cancer when administered to a target hemoglobin of more than 11 g/dL. Increases rate of deep vein thrombosis in perioperative pts not receiving anticoagulant therapy.
Increased risk of serious cardiovascular events, thromboembolic events, mortality, time-to-tumor progression in pts with head and neck cancer, metastatic breast cancer, non–small-cell lung cancer when administered to a target hemoglobin of more than 11 g/dL. Increases rate of deep vein thrombosis in perioperative pts not receiving anticoagulant therapy.
Do not confuse epoetin with darbepoetin, or Epogen with Neupogen.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Glycoprotein. CLINICAL: Erythropoietin.
USES
Treatment of anemia in pts receiving or who have received myelosuppressive chemotherapy for a planned minimum of 2 mos of chemotherapy pts with chronic renal failure to decrease need for RBC transfusion; HIV-infected pts on zidovudine (AZT) therapy when endogenous erythropoietin levels are 500 mUnits/ml or less; pts scheduled for elective noncardiac, nonvascular surgery, reducing need for allogenic blood transfusions when perioperative Hgb is greater than 10 or less than or equal to 13 g/dl and high risk for blood loss. OFF-LABEL: Anemia in myelodysplastic syndromes.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to epoetin. Pure red cell aplasia, uncontrolled hypertension. Cautions: History of seizures or controlled hypertension. Cancer pts: Tumor growth, shortened survival may occur when Hgb levels of 11 g/dL or greater are achieved with epoetin alfa. Chronic renal failure pts: Increased risk for serious cardiovascular reactions (e.g., stroke, MI) when Hgb levels greater than 11 g/dL are achieved with epoetin alfa.
ACTION
Stimulates division, differentiation of erythroid progenitor cells in bone marrow. Therapeutic Effect: Induces erythropoiesis, releases reticulocytes from bone marrow.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after subcutaneous administration. Following administration, an increase in reticulocyte count occurs within 10 days, and increases in Hgb, Hct, and RBC count are seen within 2–6 wks. Half-life: 4–13 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts 12 yrs and younger. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, phosphorus, potassium, creatinine, uric acid, sodium. May decrease bleeding time, iron concentration, serum ferritin.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution (Epogen, Procrit): 2,000 units/ml, 3,000 units/ml, 4,000 units/ml, 10,000 units/ml, 20,000 units/ml, 40,000 units/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Avoid excessive agitation of vial; do not shake (foaming).
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • No reconstitution necessary.
Rate of Administration • May be given as an IV bolus.
Storage • Refrigerate. • Vigorous shaking may denature medication, rendering it inactive.
Subcutaneous
• Mix in syringe with bacteriostatic 0.9% NaCl with benzyl alcohol 0.9% (bacteriostatic saline) at a 1:1 ratio (benzyl alcohol acts as local anesthetic; may reduce injection site discomfort). • Use 1 dose per vial; do not reenter vial. Discard unused portion.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix injection form with other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Anemia Associated with Chemotherapy
◀ ALERT ▶ Begin therapy only if Hgb less than 10 g/dL and anticipated duration of myelosuppressive chemotherapy is greater than 2 mos. Use minimum effective dose to maintain Hgb level that will avoid red blood cell transfusions. Discontinue upon completion of chemotherapy.
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 150 units/kg 3 times/wk (commonly used dose of 10,000 units 3 times/wk) or 40,000 units once wkly. IV: CHILDREN 5 YRS AND OLDER: 600 units/kg once wkly. Maximum: 40,000 units.
Increase dose:ADULTS, ELDERLY: If Hgb does not increase by greater than 1 g/dL and remains below 10 g/dL after initial 4 wks, may increase to 300 units/kg 3 times/wk or 60,000 units once wkly. CHILDREN: If Hgb does not increase by greater than 1 g/dL and remains less than 10 g/dL after initial 4 wks of once-wkly dosing, may increase dose to 900 units/kg/wk. Maximum: 60,000 units once wkly.
Decrease dose: Decrease dose by 25% if Hgb increases greater than 1 g/dL in any 2-wk period or Hgb levels reaches level that will avoid red blood cell transfusions.
Reduction of Allogenic Blood Transfusions in Elective Surgery
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 300 units/kg/day for 10 days before and 4 days after surgery.
Anemia in Chronic Renal Failure
◀ ALERT ▶ Individualize dose, using lowest dose to reduce need for RBC transfusions. ON DIALYSIS: Initiate when Hgb less than 10 g/dL; reduce dose or discontinue if Hgb approaches or exceeds 11 g/dL. NOT ON DIALYSIS: Initiate when Hgb less than 10 g/dL; reduce dose or stop if Hgb exceeds 10 g/dL.
IV, SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 50–100 units/kg 3 times/wk. CHILDREN: 50 units/kg 3 times/wk.
Maintenance: Decrease dose by 25%: If Hgb increases greater than 1 g/dL in any 2-wk period. Increase dose by 25%: If Hgb does not increase by greater than 1 g/dL after 4 wks of therapy. Do not increase dose more frequently than every 4 wks.
Note: If pt does not attain adequate response after appropriate dosing over 12 wks, do not continue to increase dose and use minimum effective dose to maintain Hgb level that will avoid red blood cell transfusions.
HIV Infection in Pts Treated with Zidovudine (AZT)
IV, SQ: ADULTS: Initially, 100 units/kg 3 times/wk for 8 wks; may increase by 50–100 units/kg 3 times/wk. Evaluate response q4–8wks thereafter. Adjust dosage by 50–100 units/kg 3 times/wk. If dosages larger than 300 units/kg 3 times/wk are not eliciting response, it is unlikely pt will respond. Maintenance: Titrate to maintain desired Hgb level. Hgb levels should not exceed 12 g/dL. If Hgb greater than 12 g/dL, resume treatment with 25% dose reduction when Hgb drops below 11 g/dL. Discontinue if Hgb increase not attained with 300 units/kg for 8 wks.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Pts Receiving Chemotherapy
Frequent (20%–17%): Fever, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, edema. Occasional (13%–11%): Asthenia, shortness of breath, paresthesia. Rare (5%–3%): Dizziness, trunk pain.
Pts with Chronic Renal Failure
Frequent (24%–11%): Hypertension, headache, nausea, arthralgia. Occasional (9%–7%): Fatigue, edema, diarrhea, vomiting, chest pain, skin reactions at administration site, asthenia, dizziness.
Pts with HIV Infection Treated with AZT
Frequent (38%–15%): Fever, fatigue, headache, cough, diarrhea, rash, nausea. Occasional (14%–9%): Shortness of breath, asthenia, skin reaction at injection site, dizziness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hypertensive encephalopathy, thrombosis, cerebrovascular accident, MI, seizures occur rarely. Hyperkalemia occurs occasionally in pts with chronic renal failure, usually in those who do not comply with medication regimen, dietary guidelines, frequency of dialysis regimen.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess B/P before drug initiation (80% of pts with chronic renal failure have history of hypertension). B/P often rises during early therapy in pts with history of hypertension. Consider that all pts eventually need supplemental iron therapy. Assess serum iron (should be greater than 20%), serum ferritin (should be greater than 100 ng/ml) before and during therapy. Establish baseline CBC (esp. note Hct).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess CBC rountinely (esp. Hgb, Hct). Monitor aggressively for increased B/P (25% of pts require antihypertensive therapy, dietary restrictions). Monitor temperature, esp. in cancer pts on chemotherapy and zidovudine-treated HIV pts. Monitor serum BUN, uric acid, creatinine, phosphorus, potassium, esp. in chronic renal failure pts.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Frequent laboratory assessments needed to determine correct dosage. • Immediately report any severe headache. • Avoid potentially hazardous activity during first 90 days of therapy (increased risk of seizures in pts with chronic renal failure during first 90 days). • Specific dietary regimen must be maintained.
eprosartan
ep-roe-sar-tan
(Teveten)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
FIXED COMBINATION(S)
Teveten HCT: eprosartan/hydrochlorothiazide (a diuretic): 400 mg/12.5 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Angiotensin II receptor antagonist. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive.
USES
Treatment of hypertension (alone or in combination with other medications).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to eprosartan. Concomitant use with aliskiren in pts with diabetes. Cautions: Unstented unilateral/bilateral renal artery stenosis, preexisting renal insufficiency. Concomitant use of potassium-sparing medications (e.g., spironolactone), potassium supplements, pts who are volume depleted.
ACTION
Potent vasodilator. Blocks vasoconstrictor, aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II, inhibiting binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Causes vasodilation, decreases peripheral resistance, decreases B/P.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 98%. Minimally metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted via urine, biliary system. Minimally removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 5–9 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Has caused fetal and neonatal morbidity and mortality. Potential for adverse effects on breastfeeding infant. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., spironolactone, triamterene), potassium supplements may increase risk of hyperkalemia. May produce additive effect with antihypertensive agents. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Garlic may increase antihypertensive effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, creatinine, ALT, AST. May decrease Hgb, Hct.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets: 400 mg, 600 mg.
Tablets: 400 mg, 600 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 600 mg/day. Range: 400–800 mg/day as single dose or 2 divided doses.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment: Maximum: 600 mg/day.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Maximum: 600 mg/day.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (5%–2%): Headache, cough, dizziness. Rare (less than 2%): Muscle pain, fatigue, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, dyspepsia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdosage may manifest as hypotension, tachycardia. Bradycardia occurs less often.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain B/P, apical pulse immediately before each dose, in addition to regular monitoring (be alert to fluctuations). Question for possibility of pregnancy, history of hepatic/renal impairment, renal artery stenosis. Assess medication history (esp. diuretics).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, pulse, serum BUN, creatinine, electrolytes, urinalysis.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Inform female pt regarding consequences of second- and third-trimester exposure to medication. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Restrict sodium, alcohol intake. • Follow diet, control weight. • Do not stop taking medication; hypertension requires lifelong control. • Check B/P regularly. • Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets; take whole.
eptifibatide

ep-ti-fye-ba-tide
(Integrilin)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiplatelet, antithrombotic.
USES
Treatment of pts with acute coronary syndrome (ACS), including those managed medically and those undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). OFF-LABEL: Support PCI during ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to eptifibatide. Active abnormal bleeding within previous 30 days; history of bleeding diathesis; history of stroke within 30 days or history of hemorrhagic stroke; severe hypertension (systolic B/P greater than 200 mmHg or diastolic B/P greater than 110 mmHg); major surgery within previous 6 wks, dependency on hemodialysis. Cautions: Renal impairment, hemorrhagic retinopathy, platelet count less than 100,000/mm3, elderly, history of bleeding disorder. Medications that increase risk of bleeding (e.g., oral anticoagulants, NSAIDs). Pregnancy Category B.
ACTION
Blocks platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor (binding site for fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor). Therapeutic Effect: Prevents thrombus formation within coronary arteries. Prevents platelet aggregation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Protein binding: 25%. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 2.5 hrs.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anticoagulants, heparin, NSAIDs, antiplatelets (e.g., clopidogrel), thrombolytic agents may increase risk of bleeding. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo, ginseng may increase antiplatelet effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Increases PT, aPTT. Decreases platelet count. Prolongs clotting time.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Withdraw bolus dose from 10-ml vial (2 mg/ml); for IV infusion, withdraw from 100-ml vial (0.75 mg/ml). • IV push and infusion administration may be given undiluted.
Rate of Administration • Give bolus dose IV push over 1–2 min.
Storage • Store vials in refrigerator. • Solution appears clear, colorless. • Do not shake. • Discard any unused portion left in vial or if preparation contains any opaque particles.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Administer via dedicated line; do not add other medications to infusion solution.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), argatroban, bivalirudin, metoprolol (Lopressor).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Adjunct to Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
IV Bolus, IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 180 mcg/kg (maximum: 22.6 mg) before PCI initiation; then continuous drip of 2 mcg/kg/min and a second 180 mcg/kg (maximum: 22.6 mg) bolus 10 min after the first. Maximum: 15 mg/hr. Continue until hospital discharge or for up to 18–24 hrs. Minimum 12 hrs is recommended. Concurrent aspirin and heparin therapy is recommended.
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
IV Bolus, IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 180 mcg/kg over 1–2 min (maximum: 22.6 mg) bolus then 2 mcg/kg/min until discharge or coronary artery bypass graft, up to 72 hrs. Maximum: 15 mg/hr. Concurrent aspirin and heparin therapy is recommended.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl Less than 50 ml/min: Use 180 mcg/kg bolus (maximum: 22.6 mg) and 1 mcg/kg/min infusion (maximum: 7.5 mg/hr). End-Stage Renal Disease (Dialysis): Contraindicated.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (7%): Hypotension.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Minor to major bleeding complications may occur, most commonly at arterial access site for cardiac catheterization.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess platelet count, Hgb, Hct before treatment and during therapy. If platelet count less than 90,000/mm3, additional platelet counts should be obtained routinely to avoid thrombocytopenia.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Diligently monitor for potential bleeding, particularly at other arterial, venous puncture sites. If possible, urinary catheters, nasogastric tubes should be avoided.
*eriBULin
er-i-bue-lin
(Halaven)
Do not confuse eribulin with epirubicin or erlotinib.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Microtubule inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of metastatic breast cancer in pts who previously received at least 2 chemotherapeutic regimens for treatment. Treatment of metastatic liposarcoma in pts who received a prior anthracycline-containing regimen.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to eribulin. Cautions: Prolonged QTc (congenital, other medications that prolong QT interval), hypokalemia, hypomagnesium, hepatic/renal impairment, moderate to severe neuropathy, HF.
ACTION
Binds directly on microtubules during active stage of G2 and M phases of cell cycle, preventing formation of microtubules, an essential part of process of separation of chromosomes. Therapeutic Effect: Blocks cells in mitotic phase of cell division, leading to cell death.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Extensively metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 49%–65%. Excreted in feces (82%), urine (9%). Half-life: 40 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause embryo-fetal toxicity. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. FOOD: None known. HERBAL: None significant. LAB VALUES: May decrease WBC, Hgb, Hct, platelet count, potassium. May increase ALT.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution: 1 mg/2 ml (0.5-mg/ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • May administer undiluted or dilute in 100 ml 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • Administer over 2–5 min.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Once diluted, syringe or diluted solution may be stored for up to 4 hrs at room temperature or up to 24 hrs if refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not dilute with D5W or administer through IV line containing solutions with dextrose or in same IV line with other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Metastatic Breast Cancer, Liposarcoma
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1.4 mg/m2 over 2–5 min on days 1 and 8 of 21-day cycle.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild: No dose adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment (CrCl 15–49 ml/min): 1.1 mg/m2/dose.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild: 1.1 mg/m2/dose. Moderate impairment: 0.7 mg/m2/dose. Severe impairment: Use not recommended.
Recommended Dose Delays
Do not administer day 1 or day 8 of treatment for any of the following: ANC less than 1,000/mm3, platelets less than 75,000/mm3, Grade 3 or 4 nonhematologic toxicities. Day 8 dose may be delayed for maximum of 1 wk. If toxicities do not resolve or improve to Grade 2 severity by day 15, omit dose. If toxicities resolve or improve to Grade 2 severity by day 15, continue treatment at reduced dose and initiate next cycle no sooner than 2 wks later. Do not re-escalate dose after it has been reduced.
SIDE EFFECTS
Common (54%–35%): Fatigue, asthenia, alopecia, peripheral sensory neuropathy, nausea. Frequent (25%–18%): Constipation, arthralgia/myalgia, decreased weight, anorexia, pyrexia, headache, diarrhea, vomiting. Occasional (16%–9%): Back pain, dyspnea, cough, bone pain, extremity pain, urinary tract infection, oral mucosal inflammation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Neutropenia occurs in 82% of pts, with 57% developing grade 3 neutropenia. Severe neutropenia (ANC less than 500/mm3) lasting more than 1 wk occurred in 12%. Anemia occurs in 58% of pts. Peripheral neuropathy occurs in 8% of pts but is the most common adverse reaction requiring discontinuation of therapy. Prolonged QTc may be noted on or after day 8 of treatment.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for possibility of pregnancy. Obtain baseline CBC, serum chemistries before treatment begins. Obtain CBC prior to each dose.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Diligently monitor for neutropenia, peripheral neuropathy (most frequent cause of drug discontinuation). Monitor for symptoms of neuropathy (burning sensation, hyperesthesia, hypoesthesia, paresthesia, discomfort, neuropathic pain). Assess hands, feet for erythema. Monitor CBC for evidence of neutropenia, thrombocytopenia. Assess mouth for stomatitis (erythema, ulceration, mucosal burning).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid crowds, those with known infection. • Avoid contact with anyone who recently received live virus vaccine. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers body resistance). • Promptly report fever over 100.5°F, chills, cough, burning or pain urinating, numbness, tingling, burning sensation, erythema of hands/feet.
erlotinib

er-loe-ti-nib
(Tarceva)
Do not confuse erlotinib with dasatinib, eribulin, geftinib, imatinib, or lapatinib.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Human epidermal growth factor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after failure of at least one prior chemotherapy regimen (as monotherapy). Treatment of locally advanced, unresectable, or metastatic pancreatic cancer (in combination with gemcitabine). Maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC that has not progressed after 4–6 cycles of first-line platinum-based chemotherapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to erlotinib. Cautions: Severe hepatic/renal impairment cardiovascular disease. Concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors and inducers, pts at risk for GI perforation (e.g., peptic ulcer disease, diverticular disease). Total serum bilirubin greater than 3 times upper limit of normal.
