F
famciclovir
fam-sye-klo-veer
(Apo-Famciclovir ![]() , Famvir)
, Famvir)
Do not confuse famciclovir with acyclovir, ganciclovir, or valganciclovir; or Famvir with Femara.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Synthetic nucleoside. CLINICAL: Antiviral.
USES
Treatment of acute herpes zoster (shingles) in immunocompetent pts, treatment and suppression of recurrent genital herpes in immunocompetent pts, treatment of recurrent mucocutaneous herpes simplex in HIV-infected pts. Treatment of recurrent herpes labialis (cold sores) in immunocompetent pts.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to famciclovir, penciclovir. Cautions: Renal impairment. Avoid use in galactose intolerance, severe lactose deficiency, or glucose-galactose malabsorption syndromes.
ACTION
Inhibits HSV-2 polymerase, inhibiting herpes viral DNA synthesis and replication. Therapeutic Effect: Suppresses replication of herpes simplex virus, varicella-zoster virus.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed. Protein binding: 20%–25%. Rapidly metabolized to penciclovir by enzymes in GI tract, liver, plasma. Eliminated unchanged in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2–3 hrs (increased in severe renal failure).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if excreted in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Probenecid, methotrexate may increase adverse effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase ALT, AST, amylase, bilirubin, lipase. May decrease neutrophils, platelets.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 125 mg, 250 mg, 500 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Give with food to decrease GI distress.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
PO: ADULTS: 500 mg q8h for 7 days. Begin as soon as possible after diagnosis and within 72 hrs of rash onset. (HIV pts): 500 mg 3 times/day for 7–10 days.
Genital Herpes Simplex (Initial)
PO: ADULTS: 250 mg 3 times/day for 7–10 days.
Genital Herpes Simplex (Recurrence)
PO: ADULTS: 1,000 mg twice daily for 1 day; or 125 mg 2 times/day for 5 days; or 500 mg once, then 250 mg 2 times/day for 2 days.
Genital Herpes Simplex (Suppression)
PO: ADULTS: 250 mg twice daily for up to 1 yr.
Genital Herpes Simplex in HIV Pts
Herpes Labialis (Cold Sores)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immunocompetent): 1,500 mg as a single dose. Initiate at first sign or symptoms. (HIV pts): 500 mg 2 times/day for 5–10 days.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage and frequency are modified based on creatinine clearance and disease process.
| Creatinine Clearance | Herpes Zoster | Recurrent Genital Herpes (single-day regimen) | Recurrent Genital Herpes (suppression) | Recurrent Herpes Labialis Treatment (single-day regimen) | Recurrent Orolabial or Genital Herpes in HIV Pts |
| 40–59 ml/min | 500 mg q12h | 500 mg q12h | — | 750 mg | — |
| 20–39 ml/min | 500 mg q24h | 500 mg | 125 mg q12h | 500 mg | 500 mg q24h |
| Less than 20 ml/min | 250 mg q24h | 250 mg | 125 mg q24h | 250 mg | 250 mg q24h |
| Hemodialysis | 250 mg after each hemodialysis session | 250 mg after each hemodialysis session | 125 mg after each hemodialysis session | 250 mg after each hemodialysis session | 250 mg after each hemodialysis session |
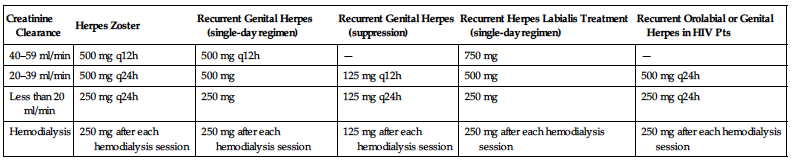
Dosage in Hemodialysis Pts
Herpes zoster: 250 mg after each dialysis treatment. Genital herpes: 125 mg after each dialysis treatment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (23%–12%): Headache, nausea. Occasional (10%–2%): Dizziness, drowsiness, paresthesia (esp. feet), diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, decreased appetite, fatigue, fever, pharyngitis, sinusitis, pruritus. Rare (less than 2%): Insomnia, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, flatulence, back pain, arthralgia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Urticaria, severe skin rash, hallucinations, confusion (delirium, disorientation occur predominantly in elderly) has been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline chemistry tests, esp. renal function. Question history of galactose intolerance, severe lactose deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption, renal impairment. Assess herpetic lesions.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Evaluate cutaneous lesions. Be alert to neurologic effects: headache, dizziness. Provide analgesics, comfort measures. Monitor renal function, hepatic enzymes, CBC.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Drink adequate fluids. • Fingernails should be kept short, hands clean. • Do not touch lesions with fingers to avoid spreading infection to new site. • Genital herpes: Continue therapy for full length of treatment. • Avoid contact with lesions during duration of outbreak to prevent cross-contamination. • Use condoms during sexual activity. • Report if lesions recur or do not improve. • Slowly go from lying to standing to avoid dizziness. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established.
famotidine
fa-moe-ta-deen
(Acid Reducer Maximum Strength, Apo-Famotidine ![]() , Pepcid, Ulcidine
, Pepcid, Ulcidine ![]() )
)
Do not confuse famotidine, cimetidine, ranitidine, with fluoxetine or furosemide.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Duexis: famotidine/ibuprofen (an NSAID): 26.6 mg/800 mg. Pepcid Complete: famotidine/calcium chloride/magnesium hydroxide (antacids): 10 mg/800 mg/165 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: H2 receptor antagonist. CLINICAL: Antiulcer, gastric acid secretion inhibitor.
USES
Short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer. Prevention, maintenance of duodenal ulcer recurrence. Treatment of active benign gastric ulcer, pathologic GI hypersecretory conditions. Short-term treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). OTC formulation for relief of heartburn, acid indigestion, sour stomach. OFF-LABEL: H. pylori eradication, risk reduction of duodenal ulcer recurrence (part of multidrug regimen), stress ulcer prophylaxis in critically ill pts, relief of gastritis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to famotidine, other H2 antagonists. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, elderly, thrombocytopenia.
ACTION
Inhibits histamine action of H2 receptors of parietal cells. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits gastric acid secretion (fasting, nocturnal, or stimulated by food, caffeine, insulin).
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 1 hr | 1–4 hrs | 10–12 hrs |
| IV | 0.5 hr | 0.5–3 hrs | 10–12 hrs |
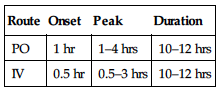
Rapidly, incompletely absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 15%–20%. Partially metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2.5–3.5 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Confusion more likely to occur, esp. in pts with renal/hepatic impairment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease absorption of atazanavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Interferes with skin tests using allergen extracts. May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST. May decrease platelet count.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Infusion, Premix: 20 mg in 50 ml 0.9% NaCl. Injection, Solution: 10 mg/ml (2 ml vial). Powder for Oral Suspension (Pepcid): 40 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 10 mg. (Pepcid): 20 mg, 40 mg. Tablets, Chewable: 20 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • For IV push, dilute 20 mg with 5–10 ml 0.9% NaCl. • For intermittent IV infusion (piggyback), dilute with 50–100 ml D5W, or 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • Give IV push over at least 2 min. • Infuse piggyback over 15–30 min.
Storage • Refrigerate unused vials. • IV solution appears clear, colorless. • After dilution, IV solution is stable for 48 hrs if refrigerated.
PO
• Store tablets, suspension at room temperature. • Following reconstitution, oral suspension is stable for 30 days at room temperature. • Give without regard to meals. • Shake suspension well before use.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Calcium gluconate, dexamethasone (Decadron), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), doxorubicin (Adriamycin), furosemide (Lasix), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), insulin (regular), lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, midazolam (Versed), morphine, nitroglycerin, norepinephrine (Levophed), ondansetron (Zofran), potassium chloride, potassium phosphate, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Duodenal Ulcer
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Acute therapy: 40 mg/day at bedtime or 20 mg twice daily for 4–8 wks. Maintenance: 20 mg/day at bedtime.
Peptic Ulcer
PO: CHILDREN 1–16 YRS: 0.5 mg/kg/day at bedtime or 2 divided doses. Maximum: 40 mg/day.
Gastric Ulcer
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Acute therapy): 40 mg/day at bedtime.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20 mg twice daily for 6 wks. CHILDREN 1–16 YRS: 1 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses. Maximum: 40 mg 2 times/day. CHILDREN 3 MOS–11 MOS: 0.5 mg/kg/dose twice daily. CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 3 MOS, NEONATES: 0.5 mg/kg/dose once daily.
Esophagitis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 20–40 mg twice daily for up to 12 wks.
Hypersecretory Conditions
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 20 mg q6h. May increase up to 160 mg q6h.
Acid Indigestion, Heartburn (OTC Use)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 10–20 mg q12h. May take 15–60 min before eating. Maximum: 2 doses/day.
Usual Parenteral Dosage
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 12 YRS: 20 mg q12h. CHILDREN 1–12 YRS: 0.25–0.5 mg/kg q12h. Maximum: 40 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| Less than 50 ml/min | 50% normal dose or increase dosing interval to 48 hrs |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (5%): Headache. Rare (2% or less): Confusion, constipation, diarrhea, dizziness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess epigastric/abdominal pain. Verify platelet count in critically ill pts.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor for headache. Assess for confusion in elderly. Consider interrupting treatment in pts who develop thrombocytopenia.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• May take without regard to meals, antacids. • Report headache. • Avoid excessive amounts of coffee, aspirin. • Report persistent symptoms of heartburn, acid indigestion, sour stomach.
febuxostat
fe-bux-oh-stat
(Uloric)
Do not confuse febuxostat with panobinostat or Femstat.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Xanthine oxidase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antigout agent.
USES
Management of hyperuricemia in pts with gout. Not recommended for treatment of asymptomatic hyperuricemia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to febuxostat. Concomitant use with azathioprine, mercaptopurine. Cautions: Severe renal/hepatic impairment, history of heart disease or stroke. Hypersensitivity to allopurinol. Pts at risk for urate formation.
ACTION
Decreases uric acid production by inhibiting the enzyme xanthine oxidase. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces uric acid concentrations in serum and urine.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Widely distributed. Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated in urine (49%), feces (45%). Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 5–8 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration, toxicity of azathioprine, mercaptopurine, theophylline. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, LDH, amylase, sodium, potassium, cholesterol, triglycerides, BUN, creatinine. May decrease platelets, Hgb, Hct, neutrophils. May prolong prothrombin time.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 40 mg, 80 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals or antacids.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Recommended concomitant NSAID or colchicine with initiation of therapy and continue for up to 6 mos to prevent exacerbations of gout.
Hyperuricemia
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 40 mg once daily. If pt does not achieve serum uric acid level less than 6 mg/dL after 2 wks with 40 mg, may give 80 mg once daily. Maximum: 120 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hepatic function abnormalities occur in 6% of pts. May increase risk of thromboembolic events including CVA, MI.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess baseline renal function, LFT; concomitant use with azathioprine, mercaptopurine, theophylline (contraindicated).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Discontinue medication immediately if rash appears. Encourage high fluid intake (3,000 ml/day). Monitor I&O (output should be at least 2,000 ml/day). Monitor CBC, serum uric acid, renal function, LFT. Assess urine for cloudiness, unusual color, odor. Assess for therapeutic response (reduced joint tenderness, swelling, redness, limitation of motion). Monitor for symptoms of CVA, MI.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Encourage drinking 8–10 glasses (8 oz) of fluid daily while taking medication. • Report rash, chest pain, shortness of breath, symptoms suggestive of stroke. • Gout attacks may occur for several months after starting treatment (medication is not a pain reliever). • Continue taking even if gout attack occurs.
felodipine
fe-loe-di-peen
(Plendil ![]() )
)
Do not confuse Plendil with Isordil, Pletal, Prilosec, or Prinivil, or Renedil with Prinivil.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Lexxel: felodipine/enalapril (ACE inhibitor): 2.5 mg/5 mg, 5 mg/5 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Calcium channel blocker. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive, antianginal.
USES
Management of hypertension. May be used alone or with other antihypertensives. OFF-LABEL: Management of pediatric hypertension.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to felodipine or other calcium channel blocker. Cautions: Severe left ventricular dysfunction, HF, hepatic impairment, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with outflow tract obstruction, peripheral edema, severe aortic stenosis, elderly. Concomitant CYP3A4 inhibitors (see Appendix I).
ACTION
Inhibits calcium movement across cardiac, vascular smooth muscle cell membranes. Therapeutic Effect: Relaxes coronary vascular smooth muscle and causes vasodilation. Increases myocardial oxygen delivery.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 2–5 hrs | N/A | 24 hrs |
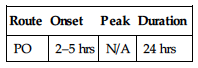
Rapidly, completely absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: greater than 99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 11–16 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May experience greater hypotensive response. Constipation may be more problematic.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, erythromycin, cimetidine) may increase concentration. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Ephedra, ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Garlic may increase antihypertensive effect. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase absorption, concentration. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets (Extended-Release): 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg.
Tablets (Extended-Release): 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with or without food. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide extended-release tablets. Swallow whole.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 5 mg/day as single dose. Increase by 5 mg at 2-wk intervals. Usual dose: 5–10 mg once daily. ELDERLY: Initially, 2.5 mg/day. Adjust dosage at no less than 2-wk intervals. Usual dose: 2.5–10 mg once daily. CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 2.5 mg once daily. May increase at 2-wk intervals. Maximum: 10 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Initially, 2.5 mg once daily. Titrate carefully.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (22%–18%): Headache, peripheral edema. Occasional (6%–4%): Flushing, respiratory infection, dizziness, light-headedness, asthenia. Rare (less than 3%): Angina, gingival hyperplasia, paresthesia, abdominal discomfort, anxiety, muscle cramping, cough, diarrhea, constipation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose produces nausea, drowsiness, confusion, slurred speech, hypotension, bradycardia.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess B/P, apical pulse immediately before drug administration (if pulse is 60 or less/min or systolic B/P is less than 90 mm Hg, withhold medication, contact physician).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Assess for peripheral edema. Monitor pulse rate for bradycardia. Assess skin for flushing. Monitor hepatic function. Question for headache, asthenia.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not abruptly discontinue medication. • Compliance with therapy regimen is essential to control hypertension. • To avoid hypotensive effect, go from lying to standing slowly. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Report palpitations, shortness of breath, pronounced dizziness, nausea. • Swallow tablet whole; do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide. • Avoid grapefruit products, alcohol. • Report exacerbation of angina.
fenofibrate 
fen-o-fye-brate
(Antara, Apo-Fenofibrate ![]() , Fenoglide, Fibricor, Lipofen, Lofibra, Novo-Fenofibrate
, Fenoglide, Fibricor, Lipofen, Lofibra, Novo-Fenofibrate ![]() , Tricor, Triglide, Trilipix)
, Tricor, Triglide, Trilipix)
Do not confuse Tricor with Fibricor or Tracleer.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Fibric acid derivative. CLINICAL: Antihyperlipidemic.
