H
haloperidol
hal-o-per-i-dol
(Apo-Haloperidol
![]() , Haldol, Haldol Decanoate, Novo-Peridol
, Haldol, Haldol Decanoate, Novo-Peridol
![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of mortality in elderly pts with dementia-related psychosis with use of injections.
Increased risk of mortality in elderly pts with dementia-related psychosis with use of injections.
Do not confuse Haldol with Halcion or Stadol.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Butyrophenone antipsychotic. CLINICAL: Antipsychotic, antiemetic, antidyskinetic.
USES
Treatment of schizophrenia, Tourette’s disorder (controls tics and vocal utterances), severe behavioral problems in children with combative explosive hyperexcitability without immediate provocation. Management of psychotic disorder, short-term treatment of hyperactive children. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of nonschizophrenic psychosis, alcohol dependence, psychosis/agitation related to Alzheimer’s dementia, emergency sedation of severely agitated/psychotic pts.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to haloperidol, CNS depression, coma, myelosuppression, Parkinson’s disease, severe cardiac/hepatic disease. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, cardiovascular disease, history of seizures, prolonged QT syndrome, medications that prolong QT interval, hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis, electrolyte imbalance (e.g., hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia), EEG abnormalities, narrow–angle glaucoma, elderly, pts at risk for pneumonia, decreased GI motility, urinary retention, BPH, visual disturbances. Pts at risk for orthostatic hypotension (e.g., cerebrovascular disease).
ACTION
Competitively blocks postsynaptic dopamine receptors in brain. Therapeutic Effect: Produces tranquilizing effect. Strong extrapyramidal, antiemetic effects; weak anticholinergic, sedative effects.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 92%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 20 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children: More susceptible to dystonias; not recommended in pts younger than 3 yrs. Elderly: More susceptible to orthostatic hypotension, anticholinergic effects, sedation; increased risk for extrapyramidal effects. Decreased dosage recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g., diphenhydramine, gabapentin, lorazepam, morphine) may increase CNS depression. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine) may decrease concentration. Medications prolonging QT interval (e.g., amiodarone, ciprofloxacin, ondansetron) may increase risk of QT prolongation. Medications producing extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) (e.g., diphenhydramine, benztropine) may increase EPS. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant. Therapeutic serum level: 0.2–1 mcg/ml; toxic serum level: Greater than 1 mcg/ml.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Oil (Decanoate [Haldol Decanoate]): 50 mg/ml, 100 mg/ml. Injection, Solution (Lactate [Haldol]): 5 mg/ml. Oral Concentrate: 2 mg/ml. Tablets (Haldol): 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
◀ ALERT ▶ Only haloperidol lactate is given IV.
Reconstitution • May give undiluted. • May add to 50–100 ml of D5W.
Rate of Administration • Give IV push at rate of 5 mg/min. • Infuse IV piggyback over 30 min. • For IV infusion, up to 25 mg/hr has been used (titrated to pt response).
Storage • Discard if precipitate forms, discoloration occurs. • Store at room temperature; do not freeze. • Protect from light.
IM
Parenteral Administration • Pt should remain recumbent for 30–60 min to minimize hypotensive effect. • Prepare Decanoate IM injection using 21-gauge needle. • Do not exceed maximum volume of 3 ml per IM injection site. • Inject slow, deep IM into upper outer quadrant of gluteus maximus.
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Scored tablets may be crushed. • Dilute oral concentrate with water or juice. • Avoid skin contact with oral concentrate; may cause contact dermatitis.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Allopurinol (Aloprim), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), cefepime (Maxipime), fluconazole (Diflucan), foscarnet (Foscavir), heparin, nitroprusside (Nipride), piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), fentanyl (Sublimaze), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), midazolam (Versed), morphine, nitroglycerin, norepinephrine (Levophed), propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage
IM (Lactate): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2–5 mg q4–8h as needed. CHILDREN 6–12 YRS: 1–3 mg/dose q4–8h as needed. Maximum: 0.15 mg/kg/day. Change to PO as soon as possible. (Decanoate): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10–20 times stabilized oral dose. Maximum: 100 mg. Maintenance: 10–15 times daily oral dose or 50–200 mg q4wks.
PO: ADULTS: 0.5–5 mg 2–3 times/day. Usual dose: 5–20 mg/day. Maximum: 100 mg/day. ELDERLY: 0.2–2 mg/day. Usual dose: 5–20 mg/day. Maximum: 100 mg/day. CHILDREN WEIGHING MORE THAN 40 KG, ADOLESCENTS: 0.5–15 mg/day in 2–3 divided doses. May increase at no less than 5–7 days. Maximum: 15 mg/day. CHILDREN 3–12 YRS (15–40 KG): 0.25–0.5 mg/day. May increase by 0.25–0.5 mg q5–7days. Range: 0.05–0.15 mg/kg/day in 2–3 divided doses. Maximum: 15 mg/day.
Tourette’s Disorder
PO: CHILDREN 3–12 YRS: 0.05–0.075 mg/kg/day in 2–3 divided doses.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Blurred vision, constipation, orthostatic hypotension, dry mouth, swelling or soreness of female breasts, peripheral edema. Occasional: Allergic reaction, difficulty urinating, decreased thirst, dizziness, diminished sexual function, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, photosensitivity, lethargy.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) appear to be dose related and typically occur in first few days of therapy. Marked drowsiness/lethargy, excessive salivation, fixed stare may be mild to severe in intensity. Less frequently noted are severe akathisia (motor restlessness), acute dystonias: torticollis (neck muscle spasm), opisthotonos (rigidity of back muscles), oculogyric crisis (rolling back of eyes). Tardive dyskinesia (tongue protrusion, puffing of cheeks, chewing/puckering of the mouth) may occur during long-term therapy or after drug discontinuance and may be irreversible. Elderly female pts have greater risk of developing this reaction.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess behavior, appearance, emotional status, response to environment, speech pattern, thought content. Assess LOC. Screen for co-morbidities as listed in Precautions (esp. seizure disorder, long QT syndrome).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, heart rate/rhythm. Supervise suicidal-risk pt closely during early therapy (as depression lessens, energy level improves, increasing suicide potential). Monitor for rigidity, tremor, mask-like facial expression, fine tongue movement. Assess for therapeutic response (interest in surroundings, improvement in self-care, increased ability to concentrate, relaxed facial expression). Monitor EKG and QT interval. Therapeutic serum level: 0.2–1 mcg/ml; toxic serum level: greater than 1 mcg/ml.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Full therapeutic effect may take up to 6 wks. • Do not abruptly withdraw from long-term drug therapy. • Sugarless gum, sips of water may relieve dry mouth. • Drowsiness generally subsides during continued therapy. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol. • Report muscle stiffness. • Avoid exposure to sunlight, overheating, dehydration (increased risk of heatstroke).
heparin

hep-a-rin
(Hepalean Leo
![]() , Hep-Lock)
, Hep-Lock)
Do not confuse heparin with Hespan.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Sulfated polysaccharide; blood modifier. CLINICAL: Anticoagulant.
USES
Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic disorders; anticoagulant for extracorporeal and dialysis procedures; maintain patency of IV devices. OFF-LABEL: STEMI, non-STEMI, unstable angina, anticoagulant used during percutaneous coronary intervention.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to heparin. Severe thrombocytopenia, uncontrolled active bleeding (unless secondary to disseminated intravascular coagulation [DIC]), history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with thrombosis (HITT), or pts who test positive for HIT antibody. Cautions: Allergy to pork. Pts at risk for bleeding (e.g., congenital/acquired bleeding disorders, active GI ulcerative disease, hemophilia, concomitant platelet inhibitors, severe hypertension, menses, recent lumbar puncture or spinal anesthesia; recent major surgery, trauma). Use of preservative-free heparin recommended in neonates, infants, pregnant or nursing mothers.
