Q
*QUEtiapine

kwet-eye-a-peen
(Apo-Quetiapine
![]() , Seroquel, Seroquel XR)
, Seroquel, Seroquel XR)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders. Elderly with dementia-related psychosis are at increased risk for death.
Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders. Elderly with dementia-related psychosis are at increased risk for death.
Do not confuse quetiapine with olanzapine, or Seroquel with Sinequan.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Dibenzapine derivative. CLINICAL: Antipsychotic.
USES
Treatment of schizophrenia. Treatment of acute manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder (alone or in combination with lithium or valproate). Maintenance treatment of bipolar disorder as an adjunct to lithium or valproic acid. Treatment of acute depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder. Adjunctive treatment to antidepressants in major depressive disorder (MDD). OFF-LABEL: Delirium in critically ill pts, psychosis/agitation related to Alzheimer’s dementia. Treatment of autism, treatment-resistant obsessive compulsive disorder.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to quetiapine. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, preexisting abnormal lipid profile, pts at risk for aspiration pneumonia, cardiovascular disease (e.g., HF, history of MI), cerebrovascular disease, dehydration, hypovolemia, history of drug abuse/dependence, seizures, hypothyroidism, pts at risk for suicide, Parkinson’s disease, decreased GI motility, urinary retention, narrow-angle glaucoma, diabetes, visual problems, elderly, pts at risk for orthostatic hypotension. Avoid use in pts at risk for torsades de pointes (hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, history of cardiac arrhythmias, congential prolongation QT interval, concurrent medications that prolong QT interval).
ACTION
Antagonizes dopamine, serotonin, histamine, alpha1-adrenergic receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Diminishes symptoms associated with schizophrenia/bipolar disorders.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed. Protein binding: 83%. Widely distributed in tissues; CNS concentration exceeds plasma concentration. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Not recommended for breastfeeding mothers. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted, but lower initial and target dosages may be necessary.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Medications prolonging QT interval (e.g., amiodarone, citalopram, dasatinib, haloperidol, levofloxacin, ondansetron) may increase risk of QT prolongation. Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g., lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase CNS depression. May increase hypotensive effects of antihypertensives. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., phenytoin) may increase clearance. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, erythromycin, fluconazole, itraconazole) may increase effects. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease total free thyroxine (T4) serum levels. May increase serum cholesterol, triglycerides, ALT, AST, WBC, GGT. May produce false-positive pregnancy test result.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg.
![]() Tablets, Extended-Release: 50 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release: 50 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give immediate-release tablets without regard to food. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide extended-release tablets. • Extended-release tablets should be given without regard to food or with a light meal in evening.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: When restarting pts who have been off quetiapine for less than 1 wk, titration is not required and maintenance dose can be reinstituted. • When restarting pts who have been off quetiapine for longer than 1 wk, follow initial titration schedule.
Schizophrenia
PO: (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 25 mg twice daily, then increase in 25–50-mg increments divided 2–3 times/day on the second and third days, up to 300–400 mg/day in 2–3 divided doses by the fourth day. Further adjustments of 25–50 mg twice daily may be made at intervals of 2 days or longer. Maintenance: 150–750 mg/day (adults); 50–200 mg/day (elderly). (Extended-Release): Initially, 300 mg/day. May increase at intervals as short as 1 day up to 300 mg/day. Range: 400–800 mg/day. (Immediate-Release): CHILDREN 13 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 25 mg twice daily on day 1, 50 mg twice daily on day 2, then increase by 100 mg/day to target dose of 400 mg twice daily on day 5. May further increase to 800 mg/day in increments of 100 mg or less daily. Range: 400–800 mg/day. Maximum: 800 mg. Total dose in 3 divided doses. (Extended-Release): Initially, 50 mg once daily on day 1, 100 mg on day 2, until 400 mg once daily is reached on day 5. Range: 400–800 mg/day. Maximum: 800 mg/day.
Mania in Bipolar Disorder
PO: (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 50 mg twice daily for 1 day. May increase in increments of 100 mg/day to 200 mg twice daily on day 4. May further increase in increments of 200 mg/day to 800 mg/day on day 6. Range: 400–800 mg/day. (Extended-Release): Initially, 300 mg on day 1 in the evening; 600 mg on day 2 and adjust between 400–800 mg/day thereafter. (Immediate-Release): CHILDREN 10 YRS AND OLDER: 25 mg twice daily on day 1, 50 mg twice daily on day 2, then increase by 100 mg/day until target dose of 400 mg/day reached on day 5. May increase up to 600 mg/day. Range: 400–600 mg/day. (Extended-Release): 50 mg on day 1; 100 mg on day 2; further increases of 100 mg/day until 400 mg once daily is reached on day 4; Usual range: 400–600 mg once daily.
Depression in Bipolar Disorder
PO:(Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 50 mg/day on day 1, increase to 100 mg/day on day 2, then increase by 100 mg/day up to target dose of 300 mg/day. (Extended-Release): Initially, 50 mg on day 1 in the evening, 100 mg on day 2, 200 mg on day 3, 300 mg on day 4 and thereafter.
Adjunctive Therapy in MDD
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Extended-Release): Initially, 50 mg on days 1 and 2; then 150 mg on days 3 and 4; then 150–300 mg/day thereafter.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
(Immediate-Release): Initially, 25 mg/day. Increase by 25–50 mg/day to effective dose.
