I
ibandronate
eye-ban-droe-nate
(Boniva)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Bisphosphonate. CLINICAL: Calcium regulator.
USES
Treatment/prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. OFF-LABEL: Hypercalcemia of malignancy; reduces bone pain and skeletal complications from metastatic bone disease due to breast cancer.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ibandronate, other bisphosphonates; oral tablets in pts unable to stand or sit upright for at least 60 min; pts with abnormalities of the esophagus that would delay emptying, hypocalcemia. Cautions: GI diseases (duodenitis, dysphagia, esophagitis, gastritis, ulcers [drug may exacerbate these conditions]), renal impairment with CrCl less than 30 ml/min.
ACTION
Inhibits bone resorption via activity on osteoclasts. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces rate of bone resorption, resulting in increased bone mineral density.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Absorbed in upper GI tract. Extent of absorption impaired by food, beverages (other than plain water). Protein binding: 85%–99%. Rapidly binds to bone. Unabsorbed portion eliminated in urine. Half-life: PO: 37–157 hrs; IV: 5–25 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Potential for teratogenic effects. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antacids containing aluminum, calcium, magnesium; vitamin D decrease absorption. Aspirin, NSAIDs may increase GI irritation. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: Beverages (other than plain water), dietary supplements, food interfere with absorption. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum alkaline phosphatase. May increase serum cholesterol.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 3 mg/3 ml syringe. Tablets: 150 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give 60 min before first food or beverage of the day, on an empty stomach with 6–8 oz plain water (not mineral water) while pt is standing or sitting in upright position. • Pt cannot lie down for 60 min following drug administration. • Instruct pt to swallow whole; do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablet (potential for oropharyngeal ulceration).
![]() IV
IV
• Give over 15–30 sec. • Give over 1 hr for metastatic bone disease; over 1–2 hrs for hypercalcemia of malignancy.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Osteoporosis
PO (Prevention/Treatment): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 150 mg once monthly.
IV (Treatment): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 3 mg q3mos.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Not recommended for pts with CrCl less than 30 ml/min.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (13%–6%): Back pain, dyspepsia, peripheral discomfort, diarrhea, headache, myalgia. IV: Abdominal pain, dyspepsia, constipation, nausea, diarrhea. Occasional (4%–3%): Dizziness, arthralgia, asthenia. Rare (2% or less): Vomiting, hypersensitivity reaction.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Upper respiratory infection occurs occasionally. Overdose results in hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, significant GI disturbances.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Hypocalcemia, vitamin D deficiency must be corrected before beginning therapy. Obtain laboratory baselines, esp. serum chemistries, renal function. Obtain results of bone density study.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor electrolytes, esp. serum calcium, phosphate. Monitor renal function tests.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Expected benefits occur only when medication is taken with full glass (6–8 oz) of plain water, first thing in the morning and at least 60 min before first food, beverage, medication of the day. Any other beverage (mineral water, orange juice, coffee) significantly reduces absorption of medication. • Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets; swallow whole. • Do not lie down for at least 60 min after taking medication (potentiates delivery to stomach, reduces risk of esophageal irritation). • Report swallowing difficulties, pain when swallowing, chest pain, new/worsening heartburn. • Consider weight-bearing exercises; modify behavioral factors (e.g., cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption). • Calcium and vitamin D supplements should be taken if dietary intake inadequate.
ibrutinib
eye-broo-ti-nib
(Imbruvica)
Do not confuse ibrutinib with axitinib, dasatinib, erlotinib, gefitinib, imatinib, nilotinib, ponatinib, sorafenib, sunitinib, or vandetanib.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Kinase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of pts with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) with at least one prior therapy or with 17p deletion, first-line treatment of CLL. Waldenstrom’s macroglobulemia (WM).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ibrutinib. Cautions: Hepatic/renal impairment, elderly, pregnancy, history of GI disease (e.g., bleeding, ulcers).
ACTION
Inhibits enzymatic activity of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK), a signaling molecule that promotes malignant B-cell proliferation and survival. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed following PO. Metabolized in liver. Peak plasma concentration: 1–2 hrs. Protein binding: 97%. Excreted in feces (80%), urine (10%). Half-life: 4–6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Avoid pregnancy. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Must either discontinue drug or discontinue breastfeeding. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Increased risk of cardiac events (atrial fibrillation, hypertension), infections (pneumonia, cellulitis), GI events (diarrhea, dehydration, bleeding).
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, clarithromycin) may increase plasma concentration/effect; avoid use. Strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin) may decrease plasma concentration/effect; avoid use. Anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelets (e.g., aspirin, clopidogrel), NSAIDs may increase risk of bleeding. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effect. FOOD: Grapefruit products, Seville oranges may increase concentration/effect. All foods may increase absorption/concentration. LAB VALUES: May decrease Hgb, Hct, neutrophils, platelets.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Capsules: 140 mg.
Capsules: 140 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with water. • Do not break, crush, or open capsule.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
PO: ADULTS/ELDERLY: 560 mg (4 × 140-mg capsules) once daily.
CLL, WM
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 420 mg (3 × 140 mg) once daily.
Dose Modification
Based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE).
Any Grade 3 or Greater Nonhematologic Event, Grade 3 or Greater Neutropenia with Infection or Fever, or Any Grade 4 Hematologic Toxicities
Interrupt treatment until resolution to grade 1 or baseline, then restart at initial dose. If toxicity reoccurs, interrupt treatment until resolution to grade 1 or baseline, then reduce dose to 420 mg daily (one capsule less). If toxicity reoccurs, interrupt treatment until resolution to grade 1 or baseline, then reduce dose to 280 mg once daily (one capsule less). If toxicity still occurs at 280 mg dose, discontinue treatment.
Concomitant Use of Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors (e.g., Fluconazole, Diltiazem, Verapamil)
Start at reduced dose of 140 mg daily. If toxicity occurs, either discontinue treatment or find alternate agent with less CYP3A inhibition.
Concomitant Short-Term Use of Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors (7 days or less) (e.g., Antifungals, Antibiotics)
Interrupt treatment until strong CYP3A medications no longer needed.
Concomitant Chronic Use of Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors or Inducers
Treatment not recommended.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: Decrease dose to 140 mg. Moderate to severe impairment: Avoid use.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (51%–23%): Diarrhea, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, peripheral edema, nausea, bruising, dyspnea, constipation, rash, abdominal pain, vomiting. Occasional (21%–11%): Decreased appetite, cough, pyrexia, stomatitis, asthenia, dizziness, muscle spasms, dehydration, headache, dyspepsia, petechiae, arthralgia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Anemia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia is expected response to therapy. Treatment-emergent myelosuppression (grade 3–4 CTCAE) reported in 41% of pts: neutropenia (29%), thrombocytopenia (17%), anemia (9%). Infections including upper respiratory tract infection, UTI, pneumonia, skin infection, sinusitis were reported. Hemorrhagic events including epistaxis, GI bleeding, hematuria, intracranial hemorrhage, subdural hematoma reported in 5% of pts. Serious and fatal cases of renal toxicity reported: increased serum creatinine 1.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN) (67% of pts), increased serum creatinine 1.53 times UNL (9% of pts). Second primary malignancies including skin cancer (4%), other carcinomas (1%) occurred.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline vital signs, CBC, serum chemistries, LFT, PT/INR if on anticoagulants. Question history of arrhythmias, HF, GI bleed, hepatic/renal impairment, peripheral edema, pulmonary disease. Obtain negative urine pregnancy before initiating treatment. Assess hydration status. Receive full medication history including herbal products. Assess skin for open/unhealed wounds, lesions, moles. Conduct baseline neurologic exam.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC monthly; LFT, serum chemistries, renal function routinely. Monitor stool frequency, consistency, characteristics. Immediately report hemorrhagic events: epistaxis, hematuria, hemoptysis, melena. Encourage PO intake. Obtain EKG for arrhythmias, dyspnea, palpitations. Screen for possible intracranial hemorrhage: altered mental status, aphasia, hemiparesis, unequal pupils, homonymous hemianopsia (blindness of one half of vision on same side of both eyes). Monitor for renal toxicity (anuria, hypertension, generalized edema, flank pain). Assess skin for new lesions.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Blood levels will be monitored routinely. • Difficulty breathing, fever, cough, burning with urination, body aches, chills may indicate acute infection. • Avoid pregnancy. • Report any black/tarry stools, bruising, nausea, RUQ abdominal pain, yellowing of skin or eyes, palpitations, nose bleeds, blood in urine or stool, decreased urine output. • Avoid alcohol. • Do not take herbal products. • Do not ingest grapefruit products. • Severe diarrhea may lead to dehydration. • Contact physician before any planned surgical/dental procedures. • Immediately report neurological changes: confusion, one-sided paralysis, difficulty speaking, partial blindness. • Do not receive live vaccines. • Do not break, crush, or open capsule.
ibuprofen
eye-bue-pro-fen
(Advil, Apo-Ibuprofen
![]() , Caldolor, Motrin, NeoProfen, Novo-Profen
, Caldolor, Motrin, NeoProfen, Novo-Profen
![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction, CVA. Increased risk of severe GI reactions, including ulceration, bleeding, perforation.
Increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction, CVA. Increased risk of severe GI reactions, including ulceration, bleeding, perforation.
Do not confuse Motrin with Neurontin.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Children’s Advil Cold: ibuprofen/pseudoephedrine (a nasal decongestant): 100 mg/15 mg per 5 ml. Combunox: ibuprofen/oxycodone (a narcotic analgesic): 400 mg/5 mg. Duexis: ibuprofen/famotidine (an H2 antagonist): 800 mg/26.6 mg. Reprexain CIII: ibuprofen/hydrocodone (a narcotic analgesic): 200 mg/5 mg. Vicoprofen: ibuprofen/hydrocodone (a narcotic analgesic): 200 mg/7.5 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: NSAID. CLINICAL: Antirheumatic, analgesic, antipyretic, antidysmenorrheal, vascular headache suppressant.
USES
Oral: Treatment of fever, rheumatoid disorders, osteoarthritis, mild to moderate pain, primary dysmenorrhea. Caldolor: Mild to moderate pain; severe pain in combination with an opioid analgesic; fever. NeoProfen: Induces closure in clinically significant patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in premature infants weighing between 500 and 1,500 g who are no more than 32 wks gestational age when usual medical management is ineffective. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of cystic fibrosis, pericarditis. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: History of hypersensitivity to ibuprofen, aspirin, other NSAIDs. Treatment of perioperative pain in coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. Aspirin triad (bronchial asthma, aspirin intolerance, rhinitis). NeoProfen: Infants with proven or suspected untreated infection, elevated total bilirubin, congenital heart disease in whom patency of the patent ductus arteriosus is necessary for satisfactory pulmonary or systemic blood flow (e.g., pulmonary atresia), bleeding, thrombocytopenia, coagulation defects, suspected necrotizing enterocolitis, significant renal impairment. Cautions: Pts with fluid retention, HF, dehydration, coagulation disorders, concurrent use with aspirin, anticoagulants, steroids; history of GI disease (e.g., bleeding, ulcers), smoking, use of alcohol, elderly, debilitated, hepatic/renal impairment, asthma.
ACTION
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Produces analgesic, anti-inflammatory effects; decreases fever.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO (analgesic) | 0.5 hr | N/A | 4–6 hrs |
| PO (antirheumatic) | 2 days | 1–2 wks | N/A |
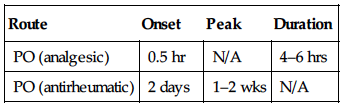
Rapidly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 90%–99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2–4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Avoid use during third trimester (may adversely affect fetal cardiovascular system: premature closure of ductus arteriosus). Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 6 mos. Elderly: GI bleeding, ulceration more likely to cause serious adverse effects. Age-related renal impairment may increase risk of hepatic/renal toxicity; reduced dosage recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of antihypertensives (e.g., amlodipine, lisinopril, valsartan), diuretics (e.g., furosemide). Aspirin, other salicylates may increase risk of GI side effects, bleeding. May increase effects of oral anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin). May increase concentration, risk of toxicity of lithium, methotrexate. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginkgo, ginseng, horse chestnut, red clover may increase antiplatelet activity. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May prolong bleeding time. May alter serum glucose level. May increase serum BUN, creatinine, potassium, ALT, AST. May decrease serum calcium, glucose; Hgb, Hct, platelets.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 200 mg. Injection, Solution (NeoProfen): 10 mg/ml. (Caldolor): 100 mg/ml. Suspension, Oral: 100 mg/5 ml. Suspension, Oral Drops: 40 mg/ml. Tablets: 200 mg, 400 mg, 600 mg, 800 mg. Tablets, Chewable: 50 mg, 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV (Caldolor)
IV (Caldolor)
Reconstitution • Dilute with D5W or 0.9% NaCl to final concentration of 4 mg/ml or less.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over at least 30 min.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Stable for 24 hrs after dilution.
![]() IV (Neoprofen)
IV (Neoprofen)
Reconstitution • Dilute to appropriate volume with D5W or 0.9% NaCl. • Discard any remaining medication after first withdrawal from vial.
Rate of Administration • Administer via IV port nearest the insertion site. • Infuse continuously over 15 min.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Stable for 30 min after dilution.
PO
• Give with food, milk, antacids if GI distress occurs.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Fever
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 200–400 mg q4–6h prn. CHILDREN 6 MOS AND OLDER: 5–10 mg/kg q6–8h. Maximum: 400 mg/dose; 1,200 mg/day.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg q4–6h or 100–200 mg q4h prn. Maximum: 3.2 g/day.
CHILDREN 12–17 YRS: 400 mg q4–6h prn. Maximum: 2,400 mg/day. CHILDREN 6 MOS–11 YRS: 10 mg/kg q4–6h prn. Maximum/dose: 400 mg. Maximum: 40 mg/kg up to 2,400 mg/day.
Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Disorders
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400–800 mg 3–4 times/day. Maximum: 3.2 g/day.
Pain
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 200–400 mg q4–6h prn. CHILDREN 6 MOS–11 YRS: 4–10 mg/kg q6–8h prn. Maximum: 40 mg/kg/day.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400–800 mg q6h prn. Maximum: 3.2 g/day.
Primary Dysmenorrhea
PO: ADULTS: 200–400 mg q4–6h prn. Maximum: 1,200 mg/day.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
IV: INFANTS: Initially, 10 mg/kg then 2 doses of 5 mg/kg, after 24 hrs and 48 hrs. All doses based on birth weight.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Hold if anuria or oliguria evident. Avoid use in severe impairment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use in severe impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (9%–3%): Nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, dizziness, rash. Rare (less than 3%): Diarrhea or constipation, flatulence, abdominal cramps or pain, pruritus, increased B/P.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may result in metabolic acidosis. Rare reactions with long-term use include peptic ulcer, GI bleeding, gastritis, severe hepatic reaction (cholestasis, jaundice), nephrotoxicity (dysuria, hematuria, proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome), severe hypersensitivity reaction (particularly in pts with systemic lupus erythematosus or other collagen diseases). NeoProfen: Hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, respiratory failure, UTI, edema, atelectasis may occur. Caldolor: Abdominal pain, anemia, cough, dizziness, dyspnea, edema, hypertension, nausea, vomiting have been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess onset, type, location, duration of pain, inflammation. Inspect appearance of affected joints for immobility, deformities, skin condition. Assess temperature.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for evidence of nausea, dyspepsia. Monitor CBC, renal function, LFT. Assess skin for rash. Observe for bleeding, bruising, occult blood loss. Evaluate for therapeutic response: relief of pain, stiffness, swelling; increased joint mobility; reduced joint tenderness; improved grip strength. Monitor for fever.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid aspirin, alcohol during therapy (increases risk of GI bleeding). • If GI upset occurs, take with food, milk, antacids. • May cause dizziness. • Report ringing in ears, persistent stomach pain, respiratory difficulty, unusual bruising/bleeding, swelling of extremities, chest pain/palpitations.
*IDArubicin

eye-da-rue-bi-sin
(Idamycin PFS)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Cardiotoxicity may occur (HF, arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy). Severe myelosuppressant. Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. Severe local tissue damage, necrosis if extravasation occurs. Dosage reduction recommended with renal/hepatic impairment.
Cardiotoxicity may occur (HF, arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy). Severe myelosuppressant. Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. Severe local tissue damage, necrosis if extravasation occurs. Dosage reduction recommended with renal/hepatic impairment.
Do not confuse Idamycin with Adriamycin, or idarubicin with daunorubicin, doxorubicin, or epirubicin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Anthracycline antibiotic. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). OFF-LABEL: Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to idarubicin. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, concurrent radiation therapy, anemia, bone marrow depression, active infections, arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy, severe HF.
ACTION
Inhibits DNA/RNA synthesis by intercalating between DNA base pairs. Therapeutic Effect: Produces apoptosis of rapidly dividing cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Protein binding: 97%. Rapidly metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated by biliary excretion. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 12–27 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy (may be embryotoxic). Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk (advise to discontinue breast-feeding before drug initiation). Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Cardiotoxicity may be more prevalent. Caution in pts with inadequate bone marrow reserves. Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of antigout medications (e.g., allopurinol, probenecid). Bone marrow depressants (e.g., alemtuzumab, methotrexate) may increase myelosuppression. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, uric acid, ALT, AST. May cause EKG changes.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 1 mg/ml in 5-ml, 10-ml, 20-ml vials.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Give by free-flowing IV infusion (never subcutaneous or IM). Gloves, gowns, eye goggles recommended during preparation/administration of medication. If powder/solution comes in contact with skin, wash thoroughly. Avoid small veins, swollen/edematous extremities, areas overlying joints/tendons.
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • May give undiluted or dilute with 0.9% NaCl or D5W.
Rate of Administration • Administer IV push into tubing of freely running IV infusion of D5W or 0.9% NaCl, preferably via butterfly needle, slowly over 3–5 min. • May give intermittent infusion over 10–15 min. • Extravasation produces immediate pain, severe local tissue damage. Terminate infusion immediately. Apply cold compresses for 30 min immediately, then q30min 4 times/day for 3 days. Keep extremity elevated.
Storage • Refrigerate vials. • Diluted solutions in 0.9% NaCl or D5W are stable for 72 hrs at room temperature or 7 days if refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Acyclovir (Zovirax), allopurinol (Aloprim), ampicillin and sulbactam (Unasyn), cefazolin (Ancef, Kefzol), cefepime (Maxipime), ceftazidime (Fortaz), clindamycin (Cleocin), dexamethasone (Decadron), furosemide (Lasix), hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef), lorazepam (Ativan), methotrexate, piperacillin and tazobactam (Zosyn), sodium bicarbonate, teniposide (Vumon), vancomycin (Vancocin), vincristine (Oncovin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl), granisetron (Kytril), magnesium, potassium.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Refer to individual protocols.
AML
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Induction): 12 mg/m2/day for 3 days (in combination with cytarabine). A second induction cycle may be administered if necessary.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
ADULTS: CrCl 10–50 ml/min: Give 75% of dose. CrCl less than 10 ml/min: Give 50% of dose. CHILDREN: CrCl less than 50 ml/min: Give 75% of dose.
Hemodialysis, Peritoneal Dialysis, Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: Administer 75% of dose.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Bilirubin 2.6–5 mg/dL: Give 50% of dose. Bilirubin greater than 5 mg/dL: Avoid use.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (82%–50%): Nausea, vomiting, complete alopecia (scalp, axillary, pubic hair), abdominal cramping, diarrhea, mucositis. Occasional (46%–20%): Hyperpigmentation of nailbeds, phalangeal, dermal creases; fever, headache. Rare: Conjunctivitis, neuropathy.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Myelosuppression (principally leukopenia and, to lesser extent, anemia, thrombocytopenia) generally occurs within 10–15 days after starting therapy, returns to normal levels by third wk. Cardiotoxicity (either acute, manifested as transient EKG abnormalities, or chronic, manifested as HF) may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC, BMP, LFT. Obtain EKG before therapy. Antiemetic medication before and during therapy may prevent or relieve nausea, vomiting. Inform pt of high potential for alopecia.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, serum electrolytes, EKG, renal function, LFT. Monitor for hematologic toxicity (fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site), symptoms of anemia (excessive fatigue, weakness). Avoid IM injections, rectal temperatures, other trauma that may precipitate bleeding. Check infusion site frequently for extravasation (causes severe local necrosis). Assess for potentially fatal HF (dyspnea, rales, pulmonary edema), life-threatening arrhythmias.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Total body hair loss is frequent but reversible. • New hair growth resumes 2–3 mos after last therapy dose and may have different color, texture. • Maintain strict oral hygiene. • Avoid crowds, those with infections. • Report fever, sore throat, bruising/bleeding. • Urine may turn pink or red. • Frequent lab testing is a normal part of therapy. • Use contraceptive measures.
idelalisib
eye-del-a-lis-ib
(Zydelig)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Fatal and/or serious hepatotoxicity may occur. Monitor hepatic function prior to and during treatment. Fatal and/or serious and severe diarrhea or colitis may occur. Monitor for GI symptoms. Fatal and serious pneumonitis may occur. Monitor for pulmonary symptoms and bilateral interstitial infiltrates. Interrupt, then reduce or discontinue treatment if hepatotoxicity, severe diarrhea, or pneumonitis occurs. Fatal and serious intestinal perforation may occur. Discontinue if perforation suspected.
Fatal and/or serious hepatotoxicity may occur. Monitor hepatic function prior to and during treatment. Fatal and/or serious and severe diarrhea or colitis may occur. Monitor for GI symptoms. Fatal and serious pneumonitis may occur. Monitor for pulmonary symptoms and bilateral interstitial infiltrates. Interrupt, then reduce or discontinue treatment if hepatotoxicity, severe diarrhea, or pneumonitis occurs. Fatal and serious intestinal perforation may occur. Discontinue if perforation suspected.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Kinase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), in combination with rituximab, in pts for whom rituximab alone would not be considered appropriate therapy due to other co-morbidities. Treatment of relapsed follicular B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (FL) or relapsed small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) in pts who have received at least two prior systemic therapies.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: History of serious allergic reactions to idelalisib (e.g., anaphylaxis, toxic epidermal necrolysis). Cautions: Baseline anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia; GI bleeding, hepatic impairment. Pts with active infection, high tumor burden. Avoid concomitant use of hepatotoxic or promotility medications.
ACTION
Inhibits several cell signaling pathways including B-cell receptor signaling and CXCR4 and CXCR5 signaling, which are involved in trafficking B cells to lymph nodes and bone marrow. Therapeutic Effect: Induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation in cell lines derived from malignant B cells and primary tumor cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following PO administration. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 84%. Peak plasma concentration: 1.5 hrs. Eliminated in feces (78%), urine (14%). Half-life: 8.3 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm; avoid pregnancy. Use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 1 mo after discontinuation. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Must either discontinue drug or discontinue breastfeeding. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: May have increased risk of side effects/adverse reactions.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin) may decrease concentration/effect. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (ketoconazole, ritonavir) may increase concentration/effect. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, bilirubin, GGT; triglycerides. May decrease Hgb, neutrophils, platelets, serum sodium. May increase or decrease lymphocytes, serum glucose.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 100 mg, 150 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Swallow tablets whole.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (in Combination with Rituximab), Follicular B-cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
PO: ADULTS/ELDERLY: 150 mg twice daily. Continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dose Modification
Elevated ALT, AST
3–5 Times Upper Limit of Normal (ULN): Maintain dose. 5–20 Times ULN: Monitor serum ALT, AST wkly. Withhold until ALT, AST less than 1 times ULN, then resume at 100 mg twice daily. Greater Than 20 Times ULN: Permanently discontinue.
Elevated Bilirubin
1.5–3 Times ULN: Monitor serum bilirubin wkly. Maintain dose.
3–10 Times ULN: Monitor serum bilirubin wkly. Withhold until bilirubin less than 1 times ULN, then resume at 100-mg dose.
Greater Than 10 Times ULN: Permanently discontinue.
Diarrhea
Moderate Diarrhea: Maintain dose.
Severe Diarrhea or Hospitalization: Withhold until resolved, then resume at 100-mg dose. Life-Threatening Diarrhea: Permanently discontinue.
Neutropenia
ANC 1,000–1,500 cells/mm3: Maintain dose. ANC 500–1,000 cells/mm3: Monitor ANC wkly and maintain dose. ANC Less Than 500 cells/mm3: Permanently discontinue.
Thrombocytopenia
Platelets 50,000–75,000/mm3: Maintain dose. Platelets 25,000–50,000/mm3: Monitor platelet count wkly and maintain dose. Platelets Less Than 25,000/mm3: Monitor platelet count wkly. Withhold until platelets greater than 25,000 mm3, then resume at 100-mg dose.
Pneumonitis
Any Symptoms: Permanently discontinue.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution. See dose modification.
SIDE EFFECTS
CLL
Frequent (35%–21%): Pyrexia, nausea, diarrhea, chills. Occasional (10%–5%): Headache, vomiting, generalized pain, arthralgia, stomatitis, gastric reflux, nasal congestion.
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Frequent (47%–21%): Diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, cough, pyrexia, abdominal pain, rash. Occasional (17%–10%): Dyspnea, decreased appetite, vomiting, asthenia, night sweats, insomnia, headache, peripheral edema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, leukopenia, lymphopenia are expected responses to therapy, but more severe reactions, including bone marrow failure, febrile neutropenia, may occur. Fatal and/or serious events including hepatotoxicity (14% of pts), severe diarrhea or colitis (14% of pts), hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis), pneumonitis, intestinal perforation were reported. Neutropenia occurred in 31% of pts, which may greatly increase risk of infection. Severe skin reactions including toxic epidermal necrolysis, generalized rash, exfoliative rash were reported. Other infections processes may include bronchitis, Clostridium difficile colitis, pneumonia, sepsis, UTI. Fatal and/or serious intestinal perforation may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain ANC, CBC, BMP, LFT, PT/INR, vital signs, urine pregnancy. Receive full medication history including herbal products. Question possibility of pregnancy, current breastfeeding status, use of contraceptive measures in female pts of reproductive potential. Questions history of hypersensitivity reaction or acute skin reactions to drug class. Perform full dermatologic exam with routine assessment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Diligently monitor blood counts (esp. ANC, CBC, platelet count) frequently. Any interruption of therapy or dosage change may require wkly lab monitoring until symptoms resolve. Obtain C. difficile toxin PCR if severe diarrhea occurs. Screen for acute cutaneous reactions, allergic reactions, other acute infections (sepsis, UTI), hepatic impairment, pulmonary events (dyspnea, pneumonitis, pneumonia), or tumor lysis syndrome (electrolyte imbalance, uric acid nephropathy, acute renal failure). Monitor strict I&Os, hydration status, stool frequency and consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Blood levels will be routinely monitored. Any change in dose or interruption of therapy may require blood draws every week • Avoid pregnancy; do not breastfeed. • Report abdominal pain, amber or bloody urine, bruising, black/tarry stools, persistent diarrhea, yellowing of skin or eyes. • Fever, cough, burning with urination, body aches, chills may indicate acute infection. • Avoid alcohol. • Immediately report difficult breathing, severe coughing, chest tightness. • Therapy may cause severe allergic reactions, intestinal tearing, or skin rashes or severe diarrhea related to an infected colon. • Do not take any over-the-counter medications including herbal products unless approved by your doctor.
ifosfamide

eye-fos-fa-mide
(Ifex)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Hemorrhagic cystitis may occur. Severe myelosuppressant. May cause CNS toxicity, including confusion, coma. Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. May cause severe nephrotoxicity, resulting in renal failure.
Hemorrhagic cystitis may occur. Severe myelosuppressant. May cause CNS toxicity, including confusion, coma. Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. May cause severe nephrotoxicity, resulting in renal failure.
Do not confuse ifosfamide with cyclophosphamide.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Alkylating agent. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of germ cell testicular carcinoma (used in combination with other chemotherapy agents and with concurrent mesna). OFF-LABEL: Small cell lung, non–small-cell lung, ovarian, cervical, bladder cancer; soft tissue sarcomas, Hodgkin’s, non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas; osteosarcoma; head and neck, Ewing’s sarcoma.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ifosfamide. Urinary outflow obstruction. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, compromised bone marrow reserve, active urinary tract infection, preexisting cardiac disease, prior radiation therapy. Avoid use in pts with WBCs less than 2,000/mm3 and platelets less than 50,000/mm3.
ACTION
Inhibits DNA, RNA protein synthesis by cross-linking with DNA, RNA strands, preventing cell growth. Cell cycle–phase nonspecific. Therapeutic Effect: Interferes with DNA, RNA function.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: Negligible. Crosses blood-brain barrier (to a limited extent). Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 11–15 hrs (high dose); 4–7 hrs (low dose).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy, esp. first trimester. May cause fetal harm. Distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Not intended for this pt population. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Bone marrow depressants (e.g., alemtuzumab, methotrexate) may increase myelosuppression. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, bilirubin, creatinine, uric acid, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Ifex): 1 g, 3 g. Injection, Solution: 50 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Hemorrhagic cystitis occurs if mesna is not given concurrently. Mesna should always be given with ifosfamide.
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute vial with Sterile Water for Injection or Bacteriostatic Water for Injection to provide concentration of 50 mg/ml. Shake to dissolve. • Further dilute with 50–1,000 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl to provide concentration of 0.6–20 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over minimum of 30 min. • Give with at least 2,000 ml PO or IV fluid (prevents bladder toxicity). • Give with protectant against hemorrhagic cystitis (i.e., mesna).
Storage • Store vials of powder at room temperature. • Refrigerate vials of solution. • After reconstitution with Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, vials and diluted solutions stable for 24 hrs if refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Cefepime (Maxipime), methotrexate.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Granisetron (Kytril), ondansetron (Zofran).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Dosage individualized based on clinical response, tolerance to adverse effects. When used in combination therapy, consult specific protocols for optimum dosage, sequence of drug administration.
Germ Cell Testicular Carcinoma
IV: ADULTS: 1,200 mg/m2/day for 5 consecutive days. Repeat q3wks or after recovery from hematologic toxicity. Administer with mesna (to prevent bladder toxicity).
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (83%–58%): Alopecia, nausea, vomiting. Occasional (15%–5%): Confusion, drowsiness, hallucinations, infection. Rare (less than 5%): Dizziness, seizures, disorientation, fever, malaise, stomatitis (mucosal irritation, glossitis, gingivitis).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hemorrhagic cystitis with hematuria, dysuria occurs frequently if protective agent (mesna) is not used. Myelosuppression (leukopenia, thrombocytopenia) occurs frequently. Pulmonary toxicity, hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, cardiotoxicity, CNS toxicity (confusion, hallucinations, drowsiness, coma) may require discontinuation of therapy.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain urinalysis before each dose. If hematuria occurs (greater than 10 RBCs per field), therapy should be withheld until resolution occurs. Obtain WBC, platelet count, Hgb before each dose.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor hematologic studies, urinalysis, renal function, LFT. Assess for fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site, symptoms of anemia (excessive fatigue, weakness).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Alopecia is reversible, but new hair growth may have a different color or texture. • Drink plenty of fluids (protects against cystitis). • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance). • Avoid contact with those who have recently received live virus vaccine. • Avoid crowds, those with infections. • Report unusual bleeding/bruising, fever, chills, sore throat, joint pain, sores in mouth or on lips, yellowing skin or eyes.
iloperidone
eye-loe-per-i-doan
(Fanapt)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Elderly pts with dementia-related psychosis are at increased risk for mortality due to cerebrovascular events.
Elderly pts with dementia-related psychosis are at increased risk for mortality due to cerebrovascular events.
Do not confuse iloperidone with amiodarone or dronedarone.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Piperidinyl-benzisoxazole derivative. CLINICAL: Antipsychotic.
USES
Acute treatment of schizophrenia in adults.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to iloperidone. Cautions: Cardiovascular disease (HF, history of MI, ischemia, cardiac conduction abnormalities), cerebrovascular disease (increases risk of CVA in pts with dementia, seizure disorders). Pts at risk for orthostatic hypotension. Pts with bradycardia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia may be at greater risk for torsades de pointes. History of seizures, conditions lowering seizure threshold, high risk of suicide, risk of aspiration pneumonia, congenital QT syndrome, concurrent use of medications that prolong QT interval, decreased GI motility, urinary retention, BPH, xerostomia, visual problems, hepatic impairment, narrow-angle glaucoma, diabetes, elderly.
ACTION
Exact mechanism mediated through combination of dopamine type 2 (D2) and serotonin type 2 (5-HT2) antagonisms. Therapeutic Effect: Diminishes symptoms of schizophrenia and reduces incidence of extrapyramidal side effects.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Steady-state concentration occurs in 3–4 days. Well absorbed from GI tract (unaffected by food). Protein binding: 95%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine, with a lesser amount eliminated in feces. Half-life: 18–33 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is excreted in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: More susceptible to postural hypotension. Increased risk of cerebrovascular events, mortality, including stroke in elderly pts with psychosis.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, CNS depressants (e.g., diphenhydramine, lorazepam, morphine) may increase CNS depression. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, ketoconazole) or strong CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g., fluoxetine, paroxetine) may increase concentration. Medications causing prolongation of QT interval (e.g., amiodarone, dofetilide, sotalol) may increase effects on cardiac conduction, leading to malignant arrhythmias (torsades de pointes). HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum prolactin levels.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 1 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg, 6 mg, 8 mg, 10 mg, 12 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Tablets may be crushed.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Titrate to the proper dose range with dosage adjustments not to exceed 2 mg twice daily q24h.
Schizophrenia
PO: ADULTS: To avoid orthostatic hypotension, begin with 1 mg twice daily, then adjust dosage to 2 mg twice daily, 4 mg twice daily, 6 mg twice daily, 8 mg twice daily, 10 mg twice daily, and 12 mg twice daily on days 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7, respectively, to reach target daily dose of 12–24 mg/day in 2 divided doses. Note: Reduce dose by 50% when receiving strong CYP2D6 or CYP3A4 inhibitors or poor metabolizers of CYP2D6 (see Interactions).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No adjustment. Moderate impairment: Use caution. Severe impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (20%–12%): Dizziness, drowsiness, tachycardia. Occasional (10%–4%): Nausea, dry mouth, nasal congestion, weight increase, diarrhea, fatigue, orthostatic hypotension. Rare (3%–1%): Arthralgia, musculoskeletal stiffness, abdominal discomfort, nasopharyngitis, tremor, hypotension, rash, ejaculatory failure, dyspnea, blurred vision, lethargy.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Extrapyramidal disorders, including tardive dyskinesia (protrusion of tongue, puffing of cheeks, chewing/puckering of the mouth), occur in 4% of pts. Upper respiratory infection occurs in 3% of pts. QT interval prolongation may produce torsades de pointes, a form of ventricular tachycardia. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (e.g., hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, irregular pulse or B/P) has been noted.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess pt’s behavior, appearance, emotional status, response to environment, speech pattern, thought content. EKG should be obtained to assess for QT prolongation before instituting medication.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for orthostatic hypotension; assist with ambulation. Monitor for fine tongue movement (may be first sign of tardive dyskinesia, possibly irreversible). Monitor serum potassium, magnesium in pts at risk for electrolyte disturbances. Assess for therapeutic response (greater interest in surroundings, improved self-care, increased ability to concentrate, relaxed facial expression).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Be alert to symptoms of orthostatic hypotension; slowly go from lying to standing. • Report if feeling faint, experience heart palpitations or if fever or muscle rigidity occurs. • Report extrapyramidal symptoms (e.g., involuntary muscle movements, tics) immediately.
imatinib


im-at-in-ib
(Gleevec)
Do not confuse imatinib with dasatininb, erlotinib, lapatinib, nilotinib, sorafenib, or sunitinib.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Newly diagnosed chronic-phase Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) in children and adults. Pts in blast crisis, accelerated phase, or chronic phase Ph+ CML who have already failed interferon therapy. Adults with relapsed or refractory Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Treatment in children with Ph+ ALL. Adults with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disease (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene rearrangements. Adults with aggressive systemic mastocytosis (ASM) without mutation of the D816V c-Kit or unknown mutation status of the c-Kit. Adults with hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL) with positive, negative, or unknown FIP1L1-PDGFR fusion kinase. Adults with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) that is unresectable, recurrent, and/or metastatic. Pts with malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) that are unresectable and/or metastatic. Prevention of cancer recurrence in pts following surgical removal of GIST. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of desmoid tumors (soft tissue sarcoma). Post–stem cell transplant (allogenic), follow-up treatment in recurrent CML. Treatment of advanced or metastatic melanoma.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to imatinib. Cautions: Hepatic/renal impairment, thyroidectomy pts, hypothyroidism, gastric surgery pts. Pts in whom fluid accumulation is poorly tolerated (e.g., HF, hypertension, pulmonary disease).
ACTION
Inhibits Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase, an enzyme created by Philadelphia chromosome abnormality found in pts with chronic myeloid leukemia. Therapeutic Effect: Suppresses tumor growth during the three stages of CML: blast crisis, accelerated phase, chronic phase. Induces apoptosis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 95%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated in feces (68%), urine (13%). Half-life: 18 hrs; metabolite, 40 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Increased frequency of fluid retention.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease concentration. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, erythromycin, ketoconazole) may increase concentration. Bone marrow depressants (e.g., alemtuzumab, methotrexate) may increase myelosuppression. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. May reduce effect of warfarin. HERBAL: St. John’s wort decreases concentration. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase concentration. LAB VALUES: May increase serum bilirubin, ALT, AST, creatinine. May decrease platelet count, RBC, WBC count; serum potassium, albumin, calcium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 100 mg, 400 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with a meal and large glass of water. • Tablets may be dispersed in water or apple juice (stir until dissolved; give immediately). Do not crush or chew tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Ph+ Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) (Chronic Phase)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg once daily; may increase to 600 mg/day. CHILDREN: 340 mg/m2/day. Maximum: 600 mg.
Ph+ CML (Accelerated Phase)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 600 mg once daily. May increase to 800 mg/day in 2 divided doses (400 mg twice daily). CHILDREN: 340 mg/m2/day. Maximum: 600 mg.
Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 600 mg once daily.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) (Following Complete Resection)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400–600 mg/day.
GIST (Unresectable)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400–800 mg/day.
Aggressive Systemic Mastocytosis (ASM) with Eosinophilia
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 100 mg/day. May increase up to 400 mg/day.
ASM without Mutation of the D816V C-Kit or Unknown Mutation Status of C-Kit
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg once daily.
Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans (DFSP)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg twice daily.
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES)/Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia (CEL)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg once daily.
HES/CEL with Positive or Unknown FIP1L1-PDGFR Fusion Kinase
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 100 mg/day. May increase up to 400 mg/day.
Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Disease (MDS/MPD)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg once daily.
Usual Dosage for Children (2 Yrs and Older)
Ph+ CML (Chronic Phase, Recurrent or Resistant): 340 mg/m2/day. Maximum: 600 mg/day.
Ph+ CML (Chronic Phase, Newly Diagnosed, Ph+ ALL): 340 mg/m2/day. Maximum: 600 mg/day.
Dosage with Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Increase dose by 50% with careful monitoring.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Maximum Dose |
| 40–59 ml/min | 600 mg |
| 20–39 ml/min | 400 mg |
| Less than 20 ml/min | 100 mg |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No adjustment. Severe impairment: Reduce dosage by 25%.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (68%–24%): Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, headache, fluid retention, rash, musculoskeletal pain, muscle cramps, arthralgia. Occasional (23%–10%): Abdominal pain, cough, myalgia, fatigue, fever, anorexia, dyspepsia, constipation, night sweats, pruritus, dizziness, blurred vision, somnolence. Rare (less than 10%): Nasopharyngitis, petechiae, asthenia, epistaxis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Severe fluid retention (pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, pulmonary edema, ascites), hepatotoxicity occur rarely. Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia are expected responses to the therapy. Respiratory toxicity is manifested as dyspnea, pneumonia. Heart damage (left ventricular dysfunction, HF) may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, serum chemistries, renal function test. Monitor LFT before beginning treatment, monthly thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess periorbital area, lower extremities for early evidence of fluid retention. Monitor for unexpected, rapid weight gain. Offer antiemetics to control nausea, vomiting. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor CBC wkly for first mo, biweekly for second mo, periodically thereafter for evidence of neutropenia, thrombocytopenia; assess hepatic function tests for hepatotoxicity. Monitor renal function, serum electrolytes. Duration of neutropenia or thrombocytopenia ranges from 2–4 wks.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid crowds, those with known infection. • Avoid contact with anyone who recently received live virus vaccine; do not receive vaccinations. • Take with food and a full glass of water. • Avoid grapefruit products. • Report chest pain, swelling of extremities, weight gain greater than 5 lb, easy bruising/bleeding. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established.
imipenem/cilastatin
im-i-pen-em/sye-la-stat-in
(Primaxin)
Do not confuse imipenem with doripenem, ertapenem, or meropenem, or Primaxin with Premarin or Primacor.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Fixed-combination carbapenem. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of susceptible infections due to gram-negative (ESBL Escherichia coli and Klebsiella, Enterobacter spp. PsAs), gram-positive (MSSA, Streptococcus spp.), anaerobic organisms including respiratory tract, skin/skin structure, gynecologic, bone, joint, intra-abdominal, complicated or uncomplicated UTIs; endocarditis (caused by S. aureus); polymicrobic infections; septicemia; serious nosocomial infections. OFF-LABEL: Hepatic abscess, neutropenic fever, melioidosis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to imipenem/cilastatin. Cautions: CNS disorders (e.g., brain lesions and history of seizures), sensitivity to beta-lactams (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins), renal impairment, elderly.
ACTION
Imipenem: Penetrates bacterial cell membrane, inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Cilastatin: Competitively inhibits the enzyme dehydropeptidase, preventing renal metabolism of imipenem. Therapeutic Effect: Produces bacterial cell death.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed after IM administration. Protein binding: Imipenem: 20%; Cilastatin: 40%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in kidneys. Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 1 hr (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in cord blood, amniotic fluid, breast milk. Children: No precautions noted. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease concentration of valproic acid. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, BUN, bilirubin, creatinine, LDH, ALT, AST. May decrease Hgb, Hct.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Primaxin): 250 mg, 500 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Dilute each 250- or 500-mg vial with 100–250 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl. Final concentration not to exceed 5 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • Give by intermittent IV infusion (piggyback). • Do not give IV push. • Infuse over 20–30 min (doses greater than 500 mg over 40–60 min). • Observe pt during initial 30 min of first-time infusion for possible hypersensitivity reaction.
Storage • Solution appears colorless to yellow; discard if solution turns brown. • IV infusion (piggyback) is stable for 4 hrs at room temperature, 24 hrs if refrigerated. • Discard if precipitate forms.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Allopurinol (Aloprim), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), fluconazole (Diflucan).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Diltiazem (Cardizem), insulin, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage Ranges
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, WEIGHING 70 KG OR MORE: 250 mg q6h up to 1,000 mg q6h. 60–69 KG: 250 mg q8h up to 1 g q8h. 50–59 KG: 125 mg q6h up to 750 mg q8h. 40–49 KG: 125 mg q6h up to 500 mg q6h. 30–39 KG: 125 mg q8h up to 500 mg q8h. CHILDREN OLDER THAN 3 MOS–12 YRS: 15–25 mg/kg q6h. Maximum: 4 g/day. CHILDREN 1–3 MOS: 25 mg/kg q6h. CHILDREN 1–4 WKS: 20–25 mg/kg q8h. CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 1 WK: 20–25 mg/kg q12h.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage and frequency are modified based on creatinine clearance and severity of infection. (See table.)
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Consider reducing dose frequency.
| Creatinine Clearance (ml/min) | 70 kg or greater | 60–69 kg | 50–59 kg | 40–49 kg | 30–39 kg |
| 41–70 | 250 mg q8h–750 mg q8h | 125 mg q6h–750 mg q8h | 125 mg q6h–500 mg q6h | 125 mg q6h–500 mg q8h | 125 mg q8h–250 mg q6h |
| 21–40 | 250 mg q12h–500 mg q6h | 250 mg q12h–500 mg q8h | 125 mg q8h–500 mg q8h | 125 mg q12h–250 mg q6h | 125 mg q12h–250 mg q8h |
| 6–20 | 250 mg q12h–500 mg q12h | 125 mg q12h–500 mg q12h | 125 mg q12h–500 mg q12h | 125 mg q12h–250 mg q12h | 125 mg q12h–250 mg q12h |
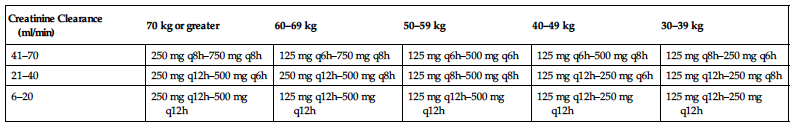
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (3%): Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. Rare (1%): Rash.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Antibiotic-associated colitis, other superinfections (abdominal cramps, severe watery diarrhea, fever) may result from altered bacterial balance in GI tract. Anaphylactic reactions have been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of allergies, particularly to beta-lactams, penicillins, cephalosporins. Inquire about history of seizures.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor renal, hepatic, hematologic function tests. Evaluate for phlebitis (heat, pain, red streaking over vein), pain at IV injection site. Assess for GI discomfort, nausea, vomiting. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess skin for rash. Be alert to tremors, possible seizures.
imipramine
i-mip-ra-meen
Novo-Pramine
![]() , Tofranil, Tofranil-PM)
, Tofranil, Tofranil-PM)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Do not confuse imipramine with amitriptyline, desipramine, or Norpramin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Tricyclic antidepressant. CLINICAL: Antidepressant, antineuritic, antipanic, antineuralgic, antinarcoleptic adjunct, anticataplectic, antibulimic.
USES
Treatment of depression. Treatment of nocturnal enuresis in children older than 6 yrs. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), neurogenic pain, panic disorder.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to imipramine. Acute recovery period after MI, use within 14 days of MAOIs; initiation of imipramine in pts with concurrent use with linezolid or IV methylene blue. Cautions: Prostatic hypertrophy; history of urinary retention, history of bowel obstruction; glaucoma, diabetes mellitus, history of seizures, hyperthyroidism; cardiac, hepatic, renal disease; increased intraocular pressure, pts with high risk for suicide. Decreased GI motility, paralytic ileus, visual problems, respiratory disease, elderly.
ACTION
Blocks reuptake of neurotransmitters (norepinephrine, serotonin) at presynaptic membranes, increasing concentration at postsynaptic receptor sites. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves depression, controls nocturnal enuresis.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g., diphenhydramine, lorazepam, morphine) may increase hypotensive effects, CNS, respiratory depression. Cimetidine, fluoxetine may increase concentration, risk of toxicity. Phenytoin, barbiturates may decrease concentration. HERBAL: Kava kava, SAMe, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase risk of serotonin syndrome, CNS depression. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase concentration/toxicity. LAB VALUES: May alter serum glucose, EKG readings. Therapeutic serum level: 225–300 ng/ml; toxic serum level: greater than 500 ng/ml.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules (Tofranil-PM): 75 mg, 100 mg, 125 mg, 150 mg. Tablets (Tofranil): 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with food, milk if GI distress occurs.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Depression
PO: ADULTS: (Outpatient): Initially, 75 mg/day. May gradually increase to 150 mg/day as single dose at bedtime or in divided doses. Maintenance: 50–150 mg/day. Maximum: 200 mg/day. (Inpatient): Initially, 100–150 mg/day. May increase to 200 mg/day. May further increase to 250–300 mg/day after 2 wks. May give as single dose at bedtime or in divided doses. Maximum: 300 mg/day. Initially, 75–100 mg/day in 3–4 divided doses. May gradually increase to maximum of 200 mg/day (outpatient) or 300 mg/day (inpatient). ELDERLY, ADOLESCENTS: Initially, 25–50 mg/day at bedtime. May increase by 10–25 mg every 3–7 days. Maximum: 100 mg/day. CHILDREN: 1.5 mg/kg/day. May increase by 1 mg/kg every 3–4 days. Maximum: 5 mg/kg/day in 1–4 divided doses.
Enuresis
PO: CHILDREN, 6 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 25 mg 1 hr before bedtime. May increase by 25 mg if inadequate response seen after 1 wk. Maximum: 2.5 mg/kg/day or 50 mg at bedtime for ages 6–12 yrs; 75 mg at bedtime for ages over 12 yrs.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Drowsiness, fatigue, dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, delayed micturition, orthostatic hypotension, diaphoresis, impaired concentration, increased appetite, urinary retention, photosensitivity. Occasional: GI disturbances (nausea, metallic taste). Rare: Paradoxical reactions (agitation, restlessness, nightmares, insomnia), extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) (particularly fine hand tremor).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may produce seizures, cardiovascular effects (severe orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, tachycardia, palpitations, arrhythmias). May result in altered temperature regulation (hyperpyrexia, hypothermia). Abrupt withdrawal from prolonged therapy may produce headache, malaise, nausea, vomiting, vivid dreams.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess appearance, behavior, speech pattern, level of interest, mood. Obtain renal function, LFT.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Supervise suicidal-risk pt closely during early therapy (as depression lessens, energy level improves, increasing suicide potential). Monitor appearance, behavior, speech pattern, level of interest, mood. For pts on long-term therapy, hepatic/renal function tests, blood counts should be performed periodically. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor B/P, pulse for hypotension, arrhythmias. Assess for urinary retention by bladder palpation. Therapeutic serum level: 225–300 ng/ml; toxic serum level: greater than 500 ng/ml.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report worsening depression, thoughts of suicide, agitation, irritability. • Slowly go from lying to standing to avoid hypotensive effect. • Tolerance to postural hypotension, sedative, anticholinergic effects usually develops during early therapy. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Therapeutic effect may be noted within 2–5 days, maximum effect within 2–3 wks. • Sugarless gum, sips of water may relieve dry mouth. • Do not abruptly discontinue medication. • Limit caffeine; avoid alcohol.
immune globulin IV (IGIV)
im-mune glob-u-lin
(Bivigam, Carimune NF, Flebogamma DIF, Gammagard Liquid, Gammagard S/D, Gammaplex, Gamunex-C, Hizentra, Octagam 5%, Privigen)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Acute renal impairment characterized by increased serum creatinine, oliguria, acute renal failure, osmotic nephrosis, particularly pts with any degree of renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, volume depletion, sepsis, and those older than age 65 yrs. Thrombosis may occur.
Acute renal impairment characterized by increased serum creatinine, oliguria, acute renal failure, osmotic nephrosis, particularly pts with any degree of renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, volume depletion, sepsis, and those older than age 65 yrs. Thrombosis may occur.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Immune globulin, blood product. CLINICAL: Immunizing agent.
USES
Treatment of pts with primary humoral immunodeficiency syndromes, acute/chronic immune idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), prevention of coronary artery aneurysms associated with Kawasaki disease, prevention of recurrent bacterial infections in pts with hypogammaglobulinemia associated with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathies. Provide passive immunity in pts with hepatitis A, measles, rubella, varicella. OFF-LABEL: Guillain-Barré syndrome; myasthenia gravis; prevention of acute infections in immunosuppressed pts; prevention, treatment of infection in high-risk, preterm, low birth-weight neonates; treatment of multiple sclerosis, HIV-associated thrombocytopenia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to immune globulin. Selective IgA deficiency, hyperprolinemia (Hizentra, Privigen), severe thrombocytopenia, coagulation disorders where IM injections contraindicated. Cautions: Cardiovascular disease, history of thrombosis, renal impairment.
ACTION
Replacement therapy for primary/secondary immunodeficiencies and lgG antibodies against bacteria, viral antigens; interferes with receptors on cells of reticuloendothelial system for autoimmune cytopenias/idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP); increases antibody titer and antigen-antibody reaction potential. Therapeutic Effect: Provides passive immunity replacement for immunodeficiencies, increases antibody titer.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Evenly distributed between intravascular and extravascular space. Half-life: 21–23 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Live virus vaccines may increase vaccine side effects, potentiate virus replication, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Carimune NF): 3 g, 6 g, 12 g. (Gammagard S/D): 5 g, 10 g. Injection, Solution (Bivigam 10%, Flebogamma DIF 5%, 10%, Gammagard Liquid 10%, Gammaplex 5%, Gamunex-C 10%, Octagam 5%, Privigen 10%).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
◀ ALERT ▶ Monitor vital signs, B/P diligently during and immediately after IV administration (precipitous fall in B/P may indicate anaphylactic reaction). Stop infusion immediately. Epinephrine should be readily available.
Reconstitution • Reconstitute only with diluent provided by manufacturer. • Discard partially used or turbid preparations.
Rate of Administration • Give by infusion only. • After reconstitution, administer via separate tubing. • Rate of infusion varies with product used.
Storage • Refer to individual IV preparations for storage requirements, stability after reconstitution.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Primary Immunodeficiency Syndrome
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: (Privigen): 200–800 mg/kg q3–4wks.(Carimune NF): 400–800 mg/kg q3–4 wks.(Flebogamma DIF, Gammagard, Gamunex-C, Octagam): 300–600 mg/kg/q3–4wks. (Bivigam, Gammaplex):300–800 mg/kg q3–4wks.
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: (Carimune NF): 400 mg/kg/day for 2–5 days. Maintenance: 400–1,000 mg/kg/dose to maintain platelet count or control bleeding. (Gammagard):1,000 MG/KG: up to 3 additional doses may be given on alternate days.
Kawasaki Disease
Note: Must be used with aspirin.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: (Gammagard): 1,000 mg/kg as single dose or 400 mg/kg/day for 4 consecutive days. Begin within 7 days of onset of fever. American Heart Association Guidelines: 2,000 mg/kg as a single dose given over 10–12 hrs within 10 days of disease onset.
Chronic Leukocytic Leukemia (CLL)
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: (Gammagard): 400 mg/kg/dose q3–4wks.
Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: (Gamunex-C): 2,000 mg/kg divided over 2–4 days (consecutive). Maintenance: 1,000 mg/kg/day q3wks or 500 mg/kg for 2 consecutive days q3wks.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Caution when giving IV.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Tachycardia, backache, headache, arthralgia, myalgia. Occasional: Fatigue, wheezing, injection site rash/pain, leg cramps, urticaria, bluish color of lips/nailbeds, light-headedness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Anaphylactic reactions occur rarely but incidence increases with repeated injections. Epinephrine should be readily available. Overdose may produce chest tightness, chills, diaphoresis, dizziness, facial flushing, nausea, vomiting, fever, hypotension. Hypersensitivity reaction (anxiety, arthralgia, dizziness, flushing, myalgia, palpitations, pruritus) occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Inquire about exposure history to disease for pt/family as appropriate. Have epinephrine readily available. Pt should be well hydrated prior to administration.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Control rate of IV infusion carefully; too-rapid infusion increases risk of precipitous fall in B/P, signs of anaphylaxis (facial flushing, chest tightness, chills, fever, nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis). Assess pt closely during infusion, esp. first hr; monitor vital signs continuously. Stop infusion if aforementioned signs noted. For treatment of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), monitor platelet count.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Explain rationale for therapy. • Report sudden weight gain, fluid retention, edema, decreased urine output, shortness of breath.
indacaterol
in-da-ka-ter-ol
(Arcapta Neohaler, Onbrez Breezhaler
![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonists (LABAs) have an increased risk of asthma-related deaths. Not indicated for treatment of asthma.
Long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonists (LABAs) have an increased risk of asthma-related deaths. Not indicated for treatment of asthma.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist. CLINICAL: Bronchodilator.
USES
Long-term maintenance treatment of airflow obstruction in pts with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
PRECAUTIONS
◀ ALERT ▶ Not indicated for the treatment of asthma, acute exacerbations of COPD.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to indacaterol. Monotherapy in treatment of asthma. Cautions: Cardiovascular disease (coronary insufficiency, arrhythmias, hypertension, history of hypersensitivity to sympathomimetics), seizure disorders, hyperthyroidism, hypokalemia, diabetes mellitus. May cause paradoxical bronchospasm, severe asthma.
ACTION
Stimulates beta2-adrenergic receptors in lungs, resulting in relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves bronchospasm, reduces airway resistance, improves bronchodilation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Extensive activation of systemic beta-adrenergic receptors; acts primarily in lungs. Protein binding: 94%–95%. Metabolized in liver. Steady-state level: 12–15 days. Primarily excreted in feces. Half-life: 45–126 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May be more sensitive to tremor, tachycardia due to age-related increased sympathetic sensitivity.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effectiveness of beta blockers (e.g., carvedilol, metoprolol). Diuretics (e.g, furosemide, HCTZ), corticosteroids (e.g., dexamethasone, prednisone), xanthine derivatives may increase risk of hypokalemia. Drugs that can prolong QT interval (e.g., erythromycin, quinidine, thioridazine), antiarrhythmics (e.g., amiodarone), MAOIs, tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, doxepin) may potentiate cardiovascular effects (increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias). Erythromycin, ketoconazole, ritonavir, verapamil may increase serum concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum potassium. May increase serum glucose.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Powder for Inhalation: 75 mcg (in blister packs).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Inhalation
• Open cap of Neohaler by pulling upward, then open mouthpiece. • Remove capsule from blister package and place in center of chamber. Firmly close until click is heard. • Hold inhaler upright and pierce capsule by pressing side buttons once only. • Instruct pt to exhale completely. Place mouthpiece into mouth, close lips, and inhale quickly and deeply through mouth (this causes capsule to spin, dispensing the drug). A slight whirring noise should occur. If not, this may indicate capsule is stuck. Gently tap inhaler to loosen and reattempt. • Pt should hold breath as long as possible before exhaling. • Check capsule to ensure all the powder is gone. Instruct pt to reinhale if powder remains.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Maintain capsules within individual blister pack until time of use. • Do not store capsules in Neohaler device.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Maintenance Therapy and Prevention of COPD
Inhalation: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 75 mcg (1 capsule) once daily via Neohaler inhalation device.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (7%–5%): Cough, nasopharyngitis, headache. Rare (2%): Oropharyngeal pain, nausea.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Peripheral edema, diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, sinusitis, URI reported in greater than 2% of pts. Excessive sympathomimetic stimulation, hypokalemia may produce palpitations, arrhythmias, angina pectoris, tachycardia, muscle cramps, weakness. Hyperglycemia symptoms present with increased thirst, polyuria, dry mouth, drowsiness/confusion, blurred vision. Severe shortness of breath may indicate paradoxical bronchospasm, deteriorating COPD. Serious asthma-related events including death reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess rate, depth, rhythm, type of respirations. Monitor EKG, serum potassium, ABG determinations, O2 saturation, pulmonary function test. Assess lung sounds for wheezing (bronchoconstriction), rales. Obtain baseline electrolytes, blood glucose. Receive full medication history and screen for possible drug interactions. Question for history of asthma, angina pectoris, diabetes mellitus, peripheral edema.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Routinely monitor serum electrolytes, blood glucose, O2 saturation. Recommend discontinuation of short-acting beta2-agonists (use only for symptomatic relief of acute respiratory symptoms). Monitor for palpitations, tachycardia, serum hypokalemia. Inspect oropharyngeal cavity for irritation.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper use of inhaler. • Increase fluid intake (decreases lung secretion viscosity). • Rinse mouth with water after inhalation to decrease mouth/throat irritation. • Avoid excessive use of caffeine derivatives (chocolate, coffee, tea, cola). • An immediate cough lasting 15 sec may occur after inhaler use. • Report any fever, productive cough, body aches, difficulty breathing.
indapamide
in-dap-a-mide
(Apo-Indapamide
![]() , Lozide
, Lozide
![]() , Novo-Indapamide
, Novo-Indapamide
![]() )
)
Do not confuse indapamide with lopidine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Thiazide. CLINICAL: Diuretic, antihypertensive.
USES
Management of mild to moderate hypertension. Treatment of edema associated with HF. OFF-LABEL: Calcium nephrolithiasis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to indapamide. Anuria, sulfonamide-derived drugs. Cautions: History of hypersensitivity to sulfonamides or thiazide diuretics. Severe renal disease, hepatic impairment, prediabetes, diabetes mellitus, elderly, severe hyponatremia, elevated serum cholesterol.
ACTION
Diuretic: Blocks reabsorption of water, sodium, potassium at cortical diluting segment of distal renal tubule. Antihypertensive: Reduces plasma, extracellular fluid volume, and peripheral vascular resistance by direct effect on blood vessels. Therapeutic Effect: Promotes diuresis, reduces B/P.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Almost completely absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 71%–79%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated in urine. Half-life: 14–18 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May be more sensitive to hypotensive, electrolyte effects.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase risk of lithium toxicity. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginseng, licorice, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Black cohosh may increase antihypertensive effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase plasma renin activity. May decrease protein-bound iodine; serum calcium, potassium, sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 1.25 mg, 2.5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with food, milk if GI upset occurs, preferably with breakfast (may prevent nocturia).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Edema
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 2.5 mg/day, may increase to 5 mg/day after 1 wk.
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 1.25 mg. May increase to 2.5 mg/day after 4 wks or 5 mg/day after additional 4 wks. Usual dose: 1.25–2.5 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (5% and greater): Fatigue, paresthesia of extremities, tension, irritability, agitation, headache, dizziness, light-headedness, insomnia, muscle cramps. Occasional (less than 5%): Urinary frequency, urticaria, rhinorrhea, flushing, weight loss, orthostatic hypotension, depression, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, dry mouth, impotence, rash, pruritus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Vigorous diuresis may lead to profound water and electrolyte depletion, resulting in hypokalemia, hyponatremia, dehydration. Acute hypotensive episodes may occur. Hyperglycemia may be noted during prolonged therapy. Pancreatitis, blood dyscrasias, pulmonary edema, allergic pneumonitis, dermatologic reactions occur rarely. Overdose can lead to lethargy, coma without changes in electrolytes or hydration.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Check vital signs, esp. B/P for hypotension, before administration. Assess baseline electrolytes, particularly hypokalemia. Observe for edema; assess skin turgor, mucous membranes for hydration status. Assess muscle strength, mental status. Note skin temperature, moisture. Obtain baseline weight. Initiate I&O.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Continue to monitor B/P, vital signs, electrolytes, I&O, weight. Note extent of diuresis. Watch for electrolyte disturbances (hypokalemia may result in weakness, tremor, muscle cramps, nausea, vomiting, altered mental status, tachycardia; hyponatremia may result in confusion, thirst, cold/clammy skin).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Expect increased frequency, volume of urination. • To reduce hypotensive effect, go from lying to standing slowly. • Eat foods high in potassium such as whole grains (cereals), legumes, meat, bananas, apricots, orange juice, potatoes (white, sweet), raisins. • Take early in the day to avoid nocturia.
indomethacin
in-doe-meth-a-sin
(Indocin, Novo-Methacin
![]() , Tivorbex)
, Tivorbex)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction, CVA. Increased risk of severe GI reactions, including ulceration, bleeding, perforation.
Increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction, CVA. Increased risk of severe GI reactions, including ulceration, bleeding, perforation.
Do not confuse Indocin with Imodium, Minocin, or Vicodin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: NSAID. CLINICAL: Anti-inflammatory, analgesic.
USES
Treatment of active stages of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, acute gouty arthritis. Relieves acute bursitis, tendonitis. (Tivorbex): Treatment of mild to moderate acute pain in adults. (IV Form): For closure of hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus of premature infants. OFF-LABEL: Management of preterm labor.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to aspirin, indomethacin, other NSAIDs. Perioperative pain in setting of CABG surgery. History of asthma, urticaria, allergic reactions after taking aspirin, other NSAIDs. Suppositories: History of proctitis, recent rectal bleeding. Injection: In preterm infants with untreated/systemic infection or congenital heart disease where patency of PDA necessary for pulmonary or systemic blood flow; bleeding, thrombocytopenia, coagulation defects, necrotizing enterocolitis, significant renal dysfunction. Cautions: Cardiac dysfunction, fluid retention, HF, hypertension, renal/hepatic impairment, epilepsy; concurrent aspirin, steroids, anticoagulant therapy. Treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in children. History of GI disease (bleeding or ulcers), elderly, debilitated, asthma, depression, Parkinson’s disease.
ACTION
Produces antipyretic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces inflammatory response, fever, intensity of pain. Closure of patent ductus arteriosus.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 30 min | — | 4–6 hrs |
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 4.5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in those younger than 14 yrs. Elderly: GI bleeding, ulceration increase risk of serious adverse effects.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of antihypertensives (e.g., amlodipine, lisinopril, valsartan), diuretics (e.g., furosemide). Aspirin, other salicylates may increase risk of GI side effects, bleeding. Bone marrow depressants (e.g., alemtuzumab, methotrexate) may increase risk of hematologic reactions. May increase risk of bleeding with heparin, anticoagulants, thrombolytics. May increase concentration, risk of toxicity of lithium. May increase risk of cyclosporine, methotrexate toxicity. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginkgo, ginseng, horse chestnut, red clover may increase antiplatelet activity. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May prolong bleeding time. May alter serum glucose. May increase serum BUN, creatinine, potassium, ALT, AST. May decrease serum sodium, platelet count, leukocytes.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 25 mg, 50 mg. (Tivorbex): 20 mg, 40 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Indocin IV): 1 mg. Oral Suspension (Indocin): 25 mg/5 ml. Suppository: 50 mg.
![]() Capsules, Extended-Release: 75 mg.
Capsules, Extended-Release: 75 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • To 1-mg vial, add 1–2 ml preservative-free Sterile Water for Injection or 0.9% NaCl to provide concentration of 1 mg/ml or 0.5 mg/ml, respectively. • Do not further dilute.
Rate of Administration • Administer over 20–30 min.
Storage • Use IV solution immediately following reconstitution. • IV solution appears clear; discard if cloudy or precipitate forms. • Discard unused portion.
PO
• Give after meals or with food, antacids. • Do not break, crush, or open extended-release capsule. Swallow whole.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amino acid injection, calcium gluconate, dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), gentamicin (Garamycin), tobramycin (Nebcin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Insulin, potassium.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Osteoarthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis
PO: RECTAL: ADULTS, ELDERLY (Immediate-Release): Initially, 25–50 mg 2–3 times/day; increased by 25–50 mg/wk up to 200 mg/day.(Extended-Release):Initially, 75 mg once daily. May increase to 75 mg twice daily. Maximum: 150 mg/day. CHILDREN 2 YRS AND OLDER (Immediate-Release): 1–2 mg/kg/day in 2–4 divided doses. Maximum: 4 mg/kg/day not to exceed 150–200 mg/day.
Acute Gouty Arthritis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY (Immediate-Release): 50 mg 3 times/day for 3–5 days.
Acute Bursitis, Tendonitis
PO: RECTAL: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate-Release): 75–150 mg/day in 3–4 divided doses for 7–14 days. (Extended-Release):75–150 mg/day in 1–2 doses/day.
Acute Pain
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY:(Tivorbex):20 mg 3 times/day or 40 mg 2–3 times/day.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
IV: NEONATES: Initially, 0.2 mg/kg. Subsequent doses are based on age, as follows: NEONATES OLDER THAN 7 DAYS: 0.25 mg/kg for 2nd and 3rd doses. NEONATES 2–7 DAYS: 0.2 mg/kg for 2nd and 3rd doses. NEONATES LESS THAN 48 HRS: 0.1 mg/kg for 2nd and 3rd doses. In general, dosing interval is 12 hrs if urine output is greater than 1 ml/kg/hr after prior dose, 24 hrs if urine output is less than 1 ml/kg/hr but greater than 0.6 ml/kg/hr. Dose is held if urine output is less than 0.6. ml/kg/hr or if neonate is anuric.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment:Not recommended.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (11%–3%): Headache, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, dizziness. Occasional (less than 3%): Depression, tinnitus, diaphoresis, drowsiness, constipation, diarrhea. Patent ductus arteriosus: Bleeding abnormalities. Rare: Hypertension, confusion, urticaria, pruritus, rash, blurred vision.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Paralytic ileus, ulceration of esophagus, stomach, duodenum, small intestine may occur. Pts with renal impairment may develop hyperkalemia with worsening of renal impairment. May aggravate depression or other psychiatric disturbances, epilepsy, parkinsonism. Nephrotoxicity (dysuria, hematuria, proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome) occurs rarely. Metabolic acidosis/alkalosis, bradycardia occur rarely in neonates with patent ductus arteriosus.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess onset, type, location, duration of pain, fever, inflammation. Inspect appearance of affected joints for immobility, deformities, skin condition.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum BUN, creatinine, potassium, LFT. Monitor for evidence of nausea, dyspepsia. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Evaluate for therapeutic response: relief of pain, stiffness, swelling; increased joint mobility; reduced joint tenderness; improved grip strength. Observe for weight gain, edema, bleeding, bruising. In neonates, also monitor heart rate, heart sounds for murmur, B/P, urine output, EKG, serum sodium, glucose, platelets.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid aspirin, alcohol during therapy (increases risk of GI bleeding). • If GI upset occurs, take with food, milk. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Report ringing in ears, persistent stomach pain, unusual bruising/bleeding.
*inFLIXimab

in-flix-i-mab
(Remicade)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Risk of severe/fatal opportunistic infections (tuberculosis, sepsis, fungal), reactivation of latent infections. Rare cases of very aggressive, usually fatal hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma reported in adolescents, young adults with Crohn’s disease.
Risk of severe/fatal opportunistic infections (tuberculosis, sepsis, fungal), reactivation of latent infections. Rare cases of very aggressive, usually fatal hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma reported in adolescents, young adults with Crohn’s disease.
Do not confuse infliximab with rituximab, or Remicade with Reminyl.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Monoclonal antibody. CLINICAL: GI anti-inflammatory.
USES
In combination with methotrexate, reduces signs/symptoms, inhibits progression of structural damage, improves physical function in moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis. Reduces signs/symptoms, induces and maintains remission in moderate to severe active Crohn’s disease. Reduces number of draining enterocutaneous/rectovaginal fistulas, maintains fistula closure in fistulizing Crohn’s disease. Reduces sign/symptoms of active ankylosing spondylitis. Treatment of chronic severe plaque psoriasis in pts who are candidates for systemic therapy. Reduces sign/symptoms, induces and maintains clinical remission and mucosal healing, eliminates corticosteroid use in moderate to severe active ulcerative colitis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to infliximab. Moderate to severe HF (doses greater than 5 mg/kg should be avoided). Sensitivity to murine proteins, sepsis, serious active infection. Cautions: Hematologic abnormalities, history of COPD, preexisting or recent onset CNS demyelinating disorders, seizures, mild HF, history of recurrent infections, conditions predisposing pt to infections (e.g., diabetes), pts exposed to tuberculosis, elderly, chronic hepatitis B virus infection.
ACTION
Binds to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), inhibiting functional activity of TNF (induction of proinflammatory cytokines, enhanced leukocytic migration, activation of neutrophils/eosinophils). Therapeutic Effect: Prevents disease and allows diseased joints to heal.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Absorbed into GI tissue; primarily distributed in vascular compartment. Half-life: 8–9.5 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Use cautiously due to higher rate of infection.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anakinra, abatacept may increase risk of infection. Immunosuppressants may reduce frequency of infusion reactions, antibodies to infliximab. Live virus vaccines may decrease immune response (do not give concurrently). HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, bilirubin.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute each vial with 10 ml Sterile Water for Injection, using 21-gauge or smaller needle. Direct stream of Sterile Water for Injection to glass wall of vial. • Swirl vial gently to dissolve contents (do not shake). • Allow solution to stand for 5 min and inject into 250-ml bag 0.9% NaCl; gently mix. Concentration should range between 0.4 and 4 mg/ml. • Begin infusion within 3 hrs after reconstitution.
Rate of Administration • Administer IV infusion over at least 2 hrs using a low protein-binding filter.
Storage • Refrigerate vials. • Solution should appear colorless to light yellow and opalescent; do not use if discolored or particulate forms.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not infuse in same IV line with other agents.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Premedicate with antihistamines, acetaminophen, steroids to prevent/manage infusion reactions.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (in combination with methotrexate): 3 mg/kg followed by additional doses at 2 and 6 wks after first infusion, then q8wks thereafter. Range: 3–10 mg/kg at 4- to 8-wk intervals.
Crohn’s Disease
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER: 5 mg/kg followed by additional doses at 2 and 6 wks after first infusion, then q8wks thereafter. For adults who respond then lose response, consideration may be given to treatment with 10 mg/kg.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5 mg/kg followed by additional doses at 2 and 6 wks after first infusion, then q6wks thereafter.
Psoriatric Arthritis
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5 mg/kg followed by additional doses at 2 and 6 wks after first infusion, then q8wks thereafter. May be used with or without methotrexate.
Plaque Psoriasis
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5 mg/kg followed by additional doses at 2 and 6 wks after first infusion, then q8wks thereafter.
Ulcerative Colitis
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER: 5 mg/kg followed by additional doses at 2 and 6 wks after first infusion, then q8wks thereafter.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (22%–10%): Headache, nausea, fatigue, fever. Occasional (9%–5%): Fever/chills during infusion, pharyngitis, vomiting, pain, dizziness, bronchitis, rash, rhinitis, cough, pruritus, sinusitis, myalgia, back pain. Rare (4%–1%): Hypotension or hypertension, paresthesia, anxiety, depression, insomnia, diarrhea, UTI.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Serious infections, including sepsis, occur rarely. Potential for hypersensitivity reaction, lupus-like syndrome, severe hepatic reaction, HF.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Evaluate baseline hydration status (skin turgor urinary status).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor urinalysis, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), B/P. Monitor for signs of infection. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Crohn’s disease: Monitor C-reactive protein, frequency of stools. Assess for abdominal pain. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): Monitor C-reactive protein. Assess for decreased pain, swollen joints, stiffness.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report persistent fever, cough, abdominal pain, swelling of ankles/feet.
insulin


in-su-lin
Rapid-acting: (Afrezza): INHALATION POWDER, INSULIN ASPART: (Novolog), INSULIN GLULISINE: (Apidra), INSULIN LISPRO: (Humalog)
Short-acting: REGULAR INSULIN: (Humulin R, Novolin R)
Intermediate-acting: NPH: (Humulin N, Novolin N)
Long-acting: INSULIN DEGLUDEC: (Tresiba), INSULIN DETEMIR: (Levemir), INSULIN GLARGINE: (Basaglar, Lantus, Toujeo)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() (Afrezza): Acute bronchospasms reported in pts with asthma and COPD.
(Afrezza): Acute bronchospasms reported in pts with asthma and COPD.
Do not confuse Novolog with Humalog or Novolin.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Humalog Mix 75/25: lispro suspension 75% and lispro solution 25%. Humulin Mix 50/50: NPH 50% and regular 50%. Humulin 70/30, Novolin 70/30: NPH 70% and rapid-acting regular 30%. Novolog Mix 70/30: aspart suspension 70% and aspart solution 30%. Ryzodeg 70/30: degludec suspension 70% and aspart solution 30%. Soliqua 100/33: glargine 100 units/ml and lixisenatide (a GLP-1 receptor agonist) 33 mcg/ml. Xultophy 100/3.6: degludec 100 units/ml and liraglutide (a GLP-1 receptor agonist) 3.6 mg/ml.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Exogenous insulin. CLINICAL: Antidiabetic.
USES
Treatment of insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes mellitus; non–insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) to improve glycemic control. OFF-LABEL: Insulin aspart, insulin lispro, insulin regular: Gestational diabetes, mild to moderate diabetic ketoacidosis, mild to moderate hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. Insulin NPH: Gestational diabetes.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to insulin, use during episodes of hypoglycemia. Afrezza: Chronic lung disease. Cautions: Pts at risk for hypokalemia; renal/hepatic impairment, elderly. Afrezza: Must be used with a long-acting insulin in type 1 diabetes. Not recommended for use in diabetic ketoacidosis or in smokers. Afrezza: Pts with active lung cancer, history of lung cancer or at risk for lung cancer.
ACTION
Acts via specific receptor to regulate metabolism of carbohydrates, protein, and fats. Acts on liver, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue. Liver: Stimulates hepatic glycogen synthesis, synthesis of fatty acids. Muscle: Increases protein, glycogen synthesis. Adipose tissue: Stimulates lipoproteins to provide free fatty acids, triglyceride synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Controls serum glucose levels.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapid-Acting
| Onset (min) | Peak (hrs) | Duration (hrs) | |
| Aspart (Novolog) | 10–20 | 1–3 | 3–5 |
| Glulisine (Apidra) | 5–15 | 0.75–1.25 | 2–4 |
| Insulin Human (Afrezza) | 15–30 | 1 | 2 |
| Lispro (Humalog) | 15–30 | 0.5–2.5 | 3–6.5 |
Short-Acting
| Onset (min) | Peak (hrs) | Duration (hrs) | |
| Regular (Humulin R) | 30–60 | 1–5 | 6–10 |
| Regular (Novolin R) | 30–60 | 1–5 | 6–10 |
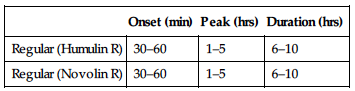
Intermediate-Acting
| Onset (hrs) | Peak (hrs) | Duration (hrs) | |
| NPH (Humulin N) | 1–2 | 6–14 | 16–24+ |
| NPH (Novolin N) | 1–2 | 6–14 | 16–24+ |
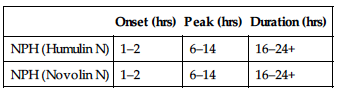
Long-Acting
| Onset (hrs) | Peak (hrs) | Duration (hrs) | |
| Degludec (Tresiba) | 0.5–1.5 | 12 | 42 |
| Detemir (Levemir) | 3–4 | 3–9 | 6–23 |
| Glargine (Lantus) | 3–4 | No peak | 24 |
| Glargine (Toujeo) | Over 6 | No peak | Over 24 |
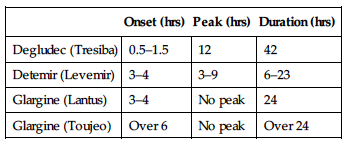
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Insulin is drug of choice for diabetes in pregnancy; close medical supervision is needed. Following delivery, insulin needs may drop for 24–72 hrs, then rise to pre-pregnancy levels. Not distributed in breast milk; lactation may decrease insulin requirements. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Decreased vision, fine motor tremors may lead to inaccurate self-dosing.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol may increase risk of hypoglycemia. Beta blockers (e.g., carvedilol, metoprolol) may alter effects; may mask signs, prolong periods of hypoglycemia. Glucocorticoids, thiazide diuretics may increase serum glucose. HERBAL: Garlic, ginger, ginseng may increase risk of hypoglycemia. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum magnesium, phosphate, potassium.
Availability
Rapid-Acting
(Afrezza) Inhalation Powder: 4 units, 8 units, 12 units as single-use inhalation cartridges. Aspart (Novolog): 100 units/ml vial, 3 ml cartridge, 3 ml Flex-Pen. Glulisine (Apidra): 100 units/ml vial, 3 ml cartridge. Lispro (Humalog): 100 units/ml vial, 3 ml cartridge, 3 ml pen.
Short-Acting
Regular (Humulin R): 100 units/ml vial, U-500 Kwik Pen. Regular (Novolin R): 100 units/ml vial, 3 ml cartridge, 3 ml Innolet prefilled syringe.
Intermediate-Acting
NPH (Humulin N): 100 units/ml vial, 3 ml pen. NPH (Novolin N): 100 units/ml vial, 3 ml cartridge, 3 ml Innolet prefilled syringe.
Long-Acting
Detemir (Levemir): 100 units/ml vial, 3 ml Flex-Pen. Glargine (Lantus): 100 units/ml vial, 3 ml cartridge.
Intermediate- and Short-Acting Mixtures
Humulin 50/50, Humulin 70/30, Humalog Mix 75/25, Humalog Mix 50/50, Novolin 70/30, Novolog Mix 70/30.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV (Regular and Insulin Glulisine [Apidra])
IV (Regular and Insulin Glulisine [Apidra])
• Use only if solution is clear. • May give undiluted.
Rapid-Acting
Afrezza • Administer using a single inhalation/cartridge. Give at beginning of a meal. Aspart (Novolog) • May give subcutaneous, IV infusion. • Can mix with NPH (draw aspart into syringe first; inject immediately after mixing). • After first use, stable at room temperature for 28 days. • Administer 5–10 min before meals.
Glulisine (Apidra) • May mix with NPH (draw glulisine into syringe first; inject immediately after mixing). • After first use, stable at room temperature for 28 days. • Administer 15 min before or within 20 min after starting a meal.
Lispro (Humalog) • For subcutaneous use only. • May mix with NPH. Stable for 28 days at room temperature; syringe is stable for 14 days if refrigerated. • After first use, stable at room temperature for 28 days. • Administer 15 min before or immediately after meals.
Short-Acting
Regular (Humulin R, Novolin R) • May give subcutaneous, IM, IV. • May mix with NPH for immediate use or for storage for future use. Stable for 1 mo at room temperature, 3 mos if refrigerated. • Can mix with Sterile Water for Injection or 0.9% NaCl. • After first use, stable at room temperature for 28 days. • Administer 30 min before meals.
Intermediate-Acting
NPH (Humulin N, Novolin N) • For subcutaneous use only. • May mix with aspart (Novolog) or lispro (Humalog). Draw aspart or lispro first and use immediately. • May mix with regular (Humulin R, Novolin R) insulin. Draw regular insulin first, use immediately or may store for future use (up to 28 days). • After first use, stable at room temperature for 28 days. • Administer 15 min before meals when mixed with aspart or lispro; 30 min before meals when mixed with regular insulin.
Long-Acting
Degludec (Tresiba) • For subcutaneous use only. • Do not mix with other insulins. • After first use, stable at room temperature for 56 days. • May take once daily any time of day.
Detemir (Levemir) • For subcutaneous use only. • Do not mix with other insulins. • After first use, stable at room temperature for 42 days. • Evening dose given at dinner or at bedtime. Twice-daily regimens can be given 12 hrs after morning dose.
Glargine (Lantus, Toujeo) • For subcutaneous use only. • Do not mix with other insulins. • After first use, stable at room temperature for 28 days. • Administer once daily at same time. Meal timing is not applicable.
Subcutaneous
• Check serum glucose concentration before administration; dosage highly individualized. • Subcutaneous injections may be given in thigh, abdomen, upper arm, buttocks, upper back if there is adequate adipose tissue. • Rotation of injection sites is essential; maintain careful record. • Prefilled syringes should be stored in vertical or oblique position to avoid plugging; plunger should be pulled back slightly and syringe rocked to remix solution before injection.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Diltiazem (Cardizem), dopamine (Intropin), nafcillin (Nafcil).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), ampicillin/sulbactam (Unasyn), cefazolin (Ancef), digoxin (Lanoxin), dobutamine (Dobutrex), famotidine (Pepcid), gentamicin, heparin, magnesium sulfate, metoclopramide (Reglan), midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, nitroglycerin, potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan), vancomycin (Vancocin).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Insulin requirments vary dramatically between pts requiring dosage adjustment.
Type 1 Diabetes: Multiple daily injections, guided by glucose monitoring or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusions, is standard of care.
Initial dose: 0.5–1 unit/kg/day in divided doses. Maintenance: 0.5–1.2 units/kg/day in divided doses.
Type 2 Diabetes: General goal is to achieve HbA1c less than 7% using safe medication titration.
Afrezza: Dosage based on metabolic needs, blood glucose results, glycemic goal control.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Dose |
| 10–50 ml/min | 75% normal dose |
| Less than 10 ml/min | 25–50% normal dose |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Insulin requirement may be reduced.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Localized redness, swelling, itching (due to improper insulin injection technique), allergy to insulin cleansing solution. Infrequent: Somogyi effect (rebound hyperglycemia) with chronically excessive insulin dosages. Systemic allergic reaction (rash, angioedema, anaphylaxis), lipodystrophy (depression at injection site due to breakdown of adipose tissue), lipohypertrophy (accumulation of subcutaneous tissue at injection site due to inadequate site rotation). Rare: Insulin resistance.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Severe hypoglycemia (due to hyperinsulinism) may occur with insulin overdose, decrease/delay of food intake, excessive exercise, pts with brittle diabetes. Diabetic ketoacidosis may result from stress, illness, omission of insulin dose, long-term poor insulin control.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Check blood glucose level. Discuss lifestyle to determine extent of learning, emotional needs. If given IV, obtain serum chemistries (esp. serum potassium).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for hypoglycemia (refer to pharmacokinetics table for peak times and duration): cool, wet skin, tremors, dizziness, headache, anxiety, tachycardia, numbness in mouth, hunger, diplopia. Assess sleeping pt for restlessness, diaphoresis. Check for hyperglycemia: polyuria (excessive urine output), polyphagia (excessive food intake), polydipsia (excessive thirst), nausea/vomiting, dim vision, fatigue, deep and rapid breathing (Kussmaul respirations). Be alert to conditions altering glucose requirements: fever, trauma, increased activity/stress, surgical procedure.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Instruct on proper technique for drug administration, testing of glucose, signs/symptoms of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. • Prescribed diet is an essential part of treatment; do not skip/delay meals. • Carry candy, sugar packets, other sugar supplements for immediate response to hypoglycemia. • Wear or carry medical alert identification. • Check with physician when insulin demands are altered (e.g., fever, infection, trauma, stress, heavy physical activity). • Do not take other medication without consulting physician. • Weight control, exercise, hygiene (including foot care), not smoking are integral parts of therapy. • Protect skin, limit sun exposure. • Inform dentist, physician, surgeon of medication before any treatment is given.
interferon alfa-2b

in-ter-feer-on
(Intron-A)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause or aggravate fatal or life-threatening autoimmune disorders, ischemia, neuropsychiatric symptoms (profound depression, suicidal thoughts/behaviors), infectious disorders.
May cause or aggravate fatal or life-threatening autoimmune disorders, ischemia, neuropsychiatric symptoms (profound depression, suicidal thoughts/behaviors), infectious disorders.
Do not confuse interferon alfa-2b with interferon alfa-2a, interferon alfa-n3, or peginterferon alfa-2b, or Intron with Peg-Intron.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Rebetron: interferon alfa-2b/ribavirin (an antiviral): 3 million units/200 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Biologic response modifier. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of hairy cell leukemia, condylomata acuminata (genital, venereal warts), malignant melanoma, AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma, chronic hepatitis C virus infection (including children 3 yrs of age and older), chronic hepatitis B (including children 1 yr and older), follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of bladder, cervical, renal carcinoma; chronic myelocytic leukemia; laryngeal papillomatosis; multiple myeloma; cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; mycosis fungoides; West Nile virus.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to interferon alfa-2b. Decompensated hepatic disease, autoimmune hepatitis. In combination with ribavirin: Women who are pregnant, males with pregnant partners, pts with hemoglobinemias (e.g., sickle cell anemia, CrCl less than 50 ml/min). Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, seizure disorder, compromised CNS function, cardiac diseases, myelosuppression, concurrent use of medications causing myelosuppression, pulmonary impairment, multiple sclerosis, diabetes, thyroid disease, coagulopathy, hypertension, preexisting eye disorders, history of psychiatric disorders. History of autoimmune disorders, MI, arrhythmias, cardiac abnormalities.
ACTION
Inhibits viral replication in virus-infected cells, suppresses cell proliferation, augments specific cytotoxicity of lymphocytes. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents rapid growth of malignant cells; inhibits hepatitis virus.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after IM, subcutaneous administration. Undergoes proteolytic degradation during reabsorption in kidneys. Half-life: 2–3 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Neurotoxicity, cardiotoxicity may occur more frequently. Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Bone marrow depressants (e.g., alemtuzumab, methotrexate) may increase myelosuppression. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase PT, aPTT, LDH, serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST. May decrease Hgb, Hct, leukocyte, platelet counts.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 10 million units, 18 million units, 50 million units.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Prepare immediately before use. • Reconstitute with diluent provided by manufacturer. • Withdraw desired dose and further dilute with 100 ml 0.9% NaCl to provide final concentration of at least 10 million international units/100 ml.
Rate of Administration • Administer over 20 min.
Storage • Refrigerate unopened vials. • Following reconstitution, stable for 24 hrs if refrigerated.
IM, Subcutaneous
IM • Administer in evening (if possible). SQ • Reconstitute with recommended amount of Sterile Water for Injection. Agitate gently; do not shake.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
D5W. Do not mix with other medications via Y-site administration.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
0.9% NaCl, lactated Ringer’s.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hairy Cell Leukemia
IM, SQ: ADULTS: 2 million units/m2 3 times/wk for 2–6 mos. If severe adverse reactions occur, modify dose or temporarily discontinue drug.
Condylomata Acuminata
Intralesional: ADULTS: 1 million units/lesion 3 times/wk for 3 wks. May administer a second course at 12–16 wks. Use only 10-million-unit vial, and reconstitute with no more than 1 ml diluent. Maximum: 5 lesions per treatment.
Aids-Related Kaposi’s Sarcoma
IM, SQ: ADULTS: 30 million units/m2 3 times/wk. Use only 50-million-unit vials. Continue until disease progression or maximal response achieved after 16 wks. If severe adverse reactions occur, modify dose or temporarily discontinue drug.
Chronic Hepatitis C
IM, SQ: ADULTS: 3 million units 3 times/wk for up to 6 mos. For pts who tolerate therapy and whose ALT level normalizes within 16 wks, therapy may be extended for up to 18–24 mos. May be used in combination with ribavirin. CHILDREN, 3–17 YRS (WITH HIV CO-INFECTION): 3–5 million units/m2 3 times/wk with ribavirin for 48 wks.
Chronic Hepatitis B
IM, SQ: ADULTS: 30–35 million units wkly, either as 5 million units/day or 10 million units 3 times/wk for 16 wks.
SQ: CHILDREN 1–17 YRS: 3 million units/m2 3 times/wk for 1 wk, then 6 million units/m2 3 times/wk for 16–24 wks. Maximum: 10 million units 3 times/wk.
Malignant Melanoma
IV: ADULTS: Initially, 20 million units/m2 5 times/wk for 4 wks. Maintenance: 10 million units subcutaneously 3 times/wk for 48 wks.
Follicular Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
SQ: ADULTS: 5 million units 3 times/wk for up to 18 mos.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Do not use when combined with ribavirin.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment (see Contraindications).
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Flu-like symptoms (fever, fatigue, headache, myalgia, anorexia, chills), rash (hairy cell leukemia, Kaposi’s sarcoma only). Pts with Kaposi’s sarcoma: All previously mentioned side effects plus depression, dyspepsia, dry mouth or thirst, alopecia, rigors. Occasional: Dizziness, pruritus, dry skin, dermatitis, altered taste. Rare: Confusion, leg cramps, back pain, gingivitis, flushing, tremor, anxiety, eye pain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hypersensitivity reactions occur rarely. Severe flu-like symptoms appear dose-related.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
CBC, blood chemistries, urinalysis, renal function, LFT should be performed before initial therapy and routinely thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Offer emotional support. Monitor all levels of clinical function (numerous side effects). Encourage PO intake, particularly during early therapy. Monitor for worsening depression, suicidal ideation, associated behaviors.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Clinical response occurs in 1–3 mos. • Flu-like symptoms tend to diminish with continued therapy. • Some symptoms may be alleviated or minimized by bedtime doses. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance). • Avoid contact with those who have recently received live virus vaccine. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Sips of tepid water may relieve dry mouth. • Report depression, thoughts of suicide, unusual behavior.
interferon beta-1a

in-ter-feer-on
(Avonex, Rebif)
Do not confuse Avonex with Avelox, or interferon beta-1a with interferon beta-1b.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Biologic response modifier. CLINICAL: Multiple sclerosis agent.
USES
Treatment of relapsing multiple sclerosis to slow progression of physical disability, decrease frequency of clinical exacerbations.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to natural or recombinant interferon, human albumin (only for albumin-containing products). Cautions: Depression, severe psychiatric disorders, hepatic impairment, increased serum ALT at baseline, alcohol abuse, cardiovascular disease, seizure disorders, myelosuppression.
ACTION
Alters expression and response to surface antigens and may enhance immune cell activity. Therapeutic Effect: Slows progression of multiple sclerosis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Peak serum levels attained 3–15 hrs after IM administration. Biologic markers increase within 12 hrs and remain elevated for 4 days. Half-life: 10 hrs (Avonex); 69 hrs (Rebif).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Has abortifacient potential. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No information available.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, hepatotoxic drugs (e.g., acetaminophen, simvastatin) may increase risk of hepatic injury. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, BUN, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, calcium, ALT, AST. May decrease Hgb, neutrophil, platelet, WBC counts.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Avonex): 30 mcg. Injection Solution (Prefilled Syringe): 22 mcg/0.5 ml (Rebif), 30 mcg/0.5 ml (Avonex Prefilled Syringe), 44 mcg/0.5 ml (Rebif). Titration Pack (Prefilled Syringe [Rebif]): 8.8 mcg/0.2 ml, 22 mcg/0.5 ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
IM (Avonex) Syringe
• Refrigerate syringe. • Allow to warm to room temperature before use. • May store up to 7 days at room temperature.
IM (Avonex) Vial
• Refrigerate vials (may store at room temperature up to 30 days). • Following reconstitution, may refrigerate again but use within 6 hrs if refrigerated. • Reconstitute 30-mcg MicroPin (6.6 million international units) vial with 1.1 ml diluent (supplied by manufacturer). • Gently swirl to dissolve medication; do not shake. • Discard if discolored or particulate forms. • Discard unused portion (contains no preservative).
Subcutaneous (Rebif)
• Refrigerate. May store at room temperature up to 30 days. Avoid heat, light. • Administer at same time of day 3 days each wk. Separate doses by at least 48 hrs.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis
IM (Avonex): ADULTS: 30 mcg once wkly.
SQ (Rebif): ADULTS: (Target dose 44 mcg 3 times/wk): Initially, 8.8 mcg 3 times/wk for 2 wks, then 22 mcg 3 times/wk for 2 wks, then 44 mcg 3 times/wk thereafter. (Target dose 22 mcg 3 times/wk): Initially, 4.4 mcg 3 times/wk for 2 wks, then 11 mcg 3 times/wk for 2 wks, then 22 mcg 3 times/wk thereafter.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment (Rebif)
Use with caution in pts with history of active hepatic disease or ALT more than 2.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN).
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (67%–11%): Headache, flu-like symptoms, myalgia, upper respiratory tract infection, depression with suicidal ideation, generalized pain, asthenia, chills, sinusitis, infection. Occasional (9%–4%): Abdominal pain, arthralgia, chest pain, dyspnea, malaise, syncope. Rare (3%): Injection site reaction, hypersensitivity reaction.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Anemia occurs in 8% of pts. Hepatic failure has been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC, BMP, LFT. Assess home situation for support of therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for headache, flu-like symptoms, myalgia. Periodically monitor lab results, re-evaluate injection technique. Assess for depression, suicidal ideation.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not change schedule, dosage without consulting physician. • Follow guidelines for reconstitution of product and administration, including aseptic technique. • Use puncture-resistant container for used needles, syringes; dispose of used needles, syringes properly. • Injection site reactions may occur. These do not require discontinuation of therapy, but type and extent should be carefully noted. Report flu-like symptoms (fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches).
interferon beta-1b

in-ter-feer-on
(Betaseron, Extavia)
Do not confuse interferon beta-1b with interferon beta-1a.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Biologic response modifier. CLINICAL: Multiple sclerosis agent.
USES
Reduces frequency of clinical exacerbations in pts with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (recurrent attacks of neurologic dysfunction). Treatment of early stages of multiple sclerosis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to albumin, interferon. Cautions: Depression, severe psychiatric disorders, hepatic/renal impairment, alcohol abuse, cardiovascular disease, seizure disorders, myelosuppression, pulmonary disease.
ACTION
Exact mechanism unknown. Participates in immunoregulation by enhancing oxidative metabolism of macrophages, antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity and activating natural killer cells. Therapeutic Effect: Improves MRI lesions, decreases relapse rate and disease severity in multiple sclerosis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Slowly absorbed following subcutaneous administration. Half-life: 8 min–4.3 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No information available.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase bilirubin, ALT, AST. May decrease neutrophil, lymphocyte, WBC counts.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 0.3 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Subcutaneous
• Store vials at room temperature. • After reconstitution, stable for 3 hrs if refrigerated. • Use within 3 hrs of reconstitution. • Discard if discolored or precipitate forms. • Reconstitute 0.3-mg (9.6 million international units) vial with 1.2 ml diluent (supplied by manufacturer) to provide concentration of 0.25 mg/ml (8 million units/ml). • Gently swirl to dissolve medication; do not shake. • Withdraw 1 ml solution and inject subcutaneous into arms, abdomen, hips, thighs using 27-gauge needle. • Discard unused portion (contains no preservative).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis
SQ: ADULTS: Initially, 0.0625 mg every other day; gradually increase by 0.0625 mg every 2 wks. Target dose: 0.25 mg every other day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (85%–21%): Injection site reaction, headache, flu-like symptoms, fever, asthenia, myalgia, sinusitis, diarrhea, dizziness, altered mental status, constipation, diaphoresis, vomiting. Occasional (15%–4%): Malaise, drowsiness, alopecia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Seizures occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC, BMP, LFT. Assess home situation for support of therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Periodically monitor lab results, re-evaluate injection technique. Assess for nausea (high incidence). Monitor sleep pattern. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Monitor food intake.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report flu-like symptoms (fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches); occur commonly but decrease over time. • Wear sunscreen, protective clothing if exposed to sunlight, ultraviolet light until tolerance known.
interferon gamma-1b
in-ter-feer-on
(Actimmune)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Biologic response modifier. CLINICAL: Immunologic agent.
USES
Reduces frequency, severity of serious infections due to chronic granulomatous disease. Delays time to disease progression in pts with severe, malignant osteopetrosis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to interferon gamma-1b, Escherichia coli–derived products. Cautions: Seizure disorders, compromised CNS function, preexisting cardiac disease (e.g., ischemia, HF, arrhythmias), hepatic disease, myelosuppression.
ACTION
Exact mechanism unknown. Enhances oxidative metabolism of macrophages, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; activates natural killer cells. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases signs/symptoms of serious infections in chronic granulomatous disease.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Slowly absorbed after subcutaneous administration. Half-life: 3–6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 1 yr. Flu-like symptoms may occur more frequently. Elderly: No information available.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Bone marrow depressants (e.g., alemtuzumab, methotrexate) may increase myelosuppression. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, LDH, triglycerides, cortisol concentrations. May decrease leukocytes, neutrophils, platelets.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 100 mcg/0.5 ml (2 million units).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Avoid excessive agitation of vial; do not shake.
Subcutaneous
• Refrigerate vials. Do not freeze. • Do not keep at room temperature for more than 12 hrs; discard after 12 hrs. • Vials are single dose; discard unused portion. • Solution is clear, colorless. Do not use if discolored or precipitate forms. • When given 3 times/wk, rotate injection sites.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Chronic Granulomatous Disease; Severe, Malignant Osteopetrosis
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 1 YR: 50 mcg/m2 (1 million units/m2) 3 times/wk in pts with body surface area (BSA) greater than 0.5 m2; 1.5 mcg/kg/dose 3 times/wk in pts with BSA 0.5 m2 or less.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (52%–14%): Fever, headache, rash, chills, fatigue, diarrhea. Occasional (13%–10%): Vomiting, nausea. Rare (6%–3%): Weight loss, myalgia, anorexia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
May exacerbate preexisting CNS dysfunction (manifested as decreased mental status, gait disturbance, dizziness), cardiac abnormalities.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
CBC, serum electrolytes, urinalysis, renal function, LFT should be performed before initial therapy and at 3-mo intervals during course of treatment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for flu-like symptoms. Assess skin for evidence of rash.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Flu-like symptoms (fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches) are generally mild and tend to disappear as treatment continues. Symptoms may be minimized with bedtime administration. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • If home use prescribed, follow guidelines for proper technique of administration; care in proper disposal of needles, syringes. • Vials should remain refrigerated.
interleukin-2 (aldesleukin)

in-ter-loo-kin
(Proleukin)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() High-dose therapy is associated with capillary leak syndrome resulting in significant hypotension and reduced organ perfusion. Use restricted to pts with normal cardiac/pulmonary function. Increased risk of disseminated infection (sepsis, bacterial endocarditis). Withhold treatment for pts developing moderate-to-severe lethargy or drowsiness (continued treatment may result in coma). Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents.
High-dose therapy is associated with capillary leak syndrome resulting in significant hypotension and reduced organ perfusion. Use restricted to pts with normal cardiac/pulmonary function. Increased risk of disseminated infection (sepsis, bacterial endocarditis). Withhold treatment for pts developing moderate-to-severe lethargy or drowsiness (continued treatment may result in coma). Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents.
Do not confuse aldesleukin with oprelvekin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Biologic response modifier. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma, metastatic melanoma. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to aldesleukin. Abnormal pulmonary function or thallium stress test results, bowel ischemia or perforation, coma or toxic psychosis lasting longer than 48 hrs, GI bleeding requiring surgery, intubation lasting more than 72 hrs, organ allografts, pericardial tamponade, renal dysfunction requiring dialysis for longer than 72 hrs, repetitive or difficult-to-control seizures; retreatment in pts who experience any of the following toxicities: angina, MI, recurrent chest pain with EKG changes, sustained ventricular tachycardia, uncontrolled or unresponsive cardiac rhythm disturbances. Extreme Caution: Pts with normal thallium stress tests and pulmonary function tests who have history of cardiac or pulmonary disease. Cautions: Pts with fixed requirements for large volumes of fluid (e.g., those with hypercalcemia), history of seizures, renal/hepatic impairment, autoimmune disease, inflammatory disorders.
ACTION
Promotes proliferation, differentiation, recruitment of T and B cells, lymphokine-activated and natural killer cells, thymocytes. Therapeutic Effect: Enhances cytolytic activity in lymphocytes.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Primarily distributed into plasma, lymphocytes, lungs, liver, kidney, spleen. Metabolized to amino acids in cells lining the kidneys. Half-life: 80–120 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Avoid use in those of either sex not practicing effective contraception. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment; will not tolerate toxicity.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antihypertensives may increase hypotensive effect. Cardiotoxic, hepatotoxic, myelotoxic, nephrotoxic medications may increase risk of toxicity. Glucocorticoids may decrease effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, creatinine, ALT, AST. May decrease serum calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Proleukin): 22 million units (1.3 mg) (18 million units/ml = 1.1 mg/ml when reconstituted).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Hold administration in pts who develop moderate to severe lethargy or drowsiness (continued administration may result in coma).
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute 22 million units vial with 1.2 ml Sterile Water for Injection to provide concentration of 18 million units/ml (1.1 mg/ml). • Bacteriostatic Water for Injection or NaCl should not be used to reconstitute because of increased aggregation. • During reconstitution, direct Sterile Water for Injection at the side of vial. Swirl contents gently to avoid foaming. Do not shake.
Rate of Administration • Further dilute dose in 50 ml D5W to a final concentration between 0.49 and 1.1 million international units/ml (30–70 mcg/ml) and infuse over 15 min. Do not use an in-line filter. • Solution should be warmed to room temperature before infusion. • Monitor diligently for drop in mean arterial B/P (sign of capillary leak syndrome [CLS]). Continued treatment may result in significant hypotension (less than 90 mm Hg or a 20 mm Hg drop from baseline systolic pressure), edema, pleural effusion, altered mental status.
Storage • Refrigerate vials; do not freeze. • Reconstituted solution is stable for 48 hrs refrigerated or at room temperature (refrigeration preferred).
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Ganciclovir (Cytovene), pentamidine (Pentam), prochlorperazine (Compazine), promethazine (Phenergan).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Calcium gluconate, dopamine (Intropin), heparin, lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium, potassium.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Metastatic Melanoma, Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
IV: ADULTS 18 YRS AND OLDER: 600,000 units/kg q8h for 14 doses; followed by 9 days of rest, then another 14 doses for a total of 28 doses per course. Course may be repeated if tumor shrinkage observed after rest period of at least 7 wks from date of hospital discharge.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Do not initiate if serum creatinine greater than 1.5 mg/dl.
Dosage Modification for Toxicity
Withhold or interrupt therapy; do not reduce dose. Retreatment contraindicated with the following toxicities: Sustained ventricular tachycardia, uncontrolled arrhythmias; chest pain/EKG changes consistent with angina or MI; cardiac tamponade, repetitive/refractory seizures; GI bleeding; bowel ischemia/perforation; renal failure requiring dialysis; coma lasting more than 48 hrs.
SIDE EFFECTS
Side effects are generally self-limited and resolve within 2–3 days after discontinuing therapy. Frequent (89%–48%): Fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, hypotension, diarrhea, oliguria/anuria, altered mental status, irritability, confusion, depression, sinus tachycardia, pain (abdominal, chest, back), fatigue, dyspnea, pruritus. Occasional (47%–17%): Edema, erythema, rash, stomatitis, anorexia, weight gain, infection (UTI, injection site, catheter tip), dizziness. Rare (15%–4%): Dry skin, sensory disorders (vision, speech, taste), dermatitis, headache, arthralgia, myalgia, weight loss, hematuria, conjunctivitis, proteinuria.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia occur commonly. GI bleeding, pulmonary edema occur occasionally. Capillary leak syndrome (CLS) results in hypotension (systolic pressure less than 90 mm Hg or a 20 mm Hg drop from baseline systolic pressure), extravasation of plasma proteins and fluid into extravascular space, loss of vascular tone. May result in cardiac arrhythmias, angina, MI, respiratory insufficiency. Fatal malignant hyperthermia, cardiac arrest, CVA, pulmonary emboli, bowel perforation/gangrene, severe depression leading to suicide occur in less than 1% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Pts with bacterial infection and with indwelling central lines should be treated with antibiotic therapy before treatment begins. All pts should be neurologically stable with a negative CT scan before treatment begins. CBC, BMP, LFT, chest X-ray should be performed before therapy begins and daily thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC with differential, amylase, electrolytes, renal function, LFT, weight, pulse oximetry. Discontinue medication at first sign of hypotension and hold for moderate to severe lethargy (physician must decide whether therapy should continue). Assess for altered mental status (irritability, confusion, depression), weight gain/loss. Maintain strict I&O. Assess for extravascular fluid accumulation (rales in lungs, edema in dependent areas).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Nausea may decrease during therapy. • At home, increase fluid intake (protects against renal impairment). • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance). • Avoid exposure to persons with infection. • Report fever, chills, lower back pain, difficulty with urination, unusual bleeding/bruising, black tarry stools, blood in urine, petechial rash (pinpoint red spots on skin). • Report symptoms of depression or suicidal ideation immediately.
ipilimumab
ip-i-lim-ue-mab
(Yervoy)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions due to T-cell activation and proliferation are capable of involving any organ system. Specific reactions include enterocolitis, hepatitis, dermatitis, neuropathy, endocrinopathy. Majority of immune-mediated reactions may initially manifest during treatment or weeks to months after treatment. Permanently discontinue treatment and initiate high-dose corticosteroid therapy for severe immune-mediated adverse reactions. Assess all pts for signs/symptoms of enterocolitis, hepatitis, dermatitis (including toxic epidermal necrolysis), neuropathy, endocrinopathy and evaluate clinical chemistries including hepatic function tests and thyroid tests at baseline and before each treatment.
Severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions due to T-cell activation and proliferation are capable of involving any organ system. Specific reactions include enterocolitis, hepatitis, dermatitis, neuropathy, endocrinopathy. Majority of immune-mediated reactions may initially manifest during treatment or weeks to months after treatment. Permanently discontinue treatment and initiate high-dose corticosteroid therapy for severe immune-mediated adverse reactions. Assess all pts for signs/symptoms of enterocolitis, hepatitis, dermatitis (including toxic epidermal necrolysis), neuropathy, endocrinopathy and evaluate clinical chemistries including hepatic function tests and thyroid tests at baseline and before each treatment.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4)-blocking antibody. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Adjuvant treatment of pts with cutaneous melanoma with pathologic involvement of regional lymph nodes and have undergone complete resection, including total lymphadenectomy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ipilimumab. Cautions: Hepatic impairment, chronic peripheral neuropathy, thyroid/adrenal/pituitary dysfunction, autoimmune disorders (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, lupus, sarcoidosis).
ACTION
Augments T-cell activation and proliferation. Binds to cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and blocks interaction of CTLA-4 with its ligands. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor cell growth.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Metabolized in liver. Steady state reached by third dose. Half-life: 14.7 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Discontinue drug or discontinue breastfeeding. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, bilirubin; eosinophils.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution: 5 mg/ml (10 ml, 40 ml vials).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
◀ ALERT ▶ Use sterile, nonpyrogenic, low protein-binding in-line filter. Use dedicated line only.
Reconstitution • Calculate number of vials needed for injection. • Inspect for particulate matter or discoloration. • Allow vials to stand at room temperature for approximately 5 min. • Withdraw proper volume and transfer to infusion bag. Dilute in NaCl or D5W with final concentration ranging from 1–2 mg/ml. • Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake or agitate.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 90 min. Flush with 0.9% NaCl or D5W at end of infusion.
Storage • Solution should be translucent to white or pale yellow with amorphous particles. • Discard vial if cloudy or discolored. • Refrigerate vials until time of use. • May store diluted solution either under refrigeration or at room temperature for no more than 24 hrs.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Metastatic Melanoma
IV: ADULTS: 3 mg/kg q3wks for 4 doses. Doses may be delayed due to toxicity, but all doses must be given within 16 wks of initial dose.
◀ ALERT ▶ Pts who are presenting with severe immune-mediated adverse reactions must immediately discontinue drug therapy and start prednisone 1 mg/kg/day.
Cutaneous Melanoma
IV: ADULTS: 10 mg/kg q3wks for 4 doses, then 10 mg/kg q12wks for up to 3 yrs. If toxicity occurs, doses are omitted (not delayed).
Dosage Modification
Hold scheduled dose for moderate immune-mediated adverse reactions. Pts with complete or partial resolution of adverse reactions and who are receiving less than 7.5 mg/day of prednisone may resume scheduled doses. Permanently discontinue for persistent moderate adverse reactions or inability to reduce corticosteroid dose to 7.5 mg/day, failure to complete full treatment course in 16 wks, any severe or life-threatening adverse reactions.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Hepatotoxicity During Treatment
ALT/AST greater than 2.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN) or bilirubin greater than 1.5–3 times ULN: Withhold treatment. ALT/AST greater than 5 times ULN or bilirubin greater than 3 times ULN: Permanently discontinue.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (42%): Fatigue. Occasional (32%–29%): Diarrhea, pruritus, rash, colitis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions have occurred. Enterocolitis (7% of pts) may present with fever, ileus, abdominal pain, GI bleeding, intestinal perforation, severe dehydrating diarrhea. Endocrinopathies (4% of pts), including hypopituitarism, adrenal insufficiency, hypogonadism, hypothyroidism may present with fatigue, headache, mental status change, unusual bowel habits, hypotension and may require emergent hormone replacement therapy. Dermatitis including toxic epidermal necrolysis (2% of pts) may present with full-thickness ulceration or necrotic, bullous, hemorrhagic manifestations. Hepatotoxicity (1% of pts), defined as LFT greater than 2.5–5 times ULN, may present with right upper abdominal pain, jaundice, black/tarry stools, bruising, dark-colored urine, nausea, vomiting. Neuropathy (1% of pts), including Guillain-Barré syndrome or myasthenia gravis, may present with weakness, sensory alterations, paresthesia, paralysis. Other serious adverse reactions such as pneumonitis, meningitis, nephritis, eosinophilia, pericarditis, myocarditis, angiopathy, temporal arteritis, vasculitis, polymyalgia rheumatica, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, episcleritis, scleritis, leukocytoclastic vasculitis, erythema multiforme, psoriasis, pancreatitis, arthritis, autoimmune thyroiditis reported. Anti-ipilimumab antibodies reported in 1.1% of pts. All severe immune-mediated adverse reactions require immediate high-dose corticosteroid therapy.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, complete metabolic profile, LFT, TSH, free T4, urine pregnancy. Screen for history of hepatic impairment, chronic neuropathy, thyroid/adrenal/pituitary dysfunction, autoimmune disorders. Focused assessment relating to possible adverse reactions includes abdominal area (inspection, auscultation, percussion, palpation, bowel pattern, symmetry), skin (color, lesions, mucosal inspection, edema), neurologic (mental status, gait, numbness, tingling, pain, strength, visual acuity), hormonal glands (lymph node inspection/palpation, pyrexia, goiter, palpitations). Question possibility of pregnancy or plans of breastfeeding. Receive full medication history including vitamins, minerals, herbal products.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor vital signs, hepatic function, thyroid panel before each dose. Continue focused assessment and screen for life-threatening immune-mediated adverse reactions. If adverse reactions occur, immediately notify physician and initiate proper treatment. Report suspected pregnancy. Obtain CBC, blood cultures for fever, suspected infection. EKG for palpitations, chest pain, difficulty breathing, dizziness. If prednisone therapy initiated, monitor capillary blood glucose and screen for side effects.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Inform pt that serious and fatal adverse reactions indicate inflammation to certain systems: intestines (diarrhea, dark/tarry stools, abdominal pain), liver (yellowing of the skin, dark-colored urine, right upper quadrant pain, bruising), skin (rash, mouth sores, blisters, ulcers), nerves (weakness, numbness, tingling, difficulty breathing, paralysis), hormonal glands (headaches, weight gain, palpitations, changes in mood or behavior, dizziness), eyes (blurry vision, double vision, eye pain/redness). • Prednisone therapy may be started if adverse reactions occur. • May cause fetal harm, stillbirth, premature delivery. • Blood levels will be drawn before each dose. • Report any chest pain, palpitations, fever, swollen glands, stomach pain, vomiting, or any sign of adverse reactions.
ipratropium

ip-ra-troe-pee-um
(Atrovent, Atrovent HFA, Novo-Ipramide
![]() , Nu-Ipratropium
, Nu-Ipratropium
![]() , PMS-Ipratropium
, PMS-Ipratropium
![]() )
)
Do not confuse Atrovent with Alupent or Serevent, or ipratropium with tiotropium.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Combivent, DuoNeb: ipratropium/albuterol (a bronchodilator): Aerosol: 18 mcg/90 mcg per actuation. Solution: 0.5 mg/2.5 mg per 3 ml.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Anticholinergic. CLINICAL: Bronchodilator.
USES
Inhalation, Nebulization: Maintenance treatment of bronchospasm due to COPD, bronchitis, emphysema, asthma. Not indicated for immediate bronchospasm relief. Nasal Spray: Symptomatic relief of rhinorrhea associated with the common cold and allergic/nonallergic rhinitis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: History of hypersensitivity to ipratropium, atropine. Cautions: Narrow-angle glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, bladder neck obstruction, myasthenia gravis.
ACTION
Blocks action of acetylcholine at parasympathetic sites in bronchial smooth muscle. Therapeutic Effect: Causes bronchodilation, inhibits nasal secretions.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| Inhalation | 1–3 min | 1.5–2 hrs | Up to 4 hrs |
| Nasal | 5 min | 1–4 hrs | 4–8 hrs |
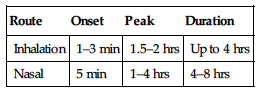
Minimal systemic absorption after inhalation. Metabolized in liver (systemic absorption). Primarily eliminated in feces. Half-life: 1.5–4 hrs (nasal).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anticholinergics (e.g., glycopyrolate, scopolamine), medications with anticholinergic properties may increase toxicity. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Aerosol for Oral Inhalation (Atrovent HFA): 17 mcg/actuation. Solution, Intranasal Spray: 0.03%; 0.06%. Solution for Nebulization: 0.02% (500 mcg).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Inhalation
• Shake container well. • Instruct pt to exhale completely, place mouthpiece between lips, inhale deeply through mouth while fully depressing top of canister. Hold breath as long as possible before exhaling slowly. • Allow at least 1 minute between inhalations. • Rinse mouth with water immediately after inhalation (prevents mouth/throat dryness).
Nebulization
• May be administered with or without dilution in 0.9% NaCl. • Stable for 1 hr when mixed with albuterol. • Give over 5–15 min.
Nasal
• Store at room temperature. • Initial pump priming requires 7 actuations of pump. • If used regularly as recommended, no further priming is required. If not used for more than 4 hrs, pump will require 2 actuations, or if not used for more than 7 days, the pump will require 7 actuations to reprime.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Bronchodilator for COPD
Inhalation: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 12 YRS: 2 inhalations 4 times/day. Maximum: 12 inhalations/day.
Nebulization: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 12 YRS: 500 mcg (1 unit dose vial) 3–4 times/day (doses 6–8 hrs apart).
Asthma Exacerbation
Note: Should be given in combination with a short-acting beta-adrenergic agonist.
Inhalation: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 12 YRS: 8 inhalations q20min as needed for up to 3 hrs. CHILDREN 6–12 YRS: 4–8 inhalations q20min as needed for up to 3 hrs. CHILDREN 5 YRS OR YOUNGER: 2 inhalations q20 min for 1 hr.
Nebulization: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN OLDER THAN 12 YRS: 500 mcg q20min for 3 doses, then as needed. CHILDREN 6–12 YRS: 250–500 mcg q20min for 3 doses, then as needed. CHILDREN 5 YRS OR YOUNGER: 250 mcg q20 min for 1 hr.
Rhinorrhea (Perennial Allergic/Nonallergic Rhinitis)
Intranasal (0.03%): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER: 2 sprays per nostril 2–3 times/day.
Rhinorrhea (Common Cold)
Intranasal (0.06%): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 2 sprays per nostril 3–4 times/day for up to 4 days. CHILDREN 5–11 YRS: 2 sprays per nostril 3 times/day for up to 4 days.
Rhinorrhea (Seasonal Allergy)
Intranasal (0.06%): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 5 YRS AND OLDER: 2 sprays per nostril 4 times/day for up to 3 wks.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Inhalation (6%–3%): Cough, dry mouth, headache, nausea. Nasal: Dry nose/mouth, headache, nasal irritation. Occasional: Inhalation (2%): Dizziness, transient increased bronchospasm. Rare (less than 1%): Inhalation: Hypotension, insomnia, metallic/unpleasant taste, palpitations, urinary retention. Nasal: Diarrhea, constipation, dry throat, abdominal pain, nasal congestion.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Worsening of angle-closure glaucoma, acute eye pain, hypotension occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Offer emotional support (high incidence of anxiety due to difficulty in breathing, sympathomimetic response to drug).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respiration; quality, rate of pulse. Assess lung sounds for rhonchi, wheezing, rales. Monitor ABGs. Observe lips, fingernails for cyanosis (blue or dusky color in light-skinned pts; gray in dark-skinned pts). Observe for retractions (clavicular, sternal, intercostal), hand tremor. Evaluate for clinical improvement (quieter, slower respirations, relaxed facial expression, cessation of retractions). Monitor for improvement of rhinorrhea.
PATIENT/ FAMILY TEACHING
• Increase fluid intake (decreases lung secretion viscosity). • Do not take more than 2 inhalations at any one time (excessive use may produce paradoxical bronchoconstriction, decreased bronchodilating effect). • Rinsing mouth with water immediately after inhalation may prevent mouth and throat dryness. • Avoid excessive use of caffeine derivatives (chocolate, coffee, tea, cola, cocoa).
irbesartan
ir-be-sar-tan
(Apo-lrbesartan*, Avapro)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause fetal injury, mortality if used during second or third trimester of pregnancy.
May cause fetal injury, mortality if used during second or third trimester of pregnancy.
Do not confuse Avapro with Anaprox.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Avalide: irbesartan/hydrochlorothiazide (a diuretic): 150 mg/12.5 mg, 300 mg/12.5 mg, 300 mg/25 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Angiotensin II receptor antagonist. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive.
USES
Treatment of hypertension alone or in combination with other antihypertensives. Treatment of diabetic nephropathy in pts with type 2 diabetes. OFF-LABEL: Reduce proteinuria in children with chronic kidney disease.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to irbesartan. Concomitant use with aliskiren in pts with diabetes. Cautions: Renal impairment, unstented unilateral or bilateral renal artery stenosis, dehydration, HF, idiopathic or hereditary angioedema or angioedema associated with ACE inhibitor therapy.
ACTION
Blocks vasoconstriction, aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II, inhibiting binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Produces vasodilation, decreases peripheral resistance, decreases B/P.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | — | 1–2 hrs | Greater than 24 hrs |
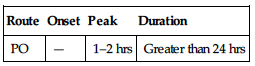
Rapidly, completely absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 90%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated in feces (80%), urine (20%). Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 11–15 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. May cause fetal or neonatal morbidity or mortality. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Diuretics (e.g., furosemide, HCTZ) produce additive hypotensive effects. Potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., spironolactone, triamterene), potassium supplements may increase risk of hyperkalemia. NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive effect. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Garlic may increase antihypertensive effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May slightly increase serum BUN, creatinine. May decrease Hgb.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 13 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 75–150 mg/day. May increase to 300 mg/day. CHILDREN 6–12 YRS: Initially, 75 mg/day. May increase to 150 mg/day.
Nephropathy
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Target dose of 300 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (9%–3%): Upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, diarrhea, cough. Rare (2%–1%): Heartburn, dizziness, headache, nausea, rash.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may manifest as hypotension, syncope, tachycardia. Bradycardia occurs less often.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain B/P, apical pulse immediately before each dose, in addition to regular monitoring (be alert to fluctuations). If excessive reduction in B/P occurs, place pt in supine position, feet slightly elevated. Question possibility of pregnancy. Assess medication history (esp. diuretic therapy).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Maintain hydration (offer fluids frequently). Assess for evidence of upper respiratory infection. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Monitor electrolytes, renal function, urinalysis, B/P, pulse. Assess for hypotension.
PATIENT/ FAMILY TEACHING
• May cause fetal or neonatal morbidity or mortality. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established (possible dizziness effect); ensure appropriate birth control measures are in place. • Report any sign of infection (sore throat, fever). • Avoid exercising during hot weather (risk of dehydration, hypotension).
irinotecan
eye-ri-noe-tee-kan
(Camptosar, Onivyde)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Can induce both early and late forms of severe diarrhea. Early diarrhea (during or shortly after administration) accompanied by salivation, rhinitis, lacrimation, diaphoresis, flushing. Late diarrhea (occurring more than 24 hrs after administration) can be prolonged and life-threatening. May produce severe, profound myelosuppression. Administer under supervision of experienced cancer chemotherapy physician.
Can induce both early and late forms of severe diarrhea. Early diarrhea (during or shortly after administration) accompanied by salivation, rhinitis, lacrimation, diaphoresis, flushing. Late diarrhea (occurring more than 24 hrs after administration) can be prolonged and life-threatening. May produce severe, profound myelosuppression. Administer under supervision of experienced cancer chemotherapy physician.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: DNA topoisomerase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Camptosar: Treatment of metastatic carcinoma of colon or rectum. Onivyde: Treatment of metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas (in combination with 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin). OFF-LABEL: Non–small-cell lung cancer; small-cell lung cancer; CNS tumor; cervical, gastric, pancreatic, ovarian, esophageal cancer; Ewing’s sarcoma; brain tumor.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to irinotecan. Cautions: Pt previously receiving pelvic, abdominal irradiation (increased risk of myelosuppression), pts older than 65 yrs, hepatic dysfunction, hyperbilirubinemia, renal impairment, preexisting pulmonary disease.
ACTION
Interacts with topoisomerase I, an enzyme that relieves torsional strain in DNA by inducing reversible single-strand breaks. Prevents religation of these single-stranded breaks resulting in damage to double-strand DNA, cell death. Therapeutic Effect: Produces cytotoxic effect on cancer cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 95% (metabolite). Excreted in urine and eliminated by biliary route. Half-life: 6–12 hrs; metabolite, 10–20 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Risk of diarrhea significantly increased.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine) may decrease concentration/effects. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) increase concentration. Avoid live vaccines during treatment. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease irinotecan effectiveness. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, AST. May decrease Hgb, leukocytes, platelets.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 20 mg/ml (2 ml, 5 ml, 15 ml, 25 ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Camptosar
Reconstitution • Dilute in D5W (preferred) or 0.9% NaCl to concentration of 0.12–2.8 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • Administer all doses as IV infusion over 30–90 min. • Assess for extravasation (flush site with Sterile Water for Injection, apply ice if extravasation occurs).
Storage • Store vials at room temperature, protect from light. • Solution diluted with D5W is stable for 24 hrs at room temperature or 48 hrs if refrigerated. • Solution diluted with 0.9% NaCl is stable for 24 hrs at room temperature. • Do not refrigerate solution if diluted with 0.9% NaCl.
Onivyde
Reconstitution • Withdraw dose from vial and dilute with 500 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl. Mix gently.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 90 min.
Storage • Refrigerate vials; do not freeze. • Protect from light. • Stable for 4 hrs at room temperature or 24 hrs refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITY
IV INCOMPATIBILITY
Gemcitabine (Gemzar).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Genotyping of UGTIAI available. Pts who are homozygous for the UGTIAI*28 allele are at increased risk for neutropenia. Decreased dose is recommended.
Carcinoma of the Colon, Rectum
IV (Single-Agent Therapy): ADULTS, ELDERLY: (WEEKLY REGIMEN): Initially, 125 mg/m2 once wkly for 4 wks, followed by a rest period of 2 wks. Additional courses may be repeated q6wks. Dosage may be adjusted in 25–50 mg/m2 increments to as high as 150 mg/m2 or as low as 50 mg/m2. (THREE-WEEK REGIMEN): 350 mg/m2 q3wks. Dosage may be adjusted to as low as 200 mg/m2.
(In Combination with Leucovorin and 5-Fluorouracil): REGIMEN ONE: 125 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, 15, 22. REGIMEN TWO: 180 mg/m2 on days 1, 15, 29.
Pancreatic Cancer
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 70 mg/m2 once q2wks (in combination with leucovorin and 5-fluorouracil).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
| Bilirubin | Dose |
| More than upper limit of normal to 2 mg/dL or less: | Reduce dose one level |
| More than 2 mg/dL: | Not recommended |
SIDE EFFECTS
Expected (64%–32%): Nausea, alopecia, vomiting, diarrhea. Frequent (29%–22%): Constipation, fatigue, fever, asthenia, skeletal pain, abdominal pain, dyspnea. Occasional (19%–16%): Anorexia, headache, stomatitis, rash.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hematologic toxicity characterized by anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia, sepsis occur frequently.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Offer emotional support. Assess hydration status, electrolytes, CBC before each dose. Premedicate with antiemetics on day of treatment, starting at least 30 min before administration. Inform pt of possibility of alopecia.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor hydration status, I&O, electrolytes, CBC, renal function, LFT. Monitor infusion site for signs of inflammation. Assess skin for rash.
PATIENT/ FAMILY TEACHING
• Report diarrhea, vomiting, fever, light-headedness, dizziness. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance). • Avoid contact with those who have recently received live virus vaccine. • Avoid crowds, those with infections.
iron dextran
iron dex-tran
(Dexiron
![]() , Infed, Infufer
, Infed, Infufer
![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Potentially fatal anaphylactic-type reaction has been associated with parenteral administration.
Potentially fatal anaphylactic-type reaction has been associated with parenteral administration.
Do not confuse DexFerrum with Desferal, or iron dextran with iron sucrose.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Trace element. CLINICAL: Hematinic iron preparation.
USES
Treatment of anemia, iron deficiency. Use only when PO administration is not feasible or when rapid replenishment of iron is warranted.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to iron formulation. All anemias not associated with iron deficiency anemia (pernicious, aplastic, normocytic, refractory). Caution: Serious hepatic impairment. History of allergies, bronchial asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, preexisting cardiac disease. Avoid use during acute kidney infection.
ACTION
Essential component in formation of Hgb. Necessary for effective erythropoiesis, transport and utilization of oxygen. Serves as cofactor of several essential enzymes. Therapeutic Effect: Replenishes Hgb, depleted iron stores.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed after IM administration. Most absorption occurs within 72 hrs; remainder within 3–4 wks. Bound to protein to form hemosiderin, ferritin, or transferrin. No physiologic system of elimination. Small amounts lost daily in shedding of skin, hair, nails and in feces, urine, perspiration. Half-life: 5–20 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cross placenta in some form (unknown). Trace distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution (Infed): 50 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Test dose is generally given before full dosage; monitor pt for several min after injection due to potential for anaphylactic reaction.
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • May give undiluted or dilute in 250–1,000 ml 0.9% NaCl for infusion. • Avoid dilution in dextrose (increased pain/phlebitis).
Rate of Administration • Do not exceed IV bolus administration rate of 50 mg/min (1 ml/min). Too-rapid IV rate may produce flushing, chest pain, hypotension, tachycardia, shock. • Infuse diluted solution over 1–6 hrs. • Pt must remain recumbent 30–45 min after IV administration (minimizes postural hypotension).
