Hepatotoxicity occurs rarely. May cause/worsen macular edema. Increased risk of HF. May increase risk of fractures. Pts with ischemic heart disease are at high risk of MI.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline chemistries, esp. LFT, before initiating therapy and periodically thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum glucose, Hgb A1c, LFT. Assess for hypoglycemia (cool/wet skin, tremors, dizziness, anxiety, headache, tachycardia, numbness in mouth, hunger, diplopia), hyperglycemia (polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, nausea, vomiting, dim vision, fatigue, deep rapid breathing). Be alert to conditions that alter serum glucose requirements: fever, increased activity, trauma, stress, surgical procedures. Monitor for signs/symptoms of HF.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Be alert for signs/symptoms of hypoglycemia and take measures to manage it. • Avoid alcohol. • Report chest pain, palpitations, abdominal pain, fever, rash, hypoglycemic reactions, yellowing of skin/eyes, dark urine, light stool, nausea, vomiting. • Report any change in vision. • Report rapid weight gain, edema, difficulty breathing. • Ensure follow-up instruction if pt, family do not thoroughly understand diabetes management, glucose-testing technique.
piperacillin sodium/tazobactam sodium
pye-per-a-sil-in/tay-zoe-bak-tam
(Tazocin
 , Zosyn)
, Zosyn)
Do not confuse Zosyn with Zofran or Zyvox.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Penicillin. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of moderate to severe bacterial infections, including community-acquired/nosocomial pneumonia, intraabdominal, pelvic, skin, and skin structure infections. Tazobactam expands piperacillin activity to include beta-lactamase-producing strains of S. aureus, H. influenzae, Bacteroides. OFF-LABEL: Surgical prophylaxis, complicated intra-abdominal infections.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to piperacillin/tazobactam, any penicillin. Cautions: History of allergies (esp. cephalosporins, other drugs), renal impairment, preexisting seizure disorder.
ACTION
Piperacillin: Inhibits cell wall synthesis by binding to bacterial cell membranes. Therapeutic Effect: Bactericidal. Tazobactam: Inactivates bacterial beta-lactamase. Therapeutic Effect: Protects piperacillin from enzymatic degradation, extends its spectrum of activity, prevents bacterial overgrowth.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Protein binding: 16%–30%. Widely distributed. Primarily excreted unchanged in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 0.7–1.2 hrs (increased in hepatic cirrhosis, renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Readily crosses placenta; appears in cord blood, amniotic fluid. Distributed in breast milk in low concentrations. May lead to allergic sensitization, diarrhea, candidiasis, skin rash in infant. Children: Dosage not established for pts younger than 12 yrs. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Concurrent use of aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin, tobramycin) may cause mutual inactivation (must give at least 1 hr apart). May increase concentration, toxicity of methotrexate. Probenecid may increase concentration, risk of toxicity. High-dose piperacillin may increase risk of bleeding with heparin, NSAIDs, platelet inhibitors (e.g., aspirin, clopidogrel), thrombolytic agents (e.g., alteplase), warfarin. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum sodium, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, LDH, ALT, AST, BUN, creatinine, PT, PTT. May decrease serum potassium. May cause positive Coombs’ test.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
◀ ALERT ▶ Piperacillin/tazobactam is a combination product in an 8:1 ratio of piperacillin to tazobactam. Injection Powder: 2.25 g, 3.375 g, 4.5 g. Premix Ready to Use: 2.25 g (50 ml), 3.375 g (50 ml), 4.5 g (100 ml).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute each 1 g with 5 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl. Shake vigorously to dissolve. • Further dilute with at least 50 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 30 min. Expanded infusion over 3–4 hrs.
Storage • Reconstituted vial is stable for 24 hrs at room temperature or 48 hrs if refrigerated. • After further dilution, stable for 24 hrs at room temperature or 7 days if refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B (Fungizone), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), famotidine (Pepcid), haloperidol (Haldol), hydroxyzine (Vistaril), vancomycin (Vancocin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Bumetanide (Bumex), calcium gluconate, dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dopamine (Intropin), enalapril (Vasotec), furosemide (Lasix), granisetron (Kytril), heparin, hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), metoclopramide (Reglan), morphine, ondansetron (Zofran), potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Extended Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 3.375–4.5 g over 4 hrs q8h.
Usual Dosage
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER WEIGHING MORE THAN 40 KG: 4.5 g q6–8h or 3.375 g q6h. Maximum: 18 g daily. CHILDREN 9 MOS AND OLDER AND 40 KG OR LESS: 100 mg piperacillin component/kg/dose q8h. Maximum: 16 g/day. CHILDREN 2–8 MOS: 80 mg piperacillin component/kg/dose q8h. NEONATES: 75–100 mg piperacillin component/kg/dose q6–12h.
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 20–40 ml/min | 2.25 g q6h (3.375 g q6h for nosocomial pneumonia) |
| Less than 20 ml/min | 2.25 g q8h (2.25 g q6h for nosocomial pneumonia) |
| Extended Infusion 3.375 g q12h |
Dosage for Hemodialysis
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2.25 g q8–12h with additional dose of 0.75 g after each dialysis session.
Dosage for CRRT
| CVVH | 2.25–3.375 g q6–8h |
| CVVHD | 2.25–3.375 g q6h |
| CVVHDF | 3.375 g q6h |
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage and frequency are modified based on creatinine clearance.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Diarrhea, headache, constipation, nausea, insomnia, rash. Occasional: Vomiting, dyspepsia, pruritus, fever, agitation, candidiasis, dizziness, abdominal pain, edema, anxiety, dyspnea, rhinitis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Antibiotic-associated colitis, other superinfections (abdominal cramps, severe watery diarrhea, fever) may result from altered bacterial balance in GI tract. Overdose, more often with renal impairment, may produce seizures, neurologic reactions. Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of allergies, esp. to penicillins, cephalosporins.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency; mild GI effects may be tolerable, but increasing severity may indicate onset of antibiotic-associated colitis. Be alert for superinfection: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, anal/genital pruritus, oral mucosal changes (ulceration, pain, erythema). Monitor I&O, urinalysis. Monitor serum electrolytes, esp. potassium, renal function tests.
piroxicam
peer-ox-i-kam
(Apo-Piroxicam
 , Feldene)
, Feldene)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  May increase risk of serious, potentially fatal cardiovascular thrombotic events, MI, stroke. Increased risk of serious GI events (bleeding, ulceration, perforation).
May increase risk of serious, potentially fatal cardiovascular thrombotic events, MI, stroke. Increased risk of serious GI events (bleeding, ulceration, perforation).
Do not confuse Feldene with fluoxetine, or piroxicam with paroxetine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: NSAID. CLINICAL: Anti-inflammatory, analgesic.
USES
Management of acute or chronic rheumatoid arthritis (RA), osteoarthritis. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to piroxicam. Perioperative pain in setting of CABG surgery, history of hypersensitivity to aspirin/NSAIDs, active GI bleeding. Pts with aspirin triad (asthma, rhinitis, and aspirin intolerance). Cautions: Advanced renal disease, hepatic impairment, asthma, coagulation disorders, concomitant use of anticoagulants, poor CYP2C9 metabolizers. History of GI bleeding or ulcers, alcohol abuse. Avoid use in late pregnancy.
ACTION
Produces analgesic, anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces inflammatory response, intensity of pain.
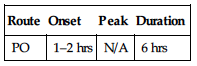
PHARMACOKINETICS
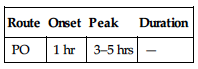
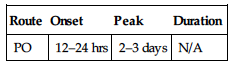
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 1 hr | 3–5 hrs | — |
Well absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine; small amount eliminated in feces. Half-life: 50 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Avoid use during third trimester (may adversely affect fetal cardiovascular system: premature closing of ductus arteriosus). Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may increase risk of hepatotoxicity, renal toxicity; reduced dosage recommended. More likely to have serious adverse effects with GI bleeding/ulceration.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of antihypertensives (e.g., amlodipine, lisinopril, valsartan), diuretics (e.g., furosemide, HCTZ). Aspirin, other salicylates may increase risk of GI side effects, bleeding. May increase effects of heparin, oral anticoagulants (e.g., rivaroxaban, warfarin), thrombolytics (e.g., alteplase). May increase concentration, risk of toxicity of lithium, methotrexate. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo, ginseng, horse chestnut, red clover possess antiplatelet activity, may increase risk of bleeding. St. John’s wort may increase risk of phototoxicity. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, creatinine, LDH, alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST. May decrease serum uric acid, Hgb, Hct, platelets, leukocytes.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Capsules: 10 mg, 20 mg.
Capsules: 10 mg, 20 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Do not break, crush, or open capsules. • May give with food, milk, antacids if GI distress occurs.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Osteoarthritis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10–20 mg/day as a single dose or in divided doses. Maximum: 20 mg/day. CHILDREN: (Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis) 0.2–0.4 mg/kg/day. Maximum: 15 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Not recommended.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (9%–4%): Dyspepsia, nausea, dizziness. Occasional (3%–1%): Diarrhea, constipation, abdominal cramps/pain, flatulence, stomatitis. Rare (less than 1%): Hypertension, urticaria, dysuria, ecchymosis, blurred vision, insomnia, phototoxicity.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Peptic ulcer, GI bleeding, gastritis, severe hepatic reaction (cholestasis, jaundice) occur rarely. Nephrotoxicity (dysuria, hematuria, proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome), hematologic toxicity (anemia, leukopenia, eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia), severe hypersensitivity reaction (fever, chills, bronchospasm) occur rarely with long-term treatment.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess onset, type, location, duration of pain/inflammation. Inspect appearance of affected joints for immobility, deformities, skin condition.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor for evidence of nausea, GI distress. Assess for therapeutic response: relief of pain, stiffness, swelling; increased joint mobility; reduced joint tenderness; improved grip strength. Monitor CBC, renal/hepatic function tests.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid aspirin, alcohol during therapy (increases risk of GI bleeding). • If GI upset occurs, take with food, milk, antacids. • Avoid tasks that require alertness until response to drug is established.
pitavastatin
pit-av-a-stat-in
(Livalo)
Do not confuse pitavastatin with atorvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, or simvastatin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antihyperlipidemic.
USES
Reduces elevated total cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins (LDLs), apolipoprotein B, triglycerides; increases low high-density lipoproteins (HDLs) in primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia. OFF-LABEL: Primary and secondary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to pitavastatin. Active hepatic disease, persistent or unexplained elevations of LFT; concurrent cyclosporine use, pregnancy, breastfeeding. Cautions: History of hepatic disease, substantial alcohol consumption, moderate renal impairment. Withholding/discontinuing pitavastatin may be necessary when pt at risk for renal failure. Pts at risk for myopathy: elderly, renal impairment, inadequately treated hypothyroidism.
ACTION
Interferes with cholesterol biosynthesis by inhibiting conversion of HMG-CoA reductase to a precursor to cholesterol. Therapeutic Effect: Lowers total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein B (Apo B), plasma triglycerides; increases HDL cholesterol.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Poorly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: greater than 99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in feces. Half-life: 12 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Contraindicated in pregnancy (suppression of cholesterol biosynthesis may cause fetal toxicity) and lactation. Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk (risk of serious adverse reactions in nursing infants). Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS:
DRUG: Increased risk of rhabdomyolysis, acute renal failure with gemfibrozil, niacin, other fibrates. Cyclosporine, erythromycin, rifampin may increase serum pitavastatin levels. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum creatine kinase (CPK), ALT, AST concentrations.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 1 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals or time of day.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Before initiating therapy, pt should be on standard cholesterol-lowering diet for minimum of 3–6 mos. Continue diet throughout pitavastatin therapy.
Usual Dosage
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 2 mg/day. Maximum: 4 mg/day. Range: 1–4 mg/day. Maximum dosage with erythromycin: 1 mg/day; with rifampin: 2 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl 30–59, 15–60 ml/min not receiving hemodialysis, or end-stage renal disease in pts on hemodialysis: Initially, 1 mg/day. Maximum: 2 mg/day.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
See contraindications.
SIDE EFFECTS
Generally well tolerated. Side effects usually mild and transient. Rare (Less Than 4%): Myalgia, constipation/diarrhea, back/extremity pain, arthralgia, headache, nasopharyngitis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hypersensitivity (rash, pruritus, urticaria) occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain LFT, serum cholesterol, triglycerides. Question for possibility of pregnancy before initiating therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor cholesterol and triglyceride levels; LFT. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Check for myalgia, arthralgia, headache. Assess for rash, pruritus. Be alert for malaise, muscle cramping/weakness.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Follow special diet (important part of treatment). • Periodic lab tests are essential part of therapy. • Report promptly any muscle pain/weakness. • Use nonhormonal contraception.
plerixafor
pler-ix-a-for
(Mozobil)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Chemokine receptor inhibitor. CLINICAL: Hematopoietic stem cell mobilizer.
USES
Indicated in combination with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) to mobilize stem cells to peripheral blood for collection and transplantation in pts with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and multiple myeloma.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to plerixafor. Cautions: Avoid use in leukemic pts, in pts with neutrophil count greater than 50,000/mm3, those with moderate to severe renal impairment.
ACTION
Immobilizes hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow. Once in the marrow, acts to help anchor these cells to marrow matrix through induction of adhesion molecules. Therapeutic Effect: Results in leukocytosis, elevation in circulating hematopoietic progenitor cells in peripheral blood system.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed after SQ administration. Generally confines to extravascular fluid space. Protein binding: 58%. Peak plasma concentration: 30–60 min. Eliminated in urine. Clearance reduced with renal impairment. Half-life: 3–5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Potential for teratogenic effects. May cause fetal harm. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase WBC count. May decrease platelet count.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 24 mg/1.2 ml vial.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
SQ
• Aspirate syringe before injection (avoid intra-arterial administration).
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Discard if particulate matter is present or if solution is discolored. • Use single-dose vial; discard unused drug.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Begin therapy after pt has received daily morning doses of G-CSF, 10 mcg/kg once daily for 4 days prior to the first evening dose of plerixafor and approximately 11 hrs prior to initiation of apheresis for up to 4 consecutive days.
Daily Dosage
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY (WEIGHING MORE THAN 83 KG): 0.24 mg/kg once daily (about 11 hrs prior to apheresis) for up to 4 consecutive days. Maximum: 40 mg/day. (83 KG or LESS): 20 mg fixed dose or 0.24 mg/kg once daily for up to 4 consecutive days.
Dosage in Moderate to Severe Renal Impairment (CrCl Equal to or Less Than 50 ml/min):
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY (WEIGHING MORE THAN 83 KG): Decrease dose to 0.16 mg/kg, not to exceed 27 mg/day. (83 KG OR LESS): 13 mg fixed dose or 0.16 mg/kg once daily.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (37%–22%): Diarrhea, nausea, injection site irritation, fatigue, headache. Occasional (13%–7%): Arthralgia, dizziness, vomiting, insomnia, flatulence.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Thrombocytopenia may occur. Dyspnea, hypoxia, vasovagal reaction, periorbital edema, urticaria have been noted; may resolve spontaneously, generally responds to antihistamines, corticosteroids.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC, renal function test in pts with renal impairment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor WBC, platelet count. Assess for potential systemic reaction (periorbital edema, dyspnea, urticaria), orthostatic hypotension during or shortly after injection. Advise female pt with reproductive potential to use effective contraceptive method.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Manage gastrointestinal disorders; report severe diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. • Report upper quadrant pain or scapular/shoulder pain.
polyethylene glycol-electrolyte solution (PEG-ES) (CoLyte, GoLYTELY)
pol-ee-eth-il-een-glye-kol
(CoLyte, GoLYTELY, Klean-Prep
 , MiraLax, NuLytely, Peglyte
, MiraLax, NuLytely, Peglyte
 , TriLyte)
, TriLyte)
Do not confuse MiraLax with Mirapex.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Osmotic/laxative. CLINICAL: Bowel evacuant.