(Extended-Release): Initially, 50 mg/day, increase by 50 mg/day until effective dose.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (19%–10%): Headache, drowsiness, dizziness. Occasional (9%–3%): Constipation, orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, dry mouth, dyspepsia, rash, asthenia, abdominal pain, rhinitis. Rare (2%): Back pain, fever, weight gain.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may produce heart block, hypotension, hypokalemia, tachycardia.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess behavior, appearance, emotional status, response to environment, speech pattern, thought content. Obtain baseline CBC, hepatic enzyme levels before initiating treatment and periodically thereafter. Question medical history as listed in Precautions.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor mental status, onset of extrapyramidal symptoms. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Supervise suicidal-risk pt closely during early therapy (as psychosis, depression lessens, energy level improves, increasing suicide potential). Monitor B/P for hypotension, lipid profile, blood glucose, CBC, or worsening depression, unusual behavior. Assess pulse for tachycardia (esp. with rapid increase in dosage). Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess for therapeutic response (improved thought content, increased ability to concentrate, improvement in self-care). Eye exam to detect cataract formation should be obtained q6mos during treatment.
PATIENT/ FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid exposure to extreme heat. • Drink fluids often, esp. during physical activity. • Take medication as ordered; do not stop taking or increase dosage. • Drowsiness generally subsides during continued therapy. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol. • Slowly go from lying to standing. • Report suicidal ideation, unusual changes in behavior.
quinapril
kwin-a-pril
(Accupril, Apo-Quinapril
![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy detected.
May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy detected.
Do not confuse Accupril with Accolate, Accutane, Aciphex, or Monopril.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Accuretic: quinapril/hydrochlorothiazide (a diuretic): 10 mg/12.5 mg, 20 mg/12.5 mg, 20 mg/25 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive.
USES
Treatment of hypertension. Used alone or in combination with other antihypertensives. Adjunctive therapy in management of HF. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of pediatric hypertension.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to quinapril. History of angioedema from previous treatment with ACE inhibitors, concomitant use with aliskiren in pts with diabetes. Cautions: Renal impairment, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with outflow tract obstruction, major surgery, HF, hypovolemia, unstented bilateral renal artery stenosis, hyperkalemia, concurrent potassium supplements, severe aortic stenosis, ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular disease.
ACTION
Suppresses renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, preventing conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor; may inhibit angiotensin II at local vascular renal sites. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces peripheral arterial resistance, B/P, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure; improves cardiac output.
PHARMACOKINETICS
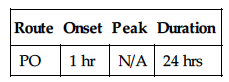
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 1 hr | N/A | 24 hrs |
Readily absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 97%. Rapidly hydrolyzed to active metabolite. Primarily excreted in urine. Minimal removal by hemodialysis. Half-life: 1–2 hrs; metabolite, 3 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. May cause fetal, neonatal mortality or morbidity. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May be more sensitive to hypotensive effects.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, antihypertensives (e.g., amlodipine, lisinopril, valsartan), diuretics (e.g., furosemide, HCTZ) may increase effects. May increase concentration, risk of toxicity of lithium. NSAIDs may decrease effects. Potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., spironolactone, triamterene), potassium supplements may cause hyperkalemia. HERBAL: Black cohosh, periwinkle may increase antihypertensive effect. Ginseng, yohimbe, licorice may worsen hypertension. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, creatinine, potassium, ALT, AST. May decrease serum sodium. May cause positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Tablets may be crushed.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension (Monotherapy)
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 10–20 mg/day. May adjust dosage at intervals of at least 2 wks or longer. Maintenance: 10–40 once daily. ELDERLY: Initially, 10 mg once daily. Titrate to optimal response.
Hypertension (Combination Diuretic Therapy)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 5 mg/day titrated to pt’s needs.
Adjunct to Manage HF
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 5 mg twice daily. Titrate at wkly intervals to 20–40 mg/day in 2 divided doses.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Hypertension
| Creatinine Clearance | Initial Dose |
| More than 60 ml/min | 10 mg |
| 30–60 ml/min | 5 mg |
| 10–29 ml/min | 2.5 mg |
HF
| Creatinine Clearance | Initial Dose |
| Greater than 30 ml/min | 5 mg |
| 10–30 ml/min | 2.5 mg |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (7%–5%): Headache, dizziness. Occasional (4%–2%): Fatigue, vomiting, nausea, hypotension, chest pain, cough, syncope. Rare (less than 2%): Diarrhea, cough, dyspnea, rash, palpitations, impotence, insomnia, drowsiness, malaise.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Excessive hypotension (“first-dose syncope”) may occur in pts with HF, those who are severely salt/volume depleted. Angioedema, hyperkalemia occur rarely. Agranulocytosis, neutropenia may be noted in those with collagen vascular disease (scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus), renal impairment. Nephrotic syndrome may be noted in those with history of renal disease.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain B/P immediately before each dose in addition to regular monitoring (be alert to fluctuations). If excessive reduction in B/P occurs, place pt in supine position with legs slightly elevated. Renal function tests should be performed before beginning therapy. In pts with prior renal disease, urine test for protein by dipstick method should be made with first urine of day before beginning therapy and periodically thereafter. In pts with renal impairment, autoimmune disease, or taking drugs that affect leukocytes or immune response, CBC, differential count should be performed before beginning therapy and q2wks for 3 mos, then periodically thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, renal function, serum potassium, WBC. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Question for evidence of headache. Noncola carbonated beverage, unsalted crackers, dry toast may relieve nausea.
PATIENT/ FAMILY TEACHING
• Go from lying to standing slowly. • Full therapeutic effect may take 1–2 wks. • Report any sign of infection (sore throat, fever). • Skipping doses or voluntarily discontinuing drug may produce severe rebound hypertension. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol.