T
tacrolimus
ta-kroe-li-mus
(Advagraf
![]() , Astagraf XL, Envarsus XR, Prograf, Protopic)
, Astagraf XL, Envarsus XR, Prograf, Protopic)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased susceptibility to infection and potential for development of lymphoma. Extended-release associated with increased mortality in female liver transplant recipients. Topical form associated with rare cases of malignancy. Topical form should be used only for short-term and intermittent treatment. Use in children less than 2 yrs of age not recommended. Use only 0.03% ointment for children 2–15 yrs of age. Administer under supervision of physician experienced in immunosuppressive therapy.
Increased susceptibility to infection and potential for development of lymphoma. Extended-release associated with increased mortality in female liver transplant recipients. Topical form associated with rare cases of malignancy. Topical form should be used only for short-term and intermittent treatment. Use in children less than 2 yrs of age not recommended. Use only 0.03% ointment for children 2–15 yrs of age. Administer under supervision of physician experienced in immunosuppressive therapy.
Do not confuse Protopic with Protonix, or tacrolimus with everolimus, pimcrolimus, sirolimus, or temsirolimus.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Immunologic agent. CLINICAL: Immunosuppressant.
USES
PO/injection: Prevention of organ rejection in pts receiving allogeneic liver, kidney, heart transplant. Should be used concurrently with adrenal corticosteroids. In heart and kidney transplants pts, should be used in conjunction with azathioprine or mycophenolate. Topical: Moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in immunocompetent pts. OFF-LABEL: Prevention of organ rejection in lung, small bowel recipients; prevention and treatment of graft-vs-host disease in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tacrolimus. Cautions: Hypersensitivity to HCO-60 polyoxyl 60 hydrogenated castor oil (used in solution for injection). Renal/hepatic impairment, concurrent use with other nephrotoxic drugs (e.g., cyclosporine). Concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers. Avoid use of potassium-sparing diuretics. Pts at risk for pure red cell aplasia (e.g., concurrent use of mycophenolate); pts at risk for QT prolongation, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia. Topical: Exposure to sunlight.
ACTION
Inhibits T-lymphocyte activation by binding to intracellular proteins, forming a complex, inhibiting phosphatase activity. Therapeutic Effect: Suppresses immunologically mediated inflammatory response; prevents organ transplant rejection.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Variably absorbed after PO administration (food reduces absorption). Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated in feces. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 21–61 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Hyperkalemia, renal dysfunction noted in neonates. Distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: May require higher dosages (decreased bioavailability, increased clearance). May make post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder more common, esp. in pts younger than 3 yrs. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Aluminium-containing antacids may increase concentration. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin, ketoconazole), protease inhibitors, calcium channel blockers (e.g., diltiazem) may increase concentration/effects. Strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin) may decrease concentration/effects. May increase concentration of cyclosporine. HERBAL: Echinacea, St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: Food decreases rate/extent of absorption. Grapefruit products may increase concentration, toxicity (potential for nephrotoxicity). LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, BUN, creatinine, potassium, triglycerides, cholesterol, bilirubin, amylase, ALT, AST. May decrease serum magnesium, Hgb, Hct, platelets. May alter leukocytes.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules (Prograf): 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 5 mg. Injection Solution (Prograf): 5 mg/ml. Ointment (Protopic): 0.03%, 0.1%.
![]() Capsule, Extended-Release (Astagraf XL): 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 5 mg. Tablet, Extended-Release (Envarsus XR): 0.75 mg, 1 mg, 4 mg.
Capsule, Extended-Release (Astagraf XL): 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 5 mg. Tablet, Extended-Release (Envarsus XR): 0.75 mg, 1 mg, 4 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Dilute with appropriate amount (250–1,000 ml, depending on desired dose) 0.9% NaCl or D5W to provide concentration between 0.004 and 0.02 mg/ml.
Rate of Administration • Give as continuous IV infusion. • Continuously monitor pt for anaphylaxis for at least 30 min after start of infusion. • Stop infusion immediately at first sign of hypersensitivity reaction.
Storage • Store diluted infusion solution in glass or polyethylene containers and discard after 24 hrs. • Do not store in PVC container (decreased stability, potential for extraction).
PO
• Avoid grapefruit products. • Immediate-Release: Administer without regard to food. Be consistent with timing of administration.
• Extended-Release. Administer at least 1 hr before or 2 hrs after a meal. Do not crush, cut, dissolve, or divide; swallow whole.
Topical
• For external use only. • Do not cover with occlusive dressing. • Rub gently, completely onto clean, dry skin.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITY
IV INCOMPATIBILITY
Acyclovir.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Calcium gluconate, dexamethasone (Decadron), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine (Dobutrex), dopamine (Intropin), furosemide (Lasix), heparin, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), insulin, leucovorin, lorazepam (Ativan), morphine, nitroglycerin, potassium chloride.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Give initial postoperative dose no sooner than 6 hrs after liver and heart transplants and within 24 hrs of kidney transplant.
Prevention of Liver Transplant Rejection
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate-Release):0.1–0.15 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses 12 hrs apart. Titrate to target trough concentration. CHILDREN: 0.15–0.2 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses 12 hrs apart. Titrate to target trough concentration.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 0.03–0.05 mg/kg/day as continuous infusion.
Prevention of Kidney Transplant Rejection
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Immediate-Release): 0.2 mg/kg/day (in combination with azathioprine) in 2 divided doses 12 hrs apart or 0.1 mg/kg/day (in combination with mycophenolate). Titrate to target trough concentration. (Extended-Release): (With Basiliximab Induction): (Prior to or within 48 hrs of transplant completion): 0.15 mg/kg once daily (in combination with corticosteroids and mycophenolate). Titrate to target trough concentration. (Without Basiliximab Induction): Preoperative dose: 0.1 mg/kg (administer within 12 hrs prior to reperfusion). Postoperative dosing: 0.2 mg/kg once daily (in combination with corticosteroids and mycophenolate). Give at least 4 hrs after preoperative dose and within 12 hrs of reperfusion. Titrate to target trough concentration.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.03–0.05 mg/kg/day as continuous infusion.
Prevention of Heart Transplant Rejection
Note: Recommend in combination with azathioprine or mycophenolate.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 0.075 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses 12 hrs apart. Titrate to target trough concentration.
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.01 mg/kg/day as continuous infusion.