USES
Polyethylene glycol-electrolyte solution: Bowel cleansing before GI examination, colon surgery. Polyethylene glycol: Treatment of occasional constipation.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to polyethylene glycol. Bowel perforation, gastric retention, GI obstruction, megacolon, toxic colitis, toxic ileus. Cautions: (Propylene glycol): Renal impairment. (Propylene glycol–electrolyte solution): Ulcerative colitis, medications altering electrolytes, hyponatremia, cardiac arrhythmias, impaired gag reflex, history of seizures, elderly.
ACTION
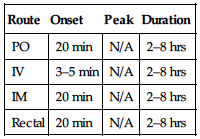
Osmotic effect. Therapeutic Effect: Induces diarrhea, cleanses bowel without depleting electrolytes.
PHARMACOKINETICS
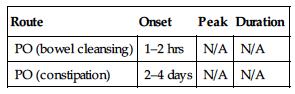
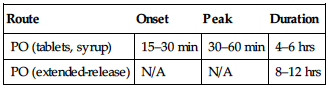
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO (bowel cleansing) | 1–2 hrs | N/A | N/A |
| PO (constipation) | 2–4 days | N/A | N/A |
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease absorption of oral medications if given within 1 hr (may be flushed from GI tract). HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Powder for Oral Solution: Propylene glycol (Miralax): 17 g/dose. Propylene glycol–electrolyte solution (CoLyte, GoLYTELY): See individual product for specific ingredients.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
Polyethylene Glycol-Electrolyte Solution
• Refrigerate reconstituted solutions; use within 48 hrs. • May use tap water to prepare solution. Shake vigorously for several min to ensure complete dissolution of powder. • Fasting should occur for more than 3 hrs prior to ingestion of solution (always avoid solid food less than 2 hrs prior to administration). • Only clear liquids permitted after administration. • May give via NG tube. • Rapid drinking preferred. Chilled solution is more palatable.
Polyethylene Glycol
• Add to 4- to 8-oz beverage.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Bowel Evacuant
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Before GI examination: 240 ml (8 oz) q10min until 4 L consumed or rectal effluent clear. NG tube: 20–30 ml/min until 4 L given. CHILDREN 6 MOS AND OLDER: 25 ml/kg/hr until rectal effluent clear. Maximum: 4 L.
Constipation
PO (Miralax): ADULTS: 17 g or 1 heaping tbsp/day. CHILDREN 6 MOS AND OLDER: 0.5–1.5 g/kg/day. Maximum: 17 g/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (50%): Some degree of abdominal fullness, nausea, bloating. Occasional (10%–1%): Abdominal cramping, vomiting, anal irritation. Rare (less than 1%): Urticaria, rhinorrhea, dermatitis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
None known.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Do not give oral medication within 1 hr of start of therapy (may not adequately be absorbed before GI cleansing).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess bowel sounds for peristalsis. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess for abdominal disturbances. Monitor serum electrolytes.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• May take 2–4 days to produce a bowel movement. • Report unusual cramps, bloating, diarrhea.
pomalidomide
poe-ma-lid-oh-mide
(Pomalyst)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  May cause life-threatening birth defects. Pregnancy contraindicated. Exclude pregnancy before initiating treatment. Females of reproductive potential must use two reliable forms of contraception or continuously abstain during treatment and for 4 wks after treatment. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism may occur. Consider venous thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis during treatment.
May cause life-threatening birth defects. Pregnancy contraindicated. Exclude pregnancy before initiating treatment. Females of reproductive potential must use two reliable forms of contraception or continuously abstain during treatment and for 4 wks after treatment. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism may occur. Consider venous thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis during treatment.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Thalidomide analogue. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of multiple myeloma in pts who have received at least two prior therapies including lenalidomide and bortezomib and have demonstrated disease progression on or within 60 days of completion of the last therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
◀ ALERT ▶ Do not donate blood products.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to pomalidomide. Cautions: Anemia, HF, hepatic/renal impairment, smoking, breastfeeding, or prior history of CVA, MI, DVT, PE.
ACTION
Inhibits tumor cell proliferation and induces apoptosis (cell death) of hematopoietic cells. Enhances T-cell– and natural killer (NK) cell–mediated immunity. Inhibits proinflammatory cytokines. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis. Promotes tumor cell death.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed following PO administration. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 12%–44%. Peak plasma concentration: 2–3 hrs. Eliminated in urine (73%), feces (15%). Half-life: 8–10 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Pregnancy/breastfeeding contraindicated. May cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Do not breastfeed. Must verify negative pregnancy status before initiation. Must use two reliable forms of birth control (intrauterine device [IUD], tubal ligation) plus barrier methods. Avoid pregnancy for at least 4 wks after discontinuation. Males: Must use condoms during treatment and up to 1 mo after treatment, despite prior history of vasectomy. Do not donate sperm. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May have increased risk of serious adverse effects, renal failure, electrolyte imbalance.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4, P-glycoprotein inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin, ketoconazole) may increase concentration/effects. CYP3A4, P-glycoprotein inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: All foods may reduce absorption/concentration. LAB VALUES: May decrease Hgb, Hct, neutrophils, platelets, leukocytes, lymphocytes, serum calcium, potassium, sodium. May increase serum calcium, creatinine, glucose.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Capsules: 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, 4 mg.
Capsules: 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, 4 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Do not break, crush, or open capsule. • Give on empty stomach; must administer at least 2 hrs before or 2 hrs after meal.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) should be 500 cells/mm3 or greater and platelets 50,000 cells/mm3 or greater prior to starting new cycles of therapy.
Multiple Myeloma
PO: ADULTS/ELDERLY: 4 mg once daily on days 1–21 of 28-day cycle (in combination with dexamethasone).
Dose Modification
Neutropenia
ANC less than 500/mm3 or febrile neutropenia: Interrupt treatment until ANC is greater than 500/mm3, then reduce dose to 3 mg once daily. Any subsequent drop of ANC less than 500/mm3 after prior reduction: Interrupt treatment until ANC is greater than 500/mm3, then reduce dose at 1 mg less than previous dose. Discontinue if 1-mg dose is intolerable.
Thrombocytopenia
Platelet count less than 25,000/mm3: Interrupt treatment until platelet count greater than 50,000/mm3, then reduce dose to 3 mg once daily. Any subsequent platelet drop to less than 25,000/mm3: Interrupt treatment until platelet count greater than 50,000-mm3, then reduce dose at 1 mg less than previous dose. Discontinue if 1-mg dose is intolerable.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Avoid use in pts with serum creatinine more than 3 mg/dL or CrCl less than 45 ml/min.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use with bilirubin more than 2 mg/dL and ALT, AST more than 3 times upper limit of normal (ULN).
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (55%–22%): Fatigue, constipation, nausea, diarrhea, dyspnea, back pain, peripheral edema, musculoskeletal chest pain, anorexia, rash. Occasional (20%–7%): Dizziness, pyrexia, muscle spasms, arthralgia, pruritus, vomiting, cough, weight loss, headache, bone pain, muscular weakness, anxiety, musculoskeletal pain, peripheral neuropathy, chills, dry skin, tremor, insomnia. Rare (6%–1%): Hyperhidrosis, extremity pain, back pain, night sweats, constipation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Neutropenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia is an expected outcome of therapy; may increase risk of infection such as pneumonia, upper respiratory tract infection, UTI. Neurologic events such as acute confusion, dizziness reported. Peripheral neuropathy occurred in 18% of pts. Venous thromboembolism including DVT, PE occurred in 3% of pts. Epistaxis occurred in 15% of pts. Increased risk of secondary malignancies reported. Acute renal failure reported in 16% of pts. Additional adverse events may include interstitial lung disease (ILD), neutropenic sepsis, Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, respiratory syncytial virus infection, urinary retention, vertigo.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain vital signs, CBC with differential, serum chemistries, esp. magnesium, phosphate, ionized calcium, PT/INR, urinalysis. Confirm negative pregnancy status 10–14 days before and 24 hrs before starting treatment. Receive full medication history. Obtain baseline neurologic exam. Question history of diabetes mellitus, electrolyte imbalance, hepatic/renal impairment, pulmonary disease, thromboembolism, smoking.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor CBC, serum chemistries, PT/INR. Offer antiemetics for nausea, vomiting. Monitor pregnancy status every mo during treatment and for at least 4 mos after discontinuation. Obtain EKG for palpitation, chest pain, hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, bradycardia, ventricular arrhythmias. Immediately report dyspnea, chest pain, hypoxia, unilateral peripheral edema/pain (may indicate thromboembolic event). Consider sequential compression device (SCD) for immobilized pts. Perform routine neurologic assessments to screen for confusion, delirium. Monitor urine output, frequency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Blood levels will be routinely monitored. • May cause birth defects or miscarriage. Do not breastfeed. Consult with gynecologist for appropriate birth control methods. Female pts must use contraception during treatment and for at least 1 mo after treatment. Immediately report suspected pregnancy. Male pts must use condoms with spermicide during sexual activity, despite history of vasectomy. • Do not donate blood. • Swallow capsules whole; do not break, crush, or open. • Go from lying to standing slowly (prevents postural hypotension, dizziness). Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Do not smoke. • Do not eat 2 hrs before or 2 hrs after dose. • Avoid alcohol. • Report difficulty breathing, chest pain, extremity pain or swelling, dizziness, confusion.
posaconazole
poe-sa-kon-a-zole
(Noxafil, Posanol
 )
)
Do not confuse Noxafil with minoxidil.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Azole derivative. CLINICAL: Antifungal.
USES
Prophylaxis of invasive Aspergillus and Candida infections in pts 13 yrs and older who are at high risk for developing these infections due to severely immunocompromised conditions. Treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis. OFF-LABEL: Salvage therapy of refractory invasive fungal infections, mucomycosis, pulmonary infections.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to posaconazole, other azole antifungals. Coadministration with pimozide, quinidine (may cause QT prolongation, torsades de pointes), HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors metabolized by CYP3A4 (e.g., atorvastatin, simvastatin), sirolimus, ergot alkaloids. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, pts at increased risk of arrhythmias. Concomitant administration of medications that prolong QT interval, pts with long QT syndrome.
ACTION
Inhibits synthesis of ergosterol, a vital component of fungal cell wall formation. Therapeutic Effect: Damages fungal cell wall membrane, altering its function.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Moderately absorbed following PO administration. Absorption increased if drug is taken with food. Widely distributed. Protein binding: 98%. Not significantly metabolized. Primarily excreted in feces. Half-life: 20–66 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 13 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentrations of atorvastatin, cyclosporine, ergot alkaloids, felodipine, midazolam, phenytoin, pimozide, quinidine, rifabutin, simvastatin, sirolimus, tacrolimus, vinblastine, vincristine. Cimetidine, phenytoin may decrease concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: Concentration higher when given with food or nutritional supplements. Grapefruit products may decrease concentration/effects. LAB VALUES: May decrease WBC, RBC, Hgb, Hct, platelets, serum calcium, potassium, magnesium. May increase serum glucose, bilirubin, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 300 mg/16.7 ml (18 mg/ml). Oral Suspension: 40 mg/ml.
 Tablets (Delayed-Release): 100 mg.
Tablets (Delayed-Release): 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Transfer 300 mg (16.7 ml) posaconazole into 150 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl bag.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 90 min via central venous line.
Storage • Refrigerate vials. Once diluted, use immediately. May refrigerate solution up to 24 hrs if not used immediately.
PO
• Administer with or within 20 min of full meal, liquid nutritional supplement, or acidic carbonated beverage (e.g., ginger ale) (enhances absorption). • Store oral suspension at room temperature. • Shake suspension well before use. Tablets • Swallow whole; do not crush, cut, dissolve, or divide. Administer with food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Prophylaxis of Invasive Aspergillus and Candida
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 13 YRS AND OLDER: (Oral Suspension): 200 mg (5 ml) 3 times/day, given with full meal or liquid nutritional supplement.(Delayed-Release):300 mg twice daily on first day, then 300 mg once daily IV: 300 mg twice daily on first day, then 300 mg once daily thereafter.
Oropharyngeal Candidiasis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 13 YRS AND OLDER: 100 mg twice daily for 1 day, then 100 mg once daily for 13 days.
Refractory Oropharyngeal Candidiasis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 400 mg twice daily for 3 days, then 400 mg once daily for up to 28 days. HIV-Infected Pts: 400 mg twice daily on day 1, then 400 mg once daily for 7–14 days (28 days in azole refractory pts).
Dosage in Renal Impairment
PO: No dose adjustment. IV: Avoid use in pts with CrCl less than 50 ml/min.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Common (42%–24%): Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, abdominal pain, cough. Frequent (20%–15%): Constipation, rigors, rash, hypertension, fatigue, insomnia, mucositis, musculoskeletal pain, edema of lower extremities, herpes simplex, anorexia. Occasional (14%–8%): Hypotension, epistaxis, tachycardia, pharyngitis, dizziness, pruritus, arthralgia, dyspepsia, back pain, generalized edema, weakness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Bacteremia occurs in 18% of pts; upper respiratory tract infection occurs in 7%. Allergic/hypersensitivity reactions, QT prolongation, hemolytic uremic syndrome, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, pulmonary embolus have been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain BMP, LFT. Receive full medication history and screen for interactions (esp. drugs known to prolong QT interval).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor LFT periodically. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Obtain order for antiemetic if excessive vomiting occurs. Monitor B/P for hypertension, hypotension. Assess for lower extremity edema.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take each dose with full meal or liquid nutritional supplement. • Report severe diarrhea, vomiting, chest pain, yellowing of skin/eyes. • Maintain strict oral hygiene.
potassium acetate

potassium bicarbonate/citrate
(Effer-K, Klor-Con EF)
potassium chloride
(Apo-K
 , Kaon-Cl, Klor-Con, Klor-Con M10, Klor-Con M20, Micro-K)
, Kaon-Cl, Klor-Con, Klor-Con M10, Klor-Con M20, Micro-K)
poe-tass-ee-um
Do not confuse Micro-K with Macrobid or Micronase.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Electrolyte. CLINICAL: Potassium replenisher.
USES
Potassium acetate, potassium bicarbonate/citrate: Treatment, prevention of hypokalemia when necessary to avoid chloride or acid/base imbalance (requires bicarbonate). Potassium chloride: Treatment, prevention of hypokalemia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Severe renal impairment, hyperkalemia. Solid oral dosage form in pts where there is structural, pathologic cause for delay in passage through GI tract. Cautions: Cardiac disease, acid-base disorders, potassium-altering disorders, digitalized pts, concomitant therapy that increases serum potassium (e.g., ACE inhibitors), renal impairment. Do not administer IV undiluted.
ACTION
Necessary for multiple cellular metabolic processes. Primary action is intracellular. Therapeutic Effect: Required for nerve impulse conduction, contraction of cardiac, skeletal, smooth muscle; maintains normal renal function, acid-base balance.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Enters cells by active transport from extracellular fluid. Primarily excreted in urine.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: May be at increased risk for hyperkalemia. Age-related ability to excrete potassium is reduced.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: ACE inhibitors (e.g., enalapril, lisinopril), potassium-containing medications, potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., spironolactone, triamterene), salt substitutes may increase serum potassium concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None known.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
POTASSIUM ACETATE
Injection, Solution: 2 mEq/ml.