ACTION
Interferes with blood coagulation by blocking conversion of prothrombin to thrombin and fibrinogen to fibrin. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents further extension of existing thrombi or new clot formation. No effect on existing clots.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following subcutaneous administration. Protein binding: Very high. Metabolized in liver. Removed from circulation via uptake by reticuloendothelial system. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 1–6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Use with caution, particularly during last trimester, immediate postpartum period (increased risk of maternal hemorrhage). Does not cross placenta. Not distributed in breast milk. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Benzyl alcohol preservative may cause gasping syndrome in infants. Elderly: More susceptible to hemorrhage. Age-related renal impairment may increase risk of bleeding.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Other anticoagulants (e.g., dabigatran, warfarin), platelet aggregation inhibitors (e.g., aspirin, clopidogrel), thrombolytics (e.g., tissue plasminogen activator [TPA]) may increase risk of bleeding. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginkgo, ginseng, horse chestnut, red clover have additional antiplatelet activity. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase free fatty acids, serum ALT, AST; aPTT. May decrease serum cholesterol.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 10 units/ml (Hep-Lock), 100 units/ml, 1,000 units/ml, 5,000 units/ml, 10,000 units/ml, 20,000 units/ml. Premix Solution for Infusion: 25,000 units/250 ml infusion, 25,000 units/500 ml infusion.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Do not give by IM injection (pain, hematoma, ulceration, erythema).
![]() IV
IV
◀ ALERT ▶ Used in full-dose therapy. Intermittent IV dosage produces higher incidence of bleeding abnormalities. Continuous IV route preferred.
Reconstitution • Premix solution requires no reconstitution.
Rate of Administration • Infuse and titrate per protocol using infusion pump.
Storage • Store at room temperature.
Subcutaneous
◀ ALERT ▶ Used in low-dose therapy. • After withdrawal of heparin from vial, change needle before injection (prevents leakage along needle track). • Inject above iliac crest or in abdominal fat layer. Do not inject within 2 inches of umbilicus or any scar tissue. • Withdraw needle rapidly, apply prolonged pressure at injection site. Do not massage or apply heat/cold to injection site. • Rotate injection sites.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), ciprofloxacin (Cipro), dacarbazine (DTIC), diazepam (Valium), dobutamine (Dobutrex), doxorubicin (Adriamycin), filgrastim (Neupogen), gentamicin (Garamycin), haloperidol (Haldol), idarubicin (Idamycin), labetalol (Trandate), nicardipine (Cardene), phenytoin (Dilantin), quinidine, tobramycin (Nebcin), vancomycin (Vancocin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Ampicillin/sulbactam (Unasyn), aztreonam (Azactam), calcium gluconate, cefazolin (Ancef), ceftazidime (Fortaz), ceftriaxone (Rocephin), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), digoxin (Lanoxin), diltiazem (Cardizem), dopamine (Intropin), enalapril (Vasotec), famotidine (Pepcid), fentanyl (Sublimaze), furosemide (Lasix), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), insulin, lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, nitroglycerin, norepinephrine (Levophed), oxytocin (Pitocin), piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn), procainamide (Pronestyl), propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Line Flushing
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 100 units q6–8h. INFANTS WEIGHING LESS THAN 10 KG: 10 units q6–8h.
Acute Coronary Syndrome
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 60 units/kg bolus (maximum: 4,000 units), then 12 units/kg/hr (maximum: 1,000 units/hr).
Treatment of DVT/PE
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 80 units/kg bolus (maximum: 5,000 units), then 18 units/kg/hr adjusted according to aPTT.
Usual Pediatric/Neonatal Dose
IV Infusion: 75 units/kg bolus over 10 min, then initial maintenance dose of 20 units/kg/hr. Adjust to maintain aPTT of 60–85 sec.
Thromboembolic Prophylaxis
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5,000 units q8–12h.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Pruritus, burning (particularly on soles of feet) caused by vasospastic reaction. Rare: Pain, cyanosis of extremity 6–10 days after initial therapy lasting 4–6 hrs, hypersensitivity reaction (chills, fever, pruritus, urticaria, asthma, rhinitis, lacrimation, headache).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Bleeding complications ranging from local ecchymoses to major hemorrhage (cutaneous/GI/genitourinary/intracranial/nasal/oral/pharyngeal/urethral/vaginal bleeding) occur more frequently in high-dose therapy, intermittent IV infusion, women 60 yrs and older. HIT can cause life-threatening thromboembolism such as CVA, MI, DVT, pulmonary embolism, renal artery thrombosis, mesenteric thrombosis. Antidote: Protamine sulfate 1–1.5 mg IV for every 100 units heparin subcutaneous within 30 min of overdose, 0.5–0.75 mg for every 100 units heparin subcutaneous if within 30–60 min of overdose, 0.25–0.375 mg for every 100 units heparin subcutaneous if 2 hrs have elapsed since overdose, 25–50 mg if heparin was given by IV infusion.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Cross-check dose with co-worker. Determine aPTT before administration and 24 hrs following initiation of therapy, then q24–48hrs for first wk of therapy or until maintenance dose is established. Follow with aPTT determinations 1–2 times wkly for 3–4 wks. In long-term therapy, monitor 1–2 times/mo.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor aPTT (therapeutic range at 1.5–2.5 times normal) diligently. Assess CBC, platelet count, ALT, AST. If platelet count decreases more than 50% from baseline, obtain stat HIT antibody test. If HIT antibody positive, discontinue heparin and consider treatment with direct thrombin inhibitor (e.g., argatroban); avoid all heparin products and place heparin allergy on chart. Monitor urine and stool for occult blood. Assess for decrease in B/P, increase in pulse rate, complaint of abdominal/back pain, severe headache (may be evidence of hemorrhage). Question for increase in amount of discharge during menses. Assess peripheral pulses; skin for ecchymosis, petechiae. Check for excessive bleeding from minor cuts, scratches. Assess gums for erythema, gingival bleeding. Assess urine output for hematuria. Avoid IM injections due to potential for hematomas. When converting to warfarin (Coumadin) therapy, monitor PT/INR results (will be 10%–20% higher while heparin is given concurrently).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Use electric razor, soft toothbrush to prevent bleeding. • Report red or dark urine, black or red stool, coffee-ground vomitus, blood-tinged mucus from cough, signs of stroke, nosebleeds, or increase in menstruation. • Do not use any OTC medication without physician approval (may interfere with platelet aggregation). • Wear or carry identification that notes anticoagulant therapy. • Inform dentist, other physicians of heparin therapy. • Limit alcohol.
*hydrALAZINE
hye-dral-a-zeen
(Apo-Hydralazine
![]() , Apresoline
, Apresoline
![]() , Novo-Hylazin
, Novo-Hylazin
![]() )
)
Do not confuse hydralazine with hydroxyzine.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Apresazide: hydralazine/hydrochlorothiazide (a diuretic): 25 mg/25 mg, 50 mg/50 mg, 100 mg/50 mg. BiDil: hydralazine/isosorbide (a nitrate): 37.5 mg/20 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Vasodilator. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive.
USES
Management of moderate to severe hypertension. OFF-LABEL: Hypertension secondary to eclampsia, preeclampsia. Treatment of HF with reduced ejection fraction, postoperative hypertension.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to hydralazine. Coronary artery disease, mitral valvular rheumatic heart disease, dissecting aortic aneurysm. Cautions: Renal impairment, cerebrovascular disease, positive ANA titer, pulmonary hypertension.
ACTION
Direct vasodilating effects on arterioles. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases B/P, systemic vascular resistance.
PHARMACOKINETICS
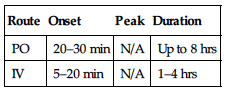
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 20–30 min | N/A | Up to 8 hrs |
| IV | 5–20 min | N/A | 1–4 hrs |
Well absorbed from GI tract. Widely distributed. Protein binding: 85%–90%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 3–7 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Drug crosses placenta. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, petechial bleeding, hematomas have occurred in newborns (resolved within 1–3 wks). Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: More sensitive to hypotensive effects. Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Diuretics (e.g., furosemide, HCTZ), other antihypertensives (e.g., amlodipine, clonidine, lisinopril, valsartan) may increase hypotensive effect. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Garlic may increase antihypertensive effect. FOOD: Any foods may increase absorption. LAB VALUES: May produce positive direct Coombs’ test.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 20 mg/ml. Tablets: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Rate of Administration • May give undiluted. • Administer slowly: maximum rate 5 mg/min (0.2 mg/kg/min for children).
Storage • Store at room temperature.
PO
• Best given with food at regularly spaced meals. • Tablets may be crushed.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Ampicillin (Polycillin), furosemide (Lasix).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Dobutamine (Dobutrex), heparin, hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef), nitroglycerin, potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10 mg 4 times/day for first 2–4 days. May increase to 25 mg 4 times/day balance of first wk. May increase by 10–25 mg/dose gradually q2–5 days to 50 mg 4 times/day. Usual range: 25–100 mg in 2–3 divided doses. Maximum: 300 mg/day in divided doses. CHILDREN: Initially, 0.75–1 mg/kg/day in 2–4 divided doses. May increase over 3–4 wks. Maximum: 7.5 mg/kg/day (5 mg/kg/day in infants). Maximum daily dose: 200 mg/day in divided doses.
IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10–20 mg/dose q4–6h. May increase to 40 mg/dose. CHILDREN: Initially, 0.1–0.2 mg/kg/dose (maximum: 20 mg) q4–6h, as needed, up to 1.7–3.5 mg/kg/day in 4–6 divided doses.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage interval is based on creatinine clearance.
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 10–50 ml/min | q8h |
| Less than 10 ml/min | q8–24h |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Headache, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, palpitations, tachycardia, angina pectoris. Rare: Constipation, ileus, edema, peripheral neuritis (paresthesia), dizziness, muscle cramps, anxiety, hypersensitivity reactions (rash, urticaria, pruritus, fever, chills, arthralgia), nasal congestion, flushing, conjunctivitis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
High dosage may produce lupus erythematosus–like reaction (fever, facial rash, muscle/joint aches, glomerulonephritis, splenomegaly). Severe orthostatic hypotension, skin flushing, severe headache, myocardial ischemia, cardiac arrhythmias may develop. Profound shock may occur with severe overdosage.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain B/P, pulse immediately before each dose, in addition to regular monitoring (be alert to fluctuations).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, pulse, ANA titer. Monitor for headache, palpitations, tachycardia. Assess for peripheral edema of hands, feet.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• To reduce hypotensive effect, go from lying to standing slowly. • Report muscle/joint aches, fever (lupus-like reaction), flu-like symptoms. • Limit alcohol use.
*hydroCHLOROthiazide
hye-dro-klor-oh-thy-ah-zide
(Apo-Hydro
![]() , Microzide)
, Microzide)
Do not confuse Microzide with Maxzide.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Accuretic: hydrochlorothiazide/quinapril (an angiotensin-converting enzyme [ACE] inhibitor): 12.5 mg/10 mg, 12.5 mg/20 mg, 25 mg/20 mg. Aldactazide: hydrochlorothiazide/spironolactone (a potassium-sparing diuretic): 25 mg/25 mg, 50 mg/50 mg. Aldoril: hydrochlorothiazide/methyldopa (an antihypertensive): 15 mg/250 mg, 25 mg/250 mg, 30 mg/500 mg, 50 mg/500 mg. Amturnide: hydrochlorothiazide/aliskiren (renin inhibitor)/amlodipine (calcium channel blocker): 12.5 mg/150 mg/5 mg, 12.5 mg/300 mg/5 mg, 25 mg/300 mg/5 mg, 12.5 mg/300 mg/10 mg, 25 mg/300 mg/10 mg. Apresazide: hydrochlorothiazide/hydralazine (a vasodilator): 25 mg/25 mg, 50 mg/50 mg, 50 mg/100 mg. Atacand HCT: hydrochlorothiazide/candesartan (an angiotensin II receptor antagonist): 12.5 mg/16 mg, 12.5 mg/32 mg. Avalide: hydrochlorothiazide/irbesartan (an angiotensin II receptor antagonist): 12.5 mg/150 mg, 12.5 mg/300 mg, 25 mg/300 mg. Benicar HCT: hydrochlorothiazide/olmesartan (an angiotensin II receptor antagonist): 12.5 mg/20 mg, 12.5 mg/40 mg, 25 mg/40 mg. Capozide: hydrochlorothiazide/captopril (an ACE inhibitor): 15 mg/25 mg, 15 mg/50 mg, 25 mg/25 mg, 25 mg/50 mg. Diovan HCT: hydrochlorothiazide/valsartan (an angiotensin II receptor antagonist): 12.5 mg/80 mg, 12.5 mg/160 mg. Dutoprol: hydrochlorothiazide/metoprolol (a beta blocker): 12.5 mg/25 mg, 12.5 mg/50 mg, 12.5 mg/100 mg. Dyazide/Maxide: hydrochlorothiazide/triamterene (a potassium-sparing diuretic): 25 mg/37.5 mg, 25 mg/50 mg, 50 mg/75 mg. Exforge HCT: hydrochlorothiazide/amlodipine (a calcium channel blocker)/valsartan (an angiotensin II receptor blocker): 12.5 mg/5 mg/160 mg, 25 mg/5 mg/160 mg, 12.5 mg/10 mg/160 mg, 25 mg/10 mg/160 mg, 25 mg/10 mg/320 mg. Hyzaar: hydrochlorothiazide/losartan (an angiotensin II receptor antagonist): 12.5 mg/50 mg, 12.5 mg/100 mg, 25 mg/100 mg. Inderide: hydrochlorothiazide/propranolol (a beta blocker): 25 mg/40 mg, 25 mg/80 mg, 50 mg/80 mg, 50 mg/120 mg, 50 mg/160 mg. Lopressor HCT: hydrochlorothiazide/metoprolol (a beta blocker): 25 mg/50 mg, 25 mg/100 mg, 50 mg/100 mg. Lotensin HCT: hydrochlorothiazide/bepridil (a calcium channel blocker): 6.25 mg/5 mg, 12.5 mg/10 mg, 12.5 mg/20 mg, 25 mg/20 mg. Micardis HCT: hydrochlorothiazide/telmisartan (an angiotensin II receptor antagonist): 12.5 mg/40 mg, 12.5 mg/80 mg. Moduretic: hydrochlorothiazide/amiloride (a potassium-sparing diuretic): 50 mg/5 mg. Normozide: hydrochlorothiazide/labetalol (a beta blocker): 25 mg/100 mg, 25 mg/300 mg. Prinzide/Zestoretic: hydrochlorothiazide/lisinopril (an ACE inhibitor): 12.5 mg/10 mg, 12.5 mg/20 mg, 25 mg/20 mg. Tekturna HCT: hydrochlorothiazide/aliskiren (a renin inhibitor): 12.5 mg/150 mg, 25 mg/300 mg. Teveten HCT: hydrochlorothiazide/eprosartan (an angiotensin II receptor antagonist): 12.5 mg/600 mg, 25 mg/600 mg. Timolide: hydrochlorothiazide/timolol (a beta blocker): 25 mg/10 mg. Tribenzor: hydrochlorothiazide/olmesartan/amlodipine: 12.5 mg/20 mg/5 mg, 12.5 mg/40 mg/5 mg, 25 mg/40 mg/5 mg, 12.5 mg/40 mg/10 mg, 25 mg/40 mg/10 mg. Uniretic: hydrochlorothiazide/moexipril (an ACE inhibitor): 12.5 mg/7.5 mg, 25 mg/15 mg. Vaseretic: hydrochlorothiazide/enalapril (an ACE inhibitor): 12.5 mg/5 mg, 25 mg/10 mg. Ziac: hydrochlorothiazide/bisoprolol (a beta blocker): 6.25 mg/5 mg, 6.25 mg/10 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Sulfonamide derivative. CLINICAL: Thiazide diuretic, antihypertensive.
USES
Treatment of mild to moderate hypertension, edema in HF, hepatic cirrhosis, renal dysfunction (e.g., nephrotic syndrome). OFF-LABEL: Treatment of calcium nephrolithiasis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to hydrochlorothiazide. Anuria, history of hypersensitivity to sulfonamides or thiazide diuretics. Cautions: Severe renal/hepatic impairment, prediabetes or diabetes mellitus, elderly or debilitated, history of gout, moderate to high serum cholesterol, hypercalcemia, hypokalemia.
ACTION
Inhibits sodium reabsorption in distal renal tubules, causing excretion of sodium, potassium, hydrogen ions, water. Therapeutic Effect: Promotes diuresis; reduces B/P.