Atopic Dermatitis
Topical: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 15 YRS AND OLDER: Apply 0.03% or 0.1% ointment to affected area twice daily. CHILDREN 2–15 YRS: Use 0.03% ointment. Continue treatment for 1 wk after symptoms have resolved. If no improvement within 6 wks, re-examine to confirm diagnosis.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (greater than 30%): Headache, tremor, insomnia, paresthesia, diarrhea, nausea, constipation, vomiting, abdominal pain, hypertension. Occasional (29%–10%): Rash, pruritus, anorexia, asthenia, peripheral edema, photosensitivity.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Nephrotoxicity (characterized by increased serum creatinine, decreased urinary output), neurotoxicity (tremor, headache, altered mental status), pleural effusion occur commonly. Thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, anemia, atelectasis, sepsis, infection occur occasionally.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess medical history, esp. renal function; medication history, use of other immunosuppressants. Have aqueous solution of epinephrine 1:1,000, O2 available at bedside before beginning IV infusion. Assess pt continuously for first 30 min following start of infusion and at frequent intervals thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Closely monitor pts with renal impairment. Monitor lab values, esp. serum creatinine, potassium levels, CBC with differential, LFT. Monitor I&O closely. CBC should be performed wkly during first mo of therapy, twice monthly during second and third mos of treatment, then monthly throughout the first yr. Report any major change in pt assessment.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid crowds, those with infection. • Report decreased urination, chest pain, headache, dizziness, respiratory infection, rash, unusual bleeding/bruising. • Avoid exposure to sun, artificial light (may cause photosensitivity reaction). • Do not take within 2 hrs of taking antacids. Do not take with grapefruit products.
tamoxifen

ta-mox-fen
(Apo-Tamox
![]() , Nolvadex-D
, Nolvadex-D
![]() , Soltamox)
, Soltamox)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Serious, possibly life-threatening stroke, pulmonary emboli, uterine malignancy (endometrial adenocarcinoma, uterine sarcoma) have occurred.
Serious, possibly life-threatening stroke, pulmonary emboli, uterine malignancy (endometrial adenocarcinoma, uterine sarcoma) have occurred.
Do not confuse tamoxifen with pentoxifylline, tamsulosin, or temazepam.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Nonsteroidal antiestrogen. CLINICAL: Anti-neoplastic.
USES
Adjunct treatment in advanced breast cancer after primary treatment with surgery and radiation, reduce risk of breast cancer in women at high risk, reduce risk of invasive breast cancer in women with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), metastatic breast cancer in women and men. OFF-LABEL: Ovarian cancer (advanced and/or recurrent), treatment of endometrial cancer; risk reduction in women with Paget’s disease of the breast.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tamoxifen. Concomitant warfarin therapy when used in treatment of breast cancer in high-risk women, history of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (in high-risk women for breast cancer and in women with DCIS). Cautions: Thrombocytopenia, pregnancy, history of thromboembolic events, hyperlipidemia, concomitant strong CYP2D6 inhibitors and/or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors.
ACTION
Competes with estradiol for estrogen-receptor binding sites in breast, uterus, vaginal cells. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits DNA synthesis, estrogen response.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Metabo-lized in liver. Primarily eliminated in feces. Half-life: 7 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: If possible, avoid use during pregnancy, esp. first trimester. May cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safe and effective in girls 2–10 yrs with McCune Albright syndrome, precocious puberty. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase effects of warfarin. May decrease effects of anastrozole. Cytotoxic agents may increase risk of thromboembolic events. Moderate/strong CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g., fluoxetine, sertraline) may decrease efficacy and increase risk of breast cancer. HERBAL: Avoid black cohosh, dong quai in estrogen-dependent tumors. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum cholesterol, calcium, triglycerides, AST, ALT.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Solution, Oral (Soltamox): 10 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Use supplied dosing cup for oral solution.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Metastatic Breast Cancer (Males and Females)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20–40 mg/day. Give doses greater than 20 mg/day in 2 divided doses.
Breast Cancer Treatment
PO: ADJUVANT THERAPY (FEMALES), PRE-MENOPAUSAL WOMEN: 20 mg once daily for 5 yrs.
POSTMENOPAUSAL WOMEN: Duration of 2–3 yrs, followed by an aromatase inhibitor to complete 5 yrs.
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20 mg once daily for 5 yrs.
Breast Cancer Risk Reduction
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20 mg once daily for 5 yrs.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Women (greater than 10%): Hot flashes, nausea, vomiting. Occasional: Women (9%–1%): Changes in menstruation, genital itching, vaginal discharge, endometrial hyperplasia, polyps. Men: Impotence, decreased libido. Men and women: Headache, nausea, vomiting, rash, bone pain, confusion, weakness, drowsiness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Retinopathy, corneal opacity, decreased visual acuity noted in pts receiving extremely high dosages (240–320 mg/day) for longer than 17 mos.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain estrogen receptor assay prior to therapy. Obtain baseline breast and gynecologic exams, mammogram results. CBC, serum calcium levels should be checked before and periodically during therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Be alert to increased bone pain; ensure adequate pain relief. Monitor I&O, weight. Observe for edema, esp. of dependent areas, signs and symptoms of DVT. Assess for hypercalcemia (increased urinary volume, excessive thirst, nausea, vomiting, constipation, hypotonicity of muscles, deep bone/flank pain, renal stones).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report vaginal bleeding/discharge/itching, leg cramps, weight gain, shortness of breath, weakness. • May initially experience increase in bone, tumor pain (appears to indicate good tumor response). • Report persistent nausea, vomiting. • Nonhormonal contraceptives are recommended during treatment.
tamsulosin
tam-soo-loe-sin
(Flomax, Apo-Tamsulosin
![]() )
)
Do not confuse Flomax with Flonase, Flovent, Foltx, Fosamax, or Volmax, or tamsulosin with tamoxifen or terazosin.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Jalyn: tamsulosin/dutasteride (an androgen hormone inhibitor): 0.4 mg/0.5 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Alpha1-adrenergic blocker. CLINICAL: Benign prostatic hyperplasia agent.
USES
Treatment of symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), alone or in combination with dutasteride (Avodart). OFF-LABEL: Treatment of bladder outlet obstruction or dysfunction. Facilitate expulsion of ureteral stones (distal).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tamsulosin. Cautions: Concurrent use of phosphodiesterase (PDE5) inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil), pts with orthostatic hypotension.
ACTION
Antagonist of alpha receptors in prostate. Therapeutic Effect: Relaxes smooth muscle, in bladder neck and prostate, improves urinary flow, symptoms of prostatic hyperplasia.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed, widely distributed. Protein binding: 94%–99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 9–13 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Not indicated for use in women. Children: Not indicated in this pt population. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Other alpha-adrenergic blocking agents (e.g., doxazosin, prazosin, terazosin) may increase alpha-blockade effects. Sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil may cause symptomatic hypotension. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) may increase concentration. HERBAL: Avoid saw palmetto (limited experience with this combination). Black cohosh, periwinkle may increase hypotensive effect. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase potential for orthostatic hypotension. LAB VALUES: None known.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
![]() Capsules: 0.4 mg.
Capsules: 0.4 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give at same time each day, 30 min after the same meal. • Do not break, crush, or open capsule.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
PO: ADULTS: 0.4 mg once daily, approximately 30 min after same meal each day. May increase dosage to 0.8 mg if inadequate response in 2–4 wks.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (9%–7%): Dizziness, drowsiness. Occasional (5%–3%): Headache, anxiety, insomnia, orthostatic hypotension. Rare (less than 2%): Nasal congestion, pharyngitis, rhinitis, nausea, vertigo, impotence.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
First-dose syncope (hypotension with sudden loss of consciousness) may occur within 30–90 min after initial dose. May be preceded by tachycardia (pulse rate of 120–160 beats/min).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess history of prostatic hyperplasia (difficulty initiating urine stream, dribbling, sense of urgency, leaking). Question for sensitivity to tamsulosin, or use of other alpha-adrenergic blocking agents. Obtain vital signs.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Monitor renal function, I&O, weight changes, peripheral edema, B/P. Monitor for first-dose syncope.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take at same time each day, 30 min after the same meal. • Go from lying to standing slowly. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Do not break, crush, open capsule.
tapentadol
ta-pen-ta-dol
(Nucynta, Nucynta ER, Nucynta IR
![]() )
)
Do not confuse tapentadol with tramadol.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Centrally acting synthetic analgesic. CLINICAL: Analgesic.