ACTION
Reversibly inhibits overall epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)–tyrosine kinase activity. Therapeutic Effect: Produces tumor cell death.
PHARMACOKINETICS
About 60% is absorbed after PO administration; bioavailability is increased by food to almost 100%. Protein binding: 93%. Extensively metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated in feces (83%), urine (8%). Half-life: 24–36 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., atanzavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir) may increase concentration/effects. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effects. Proton pump inhibitors (e.g., omeprazole), H2antagonists (e.g., ranitidine) may decrease absorption/effects (avoid use of proton pump inhibitors. Give ertapenem 10 hrs after or 2 hrs prior to H2 antagonists). HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase potential for myelotoxicity. LAB VALUES: May increase serum bilirubin, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 25 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give at least 1 hr before or 2 hrs after ingestion of food. • Avoid grapefruit products. • May dissolve in 3–4 oz water and give orally or via feeding tube.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Dosage adjustment for toxicity: Reduce dose in 50-mg increments.
Lung Cancer
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 150 mg/day until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
Pancreatic Cancer
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100 mg/day, in combination with gemcitabine, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Interrupt dosing for Grade 3 or 4 renal toxicity during treatment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use extreme caution. Reduce starting dose to 75 mg and individualize dose escalation if tolerated.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (greater than 10%): Fatigue, anxiety, headache, depression, insomnia, rash, pruritus, dry skin, erythema, diarrhea, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, mucositis, constipation, dyspepsia, weight loss, dysphagia, abdominal pain, arthralgia, dyspnea, cough. Occasional (10%–1%): Keratitis. Rare (less than 1%): Corneal ulceration.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
UTI occurs occasionally. Pneumonitis, GI bleeding occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC, serum electrolytes, hepatic enzyme levels before beginning therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess LFT and CBC, renal function, serum electrolytes, hydration status periodically.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take drug on empty stomach. • Report rash, blood in stool, diarrhea, irritated eyes, fever. • Avoid grapefruit products.
ertapenem
er-ta-pen-em
(Invanz)
Do not confuse ertapenem with doripenem, imipenem, or merropenem, or Invanz with Avinza.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
USES
Treatment of susceptible infections due to S. aureus (methicillin-susceptible only), S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible only), S. pyogenes, E. coli, H. influenzae (beta-lactamase negative strains only), K. pneumoniae, M. catarrhalis, Bacteroides spp., C. clostridioforme, Peptostreptococcus spp., including moderate to severe intra-abdominal, skin/skin structure infections; community-acquired pneumonia; complicated UTI; acute pelvic infection; adult diabetic foot infections without osteomyelitis. Prevention of surgical site infection. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of IV catheter–related bloodstream infection; prosthetic joint infection.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ertapenem. History of anaphylactic hypersensitivity to beta-lactams (e.g., imipenem and cilastin, meropenem), hypersensitivity to amide-type local anesthetics (IM). Cautions: Hypersensitivity to penicillins, cephalosporins, renal impairment, CNS disorders, esp. brain lesions or history of seizures, elderly.
ACTION
Penetrates bacterial cell wall of microorganisms, binds to penicillin-binding proteins, inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Produces bacterial cell death.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Almost completely absorbed after IM administration. Protein binding: 85%–95%. Widely distributed. Primarily excreted in urine (80%), feces (10%). Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: Advanced or end-stage renal insufficiency may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Probenecid may increase concentration/effect. May decrease concentration/effect of valproic acid. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, bilirubin, BUN, creatinine, glucose, PT, aPTT, sodium. May decrease platelet count, Hgb, Hct, WBC.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 1 g.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Dilute 1-g vial with 10 ml 0.9% NaCl or Bacteriostatic Water for Injection. • Shake well to dissolve. • Further dilute with 50 ml 0.9% NaCl (maximum concentration: 20 mg/ml).
Rate of Administration • Give by intermittent IV infusion (piggyback). Do not give IV push. • Infuse over 30 min.
Storage • Solution appears colorless to yellow (variation in color does not affect potency). • Discard if solution contains precipitate. • Reconstituted solution is stable for 6 hrs at room temperature or 24 hrs if refrigerated.
IM
• Reconstitute with 3.2 ml 1% lidocaine HCl injection (without epinephrine). • Shake vial thoroughly. • Inject deep in large muscle mass (gluteal or lateral part of thigh). • Administer suspension within 1 hr after preparation.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix or infuse with any other medications. Do not use diluents or IV solutions containing dextrose.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Heparin, potassium chloride, tigecycline (Tygacil), Sterile Water for Injection, 0.9% NaCl.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage Range
IM, IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 13 YRS AND OLDER: 1 g/day. CHILDREN 3 MOS–12 YRS: 15 mg/kg 2 times/day. Maximum: 1 g/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| CrCl 30 ml/min or less | 500 mg once daily |
| Hemodialysis | If daily dose given within 6h prior to HD, give 150 mg dose after HD. |
| Peritoneal dialysis | 500 mg once daily |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (10%–6%): Diarrhea, nausea, headache. Occasional (5%–2%): Altered mental status, insomnia, rash, abdominal pain, constipation, chest pain, vomiting, edema, fever. Rare (less than 2%): Dizziness, cough, oral candidiasis, anxiety, tachycardia, phlebitis at IV site.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Antibiotic-associated colitis, other superinfections (abdominal cramps, severe watery diarrhea, fever) may result from altered bacterial balance in GI tract. Anaphylactic reactions have been reported. Seizures may occur in those with CNS disorders (brain lesions, history of seizures), bacterial meningitis, severe renal impairment.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of allergies, particularly to beta-lactams, penicillins, cephalosporins. Inquire about history of seizures. Monitor WBC count.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor renal/hepatic function. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor for nausea, vomiting. Evaluate hydration status. Evaluate for inflammation at IV injection site. Assess skin for rash. Observe mental status; be alert to tremors, possible seizures. Assess sleep pattern for evidence of insomnia.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report tremors, seizures, rash, prolonged diarrhea, chest pain, other new symptoms.
erythromycin
er-ith-roe-mye-sin
(Akne-Mycin, Apo-Erythro Base
![]() , EES, Erybid
, EES, Erybid
![]() , Eryc, EryDerm, EryPed, Ery-Tab, Erythrocin, PCE Dispertab)
, Eryc, EryDerm, EryPed, Ery-Tab, Erythrocin, PCE Dispertab)
Do not confuse Eryc with Emcyt, or erythromycin with azithromycin or clarithromycin.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Eryzole, Pediazole: erythromycin/sulfisoxazole (sulfonamide): 200 mg/600 mg per 5 ml.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Macrolide. CLINICAL: Antibiotic, antiacne.
USES
Treatment of susceptible infections due to S. pyogenes, S. pneumoniae, S. aureus, M. pneumoniae, Legionella, Chlamydia, N. gonorrheae, E. histolytica, including syphilis, nongonococcal urethritis, diphtheria, pertussis, chancroid, Campylobacter gastroenteritis. Topical: Treatment of acne vulgaris. Ophthalmic: Prevention of gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum, superficial ocular infections. OFF-LABEL: Systemic: Treatment of acne vulgaris, chancroid, Campylobacter enteritis, gastroparesis, Lyme disease, preoperative gut sterilization. Topical: Treatment of minor bacterial skin infections. Ophthalmic: Treatment of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, chlamydial trachoma.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to erythromycin. Concomitant administration with ergot derivatives, lovastatin, simvastatin. Cautions: Elderly, myasthenia gravis, strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, hepatic impairment, pts with prolonged QT intervals, uncorrected hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, concurrent use of class IA or III antiarrhythmics.
ACTION
Penetrates bacterial cell membranes, reversibly binds to bacterial ribosomes, inhibiting protein synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Bacteriostatic.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Variably absorbed from GI tract (depending on dosage form used). Protein binding: 70%–90%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated in feces by bile. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 1.4–2 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Erythromycin estolate may increase hepatic enzymes in pregnant women. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted. High dosage in pts with decreased hepatic/renal function increases risk of hearing loss.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration of buspirone, cyclosporine, calcium channel blockers (e.g., diltiazem, verapamil), statins (e.g., atorvastatin, simvastatin). May inhibit metabolism of carbamazepine. Hepatotoxic medications may increase risk of hepatotoxicity. May increase risk of theophylline toxicity. May increase effects of warfarin. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. FOOD: Grapefruit may increase potential for torsades. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Gel, Topical: 2%. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 500 mg, 1 g. Ointment, Ophthalmic: 0.5%. Ointment, Topical (Akne-Mycin): 2%. Oral Suspension (EES, EryPed): 100 mg/2.5 ml, 200 mg/5 ml, 400 mg/5 ml. Tablet as Base: 250 mg, 333 mg, 500 mg. Tablet as Ethylsuccinate (EES): 400 mg.
![]() Capsules, Delayed-Release (Eryc):
Capsules, Delayed-Release (Eryc):
![]() 250 mg. Tablets, Delayed-Release (Ery-Tab): 250 mg, 333 mg, 500 mg.
250 mg. Tablets, Delayed-Release (Ery-Tab): 250 mg, 333 mg, 500 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute each 500 mg with 10 ml Sterile Water for Injection without preservative to provide a concentration of 50 mg/ml. • Further dilute with 100–250 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl to maximum concentration of 5 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • For intermittent IV infusion (piggyback), infuse over 20–60 min.
Storage • Store parenteral form at room temperature. • Initial reconstituted solution in vial is stable for 2 wks refrigerated or 24 hrs at room temperature. • Diluted IV solution stable for 8 hrs at room temperature or 24 hrs if refrigerated. • Discard if precipitate forms.
PO
• May give with food to decrease GI upset. Do not give with milk or acidic beverages. • Oral suspension is stable for 35 days at room temperature. • Do not crush delayed-release capsules, tablets.
Ophthalmic
• Place gloved finger on lower eyelid and pull out until a pocket is formed between eye and lower lid. • Place ¼–½ inch of ointment into pocket. • Instruct pt to close eye gently for 1–2 min (so medication will not be squeezed out of the sac) and to roll eyeball to increase contact area of drug to eye.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Fluconazole (Diflucan), furosemide (Lasix), heparin, metoclopramide (Reglan).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), diltiazem (Cardizem), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, midazolam (Versed), morphine, multivitamins, potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage Range
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: BASE: 250–500 mg q6–12h. CHILDREN: 30–50 mg/kg/day in 2–4 divided doses. Maximum: 2 g/day. ETHYLSUCCINATE: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400–800 mg q6–12h. Maximum: 4 g/day. CHILDREN: 30–50 mg/kg/day in divided doses. Maximum: 3.2 g/day. NEONATES: 10 mg/kg/dose q8–12h.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 15–20 mg/kg/day divided q6h. Maximum: 4 g/day. CHILDREN, INFANTS: 15–20 mg/kg/day divided q6h. Maximum: 4 g /day. NEONATES: 10 mg/ks/dose q8–12h.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: IV: Abdominal cramping/discomfort, phlebitis/thrombophlebitis. Topical: Dry skin (50%). Occasional: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash, urticaria. Rare: Ophthalmic: Sensitivity reaction with increased irritation, burning, itching, inflammation. Topical: Urticaria.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Antibiotic-associated colitis, other super infections (abdominal cramps, severe watery diarrhea, fever), reversible cholestatic hepatitis may occur. High dosage in pts with renal impairment may lead to reversible hearing loss. Anaphylaxis occurs rarely. Ventricular arrhythmias, prolonged QT interval occur rarely with IV form.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of allergies (particularly erythromycins), hepatitis.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess skin for rash. Assess for hepatotoxicity (malaise, fever, abdominal pain, GI disturbances). Be alert for superinfection: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, anal/genital pruritus, oral mucosal changes (ulceration, pain, erythema). Check for phlebitis (heat, pain, red streaking over vein). Monitor for high-dose hearing loss.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Continue therapy for full length of treatment. • Doses should be evenly spaced. • Take medication with 8 oz water 1 hr before or 2 hrs following food or beverage. • Ophthalmic: Report burning, itching, inflammation. • Topical: Report excessive skin dryness, itching, burning. • Improvement of acne may not occur for 1–2 mos; maximum benefit may take 3 mos; therapy may last mos or yrs. • Use caution if using other topical acne preparations containing peeling or abrasive agents, medicated or abrasive soaps, cosmetics containing alcohol (e.g., astringents, aftershave lotion).
escitalopram
es-sye-tal-o-pram
(Apo-Escitalopram
![]() , Cipralex
, Cipralex
![]() , Lexapro)
, Lexapro)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Serotonin reuptake inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antidepressant.
USES
Treatment of major depressive disorder.Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). OFF-LABEL: Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) in children and adolescents, pervasive developmental disorders (e.g., autism), vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to escitalopram. Use of MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders (concurrent or within 14 days of discontinuing either escitalopram or MAOI). Initiation in pts receiving linezolid or IV methylene blue. Concurrent use with pimozide. Cautions: Hepatic/renal impairment, history of seizures, concurrent use of CNS depressants, pts at high risk of suicide, concomitant aspirin, NSAIDs, warfarin (may potentiate bleeding risk), elderly, metabolic disease; recent history of MI, cardiovascular disease.
ACTION
Blocks uptake of neurotransmitter serotonin at neuronal presynaptic membranes, increasing its availability at postsynaptic receptor sites. Therapeutic Effect: Antidepressant effect.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 56%. Primarily metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in feces, with a lesser amount eliminated in urine. Half-life: 35 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. Children: May cause increased anticholinergic effects or hyperexcitability. Elderly: More sensitive to anticholinergic effects (e.g., dry mouth), more likely to experience dizziness, sedation, confusion, hypotension, hyperexcitability.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS suppressants may increase CNS depression. Linezolid, aspirin, NSAIDs, warfarin may increase risk of bleeding. MAOIs may cause serotonin syndrome (autonomic hyperactivity, diaphoresis, excitement, hyperthermia, rigidity, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, coma). Sumatriptan may cause weakness, hyperreflexia, poor coordination. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, SAMe, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. Ginkgo biloba, St. John’s wort may increase risk of serotonin syndrome. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Oral Solution: 5 mg/5 ml.
![]() Tablets: 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg.
Tablets: 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Depression
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 10 mg once daily in the morning or evening. May increase to 20 mg after a minimum of 1 wk. ELDERLY: 10 mg/day. CHILDREN 12–17 YRS: Initially, 10 mg once daily. May increase to 20 mg/day after at least 3 wks. Maximum: 20 mg once daily. Recommended: 10 mg once daily.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 10 mg once daily in morning or evening. May increase to 20 mg after minimum of 1 wk. ELDERLY: 10 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Use caution in pts with CrCl less than 20 ml/min.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
10 mg/day.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (21%–11%): Nausea, dry mouth, drowsiness, insomnia, diaphoresis. Occasional (8%–4%): Tremor, diarrhea, abnormal ejaculation, dyspepsia, fatigue, anxiety, vomiting, anorexia. Rare (3%–2%): Sinusitis, sexual dysfunction, menstrual disorder, abdominal pain, agitation, decreased libido.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose manifested as dizziness, drowsiness, tachycardia, confusion, seizures.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
For pts on long-term therapy, LFT, renal function tests, blood counts should be performed periodically. Observe, record behavior. Assess psychological status, thought content, sleep pattern, appearance, interest in environment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Supervise suicidal-risk pt closely during early therapy (as depression lessens, energy level improves, suicide potential increases). Assess appearance, behavior, speech pattern, level of interest, mood. Monitor for suicidal ideation (esp. at beginning of therapy or when doses are increased or decreased), social interaction, mania, panic attacks.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not stop taking medication or increase dosage. • Avoid alcohol. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Report worsening depression, suicidal ideation, unusual changes in behavior.
esmolol

es-moe-lol
(Brevibloc)
Do not confuse Brevibloc with Bumex or Buprenex, or esmolol with Osmitrol.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Beta1-adrenergic blocker. CLINICAL: Antiarrhythmic.
USES
Rapid, short-term control of ventricular rate in supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), atrial fibrillation or flutter; treatment of tachycardia and/or hypertension (esp. intraop or postop). Treatment of noncompensatory sinus tachycardia. OFF-LABEL: Postoperative hypertension or SVT in children. Arrhythmia and/or rate control in ACS, intubation, thyroid storm, pheochromocytoma, electroconvulsive therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to esmolol. Cardiogenic shock, uncompensated cardiac failure, second- or third-degree heart block (except in pts with pacemaker), severe sinus bradycardia, sick sinus syndrome in close proximity to esmolol, IV administration of calcium blockers, pulmonary hypertension. Cautions: Compensated HF; concurrent use of digoxin, verapamil, diltiazem. Diabetes, myasthenia gravis, renal impairment, history of anaphylaxis to allergens. Hypovolemia, hypertension, bronchospastic disease, peripheral vascular disease, Raynaud’s disease.
ACTION
Selectively blocks beta1-adrenergic receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Slows sinus heart rate, decreases cardiac output, reducing B/P.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly metabolized primarily by esterase in cytosol of red blood cells. Protein binding: 55%. Less than 1%–2% excreted in urine. Half-life: 9 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Opioids (e.g., fentanyl, morphine), calcium channel blockers (e.g., diltiazem, verapamil), MAOIs may increase level/effects. HERBAL: Yohimbe may decrease effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 10 mg/ml (250 ml), 20 mg/ml (100 ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Give by IV infusion. Avoid butterfly needles, very small veins (can cause thrombophlebitis).
![]() IV
IV
Rate of Administration • Administer by controlled infusion device; titrate to tolerance and response. • Infuse IV loading dose over 1–2 min. • Hypotension (systolic B/P less than 90 mm Hg) is greatest during first 30 min of IV infusion.
Storage • Use only clear and colorless to light yellow solution. • Discard solution if discolored or precipitate forms.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), furosemide (Lasix).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), dopamine (Intropin), heparin, magnesium, midazolam (Versed), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Rate Control in Supraventricular Arrhythmias
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, loading dose of 500 mcg/kg/min for 1 min, followed by 50 mcg/kg/min for 4 min. If optimum response is not attained in 5 min, give second loading dose of 500 mcg/kg/min for 1 min, followed by infusion of 100 mcg/kg/min for 4 min. A third (and final) loading dose can be given and infusion increased by 50 mcg/kg/min, up to 200 mcg/kg/min, for 4 min. Once desired response is attained, increase infusion by no more than 25 mcg/kg/min. Infusion usually administered over 24–48 hrs in most pts. Range: 50–200 mcg/kg/min (average dose 100 mcg/kg/min).
Intraop/Postop Tachycardia Hypertension (Immediate Control)
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 1 mg/kg over 30 sec, then 150 mcg/kg/min infusion up to 300 mcg/kg/min.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Generally well tolerated, with transient, mild side effects. Frequent: Hypotension (systolic B/P less than 90 mm Hg) manifested as dizziness, nausea, diaphoresis, headache, cold extremities, fatigue. Occasional: Anxiety, drowsiness, flushed skin, vomiting, confusion, inflammation at injection site, fever.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may produce profound hypotension, bradycardia, dizziness, syncope, drowsiness, breathing difficulty, bluish fingernails or palms of hands, seizures. May potentiate insulin-induced hypoglycemia in diabetic pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess B/P, apical pulse immediately before drug is administered (if pulse is 60 or less/min or systolic B/P is 90 mm Hg or less, withhold medication, contact physician).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P for hypotension, EKG, heart rate, respiratory rate, development of diaphoresis, dizziness (usually first sign of impending hypotension). Assess pulse for quality, irregular rate, bradycardia, extremities for coldness. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Assess for nausea, diaphoresis, headache, fatigue.
esomeprazole
es-o-mep-ra-zole
(Apo-Esomeprazole
![]() , Nexium, Nexium 24 HR)
, Nexium, Nexium 24 HR)
Do not confuse esomeprazole with aripiprazole or omeprazole, or Nexium with Nexavar.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Vimovo: esomeprazole/naproxen (NSAID): 20 mg/375 mg, 20 mg/500 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Proton pump inhibitor. CLINICAL: Gastric acid inhibitor.
USES
PO: Short-term treatment (4–8 wks) of erosive esophagitis; maintenance treatment of healing of erosive esophagitis; symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Treatment of pathologic hypersecretory conditions, including Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Used in triple therapy with amoxicillin and clarithromycin for treatment of H. pylori infection in pts with duodenal ulcer. Reduces risk of NSAID-induced gastric ulcer. (OTC) Treatment of frequent heartburn (2 or more days/wk). IV: Treatment of GERD with erosive esophagitis. Reduce risk of ulcer re-bleeding postprocedures.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to esomeprazole, other proton pump inhibitors. Cautions: May increase risk of hip, wrist, spine fractures; hepatic impairment; elderly; Asian populations. Concurrent use of CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin).
ACTION
Converted to active metabolites that irreversibly bind to, inhibit enzymes on surface of gastric parietal cells. Inhibits hydrogen ion transport into gastric lumen. Therapeutic Effect: Increases gastric pH; reduces gastric acid production.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 97%. Extensively metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 1–1.5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease concentration/effects of atazanavir, digoxin, iron, ketoconazole. May increase effect of warfarin. May decrease effect of clopidogrel. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin) may decrease concentration/effects. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 20 mg, 40 mg. Oral Suspension, Delayed-Release Packets: 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg.
![]() Capsules (Delayed-Release [Nexium]): 20 mg, 40 mg. [Nexium 24 HR]: 20 mg.
Capsules (Delayed-Release [Nexium]): 20 mg, 40 mg. [Nexium 24 HR]: 20 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • For IV push, add 5 ml of 0.9% NaCl to esomeprazole vial.
Infusion • For IV infusion, dissolve content of one vial in 50 ml 0.9% NaCl, or D5W.
Rate of Administration • For IV push, administer over not less than 3 min. For intermittent infusion (piggyback) infuse over 10–30 min. • Flush line with 0.9% NaCl, or D5W, both before and after administration.
Storage • Use only clear and colorless to very slightly yellow solution. • Discard solution if particulate forms. • IV infusion stable for 12 hrs in 0.9% NaCl or lactated Ringer’s; 6 hrs in D5W.
PO (Capsules)
• Give 1 hr or more before eating (best before breakfast). • Do not crush, cut capsule; administer whole. • For pts with difficulty swallowing capsules, open capsule and mix pellets with 1 tbsp applesauce. Swallow immediately without chewing.
PO (Oral Suspension)
• Empty contents into 5 ml water for 2.5 mg, 5 mg; 15 ml for 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg and stir. • Let stand 2–3 min to thicken. • Stir and drink within 30 min.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix esomeprazole with any other medications through the same IV line or tubing.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Ceftaroline (Teflaro), doripenem (Doribax).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Erosive Esophagitis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 20–40 mg once daily for 4–8 wks. May continue for additional 4–8 wks. CHILDREN 1–11 YRS, WEIGHING 20 KG OR MORE: 10–20 mg/day for up to 8 wks. WEIGHING LESS THAN 20 KG: 10 mg/day for up to 8 wks.
Maintenance Therapy for Erosive Esophagitis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20 mg/day.
Treatment of NSAID-Induced Gastric Ulcers
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20 mg/day for 4–8 wks.
Prevention of NSAID-Induced Gastric Ulcer
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20–40 mg once daily for up to 6 mos.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20 or 40 mg once daily for up to 10 days. CHILDREN 1–17 YRS, WEIGHING 55 KG OR MORE: 20 mg once daily; 1–17 YRS, WEIGHING LESS THAN 55 KG: 10 mg once daily; 1 MO TO LESS THAN 1 YR: 0.5 mg/kg once daily.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN, 12–17 YRS: 20 mg once daily for up to 8 wks. CHILDREN 1–11 YRS: 10 mg/day for up to 8 wks.
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 40 mg 2 times/day. Doses up to 240 mg/day have been used.
Duodenal Ulcer Caused by Helicobacter Pylori
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 40 mg (esomeprazole) once daily, with amoxicillin 1,000 mg and clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily for 10 days.
Heartburn (OTC)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20 mg/day for 14 days. May repeat after 4 mos if needed.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Doses should not exceed 20 mg/day.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (7%): Headache. Occasional (3%–2%): Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea. Rare (less than 2%): Dizziness, asthenia, vomiting, constipation, rash, cough.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Pancreatitis, hepatotoxicity, interstitial nephritis occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess epigastric/abdominal pain. Question history of hepatic impairment, pathologic bone fractures.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Evaluate for therapeutic response (relief of GI symptoms). Question if GI discomfort, nausea, diarrhea occur. Monitor for occult blood, observe for hemorrhage in pts with peptic ulcer.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report headache. • Take at least 1 hr before eating. • If swallowing capsules is difficult, open capsule and mix pellets with 1 tbsp applesauce. Swallow immediately without chewing.
estradiol
es-tra-dye-ole
(Alora, Climara, Delestrogen, Depo-Estradiol, Divigel, Elestrin, Estrace, Estraderm, Estrasorb, Estring, Estrogel, Evamist, Femring, Femtrace, Menostar, Minivelle, Vagifem, Vivelle-Dot)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of dementia when given to women 65 yrs and older. Use of estrogen without progestin increases risk of endometrial cancer in postmenopausal women with intact uterus. Increased risk of invasive breast cancer in postmenopausal women using conjugated estrogens with medroxyprogesterone. Do not use to prevent cardiovascular disease or dementia.
Increased risk of dementia when given to women 65 yrs and older. Use of estrogen without progestin increases risk of endometrial cancer in postmenopausal women with intact uterus. Increased risk of invasive breast cancer in postmenopausal women using conjugated estrogens with medroxyprogesterone. Do not use to prevent cardiovascular disease or dementia.
Do not confuse Alora with Aldara, or Estraderm with Testoderm.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Activella: estradiol/norethindrone (hormone): 1 mg/0.5 mg. Climara PRO: estradiol/levonorgestrel (progestin): 0.045 mg/24 hr, 0.015 mg/24 hr. Combi-patch: estradiol/norethindrone (hormone): 0.05 mg/0.14 mg, 0.05 mg/0.25 mg. Femhrt: estradiol/norethindrone (hormone): 5 mcg/1 mg. Lunelle: estradiol/medroxy-progesterone (progestin): 5 mg/25 mg per 0.5 ml.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Estrogen. CLINICAL: Estrogen, antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause, vulvar and vaginal atrophy associated with menopause, hypoestrogenism (due to hypogonadism, primary ovarian failure), metastatic breast cancer (palliation) in men and postmenopausal women, advanced prostate cancer (palliation), prevention of osteoporosis in menopausal women.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to estradiol, angioedema, hepatic dysfunction or disease, undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding, active or history of arterial thrombosis, estrogen-dependent cancer, known or suspected breast cancer (except for pts being treated for metastatic disease), pregnancy, thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders. Cautions: Renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, endometriosis, severe hypocalcemia, hyperlipidemias, asthma, epilepsy, migraines, SLE, hypertension, hypocalcemia, hypothyroidism, history of jaundice due to past estrogen use or pregnancy, cardiovascular disease, obesity, porphyria, severe hypocalcemia.
ACTION
Modulates pituitary secretion of gonadotropins; follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH). Therapeutic Effect: Promotes normal growth/development of female sex organs.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Widely distributed. Protein binding: 50%–80%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: Unknown.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. May be harmful to infant. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Caution in pts for whom bone growth is not complete (may accelerate epiphyseal closure). Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effects. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, ritonavir) may increase concentration/effect. HERBAL: Avoid black cohosh, dong quai, saw palmetto; may enhance toxic/adverse effects. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects of estrogens. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, calcium, HDL, triglycerides. May decrease serum cholesterol, LDL. May affect metapyrone testing, thyroid function tests.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Emulsion, Topical (Estrasorb): 4.35 mg estradiol/1.74 g pouch (contents of 2 pouches deliver estradiol 0.05 mg/day). Gel, Topical: (Divigel): 0.1% (0.25-g packet delivers estradiol 0.25 mg, 0.5 g-packet delivers estradiol 0.5 mg, 1-g packet delivers 1 mg). (Elestrin): 0.06% delivers 0.52 mg estradiol/actuation. (Estrogel): 0.06% delivers 0.75 mg/actuation. Injection (Cypionate): Depo-Estradiol: 5 mg/ml. (Valerate): Delestrogen: 10 mg/ml, 20 mg/ml, 40 mg/ml. Tablets: (Estrace): 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg. (Femtrace): 0.9 mg. Topical Spray (Evamist): 1.53 mg/spray. Transdermal System (Alora): twice wkly: 0.025 mg/24 hrs, 0.05 mg/24 hrs, 0.075 mg/24 hrs, 0.1 mg/24 hrs. Transdermal System (Climara): once wkly: 0.025 mg/24 hrs, 0.0375 mg/24 hrs, 0.05 mg/24 hrs, 0.06 mg/24 hrs, 0.075 mg/24 hrs, 0.1 mg/24 hrs. Transdermal System (Menostar): once wkly: 0.014 mg/24 hrs. Transdermal System (Minivelle, Vivelle-Dot): twice wkly: 0.025 mg/24 hrs, 0.0375 mg/24 hrs, 0.05 mg/24 hrs, 0.075 mg/24 hrs, 0.1 mg/24 hrs. Vaginal Cream (Estrace): 0.1 mg/g. Vaginal Ring (Estring): 2 mg (releases 7.5 mcg/day over 90 days). Vaginal Ring (Femring): 0.05 mg/day (total estradiol 12.4 mg-release 0.05 mg/day over 3 mos); 0.1 mg/day (total estradiol 24.8 mg-release 0.1 mg/day over 3 mos). Vaginal Tablet (Vagifem): 10 mcg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
IM
• Rotate vial to disperse drug in solution. • Inject deep IM in large muscle mass.
PO
• Administer at same time each day. • Administer with food.
Transdermal
• Remove old patch; select new site (buttocks are alternative application site). • Peel off protective strip to expose adhesive surface. • Apply to clean, dry, intact skin on trunk of body (area with as little hair as possible). • Press in place for at least 10 sec (do not apply to breasts or waistline).
Vaginal
• Apply at bedtime for best absorption. • Insert end of filled applicator into vagina, directed slightly toward sacrum; push plunger down completely. • Avoid skin contact with cream (prevents skin absorption).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Prostate Cancer
IM (Delestrogen): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 30 mg or more q1–2wks.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1–2 mg tid for at least 3 mos.
Breast Cancer
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 10 mg 3 times/day for at least 3 mos.
Osteoporosis Prophylaxis in Postmenopausal Females
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.45–0.5 mg/day cyclically (3 wks on, 1 wk off).
Transdermal (Climara): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 0.025 mg/24 hrs wkly, adjust dose as needed.
Transdermal (Alora, Minivelle, Vivelle-Dot): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 0.025 mg/24 hrs patch twice wkly, adjust dose as needed.
Transdermal (Menostar): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.014 mg/24 hrs patch wkly.
Female Hypoestrogenism
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1–2 mg/day, adjust dose as needed.
IM (Depo-Estradiol): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1.5–2 mg monthly.
IM (Delestrogen): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 10–20 mg q4wks.
Vasomotor Symptoms Associated with Menopause
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1–2 mg/day cyclically (3 wks on, 1 wk off), adjust dose as needed.
IM (Depo-Estradiol): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1–5 mg q3–4wks.
IM (Delestrogen): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 10–20 mg q4wks.
Topical Emulsion (Estrasorb): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 3.48 g (contents of 2 pouches) once daily in the morning.
Topical Gel (Estrogel): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1.25 g/day.
Transdermal Spray (Evamist): Initially, 1 spray daily. May increase to 2–3 sprays daily.
Transdermal (Climara): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.025 mg/24 hrs wkly. Adjust dose as needed.
Transdermal ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Alora): 0.05 mg/24 hrs twice wkly. (Vivelle-Dot): 0.0375 mg/24 hrs twice wkly.
Vaginal Ring (Femring): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.05 mg. May increase to 0.1 mg if needed.
Vaginal Atrophy
Vaginal Ring (Estring): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2 mg.
Vaginal Cream (Estrace): Insert 2–4 g/day intravaginally for 2 wks, then reduce dose by ½ initial dose for 2 wks, then maintenance dose of 1 g 1–3 times/wk.
Atrophic Vaginitis
Vaginal Tablet (Vagifem): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 1 tablet/day for 2 wks. Maintenance: 1 tablet twice wkly.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Contraindicated.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Anorexia, nausea, swelling of breasts, peripheral edema marked by swollen ankles and feet. Transdermal: Skin irritation, redness. Occasional: Vomiting (esp. with high doses), headache (may be severe), intolerance to contact lenses, hypertension, glucose intolerance, brown spots on exposed skin. Vaginal: Local irritation, vaginal discharge, changes in vaginal bleeding (spotting, breakthrough, prolonged bleeding). Rare: Chorea (involuntary movements), hirsutism (abnormal hairiness), loss of scalp hair, depression.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Prolonged administration increases risk of gallbladder disease, thromboembolic disease, breast/cervical/vaginal/endometrial/hepatic carcinoma. Cholestatic jaundice occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess frequency/severity of vasomotor symptoms. Question for hypersensitivity to estrogen, previous jaundice, thromboembolic disorders associated with pregnancy, estrogen therapy. Question for possibility of pregnancy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, weight, serum calcium, glucose, LFT. Monitor for loss of vision, sudden onset of proptosis, diplopia, migraine, thromboembolic disorders.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Limit alcohol, caffeine. • Avoid grapefruit products. • Immediately report sudden headache, vomiting, disturbance of vision/speech, numbness/weakness of extremities, chest pain, calf pain, shortness of breath, severe abdominal pain, mental depression, unusual bleeding. • Avoid smoking. • Report abnormal vaginal bleeding. • Never place patch on breast or waistline.
eszopiclone

e-zop-i-klone
(Lunesta)
Do not confuse Lunesta with Neulasta.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Nonbenzo-diazepine (Schedule IV). CLINICAL: Hypnotic.
USES
Treatment of insomnia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to eszopiclone. Cautions: Hepatic impairment, compromised respiratory function, COPD, sleep apnea, clinical depression, suicidal ideation, history of drug dependence; concomitant CNS depressants, strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole); elderly.
ACTION
May interact with GABA-receptor complexes at binding domains located close to or allosterically coupled to benzodiazepine receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents insomnia, difficulty maintaining normal sleep.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 52%–59%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 5–6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Pts with impaired motor or cognitive performance may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, anticonvulsants (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin), antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine), other CNS depressants may increase CNS depression. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nelfinavir, ritonavir) may increase concentration/toxicity. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: Onset of action may be reduced if taken with or immediately after a high-fat meal. LAB VALUES: None known.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets, Film-Coated: 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg.
Tablets, Film-Coated: 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Should be administered immediately before bedtime. • Do not give with or immediately following a high-fat or heavy meal. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablet.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Insomnia
PO: ADULTS: 1 mg before bedtime. Maximum: 3 mg. Concurrent use with CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, erythromycin, azole antifungals): 1 mg before bedtime; if needed, dose may be increased to 2 mg. ELDERLY, DEBILITATED PTS: Initially, 1 mg before bedtime. Maximum: 2 mg.
Sleep Maintenance Difficulty
PO: ADULTS: 2 mg before bedtime.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution. Initially, 1 mg immediately before bedtime. Maximum: 2 mg.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (34%–21%): Unpleasant taste, headache. Occasional (10%–4%): Drowsiness, dry mouth, dyspepsia, dizziness, nervousness, nausea, rash, pruritus, depression, diarrhea. Rare (3%–2%): Hallucinations, anxiety, confusion, abnormal dreams, decreased libido, neuralgia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Chest pain, peripheral edema occur occasionally.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess B/P, pulse, respirations. Raise bed rails, provide call light. Provide environment conducive to sleep (quiet environment, low or no lighting).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess sleep pattern of pt. Evaluate for therapeutic response (decrease in number of nocturnal awakenings, increase in length of sleep).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take only when experiencing insomnia. Do not take when insomnia is not present. • Do not break, chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablet. Take whole. • Avoid alcohol. • At least 8 hrs must be devoted for sleep time before daily activity begins. • Take immediately before bedtime. • Report insomnia that worsens or persists longer than 7–10 days, abnormal thoughts or behavior, memory loss, anxiety.
etanercept

e-tan-er-sept
(Enbrel)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Serious, potentially fatal, infections, including bacterial sepsis, tuberculosis, have occurred. Lymphomas, other malignancies may occur (reported in children/adolescents).
Serious, potentially fatal, infections, including bacterial sepsis, tuberculosis, have occurred. Lymphomas, other malignancies may occur (reported in children/adolescents).
Do not confuse Enbrel with Levbid.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Protein, TNF inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiarthritic.
USES
Treatment of moderate to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Treatment of moderately to severely active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis. Treatment of chronic, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to etanercept. Serious active infection or sepsis. Cautions: History of recurrent infections, illnesses that predispose to infection (e.g., diabetes, travel from areas of endemic mycosis). History of HF, decreased left ventricular function, significant hematologic abnormalities; moderate to severe alcoholic hepatitis, elderly, preexisting or recent-onset CNS demyelinating disorder.
ACTION
Binds to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), blocking its interaction with cell surface receptors. Elevated levels of TNF, involved in inflammatory and immune responses, are found in synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis pts. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves symptoms of arthritis, psoriasis, spondylitis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after subcutaneous administration. Half-life: 72–132 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: No age-related precautions noted in pts 4 yrs and older. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anakinra may increase risk of infection. Use of live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effect, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, bilirubin.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution (Prefilled Syringe): 25 mg/0.5 ml, 50 mg/ml. Injection, Solution (Autoinjector): 50 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Do not add other medications to solution. Do not use filter during reconstitution or administration.
Subcutaneous
• Refrigerate prefilled syringes. • Inject into thigh, abdomen, upper arm. Rotate injection sites. • Give new injection at least 1 inch from an old site and never into area where skin is tender, bruised, red, hard. • Once reconstituted, may be stored in vial for up to 14 days refrigerated.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Psoriatic Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 25 mg twice wkly given 72–96 hrs apart or 50 mg once wkly. Maximum: 50 mg/wk.
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JIA)
SQ: CHILDREN 2–17 YRS: Twice wkly: 0.4 mg/kg 2 times/wk given 72–96 hrs apart. Maximum dose: 25 mg. Once wkly: 0.8 mg/kg/dose. Maximum dose: 50 mg/wk.
Plaque Psoriasis
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 50 mg twice wkly (give 3–4 days apart) for 3 mos. (25 mg or 50 mg once wkly have also been used) Maintenance: 50 mg once wkly. CHILDREN 4 YRS AND OLDER: 0.8 mg/kg once wkly. Maximum Dose: 50 mg/wk.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (37%): Injection site erythema, pruritus, pain, swelling; abdominal pain, vomiting (more common in children than adults). Occasional (16%–4%): Headache, rhinitis, dizziness, pharyngitis, cough, asthenia, abdominal pain, dyspepsia. Rare (less than 3%): Sinusitis, allergic reaction.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Infection (pyelonephritis, cellulitis, osteomyelitis, wound infection, leg ulcer, septic arthritis, diarrhea, bronchitis, pneumonia) occurs in 29%–38% of pts. Rare adverse effects include heart failure, hypertension, hypotension, pancreatitis, GI hemorrhage.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess onset, type, location, duration of pain, inflammation. If significant exposure to varicella virus has occurred during treatment, therapy should be temporarily discontinued and treatment with varicella-zoster immune globulin should be considered.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for improvement of joint swelling, pain, tenderness. Monitor erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein level, CBC with differential, platelet count. Observe for signs of infection.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Instruct pt in subcutaneous injection technique, including areas of body acceptable as injection sites. • Injection site reaction generally occurs in first mo of treatment and decreases in frequency during continued therapy. • Do not receive live vaccines during treatment. • Report persistent fever, bruising, bleeding, pallor.
ethambutol
eth-am-bue-tol
(Etibi
![]() , Myambutol)
, Myambutol)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Isonicotinic acid derivative. CLINICAL: Antitubercular.
USES
In conjunction with other antitubercular agents for treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of atypical mycobacterial infections (e.g., Mycobacterium avium complex [MAC]).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ethambutol. Optic neuritis. Use in young children, unconscious pts, or anyone unable to report visual changes. Cautions: Renal/hepatic dysfunction, ocular defects (diabetic retinopathy, cataracts), recurrent ocular inflammatory conditions. Not recommended for children 13 yrs and younger (unless benefit outweighs risk).
ACTION
Inhibits arabinosyl transferase causing impaired mycobacterial cell wall synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Suppresses multiplication of mycobacteria.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly, well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 20%–30%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 3–4 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 13 yrs. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Aluminum hydroxide may decrease concentration/effect. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum uric acid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 100 mg, 400 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May be crushed and mixed with apple juice or applesauce. • Administer at least 4 hrs before giving aluminum hydroxide. • Give with food (decreases GI upset).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Tuberculosis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 15–25 mg/kg once daily (maximum: 1.5–2.5 g/day). CHILDREN: (HIV negative): 15–20 mg/kg/day (maximum: 1 g/day) or 50 mg/kg twice wkly (maximum: 2.5 g/dose). (HIV exposed/infected): 15–25 mg/kg/day. Maximum: 2.5 g/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage interval is modified based on creatinine clearance.
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 10–50 ml/min | q24–36h |
| Less than 10 ml/min | q48h |
| Hemodialysis | Administer post HD |
| Peritoneal dialysis | Administer q48h |
| Continuous renal replacement therapy | Administer q24–36h |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Acute gouty arthritis (chills, pain, swelling of joints with hot skin), confusion, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, headache. Rare: Rash, fever, blurred vision, red-green color blindness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Optic neuritis (more common with high-dosage, long-term therapy), peripheral neuritis, thrombocytopenia, anaphylactoid reaction occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Evaluate baseline CBC, renal function, LFT, and monitor periodically.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for vision changes (altered color perception, decreased visual acuity may be first signs). Give with food if GI distress occurs. Monitor serum uric acid. Assess for hot, painful, swollen joints, esp. great toe, ankle, knee (gout). Report numbness, tingling, burning of extremities (peripheral neuritis).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not skip doses; take for full length of therapy (may take mos or yrs). • Immediately report any visual changes (visual effects generally reversible with discontinuation of ethambutol but in rare cases may take up to 1 yr to disappear or may be permanent). • Promptly report swelling or pain of joints, numbness or tingling/burning of extremities, fever, chills.
etoposide, VP-16

e-toe-poe-side
(Etopophos, Toposar, VePesid
![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Severe myelosuppression with resulting infection, bleeding may occur. Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents.
Severe myelosuppression with resulting infection, bleeding may occur. Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents.