PHARMACOKINETICS
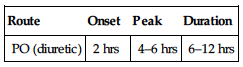
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO (diuretic) | 2 hrs | 4–6 hrs | 6–12 hrs |
Variably absorbed from GI tract. Primarily excreted unchanged in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 5.6–14.8 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Small amount distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: No age-related precautions noted, except jaundiced infants may be at risk for hyperbilirubinemia. Elderly: May be more sensitive to hypotensive, electrolyte effects. Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Cholestyramine, colestipol may decrease absorption, effects. Antihypertensives (e.g., amlodipine, clonidine, lisinopril, valsartan) may increase hypotensive effect. May increase risk of digoxin toxicity associated with hydrochlorothiazide-induced hypokalemia. May increase risk of lithium toxicity. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginseng, yohimbe may diminish effect. Black cohosh, periwinkle may increase antihypertensive effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, cholesterol, LDL, bilirubin, calcium, creatinine, uric acid, triglycerides. May decrease urinary calcium, serum magnesium, potassium, sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules (Microzide): 12.5 mg. Tablets: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May take with or without food. If GI upset occurs, give with food or milk, preferably with breakfast (may prevent nocturia). • Give last dose no later than 6 pm unless instructed otherwise.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Edema
PO: ADULTS: 25–100 mg/day in 1–2 divided doses. May give on alternate days or on 3–5 days/wk.
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 12.5–25 mg once daily. May increase up to 50 mg/day in 1–2 divided doses.
Usual Elderly Dosage
PO: 12.5–25 mg once daily. Titrate in 12.5-mg increments.
Usual Pediatric Dosage (Edema/HTN)
PO: CHILDREN 2–17 YRS: 1–2 mg/kg/day. Maximum: 50 mg/day. CHILDREN 6 MOS–2 YRS: 1–2 mg/kg/day in 1–2 divided doses. Maximum: 37.5 mg/day. CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 6 MOS: 1–3 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses. Maximum: 37.5 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl less than 30 ml/min: Generally not effective. Avoid use with CrCl less than 10 ml/min.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Expected: Increased urinary frequency, urine volume. Frequent: Potassium depletion. Occasional: Orthostatic hypotension, headache, GI disturbances, photosensitivity.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Vigorous diuresis may lead to profound water loss/electrolyte depletion, resulting in hypokalemia, hyponatremia, dehydration. Acute hypotensive episodes may occur. Hyperglycemia may occur during prolonged therapy. Pancreatitis, blood dyscrasias, pulmonary edema, allergic pneumonitis, dermatologic reactions occur rarely. Overdose can lead to lethargy, coma without changes in electrolytes or hydration.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Check vital signs, esp. B/P for hypotension before administration. Assess baseline electrolytes, esp. for hypokalemia. Evaluate skin turgor, mucous membranes for hydration status. Evaluate for peripheral edema. Assess muscle strength, mental status. Note skin temperature, moisture. Obtain baseline weight. Monitor I&O.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Continue to monitor B/P, vital signs, electrolytes, I&O, daily weight. Note extent of diuresis. Watch for changes from initial assessment (hypokalemia may result in weakness, tremor, muscle cramps, nausea, vomiting, altered mental status, tachycardia; hyponatremia may result in confusion, thirst, cold/clammy skin). Be esp. alert for potassium depletion in pts taking digoxin (cardiac arrhythmias). Potassium supplements are frequently ordered. Check for constipation (may occur with exercise diuresis).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Expect increased frequency, volume of urination. • To reduce hypotensive effect, go from lying to standing slowly. • Eat foods high in potassium, such as whole grains (cereals), legumes, meat, bananas, apricots, orange juice, potatoes (white, sweet), raisins. • Protect skin from sun, ultraviolet light (photosensitivity may occur).
*HYDROcodone


hye-droe-koe-done
(Hycodan
![]() , Hysingla ER, Robidone
, Hysingla ER, Robidone
![]() , Zohydro ER)
, Zohydro ER)
Do not confuse Hycodan with Vicodin.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Hycet: hydrocodone/acetaminophen: 7.5 mg/325 mg per 15 ml. Hycodan: hydrocodone/homatropine (an anticholinergic): 5 mg/1.5 mg. Hycotuss, Vitussin: hydrocodone/guaifenesin (an expectorant): 5 mg/100 mg. Norco: hydrocodone/acetaminophen: 5 mg/325 mg, 7.5 mg/325 mg, 10 mg/325 mg. Reprexain CIII: hydrocodone/ibuprofen (an NSAID): 5 mg/200 mg. Rezira: hydrocodone/pseudoephedrine (a nasal decongestant): 5 mg/60 mg per 5 ml. Tussend: hydrocodone/pseudoephedrine (a sympathomimetic)/guaifenesin (an expectorant): 2.5 mg/30 mg/100 mg per 5 ml. Vicodin: hydrocodone/acetaminophen: 5 mg/300 mg. Vicodin ES: hydrocodone/acetaminophen: 7.5 mg/300 mg. Vicodin HP: hydrocodone/acetaminophen: 10 mg/300 mg. Vicoprofen: hydrocodone/ibuprofen (an NSAID): 7.5 mg/200 mg. Xodol: hydrocodone/acetaminophen: 5 mg/300 mg, 7.5 mg/300 mg, 10 mg/300 mg. Zutripto: hydrocodone/chlorpheniramine (an antihistamine)/pseudoephedrine (a nasal decongestant): 5 mg/4 mg/60 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Opioid agonist (Schedule III). CLINICAL: Narcotic analgesic, antitussive.
USES
Relief of moderate to moderately severe pain, nonproductive cough. Hysingla ER, Zohydro ER: Around-the-clock management of moderate to severe chronic pain.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to hydrocodone. Significant respiratory depression, acute or severe bronchial asthma or hypercarbia, paralytic ileus. Cautions: Adrenal insufficiency, biliary tract disease, pancreatitis, CNS depression/coma, acute alcoholism, hypothyroidism; severe renal, hepatic, or pulmonary impairment; urinary stricture, prostatic hypertrophy, seizures, elderly, debilitated, other CNS depressants, history of substance abuse.
ACTION
Binds with opioid receptors in CNS. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces intensity of incoming pain stimuli from sensory nerve endings, altering pain perception, emotional response to pain; suppresses cough reflex.
PHARMACOKINETICS
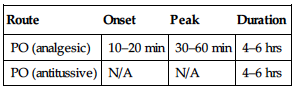
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO (analgesic) | 10–20 min | 30–60 min | 4–6 hrs |
| PO (antitussive) | N/A | N/A | 4–6 hrs |
Well absorbed from GI tract. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 3.8 hrs (increased in elderly).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Readily crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. May prolong labor if administered in latent phase of first stage of labor or before cervical dilation of 4–5 cm has occurred. Respiratory depression may occur in neonate if mother received opiates during labor. Regular use of opiates during pregnancy may produce withdrawal symptoms (irritability, excessive crying, tremors, hyperactive reflexes, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, yawning, sneezing, seizures) in the neonate. Children: Pts younger than 2 yrs may be more susceptible to respiratory depression. Elderly: May be more susceptible to respiratory depression, may cause paradoxical excitement. Age-related renal impairment, prostatic hypertrophy or obstruction may increase risk of urinary retention; dosage adjustment recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g., diphenhydramine, gabapentin, haloperidol lorazepam, morphine) may increase CNS or respiratory depression, hypotension. MAOIs, tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, doxepin) may alter effect of hydrocodone. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, ketoconazole) may increase or prolong opioid effects. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum amylase, lipase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Capsules, Extended-Release (Zohydro ER): 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg, 50 mg. Tablets, Extended-Release (Hysingla ER): 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg, 60 mg, 80 mg, 100 mg, 120 mg.
Capsules, Extended-Release (Zohydro ER): 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg, 50 mg. Tablets, Extended-Release (Hysingla ER): 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg, 60 mg, 80 mg, 100 mg, 120 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Extended-release capsules/tablets must be swallowed whole. Do not cut, crush, or dissolve.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Analgesia (Combination Products)
PO: ADULTS, CHILDREN WEIGHING 50 KG OR MORE: Initially, 5–10 mg q3–4h as needed. ADULTS, CHILDREN WEIGHING LESS THAN 50 KG: Initially, 0.1–0.2 mg/kg q3–4h as needed. ELDERLY: 2.5–5 mg q4–6h.
Analgesia (Extended-Release)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Zohydro ER):Initially, 10 mg q12h. May increase by 10 mg q12h q3–7 days to achieve adequate analgesia. (Hysingla ER):Initially, 20 mg q24h. May titrate q3-5 days.
Cough (Combination Products)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–10 mg q4–6h as needed. Maximum: 15 mg/dose. CHILDREN: 0.6 mg/kg/day in 3–4 divided doses at intervals of at least 4 hrs. Maximum single dose: 10 mg (children older than 12 yrs), 5 mg (children 2–12 yrs), 1.25 mg (children younger than 2 yrs).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Lethargy, hypotension, diaphoresis, facial flushing, dizziness, drowsiness. Occasional: Urine retention, blurred vision, constipation, dry mouth, headache, nausea, vomiting, difficult/painful urination, euphoria, dysphoria.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose results in respiratory depression, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold/clammy skin, cyanosis, extreme drowsiness progressing to seizures, stupor, coma. Tolerance to analgesic effect, physical dependence may occur with repeated use. Prolonged duration of action, cumulative effect may occur in those with hepatic/renal impairment. Antidote: Naloxone (see Appendix J).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain vital signs. If respirations are 12/min or less (20/min or less in children), withhold medication, contact physician. Analgesic: Assess onset, type, location, duration of pain. Effect of medication is reduced if full pain recurs before next dose. Antitussive: Assess type, severity, frequency of cough.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Palpate bladder for urinary retention. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Initiate deep breathing and coughing exercises, particularly in pts with pulmonary impairment. Assess for clinical improvement; record onset of relief of pain, cough. Monitor LOC.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Go from lying to standing slowly to avoid orthostatic hypotension. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol. • Tolerance or dependence may occur with prolonged use at high dosages. • Report nausea, vomiting, constipation, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing.
hydrocortisone
hye-droe-kor-ti-sone
(Anusol HC, Caldecort, Colocort, Cortaid, Cortef, Cortenema, Cortizone-10, Preparation H Hydrocortisone, Proctocort, Solu-Cortef, Westcort).
Do not confuse hydrocortisone with hydrochlorothiazide, hydrocodone, or hydroxychloroquine, Cortef with Coreg, or Solu-Cortef with Solu-Medrol.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Cortisporin: hydrocortisone/neomycin/polymyxin (an anti-infective): 5 mg/10,000 units/5 mg, 10 mg/10,000 units/5 mg. Liposivir: hydrocortisone/acyclovir (an antiviral): 1%/5%.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Adrenal corticosteroid. CLINICAL: Glucocorticoid.
USES
Systemic: Management of adrenocortical insufficiency, anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive. Topical: Inflammatory dermatoses, adjunctive treatment of ulcerative colitis, atopic dermatitis, inflamed hemorrhoids. OFF-LABEL: Management of septic shock. Treatment of thyroid storm.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to hydrocortisone. Fungal, tuberculosis, viral skin lesions; serious infections, IM administration in idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura. Cautions: Thyroid dysfunction, cirrhosis, hypertension, osteoporosis, thromboembolic tendencies or thrombophlebitis, HF, seizure disorders, diabetes, respiratory tuberculosis, untreated systemic infections, renal/hepatic impairment, acute MI, myasthenia gravis, glaucoma, cataracts, increased intraocular pressure, elderly.
ACTION
Inhibits accumulation of inflammatory cells at inflammation sites, phagocytosis, lysosomal enzyme release, synthesis and/or release of mediators of inflammation. Reverses increased capillary permeability. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents/suppresses cell-mediated immune reactions. Decreases/prevents tissue response to inflammatory process.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| IV | N/A | 4–6 hrs | 8–12 hrs |

Well absorbed after IM administration. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Half-life: Plasma, 1.5–2 hrs; biologic, 8–12 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. May produce cleft palate if used chronically during first trimester. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Prolonged treatment or high dosages may decrease short-term growth rate, cortisol secretion. Elderly: May be more susceptible to developing hypertension or osteoporosis.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of diuretics (e.g., furosemide), insulin, oral hypoglycemics (e.g., glimepiride, metformin, sitagliptin), potassium supplements. Hepatic enzyme inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease effects. Live virus vaccines may decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine, increase vaccine side effects, potentiate virus replication. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Cat’s claw, echinacea may increase immunostimulant properties. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, lipids, sodium. May decrease serum calcium, potassium, thyroxine; WBC count.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Cream, Rectal (Cortizone-10, Preparation H Hydrocortisone): 1%, 2.5%. Cream, Topical: 0.5%, 1%, 2.5%. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Solu-Cortef): 100 mg, 250 mg, 500 mg, 1 g. Ointment, Topical: 0.5%, 1%, 2.5%. Suppository (Anusol HC): 25 mg. Suspension, Rectal (Colocort, Cortenema): 100 mg/60 ml. Tablets (Cortef): 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Hydrocortisone Sodium Succinate
Reconstitution • Initially, reconstitute vial per manufacturer’s instructions. • May further dilute with D5W or 0.9% NaCl. For IV push, dilute to 50 mg/ml; for intermittent infusion, dilute to 1 mg/ml. Note: 100–3,000 mg may be added to 50 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • Administer IV push over 3–5 min (over 10 min for doses 500 mg or greater). Give intermittent infusion over 20–30 min.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Once reconstituted, stable for 3 days at room temperature. Once further diluted with 0.9% NaCl or D5W stability concentration dependent: 1 mg/ml (24 hrs) 2 mg/ml to 60 mg/ml (4 hrs).
PO
• Give with food or milk if GI distress occurs.
Rectal
• Shake homogeneous suspension well. • Instruct pt to lie on left side with left leg extended, right leg flexed. • Gently insert applicator tip into rectum, pointed slightly toward navel (umbilicus). Slowly instill medication.
Topical
• Gently cleanse area before application. • Use occlusive dressings only as ordered. • Apply sparingly; rub into area thoroughly.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro), diazepam (Valium), midazolam (Versed), phenytoin (Dilantin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin, calcium gluconate, cefepime (Maxipime), digoxin (Lanoxin), diltiazem (Cardizem), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dopamine (Intropin), insulin, lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, morphine, norepinephrine (Levophed), procainamide (Pronestyl), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Acute Adrenal Insufficiency
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100 mg IV bolus, then 50–75 mg q6h for 24 hrs, then taper slowly. CHILDREN: 1–2 mg/kg IV bolus, then 150–250 mg/day in divided doses q6–8h. INFANTS: 1–2 mg/kg/dose IV bolus, then 25–150 mg/day in divided doses q6–8h.
Anti-Inflammation, Immunosuppression
IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 15–240 mg q12h. CHILDREN: 1–5 mg/kg/day in divided doses q12h.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 15–240 mg q12h. CHILDREN: 2.5–10 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6–8h.
Physiologic Replacement
PO: CHILDREN: 8–10 mg/m2/day in 3 divided doses.
Status Asthmaticus
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 1–2 mg/kg/dose q6h for 24 hrs. Maintenance: 0.5–1 mg/kg q6h.
Adjunctive Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
Rectal (Enema): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100 mg at bedtime for 21 nights or until clinical and proctologic remission occurs (may require 2–3 mos of therapy).
Rectal Foam: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1 applicator 1–2 times/day for 2–3 wks, then every second day until therapy ends.
Usual Topical Dosage: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Apply sparingly 2–4 times/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Insomnia, heartburn, anxiety, abdominal distention, diaphoresis, acne, mood swings, increased appetite, facial flushing, delayed wound healing, increased susceptibility to infection, diarrhea or constipation. Occasional: Headache, edema, change in skin color, frequent urination. Topical: Pruritus, redness, irritation. Rare: Tachycardia, allergic reaction (rash, hives), psychological changes, hallucinations, depression. Topical: Allergic contact dermatitis, purpura. Systemic: Absorption more likely with use of occlusive dressings or extensive application in young children.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Long-term therapy: Hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, muscle wasting (esp. arms, legs), osteoporosis, spontaneous fractures, amenorrhea, cataracts, glaucoma, peptic ulcer, HF. Abrupt withdrawal after long-term therapy: Nausea, fever, headache, sudden severe joint pain, rebound inflammation, fatigue, weakness, lethargy, dizziness, orthostatic hypotension.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline weight, B/P, serum glucose, cholesterol, electrolytes. Review results of initial tests (tuberculosis [TB] skin test, X-rays, EKG).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for edema. Be alert to infection (reduced immune response): sore throat, fever, vague symptoms. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor electrolytes, B/P, weight, serum glucose. Monitor for hypocalcemia (muscle twitching, cramps), hypokalemia (weakness, paresthesia [esp. lower extremities], nausea/vomiting, irritability, EKG changes). Assess emotional status, ability to sleep.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report fever, sore throat, muscle aches, sudden weight gain, swelling, visual disturbances, behavioral changes. • Do not take aspirin or any other medication without consulting physician. • Limit caffeine, avoid alcohol. • Inform dentist, other physicians of cortisone therapy now or within past 12 mos. • Caution against overusing joints injected for symptomatic relief. • Topical: Apply after shower or bath for best absorption. • Do not cover or use occlusive dressings unless ordered by physician; do not use tight diapers, plastic pants, coverings. • Avoid contact with eyes.
*HYDROmorphone

hye-droe-mor-fone
(Apo-Hydromorphone
![]() , Dilaudid, Dilaudid HP, Exalgo, Hydromorph Contin
, Dilaudid, Dilaudid HP, Exalgo, Hydromorph Contin
![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() High abuse potential, respiratory depression risk. Other opioids, alcohol, CNS depressants increase risk of potentially fatal respiratory depression. Highly concentrated (Dilaudid HP, 10 mg/ml) form not to be interchanged with less concentrated (Dilaudid) form; overdose, death may result. Exalgo: For use in opioid-tolerant pts. Do not crush, break, chew, or dissolve. Swallow whole.
High abuse potential, respiratory depression risk. Other opioids, alcohol, CNS depressants increase risk of potentially fatal respiratory depression. Highly concentrated (Dilaudid HP, 10 mg/ml) form not to be interchanged with less concentrated (Dilaudid) form; overdose, death may result. Exalgo: For use in opioid-tolerant pts. Do not crush, break, chew, or dissolve. Swallow whole.
Do not confuse Dilaudid with demerol or Dilantin, or hydromorphone with hydrocodone or morphine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Opioid agonist (Schedule II). CLINICAL: Narcotic analgesic, antitussive.
USES
Relief of moderate to severe pain. Extended-release tablet (Exalgo): Around the clock, continuous analgesia for extended period.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to hydromorphone. Acute or severe asthma, severe respiratory depression. Additional Product-Specific Contraindications: Dilaudid liquids and tablets: Obstetric analgesia. Dilaudid injection: Opioid-intolerant pts, pts at risk of developing GI obstruction. Exalgo: Opioid-intolerant pts, preexisting GI surgery/diseases causing GI narrowing, GI obstruction, paralytic ileus. Cautions: Severe hepatic, renal, respiratory disease; hypothyroidism, adrenal cortical insufficiency, seizures, acute alcoholism, head injury, intracranial lesions, increased intracranial pressure, prostatic hypertrophy, Addison’s disease, urethral stricture, pancreatitis, biliary tract disease, cardiovascular disease, morbid obesity, delirium tremens, toxic psychosis, pts with CNS depression or coma, pts with depleted blood volume, obstructive bowel disorder.
ACTION
Binds to opioid receptors in CNS, reducing intensity of pain stimuli from sensory nerve endings. Therapeutic Effect: Alters perception, emotional response to pain; suppresses cough reflex.
PHARMACOKINETICS
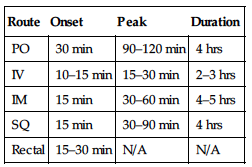
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 30 min | 90–120 min | 4 hrs |
| IV | 10–15 min | 15–30 min | 2–3 hrs |
| IM | 15 min | 30–60 min | 4–5 hrs |
| SQ | 15 min | 30–90 min | 4 hrs |
| Rectal | 15–30 min | N/A | N/A |
Well absorbed from GI tract after IM administration. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 2.6–4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Readily crosses placenta. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. May prolong labor if administered in latent phase of first stage of labor or before cervical dilation of 4–5 cm has occurred. Respiratory depression may occur in neonate if mother receives opiates during labor. Regular use of opiates during pregnancy may produce withdrawal symptoms in the neonate (irritability, excessive crying, tremors, hyperactive reflexes, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, yawning, sneezing, seizures). Children: Pts younger than 2 yrs may be more susceptible to respiratory depression. Elderly: May be more susceptible to respiratory depression, may cause paradoxical excitement. Age-related renal impairment, prostatic hypertrophy or obstruction may increase risk of urinary retention; dosage adjustment recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g., diphenhydramine, gabapentin, lorazepam, morphine) may increase CNS, respiratory depression, hypotension. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum amylase, lipase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution (Dilaudid): 1 mg/ml, 2 mg/ml, 4 mg/ml, 10 mg/ml. Liquid, Oral: 1 mg/ml. Suppository (Dilaudid): 3 mg. Tablets (Dilaudid): 2 mg, 4 mg, 8 mg.
![]() Tablets, Extended-Release (Exalgo): 8 mg, 12 mg, 16 mg, 32 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release (Exalgo): 8 mg, 12 mg, 16 mg, 32 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
◀ ALERT ▶ High concentration injection (10 mg/ml) should be used only in pts tolerant to opiate agonists, currently receiving high doses of another opiate agonist for severe, chronic pain due to cancer.
Reconstitution • May give undiluted. • May further dilute with 5 ml Sterile Water for Injection or 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • Administer IV push very slowly (over 2–3 min). • Rapid IV increases risk of severe adverse reactions (chest wall rigidity, apnea, peripheral circulatory collapse, anaphylactoid effects, cardiac arrest).
Storage • Store at room temperature; protect from light. • Slight yellow discoloration of parenteral form does not indicate loss of potency.
IM, SQ
• Use short 25- to 30-gauge needle for subcutaneous injection. • Administer slowly; rotate injection sites. • Pts with circulatory impairment experience higher risk of overdosage due to delayed absorption of repeated administration.
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Tablets may be crushed. • Extended-release tablets must be swallowed whole; do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide.
Rectal
• Refrigerate suppositories. • Moisten suppository with cold water before inserting well up into rectum.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), cefazolin (Ancef, Kefzol), diazepam (Valium), phenobarbital, phenytoin (Dilantin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), fentanyl (Sublimaze), furosemide (Lasix), heparin, lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, metoclopramide (Reglan), midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Analgesia
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate-Release): Initially 2–4 mg q4–6h prn (tablets) or 2.5–10 mg q3–6h prn (liquid). Range: 2–8 mg/dose. CHILDREN, ADOLESCENTS WEIGHING MORE THAN 50 KG: 1–2 mg q3–4h. CHILDREN OLDER THAN 6 MOS AND WEIGHING LESS THAN 50 KG: 0.03–0.08 mg/kg/dose q3–4h.
(Extended-Release): (For use in opioid-tolerant pts) ADULTS, ELDERLY: Range: 8–64 mg once daily.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN WEIGHING MORE THAN 50 KG: (For use in opiate-naive pts) 1 mg q2–3h (pts with prior opioid exposure may require higher doses.) CHILDREN WEIGHING 50 KG OR LESS: 0.03–0.06 mg/kg q4h prn.
Rectal: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 3 mg q6–8h.
Patient-Controlled Analgesia (PCA)
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Usual concentration: 0.2 mg/ml). Initially, 0.1–0.2 mg. Range: 0.05–0.4 mg. Lockout interval: 6 min. Range: 5–10 min.
Epidural: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Bolus dose of 0.4–1 mg; infusion rate: 0.03–0.3 mg/hr; demand dose: 0.02–0.05 mg. Lockout interval: 10–15 min.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Decrease initial dose; use with caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Drowsiness, dizziness, hypotension (including orthostatic hypotension), decreased appetite. Occasional: Confusion, diaphoresis, facial flushing, urinary retention, constipation, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, headache, pain at injection site. Rare: Allergic reaction, depression.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose results in respiratory depression, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold/clammy skin, cyanosis, extreme drowsiness progressing to seizures, stupor, coma. Tolerance to analgesic effect, physical dependence may occur with repeated use. Prolonged duration of action, cumulative effect may occur in those with hepatic/renal impairment. Antidote: Naloxone (see Appendix J).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain vital signs. If respirations are 12/min or less (20/min or less in children), withhold medication, contact physician. Analgesic: Assess onset, type, location, duration of pain. Effect of medication is reduced if full pain recurs before next dose. Antitussive: Assess type, severity, frequency of cough.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor vital signs; assess for pain relief, cough. To prevent pain cycles, instruct pt to request pain medication as soon as discomfort begins. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency (esp. in long-term use). Initiate deep breathing and coughing exercises, particularly in pts with pulmonary impairment. Assess for clinical improvement; record onset of relief of pain, cough.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid alcohol. • Avoid tasks that require alertness/motor skills until response to drug is established. • Tolerance or dependence may occur with prolonged use at high dosages. • Change positions slowly to avoid orthostatic hypotension. • Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide extended-release tablets.
hydroxychloroquine
hye-drox-ee-klor-oh-kwin
(Apo-Hydroxyquine
![]() , Plaquenil)
, Plaquenil)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Should be given by physicians familiar with prescribing information before use.
