ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• Give without regard to food. • Swallow whole. Do not crush/cut Afinitor or Zortress. • Avoid direct contact of crushed tablets with skin or mucous membranes. If unable to swallow, disperse Afinitor Disperz in water with gentle stirring, give immediately.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ If pt requires coadministration of a strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, dexamethasone, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifabutin, rifampin), consider doubling the dose. If strong inducer is discontinued, reduce everolimus to dose used prior to initiation. If moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors are required, reduce dose by 50%.
Renal Carcinoma, Neuroendocrine Tumors, Breast Cancer, TSC
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Afinitor): 10 mg once daily at same time every day. Co-administration with CYP3A4 inhibitors or P-gp inhibitors: 2.5 mg once daily. May increase to 5 mg/day. Coadministration with CYP3A4 inducers: Increase by 5-mg increments up to 20 mg/day.
SEGA with TSC
PO: ADULTS, CHILDREN: 4.5 mg/m2 once daily. Coadministration with CYP3A4 inhibitors or P-gb inhibitors: 2.5 mg/m2/day. Coadministration with CYP3A4 inducers: 9 mg/m2/day.
Renal Transplant Prophylaxis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Zortress): Initially, 0.75 mg 2 times/day. Give in combination with basiliximab and concurrently with reduced doses of cyclosporine and corticosteroids.
Liver Transplant Prophylaxis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Zortress): Initially, 1 mg 2 times/day. Adjust dose at 4–5-day intervals based on serum concentration, tolerability, and response.
Astrocytoma
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 4.5 mg/m2 once daily, titrated to attain trough concentration of 5–15 ng/ml. If trough greater than 15 ng/ml: reduce dose by 2.5 mg/day (tablets) or 2 mg/day (tablets for oral suspension). If trough less than 15 ng/ml: increase dose by 2.5 mg/day (tablets) or 2 mg/day (tablets for oral suspension).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
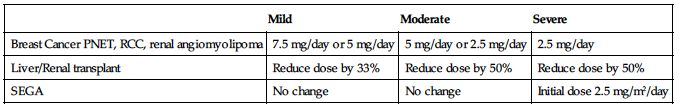
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
| Mild | Moderate | Severe |
| Breast Cancer PNET, RCC, renal angiomyolipoma | 7.5 mg/day or 5 mg/day | 5 mg/day or 2.5 mg/day | 2.5 mg/day |
| Liver/Renal transplant | Reduce dose by 33% | Reduce dose by 50% | Reduce dose by 50% |
| SEGA | No change | No change | Initial dose 2.5 mg/m2/day |
SIDE EFFECTS
Common (44%–26%): Stomatitis, asthenia. Diarrhea, cough, rash, nausea. Frequent (25%–20%): Peripheral edema, anorexia, dyspnea, vomiting, pyrexia. Occasional (19%–10%): Mucosal inflammation, headache, epistaxis, pruritus, dry skin, epigastric distress, extremity pain. Rare (less than 10%): Abdominal pain, insomnia, dry mouth, dizziness, paresthesia, eyelid edema, hypertension, nail disorder, chills.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Noninfectious pneumonitis characterized as hypoxia, pleural effusion, cough, or dyspnea was reported in 14% of pts; Grade 3 noninfectious pneumonitis reported in 4%. Localized and systemic infections, including pneumonia, other bacterial infections, and invasive fungal infections, have occurred due to everolimus immunosuppressive properties. Renal failure occurs in 3% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess medical history, esp. renal function, use of other immunosuppressants. Obtain CBC, BMP, LFT before treatment begins and routinely thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Offer antiemetics to control nausea, vomiting. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess skin for evidence of rash, edema. Monitor CBC, particularly Hgb, platelet, neutrophil count; BUN, creatinine, LFT. Monitor for shortness of breath, fatigue, hypertension. Assess mouth for stomatitis, mucositis.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take dose at same time each day. • Avoid crowds, those with known infection. • Avoid contact with anyone who recently received live virus vaccine. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers body resistance). • Promptly report fever, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site. • Avoid direct contact of crushed tablets with skin or mucous membrane (wash thoroughly if contact occurs). • Avoid grapefruit products.
evolocumab
e-voe-lok-ue-mab
(Repatha)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Do not confuse evolocumab with alirocumab or raxibacumab.