Do not confuse etoposide with etidronate, or VePesid with Pepcid or Versed.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Epipodophyllotoxin. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of refractory testicular tumors, small-cell lung carcinoma. OFF-LABEL: Acute lymphocytic, acute nonlymphocytic leukemias; Ewing’s and Kaposi’s sarcoma; Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas; endometrial, gastric, non–small-cell lung carcinomas; multiple myeloma; myelodysplastic syndromes; neuroblastoma; osteosarcoma; ovarian germ cell tumors; primary brain, gestational trophoblastic tumors; soft tissue sarcomas; Wilms tumor.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to etoposide. Cautions: Hepatic/renal impairment, myelosuppression, elderly, pts with low serum albumin.
ACTION
Induces single- and double-stranded breaks in DNA. Cell cycle-dependent and phase-specific; most effective in S and G2 phases of cell division. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits, alters DNA synthesis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Variably absorbed from GI tract. Rapidly distributed, low concentrations in CSF. Protein binding: 97%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 3–12 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy, esp. first trimester. May cause fetal harm. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Bone marrow depressants may increase myelosuppression. Live-virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: Echinacea, St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Expected decrease of leukocytes, platelets, RBC, Hgb, Hct.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 50 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Water-Soluble [Etopophos]): 100 mg. Injection Solution (Toposar): 20 mg/ml (5 ml, 25 ml, 50 ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Administer by slow IV infusion. Wear gloves when preparing solution. If powder or solution comes in contact with skin, wash immediately and thoroughly with soap, water. May be carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic. Handle with extreme care during preparation, administration.
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution
Vepesid • Dilute each 100 mg (5 ml) with at least 250 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl to provide concentration of 0.4 mg/ml (500 ml for concentration of 0.2 mg/ml). May dilute to a concentration as low as 0.1 mg/ml.
Etopophos • Reconstitute each 100 mg with 5–10 ml Sterile Water for Injection, D5W, or 0.9% NaCl to provide concentration of 20 mg/ml or 10 mg/ml, respectively. • May give without further dilution or further dilute to concentration as low as 0.1 mg/ml with 0.9% NaCl or D5W.
Rate of administration
Vepesid • Infuse slowly, at least 30–60 min (rapid IV may produce marked hypotension) at a rate not to exceed 100 mg/m2/hr. • Monitor for anaphylactic reaction during infusion (chills, fever, dyspnea, diaphoresis, lacrimation, sneezing, throat, back, chest pain).
Etopophos • May give over as little as 5 min up to 210 min.
Storage
Vepesid • Store injection at room temperature before dilution. • Concentrate for injection is clear, yellow. • Diluted solution is stable at room temperature for 96 hrs at 0.2 mg/ml, 24 hrs at 0.4 mg/ml. • Discard if crystallization occurs.
Etopophos • Refrigerate vials. • Stable at room temperature for 24 hrs or for 7 days if refrigerated after reconstitution.
PO
Storage • Refrigerate gelatin capsules.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
VePesid: Cefepime (Maxipime), filgrastim (Neupogen). Etopophos: Amphotericin B (Fungizone), cefepime (Maxipime), chlorpromazine (Thorazine), methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), prochlorperazine (Compazine).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
VePesid: Carboplatin (Paraplatin), cisplatin (Platinol), cytarabine (Cytosar), daunorubicin (Cerubidine), doxorubicin (Adriamycin), granisetron (Kytril), mitoxantrone (Novantrone), ondansetron (Zofran). Etopophos: Carboplatin (Paraplatin), cisplatin (Platinol), cytarabine (Cytosar), dacarbazine (DTIC-Dome), daunorubicin (Cerubidine), dexamethasone (Decadron), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), doxorubicin (Adriamycin), granisetron (Kytril), magnesium sulfate, mannitol, mitoxantrone (Novantrone), ondansetron (Zofran), potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Dosage individualized based on clinical response, tolerance to adverse effects. Treatment repeated at 3- to 4-wk intervals. Refer to individual protocols.
Refractory Testicular Tumors
IV: ADULTS: 50–100 mg/m2/day on days 1–5, or 100 mg/m2/day on days 1, 3, 5 (as combination therapy). Give q3–4wks for 3–4 courses.
Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma
PO: ADULTS: Twice the IV dose rounded to nearest 50 mg. Give once daily for doses 200 mg or less, in divided doses for dosages greater than 200 mg.
IV: ADULTS: 35 mg/m2/day for 4 consecutive days up to 50 mg/m2/day for 5 consecutive days q3–4wks (as combination therapy).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 15–50 ml/min | 75% of normal dose |
| Less than 15 ml/min | Consider further dose reduction. |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (66%–43%): Mild to moderate nausea/vomiting, alopecia. Occasional (13%–6%): Diarrhea, anorexia, stomatitis. Rare (2% or less): Hypotension, peripheral neuropathy.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Myelosuppression manifested as hematologic toxicity, principally anemia, leukopenia (occurring 7–14 days after drug administration), thrombocytopenia (occurring 9–16 days after administration), and, to lesser extent, pancytopenia. Bone marrow recovery occurs by day 20. Hepatotoxicity occurs occasionally.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC before and at frequent intervals during therapy. Antiemetics readily control nausea, vomiting.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor Hgb, Hct, WBC, platelet count, B/P, hepatic/renal function tests. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor for hematologic toxicity (fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site), symptoms of anemia (excessive fatigue, weakness). Assess for paresthesia (peripheral neuropathy). Monitor for stomatitis.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Hair loss is reversible, but new hair growth may have different color, texture. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance). • Avoid contact with those who have recently received live virus vaccine. • Promptly report fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising or bleeding from any site, burning or pain with urination, numbness in extremities, yellowing of skin or eyes.
everolimus

e-veer-oh-li-mus
(Afinitor, Afinitor Disperz, Zortress)
Do not confuse Afinitor with Lipitor, or everolimus with sirolimus, tacrolimus, or temsirolimus.
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Immunosuppresant (may result in infection, malignancy including lymphoma or skin cancer); increased risk of nephrotoxicity in renal transplants (avoid standard doses of cyclosporine); increased risk of renal arterial or venous thrombosis in renal transplants.
Immunosuppresant (may result in infection, malignancy including lymphoma or skin cancer); increased risk of nephrotoxicity in renal transplants (avoid standard doses of cyclosporine); increased risk of renal arterial or venous thrombosis in renal transplants.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Enzyme inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic, immunosuppressant.
USES
Afinitor: Treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma after failure of treatment with sunitinib or sorafenib. Treatment of subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) associated with tuberous sclerosis. Treatment of progressive neuroendocrine tumors of pancreatic origin and progressive, well-differentiated, non-functional neuroendocrine tumors of GI or lung origin. Treatment of advanced hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Treatment of tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) not requiring immediate surgery. Afinitor Disperz: Treatment of SEGA associated with TSC requiring intervention but that cannot be curatively resected. Zortress: Prophylaxis of organ rejection after kidney/liver transplant at low to moderate immunologic risk. OFF-LABEL: Relapsed or refractory Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Treatment of progressive advanced carcinoid tumors.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to everolimus, sirolimus, other rapamycin derivatives. Cautions: Noninfectious pneumonitis; viral, fungal, or bacterial infection; oral ulceration; mucositis; current immunosuppression; hereditary galactose intolerance; renal/hepatic impairment; hyperlipidemia; concurrent use of CYP3A4 inducers and inhibitors (see Interactions). Medications known to cause angioedema.
ACTION
Binds to the FK binding protein, reducing protein synthesis and cell proliferation. Also reduces lipoma volume. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces cell proliferation, produces cell death.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Peak concentration occurs in 1–2 hrs following administration, with steady-state levels achieved in 2 wks. Undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism. Protein binding: 74%. Eliminated in feces (80%), urine (5%). Half-life: 30 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, voriconazole) may increase concentration. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, dexamethasone, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifabutin, rifampin, rifapentine) may decrease concentration. P-gp inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine) may increase everolimus concentration, toxicity. Statins may increase risk of rhabdomyolysis. FOOD: High-fat meals may reduce plasma concentration. Grapefruit products may increase concentration (potential for myelotoxicity, nephrotoxicity). HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease plasma concentration. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, creatinine, glucose, triglycerides, lipids. May decrease WBCs, neutrophils, Hgb, platelets.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets (Zortress):
Tablets (Zortress):
![]() 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 0.75 mg. Tablets (Afinitor): 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg. Tablets for Oral Suspension (Afinitor Disperz): 2 mg, 3 mg, 5 mg.
0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 0.75 mg. Tablets (Afinitor): 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg. Tablets for Oral Suspension (Afinitor Disperz): 2 mg, 3 mg, 5 mg.