POTASSIUM BICARBONATE AND POTASSIUM CITRATE
Tablets for Solution: (Effer-K): 10 mEq, 20 mEq, 25 mEq. (Klor-Con EF): 25 mEq.
POTASSIUM CHLORIDE
Injection, Solution: 2 mEq/ml. Oral Solution: 20 mEq/15 ml, 40 mEq/15 ml. Powder for Oral Solution: 20 mEq/packet, 25 mEq/packet.
 Capsules, Extended-Release (Micro-K): 8 mEq, 10 mEq.
Capsules, Extended-Release (Micro-K): 8 mEq, 10 mEq.
 Tablets, Extended-Release: 8 mEq, 10 mEq, 15 mEq, 20 mEq.
Tablets, Extended-Release: 8 mEq, 10 mEq, 15 mEq, 20 mEq.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • For IV infusion only, must dilute before administration, mix well, infuse slowly. • Avoid adding potassium to hanging IV.
Rate of Administration • Routinely, give at concentration of no more than 40 mEq/L, no faster than 10 mEq/hr for peripheral infusion, 40 mEq/hr for central infusion. • Check IV site closely during infusion for evidence of phlebitis (heat, pain, red streaking of skin over vein, hardness to vein), extravasation (swelling, pain, cool skin, little/no blood return).
Storage • Store at room temperature. Use admixtures within 24 hrs.
PO
• Take with or after meals, with full glass of water (decreases GI upset). • Liquids, powder, effervescent tablets: Mix, dissolve with juice, water before administering. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets; give whole.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), phenytoin (Dilantin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), atropine, aztreonam (Azactam), calcium gluconate, cefepime (Maxipime), ciprofloxacin (Cipro), clindamycin (Cleocin), dexamethasone (Decadron), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), digoxin (Lanoxin), diltiazem (Cardizem), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), enalapril (Vasotec), famotidine (Pepcid), fluconazole (Diflucan), furosemide (Lasix), granisetron (Kytril), heparin, hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef), insulin, lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), metoclopramide (Reglan), midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, norepinephrine (Levophed), ondansetron (Zofran), oxytocin (Pitocin), piperacillin and tazobactam (Zosyn), procainamide (Pronestyl), propofol (Diprivan), propranolol (Inderal).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Treatment of Hypokalemia
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 40–100 mEq/day in divided doses (generally limit amount per dose to 20–25 mEq to avoid GI discomfort); further doses based on laboratory values. CHILDREN: Initially, 1–2 mEq/kg; further doses based on laboratory values.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–10 mEq/hr. Maximum: 200 mEq/day. CHILDREN: 0.5–1 mEq/kg per dose. Maximum dose: 40 mEq per dose to infuse at 0.3–0.5 mEq/kg/hr.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Use caution with potassium acetate (may increase serum aluminum and/or potassium).
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence, abdominal discomfort with distention, phlebitis with IV administration (particularly when potassium concentration of greater than 40 mEq/L is infused). Rare: Rash.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hyperkalemia (more common in elderly, pts with renal impairment) manifested as paresthesia, feeling of heaviness in lower extremities, cold skin, grayish pallor, hypotension, confusion, irritability, flaccid paralysis, cardiac arrhythmias.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess for hypokalemia (weakness, fatigue, polyuria, polydipsia). PO should be given with food or after meals with full glass of water, fruit juice (minimizes GI irritation).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum potassium (particularly in renal impairment). If GI disturbance is noted, dilute preparation further or give with meals. Be alert to decreased urinary output (may be indication of renal insufficiency). Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess I&O diligently during diuresis, IV site for extravasation, phlebitis. Be alert to evidence of hyperkalemia (skin pallor/coldness, complaints of paresthesia, feeling of heaviness of lower extremities).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Foods rich in potassium include beef, veal, ham, chicken, turkey, fish, milk, bananas, dates, prunes, raisins, avocados, watermelon, cantaloupe, apricots, molasses, beans, yams, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, lentils, potatoes, spinach. • Report paresthesia, feeling of heaviness of lower extremities, tarry or bloody stools, weakness, unusual fatigue.
*PRALAtrexate
pral-a-trex-ate
(Folotyn)
Do not confuse Folotyn with Focalin, or pralatrexate with methotrexate or pemetrexed.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antimetabolite. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL). OFF-LABEL: Treatment of relapsed/refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to pralatrexate. Cautions: Moderate to severe renal impairment, hepatic impairment. Avoid use in end-stage renal disease.
ACTION
Folate analogue metabolic inhibitor that competes with enzymes necessary for tumor cell reproduction. Inhibits DNA, RNA, protein synthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor growth.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Protein binding: 67%. Partially excreted in urine. Half-life: 12–18 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: NSAIDs, probenecid, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole may delay clearance, increase concentration. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease RBC, WBC, Hgb, Hct, platelet count, serum potassium. May increase serum ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 20 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ May be carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic. Handle with extreme care during preparation/administration. Wear gloves when preparing solution. If powder or solution comes in contact with skin, wash immediately, thoroughly with soap, water.
◀ ALERT ▶ Pt should begin taking oral folic acid (1 mg) daily starting 10 days prior to first IV pralatrexate dose and continue for 30 days after last dose. Pt should also receive vitamin B12 (1 mg) IM injection no more than 10 wks prior to first IV pralatrexate dose and every 8–10 wks thereafter.
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Withdraw calculated dose into syringe for immediate use. • Intended for single use only. • Do not dilute.
Rate of Administration • Administer as IV push over 3–5 min into IV infusion of 0.9% NaCl.
Storage • Refrigerate vials until use, protect from light. Stable at room temperature for 72 hrs. • Discard vial if solution is discolored (solution should appear clear to yellow) or particulate matter is present.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with any other medication.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Prior to any dose, mucositis should be no higher than grade 1, platelets 100,000/mm3 or greater for first dose and 50,000/mm3 or greater for subsequent doses, and absolute neutrophil count (ANC) 1,000/mm3 or greater.
Refractory/Relapsed Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 30 mg/m2 administered once wkly for 6 wks in 7-wk cycles. Dose may be decreased to 20 mg/m2 to manage adverse reactions. Continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Monitor for toxicities. Avoid use in end-stage renal disease.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Grade 3: Withhold dose; decrease to 20 mg/m3 when grade 2 or less.
Grade 4: Discontinue.
SIDE EFFECTS
Common (70%–36%): Mucositis, nausea, fatigue. Frequent (34%–10%): Constipation/diarrhea, pyrexia, edema, cough, epistaxis, vomiting, dyspnea, anorexia, rash, throat/abdominal/back pain, night sweats, asthenia, tachycardia, upper respiratory infection.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hematologic toxicity, resulting from blood dyscrasias, may manifest as thrombocytopenia (41% of pts), anemia (34% of pts), neutropenia (24% of pts), leukopenia (11% of pts). High potential for development of mucositis (70% of pts). Mucositis is less severe when folic acid, vitamin B12 therapy is ongoing. Sepsis, pyrexia, febrile neutropenia, dehydration have occurred. Overdosage requires general supportive care. Prompt administration of leucovorin should be considered in case of overdose, based on mechanism of action of pralatrexate.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Evaluate baseline CBC with differential, renal function, LFT, serum potassium level.Question for possibility of pregnancy before initiating therapy. Assess baseline vital signs, temperature. Antiemetics before and during therapy may alleviate nausea/vomiting. Initiate folic acid, vitamin B12 administration prior to and throughout therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Prior to any dose: mucositis should be grade 1 or less. Platelet count 100,000/mm3 or greater for first dose (50,000/mm3 or greater for all subsequent doses). Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) 1,000/mm3 or greater. Assess for signs of mucositis (oropharyngeal ulcers, oral/throat pain, local infection). Monitor for signs of hematologic toxicity, sepsis (fever, signs of local infection, altered CBC results). Monitor hepatic/renal function. Monitor for hypokalemia (muscle cramps, weakness, EKG changes).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Explain importance of folic acid, vitamin B12 therapy to reduce adverse effects. • Maintain strict oral hygiene. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers body’s resistance). • Avoid crowds, those with infection. • Promptly report fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site. • Use nonhormonal contraception. • Report persistent nausea/vomiting.
pramipexole
pram-i-pex-ole
(Apo-Pramipexole
 , Mirapex, Mirapex ER)
, Mirapex, Mirapex ER)
Do not confuse Mirapex with Mifeprex or MiraLax.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Dopamine receptor agonist. CLINICAL: Antiparkinson agent.
USES
Mirapex: Treatment of signs/symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease, restless legs syndrome. Mirapex ER: Treatment of Parkinson’s disease. OFF-LABEL: (Immediate-Release): Depression (due to bipolar disorder), fibromyalgia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to pramipexole. Cautions: History of orthostatic hypotension, pts at risk for hypotension, syncope, hallucinations, renal impairment (extended release not recommended with CrCl less than 30 ml/min), concomitant use of CNS depressants, preexisting dyskinesia, elderly.
ACTION
Stimulates dopamine receptors in striatum and substantia nigra. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves signs/symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly, extensively absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 15%. Widely distributed. Steady-state concentrations achieved within 2 days. Primarily eliminated in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 8 hrs (12 hrs in pts older than 65 yrs).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Increased risk of hallucinations.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase plasma concentrations of carbidopa, levodopa. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, SAMe, valerian may increase CNS depression, risk of serotonin syndrome. FOOD: All foods delay peak drug plasma levels by 1 hr (extent of absorption not affected). LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 0.125 mg, 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 0.75 mg, 1 mg, 1.5 mg.
 Tablets (Extended-Release [Mirapex ER]): 0.375 mg, 0.75 mg, 1.5 mg, 2.25 mg, 3 mg, 3.75 mg, 4.5 mg.
Tablets (Extended-Release [Mirapex ER]): 0.375 mg, 0.75 mg, 1.5 mg, 2.25 mg, 3 mg, 3.75 mg, 4.5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO (Mirapex)
• Give without regard to food.
PO (Mirapex ER)
• Give once daily, without regard to food. • Give whole; do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Parkinson’s Disease (Mirapex)
PO: (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 0.125 mg 3 times/day. Increase no more frequently than every 5–7 days. Maintenance: 0.5–1.5 mg 3 times/day.
(Extended-Release): Initially, 0.375 mg once daily. May increase to 0.75 mg, then by 0.75-mg increments no more frequently than 5–7 days. Maximum: 4.5 mg once daily. Note: May switch overnight from immediate-release to extended-release at same daily dose.
Restless Legs Syndrome
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY:(Immediate-Release): Initially, 0.125 mg once daily 2–3 hrs before bedtime. May increase to 0.25 mg after 4–7 days, then to 0.5 mg after 4–7 days (interval is 14 days in pts with renal impairment). Maximum: 0.5 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage and frequency are modified based on creatinine clearance.
(Parkison’s Disease)
Immediate-Release
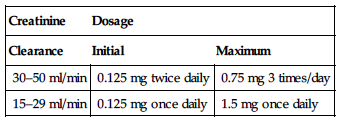
| Creatinine | Dosage |
| Clearance | Initial | Maximum |
| 30–50 ml/min | 0.125 mg twice daily | 0.75 mg 3 times/day |
| 15–29 ml/min | 0.125 mg once daily | 1.5 mg once daily |
Extended-Release
CrCl 30–50 ml/min: Initially, 0.375 mg every other day. May increase by 0.375 mg/day in 7 days or longer. Maximum: 2.25 mg once daily. CrCl less than 30 ml/min: Not recommended.
Restless Legs Syndrome
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Early Parkinson’s disease (28%–10%): Nausea, asthenia, dizziness, drowsiness, insomnia, constipation. Advanced Parkinson’s disease (53%–17%): Orthostatic hypotension, extrapyramidal reactions, insomnia, dizziness, hallucinations. Occasional: Early Parkinson’s disease (5%–2%): Edema, malaise, confusion, amnesia, akathisia, anorexia, dysphagia, peripheral edema, vision changes, impotence. Advanced Parkinson’s disease (10%–7%): Asthenia, drowsiness, confusion, constipation, abnormal gait, dry mouth. Rare: Advanced Parkinson’s disease (6%–2%): General edema, malaise, angina, amnesia, tremor, urinary frequency/incontinence, dyspnea, rhinitis, vision changes. Restless legs syndrome: Frequent (16%): Headache, nausea. Occasional (13%–9%): Insomnia, fatigue. Rare (6%–3%): Drowsiness, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Vascular disease, atrial fibrillation, arrhythmias, pulmonary embolism, impulsive/compulsive behavior (pathological gambling, hypersexuality, binge eating) have been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Parkinson’s disease: Assess for tremor, muscle weakness and rigidity, ataxia. Restless legs syndrome: Assess frequency of symptoms, sleep pattern.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for clinical improvement. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Assess for constipation; encourage fiber, fluids, exercise.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Inform pt that hallucinations may occur, esp. in the elderly. • Go from lying to standing slowly. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • If nausea occurs, take medication with food. • Avoid abrupt withdrawal. • Avoid alcohol. • Report new or increased impulsive/compulsive behaviors (e.g., gambling, sexual urges, compulsive eating or buying).
pramlintide

pram-lin-tide
(SymlinPen 60, SymlinPen 120)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Increased risk of severe hypoglycemia; usually occurs within 3 hrs of injection. Coadministration with insulin may increase incidence.
Increased risk of severe hypoglycemia; usually occurs within 3 hrs of injection. Coadministration with insulin may increase incidence.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Antihyperglycemic. CLINICAL: Antidiabetic agent.
USES
Adjunctive treatment in pts with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who use mealtime insulin therapy and who have failed to achieve desired glucose control despite optimal insulin therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to pramlintide. Diagnosed gastroparesis, hypoglycemia unawareness. Cautions: Coadministration with insulin may induce severe hypoglycemia (usually within 3 hrs following administration); concurrent use of other glucose-lowering agents may increase risk of hypoglycemia. History of nausea, visual or dexterity impairment, poor compliance with insulin monitoring or current insulin therapy, pts with hemoglobin A1c greater than 9%, pts with conditions or taking concurrent medications likely to impair gastric motility (e.g., anticholinergics), pts requiring medication to stimulate gastric emptying.
ACTION
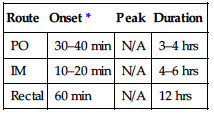
Cosecreted with insulin by pancreatic beta cells, reduces postprandial glucose increases by slowing gastric emptying time, reducing postprandial glucagon secretion, reducing caloric intake through centrally mediated appetite suppression. Therapeutic Effect: Improves glycemic control by reducing postprandial glucose concentrations in pts with type 1, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
PHARMACOKINETICS
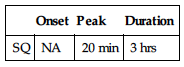
| Onset | Peak | Duration |
| SQ | NA | 20 min | 3 hrs |
Metabolized primarily by kidneys. Protein binding: 60%. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 48 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anticholinergics (e.g., dicyclomine, glycopyrrolate, scopolamine) may cause additive impairment of gastric motility. HERBAL: Garlic may increase hypoglycemia. FOOD: Ethanol may increase risk of hypoglycemia. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Solution (SymlinPen 120): Delivers fixed doses of 120 mcg. (SymlinPen 60): Delivers fixed doses of 60 mcg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
SQ
• Administer immediately before each major meal (350 or more kcal or containing 30 g or more carbohydrate). • Give in abdomen or thigh; do not give in arm (variable absorption). • Injection site should be distinct from insulin injection site. • Rotation of injection sites is essential. • Use U-100 insulin syringe for accuracy. • Always give pramlintide and insulin as separate injections.