Do not confuse evolocumab with alirocumab or raxibacumab.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Proprotein convertase subtilison kexin 9 (PCSK9) inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antihyperlipidemic, monoclonal antibody.
USES
Adjunct to diet and maximally tolerated statin therapy for the treatment of adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, who require additional lowering of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Adjunct to diet and other LDL-lowering therapies (e.g., statins, ezetimibe, LDL apheresis) in pts with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia who requires additional lowering of LDL-C.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to evolocumab. Cautions: Active infection.
ACTION
Binds to and inhibits circulating PCSK9 from binding to LDL receptor (LDLR), preventing LDLR degradation and allowing LDLR to recycle back to the liver surface. Increases number of LDLR available to clear LDL from the blood. Therapeutic Effect: Lowers LDL-C levels.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Distributed primarily in circulatory system. Metabolized and eliminated by protein degradation into small peptides, amino acids. Peak plasma concentration: 3–4 days. Steady state reached in 12 wks. Half-life: 11–17 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cross placental barrier, esp. during second and third trimester. Unknown if distributed in breast milk; however, human immunoglobulin G is present breast milk. Must either discontinue drug or discontinue breastfeeding. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia who are younger than 13 yrs. Safety and efficacy not established pts with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or primary hypercholesterolemia. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None known. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Expected to decrease serum LDL-C levels.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 140 mg/mL in single-use prefilled syringe, auto-injector. 420 mg/3.5 mL single use Pushtronex system (on body infusor with prefilled cartridge).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Subcutaneous • Remove auto-injector/prefilled syringe from refrigerator and allow to passively warm to room temperature. • Visually inspect for particulate matter or discoloration. Solution should appear clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow in color. Do not use if solution is cloudy, discolored, contains particles; if the auto-injector/prefilled syringe has been dropped, or if the cap is missing or not securely attached. • Once cap is removed, subcutaneously insert needle into abdomen, outer thigh, or upper arm region and inject solution. • Do not inject into areas of active skin disease or injury such as sunburns, skin rashes, inflammation, or skin infections. • If using auto-injector, depress gray button until a click is heard and allow 15 sec to pass to ensure solution is fully injected. • Rotate injection sites.
Storage • Refrigerate auto-injector/prefilled syringe in original carton. • May store at room temperature for no more than 30 days. • Protect from direct light. • Do not freeze.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 140 mg q2wks or 420 mg once monthly. Give 420 mg dose as 3 separate injections within 30 min. If switching between regimens, give the first dose of the new regimen on the next scheduled date of the prior regimen. If a q2wk or once monthly dose is missed, either administer as soon as possible if there are more than 7 days until the next scheduled dose or skip the missed dose and administer the next dose according to the original schedule.
Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 420 mg once monthly as 3 separate injections within 30 min. If a once monthly dose is missed, administer as soon as possible if there are more than 7 days until the next scheduled dose or skip the missed dose according to the original schedule.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Not studied; use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (6%–3%): Back pain, injection site reactions (bruising, erythema, localized pain), cough, headache, myalgia, dizziness, musculoskeletal pain, hypertension, diarrhea.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., pruritus, rash, urticaria) reported in (5.1% of pts). Infectious processes such as gastroenteritis (3% of pts), influenza (7.5% of pts), nasopharyngitis (10.5% of pts), sinusitis (4.2% of pts), upper respiratory tract infection (9.3% of pts), UTI (4.5% of pts) have occurred. Musculoskeletal events including arthralgia, back pain, myalgia reported in 14% of pts. Immunogenicity (auto-evolocumab antibodies) occurred in less than 1% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline LDL-C level. Verify whether pt is positive for heterozygous or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Question history of hypersensitivity reaction. Assess potential injection sites for sunburns, skin rashes, inflammation, skin infections. Verify pregnancy status.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Obtain LDL-C level within 4–8 wks after initiation or with any change in dosage. Monitor for hypersensitivity reaction. If hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue therapy and treat symptoms accordingly; monitor until symptoms resolve. Monitor for respiratory infections, musculoskeletal events.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• A health care provider will show you how to properly mix and inject your medication. You must demonstrate correct preparation and injection techniques before using medication at home. • Inject dose under the skin (SQ) of your outer thigh, abdomen, or upper arm; do not inject into muscle or vein. • Rotate injection sites. • Discard used needles using regulated sharps containers. • Treatment may cause serious allergic reactions such as difficulty breathing, itching, hives, rash. If allergic reaction occurs, seek immediate medical attention. • Do not reuse auto-injector/prefilled syringes. • Report symptoms of infection.
exemestane

ex-e-mes-tane
(Aromasin)
Do not confuse Aromasin with Arimidex, or exemestane with estramustine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Hormone. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women whose disease has progressed following tamoxifen therapy. Adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with estrogen-receptor positive early breast cancer after 2–3 yrs of tamoxifen therapy for completion of 5 consecutive yrs of adjuvant hormonal therapy. OFF-LABEL: Reduces risk of invasive breast cancer in postmenopausal women; treatment of endometrial cancer, uterine sarcoma.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to exemestane. Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant; use in premenopausal women. Cautions: Concomitant use of estrogen-containing agents, strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., phenobarbital, rifampin).
ACTION
Inactivates aromatase, the principal enzyme that converts androgens to estrogens in both premenopausal and postmenopausal women, lowering circulating estrogen level. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits growth of breast cancers stimulated by estrogens.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 90%. Distributed extensively into tissues. Metabolized in liver; eliminated in urine and feces. Half-life: 24 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Indicated for postmenopausal women. Children: Not indicated for use in this pt population. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., phenobarbital, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effect. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Avoid black cohosh, dong quai in estrogen-dependent tumors. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 25 mg.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Breast Cancer (Early)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 25 mg once daily after a meal (following 2–3 yrs tamoxifen therapy) for total duration of 5 yrs.
Breast Cancer (Advanced)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 25 mg once daily after a meal. 50 mg/day when used concurrently with potent CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin).
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (22%–10%): Fatigue, nausea, depression, hot flashes, pain, insomnia, anxiety, dyspnea. Occasional (8%–5%): Headache, dizziness, vomiting, peripheral edema, abdominal pain, anorexia, flu-like symptoms, diaphoresis, constipation, hypertension. Rare (4%): Diarrhea.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
MI has been noted.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for onset of depression. Assess sleep pattern. Monitor for and assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Assess for headache. Offer antiemetic for nausea/vomiting.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report if nausea, hot flashes become unmanageable. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Best taken after meals and at same time each day.
exenatide

ex-en-a-tide
(Bydureon, Byetta)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  (Bydureon): Risk of thyroid C-cell tumors.
(Bydureon): Risk of thyroid C-cell tumors.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Incretin mimetic. CLINICAL: Antidiabetic.
USES
Adjunct to diet, exercise to improve glycemic control in pts with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to exenatide. Bydureon only: History of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Pts with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN2). Cautions: Diabetic ketoacidosis, type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pts with renal transplantation or moderate renal impairment. Not recommended in severe renal impairment, severe GI disease, pancreatitis.
ACTION
Stimulates release of insulin from beta cells of pancreas, mimics enhancement of glucose-dependent insulin secretion, suppresses elevated glucagon secretion, slows gastric emptying (central action increases satiety). Therapeutic Effect: Improves glycemic control by increasing postmeal insulin secretion, decreasing postmeal glucagon levels, delaying gastric emptying, and increasing satiety.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Minimal systemic metabolism. Eliminated by glomerular filtration with subsequent proteolytic degradation. Half-life: 2.4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of digoxin, lovastatin. May increase bleeding time, risk of bleeding when used with warfarin. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None known.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution (Prefilled Pen): (Byetta) 10 mcg/0.04 ml (2.4 ml); 5 mcg/0.02 ml (1.2 ml). Injection, Suspension (Bydureon): 2 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Subcutaneous
• May be given in thigh, abdomen, upper arm. • Rotation of injection sites is essential; maintain careful injection site record. • Give within 60 min before morning and evening meals. Give suspension immediately after powder is suspended.
Storage • Refrigerate prefilled pens. • Discard if freezing occurs. • May be stored at room temperature after first use. • Discard pen 30 days after initial use.
INDICATIONS/ROUTE/DOSAGE
Diabetes Mellitus
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Byetta) 5 mcg per dose given twice daily at any time within the 60-min period before the morning and evening meals. Dose may be increased to 10 mcg twice daily after 1 mo of therapy. (Bydureon): 2 mg once q7days.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate impairment: Use caution. Severe impairment (CrCl less than 30 ml/min or ESRD): Not recommended.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
(Byetta) Frequent (44%): Nausea. Occasional (13%–6%): Diarrhea, vomiting, dizziness, anxiety, dyspepsia. Rare (less than 6%): Weakness. (Bydureon) 5% or greater: Nausea, diarrhea, headache, constipation, vomiting, dyspepsia, injection site pruritus or nodule.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
With concurrent sulfonylurea, hypoglycemia occurs in 36% when given a 10-mcg dose of exenatide, 16% when given a 5-mcg dose. May cause acute pancreatitis.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Check serum glucose before administration. Discuss lifestyle to determine extent of learning, emotional needs. Ensure follow-up instruction if pt or family does not thoroughly understand diabetes management, glucose-testing technique. At least 1 mo should elapse to assess response to drug before new dose adjustment is made.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum glucose, food intake, renal function. Assess for hypoglycemia (cool wet skin, tremors, dizziness, anxiety, headache, tachycardia, numbness in mouth, hunger, diplopia), hyperglycemia (polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, nausea, vomiting, dim vision, fatigue, deep rapid breathing). Be alert to conditions that alter glucose requirements (fever, increased activity or stress, surgical procedure).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Diabetes mellitus requires lifelong control. • Prescribed diet and exercise are principal parts of treatment. Do not skip, delay meals. • Continue to adhere to dietary instructions, regular exercise program, regular testing of serum glucose. • When taking combination therapy with a sulfonylurea, have source of glucose available to treat symptoms of hypoglycemia. • Report any unexplained severe abdominal pain with or without nausea or vomiting.
ezetimibe

e-zet-i-mib
(Apo-Ezetimibe
 , Ezetrol
, Ezetrol
 , Zetia)
, Zetia)
Do not confuse Zetia with Zebeta or Zestril.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Liptruzet: ezetimibe/atorvastatin (statin): 10 mg/10 mg, 10 mg/20 mg, 10 mg/40 mg, 10 mg/80 mg. Vytorin: ezetimibe/simvastatin (statin): 10 mg/10 mg, 10 mg/20 mg, 10 mg/40 mg, 10 mg/80 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antihyperlipidemic. CLINICAL: Anticholesterol agent.
USES
Adjunct to diet for treatment of primary hypercholesterolemia (monotherapy or in combination with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors [statins]), homozygous sitosterolemia, homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (combined with atorvastatin or simvastatin). Mixed hyperlipidemia (in combination with fenofibrate).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ezetimibe. Concurrent use of an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin) in pts with active hepatic disease or unexplained persistent elevations in serum transaminase; pregnancy and breastfeeding (when used with a statin). Cautions: Severe renal or mild hepatic impairment. Not recommended in those with moderate or severe hepatic impairment.
ACTION
Inhibits cholesterol absorption in brush border of small intestine, leading to decrease in delivery of intestinal cholesterol to liver. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces total serum cholesterol, LDL, triglyceride; increases HDL.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: greater than 90%. Metabolized in small intestine and liver. Excreted in feces (78%), urine (11%). Half-life: 22 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts 10 yrs or younger. Elderly: Age-related mild hepatic impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antacids containing aluminum or magnesium, cyclosporine, fenofibrate, gemfibrozil increase concentration. Cholestyramine resin decreases effectiveness. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 10 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• Give without regard to food. • May give at same time as statins. Give at least 2 hrs before or 4 hrs after bile acid sequestrants.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypercholesterolemia
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN, 10 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 10 mg once daily, given with or without food. If pt is also receiving a bile acid sequestrant, give ezetimibe at least 2 hrs before or at least 4 hrs after bile acid sequestrant.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (4%–3%): Back pain, diarrhea, arthralgia, sinusitis, abdominal pain. Rare (2%): Cough, pharyngitis, fatigue, depression.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hepatitis, hypersensitivity reaction, myopathy, rhabdomyolysis occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain diet history, esp. fat consumption. Obtain serum cholesterol, triglycerides, hepatic function tests, blood counts during initial therapy and periodically during treatment. Treatment should be discontinued if hepatic enzyme levels persist more than 3 times normal limit.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Question pt for signs/symptoms of back pain, abdominal disturbances. Monitor serum cholesterol, triglycerides for therapeutic response.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Periodic laboratory tests are essential part of therapy. • Do not stop medication without consulting physician. • Report muscular or bone pain. • May take at same time as statins. Take at least 2 hrs before or 4 hrs after cholestyramine, colestipol, colesevelam.
ezogabine
e-zog-a-bine
(Potiga)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Retinal abnormalities may progress to vision loss.
Retinal abnormalities may progress to vision loss.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Potassium channel opener (Schedule V). CLINICAL: Anticonvulsant.
USES
Adjunctive therapy for treatment of partial-onset seizures in pts 18 yrs of age and older.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ezogabine. Cautions: Hepatic/renal impairment, BPH, urinary retention, chronic cognitive impairment, prolonged QT interval, psychiatric history, pts at risk for suicide. Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, familial long-QT syndrome, medications that prolong QT interval, hypothyroidism, HF, ventricular arrhythmias, elderly.
ACTION
Binds to voltage-gated potassium channels, stabilizing the channels in open formation and enhancing the M current. Therapeutic Effect: Regulates neuronal excitability, suppressing seizure activity.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed after PO administration. Peak concentration: 0.5–2 hrs. Protein binding: 80%. Metabolized by glucuronidation and acetylation. Primarily excreted in urine (85%), feces (14%). Half-life: 7–11 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Must either discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue drug regimen. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts under 18 yrs of age. Elderly: Dosage adjustment recommended for pts older than 65 yrs.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Phenytoin, carbamazepine may decrease plasma concentration/effects. Alcohol may increase concentration/adverse effects. May inhibit clearance of digoxin. HERBAL: None known. FOOD: None significant. LAB VALUES: May create falsely elevated urine bilirubin level.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 50 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• May give without regard to food. Swallow tablets whole.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Partial Seizures
◀ ALERT ▶ Increase at wkly intervals by no more than 50 mg 3 times daily (150 mg/day).
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 100 mg 3 times daily. May increase to maintenance dose of 200–400 mg 3 times daily (600–1,200 mg daily). Maximum: 1,200 mg/day. ELDERLY: Initially, 50 mg 3 times/day. May increase wkly to therapeutic level. Maximum: 250 mg 3 times/day (750 mg/day).
Dosage Modification
Renal Impairment (CrCl less than 50 ml/min or ESRD): 50 mg 3 times/day for 7 days. Then increase to therapeutic level. Maximum: 200 mg 3 times/day (600 mg/day). Mild Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh score less than 9): Initially, 50 mg 3 times/day for 7 days. Then increase to therapeutic level. Maximum: 250 mg 3 times/day (750 mg/day). Severe Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh score greater than 9): Initially, 50 mg 3 times/day for 7 days. Then increase to therapeutic level. Maximum: 200 mg 3 times/day (600 mg/day). Discontinuation: Reduce gradually over period of at least 3 wks.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (23%–15%): Dizziness, somnolence, fatigue. Occasional (8%–4%): Tremor, vertigo, abnormal coordination, nausea, diplopia, attention disturbance, memory impairment, asthenia, blurred vision, gait disturbance, aphasia, dysarthria, balance disorder. Rare (3%–1%): Constipation, anxiety, weight gain, dyspepsia, amnesia, dysphasia, disorientation, dysuria, urinary hesitation, hematuria, urine discoloration, psychotic behavior.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Urinary retention requiring catheterization, prolonged QT interval, myoclonus, peripheral edema, hypokinesia, dysphasia, hyperhydrosis, malaise reported in less than 2% of pts. Hydronephrosis associated with baseline renal impairment, increased risk of psychosis, hallucinations, suicidal ideation, depression, aggression, mania noted.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Review history of seizure disorder (intensity, frequency, duration, LOC). Question history of BPH, urinary retention, cognitive impairment, psychiatric disorder, hepatic/renal impairment, alcoholism, prolonged QT syndrome. Obtain full medication history including digoxin, antiarrhythmics, adjunct anticonvulsant therapy. Obtain baseline EKG, digoxin level if applicable. Question possibility of pregnancy or current breastfeeding.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Initiate seizure precautions and observe for seizure activity. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Monitor for depression, suicidal ideation, unusual behavior, mania, anxiety. Routinely monitor digoxin levels. Monitor QT interval for pts with HF, ventricular hypertrophy, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Monitor closely for seizure activity. • Immediately report any new medications, trouble urinating, palpitations, pregnancy, or plans to breastfeed. • Avoid alcohol. • Report any thoughts of suicide, aggressive behavior, depression, anxiety, trouble sleeping, impulsiveness, unusual behavior. • Noncompliance may lead to increased risk of seizures.