Should be given by physicians familiar with prescribing information before use.
Do not confuse hydroxychloroquine with hydrocortisone or hydroxyzine, or Plaquenil with Platinol.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Aminoquinoline antimalarial. CLINICAL: Antimalarial, antirheumatic.
USES
Suppression and treatment of acute attacks of malaria. Treatment of systematic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis (RA). OFF-LABEL: Porphyria, treatment of Q fever.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to hydroxychloroquine. Porphyria, psoriasis, retinal or visual field changes. Cautions: Alcoholism, hepatic disease, G6PD deficiency. Concomitant use of hepatotoxic medications. Children are esp. susceptible to hydroxychloroquine fatalities.
ACTION
Concentrates in parasite acid vesicles, interfering with parasite protein (DNA/RNA) synthesis. Inhibits movement of neutrophils, and chemotaxis of eosinophils. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits parasite growth.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Variable rate of absorption. Widely distributed in body tissues (eyes, kidneys, liver, lungs). Protein binding: 45%. Partially metabolized in liver. Partially excreted in urine. Half-life: 32 days (in plasma), 50 days (in blood).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Children: Long-term therapy not recommended. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration of dapsone. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease concentration. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 200 mg (155 mg base).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Treatment of Acute Malaria
PO:
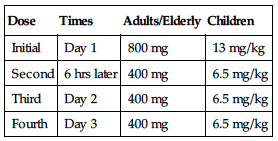
| Dose | Times | Adults/Elderly | Children |
| Initial | Day 1 | 800 mg | 13 mg/kg |
| Second | 6 hrs later | 400 mg | 6.5 mg/kg |
| Third | Day 2 | 400 mg | 6.5 mg/kg |
| Fourth | Day 3 | 400 mg | 6.5 mg/kg |
Suppression of Malaria
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg base wkly on same day each wk, beginning 2 wks before entering an endemic area and continuing for 4–6 wks after leaving the area. CHILDREN: 6.5 mg/kg/wk, beginning 2 wks before entering an endemic area and continuing for 4–6 wks after leaving the area. If therapy is not begun before exposure, administer a loading dose of 13 mg/kg in 2 equally divided doses 6 hrs apart and continue treatment for 8 wks.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 400–600 mg (310–465 mg base) daily, gradually increase to optimum response level. Maintenance (usually within 4–12 wks): Decrease dose by 50% and then continue at maintenance dose of 200–400 mg (155–310 mg base) daily. Maximum effect may not be seen for several mos.
Lupus Erythematosus
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 400 mg (310 mg base) once or twice daily for several wks or mos. Maintenance: 200–400 mg/day (155–310 mg base).
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Transient headache, anorexia, nausea, vomiting. Occasional: Visual disturbances, anxiety, fatigue, pruritus (esp. palms, soles, scalp), irritability, personality changes, diarrhea, photosensitivity. Rare: Stomatitis, dermatitis, impaired hearing.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Ocular toxicity (esp. retinopathy) may progress even after drug is discontinued. Prolonged therapy: Peripheral neuritis, neuromyopathy, hypotension, EKG changes, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, seizures, psychosis. Overdosage: Headache, vomiting, visual disturbances, drowsiness, seizures, hypokalemia followed by cardiovascular collapse, death.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Evaluate CBC, LFT vision.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, LFT. Observe for muscular weakness. Evaluate for GI distress. Assess skin/buccal mucosa; inquire about pruritus. Report impaired vision/hearing immediately.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid exposure to direct sunlight. • Avoid alcohol. • Explain need for eye exams q3mos with prolonged therapy. • Immediately report any new visual difficulties, muscular weakness, impaired hearing, tinnitus, numbness, tremors, rash, persistent diarrhea, emotional changes.
hydroxyurea

hye-drox-ee-yoo-ree-ah
(Apo-Hydroxyurea
![]() , Droxia, Hydrea)
, Droxia, Hydrea)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents or in treatment of sickle cell anemia. Carcinogenic risk; secondary leukemias reported with long-term treatment.
Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents or in treatment of sickle cell anemia. Carcinogenic risk; secondary leukemias reported with long-term treatment.
Do not confuse hydroxyurea with hydroxyzine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Synthetic urea analogue. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of melanoma, resistant chronic myelocytic leukemia, recurrent, metastatic, inoperable ovarian carcinoma. Used in combination with radiation therapy for local control of primary squamous cell carcinoma of head/neck, excluding lip. Treatment of sickle cell anemia with at least 3 painful crises in previous 12 mos. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of hematologic conditions (e.g., polycythemia vera), cervical cancer, essential thrombocythemia, hyperleukocytosis due to AML, treatment of meningiomas.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to hydroxyurea. Cautions: WBC count less than 2,500/mm3 or platelet count less than 100,000/mm3, severe anemia. Previous irradiation therapy, concurrent use with other cytoxic drugs, renal/hepatic impairment, elderly; pts with sickle cell anemia if neutrophils less than 2,000/mm3, platelets less than 80,000/mm3, Hgb less than 4.5 g/dL, or reticulocytes less than 80,000/mm3 when Hgb less than 9 g/dL.
ACTION
Inhibits DNA synthesis without interfering with RNA synthesis or protein. In sickle cell anemia, increases RBC hemoglobin levels, thereby decreasing concentration of sickled cells; alters adhesion of RBCs to endothelium. Therapeutic Effect: Interferes with normal repair process of cancer cells damaged by irradiation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 75%–80%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine as urea and unchanged drug. Half-life: 3–4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. May cause fetal harm. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: More sensitive to hydroxyurea effects; may require lower dosage.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Bone marrow depressants (e.g., alemtuzumab, methotrexate) may increase myelosuppression. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease the pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, creatinine, uric acid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 200 mg (Droxia), 300 mg (Droxia), 400 mg (Droxia), 500 mg (Hydrea).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Do not open capsules.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Antineoplastic therapy interrupted when platelet count less than 100,000/mm3 or WBC count less than 2,500/mm3. Resume when counts return to normal.
Sickle cell anemia therapy interrupted when neutrophils less than 2,000/mm3, platelets less than 80,000/mm3, Hgb less than 4.5 g/dL, or reticulocytes less than 80,000/mm3 with Hgb less than 9 g/dL. Reduce dose by 2.5 mg/kg/day following recovery.
Antineoplastic Uses
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 15 mg/kg/day. Adjust dose based on tumor type, disease state, response, pt risk factors. May give alone or in combination with other agents.
Sickle Cell Anemia
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 15 mg/kg once daily. May increase by 5 mg/kg/day every 12 wks. Maximum: 35 mg/kg/day. CHILDREN 6 MOS AND OLDER: 20 mg/kg/dose once daily; increase by 5 mg/kg/day q8wk until mild myelosuppression is achieved. Maximum: 35 mg/kg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Reduce dose to 7.5 mg/kg/day for CrCl 60 ml/min or less.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, constipation or diarrhea. Occasional: Mild, reversible rash; facial flushing, pruritus, fever, chills, malaise. Rare: Alopecia, headache, drowsiness, dizziness, disorientation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Myelosuppression manifested as hematologic toxicity (leukopenia and, to a lesser extent, thrombocytopenia, anemia).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain bone marrow studies, renal function, LFT before therapy begins, periodically thereafter. Obtain Hgb, WBC, platelet count, serum uric acid at baseline and wkly during therapy. Pts with marked renal impairment may develop visual or auditory hallucinations, marked hematologic toxicity.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor for hematologic toxicity (fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bleeding/bruising at any site), symptoms of anemia (excessive fatigue, weakness). Assess skin for rash, erythema. Monitor CBC with differential, renal/hepatic function, uric acid.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Promptly report fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bleeding/bruising at any site.
*hydrOXYzine
hye-drox-ee-zeen
(Apo-Hydroxyzine
![]() , Atarax
, Atarax
![]() , Novo-Hydroxyzin
, Novo-Hydroxyzin
![]() , Vistaril)
, Vistaril)
Do not confuse hydroxyzine with hydralazine or hydroxyurea, or Vistaril with Restoril, Versed, or Zestril.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Piperazine derivative. CLINICAL: Antihistamine, antianxiety, antispasmodic, antiemetic, antipruritic.
USES
Antiemetic, treatment of anxiety/agitation, antipruritic.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to hydroxyzine. Early pregnancy; subcutaneous, intravenous administration. Cautions: Narrow-angle glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, bladder neck obstruction, asthma, COPD, elderly.
ACTION
Competes with histamine for receptor sites in GI tract, blood vessels, respiratory tract. Therapeutic Effect: Produces anxiolytic, anticholinergic, antihistaminic, analgesic effects; relaxes skeletal muscle; controls nausea, vomiting.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 15–30 min | N/A | 4–6 hrs |
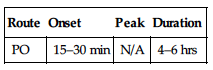
Well absorbed from GI tract and after parenteral administration. Metabolized in liver to active metabolite cetirizine. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 3–7 hrs (increased in elderly, hepatic impairment). (Cetirizine half-life: 8–20 hrs.)
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Not recommended in newborns or premature infants (increased risk of anticholinergic effects). Paradoxical excitement may occur. Elderly: Increased risk of dizziness, sedation, confusion. Hypotension, hyperexcitability may occur.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g., diphenhydramine, gabapentin, lorazepam, morphine) may increase CNS depressant effects. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May cause false-positive urine 17-hydroxycorticosteroid determinations.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Oral Solution: 10 mg/5 ml. Syrup: 10 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg.
![]() Capsules: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg.
Capsules: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May give without regard to food. • Shake oral suspension well. • Scored tablets may be crushed; do not break, crush, or open capsule.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Anxiety
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 50–100 mg 4 times/day or 37.5–75 mg/day in divided doses.
Pruritus
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 25 mg 3–4 times/day. CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER: 50–100 mg/day in divided doses. CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 6 YRS: 50 mg/day in divided doses.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Change dosing interval to q24h in pts with primary biliary cirrhosis.
SIDE EFFECTS
Side effects are generally mild, transient. Frequent: Drowsiness, dry mouth, marked discomfort with IM injection. Occasional: Dizziness, ataxia, asthenia, slurred speech, headache, agitation, increased anxiety. Rare: Paradoxical reactions (hyperactivity, anxiety in children; excitement, restlessness in elderly or debilitated pts) generally noted during first 2 wks of therapy, particularly in presence of uncontrolled pain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hypersensitivity reaction (wheezing, dyspnea, chest tightness) may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Anxiety: Offer emotional support. Assess motor responses (agitation, trembling, tension), autonomic responses (cold/clammy hands, diaphoresis). Antiemetic: Assess for dehydration (poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, longitudinal furrows in tongue).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
For pts on long-term therapy, CBC, BMP, LFT should be performed periodically. Monitor lung sounds for signs of hypersensitivity reaction. Monitor serum electrolytes in pts with severe vomiting. Assess for paradoxical reaction, particularly during early therapy. Assist with ambulation if drowsiness, light-headedness occur.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Marked discomfort may occur with IM injection. • Sugarless gum, sips of water may relieve dry mouth. • Drowsiness usually diminishes with continued therapy. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established.
hyoscyamine
hye-oh-sye-a-meen
(Anaspaz, Hyosyne, Levbid, Levsin, Levsin S/L, Nu-Lev, Symax SL, Symax SR)
Do not confuse Anaspaz with Anaprox, or Levbid with Lithobid or Lopid.
FIXED COMBINATIONS
Donnatal: hyoscyamine/atropine (anticholinergic)/phenobarbital (sedative)/scopolamine (anticholinergic): 0.1037 mg/0.0194 mg/16.2 mg/0.0065 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Anticholinergic. CLINICAL: Antimuscarinic, antispasmodic.
USES
Adjunctive therapy for relief of biliary/renal colic; control of acute episodes of gastric secretion, hypermotility in spastic colitis, pylorospasm, and abdominal cramps; relieve symptoms of infant colic; control hypermotility in spastic bladder and cystitis; adjunctive therapy in treatment of neurogenic bladder.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to hyoscyamine. GI/GU obstruction, myasthenia gravis, narrow-angle glaucoma, paralytic ileus, severe ulcerative colitis. Cautions: Hyperthyroidism, HF, cardiac arrhythmias, prostatic hypertrophy, neuropathy, chronic lung disease, biliary tract disease, children with spastic paralysis.
ACTION
Inhibits action of acetylcholine at postganglionic (muscarinic) receptor sites. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases secretions (bronchial, salivary, sweat gland, gastric juices). Reduces motility of GI, urinary tracts.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 15–30 min | — | 4–6 hrs |
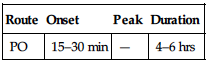
Well absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 50%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 3.5 hrs (immediate-release); 7 hrs (sustained-release).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antacids may decrease absorption. Other anticholinergics (e.g., atropine, glycopyrrolate) may increase effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules, Timed-Release: 0.375 mg. Elixir (Hyosyne, Levsin): 0.125 mg/5 ml. Injection, Solution: 0.5 mg/ml. Solution, Oral Drops: 0.125 mg/ml. Tablets: 0.125 mg. Tablets, Orally Disintegrating: 0.125 mg. Tablets, Sublingual: 0.125 mg.
![]() Tablets, Extended-Release: 0.375 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release: 0.375 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give before meals. • Immediate-release tablets may be crushed, chewed. • Extended-release tablet should be administered whole. • Allow orally disintegrating tablet placed on tongue to dissolve before swallowing; may give with or without water. • Sublingual: Place under tongue.
Parenteral
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
GI Tract Disorders
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 0.125–0.25 mg q4h as needed. Maximum: 1.5 mg/day. CHILDREN 2–11 YRS: 0.0625–0.125 mg q4h as needed. Maximum: 0.75 mg/day. ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Extended-Release): 0.375–0.75 mg q12h. Maximum: 1.5 mg/day.
IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 0.25–0.5 mg. May repeat as needed up to 4 times/day at 4-hr intervals.
Hypermotility of Lower Urinary Tract
PO (Sublingual): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.15–0.3 mg 4 times/day. (Extended-Release): 0.375 mg q12h.
Infant Colic
PO: INFANTS: Drops dosed q4h as needed (based on weight): 2.3 kg: 3 drops; 3.4 kg: 4 drops; 5 kg: 5 drops; 7 kg: 6 drops; 10 kg: 8 drops; 15 kg: 11 drops.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Dry mouth, decreased diaphoresis, constipation. Occasional: Blurred vision, bloated feeling, urinary hesitancy, drowsiness (with high dosage), headache, intolerance to light, loss of taste, anxiety, flushing, insomnia, impotence, mental confusion or excitement (particularly in elderly, children), temporary light-headedness (with parenteral form), local irritation (with parenteral form). Rare: Dizziness, faintness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may produce temporary paralysis of ciliary muscle, pupillary dilation, tachycardia, palpitations, hot/dry/flushed skin, absence of bowel sounds, hyperthermia, increased respiratory rate, EKG abnormalities, nausea, vomiting, rash over face/upper trunk, CNS stimulation, psychosis (agitation, restlessness, rambling speech, visual hallucinations, paranoid behavior, delusions) followed by depression.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Before giving medication, instruct pt to void (reduces risk of urinary retention). Question history of myasthenia gravis, narrow-angle glaucoma, BPH, ulcerative colitis.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Palpate bladder for urinary retention. Monitor changes in B/P, temperature. Assess skin turgor, mucous membranes to evaluate hydration status (encourage adequate fluid intake), bowel sounds for peristalsis. Be alert for fever (increased risk of hyperthermia).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• May cause dry mouth; maintain proper oral hygiene (lack of saliva may increase risk of cavities). • Report rash, eye pain, difficulty in urinating, constipation. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid hot baths, saunas.