USES
Adjunct to diet for reduction of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol, triglycerides (types IV and V hyperlipidemia), apo-lipoprotein B, and to increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in pts with primary hypercholesterolemia, mixed dyslipidemia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensivity to fenofibrate. Active hepatic disease, preexisting gallbladder disease, severe renal/hepatic dysfunction (including primary biliary cirrhosis, unexplained persistent hepatic function abnormality), breastfeeding. Cautions: Anticoagulant therapy (e.g., warfarin), history of hepatic disease, venous thromboembolism, mild to moderate renal impairment, substantial alcohol consumption, statin or colchicine therapy (increased risk of myopathy, rhabdomyolysis), elderly.
ACTION
Downregulates apoprotein C-III and upregulates apoprotein A-I, increasing VLDL catabolism. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases triglycerides, increases HDL.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Absorption increased when given with food. Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine (60%), feces (25%). Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 10–35 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Safety in pregnancy not established. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Potentiates effects of anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin). Bile acid sequestrants may impede absorption. Cyclosporine may increase concentration, risk of nephrotoxicity. Colchicine, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) may increase risk of severe myopathy, rhabdomyolysis, acute renal failure. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: All foods increase absorption. LAB VALUES: May increase serum creatine kinase (CK), ALT, AST. May decrease Hgb, Hct, WBC; serum uric acid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: (Antara):(Antara): 30 mg, 90 mg. (Lipofen): 50 mg, 150 mg. (Lofibra): 67 mg, 134 mg, 200 mg. (Trilipix): 45 mg, 135 mg. Tablets: (Fenoglide): 40 mg, 120 mg. (Fibricor): 35 mg, 105 mg. (Lofibra): 54 mg, 160 mg. (Tricor): 48 mg, 145 mg. (Triglide): 160 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give Fenoglide, Lipofen, Lofibra with meals. • Antara, Fibricor, Tricor, Triglide, and Trilipix may be given without regard to food. Antara, Fenoglide, Lipafen: Swallow whole; do not open (capsules), crush, dissolve, or cut.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertriglyceridemia
PO (Antara): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 30–90 mg/day.
PO (Fenoglide): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 40–120 mg/day with meals.
PO (Fibricor): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 35–105 mg/day.
PO (Lipofen): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 50–150 mg/day with meals.
PO (Lofibra): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 67–200 mg/day with meals.
PO (Tricor): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 48–145 mg/day.
PO (Triglide): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 160 mg/day.
PO (Trilipix): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 45–135 mg/day.
Hypercholesterolemia, Mixed Hyperlipidemia
PO (Antara): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 90 mg/day.
PO (Fenoglide): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 120 mg/day with meals.
PO (Fibricor): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 105 mg/day.
PO (Lipofen): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 150 mg/day with meals.
PO (Lofibra): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 200 mg/day with meals.
PO (Tricor): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 145 mg/day.
PO (Triglide): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 160 mg/day.
PO (Trilipix): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 135 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Monitor renal function before adjusting dose. Decrease dose or increase dosing interval for pts with renal failure.
| Initial doses: | Antara: 30 mg/day | Lofibra: 67 mg/day |
| Fenoglide: 40 mg/day | Tricor: 48 mg/day | |
| Lipofen: 50 mg/day | Triglide: 50 mg/day |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Contraindicated.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (8%–4%): Pain, rash, headache, asthenia, fatigue, flu-like symptoms, dyspepsia, nausea/vomiting, rhinitis. Occasional (3%–2%): Diarrhea, abdominal pain, constipation, flatulence, arthralgia, decreased libido, dizziness, pruritus. Rare (less than 2%): Increased appetite, insomnia, polyuria, cough, blurred vision, eye floaters, earache.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
May increase cholesterol excretion into bile, leading to cholelithiasis. Pancreatitis, hepatitis, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain diet history, esp. fat consumption. Obtain serum cholesterol, triglycerides, LFT, CBC during initial therapy and periodically during treatment. Treatment should be discontinued if hepatic enzyme levels persist greater than 3 times normal limit.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
For pts on concurrent therapy with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, monitor for complaints of myopathy (muscle pain, weakness). Monitor serum creatine kinase (CK). Monitor serum cholesterol, triglyceride for therapeutic response.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report severe diarrhea, constipation, nausea. • Report skin rash/irritation, insomnia, muscle pain, tremors, dizziness.
*fentaNYL 

fen-ta-nil
(Abstral, Actiq, Apo-Fentanyl ![]() Duragesic, Fentora, Ionsys, Lazanda, Onsolis, Subsys)
Duragesic, Fentora, Ionsys, Lazanda, Onsolis, Subsys)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Physical and psychological dependence may occur with prolonged use. Must be alert to abuse, misuse, or diversion. May cause life-threatening hypoventilation, respiratory depression, or death. Use with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors may result in potentially fatal respiratory depression. Buccal: Tablet and lozenge contain enough medication that may be fatal to children. Transdermal patch: Serious or life-threatening hypoventilation has occurred. Limit use to children 2 yrs of age and older. Exposure to direct heat source increases drug release, resulting in overdose/death.
Physical and psychological dependence may occur with prolonged use. Must be alert to abuse, misuse, or diversion. May cause life-threatening hypoventilation, respiratory depression, or death. Use with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors may result in potentially fatal respiratory depression. Buccal: Tablet and lozenge contain enough medication that may be fatal to children. Transdermal patch: Serious or life-threatening hypoventilation has occurred. Limit use to children 2 yrs of age and older. Exposure to direct heat source increases drug release, resulting in overdose/death.
Do not confuse fentanyl with alfentanil or sufentanil.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Opioid, narcotic agonist (Schedule II). CLINICAL: Analgesic.
USES
Injection: (Fentanyl): Pain relief, preop medication; adjunct to general or regional anesthesia. Abstral: Treatment of breakthrough pain in cancer pts 18 yrs of age and older. Actiq: Treatment of breakthrough pain in chronic cancer or AIDS-related pain. Duragesic: Management of chronic pain (transdermal). Fentora: Breakthrough pain in pts on chronic opioids. Ionsys: Short-term management of acute postoperative pain in adults. Lazanda: Management of breakthrough pain in cancer. Onsolis: Breakthrough pain in pts with cancer currently receiving opioids and tolerant to opioid therapy. Subsys: Treatment of breakthrough cancer pain.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fentanyl. Transdermal: Severe respiratory disease depression, paralytic ileus, intermittent pain. Transdermal, transmucosal, lozenges, buccal films: Management of acute or postoperative pain, pts not opioid tolerant. Cautions: Bradycardia; renal, hepatic, respiratory disease; head injuries; altered LOC; biliary tract disease; acute pancreatitis; cor pulmonale; significant COPD; increased ICP; use of MAOIs within 14 days; elderly; morbid obesity.
ACTION
Binds to opioid receptors in CNS, reducing stimuli from sensory nerve endings, inhibits ascending pain pathways. Therapeutic Effect: Alters pain reception, increases pain threshold.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| IV | 1–2 min | 3–5 min | 0.5–1 hr |
| IM | 7–15 min | 20–30 min | 1–2 hrs |
| Transdermal | 6–8 hrs | 24 hrs | 72 hrs |
| Transmucosal | 5–15 min | 20–30 min | 1–2 hrs |
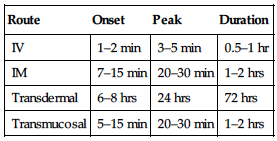
Well absorbed after IM or topical administration. Transmucosal form absorbed through buccal mucosa and GI tract. Protein binding: 80%–85%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated by biliary system. Half-life: 2–4 hrs IV; 17 hrs transdermal; 6.6 hrs transmucosal.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Readily crosses placenta. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. May prolong labor if administered in latent phase of first stage of labor or before cervical dilation of 4–5 cm has occurred. Respiratory depression may occur in neonate if mother received opiates during labor. Children: Neonates more susceptible to respiratory depressant effects. Patch: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 12 yrs. Elderly: May be more susceptible to respiratory depressant effects. Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, modafinil) may decrease concentration, effects. Alcohol, CNS depressant medications may increase CNS depression. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole, protease inhibitors [e.g., ritonavir]) may increase effects and potential for respiratory depression. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration, effects. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase potential for respiratory depression with oral, transmucosal forms. LAB VALUES: May increase serum amylase, lipase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Buccal Tablet (Fentora): 100 mcg, 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg. Buccal Soluble Film (Onsolis): 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg, 1,200 mcg. Injection Solution: 50 mcg/ml. Nasal Spray (Lazanda): 100 mcg/spray, 400 mcg/spray. Sublingual Tablets (Abstral): 100 mcg, 200 mcg, 300 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg. Sublingual Spray (Subsys): 100 mcg, 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg. Transdermal Patch (Duragesic): 12 mcg/hr, 25 mcg/hr, 50 mcg/hr, 75 mcg/hr, 100 mcg/hr. Transmucosal Lozenges (Actiq): 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg, 1,200 mcg, 1,600 mcg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Rate of Administration • Give by slow IV injection (over 1–2 min). • Too-rapid injection increases risk of severe adverse reactions (skeletal/thoracic muscle rigidity resulting in apnea, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, peripheral circulatory collapse, anaphylactoid effects, cardiac arrest).
Storage • Store parenteral form at room temperature. • Opiate antagonist (naloxone) should be readily available.
Transdermal
• Apply to hairless area of intact skin of upper torso. • Use flat, nonirritated site. • Firmly press evenly and hold for 30 sec, ensuring adhesion is in full contact with skin and edges are completely sealed. • Use only water to cleanse site before application (soaps, oils may irritate skin). • Rotate sites of application. • Carefully fold used patches so that system adheres to itself; discard in toilet.
Buccal Film
• Wet inside of cheek. • Place film inside mouth with pink side of unit against cheek. • Press film against cheek and hold for 5 sec. • Leave in place until dissolved (15–30 min). • Do not chew, swallow, cut film. • Liquids may be given after 5 min of application; food after film dissolves.
Buccal Tablets
• Place tablet above a rear molar between upper cheek and gum. • Dissolve over 30 min. • Swallow remaining pieces with water. • Do not split tablet.
Sublingual Spray
• Open blister pack with scissors immediately prior to use. • Spray contents underneath tongue.
Sublingual Tablets
• Place under tongue. • Dissolves rapidly. • Do not suck, chew, or swallow tablet.
Nasal
• Prime device before use by spraying into pouch. • Insert nozzle about ½ inch into nose, pointing toward bridge of nose, tilting bottle slightly. • Press down firmly until hearing a “click” and number on counting window advances by one. Do not blow nose for at least 30 min following administration.
Transmucosal
• Suck lozenge vigorously. • Allow to dissolve over 15 min. • Do not chew.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Azithromycin (Zithromax), pantoprazole (Protonix), phenytoin (Dilantin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Atropine, bupivacaine (Marcaine, Sensorcaine), clonidine (Duraclon), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), droperidol (Inapsine), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), ketorolac (Toradol), lorazepam (Ativan), metoclopramide (Reglan), midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, nitroglycerin, norepinephrine (Levophed), ondansetron (Zofran), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Doses titrated to desired effect dependent upon degree of analgesia, pt status.
Acute Pain Management (Fentanyl)
IM/IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 25–100 mcg/dose q1–2h as needed. CHILDREN: 0.5–2 mcg/kg/dose q1–2h as needed. INFANTS (IV push): 1–4 mcg/kg/dose q2–4h.
Continuous IV Infusion (Fentanyl)
ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1–2 mcg/kg/hr. CHILDREN: 0.5–3 mcg/kg/hr.
Usual Buccal Dose (Fentora)
ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 100 mcg. Titrate dose, providing adequate analgesia with tolerable side effects.
Usual Buccal Soluble Film Dose (Onsolis)
Note: All pts must initiate with 200 mcg.
ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 200 mcg up to 1,200 mcg. Maximum: No more than 4 doses/day, separate by at least 2 hrs.
Usual Nasal Dose (Lazanda)
Nasal: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 100 mcg. Titrate from 100 mcg to 200 mcg to 400 mcg to 800 mcg (maximum). Wait at least 2 hrs between doses; no more than 4 doses in 24 hrs.
Usual Sublingual Tablet Dose (Abstral)
ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 100 mcg, then titrate to desired dose/effect. Wait at least 2 hrs between doses; no more than 4 doses in 24 hrs.
Usual Sublingual Spray Dose (Subsys)
ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 100 mcg. May repeat in 30 min if pain not relieved. Must wait at least 4 hours before treating another episode of pain.
Usual Transdermal Dose (Duragesic)
ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 12–25 mcg/hr. May increase after 3 days.
Usual Transmucosal Dose (Actiq)
ADULTS, CHILDREN: 200–1200 mcg for breakthrough pain. Limit to 4 applications/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Injection: No dose adjustment.
Transdermal patch: Mild to moderate
impairment: Reduce dose by 50%.
Severe impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: IV: Postop drowsiness, nausea, vomiting. Transdermal (10%–3%): Headache, pruritus, nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, dyspnea, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, diarrhea, constipation, decreased appetite. Occasional: IV: Postop confusion, blurred vision, chills, orthostatic hypotension, constipation, difficulty urinating. Transdermal (3%–1%): Chest pain, arrhythmias, erythema, pruritus, syncope, agitation, skin irritations.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose or too-rapid IV administration may produce severe respiratory depression, skeletal/thoracic muscle rigidity (may lead to apnea, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, cold/clammy skin, cyanosis, coma). Tolerance to analgesic effect may occur with repeated use. Antidote: Naloxone (see Appendix J for dosage).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Resuscitative equipment, opiate antagonist (naloxone 0.5 mcg/kg) should be available for initial use. Establish baseline B/P, respirations. Assess type, location, intensity, duration of pain.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation. Encourage post-op pt to turn, cough, deep breathe q2h. Monitor respiratory rate, B/P, heart rate, oxygen saturation. Assess for relief of pain.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid alcohol; do not take other medications without consulting physician. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Teach pt proper transdermal, buccal, lozenge administration. Transdermal: Avoid saunas (increases drug release time). • Use as directed to avoid overdosage; potential for physical dependence with prolonged use. • Report constipation, absence of pain relief. • Taper slowly after long-term use.
ferric gluconate
fer-ick gloo-koe-nate
(Ferrlecit)
ferrous fumarate
fer-us fue-ma-rate
ferrous gluconate
fer-us gloo-koe-nate
(Apo-Ferrous Gluconate ![]() , Fergon)
, Fergon)
ferrous sulfate
fer-us sul-fate
(Apo-Ferrous Sulfate ![]() , Fer-In-Sol, Fer-Iron, Slow-Fe)
, Fer-In-Sol, Fer-Iron, Slow-Fe)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Enzymatic mineral. CLINICAL: Iron preparation.
USES
Prevention, treatment of iron deficiency anemia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to iron salts. Hemochromatosis, hemolytic anemias. Cautions: Peptic ulcer, regional enteritis, ulcerative colitis, pts receiving frequent blood transfusions.
ACTION
Essential component in formation of Hgb, myoglobin, enzymes. Promotes effective erythropoiesis and transport, utilization of oxygen. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents iron deficiency.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Absorbed in duodenum and upper jejunum. Ten percent absorbed in pts with normal iron stores; increased to 20%–30% in pts with inadequate iron stores. Primarily bound to serum transferrin. Excreted in urine, sweat, sloughing of intestinal mucosa, menses. Half-life: 6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antacids, calcium supplements, pancreatin, pancrelipase may decrease absorption of ferrous compounds. May decrease absorption of etidronate, quinolones, tetracyclines. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: Cereal, coffee, dietary fiber, eggs, milk, tea decrease absorption. LAB VALUES: May increase serum bilirubin, iron. May decrease serum calcium.
AVAILABILITY (OTC)
Ferric Gluconate
Injection, solution: 12.5 mg/ml.
Ferrous Fumarate
Tablets (Ferrocite): 324 mg (106 mg elemental iron).
Ferrous Gluconate
Tablets: 240 mg (27 mg elemental iron) (Fergon), 325 mg (36 mg elemental iron).
Ferrous Sulfate
Oral Solution (Fer-In-Sol, Fer-Iron): 75 mg/ml (15 mg/ml elemental iron). Tablets: 325 mg (65 mg elemental iron). Syrup: 300 mg/5 ml.
![]() Tablets (Timed-Release [Slow-Fe]): 160 mg (50 mg elemental iron).
Tablets (Timed-Release [Slow-Fe]): 160 mg (50 mg elemental iron).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Store all forms (tablets, capsules, suspension, drops) at room temperature. • Ideally, give between meals with water or juice but may give with meals if GI discomfort occurs. • Transient staining of mucous membranes, teeth occurs with liquid iron preparation. To avoid staining, place liquid on back of tongue with dropper or straw. • Do not give with milk or milk products. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide timed-release tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Dosage is expressed in terms of milligrams of elemental iron. Assess degree of anemia, pt weight, presence of any bleeding. Expect to use periodic hematologic determinations as guide to therapy.
IV: (Ferric Gluconate): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 125 mg/dose. Usual dose: 1,000 mg given over 8 sessions.
PO (Ferrous Fumarate): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100–200 mg/day in 2–3 divided doses. CHILDREN: 3–6 mg/kg/day in 2–3 divided doses.
PO (Ferrous Gluconate): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100–200 mg/day in 2–3 divided doses. CHILDREN: 3–6 mg/kg/day in 2–3 divided doses.
PO (Ferrous Sulfate): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100–200 mg/day in 2–3 divided doses. CHILDREN: 3–6 mg/kg/day in 2–3 divided doses.
Prevention of Iron Deficiency
PO (Ferrous Fumarate): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 60 mg/day. CHILDREN: 30 mg/day with folic acid.
PO (Ferrous Gluconate): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 60 mg/day. CHILDREN: 30 mg/day with folic acid.
PO (Ferrous Sulfate): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 60 mg/day. CHILDREN: 30 mg/day with folic acid.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Mild, transient nausea. Rare: Heartburn, anorexia, constipation, diarrhea.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Large doses may aggravate existing GI tract disease (peptic ulcer, regional enteritis, ulcerative colitis). Severe iron poisoning occurs most often in children, manifested as vomiting, severe abdominal pain, diarrhea, dehydration, followed by hyperventilation, pallor, cyanosis, cardiovascular collapse.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess nutritional status, dietary history. Question history of hemachromatosis, hemolytic anemia, ulcerative colitis.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum iron, total iron-binding capacity, reticulocyte count, Hgb, ferritin. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess for clinical improvement, record relief of iron deficiency symptoms (fatigue, irritability, pallor, paresthesia of extremities, headache).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Expect stool color to darken. • Oral liquid may stain teeth. • To prevent mucous membrane and teeth staining with liquid preparation, use dropper or straw and allow solution to drop on back of tongue. • If GI discomfort occurs, take after meals or with food. • Do not take within 2 hrs of other medication or eggs, milk, tea, coffee, cereal.
fesoterodine
fes-oh-ter-oh-deen
(Toviaz)
Do not confuse fesoterodine with fexofenadine or tolteradine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Muscarinic receptor antagonist. CLINICAL: Antispasmodic.
USES
Treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms including urinary incontinence, urgency, frequency.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fesoterodine. Gastric retention, uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma, urinary retention. Cautions: Severe renal impairment, severe hepatic impairment, clinically significant bladder outflow obstruction (risk of urinary retention), GI obstructive disorders (e.g., pyloric stenosis [risk of gastric retention], treated narrow-angle glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, concurrent therapy with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, elderly, use in hot weather.
ACTION
Exhibits antimuscarinic activity by interceding via cholinergic muscarinic receptors, thereby mediating urinary bladder contraction. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases urinary frequency, urgency.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 50%. Rapidly and extensively hydrolyzed to its active metabolite. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 7 hours.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Increased incidence of antimuscarinic adverse events including dry mouth, constipation, dyspepsia, increase in residual urine, dizziness, urinary tract infections higher in pts 75 yrs of age and older.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, erythromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole, miconazole) may increase concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase potential for urinary retention, constipation. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, GGT.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets, Extended-Release: 4 mg, 8 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release: 4 mg, 8 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May be administered with or without food. • Swallow whole; do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablet.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Overactive Bladder
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 4 mg once daily. May increase to 8 mg once daily. Maximum dose for pts with concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin, ketoconazole) is 4 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Maximum dose: 4 mg with CrCl less than 30 ml/min.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (34%–18%): Dry mouth. Occasional (6%–3%): Constipation, urinary tract infection dry eyes. Rare (2% or less): Nausea, dysuria, back pain, rash, insomnia, peripheral edema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Severe anticholinergic effects including abdominal cramps, facial warmth, excessive salivation/lacrimation, diaphoresis, pallor, urinary urgency, blurred vision.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess urinary pattern (e.g., urinary frequency, urgency). Obtain baseline chemistries. Question history as listed in Precautions. Receive full medication history.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Question for visual changes. Monitor incontinence, postvoid residuals. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• May produce constipation and urinary retention. • Blurred vision may occur; use caution until drug effects have been determined. • Heat prostration (due to decreased sweating) can occur if used in a hot environment. • Do not ingest grapefruit products.
fexofenadine
fex-oh-fen-a-deen
(Allegra, Allegra Children’s)
Do not confuse Allegra with Viagra, or fexofenadine with fesoterodine.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Allegra-D 12 Hour: fexofenadine/pseudoephedrine (sympathomimetic): 60 mg/120 mg. Allegra-D 24 Hour: fexofenadine/pseudoephedrine (sympathomimetic): 180 mg/240 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Piperidine. CLINICAL: Antihistamine.
USES
Relief of symptoms associated with allergic rhinitis. Treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fexofenadine. Cautions: Renal impairment. Orally disintegrating tablet not recommended in children younger than 6 yrs.
ACTION
Competes with histamine in GI tract, blood vessels, and respiratory tract. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves allergic rhinitis symptoms.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Onset | Peak | Duration | |
| PO | 60 min | — | 12 hrs or greater |
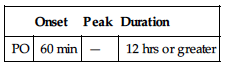
Rapidly absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 60%–70%. Does not cross blood-brain barrier. Minimally metabolized. Eliminated in feces (80%), urine (11%). Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 14.4 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 12 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Aluminum- and magnesium- containing antacids may decrease absorption if given within 15 min of fexofenadine. May increase concentrations of erythromycin, ketoconazole. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. FOOD: Fruit juices may decrease bioavailability. LAB VALUES: May suppress wheal, flare reactions to antigen skin testing unless drug is discontinued at least 4 days before testing.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Oral Suspension: 30 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 30 mg, 60 mg, 180 mg. Tablets (Orally Disintegrating): 30 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Avoid giving with fruit juices (apple, grapefruit, orange). Administer with water only. • Shake suspension well before use.
PO (Orally Disintegrating Tablet)
• Take on empty stomach. • Remove from blister pack; immediately place on tongue. • May take with or without liquid. • Do not split or cut.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Allergic Rhinitis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 60 mg twice daily or 180 mg once daily. CHILDREN 2–11 YRS: 30 mg twice daily.
Urticaria
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 60 mg twice daily or 180 mg once daily. CHILDREN 2–11 YRS: 30 mg twice daily. CHILDREN 6 MOS–LESS THAN 2 YRS: 15 mg twice daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment (CrCl Less Than 80 ml/min)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 60 mg once daily. CHILDREN 2–11 YRS: 30 mg once daily. CHILDREN 6 MOS–LESS THAN 2 YRS: 15 mg once daily.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Rare (less than 2%): Drowsiness, headache, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distress, dysmenorrhea.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hypersensitivity reaction occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
If pt is having an allergic reaction, obtain history of recently ingested foods, drugs, environmental exposure, emotional stress. Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respiration; quality, rate of pulse. Assess lung sounds for rhonchi, wheezing, rales.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for therapeutic response; relief from allergy: itching, red, watery eyes, rhinorrhea, sneezing.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol during antihistamine therapy. • Coffee, tea may help reduce drowsiness. • Do not take with any fruit juices.
fidaxomicin
fye-dax-oh-mye-sin
(Dificid)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
USES
Treatment of C. difficile–associated diarrhea.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fidaxomicin. Cautions: History of anemia, neutropenia, macrolide allergy.
ACTION
Binds to ribosomal sites of susceptible organisms, inhibiting RNA-dependent protein synthesis by RNA polymerase. Therapeutic Effect: Bactericidal against Clostridium difficile.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Minimal systemic absorption following PO administration. Mainly confined to GI tract. Excreted primarily in feces (92%). Half-life: 9 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Cyclosporine may increase serum concentration, effects. HERBAL: None known. FOOD: None significant. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 200 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• Give without regard to food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Clostridium Difficile–Associated Diarrhea
PO: ADULTS: 200 mg twice daily for 10 days.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (62%–33%): Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain. Rare (less than 2%): Pruritus, rash.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Less than 2% reported events most likely related to diarrhea-associated illness including volume loss, dehydration, GI bleeding, bloating, megacolon, abdominal distention/tenderness, flatulence, dyspepsia, dysphasia, intestinal obstruction, bicarbonate loss, hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and increased hepatic function tests. GI tract infection may cause bleeding, decreased platelets, decreased RBC count.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Verify positive C. difficile toxin test before initiating treatment. Implement infection control measures. Obtain baseline CBC, electrolytes, renal function, fecal occult blood test. Assess abdominal pain, bowel sounds, and stool characteristics (color, frequency, consistency). Assess hydration status.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for volume loss, dehydration, hypotension. Encourage nutrition/fluid intake. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Routinely assess bowel sounds. Screen for intestinal obstruction (increased nausea, abdominal pain, hyperactive bowel sounds) and consider abdominal X-ray if suspected.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Complete drug therapy, despite symptom improvement. Early discontinuation may result in antibacterial resistance and increased risk of recurrent infection. • Report weakness, fatigue, pale skin, dizziness, or red/dark, tarry stools relating to GI bleeding.
filgrastim 
fil-gras-tim
(Granix, Neupogen, Zarxio)
filgrastim-sndz
(Zarxio)
Do not confuse Neupogen with Epogen, Neulasta, Neumega, or Nutramigen.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Biologic modifier. CLINICAL: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF).
USES
Granix: Decreases duration of severe neutropenia in pts with malignancies receiving chemotherapy associated with severe neutropenia, fever. Neupogen, Zarxio: Reduces neutropenia duration, sequelae in pts with nonmyeloid malignancies having myeloablative therapy followed by bone marrow transplant (BMT). Mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells into peripheral blood for collection by apheresis. Treatment of chronic, severe neutropenia. Decreases incidence of infection in pts with malignancies receiving chemotherapy associated with increased incidence of severe neutropenia with fever. Reduces time to neutrophil recovery/duration of fever after induction/consolidation chemotherapy in AML pts. Neupogen: Increases survival in pts acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of AIDS-related neutropenia in pts receiving zidovudine; drug-induced neutropenia; anemia in myelodysplastic syndrome; hepatitis C treatment-associated neutropenia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to filgrastim. (Neupogen) Hypersensitivity to Escherichia coli–derived proteins. Cautions: Malignancy with myeloid characteristics (due to G-CSF’s potential to act as growth factor), gout, psoriasis, neutrophil count greater than 50,000 cells/mm3, sickle cell disease, concomitant use of other drugs that may result in thrombocytopenia. Do not use 24 hrs before or after cytotoxic chemotherapy.
ACTION
Stimulates production, maturation, activation of neutrophils. Therapeutic Effect: Increases migration and cytotoxicity of neutrophils.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed. Onset of action: 24 hrs (plateaus in 3–5 days). WBC return to normal in 4–7 days. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 3.5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase LDH, leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP) scores, serum alkaline phosphatase, uric acid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: (Neupogen): 300 mcg/ml, 480 mcg/1.6 ml Neupogen): 300 mcg/0.5 ml; 480 mcg/0.8 ml. Injection, Prefilled Syringe: (Granix, Zarxio): 300 mcg/0.5 ml, 480 mcg/0.8 ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ May be given by subcutaneous injection, short IV infusion (15–30 min), or continuous IV infusion. Do not dilute with normal saline.
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Allow vial to warm to room temperature (approx. 30 mins). • Visually inspect for particulate matter or discoloration. • Dilute in D5W from concentration of 300 mcg/ml to 5 mcg/ml (do not dilute to a final concentration less than 5 mcg/ml). Diluted solutions of 5–15 mcg/ml should have addition of albumin to a final concentration of 2 mg/ml. • Do not dilute with saline.
Rate of Administration • For intermittent infusion (piggyback), infuse over 15–30 min. • For continuous infusion, give single dose over 4–24 hrs. • In all situations, flush IV line with D5W before and after administration.
Storage • Refrigerate vials and syringes. • Stable for up to 24 hrs at room temperature (provided vial contents are clear and contain no particulate matter).
Subcutaneous
• Aspirate syringe before injection (avoid intra-arterial administration).
Storage • Store in refrigerator, but remove before use and allow to warm to room temperature.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin (Fungizone), cefepime (Maxipime), cefotaxime (Claforan), cefoxitin (Mefoxin), ceftizoxime (Cefizox), ceftriaxone (Rocephin), clindamycin (Cleocin), dactinomycin (Cosmegen), etoposide (VePesid), fluorouracil, furosemide (Lasix), heparin, mannitol, methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), mitomycin (Mutamycin), prochlorperazine (Compazine).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Bumetanide (Bumex), calcium gluconate, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lorazepam (Ativan), morphine, potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Begin therapy at least 24 hrs after last dose of chemotherapy and at least 24 hrs after bone marrow infusion. Dosing based on actual body weight.
Chemotherapy-Induced Neutropenia
Neupogen, Zarxio
IV or SQ Infusion, SQ Injection: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: Initially, 5 mcg/kg/day. May increase by 5 mcg/kg for each chemotherapy cycle based on duration/severity of neutropenia; continue for up to 14 days or until absolute neutrophil count (ANC) reaches 10,000/mm3.
Granix
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5 mcg/kg/day. Continue until nadir has passed and neutrophil count recovered to normal range.
Bone Marrow Transplant
IV or SQ Infusion: (Neupogen, Zarxio) ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 10 mcg/kg/day. Adjust dosage daily during period of neutrophil recovery based on neutrophil response.
Mobilization of Progenitor Cells
IV or SQ Infusion: (Neupogen, Zarxio) ADULTS: 10 mcg/kg/day in donors beginning at least 4 days before first leukapheresis and continuing until last leukapheresis (usually for 6–7 days).
Chronic Neutropenia, Congenital Neutropenia
SQ: (Neupogen, Zarxio) ADULTS, CHILDREN: 6 mcg/kg/dose twice daily. Adjust dose based on ANC/clinical response.
Idiopathic or Cyclic Neutropenia
SQ: (Neupogen, Zarxio) ADULTS, CHILDREN: 5 mcg/kg/dose once daily. Adjust dose based on ANC/clinical response.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (57%–11%): Nausea/vomiting, mild to severe bone pain (more frequent with high-dose IV form, less frequent with low-dose subcutaneous form), alopecia, diarrhea, fever, fatigue. Occasional (9%–5%): Anorexia, dyspnea, headache, cough, rash. Rare (less than 5%): Psoriasis, hematuria, proteinuria, osteoporosis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Long-term administration occasionally produces chronic neutropenia, splenomegaly. Acute respiratory distress syndrome, alveolar hemorrhage and hemoptysis (pts undergoing peripheral blood progenitor cell collection mobilization), capillary leak syndrome, cutaneous vasculitis, glomerulonephritis, leukocytosis, MI, thrombocytopenia, sickle cell crisis, splenic rupture may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
CBC, platelet count should be obtained before therapy initiation and twice wkly thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
In septic pts, be alert for adult respiratory distress syndrome. Closely monitor those with preexisting cardiac conditions. Monitor B/P (transient decrease in B/P may occur), temperature, CBC with differential, platelet count, serum uric acid, hepatic function tests.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report fever, chills, severe bone pain, chest pain, palpitations.
finasteride
fin-as-ter-ide
(Apo-Finasteride ![]() , Propecia, Proscar)
, Propecia, Proscar)
Do not confuse finasteride with furosemide, or Proscar with ProSom, Provera, or Prozac.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Androgen hormone inhibitor. CLINICAL: Benign prostatic hyperplasia agent.
USES
Proscar: Reduces risk of acute urinary retention, need for surgery in symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) alone or in combination with doxazosin (Cardura). Propecia: Treatment of male pattern hair loss. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of female hirsutism.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to finasteride, pregnancy or women of child-bearing potential. Cautions: Hepatic impairment, urinary outflow obstruction, urinary retention. Women who are attempting to conceive should avoid exposure to crushed or broken tablets.
ACTION
Inhibits 5-alpha reductase, an intracellular enzyme that converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in prostate gland, resulting in decreased serum DHT. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces size of prostate gland.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO (reduction of DHT) | 8 hrs | — | 24 hrs |
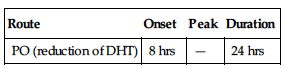
Rapidly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 90%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Half-life: 6–8 hrs. Onset of clinical effect: 3–6 mos of continued therapy.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Physical handling of tablet by those who are or may become pregnant may produce abnormalities of external genitalia of male fetus. Children: Not indicated for use in children. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Avoid concurrent use with saw palmetto (not adequately studied). FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Decreases serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, even in presence of prostate cancer. Decreases dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Increases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), testosterone.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets: 1 mg (Propecia), 5 mg (Proscar).
Tablets: 1 mg (Propecia), 5 mg (Proscar).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide film-coated tablets. • Give without regard to meals.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Proscar): 5 mg once daily (as single agent or in combination with doxazosin).
Hair Loss
PO: ADULTS: (Propecia): 1 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Rare (4%–2%): Gynecomastia, sexual dysfunction (impotence, decreased libido, decreased volume of ejaculate).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hypersensitivity reaction, circumoral swelling, testicular pain occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Digital rectal exam, serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) determination should be performed in pts with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) before initiating therapy and periodically thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Diligently monitor I&O, esp. in pts with large residual urinary volume, severely diminished urinary flow, or obstructive uropathy.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Treatment may cause impotence, decreased volume of ejaculate. • May not notice improved urinary flow even if prostate gland shrinks. • Must take medication longer than 6 mos, and it is unknown if medication decreases need for surgery. • Because of potential risk to male fetus, women who are or may become pregnant should not handle tablets or be exposed to pt’s semen.
fingolimod 
fin-goe-li-mod
(Gilenya)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Immunomodulator. CLINICAL: Multiple sclerosis agent.
USES
Treatment of pts with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) to reduce frequency of clinical exacerbations, delay accumulation of physical disability.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fingolimod. Sick sinus syndrome, second-degree or higher conduction block (unless pt has functioning pacemaker). Baseline QT interval 500 msec or greater. Concurrent use of class I or III antiarrhythmic. Recent (within 6 mos) MI, unstable angina, stroke, TIA, decompensated requiring hospitalization or NYHA class III/IV HF. Cautions: Concomitant use of antiarrhythmics, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, immunosuppresants, immune modulators, antineoplastics, QT interval–prolonging medications (e.g., amiodarone, ciprofloxacin); bradycardia, severe hepatic impairment, ischemic heart disease, diabetes, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia; history of syncope, uveitis; pts at risk for developing bradycardia or heart block.
ACTION
Blocks capacity of lymphocytes to move out from lymph nodes, reducing number of lymphocytes available to the CNS. Therapeutic Effect: May involve reduction of lymphocyte migration into central nervous system, which reduces central inflammation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Metabolized by the enzyme sphingosine kinase to active metabolite. Highly distributed in red blood cells (85%). Minimally metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 99.7%. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 6–9 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: Age-related severe hepatic impairment may increase risk of adverse reactions.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antineoplastics, immunosuppressives, immunomodulators may increase risk of immunosuppression. Ketoconazole may increase concentration/adverse effects. May decrease effect of vaccines. May increase effects of QT-prolonging medications. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease concentration. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Expect decrease in neutrophil count. May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, bilirubin, triglycerides.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 0.5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May give without regard to food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Multiple Sclerosis
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (25%–10%): Headache, diarrhea, back pain, cough. Occasional (8%–5%): Dyspnea, clinical depression, dizziness, hypertension, migraine, paresthesia, decreased weight. Rare (4%–2%): Blurred vision, alopecia, eye pain, asthenia, eczema, pruritus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
May increase risk of infections (influenza, herpes viral infection, bronchitis, sinusitis, gastroenteritis, ear infection) in 13%–4% of pts. Pts with diabetes or history of uveitis are at increased risk for developing macular edema.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, serum chemistries prior to initial treatment. At initial treatment (within first 4–6 hrs after dose), medication reduces heart rate, AV conduction, followed by progressive increase after first day of treatment. Obtain baseline vitals, with particular attention to pulse rate. Perform ophthalmologic evaluation prior to treatment and 3–4 mos after initiation of treatment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for bradycardia for 6 hrs after first dose, then as appropriate. Periodically monitor CBC, serum chemistries, particularly lymphocyte count (expected to decrease approximately 80% from baseline with continued treatment). Monitor for signs of systemic or local infection.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Obtain regular eye examinations during and for 2 mos following treatment. • Use effective methods of contraception during and for 3 mos following treatment. • Report fever, chills, aches, weakness, cough, nausea, symptoms of infection, visual changes, yellowing of skin, eyes, dark urine.
fluconazole
flu-kon-a-zole
(Apo-Fluconazole ![]() , Diflucan, Novo-Fluconazole
, Diflucan, Novo-Fluconazole ![]() )
)
Do not confuse Diflucan with diclofenac, Diprivan, or disulfiram, or fluconazole with fluoxetine, furosemide, or itraconazole.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Synthetic azole. CLINICAL: Systemic antifungal.
USES
Antifungal prophylaxis in pts undergoing bone marrow transplant; candidiasis (esophageal, oropharyngeal, urinary tract, vaginal); systemic Candida infections (e.g., candidemia); treatment of cryptococcal meningitis. OFF-LABEL: Cryptococcal pneumonia, candidal intertrigo.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fluconazole. Concomitant administration of QT-prolonging medications (e.g., erythromycin, pimozide). Cautions: Hepatic/renal impairment, hypersensitivity to other triazoles (e.g., itraconazole, terconazole), imidazoles (e.g., butoconazole, ketoconazole). Medications or conditions known to cause arrhythmias.
ACTION
Interferes with cytochrome P-450 activity, an enzyme necessary for ergosterol formation. Therapeutic Effect: Directly damages fungal membrane, altering its function. Fungistatic.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Widely distributed, including to CSF. Protein binding: 11%. Partially metabolized in liver. Excreted unchanged primarily in urine. Partially removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 20–30 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration/effect of cyclosporine, sirolimus, tacrolimus. Isoniazid, rifampin may increase drug metabolism. May increase concentration/effects of oral antidiabetic medication. May decrease metabolism of phenytoin, warfarin. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution, Pre-Mix: 100 mg (50 ml), 200 mg (100 ml), 400 mg (200 ml). Powder for Oral Suspension: 10 mg/ml, 40 mg/ml. Tablets: 50 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Rate of Administration • Do not exceed maximum flow rate of 200 mg/hr.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Do not remove from outer wrap until ready to use. • Squeeze inner bag to check for leaks. • Do not use parenteral form if solution is cloudy, precipitate forms, seal is not intact, or it is discolored. • Do not add supplementary medication.
PO
• Give without regard to meals.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B (Fungizone), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), ampicillin (Polycillin), calcium gluconate, cefotaxime (Claforan), ceftriaxone (Rocephin), cefuroxime (Zinacef), chloramphenicol (Chloromycetin), clindamycin (Cleocin), co-trimoxazole (Bactrim), diazepam (Valium), digoxin (Lanoxin), erythromycin (Erythrocin), furosemide (Lasix), haloperidol (Haldol), hydroxyzine (Vistaril), imipenem and cilastatin (Primaxin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), heparin, lipids, lorazepam (Ativan), midazolam (Versed), propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ PO and IV therapy equally effective; IV therapy for pt intolerant of drug or unable to take orally. Oral suspension stable for 14 days at room temperature or refrigerated.
Usual Dosage
Note: Duration and dose dependent on location/severity of infection.
PO/IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 150 mg once or loading dose: 200–800 mg. Maintenance dose: 200–800 mg once daily. CHILDREN AND NEONATES: Loading dose: 6–12 mg/kg. Maintenance dose: 3–12 mg/kg once daily. Maximum: 600 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
After a loading dose of 400 mg, daily dosage is based on creatinine clearance.
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| Greater than 50 ml/min | 100% |
| 50 ml/min or less | 50% |
| Dialysis | 50% |
| CCRT | 400–800 mg as loading dose |
| CVVH | then 200–800 mg/day |
| CVVHDF | 400–800 mg as loading dose, then 400–800 mg/day |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (4%–1%): Hypersensitivity reaction (chills, fever, pruritus, rash), dizziness, drowsiness, headache, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Exfoliative skin disorders, serious hepatic injury, blood dyscrasias (eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, leukopenia) have been reported rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain LFT; serum potassium in critically ill pts. Receive full medication history and screen for interactions. Assess areas of infection. Assess infected area. Establish baselines for CBC, serum potassium, hepatic function.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for hypersensitivity reaction (chills, fever). Monitor CBC, BMP, LFT. Report rash, itching promptly. Monitor temperature at least daily. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess for dizziness; provide assistance as needed.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report dark urine, pale stool, jaundiced skin or sclera of eyes, rash, pruritus. • Pts with oropharyngeal infections should maintain fastidious oral hygiene. • Consult physician before taking any other medication.
fludarabine 
floo-dar-a-been
(Fludara)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Must be administered by certified chemotherapy personnel. Severe neurologic toxicity reported. Life-threatening hemolytic anemia, autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura, hemophilia have occurred. Risk of severe myelosuppression (anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia). Concurrent use with pentostatin may produce severe/fatal pulmonary toxicity.
Must be administered by certified chemotherapy personnel. Severe neurologic toxicity reported. Life-threatening hemolytic anemia, autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura, hemophilia have occurred. Risk of severe myelosuppression (anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia). Concurrent use with pentostatin may produce severe/fatal pulmonary toxicity.
Do not confuse Fludara with FUDR, or fludarabine with cladribine or Flumadine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antimetabolite. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of progressive or refractory B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in pts who have not responded to or have not progressed with another standard alkylating agent. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, relapsed acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) or acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in children, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, reduced-intensity conditioning regimens prior to allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fludarabine. Cautions: Renal insufficiency, preexisting hematological disorders (e.g., granulocytopenia), seizure disorder, spasticity, peripheral neuropathy, infection, fever, immunodeficiency.
ACTION
Inhibits DNA synthesis by interfering with DNA polymerase alpha, ribonucleotide reductase, DNA primase. Therapeutic Effect: Induces cell death.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly dephosphorylated in serum, then phosphorylated intracellularly to active triphosphate. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 7–20 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy, esp. first trimester. May cause fetal harm. Not known whether distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Pentostatin may increase risk of pulmonary toxicity. Bone marrow depressants may increase risk of myelosuppression. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, AST, uric acid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Fludara): 50 mg. Injection, Solution: 25 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Give by IV infusion. Do not add to other IV infusions. Avoid small veins; swollen, edematous extremities; areas overlying joints, tendons.
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Handle with extreme care during preparation/administration. If contact with skin or mucous membranes occurs, wash thoroughly with soap and water; rinse eyes profusely with plain water. • Reconstitute 50-mg vial with 2 ml Sterile Water for Injection to provide concentration of 25 mg/ml. • Further dilute with 100–125 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 30 min.
Storage • Store in refrigerator. • Reconstituted vials stable for 16 days at room temperature or refrigerated. • Diluted solutions stable for 48 hrs at room temperature or refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Acyclovir (Zovirax), amphotericin B (Fungizone), daunorubicin, hydroxyzine (Vistaril), prochlorperazine (Compazine).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, morphine, multivitamins, potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
IV: ADULTS: 25 mg/m2 daily for 5 consecutive days. Continue for up to 3 additional cycles. Begin each course of treatment every 28 days.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| IV | |
| 50–79 ml/min | 20 mg/m2 |
| 30–49 ml/min | 15 mg/m2 |
| Less than 30 ml/min | Not recommended |
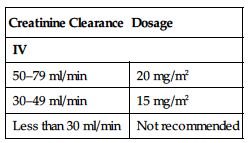
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (60%–11%): Fever, nausea/vomiting, chills. Occasional (20%–10%): Fatigue, generalized pain, rash, diarrhea, cough, asthenia, stomatitis, dyspnea, peripheral edema. Rare (7%–3%): Anorexia, sinusitis, dysuria, myalgia, paresthesia, headache, visual disturbances.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Pneumonia occurs frequently. Severe hematologic toxicity (anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia), GI bleeding may occur. Tumor lysis syndrome may begin with flank pain, hematuria; may also include hypercalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperuricemia, resulting in renal failure. High-dosage therapy may produce acute leukemia, blindness, coma. Neurotoxicity (progressive demyelinating encephalopathy, mental status deterioration) occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess baseline CBC, BMP, LFT, uric acid and monitor during treatment. Drug should be discontinued if intractable vomiting, diarrhea, stomatitis, GI bleeding occurs.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for fatigue, visual disturbances, peripheral edema. Assess for onset of pneumonia. Monitor for dyspnea, cough, rapid decrease in WBC count, intractable vomiting, diarrhea, GI bleeding (bright red or tarry stool). Assess oral mucosa for stomatitis. Assess skin for rash. Be alert to possible tumor lysis syndrome (onset of flank pain, hematuria), signs of neurotoxicity.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid crowds, exposure to infection. • Maintain strict oral hygiene. • Promptly report fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site. • Report persistent nausea/vomiting.
fluorouracil, 5-FU 
flure-oh-ue-ra-sil
(Adrucil, Carac, Efudex, Fluoroplex, Tolak)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents.
Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents.
Do not confuse Efudex with Efidac.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antimetabolite. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Parenteral: Treatment of carcinoma of colon, rectum, breast, stomach, pancreas. Topical: Treatment of multiple actinic or solar keratoses, superficial basal cell carcinomas. OFF-LABEL: Parenteral: Treatment of carcinoma of: bladder, cervical, endometrial, head/neck, anal, esophageal, renal cell, unknown primary cancer.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fluorouracil. Myelosuppression, poor nutritional status, potentially serious infections. Cautions: History of high-dose pelvic irradiation, hepatic/renal impairment, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthia syndrome (hand and foot syndrome), previous use of alkylating agents. Pts with widespread metastatic marrow involvement.
ACTION
Blocks formation of thymidylic acid. Cell cycle–specific for S phase of cell division. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits DNA, RNA synthesis. Topical: Destroys rapidly proliferating cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Crosses blood-brain barrier. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted by lungs as carbon dioxide. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 16 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy, esp. first trimester. May cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Bone marrow depressants may increase risk of myelosuppression. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease effects. Avoid use of black cohosh, dong quai in pts with estrogen-dependent tumors. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum albumin. Topical: May cause eosinophilia, leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, toxic granulation.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Cream, Topical (Carac): 0.5%. (Tolak): 4%, (Efudex): 5%. (Fluoroplex): 1%. Injection Solution (Adrucil): 50 mg/ml. Solution, Topical (Efudex): 2%, 5%.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Give by IV injection or IV infusion. Do not add to other IV infusions. Avoid small veins, swollen/edematous extremities, areas overlying joints, tendons. May be carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic. Handle with extreme care during preparation/administration.
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • IV push does not need to be diluted or reconstituted. • Inject through Y-tube or 3-way stopcock of free-flowing solution. • For IV infusion, further dilute with 50–1,000 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • Give IV push slowly over 1–2 min. • IV infusion is administered over 30 min–24 hrs (refer to individual protocols). • Extravasation produces immediate pain, severe local tissue damage.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Solution appears colorless to faint yellow. Slight discoloration does not adversely affect potency or safety. • If precipitate forms, redissolve by heating, shaking vigorously; allow to cool to body temperature. • Diluted solutions stable for 72 hrs at room temperature.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), filgrastim (Neupogen), ondansetron (Zofran), vinorelbine (Navelbine).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Granisetron (Kytril), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), leucovorin, morphine, potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Refer to individual protocols.
Usual Therapy
IV Bolus: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400–500 mg/m2/day for 4–5 days or 500–600 mg/m2/dose q3–4wks.
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 15 mg/kg/day or 500 mg/m2/day over 4 hrs for 5 days or 800–1200 mg/m2 over 24–120 hrs.
Multiple Actinic or Solar Keratoses
Topical (Carac): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Apply once daily for up to 4 wks.
Topical (Efudex): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Apply twice daily for 2–4 wks.
Topical (Fluoroplex): Apply twice daily for 2–6 wks.
Topical (Tolak): Apply once daily for 4 wks.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Topical (Efudex 5%): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Apply twice daily for 3–6 wks up to 10–12 wks.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use extreme caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Parenteral: Frequent (greater than 10%): Alopecia, dermatitis, anorexia, diarrhea, esophagitis, dyspepsia, stomatitis. Occasional (10%–1%): Cardiotoxicity (angina, EKG changes), skin dryness, epithelial fissuring, nausea, vomiting, excessive lacrimation, blurred vision. Rare (less than 1%): Headache, photosensitivity, somnolence, allergic reaction, dyspnea, hypotension, MI, pulmonary edema. Topical: Occasional: Erythema, skin ulceration, pruritus, hyperpigmentation, dermatitis, insomnia, stomatitis, irritability, photosensitivity, excessive lacrimation, blurred vision.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Earliest sign of toxicity (4–8 days after beginning therapy) is stomatitis (dry mouth, burning sensation, mucosal erythema, ulceration at inner margin of lips). Most common dermatologic toxicity is pruritic rash (generally on extremities, less frequently on trunk). Leukopenia (WBC less than 3500/mm3) generally occurs within 9–14 days after drug administration but may occur as late as 25th day. Thrombocytopenia (platelets less than 100,000/mm3) occasionally occurs within 7–17 days after administration. Pancytopenia, agranulocytosis occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC with differential, serum renal function, LFT and monitor during therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for rapidly falling WBC, platelet count; intractable diarrhea, GI bleeding (bright red or tarry stool). Assess oral mucosa for stomatitis. Drug should be discontinued if intractable diarrhea, stomatitis, GI bleeding occurs. Assess skin for rash.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Maintain strict oral hygiene. • Report signs/symptoms of infection, unusual bruising/bleeding, visual changes, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, chest pain, palpitations. • Avoid sunlight, artificial light sources; wear protective clothing, sunglasses, sunscreen. • Topical: Apply only to affected area. • Do not use occlusive coverings. • Be careful near eyes, nose, mouth. • Wash hands thoroughly after application. • Treated areas may be unsightly for several weeks after therapy.
*FLUoxetine
floo-ox-e-teen
(Apo-Fluoxetine ![]() , Novo-Fluoxetine
, Novo-Fluoxetine ![]() , Prozac, Prozac Weekly, Sarafem)
, Prozac, Prozac Weekly, Sarafem)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs of age with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs of age with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Do not confuse fluoxetine with duloxetine, famotidine, fluconazole, fluvastatin, fluvoxamine, fosinopril, furosemide, or paroxetine, or Prozac with Paxil, Prilosec, Prograf, Proscar, or ProSom, or Sarafem with Serophene.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Symbyax: fluoxetine/olanzapine (an antipsychotic): 25 mg/6 mg, 25 mg/12 mg, 50 mg/6 mg, 50 mg/12 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). CLINICAL: Antidepressant, antiobsessional agent, antibulimic.
USES
Treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), binge-eating and vomiting in moderate to severe bulimia nervosa, premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), panic disorder with or without agoraphobia. Treatment of resistant or bipolar 1 depression (with olanzapine). OFF-LABEL: Treatment of fibromyalgia, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), Raynaud’s phenomena, social anxiety disorder, selective mutism.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fluoxetine. Use of MAOIs within 5 wks of discontinuing fluoxetine or within 14 days of discontinuing MAOIs. Initiation in pts receiving linezolid or methylene blue. Use with thioridazine. Cautions: Seizure disorder, cardiac dysfunction (e.g., history of MI), diabetes, pts with risk factors for QT prolongation, concurrent use of medication that increase QT interval, renal/hepatic impairment, pts at high risk for suicide, in pts where weight loss is undesirable, elderly. Pts at risk of acute narrow-angle glaucoma or with increased intraocular pressure.
ACTION
Selectively inhibits serotonin uptake in CNS, enhancing serotonergic function. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves depression; reduces obsessive-compulsive, bulimic behavior.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Crosses blood-brain barrier. Protein binding: 94%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2–3 days; metabolite, 7–9 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown whether drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: May be more sensitive to behavioral side effects (e.g., insomnia, restlessness). Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: NSAIDs, antiplatelets (e.g., clopidogrel), anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin) may increase risk of bleeding. Alcohol, other CNS depressants may increase CNS depression. MAOIs may produce serotonin syndrome and neuroleptic malignant syndrome. May increase concentration/toxicity of phenytoin, tricyclic antidepressants. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. St. John’s wort may increase effects, risk of serotonin syndrome. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum sodium. May increase serum ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg. Oral Solution: 20 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg, 60 mg.
![]() Capsules (Delayed-Release [Prozac Weekly]): 90 mg.
Capsules (Delayed-Release [Prozac Weekly]): 90 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food, but give with food, milk if GI distress occurs. • Bipolar disorder: Give once daily in evening. • Depression OCD: Give once daily in morning or twice daily (morning and noon). • Bulimia: Give once daily in morning.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Use lower or less frequent doses in pts with renal/hepatic impairment, pts with concurrent disease or multiple medications, the elderly.
Depression
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 5–20 mg each morning. May increase after several wks by 20 mg/day. Maximum: 80 mg/day as single or 2 divided doses. Prozac Weekly: 90 mg/wk, begin 7 days after last dose of 20 mg in pts maintained on 20 mg/day. CHILDREN 8–18 YRS: Initially, 5–10 mg/day. Titrate upward as needed. Usual dosage: 20 mg/day.
Panic Disorder
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10 mg/day. May increase to 20 mg/day after 1 wk. Maximum: 60 mg/day.
Bulimia Nervosa
PO: ADULTS: 60 mg each morning. May titrate to 60 mg over several days.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 20 mg/day. May increase after several wks. Usual dose: 20–60 mg/day. Maximum: 80 mg/day. CHILDREN 7–18 YRS: Initially, 10 mg/day. May increase to 20 mg/day after 2 wks. Range: 20–60 mg/day.
Depression Associated with Bipolar Disorder
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY CHILDREN 10–17 YRS: (with olanzapine): Initially, 20 mg/day. May increase after several wks. Range: 20–50 mg/day.
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD) (Sarafem)
PO: ADULTS: 20 mg/day continuously or 20 mg/day beginning 14 days prior to menstruation and continuing through first full day of menses (repeated with each cycle).
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (greater than 10%): Headache, asthenia, insomnia, anxiety, drowsiness, nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite. Occasional (9%–2%): Dizziness, tremor, fatigue, vomiting, constipation, dry mouth, abdominal pain, nasal congestion, diaphoresis, rash. Rare (less than 2%): Flushed skin, light-headedness, impaired concentration.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
May increase risk of suicide. Agitation, coma, diarrhea, delerium, hallucinations, hyperreflexia, hyperthermia, tachycardia, seizures may indicate life-threatening serotonin syndrome.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess appearance, behavior, mood, suicidal tendencies. For pts on long-term therapy, baseline renal function, LFT, blood counts should be performed at baseline and periodically thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Supervise suicidal-risk pt closely during early therapy (as depression lessens, energy level improves, increasing suicide potential). Monitor mental status, anxiety, social functioning, appetite, nutritional intake. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess skin for rash. Monitor serum LFT, glucose, sodium; weight.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Maximum therapeutic response may require 4 or more wks of therapy. • Do not abruptly discontinue medication. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol. • To avoid insomnia, take last dose of drug before 4 PM.
fluticasone 
floo-tik-a-sone
(Apo-Fluticasone ![]() , Arnuity Ellipta, Cutivate, Flonase, Flonase Allergy Relief, Flovent Diskus, Flovent HFA, Veramyst)
, Arnuity Ellipta, Cutivate, Flonase, Flonase Allergy Relief, Flovent Diskus, Flovent HFA, Veramyst)
Do not confuse Cutivate with Ultravate, or Flonase with Flovent.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Advair, Advair Diskus, Advair HFA: fluticasone/salmeterol (bronchodilator): 100 mcg/50 mcg, 250 mcg/50 mcg, 500 mcg/50 mcg. Breo Ellipta: Fluticasone/vilanterol (bronchodilator): 100 mcg/25 mcg. Dymista: Fluticasone/azelastine (an antihistamine): 50 mcg/137 mcg per spray.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Corticosteroid. CLINICAL: Anti-inflammatory, antipruritic.
USES
Nasal: (Flonase): Management of nasal symptoms of perennial nonallergic rhinitis in adults and children 4 yrs and older. (Veramyst): Management of seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis in adults, children 2 yrs and older. Topical: Relief of inflammation/pruritus associated with steroid-responsive disorders (e.g., contact dermatitis, eczema), atopic dermatitis. Inhalation: Maintenance treatment of bronchial asthma. Assists in reducing, discontinuing oral corticosteroid therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fluticasone. (Arnuity Ellipta, Flovent Diskus): Severe hypersensitivity to milk proteins or lactose. Inhalation: Primary treatment of status asthmaticus, acute exacerbation of asthma, other acute asthmatic conditions. Cautions: Untreated systemic ocular herpes simplex; untreated fungal, bacterial infection; active or quiescent tuberculosis. Thyroid disease, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, glaucoma, hepatic/renal impairment, cataracts, myasthenia gravis, seizures, GI disease, risk for osteoporosis, untreated localized infection of nasal mucosa. Following acute MI; concurrent use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
ACTION
Controls rate of protein synthesis, depresses migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, reverses capillary permeability, stabilizes lysosomal membranes. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents, controls inflammation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Inhalation/intranasal: Protein binding: 91%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 3–7.8 hrs. Topical: Amount absorbed depends on affected area and skin condition (absorption increased with fever, hydration, inflamed or denuded skin).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 4 yrs. Children 4 yrs and older may experience growth suppression with prolonged or high doses. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (ritonavir, nelfinavir, clarithromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole) may increase concentration. Ritonavir may reduce serum cortisol concentration. HERBAL: Echinacea, St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Aerosol for Oral Inhalation (Flovent HFA): 44 mcg/inhalation, 110 mcg/inhalation, 220 mcg/inhalation. Cream (Cutivate): 0.05%. Ointment (Cutivate): 0.005%. Powder for Oral Inhalation (Flovent Diskus): 50 mcg/blister, 100 mcg/blister, 250 mcg/blister. (Arnuity Ellipta): 100 mcg/actuation, 200 mcg/actuation. Suspension Intranasal Spray: (Flonase, Flonase Allergy Relief): 50 mcg/inhalation. (Veramyst): 27.5 mcg/spray.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Inhalation
• Shake container well. Instruct pt to exhale completely. Place mouthpiece fully into mouth, inhale, hold breath as long as possible before exhaling. • Allow at least 1 min between inhalations. • Rinsing mouth after each use decreases dry mouth, hoarseness.
Intranasal
• Instruct pt to clear nasal passages as much as possible before use (topical nasal decongestants may be needed 5–15 min before use). • Tilt head slightly forward. • Insert spray tip into 1 nostril, pointing toward inflamed nasal turbinates, away from nasal septum. • Pump medication into 1 nostril while pt holds other nostril closed, concurrently inspires through nose.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Allergic Rhinitis
Intranasal: (Flonase): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 200 mcg (2 sprays in each nostril once daily or 1 spray in each nostril q12h). Maintenance: 1 spray in each nostril once daily. May increase to 100 mcg (2 sprays) in each nostril. Maximum: 200 mcg/day. CHILDREN 4 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 100 mcg (1 spray in each nostril once daily). Maximum: 200 mcg/day (2 sprays each nostril).
(Veramyst): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 110 mcg (2 sprays in each nostril) once daily. Maintenance: 55 mcg (1 spray in each nostril) once daily. CHILDREN 2–11 YRS: 55 mcg (1 spray in each nostril) once daily. May increase to 110 mcg (2 sprays each nostril) once daily.
Usual Topical Dosage
Note: Ointment for adults only.
Topical: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 3 MOS AND OLDER: Apply sparingly to affected area once or twice daily.
Maintenance Treatment of Asthma
Inhalation Powder (Arnuity Ellipta): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 100–200 mcg once daily. Maximum: 200 mcg/day.
Maintenance Treatment for Asthma (Previously Treated with Bronchodilators)
Inhalation Powder (Flovent Diskus): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 100 mcg twice daily. Maximum: 500 mcg/twice daily.
Inhalation ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: (Flovent HFA): 88 mcg twice daily. Maximum: 440 mcg twice daily.
Maintenance Treatment for Asthma (Previously Treated with Inhaled Steroids)
Inhalation Powder (Flovent Diskus): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 100–250 mcg twice daily. Maximum: 500 mcg twice daily.
Inhalation ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: (Flovent HFA): 88–220 mcg twice daily. Maximum: 440 mcg twice daily.
Maintenance Treatment for Asthma (Previously Treated with Oral Steroids)
Inhalation Powder (Flovent Diskus): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 500–1,000 mcg twice daily.
Inhalation ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: (Flovent HFA): 440–880 mcg twice daily.
Usual Pediatric Dose (4–11 Yrs)
Flovent Diskus: Initially, 50 mcg twice daily. May increase to 100 mcg twice daily. Flovent HFA: 88 mcg twice daily.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.(Arnuity Ellipta): Use caution in hepatic impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Inhalation: Throat irritation, hoarseness, dry mouth, cough, temporary wheezing, oropharyngeal candidiasis (particularly if mouth is not rinsed with water after each administration). Intranasal: Mild nasopharyngeal irritation, nasal burning, stinging, dryness, rebound congestion, rhinorrhea, altered sense of taste. Occasional: Inhalation: Oral candidiasis. Intranasal: Nasal/pharyngeal candidiasis, headache. Topical: Stinging, burning of skin.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
None known.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Establish baseline history of skin disorder, asthma, rhinitis.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respiration; quality/rate of pulse. Assess lung sounds for rhonchi, wheezing, rales. Assess oral mucous membranes for evidence of candidiasis. Monitor growth in pediatric pts. Topical: Assess involved area for therapeutic response to irritation.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Pts receiving bronchodilators by inhalation concomitantly with steroid inhalation therapy should use bronchodilator several min before corticosteroid aerosol (enhances penetration of steroid into bronchial tree). • Do not change dose/schedule or stop taking drug; must taper off gradually under medical supervision. • Maintain strict oral hygiene. • Rinse mouth with water immediately after inhalation (prevents mouth/throat dryness, oral fungal infection). • Increase fluid intake (decreases lung secretion viscosity). • Intranasal: Clear nasal passages before use. • Report if no improvement in symptoms or sneezing/nasal irritation occurs. • Improvement noted in several days. • Topical: Rub thin film gently into affected area. • Use only for prescribed area and no longer than ordered. • Avoid contact with eyes.
*fluvoxaMINE
floo-vox-a-meen
(Apo-Fluvoxumine ![]() , Luvox CR, Novo-Fluvoxamine
, Luvox CR, Novo-Fluvoxamine ![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Do not confuse fluvoxamine with flavoxate or fluoxetine, or Luvox with Lasix, Levoxyl, or Lovenox.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Serotonin reuptake inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antidepressant, antiobsessive.
USES
Immediate-Release: Treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in adults and children 8–17 yrs of age. Extended-Release: Treatment of OCD in adults. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of social anxiety disorder (SAD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fluvoxamine. Use of MAOIs concurrently or within 14 days of discontinuing MAOIs or fluvoxamine. Concomitant use with alosetron, pimozide, ramelteon, thioridazine, or tizanidine. Initiation of fluvoxamine in pts receiving linezolid or methylene blue. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment; elderly; impaired platelet aggregation; concurrent use of NSAIDs, aspirin; seizure disorder; pts that are volume depleted; third trimester of pregnancy; pts with high suicide risk; risk of bleeding or receiving concurrent anticoagulant therapy.
ACTION
Selectively inhibits neuronal reuptake of serotonin. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves depression, symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 77%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 15–20 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses the placenta; distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 8 yrs. Elderly: Potential for reduced serum clearance; maintain caution.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration, risk of toxicity of benzodiazepines (e.g., alprazolam, lorazepam), carbamazepine, clozapine, theophylline. Lithium, tryptophan may enhance fluvoxamine’s serotonergic effects. MAOIs may increase risk of serotonin syndrome (hyperthermia, rigidity, myoclonus). Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline) may increase concentration. May increase effects of warfarin. HERBAL: Valerian, St. John’s wort, SAMe, kava kava may increase risk of serotonin syndrome or CNS depression. Avoid herbs with antiplatelet activity (e.g., cat’s claw, feverfew, ginger). FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg.
![]() Capsules (Extended-Release): 100 mg, 150 mg.
Capsules (Extended-Release): 100 mg, 150 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide extended-release capsules. • May give with or without food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS: Initially, 50 mg at bedtime; may increase by 50 mg every 4–7 days. Dosages greater than 100 mg/day should be given in 2 divided doses with larger dose given at bedtime. Usual dose: 100–300 mg/day. Maximum: 300 mg/day. (Extended-Release) Initially, 100 mg once daily at bedtime. May increase by 50 mg at no less than 1-wk intervals. Range: 100–300 mg/day. Maximum: 300 mg/day. CHILDREN 8–17 YRS (Immediate-Release): Initially, 25 mg at bedtime; may increase by 25 mg every 4–7 days. Dosages greater than 50 mg/day should be given in 2 divided doses with larger dose given at bedtime. Maximum: (CHILDREN 8–11 YRS): 200 mg/day. (CHILDREN 12–17 YRS): 300 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (40%–21%): Nausea, headache, drowsiness, insomnia. Occasional (14%–8%): Dizziness, diarrhea, dry mouth, asthenia, dyspepsia, constipation, abnormal ejaculation. Rare (6%–3%): Anorexia, anxiety, tremor, vomiting, flatulence, urinary frequency, sexual dysfunction, altered taste.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Agitation, coma, diarrhea, delerium, hallucinations, hyperreflexia, hyperthermia, tachycardia, seizures may indicate life-threatening serotonin syndrome.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline chemistries, esp. renal function, LFT.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Supervise suicidal-risk pt closely during early therapy (as depression lessens, energy level improves, increasing suicide potential). Assess appearance, behavior, speech pattern, level of interest, mood. Assist with ambulation if dizziness, drowsiness occurs. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Maximum therapeutic response may require 4 wks or more of therapy. • Dry mouth may be relieved by sugarless gum, sips of water. • Do not abruptly discontinue medication. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established.
folic acid
foe-lik as-id
(Apo-Folic ![]() )
)
Do not confuse folic acid with folinic acid.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Coenzyme. CLINICAL: Nutritional supplement.
USES
Treatment of megaloblastic and macrocytic anemias due to folate deficiency.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to folic acid. Cautions: Anemias (aplastic, normocytic, pernicious, refractory) when anemia present with vitamin B12 deficiency.
ACTION
Stimulates production of platelets, RBCs, WBCs in folate deficiency anemia. Therapeutic Effect: Essential for nucleoprotein synthesis, maintenance of normal erythropoiesis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
PO form almost completely absorbed from GI tract (upper duodenum). Protein binding: High. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, raltitrexed. HERBAL: Green tea may increase concentration. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease vitamin B12 concentration.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 0.8 mg, 5 mg, 20 mg. Injection Solution: 5 mg/ml. Tablets: 0.4 mg (OTC), 0.8 mg (OTC), 1 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
IV
May give 5 mg or less undiluted over at least 1 min, or dilute with 50 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W and infuse over 30 min.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Anemia
IM/IV/SQ/PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 4 YRS AND OLDER: 0.4 mg/day. CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 4 YRS: Up to 0.3 mg/day. INFANTS: 0.1 mg/day. PREGNANT/LACTATING WOMEN: 0.8 mg/day.
Prevention of Neural Tube Defects
PO: WOMEN OF CHILDBEARING AGE: 400–800 mcg/day. WOMEN AT HIGH RISK OR FAMILY HISTORY OF NEURAL TUBE DEFECTS: 4 mg/day.
SIDE EFFECTS
None known.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Allergic hypersensitivity occurs rarely with parenteral form. Oral folic acid is nontoxic.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Pernicious anemia should be ruled out with Schilling test and vitamin B12 blood level before initiating therapy (may produce irreversible neurologic damage). Resistance to treatment may occur if decreased hematopoiesis, alcoholism, antimetabolic drugs, deficiency of vitamin B6, B12, C, E is evident.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for therapeutic improvement: improved sense of well-being, relief from iron deficiency symptoms (fatigue, shortness of breath, sore tongue, headache, pallor).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Eat foods rich in folic acid, including fruits, vegetables, organ meats.
fondaparinux 
fon-dap-a-rin-ux
(Arixtra)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Epidural or spinal anesthesia greatly increases potential for spinal or epidural hematoma, subsequent long-term or permanent paralysis.