Storage • Store unopened vials in refrigerator. • Discard if freezing occurs. • Vials that have been opened (punctured) may be stored in refrigerator or kept at room temperature for up to 30 days.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Initially, current insulin dosage in all pts with type 1, type 2 diabetes mellitus should be reduced by 50%. This includes preprandial, rapid-acting, short-acting, fixed-mixed insulins.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 15 mcg immediately before each major meal. Titrate in 15-mcg increments every 3 days (if no significant nausea occurs) to target dose of 30–60 mcg.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 60 mcg immediately before each major meal. After 3–7 days, increase to 120 mcg if no significant nausea occurs (if nausea occurs at 120 mcg dose, reduce to 60 mcg).
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
Frequent (48%): Nausea. Occasional (17%–11%): Anorexia, vomiting. Rare (7%–5%): Fatigue, arthralgia, allergic reaction, dizziness.
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Frequent (28%): Nausea. Occasional (13%–8%): Headache, anorexia, vomiting, abdominal pain. Rare (7%–5%): Fatigue, dizziness, cough, pharyngitis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose produces severe nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, vasodilation, dizziness. No hypoglycemia was reported. Increased risk of severe hypoglycemia when given concurrently with nontitrated insulin.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Check serum glucose concentration before administration, both before and after meals and at bedtime. Discuss lifestyle to determine extent of learning, emotional needs. Ensure follow-up instruction if pt, family does not thoroughly understand diabetes management, glucose testing technique.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Risk for hypoglycemia occurs within first 3 hrs following drug administration if given concurrently with insulin. Assess for hypoglycemia (diaphoresis, tremors, dizziness, anxiety, headache, tachycardia, numbness in mouth, hunger, diplopia, difficulty concentrating). Be alert to conditions that alter glucose requirements (fever, increased activity, stress, surgical procedures).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Diabetes mellitus requires lifelong control. • Prescribed diet, exercise are principal parts of treatment; do not skip/delay meals. • Continue to adhere to dietary instructions, regular exercise program, regular testing of serum glucose. • When taking combination drug therapy, have source of glucose available to treat symptoms of low blood sugar.
prasugrel

pra-soo-grel
(Effient)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Serious, sometimes fatal, hemorrhage may occur.
Serious, sometimes fatal, hemorrhage may occur.
Do not confuse Effient with Effexor, or prasugrel with praziquantel.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Thienopyridine derivative inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiplatelet agent.
USES
Reduction of thrombotic cardiovascular events (MI, CVA, stent thrombosis) in pts with acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina, non–ST-segment elevation MI, ST-segment MI) who are to be managed with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). OFF-LABEL: Initial treatment of unstable angina, STEMI in pts undergoing PCI with allergy or major GI intolerance to aspirin.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to prasugrel. Active bleeding, prior transient ischemic attack (TIA), CVA. Cautions: Pts who undergo coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) after receiving prasugrel, pts at risk for bleeding (age 75 yrs or older, body weight less than 60 kg, recent trauma/surgery, recent GI bleeding or active peptic ulcer disease, severe hepatic impairment).
ACTION
Inhibits binding of the enzyme adenosine phosphate (ADP) to its platelet receptor and subsequent ADP-mediated activation of a glycoprotein complex. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits platelet aggregation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed, with peak concentration occurring 30 min following administration. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 98%. Eliminated in urine (68%), feces (27%). Half-life: 7 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May have increased risk for intracranial hemorrhage; caution advised in pts 75 yrs and older.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Aspirin, NSAIDs, warfarin may increase risk of bleeding. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginseng, green tea, horse chestnut, red clover may have additive platelet effects. Ginkgo biloba may increase risk of bleeding. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease Hgb, Hct, WBC, platelet count. May increase bleeding time, serum cholesterol, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Tablets: 5 mg, 10 mg.
Tablets: 5 mg, 10 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Do not crush tablet.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Acute Coronary Syndrome
◀ ALERT ▶ Consider 5 mg once daily for pts weighing less than 60 kg. Not recommened in pts 75 yrs and older.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY): Initially, 60-mg loading dose, then 10 mg once daily (in combination with aspirin) for at least 12 mos.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (8%–4%): Hypertension, minor bleeding, headache, back pain, dyspnea, nausea, dizziness. Rare (Less Than 4%): Cough, hypotension, fatigue, noncardiac chest pain, bradycardia, rash, pyrexia, peripheral edema, extremity pain, diarrhea.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Major bleeding (intracranial hemorrhage, epistaxis, GI bleeding, hemoptysis, SQ hematoma, postprocedural hemorrhage, retroperitoneal hemorrhage, retinal hemorrhage) has been reported. Severe thrombocytopenia, anemia, abnormal hepatic function, anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, atrial fibrillation occur rarely. Overdosage may require platelet transfusion to restore clotting ability.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline vital signs, CBC, EKG, LFT. Question history of intracranial hemorrhage, GI bleeding, ulcers, recent surgery or trauma.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor vital signs for changes in B/P, pulse. Assess for signs of unusual bleeding or hemorrhage, pain. Monitor platelet count, LFT, EKG for changes from baseline.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• It may take longer to stop minor bleeding during drug therapy. Report unusual bleeding/bruising, blood noted in stool or urine, chest/back pain, extremity pain, symptoms of stroke. • Monitor for dyspnea. • Report fever, weakness, extreme skin paleness, purple skin patches, yellowing of skin or eyes, changes in mental status. • Do not discontinue drug therapy without physician approval. • Inform physicians, dentists before undergoing any invasive procedure or surgery.
pravastatin

pra-va-sta-tin
(Apo-Pravastatin
 , Pravachol)
, Pravachol)
Do not confuse pravastatin with atorvastatin, lovastatin, nystatin, pitavastatin, or simvastatin, or Pravachol with Prevacid, Prinivil, or propranolol.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Pravigard: pravastatin/aspirin (anticoagulant): 20 mg/81 mg, 40 mg/81 mg, 80 mg/81 mg, 20 mg/325 mg, 40 mg/325 mg, 80 mg/325 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Anti-hyperlipidemic.
USES
Treatment of primary hyperlipidemias and mixed dyslipidemias to reduce total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, triglycerides; increase HDL cholesterol. Reduces risk of MI, revascularization, and mortality in hypercholesterolemia without clinically evident CHD. Reduces mortality risk in pts with CHD. Reduces elevated triglycerides in hypertriglyceridemia. Treatment of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in pediatric pts 8–18 yrs.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to pravastatin. Active hepatic disease or unexplained, persistent elevations of hepatic function test results. Pregnancy, breastfeeding. Cautions: History of hepatic disease, substantial alcohol consumption. Withholding/discontinuing pravastatin may be necessary when pt is at risk for renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis, elderly.
ACTION
Interferes with cholesterol biosynthesis by preventing conversion of HMG-CoA reductase to mevalonate, a precursor to cholesterol. Therapeutic Effect: Lowers LDL, VLDL cholesterol, plasma triglycerides; increases HDL.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 50%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in feces via biliary system. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2–3 hrs. (Half-life including all metabolites: 77 hrs.)
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Contraindicated in pregnancy (suppression of cholesterol biosynthesis may cause fetal toxicity) and lactation. Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk, but there is risk of serious adverse reactions in breastfeeding infants. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Cyclosporine, clarithromycin, colchicine, erythromycin, gemfibrozil, immunosuppressants, niacin increase risk of myopathy, rhabdomyolysis. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. FOOD: Red yeast rice contains 2.4 mg lovastatin per 600 mg rice. LAB VALUES: May increase serum creatine kinase (CK), transaminase.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, 80 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Prior to initiating therapy, pt should be on standard cholesterol-lowering diet for 3–6 mos. Low-cholesterol diet should be continued throughout pravastatin therapy.
Hyperlipidemia, Prevention of Coronary/Cardiovascular Events
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 40 mg/day. Titrate to desired response. Range: 10–80 mg/day.
Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
PO: CHILDREN 14–18 YRS: 40 mg/day. CHILDREN 8–13 YRS: 20 mg/day.
Dosage with Clarithromycin
Maximum: 40 mg/day.
Dosage with Cyclosporine
ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10 mg/day. Maximum: 20 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
For adults, give 10 mg/day initially. Titrate to desired response.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
See contraindications.
SIDE EFFECTS
Pravastatin is generally well tolerated. Side effects are usually mild and transient. Occasional (7%–4%): Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, headache, rhinitis, rash, pruritus. Rare (3%–2%): Heartburn, myalgia, dizziness, cough, fatigue, flu-like symptoms, depression, photosensitivity.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Potential for malignancy, cataracts. Hypersensitivity, myopathy occur rarely. Rhabdomyolysis has been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain dietary history, esp. fat consumption. Question for possibility of pregnancy before initiating therapy. Assess baseline serum lab results (cholesterol, triglycerides, LFT).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum cholesterol, triglyceride lab results for therapeutic response. Monitor LFT, CPK. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess for headache, dizziness (provide assistance as needed). Assess for rash, pruritus. Be alert for malaise, muscle cramping/weakness; if accompanied by fever, may require discontinuation of medication.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Follow special diet (important part of treatment). • Periodic lab tests are essential part of therapy. • Report promptly any muscle pain/weakness, esp. if accompanied by fever, malaise. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established (potential for dizziness). • Use nonhormonal contraception. • Avoid direct exposure to sunlight.
*prednisoLONE
pred-niss-oh-lone
(Millipred, Novo-Prednisolone
 , Omnipred, Orapred ODT, Pediapred, Pred Forte, Pred Mild, Prelone, Veripred)
, Omnipred, Orapred ODT, Pediapred, Pred Forte, Pred Mild, Prelone, Veripred)
Do not confuse Pediapred with Pediazole, prednisolone with prednisone or primidone, or Prelone with Prozac.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Blephamide: prednisolone/sulfacetamide (an anti-infective): 0.2%/10%. Vasocidin: prednisolone/sulfacetamide: 0.25%/10%.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Adrenal corticosteroid. CLINICAL: Glucocorticoid.
USES
Systemic: Endocrine, rheumatic, hematologic disorders; collagen, respiratory, neoplastic, GI diseases; allergic states; acute or chronic solid organ rejection. Ophthalmic: Treatment of conjunctivitis, corneal injury (from chemical/thermal burns, foreign body).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to prednisolone. Acute superficial herpes simplex keratitis, systemic fungal infections, varicella, live or attenuated virus vaccines. Cautions: Hyperthyroidism, cirrhosis, ocular herpes simplex, respiratory tuberculosis, untreated systemic infections, renal/hepatic impairment, diabetes, cataracts, glaucoma, history of seizure disorder, peptic ulcer disease, osteoporosis, myasthenia gravis, hypertension, HF, ulcerative colitis, thromboembolic disorders, elderly.
ACTION
Inhibits accumulation of inflammatory cells at inflammation sites, phagocytosis, lysosomal enzyme release/synthesis, release of mediators of inflammation. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents/suppresses cell-mediated immune reactions. Decreases/prevents tissue response to inflammatory process.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Protein binding: 65%–91%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 3.6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Fetal cleft palate often occurs with chronic, first-trimester use. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Prolonged treatment or high dosages may decrease short-term growth rate, cortisol secretion. Elderly: May be more susceptible to developing hypertension or osteoporosis.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Hepatic enzyme inducers (e.g., phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease effects. Live virus vaccines increase vaccine side effects, potentiate virus replication, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. May increase effect of warfarin. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Cat’s claw, echinacea have immunostimulant properties. Echinacea may decrease level/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, lipids, sodium, uric acid. May decrease serum calcium, WBC, hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis function, potassium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Solution, Ophthalmic: 1%. Solution, Oral: 15 mg/5 ml. (Pediapred): 5 mg/5 ml. (Millipred): 10 mg/5 ml. (Veripred): 20 mg/5 ml. Suspension, Ophthalmic (Pred Forte): 1%; (Pred Mild): 0.12%. Syrup (Prelone): 15 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 5 mg.
 Tablets, Orally Disintegrating: 10 mg, 15 mg, 30 mg.
Tablets, Orally Disintegrating: 10 mg, 15 mg, 30 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with food or fluids to decrease GI side effects.
Orally Disintegrating Tablets
• Do not break, crush, or divide tablets. • Remove from blister just prior to giving, place on tongue. • Pt may swallow whole or allow to dissolve in mouth with/without water.
Ophthalmic
• For ophthalmic solution, shake well before using. • Instill drops into conjunctival sac, as prescribed. • Avoid touching applicator tip to conjunctiva to avoid contamination.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–60 mg/day in divided doses. CHILDREN: 0.1–2 mg/kg/day in 1–4 divided doses.
Treatment of Conjunctivitis, Corneal Injury
Ophthalmic: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 1–2 drops every hr during day and q2h during night. After response, decrease dosage to 1 drop q4h, then 1 drop 3–4 times/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Insomnia, heartburn, nervousness, abdominal distention, diaphoresis, acne, mood swings, increased appetite, facial flushing, delayed wound healing, increased susceptibility to infection, diarrhea, constipation. Occasional: Headache, edema, change in skin color, frequent urination. Rare: Tachycardia, allergic reaction (rash, urticaria), psychological changes, hallucinations, depression. Ophthalmic: Stinging/burning, posterior subcapsular cataracts.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Long-term therapy: Hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, muscle wasting (esp. arms, legs) osteoporosis, spontaneous fractures, amenorrhea, cataracts, glaucoma, peptic ulcer, HF. Abrupt withdrawal following long-term therapy: Anorexia, nausea, fever, headache, severe/sudden joint pain, rebound inflammation, fatigue, weakness, lethargy, dizziness, orthostatic hypotension. Sudden discontinuance may be fatal.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question medical history as listed in Precautions. Obtain baselines for height, weight, B/P, serum glucose, electrolytes. Check results of initial tests (tuberculosis [TB] skin test, X-rays, EKG).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, weight, serum electrolytes, glucose, results of bone mineral density test, height, weight in children. Be alert to infection (sore throat, fever, vague symptoms); assess oral cavity daily for signs of candida infection.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report fever, sore throat, muscle aches, sudden weight gain, swelling, loss of appetite, fatigue. • Avoid alcohol, limit caffeine. • Maintain fastidious oral hygiene. • Do not abruptly discontinue without physician’s approval. • Avoid exposure to chickenpox, measles.
*predniSONE
pred-ni-sone
(Apo-Prednisone
 , Prednisone Intensol, Rayos, Winpred
, Prednisone Intensol, Rayos, Winpred
 )
)
Do not confuse prednisone with methylprednisolone, prazosin, prednisolone, Prilosec, primidone, or promethazine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Adrenal corticosteroid. CLINICAL: Glucocorticoid.
USES
Substitution therapy in deficiency states: Acute or chronic adrenal insufficiency, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, adrenal insufficiency secondary to pituitary insufficiency. Nonendocrine disorders: Arthritis, rheumatic carditis; allergic, collagen, intestinal tract, multiple sclerosis exacerbations; liver, ocular, renal, skin diseases; bronchial asthma, cerebral edema, malignancies. OFF-LABEL: Prevention of postherpetic neuralgia, relief of acute pain in pts with herpes zoster, autoimmune hepatitis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to prednisone. Acute superficial herpes simplex keratitis, systemic fungal infections, varicella, administration of live or attenuated virus vaccines. Cautions: Hyperthyroidism, cirrhosis, ocular herpes simplex, respiratory tuberculosis, untreated systemic infections, renal/hepatic impairment; following acute MI, diabetes, cataracts, glaucoma, seizures, peptic ulcer disease, osteoporosis, myasthenia gravis, hypertension, HF, ulcerative colitis, thromboembolic disorders, elderly.
ACTION
Inhibits accumulation of inflammatory cells at inflammation sites, phagocytosis, lysosomal enzyme release/synthesis, release of mediators of inflammation. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents/suppresses cell-mediated immune reactions. Decreases/prevents tissue response to inflammatory process.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 70%–90%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver, converted to prednisolone. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2.5–3.5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Fetal cleft palate often occurs with chronic, first trimester use. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Prolonged treatment or high dosages may decrease short-term growth rate, cortisol secretion. Elderly: May be more susceptible to developing hypertension or osteoporosis.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Hepatic enzyme inducers (e.g., phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease effects. Live virus vaccines may increase vaccine side effects, potentiate virus replication, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. May increase effect of warfarin. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Cat’s claw, echinacea have immunostimulant properties. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, lipids, sodium, uric acid. May decrease serum calcium, potassium, WBC, hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis function.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Solution, Oral: 1 mg/ml. Solution, Oral Concentrate (Prednisone Intensol): 5 mg/ml. Tablets: 1 mg, 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, 50 mg.
 Tablet: (Delayed-Release [Rayos]): 1 mg, 2 mg, 5 mg.
Tablet: (Delayed-Release [Rayos]): 1 mg, 2 mg, 5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with food or fluids to decrease GI side effects. • Give single doses before 9 AM, multiple doses at evenly spaced intervals. • Give delayed-release tablet whole; do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Dose dependent upon condition treated, pt response rather than by rigid adherence to age, weight, or body surface area.
Usual Dosage
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–60 mg/day in divided doses. CHILDREN: 0.05–2 mg/kg/day in 1–4 divided doses.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Insomnia, heartburn, nervousness, abdominal distention, diaphoresis, acne, mood swings, increased appetite, facial flushing, delayed wound healing, increased susceptibility to infection, diarrhea, constipation. Occasional: Headache, edema, change in skin color, frequent urination. Rare: Tachycardia, allergic reaction (rash, urticaria), psychological changes, hallucinations, depression.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Long-term therapy: Muscle wasting (esp. in arms, legs), osteoporosis, spontaneous fractures, amenorrhea, cataracts, glaucoma, peptic ulcer, HF. Abrupt withdrawal following long-term therapy: Anorexia, nausea, fever, headache, rebound inflammation, fatigue, weakness, lethargy, dizziness, orthostatic hypotension. Sudden discontinuance may be fatal.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question medical history as listed in Precautions. Obtain baselines for height, weight, B/P, serum glucose, electrolytes. Check results of initial tests (tuberculosis [TB] skin test, X-rays, EKG).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, serum electrolytes, glucose, results of bone mineral density test, height, weight in children. Be alert to infection (sore throat, fever, vague symptoms); assess oral cavity daily for signs of candida infection.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report fever, sore throat, muscle aches, sudden weight gain, swelling, loss of appetite, or fatigue. • Avoid alcohol, minimize use of caffeine. • Maintain fastidious oral hygiene. • Do not abruptly discontinue without physician’s approval. • Avoid exposure to chickenpox, measles.
pregabalin

pre-gab-a-lin
(Apo-Pregabalin
 , Lyrica)
, Lyrica)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
CLINICAL: Anticonvulsant, antineuralgic, analgesic (Schedule V).
USES
Adjunctive therapy in treatment of partial-onset seizures. Management of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy or spinal cord injury. Management of postherpetic neuralgia. Management of fibromyalgia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to pregabalin. Cautions: HF, renal impairment, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, history of angioedema, pts at risk for suicide. Concurrent use of thiazolidine antidiabetics (e.g., Actos).
ACTION
Binds to calcium channel sites in CNS tissue, inhibiting excitatory neurotransmitter release. Exerts antinociceptive, anticonvulsant activity. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases symptoms of painful peripheral neuropathy; decreases frequency of partial seizures.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following PO administration. Eliminated in urine unchanged. Half-life: 6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Increased risk of fetal skeletal abnormalities. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, barbiturates, narcotic analgesics, other sedative agents may increase sedative effect. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase CPK. May cause mild PR interval prolongation. May decrease platelet count.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Solution, Oral: 20 mg/ml.
 Capsules (Lyrica): 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 225 mg, 300 mg.
Capsules (Lyrica): 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 225 mg, 300 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• Give without regard to food. • Do not break, crush, or open capsule.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Partial-Onset Seizures
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 75 mg twice daily or 50 mg 3 times/day. May increase dose based on tolerability/effect. Maximum: 600 mg/day.
Neuropathic Pain (Diabetes-Associated)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 50 mg 3 times/day. Maximum: 300 mg/day in 3 divided doses.
Postherpetic Neuralgia, Neuropathic Pain Associated with Spinal Cord Injury
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 75 mg twice daily or 50 mg 3 times/day. May increase to 300 mg/day within 1 wk. May further increase to 600 mg/day after 2–4 wks. Maximum: 600 mg/day.
Fibromyalgia
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 75 mg twice daily. May increase to 150 mg twice daily within 1 wk. Maximum: 225 mg twice daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Daily Dosage |
| 30–60 ml/min | 75–300 mg in 2–3 divided doses |
| 15–29 ml/min | 25–150 mg in 1 or 2 doses |
| Less than 15 ml/min | 25–75 mg once daily |
Dosage for Hemodialysis
◀ ALERT ▶ Take supplemental dose immediately following dialysis.
| Daily Dosage | Supplemental Dosage |
| 25 mg | Single dose of 25 mg or 50 mg |
| 25–50 mg | Single dose of 50 mg or 75 mg |
| 75 mg | Single dose of 100 mg or 150 mg |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (32%–12%): Dizziness, drowsiness, ataxia, peripheral edema. Occasional (12%–5%): Weight gain, blurred vision, diplopia, difficulty with concentration, attention, cognition; tremor, dry mouth, headache, constipation, asthenia. Rare (4%–2%): Abnormal gait, confusion, incoordination, twitching, flatulence, vomiting, edema, myopathy.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Abrupt withdrawal increases risk of seizure frequency in pts with seizure disorders; withdraw gradually over a minimum of 1 wk.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Seizure: Review history of seizure disorder (type, onset, intensity, frequency, duration, LOC). Pain: Assess onset, type, location, and duration of pain.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Provide safety measures as needed. Assess for seizure activity. Assess for clinical improvement; record onset of relief of pain. Assess for evidence of peripheral edema behind medial malleolus (usually first area of edema). Question for changes in visual acuity.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not abruptly stop taking drug; seizure frequency may be increased. • Avoid tasks that require alterness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol. • Carry identification card, bracelet to note seizure disorder, anticonvulsant therapy.
primidone
prim-i-done
(Apo-Primidone
 , Mysoline)
, Mysoline)
Do not confuse primidone with prednisone or pyridoxine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Barbiturate. CLINICAL: Anticonvulsant.
USES
Management of partial seizures, generalized tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures, focal seizures. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of essential tremor (familial tremor).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to primidone, phenobarbital; porphyria. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, pulmonary insufficiency, elderly, debilitated, children, hypoadrenalism, pts at risk for suicidal thoughts/behavior, depression, history of drug abuse.
ACTION
Decreases neuron excitability. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces seizure activity.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly, usually completely absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver to phenobarbital. Minimal excretion in urine. Half-life: 3–6 hrs. (Phenobarbital: 2–5 days.)
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Children, Elderly: May produce paradoxical excitement, restlessness.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g., lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase effects. Valproic acid increases concentration, risk of toxicity. HERBAL: Evening primrose may decrease seizure threshold. Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum bilirubin. Therapeutic serum level: 4–12 mcg/ml; toxic serum level: greater than 12 mcg/ml.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 50 mg, 250 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with food to minimize GI effects.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Seizure Control
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 8 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 100–125 mg/day at bedtime for days 1–3. Days 4–6: 100–125 mg twice daily. Days 7–9: 100–125 mg 3 times/day. Usual dose: 750–1,500 mg/day. Maximum: 2 g/day. CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 8 YRS: Initially, 50 mg/day at bedtime for days 1–3. Days 4–6: 50 mg twice daily. Days 7–9: 100 mg twice daily. Usual dose: 10–25 mg/kg/day (375–750 mg) in 3–4 divided doses. NEONATES: 12–20 mg/kg/day in divided doses 2–4 times/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatine Clearance | Interval |
| 50 ml/min or greater | q12h |
| 10–49 ml/min | q12–24h |
| Less than 10 ml/min | q24h |
| Hemodialysis (HD) | Administer dose post-HD |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Ataxia, dizziness. Occasional: Anorexia, drowsiness, altered mental status, nausea, vomiting, paradoxical excitement. Rare: Rash.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Abrupt withdrawal after prolonged therapy may produce effects ranging from markedly increased dreaming, nightmares, insomnia, tremor, diaphoresis, vomiting to hallucinations, delirium, seizures, status epilepticus. Skin eruptions may appear as hypersensitivity reaction. Blood dyscrasias, hepatic disease, hypocalcemia occur rarely. Overdose produces cold/clammy skin, hypothermia, severe CNS depression, followed by high fever, coma.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Review history of seizure disorder (intensity, frequency, duration, LOC). Observe frequently for recurrence of seizure activity. Initiate seizure precautions.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for changes in behavior, depression, suicidal ideation. Monitor CBC, neurologic status (frequency, duration, severity of seizures). Monitor for therapeutic serum level: 4–12 mcg/ml; toxic serum level: more than 12 mcg/ml.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not abruptly discontinue medication after long-term use (may precipitate seizures). • Strict maintenance of drug therapy is essential for seizure control. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established; drowsiness usually disappears during continued therapy. • Slowly go from lying to standing. • Avoid alcohol. • Report depression, thoughts of suicide, unusual changes in behavior.
prochlorperazine
proe-klor-per-a-zeen
(Apo-Prochlorperazine
 , Compazine, Compro)
, Compazine, Compro)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Increased risk for death in elderly with dementia-related psychosis.
Increased risk for death in elderly with dementia-related psychosis.
Do not confuse prochlorperazine with chlorpromazine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Phenothiazine. CLINICAL: Antiemetic, antipsychotic.
USES
Management of nausea/vomiting. Treatment of acute or chronic psychosis, nonpsychotic anxiety. OFF-LABEL: Behavior syndromes in dementia, psychosis/agitation related to Alzheimer’s dementia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to prochlorperazine. Severe CNS depression, coma, children younger than 2 yrs or less than 9 kg. Postoperative nausea/vomiting following pediatric surgery. Cautions: History of seizures, Parkinson’s disease, elderly, pts at risk for pneumonia, severe renal/hepatic impairment, decreased GI motility, urinary retention, visual problems, narrow angle glaucoma, paralytic ileus, myasthenia gravis, cerebrovascular/cardiovascular disease.
ACTION
Acts centrally to inhibit/block dopamine receptors in brain. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves nausea/vomiting.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset * | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 30–40 min | N/A | 3–4 hrs |
| IM | 10–20 min | N/A | 4–6 hrs |
| Rectal | 60 min | N/A | 12 hrs |
*As an antiemetic.
Variably absorbed after PO administration. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver, GI mucosa. Primarily excreted in urine. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: PO: 3–5 hrs, IV: 7 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts weighing less than 9 kg or younger than 2 yrs. Elderly: More susceptible to orthostatic hypotension, anticholinergic effects (e.g., dry mouth), sedation, extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS); lower dosage recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g,. lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase CNS, respiratory depression, hypotensive effects. Extrapyramidal symptom (EPS)–producing medications (e.g., haloperidol metoclopramide, SSRIs) may increase EPS. Lithium may decrease absorption, produce adverse neurologic effects. MAOIs, tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, doxepin) may increase anticholinergic, sedative effects. HERBAL: Dong quai, St. John’s wort may increase photosensitization. Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 5 mg/ml. Suppositories (Compro): 25 mg. Tablets: 5 mg, 10 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Rate of Administration • May give by IV push slowly. Maximum rate: 5 mg/min.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Protect from light. • Clear or slightly yellow solutions may be used.
IM
• Inject deep IM into outer quadrant of buttocks.
PO
• Should be administered with food or water.
Rectal
• Moisten suppository with cold water before inserting well into rectum.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Furosemide (Lasix), hydrocortisone, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), midazolam (Versed).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Calcium gluconate, dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), fentanyl, heparin, metoclopramide (Reglan), morphine, potassium chloride, promethazine (Phenergan), propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Nausea/Vomiting
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–10 mg 3–4 times/day. CHILDREN: GREATER THAN 39 KG: 5–10 mg q6–8h. Maximum: 40 mg/day. 18 KG TO 39 KG: 2.5 mg q8h or 5 mg q12h. Maximum: 15 mg/day. 13 KG TO 18 KG: 2.5 mg q8–12h. Maximum: 10 mg/day. 9–13 KG: 2.5 mg q12–24h. Maximum: 7.5 mg/day.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2.5–10 mg. May repeat q3–4h. Maximum: 10 mg/dose or 40 mg/day.
IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–10 mg q3–4h. CHILDREN: 0.1–0.15 mg/kg/dose q8–12h. Maximum: 40 mg/day.
Rectal: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 25 mg twice daily.
Psychosis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–10 mg 3–4 times/day. Maximum: 150 mg/day. CHILDREN 2–12 YRS: 2.5 mg 2–3 times/day. Maximum daily dose: 25 mg for children 6–12 yrs; 20 mg for children 2–5 yrs.
IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 10–20 mg q4h. CHILDREN: 0.13 mg/kg/dose.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Drowsiness, hypotension, dizziness, fainting (commonly occurring after first dose, occasionally after subsequent doses, rarely with oral form). Occasional: Dry mouth, blurred vision, lethargy, constipation, diarrhea, myalgia, nasal congestion, peripheral edema, urinary retention.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) appear dose related and are divided into three categories: akathisia (e.g., inability to sit still, tapping of feet), parkinsonian symptoms (mask-like face, tremors, shuffling gait, hypersalivation), acute dystonias (torticollis [neck muscle spasm], opisthotonos [rigidity of back muscles], oculogyric crisis [rolling back of eyes]). Dystonic reaction may produce diaphoresis, pallor. Tardive dyskinesia (tongue protrusion, puffing of cheeks, puckering of mouth) occurs rarely and may be irreversible. Abrupt withdrawal after long-term therapy may precipitate nausea, vomiting, gastritis, dizziness, tremors. Blood dyscrasias, particularly agranulocytosis, mild leukopenia, may occur. May lower seizure threshold.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Avoid skin contact with solution (contact dermatitis). Antiemetic: Assess for dehydration (poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, longitudinal furrows in tongue). Antipsychotic: Assess behavior, appearance, emotional status, response to environment, speech pattern, thought content.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P for hypotension. Assess for EPS. Monitor WBC, differential count for blood dyscrasias. Monitor for fine tongue movement (may be early sign of tardive dyskinesia). Supervise suicidal-risk pt closely during early therapy (as depression lessens, energy level improves, increasing suicide potential). Assess for therapeutic response (interest in surroundings, improvement in self-care, increased ability to concentrate, relaxed facial expression or relief of nausea, vomiting).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Limit caffeine. • Avoid alcohol. • Avoid tasks requiring alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established (may cause drowsiness, impairment).
progesterone
pro-jes-te-rone
(Crinone, Endometrin Vaginal Insert, Prochieve, Prometrium)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Not indicated to prevent coronary heart disease. Risk of dementia may be increased in postmenopausal women.
Not indicated to prevent coronary heart disease. Risk of dementia may be increased in postmenopausal women.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Progestin. CLINICAL: Hormone.
USES
PO: Prevent endometrial hyperplasia in nonhysterectomized, postmenopausal women receiving conjugated estrogens, secondary amenorrhea. IM: Amenorrhea, abnormal uterine bleeding due to hormonal imbalance. Vaginal gel: Treatment of infertility, secondary amenorrhea. Vaginal insert: Treatment of infertility. OFF-LABEL: Reduce risk of recurrent spontaneous preterm birth.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to progesterone. History of or suspected carcinoma of breast, active breast cancer; thromboembolic disorders, thrombophlebitis, missed abortion or ectopic pregnancy, severe hepatic dysfunction, undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding, use as a pregnancy test. Cautions: Diabetes, conditions aggravated by fluid retention (e.g., asthma, epilepsy, migraine, cardiac/renal dysfunction), history of mental depression.
ACTION
Promotes mammary gland development, relaxes uterine smooth muscle, induces secretory changes in the endometrium, blocks follicular maturation and ovulation, maintains pregnancy. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases abnormal uterine bleeding; transforms endometrium from proliferative to secretory in estrogen-primed endometrium.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Protein binding: 96%–99%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in bile, urine. Half-life (vaginal gel): 5–20 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. Avoid use during pregnancy. None established for vaginal gel, vaginal insert, or injection. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease effects. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May alter HDL, cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL. May increase hepatic function values.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules (Prometrium): 100 mg, 200 mg. Injection Oil: 50 mg/ml. Vaginal Gel (Crinone, Prochieve): 4% (45 mg/dose), 8% (90 mg/dose). Vaginal Insert (Endometrin Vaginal Insert): 100 mg. Vaginal suppository: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg, 400 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
IM
• Store at room temperature. • Administer only deep IM in large muscle mass.
PO
• If given in morning, administer 2 hrs after breakfast with full glass of water.
Vaginal Gel
• Remove applicator from sealed wrapper. Do not remove twist-off tab at this time. • Hold applicator by thick end. Shake down several times (like a thermometer) to ensure contents are at thin end. • Hold applicator by flat section of thick end and twist off tab at other end. Do not squeeze thick end while twisting tab (could force some gel to be released before insertion). • Insert applicator into vagina either in sitting position or lying on back with knees bent. • Insert thin end well into vagina. • Squeeze thick end of applicator to deposit gel. • Remove applicator, discard.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Amenorrhea
PO: ADULTS: 400 mg daily in evening for 10 days.
IM: ADULTS: 5–10 mg for 6–8 days. Withdrawal bleeding expected in 48–72 hrs if ovarian activity produced proliferative endometrium.
Vaginal: ADULTS: Apply 45 mg (4% gel) every other day for 6 or fewer doses. If response inadequate, may increase to 8% gel at same schedule.
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
IM: ADULTS: 5–10 mg/day for 6 days. When estrogen given concomitantly, begin progesterone after 2 wks of estrogen therapy; discontinue when menstruation begins.
Prevention of Endometrial Hyperplasia
PO: ADULTS: 200 mg in evening for 12 days per 28-day cycle, in combination with daily conjugated estrogen.
Infertility
Vaginal Gel: ADULTS: 90 mg (8% gel) once daily (twice daily in women with partial or complete ovarian failure). If pregnancy occurs, may continue up to 10–12 wks. Vaginal Insert: 100 mg 2–3 times/day starting at oocyte retrieval and continuing for up to 10 wks.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Contraindicated.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Breakthrough bleeding/spotting at beginning of therapy, amenorrhea, change in menstrual flow, breast tenderness. Gel: Drowsiness. Occasional: Edema, weight gain/loss, rash, pruritus, photosensitivity, skin pigmentation. Rare: Pain/swelling at injection site, acne, depression, alopecia, hirsutism.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Thrombophlebitis, cerebrovascular disorders, retinal thrombosis, pulmonary embolism occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for possibility of pregnancy, hypersensitivity to progestins before initiating therapy. Obtain baseline weight, serum glucose level, B/P.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Check weight daily; report wkly gain over 5 lbs. Assess skin for rash, urticaria. Immediately report development of chest pain, sudden shortness of breath, sudden decrease in vision, migraine headache, pain (esp. with swelling, warmth, redness) in calves, numbness of arm/leg (thrombotic disorders). Check B/P periodically. Note progesterone therapy on pathology specimens.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Use sunscreen, protective clothing to protect from sunlight, ultraviolet light until tolerance determined. • Report abnormal vaginal bleeding, other related symptoms. • Stop taking medication, contact physician at once if pregnancy suspected. • If using vaginal gel, avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established.
promethazine
proe-meth-a-zeen
(Phenadoz, Phenergan, Promethegan)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Fatalities due to respiratory depression reported in children 2 yrs and younger. Severe tissue injury, including gangrene, may occur with intravenous injection (preferred route is deep intramuscular). Be alert for signs and symptoms of tissue injury including burning or pain at injection site, phlebitis, swelling, blistering. Risk reduced by diluting promethazine with 10–20 ml 0.9% NaCl or diluting in a minibag (piggyback); administer slowly over 10–15 min; use large veins or central venous site (no hand or wrist veins).
Fatalities due to respiratory depression reported in children 2 yrs and younger. Severe tissue injury, including gangrene, may occur with intravenous injection (preferred route is deep intramuscular). Be alert for signs and symptoms of tissue injury including burning or pain at injection site, phlebitis, swelling, blistering. Risk reduced by diluting promethazine with 10–20 ml 0.9% NaCl or diluting in a minibag (piggyback); administer slowly over 10–15 min; use large veins or central venous site (no hand or wrist veins).
Do not confuse Phenergan with phenelzine, or promethazine with chlorpromazine or prednisone.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Phenergan with codeine: promethazine/codeine (a cough suppressant): 6.25 mg/10 mg/5 ml. Phenergan VC: promethazine/phenylephrine (a vasoconstrictor): 6.25 mg/5 mg/5 ml. Phenergan VC with codeine: promethazine/phenylephrine/codeine: 6.25 mg/5 mg/10 mg/5 ml.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Phenothiazine. CLINICAL: Antihistamine, antiemetic, sedative-hypnotic.
USES
Treatment of allergic conditions, motion sickness, nausea, vomiting. May be used as mild sedative. Adjunct to postoperative analgesia. OFF-LABEL: Nausea/vomiting related to pregnancy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to promethazine, other phenothiazines. Children 2 yrs and younger (may cause fatal respiratory depression), severe CNS depression, coma, treatment of lower respiratory tract symptoms including asthma. Cautions: Cardiovascular/hepatic or respiratory impairment, narrow-angle glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, GI/GU obstruction, urinary retention, visual problems, decreased GI motility, myasthenia gravis, Parkinson’s disease, elderly, bone marrow depression, asthma, peptic ulcer, history of seizures, sleep apnea, pts suspected of Reye’s syndrome.
ACTION
Block postsynaptic dopaminergic receptors; competes with histamine for histamine receptors; possesses muscarinic blocking effect. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents allergic responses mediated by histamine (urticaria, pruritus). Prevents, relieves nausea/vomiting. Produces mild sedative effect.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 20 min | N/A | 2–8 hrs |
| IV | 3–5 min | N/A | 2–8 hrs |
| IM | 20 min | N/A | 2–8 hrs |
| Rectal | 20 min | N/A | 2–8 hrs |
Well absorbed from GI tract after IM administration. Protein binding: 83%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 9–16 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Readily crosses placenta. Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. May inhibit platelet aggregation in neonates if taken within 2 wks of birth. May produce jaundice, extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) in neonates if taken during pregnancy. Children: May experience increased excitement. Not recommended for pts younger than 2 yrs. Elderly: More sensitive to dizziness, sedation, confusion, hypotension, hyperexcitability, anticholinergic effects (e.g., dry mouth).
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, CNS depressants (e.g., lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase CNS depressant effects. Anticholinergics (e.g., dicyclomine, glycopyrrolate, scopolamine) may increase anticholinergic effects. MAOIs (e.g., phenelzine, selegiline) may prolong, intensify anticholinergic, CNS depressant effects. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May suppress wheal/flare reactions to antigen skin testing unless discontinued 4 days before testing.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 25 mg/ml, 50 mg/ml. Solution, Oral: 6.25 mg/5 ml. Suppositories: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg. Syrup: 6.25 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ IM is preferred route; avoid IV if possible. Significant tissue necrosis may occur if given subcutaneously. Inadvertent intra-arterial injection may produce significant arteriospasm, resulting in severe circulation impairment.
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Dilute with 10–20 ml 0.9% NaCl or prepare minibag.
Rate of Administration • Administer slowly over 10–15 min. • Use large vein or central venous site (no hand or wrist veins). • Too-rapid rate of infusion may result in transient fall in B/P, producing orthostatic hypotension, reflex tachycardia, serious tissue injury.
Storage • Store at room temperature.
PO
• Give with food or fluids to reduce GI distress. • Scored tablets may be crushed.
Rectal
• Refrigerate suppository. • Moisten suppository with cold water before inserting well into rectum.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Allopurinol (Aloprim), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), heparin, ketorolac (Toradol), nalbuphine (Nubain), piperacillin and tazobactam (Zosyn).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), midazolam (Versed), morphine.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Contraindicated in children 2 yrs and younger.
Allergic Symptoms
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 6.25–12.5 mg 3 times/day plus 25 mg at bedtime. CHILDREN: 0.1 mg/kg/dose (Maximum: 12.5 mg) 4 times/day plus 0.5 mg/kg/dose (Maximum: 25 mg) at bedtime.
IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 25 mg. May repeat in 2 hrs.
Motion Sickness
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 25 mg 30–60 min before departure; may repeat in 8–12 hrs, then every morning on rising and before evening meal. CHILDREN: 0.5 mg/kg 30–60 min before departure; may repeat in 8–12 hrs, then every morning on rising and before evening meal. Maximum: 25 mg twice daily.
Prevention of Nausea/Vomiting
PO, IV, IM, Rectal: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 12.5–25 mg q4–6h as needed. CHILDREN: 0.25–1 mg/kg q4–6h as needed. Maximum: 25 mg/dose.
Sedative
PO, IV, IM, Rectal: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 12.5–50 mg/dose. CHILDREN: 12.5–25 mg/dose.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Drowsiness, dry mouth, nose, throat; urinary retention, thickening of bronchial secretions. Occasional: Epigastric distress, flushing, visual disturbances, hearing disturbances, wheezing, paresthesia, diaphoresis, chills, disorientation, hypotension, confusion, syncope in elderly. Rare: Dizziness, urticaria, photosensitivity, nightmares.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Paradoxical reaction (particularly in children) manifested as excitation, anxiety, tremor, hyperactive reflexes, seizures. Long-term therapy may produce extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) noted as dystonia (abnormal movements), pronounced motor restlessness (most frequently in children), parkinsonism (esp. noted in elderly). Blood dyscrasias, particularly agranulocytosis, occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess allergy symptoms. Assess B/P, pulse for bradycardia, tachycardia if pt is given parenteral form. If used as antiemetic, assess for dehydration (poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, longitudinal furrows in tongue). Assess LOC.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor serum electrolytes in pts with severe vomiting. Assist with ambulation if drowsiness, dizziness occurs. Monitor for relief of nausea, vomiting, allergic symptoms.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Drowsiness, dry mouth may be expected response to drug. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Sugarless gum, sips of water may relieve dry mouth. • Coffee, tea may help reduce drowsiness. • Report visual disturbances, involuntary movements, restlessness. • Avoid alcohol, other CNS depressants. • Avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight.
propafenone
proe-paf-e-nown
(Apo-Propafenone
 , Rythmol, Rythmol SR)
, Rythmol, Rythmol SR)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Mortality or nonfatal cardiac arrest rate (7.7%) in asymptomatic non–life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia pts with recent MI (more than 6 days but less than 2 years prior) reported.
Mortality or nonfatal cardiac arrest rate (7.7%) in asymptomatic non–life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia pts with recent MI (more than 6 days but less than 2 years prior) reported.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Class 1c antiarrhythmic. CLINICAL: Antiarrhythmic.
USES
Treatment of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias (e.g., sustained ventricular tachycardias). Treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation/flutter (PAF) or paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) in pts with disabling symptoms and without structural heart disease. Rythmol SR: Prolong the time to recurrence of atrial fibrillation/flutter or paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in pts with disabling symptoms without structural heart disease. OFF-LABEL: Treatment following cardioversion of recent-onset atrial fibrillation; supraventricular tachycardia in pts with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to propafenone. Bradycardia, bronchospastic disorders, cardiogenic shock, electrolyte imbalance, sinoatrial, AV, intraventricular impulse generation or conduction disorders (e.g., sick sinus syndrome, AV block) without pacemaker, uncontrolled HF, hypotension. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, myasthenia gravis, concurrent use of other medications that prolong QT interval, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia.
ACTION
Decreases fast sodium current in Purkinje/myocardial cells. Decreases excitability, automaticity; prolongs conduction velocity, refractory period. Therapeutic Effect: Suppresses arrhythmias.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Nearly completely absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 85%–97%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in feces. Half-life: 2–10 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Amiodarone may affect cardiac conduction, repolarization. May increase digoxin concentration. May increase effects of warfarin. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, erythromycin) may increase concentration/toxicity. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effect. Ephedra may worsen arrhythmias. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase concentration. LAB VALUES: May cause EKG changes (e.g., QRS widening, PR interval prolongation), positive ANA titer.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets (Rythmol): 150 mg, 225 mg, 300 mg.
 Capsules (Extended-Release [Rythmol SR]): 225 mg, 325 mg, 425 mg.
Capsules (Extended-Release [Rythmol SR]): 225 mg, 325 mg, 425 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May take without regard to meals. • Give whole; do not break, crush, divide, or open capsules.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Ventricular Arrhythmias, PAT, PSVT
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 150 mg q8h. May increase at 3- to 4-day intervals to 225 mg q8h, then to 300 mg q8h. Maximum: 900 mg/day.
Atrial Fibrillation (Prevention of Recurrence)
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 150 mg q8h. May increase at 3- to 4-day intervals to 225 mg q8h, then to 300 mg q8h. Maximum: 900 mg/day. (Extended-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 225 mg q12h. May increase at 5-day intervals to 325 mg q12h. Maximum: 425 mg q12h.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (13%–7%): Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, altered taste, constipation. Occasional (6%–3%): Headache, dyspnea, blurred vision, dyspepsia. Rare (Less Than 2%): Rash, weakness, dry mouth, diarrhea, edema, hot flashes.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
May produce, worsen arrhythmias. Overdose may produce hypotension, drowsiness, bradycardia, atrioventricular conduction disturbances.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Correct electrolyte imbalance before administering medication. Obtain baseline EKG. Screen for cardiac contraindications.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess pulse for quality, rhythm, rate. Monitor EKG for cardiac performance or changes, particularly widening of QRS, prolongation of PR interval. Question for visual disturbances, headache, GI upset. Monitor fluid, serum electrolyte levels. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess for dizziness, unsteadiness. Monitor LFT. Monitor for therapeutic serum level (0.06–1 mcg/ml).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Compliance with therapy regimen is essential to control arrhythmias. • Altered taste sensation may occur. • Report headache, blurred vision. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Report chest pain, difficulty breathing, palpitations.
propofol

proe-poe-fol
(Diprivan, Fresenius Propoven)
Do not confuse Diprivan with Diflucan or Ditropan, or propafol with fospropofol.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Rapid-acting general anesthetic. CLINICAL: Sedative-hypnotic.
USES
Induction/maintenance of anesthesia. Continuous sedation in intubated and respiratory controlled adult pts in ICU. OFF-LABEL: Postop antiemetic, refractory status epilepticus.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to propofol, eggs, egg products, soybean or soy products. Cautions: Hemodynamically unstable pts, hypovolemia, severe cardiac/respiratory disease, elevated ICP, impaired cerebral circulation, preexisting pancreatitis, hyperlipidemia, history of epilepsy, seizure disorder, elderly, debilitated, pts allergic to peanuts.
ACTION
Cause CNS depression through agonist action of GABA receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Produces hypnosis rapidly.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| IV | 40 sec | N/A | 3–10 min |
Rapidly, extensively distributed. Protein binding: 97%–99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Rapid awakening can occur 10–15 min after discontinuation. Half-life: 3–12 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Not recommended for obstetrics, breastfeeding mothers. Pregnancy Category B. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. FDA approved for use in those 2 mos and older. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted; lower dosages recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, CNS depressants (e.g., lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase CNS, respiratory depression, hypotensive effects. Antihypertensive medications (e.g. amlodipine, lisinopril, valsartan) may increase hypotensive effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum triglycerides.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Emulsion: 10 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
◀ ALERT ▶ Do not give through same IV line with blood or plasma.
Reconstitution • May give undiluted, or dilute only with D5W. • Do not dilute to concentration less than 2 mg/ml (4 ml D5W to 1 ml propofol yields 2 mg/ml).
Rate of Administration • Too-rapid IV administration may produce marked severe hypotension, respiratory depression, irregular muscular movements. • Observe for signs of extravasation (pain, discolored skin patches, white or blue color to peripheral IV site area, delayed onset of drug action).
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Discard unused portions. • Do not use if emulsion separates. • Shake well before using.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amikacin (Amikin), amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), bretylium (Bretylol), calcium chloride, ciprofloxacin (Cipro), diazepam (Valium), digoxin (Lanoxin), doxorubicin (Adriamycin), gentamicin (Garamycin), methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), minocycline (Minocin), phenytoin (Dilantin), tobramycin (Nebcin), verapamil (Isoptin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Acyclovir (Zovirax), bumetanide (Bumex), calcium gluconate, ceftazidime (Fortaz), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), enalapril (Vasotec), fentanyl, heparin, insulin, labetalol (Normodyne, Trandate), lidocaine, lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium, milrinone (Primacor), nitroglycerin, norepinephrine (Levophed), potassium chloride, vancomycin (Vancocin).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Anesthesia
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Induction, 2–2.5 mg/kg (approximately 40 mg q10sec until onset of anesthesia). Maintenance: Initially, 100–200 mcg/kg/min or 6–12 mg/kg/hr for 10–15 min. Usual maintenance infusion: 50–100 mcg/kg/min or 3–6 mg/kg/hr. CHILDREN 3–16 YRS: Induction, 2.5–3.5 mg/kg over 20–30 sec, then infusion of 125–300 mcg/kg/min or 7.5–18 mg/kg/hr.
Sedation in ICU
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 5 mcg/kg/min (0.3 mg/kg/hr) for 5 min, then titrate to 5–80 mcg/kg/min (0.3–4.8 mg/kg/hr) in 5–10 mcg/kg/min (0.3–0.6 mg/kg/hr) increments allowing minimum of 5 min between dose adjustments. Usual maintenance: 5–50 mcg/kg/min (0.3–3 mg/kg/hr).
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Involuntary muscle movements, apnea (common during induction; often lasts longer than 60 sec), hypotension, nausea, vomiting, IV site burning/stinging. Occasional: Twitching, thrashing, headache, dizziness, bradycardia, hypertension, fever, abdominal cramps, paresthesia, coldness, cough, hiccups, facial flushing, green-tinted urine. Rare: Rash, dry mouth, agitation, confusion, myalgia, thrombophlebitis.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Continuous infusion or repeated intermittent infusions of propofol may result in extreme drowsiness, respiratory depression, circulatory depression, delirium. Too-rapid IV administration may produce severe hypotension, respiratory depression, involuntary muscle movements. Pt may experience acute allergic reaction, characterized by abdominal pain, anxiety, restlessness, dyspnea, erythema, hypotension, pruritus, rhinitis, urticaria.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Resuscitative equipment, suction, O2 must be available. Obtain vital signs before administration.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Observe pt for signs of wakefulness, agitation. Monitor respiratory rate, B/P, heart rate, O2 saturation, ABGs, depth of sedation, serum lipid, triglycerides (if used longer than 24 hrs). May change urine color to green.
propranolol

proe-pran-oh-lol
(Apo-Propranolol
 , Hemangeol, Inderal LA, Inderal XL, InnoPran XL, Novo-Pranol
, Hemangeol, Inderal LA, Inderal XL, InnoPran XL, Novo-Pranol
 )
)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Severe angina exacerbation, MI, ventricular arrhythmias may occur in angina pts after abrupt discontinuation; must taper gradually over 1–2 wks.
Severe angina exacerbation, MI, ventricular arrhythmias may occur in angina pts after abrupt discontinuation; must taper gradually over 1–2 wks.
Do not confuse Inderal LA with Adderall, Imdur, Isordil, or Toradol, or propranolol with Pravachol.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Inderide: propranolol/hydrochlorothiazide (a diuretic): 40 mg/25 mg, 80 mg/25 mg. Inderide LA: propranolol/hydrochlorothiazide (a diuretic): 80 mg/50 mg, 120 mg/50 mg, 160 mg/50 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Beta-adrenergic blocker. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive, antianginal, antiarrhythmic, antimigraine.
USES
Treatment of angina pectoris, supraventricular arrhythmias, essential tremors, hypertension, ventricular tachycardia, obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, treatment of proliferating infantile hemagioma requiring systemic therapy, migraine headache, pheochromocytoma, prevention of MI. Hemangeol: Treatment of proliferating infantile hemangioma needing systemic therapy. OFF-LABEL: Treatment adjunct for anxiety, tremor due to Parkinson’s disease, alcohol withdrawal, aggressive behavior, schizophrenia, antipsychotic-induced akathisia, variceal hemorrhage, acute panic.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to propranolol. Bronchial asthma, severe sinus bradycardia, cardiogenic shock, COPD, sick sinus syndrome, heart block other than first-degree (unless pt has functional pacemaker), uncompensated HF. Hemangeol (Additional): Premature infants with corrected age younger than 5 wks, infants weighing less than 2 kg; asthma, history of bronchospasm, bradycardia (less than 80 beats/min), greater than first-degree heart block, decompensated HF; B/P less than 50/30 mmHg, pheochromocytoma. Cautions: Diabetes, renal/hepatic impairment, Raynaud’s disease, hyperthyroidism, myasthenia gravis, psychiatric disease, bronchospastic disease, elderly, history of severe anaphylaxis to allergens.
ACTION
Blocks beta1-, beta2-adrenergic receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Slows heart rate; decreases B/P, myocardial contractility, myocardial oxygen demand.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 1–2 hrs | N/A | 6 hrs |
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 93%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 4–6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Avoid use during first trimester. May produce low birth-weight infants, bradycardia, apnea, hypoglycemia, hypothermia during delivery. Children: No age-related precautions noted. Elderly: Age-related peripheral vascular disease may increase susceptibility to decreased peripheral circulation.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Diuretics (e.g., furosemide, HCTZ), other antihypertensives (e.g., amlodipine, lisinopril, valsartan) may increase hypotensive effect. May mask symptoms of hypoglycemia, prolong hypoglycemic effect of insulin, oral hypoglycemics (e.g., glipizide, metformin). Digoxin may increase risk for bradycardia. NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive effect. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginger, licorice, ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Licorice may increase water retention. Garlic, periwinkle have antihypertensive effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer, serum BUN, LDH, lipoprotein, alkaline phosphatase, potassium, uric acid, ALT, AST, triglycerides.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 1 mg/ml. Oral Solution: 20 mg/5 ml, 40 mg/5 ml. Oral Solution (Hemangeol): 4.28 mg/ml. Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, 60 mg, 80 mg.
 Capsules (Extended-Release [InnoPran XL]): 80 mg, 120 mg.
Capsules (Extended-Release [InnoPran XL]): 80 mg, 120 mg.
 Capsules (Sustained-Release [Inderal LA]): 60 mg, 80 mg, 120 mg, 160 mg.
Capsules (Sustained-Release [Inderal LA]): 60 mg, 80 mg, 120 mg, 160 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Give undiluted for IV push. • For IV infusion, may dilute each 1 mg in 10 ml D5W.
Rate of Administration • Do not exceed 1 mg/min injection rate. • For IV infusion, give over 30 min.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • Once diluted, stable for 24 hrs at room temperature.
PO
• May crush scored tablets. • Do not break, crush, or open extended- or sustained-release capsules. • Give immediate-release tablets on empty stomach. • Give extended-release, sustained-release without regard to food.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Alteplase (Activase), heparin, milrinone (Primacor), potassium chloride, propofol (Diprivan).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate Release): Initially, 40 mg twice daily. May increase dose q3–7days. Usual dose: 120–240 mg/day in 2–3 divided doses. Maximum: 640 mg/day. CHILDREN: Initially, 1–2 mg/kg/day in 2–3 divided doses. May increase at 3- to 5-day intervals. Usual dose: 4 mg/kg/day. Maximum: 4 mg/kg/day.
PO ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Sustained-Release): (Inderal LA): Initially, 80 mg once daily. Maintenance: 120–160 mg/day.
(Extended-Release): Initially, 80 mg at bedtime. May increase at 2- to 3-wk intervals. Maximum: 120 mg.
Angina
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate Release): 80–320 mg/day in 2–4 divided doses.
PO (Extended-Release): Initially, 80 mg/day. Maximum: 320 mg/day.
Arrhythmia
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1–3 mg. Repeat q2–5min up to total of 5 mg. CHILDREN: 0.01–0.1 mg/kg. Maximum: Infants, 1 mg; children, 3 mg.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate Release): 10–30 mg q6–8h or 10–40 mg 3–4 times/day. CHILDREN: Initially, 0.5–1 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6–8h. May increase q3days. Usual dosage: 2–6 mg/kg/day. Maximum: 16 mg/kg/day or 60 mg/day.
Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate Release): 20–40 mg 3–4 times/day or 80–160 mg once daily as extended-release capsule.
Adjunct to Alpha-Blocking Agents to Treat Pheochromocytoma
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 30–60 mg/day in divided doses.
Migraine Headache
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate Release): Initially, 80 mg/day in 3–4 divided doses or 80 mg once daily as extended-release capsule. May increase by 20–40 mg/dose q3–4wks up to 160–240 mg/day in divided doses. CHILDREN WEIGHING 35 KG OR LESS: 10–20 mg 3 times/day. CHILDREN WEIGHING OVER 35 KG: 20–40 mg 3 times/day.
Extended-Release (Inderal LA): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 80 mg daily. Effective range: 160–240 mg/day.
Reduction of Cardiovascular Mortality, Reinfarction in Pts with Previous MI
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate Release): Initially, 40 mg 3 times/day. Range: 180–240 mg/day in 3–4 divided doses.
Essential Tremor
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 40 mg twice daily increased up to 120–320 mg/day in 3 divided doses.
Infantile Hemangioma
Note: Separate doses by at least 9 hrs during or after feeding.
PO: INFANTS 5 WKS TO 5 MOS: Initially, 0.15 ml/kg (0.6 mg/kg) twice daily. After 1 wk, increase to 0.3 ml/kg (1.1 mg/kg) twice daily. After 2 wks, increase to maintenance dose of 0.4 ml/kg (1.7 mg/kg) twice daily.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Diminished sexual function, drowsiness, difficulty sleeping, unusual fatigue/weakness. Occasional: Bradycardia, depression, sensation of coldness in extremities, diarrhea, constipation, anxiety, nasal congestion, nausea, vomiting. Rare: Altered taste, dry eyes, pruritus, paresthesia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may produce profound bradycardia, hypotension. Abrupt withdrawal may result in diaphoresis, palpitations, headache, tremulousness. May precipitate HF, MI in pts with cardiac disease, thyroid storm in pts with thyrotoxicosis, peripheral ischemia in pts with existing peripheral vascular disease. Hypoglycemia may occur in pts with previously controlled diabetes. Antidote: Glucagon (see Appendix K for dosage).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess baseline renal function, LFT. Assess B/P, apical pulse immediately before administering drug (if pulse is 60/min or less or systolic B/P is less than 90 mm Hg, withhold medication, contact physician). Angina: Record onset, quality, radiation, location, intensity, duration of anginal pain, precipitating factors (exertion, emotional stress).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess pulse for quality, regularity, bradycardia. Monitor EKG for cardiac arrhythmias. Assess fingers for color, numbness (Raynaud’s). Assess for evidence of HF (dyspnea [particularly on exertion or lying down], night cough, peripheral edema, distended neck veins). Monitor I&O (increase in weight, decrease in urinary output may indicate HF). Assess for rash, fatigue, behavioral changes. Therapeutic response time ranges from a few days to several wks. Measure B/P near end of dosing interval (determines if B/P is controlled throughout day).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not abruptly discontinue medication. • Compliance with therapy regimen is essential to control hypertension, arrhythmia, anginal pain. • To avoid hypotensive effect, slowly go from lying to standing. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Report excessively slow pulse rate (less than 50 beats/min), peripheral numbness, dizziness. • Do not use nasal decongestants, OTC cold preparations (stimulants) without physician approval. • Restrict salt, alcohol intake.
propylthiouracil
proe-pil-thye-oh-ure-a-sil
(Propyl-Thyracil
 )
)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  May cause severe hepatic injury, acute hepatic failure, death.
May cause severe hepatic injury, acute hepatic failure, death.
Do not confuse propylthiouracil with purinethol.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Thiourea derivative. CLINICAL: Antithyroid agent.
USES
Palliative treatment of hyperthyroidism; adjunct to ameliorate hyperthyroidism in preparation for surgical treatment, radioactive iodine therapy. OFF-LABEL: Management of thyrotoxic crises, Graves’ disease, thyroid storm.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to propylthiouracil. Cautions: In combination with other agranulocytosis-inducing drugs.
ACTION
Blocks oxidation of iodine in thyroid gland, blocks synthesis of thyroxine, triiodothyronine. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormone.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 80%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 1.5–5 hrs.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration of digoxin (as pt becomes euthyroid). May increase effect of oral anticoagulants (e.g., apixaban, warfarin). HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase LDH, serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, ALT, AST, prothrombin time.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 50 mg.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hyperthyroidism
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 300–400 mg/day (ELDERLY: 150–300 mg/day) in divided doses q8h. Maintenance: 100–150 mg/day in divided doses q8–12h.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Urticaria, rash, pruritus, nausea, skin pigmentation, hair loss, headache, paresthesia. Occasional: Drowsiness, lymphadenopathy, vertigo. Rare: Drug fever, lupus-like syndrome.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Agranulocytosis (may occur as long as 4 mos after therapy), pancytopenia, fatal hepatitis have occurred.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline weight, pulse.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor pulse, weight daily. Check for skin eruptions, pruritus, swollen lymph glands. Be alert for signs, symptoms of hepatic injury, hepatitis (nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, jaundice). Monitor hematology results for bone marrow suppression; observe for signs of infection, bleeding.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Space doses evenly around the clock. • Take resting pulse daily. • Report pulse rate less than 60 beats/min. • Seafood, iodine products may be restricted. • Report fever, sore throat, yellowing of skin/eyes, unusual bleeding/bruising immediately. • Report sudden or continuous weight gain, cold intolerance, depression.
pseudoephedrine
soo-doe-e-fed-rin
(Balminil Decongestant
 , Nexafed, PMS-Pseudoephedrine
, Nexafed, PMS-Pseudoephedrine
 , Robidrine
, Robidrine
 , Sudafed, Sudafed 12 Hour, Sudafed 24 Hour, Sudafed Children’s)
, Sudafed, Sudafed 12 Hour, Sudafed 24 Hour, Sudafed Children’s)
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Advil Cold, Motrin Cold: pseudoephedrine/ibuprofen (an NSAID): 30 mg/200 mg, 15 mg/100 mg per 5 ml. Allegra-D: pseudoephedrine/fexofenadine (an antihistamine): 120 mg/60 mg. Allegra-D 24 Hour: pseudoephedrine/fexofenadine: 240 mg/180 mg. Claritin-D: pseudoephedrine/loratadine (an antihistamine): 120 mg/5 mg, 240 mg/10 mg. Clarinex-D 24-Hour: pseudoephedrine/desloratadine (an antihistamine): 240 mg/5 mg. Clarinex-D 12-Hour: pseudoephedrine/desloratadine: 120 mg/2.5 mg. Rezira: pseudoephedrine/hydrocodone (an opioid analgesic): 60 mg/5 mg per 5 ml. Zyrtec-D: pseudoephedrine/cetirizine (an antihistamine): 120 mg/5 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Sympathomimetic. CLINICAL: Nasal decongestant.
USES
Temporary relief of nasal congestion due to common cold, upper respiratory allergies, sinusitis. Enhances nasal, sinus drainage.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to pseudoephedrine. Use of MAOIs within 14 days. Severe hypertension, coronary artery disease. Cautions: Elderly, hyperthyroidism, diabetes, ischemic heart disease, prostatic hypertrophy, mild to moderate hypertension, arrhythmias, renal impairment, seizure disorder, increased intraocular pressure.
ACTION
Directly stimulates alpha-adrenergic, beta-adrenergic receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Produces vasoconstriction; causes bronchial relaxation, increased heart rate/contractility.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO (tablets, syrup) | 15–30 min | 30–60 min | 4–6 hrs |
| PO (extended-release) | N/A | N/A | 8–12 hrs |
Well absorbed from GI tract. Partially metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 9–16 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 2 yrs. Elderly: Age-related prostatic hypertrophy may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of antihypertensives (e.g., amlodipine, lisinopril, valsartan), beta blockers (e.g., carvedilol, metoprolol), diuretics (e.g., furosemide, HCTZ). HERBAL: Ephedra, yohimbe may cause hypertension. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (OTC)
Liquid: 15 mg/5 ml, 30 mg/5 ml. Syrup: 30 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 30 mg.
 Tablets, Extended-Release: (12 Hour): 120 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release: (12 Hour): 120 mg.
 Tablets, Extended-Release: (24 Hour): 240 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release: (24 Hour): 240 mg.
◀ ALERT ▶ Pseudoephedrine is key ingredient in synthesizing methamphetamine. Many pharmacies have moved pseudoephedrine behind the counter due to concerns about its purchase and theft for purposes of methamphetamine manufacture.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Administer with water or milk to decrease GI upset. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide extended-release forms; give whole.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Decongestant
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 30–60 mg q4–6h. Maximum: 240 mg/day. CHILDREN 6–11 YRS: 30 mg q4–6h. Maximum: 120 mg/day. CHILDREN 4–5 YRS: 15 mg q4–6h. Maximum: 60 mg/day.
PO (Extended-Release): ADULTS, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 120 mg q12h or 240 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (10%–5%): Nervousness, restlessness, insomnia, tremor, headache. Rare (4%–1%): Diaphoresis, weakness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Large doses may produce tachycardia, palpitations (particularly in pts with cardiac disease), light-headedness, nausea, vomiting. Overdose in those older than 60 yrs may result in hallucinations, CNS depression, seizures.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Discontinue drug if adverse reactions occur. • Report insomnia, dizziness, tremors, tachycardia, palpitations.
psyllium
sil-ee-yum
(Konsyl, Metamucil, Multihealth Fiber)
Do not confuse Fiberall with Feverall.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Bulk-forming agent. CLINICAL: Laxative.
USES
Treatment of occasional constipation. Dietary fiber supplement. Reduce risk of CHD.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to psyllium, difficulty swallowing. Cautions: Esophageal strictures, ulcers, stenosis, intestinal adhesions, difficulty swallowing, management of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), elderly. Pts with or prone to fecal impaction or GI obstruction. Avoid use in pts with nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain.
ACTION
Dissolves and swells in water providing increased bulk, moisture content in stool. Therapeutic Effect: Promotes peristalsis, bowel motility.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 12–24 hrs | 2–3 days | N/A |
Acts in small, large intestines.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Safe for use in pregnancy. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 6 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose. May decrease serum potassium.
AVAILABILITY (OTC)
Capsules: 500 mg. Powder: 300 g, 450 g bulk powder.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Administer at least 2 hrs before or after other medication. • All doses should be followed with 8 oz liquid. • Drink 6–8 glasses of water/day (aids stool softening). • Do not swallow in dry form; mix with at least 1 full glass (8 oz) of liquid.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Constipation
Refer to specific dosing guidelines on product labeling.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (2.5–30 g/day in divided doses) 2–5 capsules/dose up to 3 times/day. 1 rounded tsp or 1 tbsp of powder up to 3 times/day. CHILDREN 6–11 YRS: (1.25–15 g/day in divided doses). Approximately ½ adult dose up to 3 times/day.
Reduce Risk of CHD
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 7 g or more daily.
SIDE EFFECTS
Rare: Some degree of abdominal discomfort, nausea, mild abdominal cramps, griping, faintness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Esophageal/bowel obstruction may occur if administered with insufficient liquid (less than 250 ml).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Encourage adequate fluid intake. Assess bowel sounds for peristalsis. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor serum electrolytes in pts exposed to prolonged, frequent, excessive use of medication.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take each dose with full glass (250 ml) of water. • Inadequate fluid intake may cause GI obstruction. • Institute measures to promote defecation (increase fluid intake, exercise, high-fiber diet).
pyrazinamide
peer-a-zin-a-mide
(Tebrazid
 )
)
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Rifater: pyrazinamide/isoniazid/rifampin (an antitubercular): 300 mg/50 mg/120 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Synthetic pyrazine analogue. CLINICAL: Antitubercular.
USES
Treatment of clinical tuberculosis in conjunction with other antitubercular agents.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to pyrazinamide. Acute gout, severe hepatic dysfunction. Cautions: Diabetes mellitus, porphyria, renal impairment, history of gout, history of alcoholism, concurrent medication associated with hepatotoxicity.
ACTION
Exact mechanism unknown. May disrupt mycobacterium tuberculosis membrane transport. Therapeutic Effect: Bacteriostatic or bactericidal, depending on drug concentration at infection site, susceptibility of infecting bacteria.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 5%–10%. Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 9–10 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, uric acid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 500 mg.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Tuberculosis (in Combination With Other Antituberculars)
PO: ADULTS: Based on lean body weight. 40–55 KG: 1,000 mg daily; 56–75 KG: 1,500 mg daily; 76–90 KG: 2,000 mg (maximum dose regardless of weight). CHILDREN: 15–30 mg/kg/day in 1 or 2 doses. Maximum: 2 g/day.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
CrCl less than 30 ml/min or receiving HD: 25–35 mg/kg/dose 3 times/wk (give after dialysis). Contraindicated in severe hepatic impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Arthralgia, myalgia (usually mild, self-limited). Rare: Hypersensitivity reaction (rash, pruritus, urticaria), photosensitivity, gouty arthritis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hepatotoxicity, gouty arthritis, thrombocytopenia, anemia occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for hypersensitivity to pyrazinamide, isoniazid, ethionamide, niacin. Ensure collection of specimens for culture, sensitivity. Obtain CBC, LFT, serum uric acid levels.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor LFT results; be alert for hepatic reactions: jaundice, malaise, fever, abdominal (RUQ) tenderness, anorexia, nausea, vomiting (stop drug, notify physician promptly). Check serum uric acid levels; assess for hot, painful, swollen joints, esp. big toe, ankle, knee (gout). Evaluate serum blood glucose levels, diabetic status carefully (pyrazinamide makes management difficult). Assess for rash, skin eruptions. Monitor CBC for thrombocytopenia, anemia.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not skip doses; complete full length of therapy (may be mos or yrs). • Office visits, lab tests are essential part of treatment. • Take with food to reduce GI upset. • Avoid excessive exposure to sun, ultraviolet light until photosensitivity is determined. • Report any new symptom, immediately for jaundice (yellowing sclera of eyes/skin); unusual fatigue; fever; loss of appetite; hot, painful, swollen joints.
pyridostigmine
peer-id-oh-stig-meen
(Mestinon, Mestinon SR
 , Regonol)
, Regonol)
Do not confuse pyridostigmine with physostigmine, or Regonol with Reglan or Renagel.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Anticholinesterase. CLINICAL: Cholinergic muscle stimulant.
USES
Improvement of muscle strength in control of myasthenia gravis, reversal of effects of nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents after surgery.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to pyridostigmine. Mechanical GI/urinary tract obstruction. Cautions: Bronchial asthma, bradycardia, seizure disorder, hyperthyroidism, cardiac arrhythmias, peptic ulcer, renal impairment.
ACTION
Prevents destruction of acetylcholine by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, enhancing impulse transmission across myoneural junction. Therapeutic Effect: Produces miosis; increases intestinal, skeletal muscle tone; stimulates salivary, sweat gland secretions.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Poorly absorbed from GI tract. Metabolized in liver. Excreted primarily unchanged in urine. Half-life: 1–2 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Antagonizes effects of neuromuscular blockers (e.g., succinylcholine, vecuronium). Anticholinergics (e.g., dicyclomine, glycopyrrolate, scopolamine) prevent, reverse effects. Cholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., donepezil, tacrine) may increase risk of toxicity. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution (Regonol): 5 mg/ml. Syrup (Mestinon): 60 mg/5 ml. Tablets (Mestinon): 60 mg.
 Tablets (Extended-Release [Mestinon Timespan]): 180 mg.
Tablets (Extended-Release [Mestinon Timespan]): 180 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV, IM
IV, IM
• Give large parenteral doses concurrently with 0.6–1.2 mg atropine sulfate IV to minimize side effects.
PO
• Give with food, milk. • Tablets may be crushed. Do not chew, crush extended-release tablets (may be broken). • Give larger dose at times of increased fatigue (e.g., for those with difficulty in chewing, 30–45 min before meals).
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with any other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Highly individualized dosing ranges.
Myasthenia Gravis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate- Release):Initially, 60 mg 3 times/day. Dosage increased at 48-hr intervals. Maintenance: 60 mg–1.5 g/day divided into 5–6 doses/day. (Usual dose: 600 mg/day.) CHILDREN: Initially, 1 mg/kg/dose q4–6h. Maximum: 7 mg/kg/24 hr divided into 5–6 doses. Usual dose: 600 mg/day.
PO (Extended-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 180–540 mg 1–2 times/day with at least a 6-hr interval between doses.
IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2 mg or 1/30th of oral dose q2–3h. CHILDREN: 0.05–0.15 mg/kg/dose. Maximum single dose: 10 mg.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Miosis, increased GI/skeletal muscle tone, bradycardia, constriction of bronchi/ureters, diaphoresis, increased salivation. Occasional: Headache, rash, temporary decrease in diastolic B/P with mild reflex tachycardia, short periods of atrial fibrillation (in hyperthyroid pts), marked drop in B/P (in hypertensive pts).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may produce cholinergic crisis, manifested as increasingly severe descending muscle weakness (appears first in muscles involving chewing, swallowing, followed by muscle weakness of shoulder girdle, upper extremities), respiratory muscle paralysis, followed by pelvis girdle/leg muscle paralysis. Requires withdrawal of all cholinergic drugs and immediate use of 1–4 mg atropine sulfate IV for adults, 0.01 mg/kg for infants and children younger than 12 yrs.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Larger doses should be given at time of greatest fatigue. Assess muscle strength before testing for diagnosis of myasthenia gravis and following drug administration. Avoid large doses in pts with megacolon, reduced GI motility.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Have facial tissues readily available at pt’s bedside. Monitor respirations closely during myasthenia gravis testing or if dosage is increased. Assess diligently for cholinergic reaction, bradycardia in myasthenic pt in crisis. Coordinate dosage time with periods of fatigue and increased/decreased muscle strength. Monitor for therapeutic response to medication (increased muscle strength, decreased fatigue, improved chewing/swallowing functions).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, diaphoresis, profuse salivary secretions, palpitations, muscle weakness, severe abdominal pain, difficulty breathing.
pyridoxine (vitamin B6)
peer-i-dox-een
(Pyri-500)
Do not confuse pyridoxine with paroxetine, pralidoxime, or Pyridium.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Coenzyme. CLINICAL: Vitamin (B6).
USES
Prevention/treatment of vitamin B6 deficiency. OFF-LABEL: Pyridoxine-dependent seizures in infants, drug-induced neuritis (e.g., associated with isoniazid). Treatment of peripheral neuropathy associated with isoniazid; nausea and vomiting of pregnancy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to pyridoxine. Cautions: Impaired renal function, neonates.
ACTION
Coenzyme for various metabolic functions, including metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, fats. Aids in breakdown of glycogen and in synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in CNS. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents pyridoxine deficiency. Increases excretion of certain drugs (e.g., isoniazid) that are pyridoxine antagonists.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed, primarily in jejunum. Stored in liver, muscle, brain. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 15–20 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. High dosages in utero may produce seizures in neonates. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Decreases effects of levodopa. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (OTC)
Capsules: 250 mg. Injection Solution: 100 mg/ml. Tablets: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 250 mg, 500 mg. Tablet, Extended-Release: 200 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Give PO unless nausea, vomiting, malabsorption occurs. Avoid IV use in cardiac pts.
 IV
IV
• Give undiluted or may be added to IV solutions and given as infusion.
PO
• Give without regard to food.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with any other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Pyridoxine Deficiency
PO/IM/IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 10–20 mg/day for 3 wks, followed by oral therapy up to 600 mg/day.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Stinging at IM injection site. Rare: Headache, nausea, drowsiness, sensory neuropathy (paresthesia, unstable gait, clumsiness of hands) with high doses.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Long-term megadoses (2–6 g for longer than 2 mos) may produce sensory neuropathy (reduced deep tendon reflexes, profound impairment of sense of position in distal limbs, gradual sensory ataxia). Toxic symptoms subside when drug is discontinued. Seizures have occurred after IV megadoses.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Observe for improvement of deficiency symptoms, glossitis. Evaluate for nutritional adequacy.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Discomfort may occur with IM injection. • Consume foods rich in pyridoxine (legumes, soybeans, eggs, sunflower seeds, hazelnuts, organ meats, tuna, shrimp, carrots, avocados, bananas, wheat germ, bran).
![]() , Zosyn)
, Zosyn) LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS![]() IV
IV IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES