mirabegron
mir-a-beg-ron
(Myrbetriq)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Beta3-adrenergic agonist. CLINICAL: Smooth muscle relaxant.
USES
Treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urinary incontinence, urgency, frequency.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to mirabegron. Cautions: Bladder outlet obstruction, pts taking antimuscarinic medications (increases urinary retention), mild to moderate hepatic/renal impairment, history of QT-interval prolongation, medications known to prolong QT interval. Not recommended for use in pts with severe uncontrolled hypertension (SBP equal to or greater than 180 mm Hg and/or DBP equal to or greater than 110 mm Hg).
ACTION
Relaxes detrusor smooth muscle of bladder through beta3 stimulation during storage phase of urinary bladder fill–void cycle. Therapeutic Effect: Increases bladder capacity, reduces symptoms of urinary urgency, increased voiding frequency, urge incontinence, nocturia.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed following PO administration; widely distributed. Protein binding: 71%. Renal elimination primarily through active tubular secretion along with glomerular filtration. Eliminated in urine (55%), feces (35%). Half-life: 50 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration of desipramine, digoxin, metoprolol, thioridazine, flecainide, propafenone. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase GGT, LDH; temporarily increase ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Tablets, Extended-Release: 25 mg, 50 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release: 25 mg, 50 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Administer with water; instruct pt to swallow whole. • Do not break, crush, dissolve or divide film-coated tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Overactive Bladder
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 25 mg once daily. Efficacy seen within 8 wks for 25 mg dose. May increase to 50 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dosage adjustment. Severe impairment: Do not exceed 25 mg once daily.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dosage adjustment. Moderate impairment: Do not exceed 25 mg once daily. Severe impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (9%–4%): Hypertension, headache, nasopharyngitis. Rare (2%–1%): Constipation, arthralgia, diarrhea, tachycardia, fatigue.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Worsening of preexisting hypertension reported infrequently. Urinary tract infection occured in 6% of pts, influenza in 3%, and upper respiratory infection in 1.5%.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Check B/P; assess for hypertension. Monitor EKG. Receive full medication history and screen for possible drug interactions. Monitor I&O (particularly in pts with history of urinary retention).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor ALT, AST, LDH, GGT periodically. Palpate bladder for urinary retention. Measure B/P near end of dosing interval (determines whether B/P is controlled throughout day). Periodic B/P determinations are recommended, especially in hypertensive pts. For pts taking digoxin, monitor digoxin serum level for therapeutic effect (very narrow line between therapeutic and toxic level). Assess pulse for quality, irregular rate, bradycardia. Question for evidence of headache.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report urinary retention. • Do not use nasal decongestants, over-the-counter cold preparations without doctor approval. Restrict salt, alcohol intake. • Take mirabegron with water; swallow tablet whole; do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablet. • May take with or without food.
mirtazapine
mir-taz-a-peen
(Apo-Mirtazapine
 , Remeron, Remeron Soltab)
, Remeron, Remeron Soltab)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Do not confuse Remeron with Premarin, Rozerem, or Zemuron.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Tetracyclic compound. CLINICAL: Antidepressant.
USES
Treatment of depression.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to mirtazapine. Use of MAOIs to treat psychiatric disorders (concurrently or within 14 days of discontinuing either MAOI or mirtazapine), initiation of mirtazapine in pts receiving linezolid or IV methylene blue. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, elderly, high-risk pts for seizures, suicidal ideation or behavior, alcoholism, concurrent medications that lower seizure threshold, cardiovascular disease, pts at risk for QT prolongation, history of QT prolongation, medications known to prolong QT interval.
ACTION
Acts as antagonist at presynaptic alpha2-adrenergic receptors, increasing norepinephrine, serotonin neurotransmission. Has low anticholinergic activity. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves depression, produces sedative effects.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly, completely absorbed after PO administration; absorption not affected by food. Protein binding: 85%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 20–40 hrs (longer in males [37 hrs] than females [26 hrs]).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, CNS depressant medications (e.g., lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase impairment of cognition, motor skills. Serotonergic drugs (e.g., venlafaxine) may increase risk of serotonin syndrome. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., phenytoin) may decrease concentration/effects. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) may increase concentration/effects. MAOIs may increase risk of neuroleptic malignant syndrome, hypertensive crisis, severe seizures. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects, may increase risk of serotonin syndrome. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum cholesterol, triglycerides, ALT.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets (Remeron): 7.5 mg, 15 mg, 30 mg, 45 mg. Tablets (Orally Disintegrating [Remeron Soltab]): 15 mg, 30 mg, 45 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • May crush/break scored tablets.
Orally Disintegrating Tablets
• Give without regard to food. • Do not split tablet. • Place on tongue; dissolves without water.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Depression
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 15 mg at bedtime. May increase by 15 mg/day q1–2wks. Maximum: 45 mg/day. ELDERLY: Initially, 7.5 mg at bedtime. May increase by 7.5–15 mg/day q1–2wks. Maximum: 45 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (54%–12%): Drowsiness, dry mouth, increased appetite, constipation, weight gain. Occasional (89%–4%): Asthenia, dizziness, flu-like symptoms, abnormal dreams. Rare: Abdominal discomfort, vasodilation, paresthesia, acne, dry skin, thirst, arthralgia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Higher incidence of seizures than with tricyclic antidepressants (esp. in those with no history of seizures). Overdose may produce cardiovascular effects (severe orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, tachycardia, palpitations, arrhythmias). Abrupt discontinuation from prolonged therapy may produce headache, malaise, nausea, vomiting, vivid dreams. Agranulocytosis occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess mental status, appearance, behavior, speech pattern, level of interest, mood. Obtain baseline weight. For pts on long-term therapy, renal function, LFT, CBC should be performed periodically.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Supervise suicidal-risk pt closely during early therapy (as depression lessens, energy level improves, increasing suicide potential). Children, adolescents are at increased risk for suicidal thoughts/behavior and worsening of depression, esp. during first few mos of therapy. Assess appearance, behavior, speech pattern, level of interest, mood. Monitor for hypotension, arrhythmias.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take as single bedtime dose. • Avoid alcohol, depressant/sedating medications. • Avoid tasks requiring alertness, motor skills until response to drug established. • Report worsening depression, suicidal ideation, unusual changes in behavior.
*miSOPROStol
mis-oh-pros-tol
(Cytotec, Novo-Misoprostol
 )
)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Pregnancy Category X. Use during pregnancy can cause abortion, premature birth, birth defects. Not recommended in women of childbearing potential unless pt is capable of complying with effective contraception.
Pregnancy Category X. Use during pregnancy can cause abortion, premature birth, birth defects. Not recommended in women of childbearing potential unless pt is capable of complying with effective contraception.
Do not confuse Cytotec with Cytoxan, or misoprostol with metoprolol or mifepristone.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Arthrotec: misoprostol/diclofenac (an NSAID): 200 mcg/50 mg, 200 mcg/75 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Prostaglandin. CLINICAL: Antisecretory, gastric protectant.
USES
Prevention of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers and in pts at high risk for developing gastric ulcer/gastric ulcer complications. Medical termination of pregnancy 49 days or less. (in conjunction with mifepristone). OFF-LABEL: Cervical ripening, labor induction, treatment/prevention of postpartum hemorrhage, treatment of incomplete or missed abortion.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to prostaglandins; pregnancy when used to reduce NSAID-induced ulcers (produces uterine contractions). Cautions: Renal impairment, cardiovascular disease, elderly.
ACTION
Replaces protective prostaglandins consumed with prostaglandin-inhibiting therapies (e.g., NSAIDs). Induces uterine contractions. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces acid secretion from gastric parietal cells, stimulates bicarbonate production from gastric/duodenal mucosa.
PHARMACOKINETICS
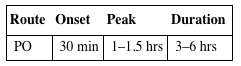
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 30 min | 1–1.5 hrs | 3–6 hrs |
Rapidly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 80%–90%. Rapidly converted to active metabolite. Primarily excreted in urine. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 20–40 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Produces uterine contractions, uterine bleeding, expulsion of products of conception (abortifacient property). Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antacids may increase concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 100 mcg, 200 mcg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with or after meals (minimizes diarrhea).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Prevention of NSAID-Induced Gastric Ulcer
PO: ADULTS: 200 mcg 4 times/day with food (last dose at bedtime). Continue for duration of NSAID therapy. May reduce dosage to 100 mcg 4 times/day or 200 mcg 2 times/day with food. ELDERLY: 100–200 mcg 4 times/day with food.
Chemical Termination of Pregnancy
See manufacturer guidelines of mifepristone.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (40%–20%): Abdominal pain, diarrhea. Occasional (3%–2%): Nausea, flatulence, dyspepsia, headache. Rare (1%): Vomiting, constipation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdosage may produce sedation, tremor, seizures, dyspnea, palpitations, hypotension, bradycardia.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for possibility of pregnancy before initiating therapy.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid magnesium-containing antacids (minimizes potential for diarrhea). • Women of childbearing potential must not be pregnant before or during medication therapy (may result in hospitalization, surgery, infertility, fetal death). • Incidence of diarrhea may be lessened by taking immediately following meals.
*mitoMYcin

mye-toe-mye-sin
(Mutamycin
 )
)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Potent vesicant. Marked myelosuppression. Infiltration produces ulceration, necrosis, cellulitis, tissue sloughing. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome reported. Must be administered by certified chemotherapy personnel.
Potent vesicant. Marked myelosuppression. Infiltration produces ulceration, necrosis, cellulitis, tissue sloughing. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome reported. Must be administered by certified chemotherapy personnel.
Do not confuse mitomycin with mithramycin or mitoxantrone.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antibiotic. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of disseminated adenocarcinoma of stomach, pancreas. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of bladder cancer, anal carcinoma; cervical, esophageal, gastric, non–small-cell lung cancer.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to mitomycin. Coagulation disorders, other increased bleeding tendencies, thrombocytopenia. Cautions: Myelosuppression, renal (serum creatinine greater than 1.7 mg/dL)/hepatic impairment, pregnancy, prior radiation treatment.
ACTION
Alkylating agent, cross-linking with strands of DNA. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits DNA, RNA synthesis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Does not cross blood-brain barrier. Primarily metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 50 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy, esp. first trimester. Breastfeeding not recommended. Safety in pregnancy not established. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Bone marrow depressants may increase myelosuppression. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: Avoid black cohosh, dong quai in estrogen-dependent tumors. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, creatinine.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 5 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ May be carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic. Handle with extreme care during preparation/administration. Give via IV push, IV infusion. Extremely irritating to vein. Injection may produce pain with induration, thrombophlebitis, paresthesia.
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute with Sterile Water for Injection to provide solution containing 0.5–1 mg/ml. • Do not shake vial to dissolve. • Allow vial to stand at room temperature until complete dissolution occurs. • For IV infusion, further dilute with 50–100 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl (concentration 20–40 mcg/ml).
Rate of Administration • Give slow IV push or by IV infusion over 15–30 min. • Extravasation may produce cellulitis, ulceration, tissue sloughing. Terminate administration immediately, inject ordered antidote. Apply ice intermittently for up to 72 hrs; keep area elevated.
Storage • Use only clear, blue-gray solutions. • Concentration of 0.5 mg/ml (reconstituted vial or syringe) is stable for 7 days at room temperature or 2 wks if refrigerated. Further diluted solution with D5W is stable for 3 hrs, 12 hrs if diluted with 0.9% NaCl at room temperature.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Aztreonam (Azactam), bleomycin (Blenoxane), cefepime (Maxipime), filgrastim (Neupogen), heparin, piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn), sargramostim (Leukine), vinorelbine (Navelbine).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Cisplatin (Platinol AQ), cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), doxorubicin (Adriamycin), 5-fluorouracil, granisetron (Kytril), leucovorin, methotrexate, ondansetron (Zofran), vinblastine (Velban), vincristine (Oncovin).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Refer to individual protocols.
Stomach, Pancreatic Cancer
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 20 mg/m2 as single dose. Repeat q6–8wks.
Bladder Cancer (Non–Muscle Invasive)
Intravesicular Instillation: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Low risk of recurrence: 40 mg as single dose postoperatively (retain in bladder for 1–2 hrs). High risk of recurrence: 20 mg/wk for 6 wks, then 20 mg qmo for 3 yrs (retain in bladder for 1–2 hrs).
Dose Modification for Toxicity
| Leukocytes 2,000 to less than 3,000/mm3 | Hold therapy until leukocytes 4,000 or more/mm3, reduce dose to 70% or more in subsequent cycles |
| Leukocyte less than 2,000/mm3 | Hold therapy until leukocytes 4,000 or more/mm3, reduce dose to 50% in subsequent cycles |
| Platelets 25,000 to less than 75,000/mm3 | Hold therapy until platelets 100,000 or more/mm3, reduce dose to 70% in subsequent cycles |
| Platelets less than 25,000/mm3 | Hold therapy until platelets 100,000 or more/mm3, reduce dose to 50% in subsequent cycles |
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl less than 10 ml/min: Give 75% of normal dose.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (Greater Than 10%): Fever, anorexia, nausea, vomiting. Occasional (10%–2%): Stomatitis, paresthesia, purple colored bands on nails, rash, alopecia, unusual fatigue. Rare (Less Than 1%): Thrombophlebitis, cellulitis with extravasation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Marked myelosuppression results in hematologic toxicity manifested as leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and, to a lesser extent, anemia (generally occurs within 2–4 wks after initial therapy). Renal toxicity may be evidenced by increased serum BUN, creatinine levels. Pulmonary toxicity manifested as dyspnea, cough, hemoptysis, pneumonia. Long-term therapy may produce hemolytic uremic syndrome, characterized by hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure, hypertension.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC with differential, PT, bleeding time, before and periodically during therapy. Antiemetics before and during therapy may alleviate nausea/vomiting.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor hematologic status, renal function studies. Assess IV site for phlebitis, extravasation. Monitor for hematologic toxicity (fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site), symptoms of anemia (excessive fatigue, weakness). Assess for renal toxicity (foul odor from urine, elevated serum BUN, creatinine).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Maintain strict oral hygiene. • Immediately report stinging, burning, pain at injection site. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance to infection). • Avoid contact with those who have recently received live virus vaccine. • Hair loss is reversible, but new hair growth may have different color, texture. • Report nausea/vomiting, fever, sore throat, bruising, bleeding, shortness of breath, painful urination.
modafinil

moe-daf-i-nil
(Alertec
 , Apo-Modafinil
, Apo-Modafinil
 , Provigil)
, Provigil)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Alpha1-agonist, CNS stimulant (Schedule IV). CLINICAL: Wakefulness-promoting agent, antinarcoleptic.
USES
Treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness associated with narcolepsy, shift work sleep disorder, adjunct therapy for obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of ADHD, multiple sclerosis–related fatigue.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to modafinil, armodafinil. Cautions: History of clinically significant mitral valve prolapse, left ventricular hypertrophy, renal/hepatic impairment, angina, cardiac disease, myocardial ischemia, recent MI, preexisting psychosis or bipolar disorder, Tourette’s syndrome.
ACTION
Increases alpha activity, decreasing delta, theta, brain wave activity. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces number of sleep episodes, total daytime sleep.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 60%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Excreted by kidneys. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 15 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug is excreted in breast milk. Use caution if given to pregnant women. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 16 yrs. Elderly: Age-related renal/hepatic impairment may require decreased dosage.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease concentrations of cyclosporine, oral contraceptives. May increase concentrations of tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, doxepin), warfarin. Other CNS stimulants may increase CNS stimulation. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets (Provigil): 100 mg, 200 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Narcolepsy, Obstructive Sleep Apnea/Hypopnea Syndrome
PO: ADULTS: 200 mg/day in the morning. ELDERLY: 100 mg/day in the morning.
Shift Work Sleep Disorder
PO: ADULTS: 200 mg about 1 hr prior to start of work shift.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Reduce dose 50% with severe impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Generally well tolerated. Occasional (5%): Headache, nausea, dizziness, insomnia, palpitations, diarrhea.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Agitation, excitation, increased B/P, insomnia may occur. Psychiatric disturbances (anxiety, hallucinations, suicidal ideation), serious allergic reactions (angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome) have been noted.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline evidence of narcolepsy or other sleep disorders, including pattern, environmental situations, length of sleep episodes. Question for sudden loss of muscle tone (cataplexy) precipitated by strong emotional responses before sleep episode. Assess frequency/severity of sleep episodes before drug therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor sleep pattern, evidence of restlessness during sleep, length of insomnia episodes at night. Assess for dizziness, anxiety; initiate fall precautions.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid alcohol. • Sugarless gum, sips of water may relieve dry mouth. • Do not increase dose without physician approval. • Use alternative contraceptives during therapy and 1 mo after discontinuing modafinil (reduces effectiveness of oral contraceptives).
mometasone

moe-met-a-sone
(Asmanex, Asmanex HFA, Elocon, Nasonex)
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Dulera: mometasone/formoterol (beta-adrenergic agonist): 100 mcg/5 mcg, 200 mcg/5 mcg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Adrenocorticosteroid. CLINICAL: Anti-inflammatory.
USES
Nasal: Treatment of nasal symptoms of seasonal/perennial allergic rhinitis in adults, children 2 yrs and older. Prophylaxis of nasal symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis in adults, adolescents 12 yrs and older. Treatment of nasal polyps in adults. Inhalation: Maintenance treatment of asthma as prophylactic therapy. Topical: Relief of inflammatory, pruritic manifestations of steroid-responsive dermatoses.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to mometasone, milk proteins. Primary treatment of status asthmaticus or acute bronchospasm. Cautions: Thyroid/hepatic/renal impairment, elderly, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, glaucoma, cataracts, myasthenia gravis, pts at risk for osteoporosis, seizures, GI disease (e.g., ulcer, colitis); following MI. Untreated systemic fungal, viral, bacterial infections.
ACTION
Inhibits release of mediators of inflammation. (e.g., histamine, kinins). Therapeutic Effect: Improves symptoms of asthma, rhinitis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Undetectable in plasma. Protein binding: 98%–99%. Swallowed portion undergoes extensive metabolism. Excreted through bile (74%), urine (8%). Half-life: 5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Prolonged treatment/high doses may decrease short-term growth rate, cortisol secretion. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Ketoconazole may increase concentration (inhalation). HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Cream (Elocon): 0.1%. Lotion (Elocon): 0.1%. Nasal Spray (Nasonex): 50 mcg/spray. Ointment (Elocon): 0.1%. Powder for Oral Inhaler (Asmanex): 110 mcg (delivers 100 mcg/actuation), 220 mcg (delivers 200 mcg/actuation). (Asmanex HFA): 100 mcg/actuation, 200 mcg/actuation.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Inhalation
• Hold twisthaler straight up with pink portion (base) on bottom, remove cap. • Exhale fully. • Firmly close lips around mouthpiece and inhale a fast, deep breath. • Hold breath for 10 sec.
Intranasal
• Instruct pt to clear nasal passages as much as possible before use. • Tilt head slightly forward. • Insert spray tip into nostril, pointing toward nasal passages, away from nasal septum. • Spray into one nostril while pt holds other nostril closed, concurrently inspires through nose to permit medication as high into nasal passages as possible.
Topical
• Apply thin layer of cream, lotion, ointment to cover affected area. Rub in gently. • Do not cover area with occlusive dressing.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Allergic Rhinitis
Nasal Spray: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 2 sprays in each nostril once daily. When used to prevent nasal rhinitis, begin 2–4 wks prior to start of pollen season. CHILDREN 2–11 YRS: 1 spray in each nostril once daily.
Asthma
Inhalation: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER (Previous therapy with bronchodilators: (Asmanex): Initially, inhale 220 mcg (1 puff) once daily. Maximum: 440 mcg/day as single or 2 divided doses. (Previous therapy with inhaled corticosteroids): (Asmanex HFA): Initially, 100–200 mcg twice daily. Maximum: 400 mcg twice daily. (Previous therapy with oral corticosteroids): (Asmanex): 440 mcg (2 puffs) twice daily. (Asmanex HFA): 400 mcg twice daily. Reduce prednisone no faster than 2.5 mg/day beginning after at least 1 wk of mometasone. CHILDREN 4–11 YRS: (Asmanex): 110 mcg once daily in evening.
Skin Disease
Topical: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: Apply cream, lotion, or ointment sparingly to affected area once daily.
Nasal Polyp
Nasal Spray: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2 sprays (100 mcg) in each nostril twice daily. Total dose: 400 mcg.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Inhalation: Headache, allergic rhinitis, upper respiratory infection, muscle pain, fatigue. Nasal: Nasal irritation, stinging. Topical: Burning. Rare: Inhalation: Abdominal pain, dyspepsia, nausea. Nasal: Nasal/pharyngeal candidiasis. Topical: Pruritus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Acute hypersensitivity reaction (urticaria, angioedema, severe bronchospasm) occurs rarely. Transfer from systemic to local steroid therapy may unmask previously suppressed bronchial asthma condition.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for hypersensitivity to any corticosteroids.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Teach proper use of nasal spray, oral inhaler. Instruct pt to clear nasal passages before use. Report if no improvement in symptoms, sneezing, nasal irritation occur. Assess lung sounds for wheezing, rales.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not change dose schedule or stop taking drug; must taper off gradually under medical supervision. Nasal: Report if symptoms do not improve; sneezing, nasal irritation occur. • Clear nasal passages prior to use. Inhalation: Inhale rapidly, deeply; rinse mouth after inhalation. • Not indicated for acute asthma attacks. Topical: Do not cover affected area with bandage, dressing.
montelukast
mon-tee-loo-kast
(Apo-Montelukast
 , Singulair)
, Singulair)
Do not confuse Singulair with Sinequan.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Leukotriene receptor inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiasthmatic.
USES
Prophylaxis, chronic treatment of asthma. Prevention of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis (hay fever). Relief of perennial allergic rhinitis. OFF-LABEL: Urticaria.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to montelukast. Cautions: Systemic corticosteroid treatment reduction during montelukast therapy. Concomitant use of CYP3A4 inducers. Not for use in acute asthma attacks.
ACTION
Binds to cysteinyl leukotriene receptors, inhibiting effects of leukotrienes on bronchial smooth muscle. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases bronchoconstriction, vascular permeability, mucosal edema, mucus production.
PHARMACOKINETICS
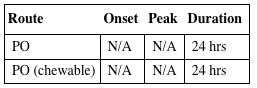
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | N/A | N/A | 24 hrs |
| PO (chewable) | N/A | N/A | 24 hrs |
Rapidly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 99%. Extensively metabolized in liver. Excreted almost exclusively in feces. Half-life: 2.7–5.5 hrs (slightly longer in elderly).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Use during pregnancy only if necessary. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted in pts older than 6 yrs or the elderly.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenobarbital, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effects. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, eosinophils.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Oral Granules: 4 mg per packet. Tablets: 10 mg. Tablets (Chewable): 4 mg, 5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May take without regard to food/meals. When treating asthma, administer in evening. • When treating allergic rhinitis, may individualize administration times. • Granules may be given directly in mouth or mixed with carrots, rice, applesauce, ice cream, baby formula, or breast milk (do not add to any other liquid or food). • Give within 15 min of opening packet.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Bronchial Asthma
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 15 YRS AND OLDER: One 10-mg tablet daily, taken in the evening. CHILDREN 6–14 YRS: One 5-mg chewable tablet daily, taken in the evening. CHILDREN 2–5 YRS: One 4-mg chewable tablet daily, taken in the evening. CHILDREN 6–23 MOS: 4 mg (oral granules) once daily in the evening.
Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 15 YRS AND OLDER: One 10-mg tablet, taken in the evening. CHILDREN 6–14 YRS: One 5-mg chewable tablet, taken in the evening. CHILDREN 2–5 YRS: One 4-mg chewable tablet, taken in the evening.
Perennial Allergic Rhinitis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 15 YRS AND OLDER: One 10-mg tablet, taken in the evening. CHILDREN 6–14 YRS: One 5-mg chewable tablet, taken in the evening. CHILDREN 2–5 YRS: One 4-mg chewable tablet, taken in the evening. CHILDREN 6–23 MOS: 4 mg oral granules, taken in the evening.
Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction Prevention
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 15 YRS AND OLDER: 10 mg 2 or more hrs before exercise. No additional doses within 24 hrs. CHILDREN 6–14 YRS: 5 mg (chew tab) 2 or more hrs prior to exercise. No additional doses within 24 hrs.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
ADULTS, CHILDREN 15 YRS AND OLDER: Frequent (18%): Headache. Occasional (4%): Influenza. Rare (3%–2%): Abdominal pain, cough, dyspepsia, dizziness, fatigue, dental pain. CHILDREN 6–14 YRS: Rare (less than 2%): Diarrhea, laryngitis, pharyngitis, nausea, otitis media, sinusitis, viral infection.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Suicidal ideation and behavior, depression has been noted.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Chewable tablet contains phenylalanine (component of aspartame); parents of phenylketonuric pts should be informed. Assess lung sounds for wheezing. Assess for allergy symptoms.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respirations; quality/rate of pulse. Assess lung sounds for wheezing. Monitor for change in mood, behavior.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Increase fluid intake (decreases lung secretion viscosity). • Take as prescribed, even during symptom-free periods as well as during exacerbations of asthma. • Do not alter/stop other asthma medications. • Drug is not for treatment of acute asthma attacks. • Report increased use or frequency of short-acting bronchodilators, changes in behavior, suicidal ideation.
morphine


mor-feen
(Astramorph PF, Duramorph, Infumorph, Kadian, M-Eslon
 , MS Contin, MSIR
, MS Contin, MSIR
 )
)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Be alert for signs of abuse, misuse, diversion. Epidural: Monitor for delayed sedation. Sustained-release: Do not crush or chew. MS Contin: Use only in opioid-tolerant pts requiring over 400 mg/day. Kadian: Use only in opioid-tolerant pts. Avinza: Alcohol disrupts extended-release timing. Duramorph: Risk of severe and/or sustained cardiopulmonary depression.
Be alert for signs of abuse, misuse, diversion. Epidural: Monitor for delayed sedation. Sustained-release: Do not crush or chew. MS Contin: Use only in opioid-tolerant pts requiring over 400 mg/day. Kadian: Use only in opioid-tolerant pts. Avinza: Alcohol disrupts extended-release timing. Duramorph: Risk of severe and/or sustained cardiopulmonary depression.
Do not confuse Avinza with Evista or Invanz, morphine with hydromorphone, morphine sulfate with magnesium sulfate, MS Contin with Oxycontin. MSO4 and MS are error-prone abbreviations.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Embeda: morphine/naloxone (an opioid antagonist): 20 mg/0.8 mg, 30 mg/1.2 mg, 50 mg/2 mg, 60 mg/2.4 mg, 80 mg/3.2 mg, 100 mg/4 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Narcotic agonist (Schedule II). CLINICAL: Opiate analgesic.
USES
Relief of moderate to severe, acute, or chronic pain; analgesia during labor, pain due to MI, dyspnea from pulmonary edema not resulting from chemical respiratory irritant. Infumorph: Use in devices for managing intractable chronic pain. Extended-release: Use only when repeated doses for extended periods of time are required.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: All Formulations: Hypersensitivity to morphine. Acute or severe asthma, GI obstruction, known or suspected paralytic ileus, severe hepatic/renal impairment, severe respiratory depression. Extended-Release: GI obstruction, acute postoperative pain. Injection: HF due to lung disease; arrhythmias, head injury, seizures, acute alcoholism. Labor when premature birth expected. Immediate-Release (Tablets, Oral Solution): Hypercarbia. Extreme Caution: COPD, cor pulmonale, hypoxia, hypercapnia, preexisting respiratory depression, head injury, increased ICP, severe hypotension. Cautions: Biliary tract disease, pancreatitis, Addison’s disease, cardiovascular disease, morbid obesity, adrenal insufficiency, elderly, hypothyroidism, urethral stricture, prostatic hyperplasia, debilitated pts, pts with CNS depression, toxic psychosis, seizure disorders, alcoholism.
ACTION
Binds with opioid receptors within CNS, inhibiting ascending pain pathways. Therapeutic Effect: Alters pain perception, emotional response to pain.
PHARMACOKINETICS
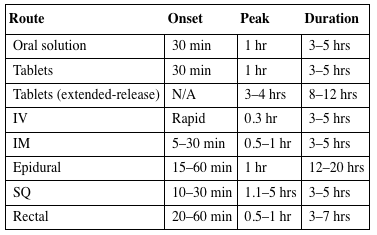
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| Oral solution | 30 min | 1 hr | 3–5 hrs |
| Tablets | 30 min | 1 hr | 3–5 hrs |
| Tablets (extended-release) | N/A | 3–4 hrs | 8–12 hrs |
| IV | Rapid | 0.3 hr | 3–5 hrs |
| IM | 5–30 min | 0.5–1 hr | 3–5 hrs |
| Epidural | 15–60 min | 1 hr | 12–20 hrs |
| SQ | 10–30 min | 1.1–5 hrs | 3–5 hrs |
| Rectal | 20–60 min | 0.5–1 hr | 3–7 hrs |
Variably absorbed from GI tract. Readily absorbed after IM, SQ administration. Protein binding: 20%–35%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2–4 hrs (increased in hepatic disease).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. May prolong labor if administered in latent phase of first stage of labor or before cervical dilation of 4–5 cm has occurred. Respiratory depression may occur in neonate if mother received opiates during labor. Regular use of opiates during pregnancy may produce withdrawal symptoms in neonate (irritability, excessive crying, tremors, hyperactive reflexes, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, yawning, sneezing, seizures). Children: Paradoxical excitement may occur; those younger than 2 yrs are more susceptible to respiratory depressant effects. Elderly: Paradoxical excitement may occur. Age-related renal impairment may increase risk of urinary retention.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants may increase CNS effects, respiratory depression, hypotension. MAOIs may produce serotonin syndrome. (Reduce dosage to ¼ of usual morphine dose). HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum amylase, lipase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution: 2 mg/ml, 4 mg/ml, 5 mg/ml, 10 mg/ml, 15 mg/ml, 25 mg/ml, 50 mg/ml. Injection, Solution (Epidural, Intrathecal, IV Infusion) (Astramorph PF, Duramorph): 0.5 mg/ml, 1 mg/ml. Injection, Solution (Epidural or Intrathecal) (Infumorph): 10 mg/ml, 25 mg/ml. Injection, Solution Patient-Controlled Analgesia (PCA) Pump: 1 mg/ml, 5 mg/ml. Solution Oral: 20 mg/ml, 10 mg/5 ml, 20 mg/5 ml. Suppository: 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg. Tablets: 15 mg, 30 mg.
 Capsules, Extended-Release (Avinza): 30 mg, 45 mg, 60 mg, 75 mg, 90 mg, 120 mg.
Capsules, Extended-Release (Avinza): 30 mg, 45 mg, 60 mg, 75 mg, 90 mg, 120 mg.
 Capsules, Sustained-Release (Kadian): 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 50 mg, 60 mg, 80 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg.
Capsules, Sustained-Release (Kadian): 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 50 mg, 60 mg, 80 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg.
 Tablets, Extended-Release (MS Contin): 15 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release (MS Contin): 15 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • May give undiluted. • For IV injection, may dilute in Sterile Water for Injection or 0.9% NaCl to final concentration of 1–2 mg/ml. • For continuous IV infusion, dilute to concentration of 0.1–1 mg/ml in D5W and give through controlled infusion device.
Rate of Administration • Always administer very slowly. Rapid IV increases risk of severe adverse reactions (apnea, chest wall rigidity, peripheral circulatory collapse, cardiac arrest, anaphylactoid effects).
Storage • Store at room temperature.
IM, SQ
• Administer slowly, rotating injection sites. • Pts with circulatory impairment experience higher risk of overdosage due to delayed absorption of repeated administration.
PO
• May give without regard to food. • Mix liquid form with fruit juice to improve taste. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide extended-release capsule, tablets. • Avinza, Kadian: May mix with applesauce immediately prior to administration.
Rectal
• If suppository is too soft, chill for 30 min in refrigerator or run cold water over foil wrapper. • Moisten suppository with cold water before inserting well into rectum.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), cefepime (Maxipime), doxorubicin (Doxil), phenytoin (Dilantin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), atropine, bumetanide (Bumex), bupivacaine (Marcaine, Sensorcaine), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), glycopyrrolate (Robinul), heparin, hydroxyzine (Vistaril), lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium, midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), nitroglycerin, potassium, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Dosage should be titrated to desired effect.
Analgesia
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 10–30 mg q4h as needed. (Solution): 10–20 mg q4h as needed. (Tablet): 15–30 mg q4h as needed. CHILDREN: 0.15–0.3 mg/kg q3–4h as needed.
◀ ALERT ▶ For the Avinza dosage below, be aware that this drug is to be administered once daily only.
◀ ALERT ▶ For the Kadian dosage information below, be aware that this drug is to be administered q12h or once daily.
◀ ALERT ▶ Be aware that pediatric dosages of extended-release preparations of Kadian and Avinza have not been established.
◀ ALERT ▶ For the MS Contin dosage information below, be aware that the daily dosage is divided and given q8h or q12h.
PO (Extended-Release [Avinza]): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Dosage requirement should be established using prompt-release formulations and is based on total daily dose. Avinza is given once daily only.
PO (Extended-Release [Kadian]): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Dosage requirement should be established using prompt-release formulations and is based on total daily dose. Dose is given once daily or divided and given q12h.
PO (Extended-Release [MS Contin]): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Dosage requirement should be established using prompt-release formulations and is based on total daily dose. Daily dose is divided and given q8h or q12h.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2.5–5 mg q3–4h as needed. Note: Repeated doses (e.g., 1–2 mg) may be given more frequently (e.g., every hr) if needed. CHILDREN: 0.05–0.3 mg/kg q3–4h as needed. NEONATES: Initially, 0.05–0.1 mg/kg/dose q4–6h as needed.
IV Continuous Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.8–10 mg/hr. Range: Titrate up to 80 mg/hr. CHILDREN: Initially, 10–30 mcg/kg/hr. Titrate as needed to control pain. NEONATES: Initially, 0.01 mg/kg/hr (10 mcg/kg/hr). Maximum: 0.015–0.02 mg/kg/hr.
Note: IM injection not recommended
IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–10 mg q3–4h as needed. CHILDREN: 0.1–0.2 mg/kg q3–4h as needed.
Patient-Controlled Analgesia (PCA)
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Usual concentration: 1 mg/ml. Demand dose: 1 mg (range: 0.5–2.5 mg). Lockout interval: 5–10 min.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Dose |
| 10–50 ml/min, CRRT: | 75% of normal dose |
| less than 10 ml/min, HD, PD: | 50% of normal dose |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
◀ ALERT ▶ Ambulatory pts, pts not in severe pain may experience nausea, vomiting more frequently than pts in supine position or who have severe pain. Frequent: Sedation, decreased B/P (including orthostatic hypotension), diaphoresis, facial flushing, constipation, dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting. Occasional: Allergic reaction (rash, pruritus), dyspnea, confusion, palpitations, tremors, urinary retention, abdominal cramps, vision changes, dry mouth, headache, decreased appetite, pain/burning at injection site. Rare: Paralytic ileus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose results in respiratory depression, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold/clammy skin, cyanosis, extreme drowsiness progressing to seizures, stupor, coma. Tolerance to analgesic effect, physical dependence may occur with repeated use. Prolonged duration of action, cumulative effect may occur in those with hepatic/renal impairment. Antidote: Naloxone (see Appendix J for dosage).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Pt should be in recumbent position before drug is given by parenteral route. Assess onset, type, location, duration of pain. Obtain vital signs before giving medication. If respirations are 12/min or less (20/min or less in children), withhold medication, contact physician. Effect of medication is reduced if full pain recurs before next dose.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor vital signs 5–10 min after IV administration, 15–30 min after SQ, IM. Be alert for decreased respirations, B/P. Check for adequate voiding. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency; avoid constipation. Initiate deep breathing, coughing exercises, particularly in those with pulmonary impairment. Assess for clinical improvement, record onset of pain relief. Consult physician if pain relief is not adequate.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Discomfort may occur with injection. • Change positions slowly to avoid orthostatic hypotension. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol, CNS depressants. • Tolerance, dependence may occur with prolonged use of high doses. • Report ineffective pain control, constipation, urinary retention.
moxifloxacin
mox-i-flox-a-sin
(Avelox, Avelox IV, Moxeza, Vigamox)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  May increase risk of tendonitis, tendon rupture (increased with concurrent corticosteroids, organ transplant recipients, those older than 60 yrs). May aggravate myasthenia gravis (avoid use).
May increase risk of tendonitis, tendon rupture (increased with concurrent corticosteroids, organ transplant recipients, those older than 60 yrs). May aggravate myasthenia gravis (avoid use).
Do not confuse Avelox with Avonex.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Fluoroquinolone. CLINICAL: Antibacterial, antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of susceptible infections due to S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, S. aureus, H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis, K. pneumoniae, M. pneumoniae, C. pneumoniae including acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, acute bacterial sinusitis, intra-abdominal infection, community-acquired pneumonia, uncomplicated skin/skin structure infections. Ophthalmic: Topical treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis due to susceptible strains of bacteria. OFF-LABEL: Legionella, pneumonia, tuberculosis (second-line therapy).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to moxifloxacin, other quinolones. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, bradycardia, acute myocardial ischemia, myasthenia gravis, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, seizures, pts with prolonged QT interval, medications known to prolong QT interval, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, elderly, pts with suspected CNS disorder, history of tendon disorders.
ACTION
Inhibits two enzymes, topoisomerase II and IV, in susceptible microorganisms. Therapeutic Effect: Interferes with bacterial DNA replication. Prevents/delays emergence of resistant organisms. Bactericidal.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract after PO administration. Protein binding: 50%. Widely distributed throughout body with tissue concentration often exceeding plasma concentration. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine (20%), feces (25%) unchanged. Half-life: PO: 12 hrs; IV: 15 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May be distributed in breast milk. May produce teratogenic effects. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antacids, iron preparations, sucralfate may decrease absorption. NSAIDs may increase risks of CNS stimulation/seizures. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Infusion (Avelox IV): 400 mg (250 ml). Ophthalmic Solution (Moxeza, Vigamox): 0.5%. Tablets (Avelox): 400 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Available in ready-to-use containers.
Rate of Administration • Give by IV infusion only. • Avoid rapid or bolus IV infusion. • Infuse over 60 min.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Do not refrigerate.
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Oral moxifloxacin should be administered 4 hrs before or 8 hrs after antacids, multivitamins, iron preparations, sucralfate, didanosine chewable/buffered tablets, pediatric powder for oral solution.
Ophthalmic
• Place gloved finger on lower eyelid and pull out until a pocket is formed between eye and lower lid. • Place prescribed number of drops into pocket. • Instruct pt to close eye gently (so medication will not be squeezed out of the sac) and to apply digital pressure to lacrimal sac at inner canthus for 1 min to minimize systemic absorption.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not add or infuse other drugs simultaneously through the same IV line. Flush line before and after use if same IV line is used with other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dose
PO, IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg q24h. Duration dependent on severity of infection.
Acute Bacterial Sinusitis
PO, IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg q24h for 10 days.
Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis
PO, IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg q24h for 5 days.
Community-Acquired Pneumonia
PO, IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg q24h for 7–14 days.
Intra-Abdominal Infection
PO, IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg q24h for 5–14 days.
Skin/Skin Structure Infection
PO, IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg once daily for 7–21 days.
Topical Treatment of Bacterial Conjunctivitis Due to Susceptible Strains of Bacteria
Ophthalmic: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 1 YR AND OLDER: (Vigamox): 1 drop 3 times/day for 7 days. (Moxeza): 1 drop 2 times/day for 7 days.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (8%–6%): Nausea, diarrhea. Occasional: PO, IV (3%–2%): Dizziness, headache, abdominal pain, vomiting. Ophthalmic (6%–1%): Conjunctival irritation, reduced visual acuity, dry eye, keratitis, eye pain, ocular itching, swelling of tissue around cornea, eye discharge, fever, cough, pharyngitis, rash, rhinitis. Rare (1%): Altered taste, dyspepsia, photosensitivity.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Pseudomembranous colitis (severe abdominal cramps/pain, severe watery diarrhea, fever) may occur. Superinfection (anal/genital pruritus, moderate to severe diarrhea, stomatitis) may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of hypersensitivity to moxifloxacin, quinolones.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Assess for headache, abdominal pain, vomiting, altered taste, dyspepsia. Monitor WBC, signs of infection.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• May be taken without regard to food. • Drink plenty of fluids. • Avoid exposure to direct sunlight; may cause photosensitivity reaction. • Do not take antacids 4 hrs before or 8 hrs after dosing. • Take full course of therapy. • Report abdominal cramping/pain, persistent diarrhea.
mupirocin
mue-peer-oh-sin
(Bactroban, Bactroban Nasal)
Do not confuse Bactroban or Bactroban Nasal with bacitracin, baclofen, or Bactrim.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antibacterial. CLINICAL: Topical antibiotic.
USES
Ointment: Topical treatment of impetigo caused by S. aureus, S. pyogenes. Cream: Treatment of traumatic skin lesions due to S. aureus, S. pyogenes. Intranasal ointment: Eradication of S. aureus from nasal, perineal carriage sites. OFF-LABEL: Surgical prophylaxis to prevent wound infections (intranasal).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to mupirocin. Cautions: Renal impairment, burn pts.
ACTION
Inhibits bacterial protein, RNA synthesis. Less effective on DNA synthesis. Nasal: Eradicates nasal colonization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Therapeutic Effect: Prevents bacterial growth, replication. Bacteriostatic.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Following topical administration, penetrates outer layer of skin (minimal through intact skin). Protein binding: 95%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 17–36 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Cream, Topical (Bactroban): 2%. Ointment, Intranasal (1-g single-use tube) (Bactroban Nasal): 2%. Ointment, Topical (Bactroban): 2%.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Topical
Cream, Ointment • For topical use only. • May cover with gauze dressing. • Avoid contact with eyes.
Intranasal
• Apply ½ of the ointment from single-use tube into each nostril. • Avoid contact with eyes.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Topical Dosage
Topical Cream: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 3 MOS AND OLDER: Apply small amount 3 times/day for 10 days. Topical Ointment: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 2 MOS AND OLDER: Apply small amount 3 times/day for 5–14 days.
Usual Nasal Dosage
Intranasal: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: Apply small amount 2 times/day for 5–10 days.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Nasal (9%–3%): Headache, rhinitis, upper respiratory congestion, pharyngitis, altered taste. Occasional: Nasal (2%): Burning, stinging, cough. Topical (2%–1%): Pain, burning, stinging, pruritus. Rare: Nasal (less than 1%): Pruritus, diarrhea, dry mouth, epistaxis, nausea, rash. Topical (less than 1%): Rash, nausea, dry skin, contact dermatitis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Superinfection may result in bacterial, fungal infections, esp. with prolonged, repeated therapy.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess skin for type, extent of lesions.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor healing of skin lesions. In event of skin reaction, stop applications, cleanse area gently, notify physician.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• For external use only. • Avoid contact with eyes. • Explain precautions to avoid spread of infection; teach how to apply medication. • Report skin reactions, irritation. • Report if no improvement is noted in 3–5 days.
mycophenolate
mye-koe-fen-o-late
(Apo-Mycophenolate
 , CellCept, Myfortic, Novo-Mycophenolate)
, CellCept, Myfortic, Novo-Mycophenolate)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Increased risk of congenital malformation, spontaneous abortion. Increased risk for development of lymphoma, skin malignancy. Increased susceptibility to infections. Administer under supervision of physician experienced in immunosuppressive therapy.
Increased risk of congenital malformation, spontaneous abortion. Increased risk for development of lymphoma, skin malignancy. Increased susceptibility to infections. Administer under supervision of physician experienced in immunosuppressive therapy.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Immunologic agent. CLINICAL: Immunosuppressant.
USES
Should be used concurrently with cyclosporine and corticosteroids. CellCept: Prophylaxis of organ rejection in pts receiving allogeneic hepatic/renal/cardiac transplant. Myfortic: Renal transplants. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of hepatic transplant rejection in pts unable to tolerate tacrolimus or cyclosporine due to toxicity, mild heart transplant rejection, moderate to severe psoriasis, proliferative lupus nephritis, myasthenia gravis, graft-vs-host disease. Treatment of autoimmune hepatitis (refractory).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to mycophenolic acid or polysorbate 80 (IV formulation). Cautions: Active severe GI disease, renal impairment, neutropenia, women of childbearing potential (use caution when handling).
ACTION
Suppresses immunologically-mediated inflammatory response by inhibiting inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, an enzyme that deprives lymphocytes of nucleotides necessary for DNA, RNA synthesis, thus inhibiting proliferation of T and B lymphocytes. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents transplant rejection.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly, extensively absorbed after PO administration (food decreases drug plasma concentration but does not affect absorption). Protein binding: 97%. Completely hydrolyzed to active metabolite mycophenolic acid. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 17.9 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Increased risk of miscarriage, birth defects. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentrations of acyclovir, ganciclovir in pts with renal impairment. Antacids (aluminum- and magnesium-containing), cholestyramine may decrease absorption. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. Other immunosuppressants (e.g., cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, tacrolimus) may increase risk of infection, lymphomas. Probenecid may increase concentration. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, echinacea may decrease effects (have immunostimulant properties). FOOD: All foods may decrease concentration. LAB VALUES: May increase serum cholesterol, alkaline phosphatase, creatinine, ALT, AST. May alter serum glucose, lipids, calcium, potassium, phosphate, uric acid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules (CellCept): 250 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (CellCept): 500 mg. Oral Suspension (CellCept): 200 mg/ml. Tablets (CellCept): 500 mg.
 Tablets (Delayed-Release [Myfortic]): 180 mg, 360 mg.
Tablets (Delayed-Release [Myfortic]): 180 mg, 360 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute each 500-mg vial with 14 ml D5W. Gently agitate. • For 1-g dose, further dilute with 140 ml D5W; for 1.5-g dose further dilute with 210 ml D5W, providing a concentration of 6 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over at least 2 hrs. • Begin infusion within 4 hrs of reconstitution.
Storage • Store at room temperature.
PO
• Give on empty stomach (1 hr before or 2 hrs after food). • Do not break, crush, or open capsules or break, crush, dissolve, or divide delayed-release tablets. Avoid inhalation of powder in capsules, direct contact of powder on skin/mucous membranes. If contact occurs, wash thoroughly, with soap, water. Rinse eyes profusely with plain water. • May store reconstituted suspension in refrigerator or at room temperature. • Suspension is stable for 60 days after reconstitution. • Suspension can be administered orally or via an NG tube (minimum size 8 French).
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Mycophenolate is compatible only with D5W. Do not infuse concurrently with other drugs or IV solutions.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Prevention of Renal Transplant Rejection
PO, IV (Cellcept): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1 g twice daily. PO: CHILDREN (Cellcept Suspension): 600 mg/m2/dose twice daily. Maximum: 1 g twice daily.
PO (Myfortic): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 720 mg twice daily. CHILDREN 5–16 YRS: 400 mg/m2 twice daily. Maximum: 720 mg twice daily.
Prevention of Heart Transplant Rejection
PO, IV (Cellcept): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1.5 g twice daily.
Prevention of Hepatic Transplant Rejection
PO (Cellcept): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1.5 g twice daily.
IV (Cellcept): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1 g twice daily.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (37%–20%): UTI, hypertension, peripheral edema, diarrhea, constipation, fever, headache, nausea. Occasional (18%–10%): Dyspepsia, dyspnea, cough, hematuria, asthenia, vomiting, edema, tremors, abdominal, chest, back pain; oral candidiasis, acne. Rare (9%–6%): Insomnia, respiratory tract infection, rash, dizziness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Significant anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, leukocytosis may occur, particularly in those undergoing renal transplant rejection. Sepsis, infection occur occasionally. GI tract hemorrhage occurs rarely. There is an increased risk of developing neoplasms. Immunosuppression results in increased susceptibility to infection.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Women of childbearing potential should have a negative serum or urine pregnancy test within 1 wk before initiation. Assess medical history, esp. renal function, existence of active digestive system disease, drug history, esp. other immunosuppressants.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
CBC should be performed wkly during first mo of therapy, twice monthly during second and third mos of treatment, then monthly throughout the first yr. If rapid fall in WBC occurs, dosage should be reduced or discontinued. Assess particularly for delayed bone marrow suppression. Report any major change in assessment of pt.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Effective contraception should be used before, during, and for 6 wks after discontinuing therapy, even if pt has a history of infertility, other than hysterectomy. • Two forms of contraception must be used concurrently unless abstinence is absolute. • Report unusual bleeding/bruising, sore throat, mouth sores, abdominal pain, fever. • Laboratory follow-up while taking medication is important part of therapy. • Malignancies may occur.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS![]() Tablets, Extended-Release: 25 mg, 50 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release: 25 mg, 50 mg.