Epidural or spinal anesthesia greatly increases potential for spinal or epidural hematoma, subsequent long-term or permanent paralysis.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Factor Xa inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antithrombotic.
USES
Prevention of venous thromboembolism in pts undergoing total hip replacement, hip fracture surgery, knee replacement surgery, abdominal surgery. Treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis (DVT), acute pulmonary embolism. OFF-LABEL: Prophylaxis of DVT in pts with history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), acute symptomatic superficial vein thrombosis of the legs.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fondaparinux, active major bleeding, bacterial endocarditis, prophylaxis treatment in pts with body weight less than 50 kg, severe renal impairment (CrCl less than 30 ml/min), thrombocytopenia associated with antiplatelet antibody formation in presence of fondaparinux. Cautions: Conditions with increased risk of bleeding, bacterial endocarditis, active ulcerative GI disease, hemorrhagic stroke; shortly after brain, spinal, or ophthalmologic surgery; concurrent platelet inhibitors, severe uncontrolled hypertension, history of CVA), history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, renal/hepatic impairment, elderly, indwelling epidural catheter use.
ACTION
Factor Xa inhibitor that selectively binds to antithrombin and increases its affinity for factor Xa, inhibiting factor Xa, stopping blood coagulation cascade. Therapeutic Effect: Indirectly prevents formation of thrombin and subsequently fibrin clot.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after subcutaneous administration. Undergoes minimal, if any, metabolism. Highly bound to antithrombin III. Distributed mainly in blood and to a minor extent in extravascular fluid. Excreted unchanged in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 17–21 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Use with caution, particularly during third trimester, immediate postpartum period (increased risk of maternal hemorrhage). Unknown if excreted in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may increase risk of bleeding.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anticoagulants, antiplatelet medications, aspirin, drotrecogin alfa, NSAIDs, thrombolytics may increase risk of bleeding. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo, ginseng, horse chestnut, red clover, Omega-3 may increase antiplatelet activity. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May cause reversible increases in serum creatinine, ALT, AST. May decrease Hgb, Hct, platelet count.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution: 2.5 mg/0.5 ml, 5 mg/0.4 ml, 7.5 mg/0.6 ml, 10 mg/0.8 ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Subcutaneous
• Parenteral form appears clear, colorless. Discard if discoloration or particulate matter is noted. • Store at room temperature. • Do not expel air bubble from prefilled syringe before injection. • Insert needle subcutaneously into upper arms, outer thigh, or abdomen and inject solution. • Do not inject into areas of active skin disease or injury such as sunburns, rashes, inflammation, skin infections, or active psoriasis. • Rotate injection sites.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ For subcutaneous administration only.
Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism
SQ: ADULTS WEIGHING 50 KG OR MORE: 2.5 mg once daily for 5–9 days after surgery (up to 10 days following abdominal surgery; 11 days following hip or knee replacement). Initial dose should be given no earlier than 6–8h after surgery. Initiate dose once hemeostasis established. WEIGHING LESS THAN 50 KG: Contraindicated.
Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism, Pulmonary Embolism
Note: Start warfarin on first treatment day and continue fondaparinux until INR reaches 2 to 3 for at least 24 hr. Usual duration of fondaparinux: 5–9 days.
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY WEIGHING MORE THAN 100 KG: 10 mg once daily. ADULTS, ELDERLY WEIGHING 50–100 KG: 7.5 mg once daily. ADULTS, ELDERLY WEIGHING LESS THAN 50 KG: 5 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl greater than 50 ml/min: No dose adjustment. CrCl 30–50 ml/min: Use caution (50% dose reduction or use of low-dose heparin). CrCl less than 30 ml/min: Contraindicated.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (19%–11%): Anemia, fever, nausea. Occasional (10%–4%): Edema, constipation, rash, vomiting, insomnia, increased wound drainage, hypokalemia. Rare (less than 4%): Dizziness, hypotension, confusion, urinary retention, injection site hematoma, diarrhea, dyspepsia, headache.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Accidental overdose may lead to bleeding complications ranging from local ecchymoses to major hemorrhage. Thrombocytopenia occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess CBC, renal function test. Evaluate potential risk for bleeding. Question history of recent surgery, trauma, intracranial hemorrhage, GI bleeding.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Periodically monitor CBC, esp. platelet count, stool for occult blood (no need for daily monitoring in pts with normal presurgical coagulation parameters). Assess for any signs of bleeding: bleeding at surgical site, hematuria, blood in stool, bleeding from gums, petechiae, ecchymosis, bleeding from injection sites. Monitor B/P, pulse; hypotension, tachycardia may indicate bleeding, hypovolemia.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Usual length of therapy is 5–9 days. • Do not take any OTC medication (esp. aspirin, NSAIDs). • Report swelling of hands/feet, unusual back pain, unusual bleeding/bruising, weakness, sudden or severe headache.
foscarnet
foss-kar-net
(Foscavir)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Renal toxicity occurs to some degree in majority of pts. For use only in immunocompromised pts with cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis and mucocutaneous acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection. Seizures due to electrolyte/mineral imbalance may occur.
Renal toxicity occurs to some degree in majority of pts. For use only in immunocompromised pts with cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis and mucocutaneous acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection. Seizures due to electrolyte/mineral imbalance may occur.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Phosphonic acid derivative. CLINICAL: Antiviral.
USES
Treatment of acyclovir-resistant mucocutaneous HSV in immunocompromised pts; treatment of CMV retinitis in HIV pts. OFF-LABEL: Other CMV infections (e.g., colitis, esophagitis); CMV prophylaxis for cancer pts receiving alemtuzumab or allogenic stem cell transplant.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to foscarnet. Cautions: Neurologic/cardiac abnormalities, history of hepatic/renal impairment, altered calcium, other electrolyte imbalances.
ACTION
Selectively inhibits binding sites on virus-specific DNA polymerase, HIV reverse transcriptase. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits replication of herpes virus. Virustatic.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Sequestered into bone, cartilage. Protein binding: 14%–17%. Primarily excreted unchanged in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 3.3–6.8 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Nephrotoxic medications (e.g., lisinopril, IV contrast dye, vancomycin) may increase risk of renal toxicity. Pentamidine (IV) may cause reversible hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, nephrotoxicity. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, creatinine, ALT, AST. May decrease serum magnesium, potassium. May alter serum calcium, phosphate.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 24 mg/ml (250 ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Standard 24 mg/ml solution may be used without dilution when central venous catheter is used for infusion; 24 mg/ml solution must be diluted to maximum concentration of 12 mg/ml when peripheral vein catheter is being used. • Dilute only with D5W or 0.9% NaCl solution.
Rate of Administration • Because dosage is calculated on body weight, unneeded quantity should be removed before start of infusion to avoid overdosage. Aseptic technique must be used and solution administered within 24 hrs of first entry into sealed bottle. • Do not give by IV injection or rapid infusion (increases toxicity). • Administer at rate not exceeding 1 mg/kg/min. • To minimize toxicity and phlebitis, use central venous lines or veins with adequate blood flow to permit rapid dilution, dissemination. • Use IV infusion pump to prevent accidental overdose.
Storage • Store parenteral vials at room temperature. • After dilution, stable for 24 hrs at room temperature. • Do not use if solution is discolored or particulate forms.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Acyclovir (Zovirax), amphotericin B (Fungizone), calcium, co-trimoxazole (Bactrim), diazepam (Valium), digoxin (Lanoxin), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine (Dobutrex), ganciclovir (Cytovene), haloperidol (Haldol), leucovorin, magnesium, midazolam (Versed), pentamidine (Pentam IV), prochlorperazine (Compazine), vancomycin (Vancocin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Dopamine (Intropin), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lorazepam (Ativan), morphine, potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Retinitis
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, ADOLESCENTS: Initially, 60 mg/kg q8h or 90 mg/kg q12h for 2–3 wks. Maintenance: 90–120 mg/kg/day as a single IV infusion.
Herpes Simplex Infection
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, ADOLESCENTS: 40 mg/kg q8–12h for 2–3 wks or until healed.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosages are individualized based on creatinine clearance. Refer to dosing guide provided by manufacturer.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (65%–30%): Fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. Occasional (29%–5%): Anorexia, pain/inflammation at injection site, rigors, malaise, altered B/P, headache, paresthesia, dizziness, rash, diaphoresis, abdominal pain. Rare (4%–1%): Back/chest pain, edema, flushing, pruritus, constipation, dry mouth.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Nephrotoxicity occurs to some extent in most pts. Seizures, serum mineral/electrolyte imbalances may be life-threatening.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, serum electrolyte levels, renal function test, vital signs. Risk of renal impairment can be reduced by sufficient fluid intake to ensure diuresis prior to and during therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum chemistries, renal function tests. Assess for signs of hypocalcemia (perioral paresthesia, paresthesia of extremities), hypokalemia (weakness, muscle cramps, paresthesia of extremities, irritability). Assess for tremors; provide safety measures for potential seizures. Assess for bleeding, anemia, developing superinfections. Obtain periodic ophthalmologic exams.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report perioral tingling, numbness in extremities, paresthesia during or following infusion (may indicate electrolyte abnormalities). • Tremors should be reported promptly due to potential for seizures.
fosinopril
foe-sin-oh-pril
(Apo-Fosinopril ![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
Do not confuse fosinopril with Fosamax, or lisinopril, or Monopril with Accupril, minoxidil, moexipril, or ramipril.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: ACE inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive.
USES
Treatment of hypertension, used alone or in combination with other antihypertensives. Treatment of HF.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fosinopril. History of angioedema from previous treatment with ACE inhibitors. Concomitant use with aliskiren in pts with diabetes. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, pts with sodium depletion or on diuretic therapy, dialysis, hypovolemia, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with outflow tract obstruction, hyperkalemia, concomitant use of potassium supplements, unstented unilateral/bilateral renal stenosis, diabetes, severe aortic stenosis. Before, during, or immediately after major surgery.
ACTION
Suppresses renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (prevents conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor; may inhibit angiotensin II at local vascular, renal sites). Decreases plasma angiotensin II, increases plasma renin activity, decreases aldosterone secretion. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces B/P.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 1 hr | 2–6 hrs | 24 hrs |
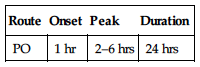
Slowly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 97%–98%. Metabolized in liver and GI mucosa. Primarily excreted in urine. Minimal removal by hemodialysis. Half-life: 11.5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. May cause fetal or neonatal mortality or morbidity. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Neonates, infants may be at increased risk for oliguria, neurologic abnormalities. Elderly: May be more sensitive to hypotensive effects.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, antihypertensive agents (e.g., amlodipine, valsartan), diuretics (e.g., furosemide, HCTZ), NSAIDs may increase effects. Potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., spironolactone), potassium supplements may cause hyperkalemia. May increase lithium concentration/toxicity. Antacids may decrease absorption. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Garlic may increase antihypertensive effect. Licorice may cause sodium/water retention, loss of potassium. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, creatinine, potassium, ALT, AST. May decrease serum sodium. May cause positive antinuclear antibody titer (ANA).
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Tablets may be crushed.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10 mg/day. Maintenance: 20–40 mg/day as a single dose or 2 divided doses. Maximum: 80 mg/day. CHILDREN 6–16 YRS WEIGHING MORE THAN 50 KG: Initially, 5–10 mg/day. Maximum: 40 mg/day.
HF
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 5–10 mg/day. May increase dose over several wks. Maintenance: 20–40 mg/day. Maximum: 40 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Reduce initial dose to 5 mg in pts with HF.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (12%–9%): Dizziness, cough. Occasional (4%–2%): Hypotension, nausea, vomiting, upper respiratory tract infection.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Excessive hypotension (“first-dose syncope”) may occur in pts with HF, severely salt/volume depleted. Angioedema (swelling of face/lips), hyperkalemia occur rarely. Agranulocytosis, neutropenia may be noted in pts with renal impairment, collagen vascular disease (scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus). Nephrotic syndrome may be noted in those with history of renal disease.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain B/P immediately before each dose, in addition to regular monitoring (be alert to fluctuations). Renal function tests should be performed before beginning therapy. In pts with renal impairment, autoimmune disease, or taking drugs that affect leukocytes or immune response, CBC, differential count should be performed before therapy begins and q2wks for 3 mos, then periodically thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
If excessive reduction in B/P occurs, place pt in supine position with legs elevated. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Assess for urinary frequency. Auscultate lung sounds for rales, wheezing in pts with HF. Monitor renal function tests, CBC, urinalysis for proteinuria. Observe for angioedema (swelling of face, lips, tongue). Monitor serum potassium in those on concurrent diuretic therapy.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report any sign of infection (sore throat, fever). • Several wks may be needed for full therapeutic effect of B/P reduction. • Skipping doses or voluntarily discontinuing drug may produce severe, rebound hypertension. • To reduce hypotensive effect, go from lying to standing slowly. • Immediately report swelling of face, lips, tongue, difficulty breathing, vomiting, excessive perspiration, persistent cough. • Avoid potassium salt substitutes.
fosphenytoin
fos-fen-i-toyn
(Cerebyx)
Do not confuse Cerebyx with Celebrex or Celexa, or fosphenytoin with fospropofol.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Hydantoin. CLINICAL: Anticonvulsant.
USES
Acute treatment, control of generalized convulsive status epilepticus; prevention, treatment of seizures occurring during neurosurgery; short-term substitution for oral phenytoin.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fosphenytoin, phenytoin, other hydantoins. Adams-Stokes syndrome; second- or third-degree AV block; sinus bradycardia; SA block; concurrent use of delavirdine. Cautions: Porphyria, diabetes, hypothyroidism, hypotension, severe myocardial insufficiency, renal/hepatic disease, hypoalbuminemia.
ACTION
Stabilizes neuronal membranes, limits spread of seizure activity. Decreases sodium, calcium ion influx into neurons. Decreases post-tetanic potentiation, repetitive discharge. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases seizure activity.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Completely absorbed after IM administration. Protein binding: 95%–99%. Rapidly and completely hydrolyzed to phenytoin after IM or IV administration. Time of complete conversion to phenytoin: 4 hrs after IM injection; 2 hrs after IV infusion. Half-life: 8–15 min (for conversion to phenytoin). (Phenytoin: 12–29 hrs.)
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May increase frequency of seizures during pregnancy. Increased risk of congenital malformations. Unknown if excreted in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Lower dosage recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants may increase CNS depression. Amiodarone, anticoagulants, cimetidine, disulfiram, fluoxetine, isoniazid, sulfonamides may increase concentration/effects, risk of toxicity. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., fluconazole, ketoconazole, miconazole) may increase concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, GGT, alkaline phosphatase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 75 mg/ml (equivalent to 50 mg phenytoin equivalents (PE)/ml phenytoin).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Dilute in D5W or 0.9% NaCl to a concentration ranging from 1.5–25 mg PE/ml.
Rate of Administration • Administer at rate less than 150 mg PE/min (decreases risk of hypotension, arrhythmias). Children: 1–3 mg PE/kg/min. Maximum: 150 mg PE/min.
Storage • Refrigerate. • Do not store at room temperature for longer than 48 hrs. • After dilution, solution is stable for 8 hrs at room temperature or 24 hrs if refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITY
IV INCOMPATIBILITY
Midazolam (Versed).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Lorazepam (Ativan), phenobarbital, potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ 150 mg fosphenytoin yields 100 mg phenytoin. Dosage, concentration solution, infusion rate of fosphenytoin are expressed in terms of phenytoin equivalents (PE).
Status Epilepticus
IV: ADULTS: Loading dose: 15–20 mg PE/kg infused at rate of 100–150 mg PE/min. Follow with maintenance dose of either fosphenytoin or phenytoin.
Nonemergent Seizures
IV, IM: ADULTS: Loading dose: 10–20 mg PE/kg. Maintenance: 4–6 mg PE/kg/day in divided doses.
Short-Term Substitution for Oral Phenytoin
IV, IM: ADULTS: May substitute for oral phenytoin at same total daily dose.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Dizziness, paresthesia, tinnitus, pruritus, headache, drowsiness. Occasional: Morbilliform rash.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Toxic fosphenytoin serum concentration may produce ataxia (muscular incoordination), nystagmus (rhythmic oscillation of eyes), diplopia, lethargy, slurred speech, nausea, vomiting, hypotension. As drug level increases, extreme lethargy may progress to coma.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Review history of seizure disorder (intensity, frequency, duration, LOC). Initiate seizure precautions. Obtain vital signs, medication history (esp. use of phenytoin, other anticonvulsants). Observe clinically.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor EKG, measure cardiac function, respiratory function, B/P during and immediately following infusion (10–20 min). Discontinue if skin rash appears. Interrupt or decrease rate if hypotension, arrhythmias are detected. Assess pt postinfusion (may feel dizzy, ataxic, drowsy). Monitor free and total dilatin levels (2 hrs after IV infusion or 4 hrs after IM injection).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• If noncompliance is cause of acute seizures, discuss and address reasons for noncompliance. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established.
frovatriptan
froe-va-trip-tan
(Frova)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Serotonin receptor agonist. CLINICAL: Antimigraine.
USES
Treatment of acute migraine headache with or without aura in adults.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to frovatriptan. Management of basilar or hemiplegic migraine, cerebrovascular or peripheral vascular disease, coronary artery disease, ischemic heart disease (angina pectoris, history of MI, silent ischemia, Prinzmetal’s angina), severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh grade C), uncontrolled hypertension, use within 24 hrs of ergotamine-containing preparations or another serotonin receptor agonist. Cautions: Mild to moderate hepatic impairment, pt profile suggesting cardiovascular risks. History of seizures or structural brain lesions.
ACTION
Agonist for serotonin in cranial arteries causing vasoconstriction and reduction of inflammation. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves migraine headache.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 15%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated in feces (62%), urine (32%). Half-life: 26 hrs (increased in hepatic impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug is excreted in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Not recommended for use in this pt population.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Ergotamine-containing medications may produce vasospastic reaction. SSRI, SNRI (e.g., duloxetine, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, venlafaxine) may produce weakness, hyperreflexia, uncoordination. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Tablets: 2.5 mg.
Tablets: 2.5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with fluids as soon as symptoms appear. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide film-coated tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Acute Migraine Headache
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 2.5 mg. If headache improves but then returns, dose may be repeated after at least 2 hrs. Maximum: 7.5 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (8%–4%): Dizziness, paresthesia, fatigue, flushing. Rare (3%–2%): Hot/cold sensation, dry mouth, dyspepsia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Cardiac reactions (ischemia, coronary artery vasospasm, MI), noncardiac vasospasm-related reactions (cerebral hemorrhage, CVA) occur rarely, particularly in pts with hypertension, obesity, smokers, diabetes, strong family history of coronary artery disease; males older than 40 yrs; postmenopausal women.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of peripheral vascular disease, renal/hepatic impairment, possibility of pregnancy. Question regarding onset, location, duration of migraine, possible precipitating factors.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for relief of migraine headache, potential for photophobia, phonophobia (sound sensitivity), nausea, vomiting.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take a single dose as soon as symptoms of an actual migraine attack appear. • Medication is intended to relieve migraine headaches, not to prevent or reduce number of attacks. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Immediately report palpitations, pain, tightness in chest or throat, sudden or severe abdominal pain, pain or weakness of extremities.
fulvestrant 
ful-vest-rant
(Faslodex)
Do not confuse Faslodex with Fosamax.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Estrogen antagonist. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of hormone receptor–positive metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women with disease progression following antiestrogen therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fulvestrant. Cautions: Thrombocytopenia, bleeding diathesis, anticoagulant therapy, hepatic impairment, reduced hepatic blood flow, pregnancy.
ACTION
Competes with endogenous estrogen at estrogen receptor binding sites. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor growth.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Extensively, rapidly distributed after IM administration. Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated by hepatobiliary route; excreted in feces. Half-life: 40 days in postmenopausal women. Peak serum levels occur in 7–9 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Do not administer to pregnant women. Unknown if excreted in breast milk. May cause fetal harm. Children: Not used in this pt population. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution: 50 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
IM
• Administer slowly into upper, outer quadrant or ventrogluteal area of buttock as two injections, one in each buttock over 1–2 min.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Breast Cancer
IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 500 mg (two 250-mg injections) on days 1, 15, and 29. Maintenance: 500 mg once monthly thereafter.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate impairment: Reduce initial and maintenance dose to 250 mg. Severe impairment: Use caution (not studied).
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (26%–13%): Nausea, hot flashes, pharyngitis, asthenia, vomiting, vasodilation, headache. Occasional (12%–5%): Injection site pain, constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, anorexia, dizziness, insomnia, paresthesia, bone/back pain, depression, anxiety, peripheral edema, rash, diaphoresis, fever. Rare (2%–1%): Vertigo, weight gain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
UTI occurs occasionally. Vaginitis, anemia, thromboembolic phenomena, leukopenia occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Estrogen receptor assay should be done before beginning therapy. Baseline radiologic testing should be performed initially and periodically thereafter for evidence of tumor regression.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum chemistries, plasma lipids. Be alert to increased bone pain, ensure adequate pain relief. Check for edema, esp. of dependent areas. Monitor for and assist with ambulation if asthenia or dizziness occurs. Assess for headache. Offer antiemetic for nausea/vomiting.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Notify physician if nausea/vomiting, asthenia (loss of strength, energy), hot flashes become unmanageable.
furosemide 
fur-oh-se-myde
(Apo-Furosemide ![]() , Lasix, Novo-Semide
, Lasix, Novo-Semide ![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Large amounts can lead to profound diuresis with water and electrolyte depletion.
Large amounts can lead to profound diuresis with water and electrolyte depletion.
Do not confuse furosemide with famotidine, finasteride, fluconazole, fluoxetine, loperamide, or torsemide, or Lasix with Lidex, Lovenox, Luvox, or Luxiq.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Loop diuretic. CLINICAL: Diuretic.
USES
Treatment of edema associated with HF and renal/hepatic disease; acute pulmonary edema. Treatment of hypertension, either alone or in combination with other antihypertensives.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to furosemide. Anuria. Cautions: Hepatic cirrhosis, hepatic coma, severe electrolyte depletion, prediabetes, diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus. Pts with prostatic hyperplasia/urinary stricture.
ACTION
Enhances excretion of sodium, chloride, potassium by direct action at ascending limb of loop of Henle. Therapeutic Effect: Produces diuresis, lowers B/P.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 30–60 min | 1–2 hrs | 6–8 hrs |
| IV | 5 min | 20–60 min | 2 hrs |
| IM | 30 min | N/A | N/A |
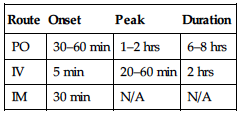
Moderately absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: greater than 98%. Partially metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine (nonrenal clearance increases in severe renal impairment). Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 30–90 min (increased in renal/hepatic impairment, neonates).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children: Half-life increased in neonates; may require increased dosage interval. Elderly: May be more sensitive to hypotensive, electrolyte effects, developing circulatory collapse, thromboembolic effect. Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Amphotericin B, nephrotoxic ototoxic medications (e.g., lisinopril, IV contrast dye, vancomycin) may increase risk of nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity. May increase risk of lithium toxicity. Other medications causing hypokalemia (e.g., HCTZ, laxatives) may increase risk of hypokalemia. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Garlic may increase antihypertensive effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, BUN, uric acid. May decrease serum calcium, chloride, magnesium, potassium, sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 10 mg/ml. Oral Solution: 10 mg/ml, 40 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 20 mg, 40 mg, 80 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Rate of Administration • May give undiluted but is compatible with D5W or 0.9% NaCl. • May be diluted for infusion to 1–2 mg/ml (maximum: 10 mg/ml). • Administer each 40 mg or fraction by IV push over 1–2 min. Do not exceed administration rate of 4 mg/min for short-term intermittent infusion.
Storage • Solution appears clear, colorless. • Discard yellow solutions. • Stable for 24 hrs at room temperature when mixed with 0.9% NaCl or D5W.
IM
• Temporary pain at injection site may be noted.
PO
• Administer on empty stomach. • Give with food to avoid GI upset, preferably with breakfast (may prevent nocturia). • Food may decrease diuretic effect.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro), diltiazem (Cardizem), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), doxorubicin (Adriamycin), droperidol (Inapsine), esmolol (Brevibloc), famotidine (Pepcid), filgrastim (Neupogen), fluconazole (Diflucan), gemcitabine (Gemzar), gentamicin (Garamycin), idarubicin (Idamycin), labetalol (Trandate), metoclopramide (Reglan), midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), nicardipine (Cardene), ondansetron (Zofran), quinidine, thiopental (Pentothal), vinblastine (Velban), vincristine (Oncovin), vinorelbine (Navelbine).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), bumetanide (Bumex), calcium gluconate, cimetidine (Tagamet), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lidocaine, lipids, morphine, nitroglycerin, norepinephrine (Levophed), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Edema, HF
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 20–80 mg/dose; may increase by 20–40 mg/dose q6–8h. May titrate up to 600 mg/day in severe edematous states. CHILDREN: Initially, 2 mg/kg/dose. May increase by 1–2 mg/kg/dose at 6–8 hr intervals. Maximum: 6 mg/kg/dose. NEONATES: 1 mg/kg/dose 1–2 times/day.
IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20–40 mg/dose; may increase by 20 mg/dose q1–2h. Maximum single dose: 160–200 mg. CHILDREN: Initially, 1 mg/kg/dose. May increase by 1 mg/kg/dose no sooner than 2 hrs after previous dose. Maximum: 6 mg/kg/dose. NEONATES: 1–2 mg/kg/dose q12–24h.
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Bolus of 40–100 mg over 1–2 min, followed by infusion of 10–40 mg/hr; may double q2h. Maximum: 80–160 mg/hr. CHILDREN: 0.05 mg/kg/hr; titrate to desired effect. NEONATES: Initially, 0.2 mg/kg/hr. May increase by 0.1 mg/kg/hr q12–24h. Maximum: 0.4 mg/kg/hr.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Avoid use in oliguric states.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Decreased effect, increased sensitivity to hypokalemia/volume depletion in cirrhosis.
SIDE EFFECTS
Expected: Increased urinary frequency/volume. Frequent: Nausea, dyspepsia, abdominal cramps, diarrhea or constipation, electrolyte disturbances. Occasional: Dizziness, light-headedness, headache, blurred vision, paresthesia, photosensitivity, rash, fatigue, bladder spasm, restlessness, diaphoresis. Rare: Flank pain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Vigorous diuresis may lead to profound water loss/electrolyte depletion, resulting in hypokalemia, hyponatremia, dehydration. Sudden volume depletion may result in increased risk of thrombosis, circulatory collapse, sudden death. Acute hypotensive episodes may occur, sometimes several days after beginning therapy. Ototoxicity (deafness, vertigo, tinnitus) may occur, esp. in pts with severe renal impairment. Can exacerbate diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, gout, pancreatitis. Blood dyscrasias have been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Check vital signs, esp. B/P, pulse, for hypotension before administration. Assess baseline renal function, serum electrolytes, esp. serum sodium, potassium. Assess skin turgor, mucous membranes for hydration status; observe for edema. Assess muscle strength, mental status. Note skin temperature, moisture. Obtain baseline weight. Initiate I&O monitoring.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, vital signs, serum electrolytes, I&O, weight. Note extent of diuresis. Watch for symptoms of electrolyte imbalance: Hypokalemia may result in changes in muscle strength, tremor, muscle cramps, altered mental status, cardiac arrhythmias; hyponatremia may result in confusion, thirst, cold/clammy skin.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Expect increased frequency, volume of urination. • Report palpitations, signs of electrolyte imbalances (noted previously), hearing abnormalities (sense of fullness in ears, tinnitus). • Eat foods high in potassium such as whole grains (cereals), legumes, meat, bananas, apricots, orange juice, potatoes (white, sweet), raisins. • Avoid sunlight, sunlamps.