IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Bumetanide (Bumex), cefepime (Maxipime), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), heparin, labetalol (Normodyne, Trandate), milrinone (Primacor), norepinephrine (Levophed), piperacillin and tazobactam (Zosyn), potassium, propofol (Diprivan).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Abrupt or too-rapid withdrawal may result in pronounced restlessness, irritability, insomnia, hand tremor, abdominal cramping, muscle cramps, diaphoresis, vomiting, seizures. Overdose results in drowsiness, confusion, diminished reflexes, coma. Antidote: Flumazenil (see Appendix J for dosage).
lorcaserin
lor-kas-er-in
(Belviq, Belviq XR)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Serotonin receptor agonist. CLINICAL: Weight loss agent.
USES
Adjunct to reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity for chronic weight management in adults with an initial body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m2 or greater (obese), or 27 kg/m2 or greater (overweight) with at least one weight-related comorbid condition (e.g., hypertension, dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to lorcaserin, pregnancy. Cautions: Use in pts with severe renal impairment, end-stage renal disease is not recommended. Concurrent use with medications that affect serotonergic neurotransmitter system (particularly during initiation of therapy and dose increases). Moderate renal impairment, severe hepatic impairment, HF, pts predisposed to priapism (e.g., leukemia). Pts at high risk for suicidal thoughts, behavior. Bradycardia, heart block, diabetes.
ACTION
Activates 5HT20 receptors on anorexigenic neurons located in the hypothalamus. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases food consumption, promotes satiety.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed from GI tract. Peak plasma concentration: 1.5–2h. Distributed in cerebrospinal fluid and CNS. Protein binding: 70%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Not for use in this age group. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dose adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration/effects of CYP3D6 substrates (e.g., amitriptyline, metoprolol, venlafaxine). Triptans, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs, including linezolid), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), selective serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, dextromethorphan, tricyclic antidepressants, bupropion, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan may increase risk for serotonin syndrome. HERBAL: St. John’s wort increases potential for serotonin syndrome. FOOD: None known. ALTERED LAB VALUES: May lower Hgb, neutrophil count. May increase serum prolactin.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Capsules, Extended-Release: (Belviq XR) 20 mg. Tablets, Film-Coated: (Belviq) 10 mg.
Capsules, Extended-Release: (Belviq XR) 20 mg. Tablets, Film-Coated: (Belviq) 10 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide film-coated tablet. May give without regard to food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Weight Management
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Belviq) 10 mg twice daily. Do not exceed 10 mg twice daily. (Belviq XR) 20 mg once daily. Belviq should be discontinued if 5% weight loss is not achieved by week 12 of therapy.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate: Use caution. Severe impairment, end-stage renal disease: Not recommended.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Note: Side effects tend to be mild and transient in nature, gradually diminishing during treatment. Frequent (16%–5%): Headache, dizziness, fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, dry mouth, constipation. Type 2 Diabetic Pts (29%–7%): Hypoglycemia, headache, back pain, nasopharyngitis, nausea, cough, fatigue, dizziness. Occasional (6%–2%): Cough, oropharyngeal pain, sinus congestion, musculoskeletal pain, rash. Rare (4%–2%): Type 2 Diabetic Pts: Muscle spasm, peripheral edema, anxiety, insomnia, seasonal allergy, gastroenteritis, toothache, decreased appetite, depression.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Potential for Serotonin Syndrome Serotonin syndrome symptoms including mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile B/P, hyperthermia), neuromuscular changes (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination), and/or GI symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) have been observed. Serotonin syndrome, in its most severe form, can resemble neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which includes hyperthermia, muscle rigidity, autonomic instability with possible rapid fluctuation of vital signs, and mental status changes. Urinary tract infection occurs in 9% of type 2 diabetic pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Ensure negative pregnancy test prior to initiating treatment. Obtain baseline chemistries, particularly renal function, LFT. Obtain weight, BMI.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
In trials, most patients lost at least 5% of their body weight over a year, and a further one third lost at least 10%. Pts who develop signs or symptoms of valvular cardiac disease, including dyspnea, dependent edema, HF, or a new cardiac murmur while on medication should be consistently monitored; discontinuation of treatment may be necessary.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Discontinue therapy if 5% weight loss has not been achieved by 12 wks of treatment. • High-fiber, low-fat diet decreases fat evacuation. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Do not break, chew, dissolve, or divide tablets; swallow whole.
losartan
loe-sar-tan
(Apo-Losartan
 , Cozaar)
, Cozaar)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
Do not confuse Cozaar with Colace, Coreg, Hyzaar, or Zocor, or losartan with lorcaserin, valsartan.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Hyzaar: losartan/hydrochlorothiazide (a diuretic): 50 mg/12.5 mg, 100 mg/12.5 mg, 100 mg/25 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Angiotensin II receptor antagonist. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive.
USES
Treatment of hypertension. Used alone or in combination with other antihypertensives. Treatment of diabetic nephropathy (in pts with type 2 diabetes and hypertension), prevention of stroke in pts with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy. OFF-LABEL: Slow rate of progression of aortic root dilation in children with Marfan’s syndrome. HF in pts intolerant of ACE inhibitors.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to losartan. Concomitant use of aliskiren in pts with diabetes. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, unstented renal arterial stenosis, significant aortic/mitral stenosis. Concurrent use of potassium supplements. Pts with history of angioedema.
ACTION
Blocks vasoconstrictor, aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II, inhibiting binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Causes vasodilation, decreases peripheral resistance, decreases B/P.
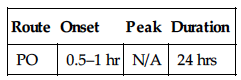
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | N/A | 6 hrs | 24 hrs |
Well absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 98%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated in urine (35%), feces (60%). Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2 hrs; metabolite, 6–9 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Has caused fetal/neonatal morbidity, mortality. Potential for adverse effects on breastfed infant. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: NSAIDs may decrease effects. Potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., spironolactone, triamterene), potassium supplements may increase serum potassium. Diuretics (e.g., furosemide, HCTZ), antihypertensive medications (e.g., amlodipine, lisinopril, valsartan) may produce additive hypotension. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginseng, licorice, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Black cohosh, periwinkle may increase antihypertensive effect. Garlic, ginger, ginseng may increase hypoglycemic effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum bilirubin, ALT, AST, Hgb, Hct. May decrease serum glucose.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May give without regard to food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 50 mg once daily. Maximum: May be given once or twice daily, with total daily doses ranging from 25–100 mg. CHILDREN 6–16 YRS: 0.7 mg/kg once daily. Maximum: 50 mg/day.
Diabetic Nephropathy
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 50 mg/day. May increase to 100 mg/day based on B/P response.
Stroke Prevention (Hypertension with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 50 mg/day. Maximum: 100 mg/day.
Renal Impairment
Not recommended if glomerular filtration rate (GFR) less than 30 ml/min.
Hepatic Impairment
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 25 mg/day. May increase up to 100 mg/day.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (8%): Upper respiratory tract infection. Occasional (4%–2%): Dizziness, diarrhea, cough. Rare (1% or less): Insomnia, dyspepsia, heartburn, back/leg pain, muscle cramps, myalgia, nasal congestion, sinusitis, depression.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdosage may manifest as hypotension and tachycardia. Bradycardia occurs less often. Institute supportive measures.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain B/P, apical pulse immediately before each dose, in addition to regular monitoring (be alert to fluctuations). Question for possibility of pregnancy. Assess medication history (esp. diuretics).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Maintain hydration (offer fluids frequently). Assess for evidence of upper respiratory infection, cough. Monitor B/P, pulse. If excessive reduction in B/P occurs, place pt in supine position, feet slightly elevated. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Female pts of childbearing age should take measures to avoid pregnancy. • Report pregnancy as soon as possible. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established (possible dizziness effect). • Report any sign of infection (sore throat, fever), chest pain. • Do not take OTC cold preparations, nasal decongestants. • Do not stop taking medication. • Limit salt intake.
lovastatin
loe-va-stat-in
(Altoprev, Apo-Lovastatin
 , Mevacor)
, Mevacor)
Do not confuse lovastatin with atorvastatin, Leustatin, Lotensin, nystatin, pitavastatin, or pravastatin, or Mevacor with Benicar or Lipitor.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Advicor: lovastatin/niacin: 20 mg/500 mg, 20 mg/750 mg, 20 mg/1,000 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Anti-hyperlipidemic.
USES
Decreases elevated serum total and LDL cholesterol in primary hypercholesterolemia; primary prevention of coronary artery disease. Slows progression of coronary atherosclerosis in pts with coronary heart disease. Adjunct to diet in adolescent pts (10–17 yrs) with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to lovastatin. Active hepatic disease, pregnancy, unexplained elevated LFT. Pregnancy, breastfeeding. Concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Cautions: History of heavy/chronic alcohol use, renal impairment, hepatic disease; concomitant use of amiodarone, cyclosporine, fibrates, gemfibrozil, niacin, verapamil (increased risk of myopathy), elderly.
ACTION
Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the early step in cholesterol synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases LDL, VLDL, triglycerides; increases HDL.
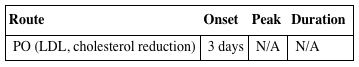
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO (LDL, cholesterol reduction) | 3 days | N/A | N/A |
Incompletely absorbed from GI tract (increased on empty stomach). Protein binding: 95%. Hydrolyzed in liver. Primarily eliminated in feces. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 1.1–1.7 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Contraindicated in pregnancy (suppression of cholesterol biosynthesis may cause fetal toxicity) and lactation. Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, clarithromycin) may increase concentration, risk of myopathy, rhabdomyolysis. Cyclosporine, fibrates, gemfibrozil, niacin, amiodarone, verapamil may increase risk of rhabdomyolysis, acute renal failure. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: Large quantities of grapefruit juice may increase risk of side effects (e.g., myalgia, weakness). Red yeast rice may increase concentration (2.4 mg lovastatin/600 mg rice). LAB VALUES: May increase serum creatine kinase (CK), transaminase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets (Mevacor): 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg.
 Tablets (Extended-Release [Altoprev]): 20 mg, 40 mg, 60 mg.
Tablets (Extended-Release [Altoprev]): 20 mg, 40 mg, 60 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Immediate-release tablet given with evening meal; extended-release at bedtime. • Avoid intake of large quantities of grapefruit juice (greater than 1 quart). • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide extended-release tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypercholesterolemia
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 20 mg/day. Adjust at 4-wk intervals. Maintenance: 10–80 mg once daily or in 2 divided doses. Maximum: 80 mg/day.
PO (Extended-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 20–60 mg once daily at bedtime. Adjust at 4-wk intervals. Maximum: 60 mg once daily at bedtime.
Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
PO (Immediate-Release): CHILDREN 10–17 YRS: Initially, 10–20 mg/day. Adjust at 4-wk intervals. Range: 10–40 mg daily.
Dosage with Concurrent Medication
Amiodarone: Maximum: 40 mg/day. Diltiazem, Dronedarone, Verapamil: Maximum: (Immediate-Release): 10 mg/day. (Extended-Release): 20 mg/day. Lomitapide: Consider reduction in dose.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Use caution.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Generally well tolerated. Side effects usually mild and transient. Frequent (9%–5%): Headache, flatulence, diarrhea, abdominal pain, abdominal cramping, rash, pruritus. Occasional (4%–3%): Nausea, vomiting, constipation, dyspepsia. Rare (2%–1%): Dizziness, heartburn, myalgia, blurred vision, eye irritation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Potential for cataract development. Occasionally produces myopathy manifested as muscle pain, tenderness, weakness with elevated creatine kinase (CK). Severe myopathy may lead to rhabdomyolysis.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain dietary history. Question for possibility of pregnancy before initiating therapy. Assess baseline lab results: serum cholesterol, triglycerides, LFT.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor for headache, dizziness, blurred vision. Assess for rash, pruritus. Monitor serum cholesterol, triglycerides for therapeutic response. Be alert for malaise, muscle cramping/weakness. Monitor LFT.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Follow special diet (important part of treatment). • Periodic lab tests are essential part of therapy. • Maintain appropriate birth control measures. • Avoid grapefruit juice, alcohol. • Report severe gastric upset, vision changes, myalgia, weakness, changes in color of urine/stool, yellowing of eyes/skin, unusual bruising.
lubiprostone
loo-bi-pros-tone
(Amitiza)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Chloride channel activator. CLINICAL: Laxative.
USES
Treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation in adults. Treatment of opioid-induced constipation. Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) with constipation in women 18 yrs and older.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to lubiprostone. History of mechanical GI obstruction. Cautions: Severe diarrhea.
ACTION
Secretes fluid into abdominal lumen through activation of chloride channels in apical membranes of GI epithelium. Therapeutic Effect: Increases intestinal motility, thereby increasing passage of stool, alleviating symptoms associated with chronic idiopathic constipation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly, extensively metabolized within stomach and jejunum. Minimal distribution beyond GI tissue. Protein binding: 94%. Excreted in urine (60%), feces (30%). Half-life: 0.9–1.4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
May have potential for teratogenic effects. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 8 mcg, 24 mcg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with food and water.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Chronic Idiopathic Constipation, Opioid-Induced Constipation
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 24 mcg twice daily with food and water.
IBS
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY (FEMALES): 8 mcg twice daily with food and water.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate impairment: (IBS): No dose adjustment. (Constipation): 16 mcg twice daily. May increase to 24 mcg twice daily. Severe impairment: (IBS): 8 mcg once daily. May increase to 8 mcg twice daily. (Constipation): 8 mcg twice daily. May increase to 16–24 mcg twice daily.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (31%): Nausea. Occasional (13%–4%): Headache, diarrhea, abdominal distention, abdominal pain, flatulence, vomiting, peripheral edema, dizziness. Rare (3%–2%): Dyspepsia, loose stools, fatigue, dry mouth, arthralgia, back pain, cough.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
UTI, upper respiratory tract infection occurs in 4% of pts.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Confirm negative pregnancy test prior to beginning therapy and comply with effective contraceptive measures during therapy. Assess for diarrhea (avoid use in these pts). Question characteristics of bowel movements.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for improvement in symptoms (relief from bloating, cramping, urgency, abdominal discomfort). Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report new/worsening episodes of abdominal pain, severe diarrhea. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established.
lurasidone
loo-ras-i-done
(Latuda)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Elderly pts with dementia-related psychosis are at increased risk for mortality due to cardiovascular events, infectious diseases. Increased risk of suicidal thinking/behavior in children, adolescents, young adults.
Elderly pts with dementia-related psychosis are at increased risk for mortality due to cardiovascular events, infectious diseases. Increased risk of suicidal thinking/behavior in children, adolescents, young adults.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Dopamine, serotonin receptor antagonist. CLINICAL: Antipsychotic.
USES
Treatment of schizophrenia. Depression associated with bipolar I disorder as monotherapy and as adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to lurasidone. Concurrent use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) and inducers (e.g., rifampin). Cautions: Cardiovascular disease (HF, history of MI, ischemia, conduction abnormalities), cerebrovascular disease (history of CVA in pts with dementia, seizure disorders), diabetes mellitus, Parkinson’s disease, renal/hepatic impairment, pts at risk for aspiration pneumonia, pts at risk for suicide, disorders where CNS depression is a feature, pts at risk for hypotension, elderly, head trauma, alcoholism, medications that lower seizure threshold.
ACTION
Antagonizes central dopamine type 2 and serotonin type 2 receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Diminishes symptoms of schizophrenia. Reduces incidence of extrapyramidal side effects.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Absorbed in 1–3 hrs. Steady-state concentration occurs in 7 days. Well absorbed from GI tract (unaffected by food). Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in feces (80%), urine (9%). Half-life: 18 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: More susceptible to postural hypotension. Increased risk of cerebrovascular events, mortality, including stroke, in elderly pts with psychosis.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, CNS depressants (e.g., lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase CNS depression. Rifampin decreases concentration/effects. Diltiazem, ketoconazole, ritonavir may increase concentration/effects. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase risk of torsades, orthostatic hypotension. LAB VALUES: May increase prolactin levels.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 20 mg, 40 mg, 80 mg, 120 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with food. • Tablets may be crushed.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Schizophrenia
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 40 mg once daily with food. Maximum: 160 mg once daily with food.
Depressive Episode Associated with Bipolar Disorder
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 20 mg once daily. Maximum: 120 mg/day. Titration not required.
Concomitant Use of Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 20 mg/day. Maximum: 80 mg/day.
Moderate to Severe Renal Impairment
CrCl less than 50 ml/min: Initially, 20 mg/day. Maximum: 80 mg/day.
Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate impairment: Initially, 20 mg/day. Maximum: 80 mg/day. Severe impairment: Initially, 20 mg/day. Maximum: 40 mg/day.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (15%–7%): Drowsiness, sedation, insomnia (paradoxical reaction). Occasional (6%–3%): Nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, fatigue, back pain, akathisia, dizziness, agitation, anxiety. Rare (2%–1%): Restlessness, salivary hypersecretion, tongue spasm, torticollis, trismus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Extrapyramidal disorder (including cogwheel rigidity, drooling, bradykinesia, tardive dyskinesia, tremors) occurs in 5% of pts. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (fever, muscle rigidity, irregular B/P or pulse, altered mental status, visual changes, dyspnea) occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess behavior, appearance, emotional status, response to environment, speech pattern, thought content. Renal function, LFT should be obtained before therapy as dose adjustment is required when initiating therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Supervise suicidal risk pt closely during early therapy (as depression lessens, energy level improves, increasing suicide potential). Monitor for potential neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Assess for therapeutic response (greater interest in surroundings, improved self-care, increased ability to concentrate, relaxed facial expression).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that may require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established (may cause drowsiness, dizziness). • Avoid alcohol. • Report trembling in fingers, altered gait, unusual muscle/skeletal movements, palpitations, severe dizziness, fainting, visual changes, rash, difficulty breathing. • Report suicidal ideation, unusual changes in behavior.
![]() IV
IV