Storage • Store at room temperature.
IM
• Draw up medication with one needle; use new needle for injection (minimizes skin staining). • Administer deep IM in upper outer quadrant of buttock only. • Use Z-tract technique (displacement of subcutaneous tissue lateral to injection site before inserting needle) to minimize skin staining.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
0.5-ml test dose (0.25 ml in infants). Give prior to initiating iron dextran therapy.
◀ ALERT ▶ Discontinue oral iron preparations before administering iron dextran. Dosage expressed in terms of milligrams of elemental iron. Dosage individualized based on degree of anemia, pt weight, presence of any bleeding. Use periodic hematologic determinations as guide to therapy.
◀ ALERT ▶ Not normally given in first 4 mos of life.
Iron Deficiency Anemia
IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN WEIGHING MORE THAN 15 KG: Dose in ml (50 mg elemental iron/ml) = 0.0442 (desired Hgb less observed Hgb) × lean body weight (in kg) + (0.26 × lean body weight). Give 2 ml or less once daily until total dose reached. CHILDREN WEIGHING 5–15 KG: Dose in ml (50 mg elemental iron/ml) = 0.0442 (desired Hgb less observed Hgb) × body weight (in kg) + (0.26 × body weight). Give 2 ml or less once daily until total dose reached.
Maximum Daily Dosages
ADULTS WEIGHING MORE THAN 50 KG: 100 mg. CHILDREN WEIGHING MORE THAN 10 KG: 100 mg. CHILDREN WEIGHING 5–10 KG: 50 mg. CHILDREN WEIGHING LESS THAN 5 KG: 25 mg.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Allergic reaction (rash, pruritus), backache, myalgia, chills, dizziness, headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, flushed skin, pain/redness at injection site, brown discoloration of skin, metallic taste.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Anaphylaxis occurs rarely in first few min following injection. Leukocytosis, lymphadenopathy occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Do not give concurrently with oral iron form (excessive iron may produce excessive iron storage [hemosiderosis]). Be alert to pts with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), iron deficiency anemia (acute exacerbation of joint pain, swelling may occur). Inguinal lymphadenopathy may occur with IM injection. Assess for adequate muscle mass before injecting medication.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Question pt regarding soreness, pain, inflammation at/near IM injection site. Monitor IM site for abscess formation, necrosis, atrophy, swelling, brownish color of skin. Check IV site for phlebitis. Monitor serum ferritin. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Pain, brown staining may occur at injection site. • Oral iron should not be taken when receiving iron injections. • Stools often become black with iron therapy but is harmless unless accompanied by red streaking, sticky consistency of stool, abdominal pain/cramping, which should be reported to physician. • Oral hygiene, hard candy, gum may reduce metallic taste. • Immediately report fever, back pain, headache.
iron sucrose
iron soo-krose
(Venofer)
Do not confuse iron sucrose with iron dextran.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Trace element. CLINICAL: Hematinic iron preparation.
USES
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia in chronic kidney disease. OFF-LABEL: Chemotherapy-associated anemia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to iron sucrose. Cautions: History of allergies, bronchial asthma; hepatic impairment, rheumatoid arthritis, preexisting cardiac disease. Pts at risk for significant hypotension.
ACTION
Essential component in formation of Hgb. Necessary for effective erythropoiesis, transport and utilization of oxygen. Serves as cofactor of several essential enzymes. Therapeutic Effect: Replenishes body iron stores in pts on chronic hemodialysis who have iron deficiency anemia and are receiving erythropoietin.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Distributed mainly in blood and to some extent in extravascular fluid. Iron sucrose is dissociated into iron and sucrose by reticuloendothelial system. Sucrose component is eliminated mainly by urinary excretion. Half-life: 6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Increases Hgb, Hct; serum ferritin, transferrin.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 20 mg of elemental iron/ml in 2.5-ml, 5-ml, 10-ml vials.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Administer directly into dialysis line during hemodialysis.
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • May give undiluted as slow IV injection or IV infusion. For IV infusion, dilute 100-mg (5-ml) vial in maximum of 100 ml 0.9% NaCl immediately before infusion. (Do not dilute to concentration less than 1 mg/ml in children.) • Dilute large doses in maximum of 250 ml 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • For IV injection, administer 100–200 mg (5–10 ml) over 2–5 min. • For IV infusion, administer 100 mg over at least 15 min; 300 mg over 1.5 hrs; 400 mg over 2.5 hrs; 500 mg over 3.5–4 hrs.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Following dilution, stable for 7 days at room temperature or if refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with other medications or add to parenteral nutrition solution for IV infusion.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Dosage is expressed in terms of milligrams of elemental iron.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY (HEMODIALYSIS-DEPENDENT PTS): 5 ml iron sucrose (100 mg elemental iron) delivered during dialysis; administer 1–3 times/wk to total dose of 1,000 mg in 10 doses. Give no more than 3 times/wk. CHILDREN 2 YRS AND OLDER: 0.5 mg/kg/dose (Maximum: 100 mg) q4wks for 3 doses. (PERITONEAL DIALYSIS–DEPENDENT PTS): Two infusions of 300 mg over 90 min 14 days apart followed by a single 400-mg dose over 2½ hrs 14 days later. CHILDREN 2 YRS AND OLDER: 0.5 mg/kg/dose (Maximum: 100 mg) q4wks for 3 doses. (NON–DIALYSIS-DEPENDENT PTS): 200 mg over 2–5 min on 5 different occasions within 14 days. CHILDREN 2 YRS AND OLDER: 0.5 mg/kg/dose (Maximum: 100 mg) q4wks for 3 doses.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (36%–23%): Hypotension, leg cramps, diarrhea.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Too-rapid IV administration may produce severe hypotension, headache, vomiting, nausea, dizziness, paresthesia, abdominal/muscle pain, edema, cardiovascular collapse. Hypersensitivity reaction occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Initially, monitor Hgb, Hct, serum ferritin, transferrin monthly, then q2–3mos thereafter. Reliable serum iron values can be obtained 48 hrs following administration.
isavuconazonium
eye-sa-vue-kon-a-zoe-nee-um
(Cresemba)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Azole antifungal derivative. CLINICAL: Antifungal.
USES
Treatment of invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis in pts 18 yrs and older.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to isavuconazonium or isavuconazole, concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, ritonavir), strong CYP3A inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin, St. John’s wort), history of short QT syndrome. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, hypersensitivity to other azoles. Pts at risk for acute pancreatitis; concomitant use of nephrotoxic medications; pts at risk for hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia. Concomitant use of medications that prolong QT interval.
ACTION
Isavuconazonium is the prodrug of isavuconazole. Interferes with fungal cytochrome activity, decreasing ergosterol synthesis, inhibiting fungal cell membrane formation. Therapeutic Effect: Damages fungal cell wall membrane.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: greater than 99%. Peak plasma concentration: 2–3 hrs. Eliminated in feces (46%), urine (46%). Half-life: 130 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Avoid pregnancy. Avoid breastfeeding while taking Cresemba. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, ritonavir) may increase concentration/effect. Strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effect. May increase concentration/effects of atorvastatin, bupropion, cyclosporine, digoxin, midazolam, mycophenolate mofetil/sirolimus, tacrolimus. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, bilirubin. May decrease serum potassium, magnesium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Powder: 372 mg/vial (equivalent to 200 mg isavuconazole). Capsules: 186 mg (equivalent to 100 mg isavuconazole).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute vial with 5 ml Sterile Water for Injection. • Gently shake until completely dissolved. • Visually inspect for particulate matter or discoloration. Solution may contain visible translucent to white particles. • Inject reconstituted solution into 250 ml 0.9% NaCl or 5% Dextrose injection. • Gently invert bag to mix. Do not shake or agitate. Do not use pneumatic transport system. • Diluted solution may also contain visible translucent to white particles (which will be removed by in-line filter).
Administration • Do not give as IV push or bolus. Flush IV line with 0.9% NaCl or 5% Dextrose injection prior to and after infusion.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 60 min (minimum) using 0.2- to 1.2-micron in-line filter.
Storage • Diluted solution may be stored at room temperature up to 6 hrs or refrigerated up to 24 hrs. • Do not freeze.
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Do not cut, crush, divide, or open capsules.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: 372 mg is equivalent to 200 mg isavuconazole.
Invasive Aspergillosis, Invasive Mucormycosis
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Loading dose: 372 mg q8h for 6 doses (48 hrs). Maintenance: 372 mg once daily. PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Loading dose: 372 mg (2 capsules) q8h for 6 doses (48 hrs). Maintenance: 372 mg (2 capsules) once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Not specified; use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (28%–17%): Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, dyspnea. Occasional (15%–6%): Peripheral edema, constipation, fatigue, insomnia, back pain, delirium, agitation, confusion, disorientation, chest pain, rash, pruritus, hypotension, anxiety, dyspepsia, injection site reaction, decreased appetite.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Severe hepatic injury including cholestasis, hepatitis, hepatic failure reported in pts with underlying medical conditions (e.g., hematologic malignancies). Infusion-related reactions including chills, dizziness, dyspnea, hypoesthesia, hypotension, paresthesia may occur. Acute respiratory failure, renal failure, Stevens-Johnson syndrome; serious hypersensitivity reaction including anaphylaxis were reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline LFT. Confirm negative pregnancy test before initiating treatment. Specimens for fungal culture, histopathology should be obtained prior to initiating therapy. Receive full medication history and screen for interactions/contraindications. Question history of hypersensitivity reaction, hepatic impairment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor BMP, LFT periodically. Monitor for infusion-related reactions, hypersensitivity reactions, anaphylaxis. Monitor I&O. Report worsening of hepatic/renal function.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Swallow capsule whole; do not chew, crush, cut, or open capsules. • Treatment may cause fetal harm. Females of reproductive potential should use effective contraception. Immediately report suspected pregnancy. • Do not take herbal products such as St. John’s wort. • Report liver problems such as upper abdominal pain, bleeding, dark or amber-colored urine, nausea, vomiting, or yellowing of the skin or eyes. • Report decreased urinary out, extremity swelling, dark-colored urine; skin changes such as rash, skin bubbling, or sloughing.
isoniazid
eye-soe-nye-a-zid
(Isotamine
![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Severe, potentially fatal hepatitis may occur.
Severe, potentially fatal hepatitis may occur.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Rifamate: isoniazid/rifampin (antitubercular): 150 mg/300 mg.
Rifater: isoniazid/pyrazinamide/rifampin (antitubercular): 50 mg/300 mg/120 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Isonicotinic acid derivative. CLINICAL: Antitubercular.
USES
Treatment of susceptible mycobacterial infection due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Treatment of latent tuberculosis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to isoniazid (including drug-induced hepatitis) hepatic disease, hepatic injury or severe adverse reactions with previous isoniazid therapy. Cautions: Chronic hepatic disease, alcoholism, severe renal impairment. Pregnancy, pts at risk for peripheral neuropathy, HIV infection, history of hypersensitivity reactions to latent TB infection medications.
ACTION
Inhibits mycolic acid synthesis. Causes disruption of bacterial cell wall, loss of acid-fast properties in susceptible mycobacteria. Therapeutic Effect: Bactericidal against actively growing intracellular, extracellular susceptible mycobacteria.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 10%–15%. Widely distributed (including to CSF). Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 0.5–5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Prophylaxis usually postponed until after delivery. Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: More susceptible to developing hepatitis.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol may increase isoniazid metabolism, risk of hepatotoxicity. May increase toxicity of carbamazepine, phenytoin. Hepatotoxic medications (e.g., acetaminophen, simvastatin) may increase risk of hepatotoxicity. May decrease ketoconazole concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: Foods containing tyramine may cause hypertensive crisis. LAB VALUES: May increase serum bilirubin, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Oral Solution: 50 mg/5 ml. Solution, Injection: 100 mg/ml. Tablets: 100 mg, 300 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give 1 hr before or 2 hrs following meals (may give with food to decrease GI upset, but will delay absorption). • Administer at least 1 hr before antacids, esp. those containing aluminum.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Active Tuberculosis (in Combination with One or More Antituberculars)
IM/PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5 mg/kg once daily. Usual dose: 300 mg. CHILDREN: 10–15 mg/kg once daily. Maximum: 300 mg.
Note: Give isoniazid with rifampin, pyrazinamide, and with or without ethambutol for 8 wks, then give with rifampin for 18 wks.
Latent Tuberculosis
Note: Give for 9 mos.
IM/PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5 mg/kg/day (maximum: 300 mg) or 15 mg/kg twice wkly (maximum: 900 mg). CHILDREN: 10–20 mg/kg/day as a single daily dose. Maximum: 300 mg/day or 20–40 mg/kg 2 times/wk. Maximum: 900 mg/dose.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution. Contraindicated with acute hepatic disease.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain. Rare: Pain at injection site, hypersensitivity reaction.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Neurotoxicity (ataxia, paresthesia), optic neuritis, hepatotoxicity occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of hypersensitivity reactions, hepatic injury or disease, sensitivity to nicotinic acid or chemically related medications. Ensure collection of specimens for culture, sensitivity. Evaluate initial LFT.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor LFT, assess for hepatitis: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, weakness, fatigue, dark urine, jaundice (withhold concurrent INH therapy and inform physician promptly). Assess for paresthesia of extremities (pts esp. at risk for neuropathy may be given pyridoxine prophylactically: malnourished, elderly, diabetics, pts with chronic hepatic disease [including alcoholics]). Be alert for fever, skin eruptions (hypersensitivity reaction).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not skip doses; continue taking isoniazid for full length of therapy (6–24 mos). • Take preferably 1 hr before or 2 hrs following meals (with food if GI upset). • Avoid alcohol during treatment. • Do not take any other medications, including antacids, without consulting physician. • Must take isoniazid at least 1 hr before antacid. • Avoid tuna, sauerkraut, aged cheeses, smoked fish (consult list of tyramine-containing foods) that may cause hypertensive reaction (red/itching skin, palpitations, light-headedness, hot or clammy feeling, headache). • Report any new symptom, immediately for vision difficulties, nausea/vomiting, dark urine, yellowing of skin/eyes (jaundice), fatigue, paresthesia of extremities.
isosorbide dinitrate
eye-soe-sor-bide
(ISDN
![]() , IsoDitrate ER, Dilatrate-SR, Isordil)
, IsoDitrate ER, Dilatrate-SR, Isordil)
isosorbide mononitrate
Do not confuse Imdur with Imuran, Inderal, or K-Dur, Isordil with Inderal, Isuprel, or Plendil.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
BiDil: isosorbide dinitrate/hydralazine (a vasodilator): 20 mg/37.5 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Nitrate. CLINICAL: Antianginal.
USES
Dinitrate: Prevention and treatment of angina pectoris. Mononitrate: Prevention of angina pectoris.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to nitrates, concurrent use of sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil. Cautions: Inferior wall MI, head trauma, increased intracranial pressure (ICP), orthostatic hypotension, blood volume depletion from diuretic therapy, systolic B/P less than 90 mm Hg, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, alcohol consumption.
ACTION
Stimulates intracellular cyclic guanosine monophosphate. Therapeutic Effect: Relaxes vascular smooth muscle of arterial, venous vasculature. Decreases preload, afterload, cardiac oxygen demand.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| Dinitrate | |||
| Sublingual | 3 min | N/A | 1–2 hrs |
| PO | 45–60 min | N/A | up to 8 hrs |
| Mononitrate | |||
| PO (extended-release) | 30–60 min | N/A | 12–24 hrs |
Dinitrate poorly absorbed and metabolized in liver to its active metabolite isosorbide mononitrate. Mononitrate well absorbed after PO administration. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: Dinitrate, 1–4 hrs; mononitrate, 4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May be more sensitive to hypotensive effects. Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, antihypertensives (e.g., amlodipine, lisinopril, valsartan) may increase risk of orthostatic hypotension. Sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil may potentiate hypotensive effects (concurrent use of these agents is contraindicated). HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase urine catecholamine, urine vanillylmandelic acid levels.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Dinitrate
Tablets: 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg.
![]() Capsules, Extended-Release: 40 mg.
Capsules, Extended-Release: 40 mg.
![]() Tablets, Extended-Release: 40 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release: 40 mg.
Mononitrate
Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg.
![]() Tablets, Extended-Release: 30 mg, 60 mg, 120 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release: 30 mg, 60 mg, 120 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Best if taken on an empty stomach. • Do not administer around the clock. • Oral tablets may be crushed. • Do not crush/break sustained-, extended-release form.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Angina
PO (Isosorbide Dinitrate) (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 5–20 mg 2–3 times/day. Maintenance: 10–40 mg 2–3 times/day.
(Sustained-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 40 mg 1–2 times/day. Maximum: 160 mg/day.
PO (Isosorbide Mononitrate) (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–20 mg twice daily given 7 hrs apart.
(Sustained-Release): Initially, 30–60 mg/day in morning as a single dose. May increase dose at 3-day intervals. Maximum daily single dose: 240 mg.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Headache (may be severe) occurs mostly in early therapy, diminishes rapidly in intensity, usually disappears during continued treatment. Occasional: Transient flushing of face/neck, dizziness, weakness, orthostatic hypotension, nausea, vomiting, restlessness. GI upset, blurred vision, dry mouth. Sublingual: Frequent: Burning, tingling at oral point of dissolution.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Discontinue if blurred vision occurs. Severe orthostatic hypotension manifested by syncope, pulselessness, cold/clammy skin, diaphoresis has been reported. Tolerance may occur with repeated, prolonged therapy, but may not occur with extended-release form. Minor tolerance with intermittent use of sublingual tablets. High dosage tends to produce severe headache.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Record onset, type (sharp, dull, squeezing), radiation, location, intensity, duration of anginal pain; precipitating factors (exertion, emotional stress). If headache occurs during management therapy, administer medication with meals.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation if light-headedness, dizziness occurs. Assess for facial/neck flushing. Monitor number of anginal episodes, orthostatic B/P.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide sublingual, extended-release, sustained-release forms. • Take sublingual tablets while sitting down. • Go from lying to standing slowly (prevents dizziness effect). • Take oral form on empty stomach (however, if headache occurs during management therapy, take medication with meals). • Dissolve sublingual tablet under tongue; do not swallow. • Avoid alcohol (intensifies hypotensive effect). • If alcohol is ingested soon after taking nitrates, possible acute hypotensive episode (marked drop in B/P, vertigo, pallor) may occur. • Report signs/symptoms of hypotension, angina.
itraconazole
it-ra-kon-a-zole