USES
Nucynta: Relief of moderate to severe acute pain in adults 18 yrs and older. Nucynta ER: Management of moderate to severe chronic or neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy when around-the-clock analgesic needed for extended period.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tapentadol. Severe respiratory depression, acute or severe bronchial asthma, hypercapnia in uncontrolled settings, known or suspected paralytic ileus, concurrent use or ingestion within 14 days of MAOI use. Cautions: Respiratory disease or respiratory compromise (e.g., hypoxia, hypercapnia, or decreased respiratory reserve), asthma, COPD, severe obesity, sleep apnea syndrome, CNS depression, pts with head injury, intracranial lesions, pancreatic or biliary disease, renal or hepatic impairment, history of seizures, conditions that increase risk of seizures, pts at risk for hypotension, adrenal insufficiency, concurrent use with serotonergic agents, elderly, debilitated or cachetic pts.
ACTION
Binds to mu-opioid receptors in the central nervous system, causing inhibition of ascending pain pathways; increases norepinephrine by inhibiting its reabsorption into nerve cells. Therapeutic Effect: Produces analgesia.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in the urine. Widely distributed. Protein binding: 20%. Half-life: 4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Not recommended for use in this pt population. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may increase risk of side effects.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, CNS depressants (e.g., lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase CNS depression, respiratory depression. MAOIs, SSRIs (e.g., fluoxetine), tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline), triptans (e.g., sumatriptan) may increase risk of serotonin syndrome. HERBAL: Kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. St. John’s wort may increase risk for serotonin syndrome. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg.
![]() Tablets, Extended-Release: 50 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 250 mg.
Tablets, Extended-Release: 50 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 250 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Tablets may be crushed. • Give extended-release tablets whole; do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Not recommended in severe renal or hepatic impairment.
Pain Control
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Nucynta: 50–100 mg q4–6h as needed. Maximum: 600 mg/day (700 mg on day 1). Nucynta ER: Initially, 50 mg twice daily (12 hrs apart). May increase by 50 mg twice daily q3days to effective dose. Range: 100–250 mg twice daily. Maximum: 500 mg/day.
Conversion to Extended-Release
Oral Opioids: Discontinue all other opioids when extended-release tapentadol is initiated. Begin with a dose that is 50% of estimated tapentadol needed with immediate-release rescue medications as a supplement.
Immediate-Release tapentadol: Use same total daily dose but divide into 2 equal doses given twice daily. Maximum dose: 500 mg daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl 30 ml/min or greater: No adjustment. CrCl less than 30 ml/min: Not recommended.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Immediate-release: Moderate impairment: 50 mg q8h. Maximum: 3 doses/24 hrs. Extended-release: Initially, 50 mg/day. Maximum: 100 mg/day.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (greater than 10%): Nausea, dizziness, vomiting, sleepiness, headache.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Respiratory depression, serotonin syndrome have been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess onset, type, location, and duration of pain. Obtain vital signs before giving medication. If respirations are 12/min or lower, withhold medication, contact physician. Question history of hepatic impairment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Be alert for decreased respirations or B/P. Initiate deep breathing and coughing exercises, particularly in pts with impaired pulmonary function. Assess for clinical improvement and record onset of pain relief.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol, CNS depressants. • Report nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing.
tedizolid
ted-eye-zoe-lid
(Sivextro)
Do not confuse tedizolid with linezolid.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Oxazolidinone-class antibacterial. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of adult pts with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by susceptible strains of gram-positive microorganisms including Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains), Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus anginosus group (including S. anginosus, S. intermedius, S. constellatus), Streptococcus pyogenes, and Enterococcus faecalis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tedizolid. Cautions: History of Clostridium difficile infection or antibiotic-associated colitis, myelosuppression, neutropenia, peripheral/optic neuropathy.
ACTION
Inhibits cellular protein synthesis by binding to 50S subunit of bacterial ribosome. Therapeutic Effect: Antibiotic.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 70%–90%. Peak plasma concentration: PO: 3 hrs; IV: end of infusion. Eliminated in feces (82%), urine (18%). Minimally removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 12 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts less than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease Hgb, platelets, neutrophils. May increase serum ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Lyophilized Powder for Injection: 200 mg/vial. Tablets: 200 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
• Vials contain no preservatives or bacteriostatic agents. • Must reconstitute with Sterile Water for Injection and subsequently dilute with 0.9% NaCl only. • Do not inject as IV push or bolus.
Reconstitution • Reconstitute vial with 4 ml of Sterile Water for Injection. • To avoid foaming, alternate between gentle swirling and inversion until powder completely dissolved. If foaming occurs, let vial stand until foam dispersed. • Visually inspect for particulate matter or discoloration. Do not use if particulate matter observed. • Withdraw 4 ml of solution with vial in upright position; do not invert vial during draw-up. • Further dilute in 250 ml 0.9% NaCl. • Gently invert bag to mix; do not shake.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 1 hr via dedicated line.
Storage • Reconstituted solution should appear clear, colorless to yellow. • Administer within 24 hrs of reconstitution. • May refrigerate or store solution at room temperature up to 24 hrs.
PO
• Give without regard to meal.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Any solutions containing divalent cations (e.g., Ca2+, Mg2+), lactated Ringer’s injection. Do not infuse with other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infection
PO/IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 200 mg once daily for 6 days.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (8%–3%): Nausea, headache, diarrhea, vomiting. Rare (2%): Dizziness, dermatitis, insomnia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Safety and efficacy in pts with neutropenia not established. Antibacterial activity may be reduced in the absence of granulocytes. C. difficile–associated diarrhea with severity ranging from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis has been reported for up to 2 mos following administration. Treatment in the absence of proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection may increase risk of drug-resistant bacteria. Infusion/hypersensitivity reactions (pruritus, urticaria, flushing, hypertension palpitation, tachycardia), optic disorders (asthenopia, blurry vision, neuropathy, visual impairment, vitreous floaters), neurologic disorders (hypoesthesia, paresthesia, peripheral neuropathy, cranial nerve VII paralysis), infections (oral candidiasis, vulvovaginal mycotic infection) occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC (note WBC, bands), wound culture/sensitivity, vital signs. Question history of recent C. difficile infection, hypersensitivity reaction. Assess skin wound characteristics; hydration status. Question pt’s usual stool characteristics (color, frequency, consistency).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor skin infection/wound for improvement. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency; increasing severity may indicate antibiotic-associated colitis. If frequent diarrhea occurs, obtain C. difficile toxin screen and initiate isolation precautions until result confirmed. Encourage PO intake. Monitor I&O. Monitor for infusion-related/hypersensitivity reaction.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• It is essential to complete drug therapy despite symptom improvement. Early discontinuation may result in antibacterial resistance or an increased risk of recurrent infection. • Report episodes of diarrhea, esp. following wks after treatment completion. Frequent abdominal pain, blood-streaked stool, diarrhea, fever, may indicate C. difficile infection, which may be contagious. • Drink plenty of fluids.
teduglutide
te-due-gloo-tide
(Gattex)
Do not confuse teduglutide with liraglutide or albiglutide, or Gattex with Gas-X.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Human glucagon-like peptide-II. CLINICAL: Short bowel syndrome (short gut syndrome, short gut) agent.
USES
Treatment of adults with short bowel syndrome (SBS) who are dependent on parenteral support.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to teduglutide. Cautions: Cardiovascular disease, HF, pts at increased risk for malignancy, biliary tract (gallbladder, pancreatic) disease, hypervolemia, stenosis, renal impairment.
ACTION
Analogue of naturally occurring peptide secreted by L cells of distal intestine, known to increase intestinal, portal blood flow, and inhibit gastric secretion. Therapeutic Effect: Improves intestinal absorption.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Degrades into small peptides, amino acids via catabolic pathway. Primarily excreted in urine. Bioavailability: 86–89% following SQ injection. Peak plasma concentration: 3–5 hrs. Half-life: 1.3–2 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase absorption of any concomitant oral medication. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 5 mg (delivers maximum of 0.38 ml containing 3.8 mg teduglutide).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
SQ
Reconstitution • If diluent syringe (contains 0.5 ml Sterile Water for Injection) has a white snap-off cap, snap or twist off white cap. • If diluent syringe has a gray screw top, unscrew top counter clockwise. • Push prefilled syringe into vial containing teduglutide. • After all diluent has gone into vial, remove syringe, needle and discard. • Allow vial to sit for 30 sec. • Gently roll vial for 15 sec (do not shake) and let stand for 2 min. • Withdraw prescribed dose, discard remaining fluid. • Use within 3 hrs following reconstitution. • Use abdomen, thighs, upper arms for injection. • Avoid injection sites where skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard.
Storage • Store kit in refrigerator. • Reconstituted solution should appear as a clear, colorless to light straw-colored liquid. • Discard if particulate is present. • Drug should be completely dissolved before solution is withdrawn from vial.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Short Bowel Syndrome
SQ: ADULTS/ELDERLY: 0.05 mg/kg/day.
Dosage in Moderate to Severe Renal Impairment
SQ: ADULTS/ELDERLY: CrCl less than 50 ml/min: 50% dose reduction.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (30%–22%): Abdominal pain, nausea, injection site reactions. Occasional (18%–14%): Headache, abdominal distention, vomiting. Rare (9%): Flatulence, hypersensitivity, appetite disorders, sleep disturbances.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Upper respiratory tract infection occurs in 12% of pts. Fluid overload (hypervolemia) has been noted in 7% of pts. Potential for hypovolemia is increased in pts with cardiovascular disease, HF. Therapy increases risk for acceleration for neoplastic growth. Cholecystitis, cholangitis, cholelithiasis, pancreatitis has been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline serum chemistries, LFT, lipase, amylase. Colonoscopy (or alternate imaging) with removal of polyps should be completed within 5 mos prior to initiating treatment.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Follow-up colonoscopy (or alternate imaging) is recommended at the end of 1 year. If no polyp is found, subsequent colonoscopies should be done no less frequently than every 5 years. If a polyp is found, adherence to current polyp follow-up guidelines is recommended. Discovery of intestinal obstruction, intestinal malignancy necessitates discontinuation of treatment. Subsequent laboratory assessments, LFT is recommended every 6 mos. If clinically meaningful elevation is seen, further diagnostic workup is recommended as clinically indicated.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Teach proper use and administration of medication. • Be aware of need for any new supplies. • Instruct pt in preparation of medication and observe correct administration technique. • Report yellowing of skin or eyes, dark urine, changes in stool color or consistency, severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, sudden weight gain, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
telavancin
tel-a-van-sin
(Vibativ)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Pts with preexisting renal impairment (CrCl less than 50 mL/min) who are treated for hospital-acquired pneumonia may have increased mortality risk when compared to vancomycin. May cause new or worsening renal impairment. May cause fetal harm (low birth weight, limb malformations). Women of childbearing potential should have pregnancy test before treatment; avoid use during pregnancy unless benefit to pt outweighs fetal risk.
Pts with preexisting renal impairment (CrCl less than 50 mL/min) who are treated for hospital-acquired pneumonia may have increased mortality risk when compared to vancomycin. May cause new or worsening renal impairment. May cause fetal harm (low birth weight, limb malformations). Women of childbearing potential should have pregnancy test before treatment; avoid use during pregnancy unless benefit to pt outweighs fetal risk.
Do not confuse telavancin with dalbavancin or oritavancin; or Vibativ with Vibra-Tabs or vigabatrin.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Lipoglycopeptide antibacterial. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of complicated skin, soft tissue infections (cSSSI) caused by gram-positive microorganisms, including methicillin-susceptible or methicillin-resistant S. aureus, vancomycin-susceptible Enterococcus. Treatment of hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP) caused by susceptible isolates of S. aureus.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Prior hypersensitivity reactions to telavancin. Concomitant use of IV unfractionated heparin. Cautions: Renal impairment, concurrent therapy with other nephrotoxic medications (e.g., NSAIDs, ACE inhibitors, aminoglycosides). Avoid use in pts with history of congenital QT syndrome, known prolongation of QT interval, uncompensated HF, severe left ventricular hypertrophy, or receiving treatment with other drugs known to prolong QT interval, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, known vancomycin hypersensitivity.
ACTION
Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by blocking polymerization and cross-linking of peptidoglycan. Disrupts membrane potential and changes cell wall permeability. Therapeutic Effect: Bactericidal. Antibiotic.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Not metabolized in liver; pathway unspecified. Protein binding: 90%. Primarily excreted unchanged in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 8–9 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm at regular dosage. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may increase risk of nephrotoxicity; dosage adjustment recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Telavancin may increase levels/effects of dronedarone, nilotinib, pimozide, quinine, tetrabenazine, thioridazine, ziprasidone. Ciprofloxacin may increase concentration/effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May alter serum potassium. May increase serum bilirubin, ALT, AST, BUN, creatinine; PT, aPTT, INR. May decrease Hgb, Hct, WBC count.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 250 mg, 750 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
◀ ALERT ▶ Give by intermittent IV infusion (piggyback). Do not give by IV push (may result in hypotension).
Reconstitution • Reconstitute with 45 ml Sterile Water for Injection, D5W, or 0.9% NaCl to provide concentration of 15 mg/ml (total volume approximately 50 ml). • Prior to administration, further dilute with D5W or 0.9% NaCl to final concentration of 0.6–8 mg/ml. • Do not shake.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over at least 60 min. Flush line with D5W or 0.9% NaCl before and after administration.
Storage • Discard if particulate is present. • Following reconstitution, drug is stable for 4 hrs at room temperature or 72 hrs if refrigerated in vial or infusion bag.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin, colistimethate, levofloxacin (Levaquin), micafungin (Mycomine).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Azithromycin, caspofungin, cefepime, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, doripenem, doxycycline, gentamicin, ertapenem, fluconazole, meropenem, tobramycin, pantoprazole, piperacillin-tazobactam, tigecycline.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Parenteral Dosage
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 10 mg/kg once every 24 hrs for 7–14 days (cSSSI); 14–21 days (HABP/VABP). Duration based on severity, infection site, and clinical progress of pt.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 50 ml/min or greater | 10 mg/kg every 24 hrs |
| 30–49 ml/min | 7.5 mg/kg every 24 hrs |
| 10–29 ml/min | 10 mg/kg every 48 hrs |
| Less than 10 ml/min | No dose adjustment (not studied) |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment (unless concomitant renal impairment).
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (33%–27%): Altered taste, nausea. Occasional (14%–6%): Vomiting, foamy urine, diarrhea, dizziness, pruritus. Rare (4%–2%): Rigors, rash, infusion site pain, anorexia, infusion site erythema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Nephrotoxicity (acute kidney injury, acute tubular necrosis, renal failure), diarrhea due to C. difficile may occur. “Red-man syndrome” (characterized by erythema on face, neck, upper torso), tachycardia, hypotension, myalgia, angioedema may occur from too-rapid rate of infusion.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain pregnancy test prior to treatment. Obtain baseline serum BUN, creatinine, creatinine clearance prior to initiating therapy, every 48–72 hrs, and after treatment is completed. Obtain culture and sensitivity tests before giving first dose (therapy may begin before results are known).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor renal function tests, I&O. Assess skin for rash. Avoid rapid infusion (“red-man syndrome”). Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Obtain C. Difficile PCR test if diarrhea occurs.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Use effective contraception during treatment. • Report rash, signs/symptoms of nephrotoxicity, diarrhea. • Blood levels will be monitored routinely.
telmisartan
tel-mi-sar-tan
(Micardis)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
May cause fetal injury, mortality. Discontinue as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Micardis HCT: telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide (a diuretic): 40 mg/12.5 mg, 80 mg/12.5 mg. Twynsta: telmisartan/amlodipine (a calcium channel blocker): 40 mg/5 mg, 40 mg/10 mg, 80 mg/5 mg, 80 mg/10 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Angiotensin II receptor antagonist. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive.
USES
Treatment of hypertension alone or in combination with other antihypertensives. Reduces cardiovascular risk in pts 55 yrs of age and older unable to take ACE inhibitors and at high risk of major cardiovascular event (e.g., MI, stroke).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to telmisartan. Concurrent use with aliskiren in pts with diabetes. Cautions: Hypovolemia, hepatic/renal impairment, renal artery stenosis (unilateral, bilateral), biliary obstructive disease, significant aortic/mitral stenosis. Concurrent use with ramipril not recommended. Avoid potassium supplements.
ACTION
Blocks vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II, inhibiting binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Causes vasodilation, decreases peripheral resistance, decreases B/P.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO (reduce B/P) | 1–2 hrs | — | 24 hrs |
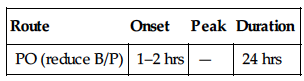
Rapidly, completely absorbed. Protein binding: greater than 99%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in feces. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 24 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: NSAIDs may decrease antihypertensive effect. May increase digoxin concentration, risk of toxicity. HERBAL: Ephedra, ginger, licorice, ginseng, yohimbe may worsen hypertension. Black cohosh, periwinkle may increase antihypertensive effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, creatinine, uric acid, cholesterol. May decrease Hgb, Hct.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 20 mg, 40 mg, 80 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hypertension
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 40 mg once daily. Usual range: 40–80 mg/day.
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 80 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use with caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (7%–3%): Upper respiratory tract infection, sinusitis, back/leg pain, diarrhea. Rare (1%): Dizziness, headache, fatigue, nausea, heartburn, myalgia, cough, peripheral edema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdosage may manifest as hypotension, tachycardia; bradycardia occurs less often.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain B/P, apical pulse immediately before each dose, in addition to regular monitoring (be alert to fluctuations). If excessive reduction in B/P occurs, place pt in supine position, feet slightly elevated. Assess medication history (esp. diuretics). Question for history of hepatic/renal impairment, renal artery stenosis. Obtain serum BUN, creatinine, Hgb, Hct, vital signs (particularly B/P, pulse rate).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor B/P, pulse, serum electrolytes, renal function. Monitor for hypotension when initiating therapy.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established (possible dizziness effect). • Maintain proper hydration. • Avoid pregnancy. • Immediately report suspected pregnancy. • Report any sign of infection (sore throat, fever). • Avoid excessive exertion during hot weather (risk of dehydration, hypotension).
temazepam
te-maz-e-pam
Do not confuse Restoril with Risperdal, Vistaril, or Zestril, or temazepam with flurazepam, lorazepam, or clonazepam.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Benzodiazepine (Schedule IV). CLINICAL: Sedative-hypnotic.
USES
Short-term treatment of insomnia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to temazepam. Narrow-angle glaucoma, CNS depression, pregnancy, breastfeeding, severe, uncontrolled pain, sleep apnea. Cautions: Mental impairment, elderly, pts with drug dependence potential.
ACTION
Enhances action of inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), resulting in CNS depression. Therapeutic Effect: Induces sleep.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 96%. Widely distributed. Crosses blood-brain barrier. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 9.5–12.4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. May be distributed in breast milk. Chronic ingestion during pregnancy may produce withdrawal symptoms, CNS depression in neonates. Children: Not recommended in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: Use small initial doses with gradual dosage increases to avoid ataxia, excessive sedation.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g., lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase CNS depression. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 7.5 mg, 15 mg, 22.5 mg, 30 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • Capsules may be emptied and mixed with food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Insomnia
PO: ADULTS: 15–30 mg at bedtime. ELDERLY, DEBILITATED: 7.5–15 mg at bedtime.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Drowsiness, sedation, rebound insomnia (may occur for 1–2 nights after drug is discontinued), dizziness, confusion, euphoria. Occasional: Asthenia, anorexia, diarrhea. Rare: Paradoxical CNS excitement, restlessness (particularly in elderly, debilitated pts).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Abrupt or too-rapid withdrawal may result in pronounced restlessness, irritability, insomnia, hand tremor, abdominal/muscle cramps, vomiting, diaphoresis, seizures. Overdose results in drowsiness, confusion, diminished reflexes, respiratory depression, coma. Antidote: Flumazenil (see Appendix J for dosage).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for possibility of pregnancy before initiating therapy. Assess B/P, pulse, respirations immediately before administration. Raise bed rails. Provide environment conducive to sleep (back rub, quiet environment, low lighting). Assess mental status, sleep patterns.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess elderly or debilitated pts for paradoxical reaction, particularly during early therapy. Monitor respiratory, cardiovascular, mental status. Evaluate for therapeutic response: decrease in number of nocturnal awakenings, increase in length of sleep.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid alcohol, other CNS depressants. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • May cause daytime drowsiness. • Take approximately 30 min before bedtime. • Inform physician if pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
temozolomide

tem-oh-zoe-loe-myde
(Temodal
![]() , Temodar)
, Temodar)
Do not confuse Temodar with Tambocor.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Imidazotetrazine derivative, alkylating agent. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of adults with refractory anaplastic astrocytoma, newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme (concomitantly with radiotherapy, then as maintenance therapy). OFF-LABEL: Malignant glioma, metastatic melanoma, metastatic CNS lesions, cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, advanced neuroendocrine tumors, soft tissue sarcoma, pediatric neuroblastoma. Ewing’s sarcoma (recurrent or progressive).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to temozolomide, dacarbazine. Cautions: Severe renal/hepatic impairment, pregnancy.
ACTION
Produces cytotoxic effect through alkylation of DNA causing DNA double strand breaks and apoptosis. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits DNA replication, causing cell death.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly, completely absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 15%. Peak plasma concentration: 1 hr. Penetrates blood-brain barrier. Eliminated in urine (38%), feces (19%). Half-life: 1.6–1.8 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. May produce malformation of external organs, soft tissue, skeleton. If possible, avoid use during pregnancy. Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Pts older than 70 yrs may experience higher risk of developing grade 4 neutropenia, grade 4 thrombocytopenia.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Medications causing blood dyscrasias (altering blood cell counts) may increase leukopenic, thrombocytopenic effects. Valproic acid may decrease oral clearance. Bone marrow depressants may increase myelosuppression. Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease effects. FOOD: All foods decrease rate, extent of drug absorption. LAB VALUES: May decrease Hgb, neutrophils, platelets, WBC count, lymphocytes.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 5 mg, 20 mg, 100 mg, 140 mg, 180 mg, 250 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 100 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
• Reconstitute each 100-mg vial with 41 ml Sterile Water for Injection to provide concentration of 2.5 mg/ml. • Swirl gently; do not shake. • Do NOT further dilute. • Infuse over 90 min. • Stable for 14 hrs (includes infusion time).
PO
• Food reduces rate, extent of absorption; increases risk of nausea, vomiting. • For best results, administer at bedtime. • Give capsule whole with glass of water. Do not break, open, or crush capsules.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Anaplastic Astrocytoma (Refractory)
IV Infusion, PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 150 mg/m2/day for 5 consecutive days of 28-day treatment cycle. Subsequent doses of 100–200 mg/m2/day based on platelet count, absolute neurophil count (ANC) during previous cycle. ANC greater than 1,500/mm3 and platelets more than 100,000/mm3 Maintenance: 200 mg/m2/day for 5 days q4wks. Continue until disease progression is observed. Minimum: 100 mg/m2/day for 5 days q4wks.
Glioblastoma Multiforme
Note: Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP) prophylaxis required during concomitant phase and continue in pts who develop lymphocytopenia until recovery to grade 1 or less. IV Infusion, PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 75 mg/m2 daily for 42 days (with focal radiotherapy). Maintenance: (begin 4 wks after concomitant phase): (Cycle 1): 150 mg/m2 once daily for 5 days followed by 23 days without treatment. (Cycles 2–6): May increase to 200 mg/m2 once daily for 5 days followed by 23 days without treatment if ANC greater than 1,500/mm3, platelets greater than 100,000/mm3, and nonhematologic toxicity with previous cycle.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Use caution in severe hepatic impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (53%–33%): Nausea, vomiting, headache, fatigue, constipation, seizure. Occasional (16%–10%): Diarrhea, asthenia, fever, dizziness, peripheral edema, incoordination, insomnia. Rare (9%–5%): Paresthesia, drowsiness, anorexia, urinary incontinence, anxiety, pharyngitis, cough.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Myelosuppression is characterized by neutropenia and thrombocytopenia, with elderly and women showing higher incidence of developing severe myelosuppression. Usually occurs within first few cycles; is not cumulative. Nadir occurs in approximately 26–28 days, with recovery within 14 days of nadir. May increase occurrence of pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, myelodysplastic syndrome including myeloid leukemia, or secondary malignancies.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC. Before dosing, ANC must be greater than 1,500/mm3 and platelet count greater than 100,000/mm3. Potential for nausea, vomiting (readily controlled with antiemetic therapy).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Obtain CBC on day 22 (21 days after first dose) or within 48 hrs of that day, and wkly, until ANC is greater than 1,500/mm3 and platelet count is greater than 100,000/mm3. Monitor for hematologic toxicity (fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site), symptoms of anemia (excessive fatigue, weakness).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• To reduce nausea/vomiting, take on an empty stomach. • Promptly report fever, sore throat, signs of local infection, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site, or difficulty breathing. • Avoid crowds, those with infection. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval. • Avoid pregnancy.
temsirolimus

tem-sir-oh-li-mus
(Torisel)
Do not confuse temsirolimus with everolimus, sirolimus, or tacrolimus.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Kinase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to temsirolimus. Moderate-severe hepatic impairment; bilirubin greater than 1.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN). Cautions: Hypersensitivity to sirolimus, mild hepatic impairment, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia. Concurrent use with other medication that may cause angioedema (e.g., ACE inhibitors).
ACTION
Prevents activation of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin), preventing tumor cell division. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor cell growth, produces tumor regression.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Metabolized in liver. Eliminated primarily in feces. Half-life: 17 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., atazanavir, clarithromycin, ketoconazole, ritonavir) may increase concentration. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin) may decrease concentration. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase plasma concentration. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease plasma concentration. Herbs with hypoglycemic properties (e.g., garlic, ginger, ginseng) may increase risk for hypoglycemia. LAB VALUES: May increase serum bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, AST, creatinine, glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides. May decrease WBCs, neutrophils, Hgb, platelets, serum phosphorus, potassium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution Kit: 25 mg/ml supplied with 1.8-ml diluent vial.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Inject 1.8 ml of diluent into vial. • The vial contains an overfill of 0.2 ml (30 mg/1.2 ml). • Due to the overfill, the drug concentration of resulting solution will be 10 mg/ml. • A total volume of 3 ml will be obtained, including the overfill. • Mix well by inverting the vial. Allow sufficient time for air bubbles to subside. • Mixture must be injected rapidly into 250 ml 0.9% NaCl. • Invert bag to mix; avoid excessive shaking (may cause foaming).
Rate of Administration • Administer through an in-line filter not greater than 5 microns; infuse over 30–60 min. • Final diluted infusion solution should be completed within 6 hrs from the time drug solution and diluent mixture is added to the 250 ml 0.9% NaCl.
Storage • Refrigerate kit. • Reconstituted solution appears clear to slightly turbid, colorless to yellow, and free from visible particulates. • The 10 mg/ml drug solution/diluent mixture is stable for up to 24 hrs at room temperature. • Solutions diluted for infusion (in 250 ml 0.9% NaCl) must be infused within 6 hrs of preparation.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Both acids and bases degrade solution; combinations of temsirolimus with agents capable of modifying solution pH should be avoided.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Pretreat with IV diphenhydramine 25–50 mg, 30 min before infusion.
Renal Cancer
IV: ADULTS/ELDERLY: 25 mg once wkly. Treatment should continue until disease progresses or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
Dosage with Concomitant CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Inducers
Inhibitors: Consider dosage of 12.5 mg/wk. Inducers: Consider dosage of 50 mg/wk.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: Reduce dose to 15 mg/wk. Moderate to severe impairment: Contraindicated.
SIDE EFFECTS
Common (51%–32%): Asthenia, rash, mucositis, nausea, edema (facial edema, peripheral edema), anorexia. Frequent (28%–20%): Generalized pain, dyspnea, diarrhea, cough, fever, abdominal pain, constipation, back pain, impaired taste. Occasional (19%–8%): Weight loss, vomiting, pruritus, chest pain, headache, nail disorder, insomnia, nosebleed, dry skin, acne, chills, myalgia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
UTI occurs in 15% of pts, hypersensitivity reaction in 9%, pneumonia in 8%, upper respiratory tract infection, hypertension, conjunctivitis in 7%.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question possibility of pregnancy. Obtain baseline CBC, serum chemistries, renal function, LFT routinely thereafter.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Offer antiemetics to control nausea, vomiting. Monitor daily pattern of bowel frequency, stool consistency. Assess skin for evidence of rash, edema. Monitor CBC, particularly Hgb, platelets, neutrophil count; LFT, renal function tests. Monitor for shortness of breath, fatigue, hypertension. Assess oropharynx for stomatitis, mucositis.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid crowds, those with known infection. • Avoid contact with anyone who recently received live virus vaccine. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers body resistance). • Promptly report fever, unusual bruising/bleeding from any site.
tenecteplase

ten-eck-te-plase
(TNKase)
Do not confuse TNKase with tPA.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Tissue plasminogen activator. CLINICAL: Thrombolytic.
USES
Management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) for lysis of thrombi to restore perfusion and reduce mortality.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tenecteplase. Active internal bleeding, cerebral aneurysm, AV malformation, bleeding diathesis, history of CVA, intracranial or intraspinal surgery or trauma within past 2 mos, intracranial neoplasm, severe uncontrolled hypertension. Cautions: Recent major surgery, GI or genitourinary (GU) bleeding, trauma, acute pericarditis, subacute bacterial endocarditis, pregnancy, severe hepatic impairment, hemorrhagic ophthalmic conditions, concurrent use of anticoagulants, elderly, cerebrovascular disease, hemostatic defects.
ACTION
Produced by recombinant DNA that binds to fibrin and converts plasminogen to plasmin. Initiates fibrinolysis by degrading fibrin clots, fibrinogen, other plasma proteins. Therapeutic Effect: Exerts thrombolytic action (dissolves clots).
PHARMACOKINETICS
Extensively distributed to tissues. Completely eliminated by hepatic metabolism. Half-life: 90–130 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May have increased risk of intracranial hemorrhage, stroke, major bleeding; caution advised.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anticoagulants (e.g., heparin, warfarin), aspirin, dipyridamole, glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors increase risk of bleeding. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginkgo biloba, ginseng, red clover may increase risk of bleeding. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Decreases plasminogen, fibrinogen levels during infusion, decreasing clotting time (confirms presence of lysis). May decrease Hgb, Hct.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 50 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Add 10 ml Sterile Water for Injection without preservative to vial to provide concentration of 5 mg/ml. • Gently swirl until dissolved. Do not shake. • If foaming occurs, leave vial undisturbed for several min.
Rate of Administration • Administer as IV push over 5 sec.
Storage • Store at room temperature. • If possible, use immediately, but may refrigerate up to 8 hrs after reconstitution. • Appears as colorless to pale yellow solution. • Do not use if discolored or contains particulates. • Discard after 8 hrs.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with dextrose-containing solutions or any other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Give as single IV bolus over 5 sec. Precipitate may occur when given in IV line containing dextrose. Flush line with saline before and after administration.
Acute MI
IV: ADULTS: Dosage is based on pt’s weight. Treatment should be initiated as soon as possible after onset of symptoms.
| Weight (kg) | (mg) | (ml) |
| 90 or more | 50 | 10 |
| 80–less than 90 | 45 | 9 |
| 70–less than 80 | 40 | 8 |
| 60–less than 70 | 35 | 7 |
| Less than 60 | 30 | 6 |
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Bleeding (minor, 21.8%; major, 4.7%).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Internal bleeding, including intracranial, retroperitoneal, GI, GU, respiratory sites, may occur. Lysis of coronary thrombi may produce atrial or ventricular arrhythmias, stroke.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline B/P, apical pulse. Record weight. Evaluate 12-lead EKG, cardiac enzymes, serum electrolytes. Assess Hgb, Hct, platelet count, thrombin time, aPTT, PT, fibrinogen level before therapy is instituted. Type and hold blood. Screen for contraindications (e.g., history of CVA, bleeding of any kind, uncontrolled hypertension).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor continuous EKG for arrhythmias, B/P, pulse, respirations q15min until stable, then hourly or per protocol. Check peripheral pulses, heart and lung sounds. Monitor for chest pain relief; notify physician of continuation/recurrence (note location, type, intensity). Assess for overt or occult blood in any body substance. Monitor aPTT per protocol. Maintain B/P. Avoid any trauma that might increase risk of bleeding (e.g., injections, shaving). Assess neurologic status with vital signs.
tenofovir

ten-oh-foe-veer
(Vemlidy, Viread)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Lactic acidosis, severe hepatomegaly with steatosis (fatty liver), including fatalities, have occurred.
Lactic acidosis, severe hepatomegaly with steatosis (fatty liver), including fatalities, have occurred.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Atripla: tenofovir (TDF)/efavirenz/emtricitabine (antiretroviral agents): 300 mg/600 mg/200 mg. Complera: tenofovir (TDF)/emtricitabine/rilpivirine (antiretroviral agents): 300 mg/200 mg/25 mg. Descovy: tenofovir (TAF)/emtricitabine: 25 mg/200 mg. Genvoya: tenofovir (TAF)/elvitegravir/cobicistat/ emtricitabine: 10 mg, 150 mg/150 mg/200 mg. Odefsey: tenofovir (TAF)/emtricitabine/rilpivirine: 25 mg/200 mg/25 mg. Stribild: tenofovir (TDF)/elvitegravir (an integrase inhibitor)/cobicistat (a pharmacokinetic enhancer)/emtricitabine (a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor): 300 mg/150 mg/150 mg/200 mg. Truvada: tenofovir (TDF)/emtricitabine (an antiretroviral agent): 300 mg/200 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Nucleotide analogue (reverse transcriptase inhibitor). CLINICAL: Antiretroviral.
USES
Treatment of HIV-1 infection in combination with at least two other antiretroviral agents. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in pts with hepatic disease. Vemlidy: Treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in adults with compensated liver disease.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tenofovir. Cautions: Hepatic/renal impairment, pts at risk for hepatic disease (e.g., obesity); concurrent nephrotoxic medications, pts with low body weight, risk factors or prior history of pancreatitis, elderly.
ACTION
Inhibits HIV reverse transcriptase by interfering with HIV viral RNA–dependent DNA polymerase. Inhibits replication of hepatitis B virus (HBV) by inhibiting HBV polymerase. Therapeutic Effect: Slows HIV replication, reduces HIV RNA levels (viral load). Inhibits HBV replication.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Bioavailability in fasted pts is approximately 25%. High-fat meals increase bioavailability. Protein binding: 0.7%–7.2%. Excreted in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 17 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase didanosine concentration. May decrease concentrations of atazanavir, indinavir, lamivudine, lopinavir, ritonavir. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: High-fat food increases bioavailability. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, creatinine, phosphate, protein; urinary glucose. May decrease neutrophils.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: (Vemlidy):25 mg. (Viread): 150 mg, 200 mg, 250 mg, 300 mg. Oral Powder: 40 mg per 1 g of oral powder.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• (Vemlidy) Give with food. (Viread) May be given without regard to meals. • Give oral powder with soft food. Do not mix in liquid; use only the supplied dosing scoop to measure power.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Hepatitis B
PO: (Vemlidy): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 25 mg once daily with food. (Viread):ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 300 mg once daily.
HIV (in Combination with Other Antiretroviral Agents)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER (WEIGHT 35 KG OR GREATER): 300 mg once daily. CHILDREN 2 YRS AND OLDER (WEIGHT LESS THAN 35 KG): 8 mg/kg/dose once daily. Maximum: 300 mg/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 30–49 ml/min | 300 mg q48h |
| 10–29 ml/min | 300 mg q72–96h |
| Hemodialysis | 300 mg q7days or after approximately 12 hrs of dialysis |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: GI disturbances (diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Lactic acidosis, hepatomegaly with steatosis (excess fat in liver) occur rarely; may be severe.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline laboratory testing, esp. serum renal function, triglycerides, LFT and at periodic intervals during therapy. Offer emotional support.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Closely monitor for evidence of GI discomfort. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor CBC, reticulocyte count, serum renal function, LFT, CD4 cell count, HIV, RNA plasma levels.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Continue therapy for full length of treatment. • Tenofovir is not a cure for HIV infection, nor does it reduce risk of transmission to others. • Take with a high-fat meal (increases absorption). • Report persistent abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting.
terbinafine
ter-bin-a-feen
(Apo-Terbinafine
![]() , Lamisil, Lamisil AT, Terbinex)
, Lamisil, Lamisil AT, Terbinex)
Do not confuse Lamisil with Lamictal, or terbinafine with terbutaline.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Synthetic allylamine antifungal. CLINICAL: Antifungal.
USES
Systemic: Treatment of onychomycosis (fungal disease of nails due to dermatophytes). Treatment of tinea capitis. Topical: Treatment of tinea cruris (jock itch), tinea pedis (athlete’s foot), tinea corporis (ringworm), tinea versicolor.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to terbinafine. Cautions: Preexisting hepatic or renal impairment (CrCl 50 ml/min or less), sensitivity to allylamine antifungals (e.g., butenafine). Not recommended in pts with active or chronic hepatic disease.
ACTION
Inhibits the enzyme squalene epoxidase, thereby interfering with fungal biosynthesis. Therapeutic Effect: Results in death of fungal cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine; minimal elimination in feces. Half-life: PO, 36 hrs; topical, 22–26 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other hepatotoxic medications (e.g., acetaminophen, amiodarone, ketoconazole, isoniazid) may increase risk of hepatotoxicity. CYP3A inducers (e.g., rifampin) may increase clearance. CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., cimetidine, fluconazole) may decrease clearance. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Cream (Lamisil AT): 1%. Gel (Lamisil Advanced): 1%. Oral Granules (Lamisil): 125 mg/packet. Tablets (Lamisil, Terbinex): 250 mg. Topical Solution (Lamisil, Lamisil AT): 1%.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• Tablets may be given without regard to food. • Granules should be sprinkled on a spoonful of nonacidic food (e.g., mashed potatoes). Instruct pt to swallow without chewing.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Tinea Pedis
Topical: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: (Cream): Apply once or twice daily for at least 1 wk. (Gel/Solution): Apply once daily for at least 1 wk.
Tinea Cruris, Tinea Corporis
Topical: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: Apply once daily for at least 1 wk until signs/symptoms significantly improve; not to exceed 4 wks.
Onychomycosis
Note: Continue for 6 wks. PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 250 mg/day for 6 wks (fingernails) or 12 wks (toenails).
Tinea Versicolor
Topical Solution: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Apply to the affected area once or twice daily for 7 days.
Tinea Capitis
Note: Continue for 6 wks.
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 250 mg once daily. CHILDREN 4 YRS AND OLDER: (Use granules). WEIGHING GREATER THAN 35 KG: 250 mg once daily. WEIGHING 25–35 KG: 187.5 mg once daily. WEIGHING LESS THAN 25 KG: 125 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Not recommended in pts with active or chronic hepatic disease.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (13%): PO: Headache. Occasional (6%–3%): PO: Abdominal pain, flatulence, urticaria, visual disturbance. Rare: PO: Diarrhea, rash, dyspepsia, pruritus, altered taste, nausea. Topical: Irritation, burning, pruritus, dryness.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hepatobiliary dysfunction (including cholestatic hepatitis), serious skin reactions, severe neutropenia occur rarely. Ocular lens, retinal changes have been noted.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Serum LFT should be obtained in pts receiving treatment for longer than 6 wks.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Check for therapeutic response. Discontinue medication, notify physician if local reaction occurs (irritation, redness, swelling, pruritus, oozing, blistering, burning). Monitor LFT in pts receiving treatment for longer than 6 wks.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Keep areas clean, dry; wear light clothing to promote ventilation. • Avoid topical cream contact with eyes, nose, mouth, other mucous membranes. • Rub well into affected, surrounding area. • Do not cover with occlusive dressing. • Report rash, dark urine, abdominal pain, anorexia, yellowing of skin.
terbutaline
ter-bue-ta-leen
(Bricanyl
![]() )
)
Do not confuse Brethine with methergine, or terbutaline with terbinafine. Should not be used for prolonged tocolysis (longer than 48–72 hrs).
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Sympathomimetic (adrenergic agonist). CLINICAL: Bronchodilator, premature labor inhibitor.
USES
Symptomatic relief of reversible bronchospasm due to bronchial asthma, bronchitis, emphysema. OFF-LABEL: Delays premature labor in pregnancies between 20 and 34 wks.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to terbutaline. Cardiac arrhythmias associated with tachycardia, tachycardia caused by digoxin toxicity. (Additional) Injection: Prolonged prevention or management of preterm labor. Oral: Prevention or treatment of preterm labor. Cautions: Cardiac impairment, diabetes mellitus, glaucoma, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, history of seizures.
ACTION
Stimulates beta2-adrenergic receptors, resulting in relaxation of uterine, bronchial smooth muscle. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits uterine contractions. Relieves bronchospasm, reduces airway resistance.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Partially absorbed in GI tract following PO administration. Protein binding: 14%–25%. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine (30%–50%), feces (unspecified). Half-life: 11–16 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 6 yrs. Elderly: Increased risk of tremors, tachycardia due to sympathomimetic sensitivity.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of beta blockers (e.g., labetolol, metoprolol). Digoxin, sympathomimetics may increase risk of arrhythmias. MAOIs may increase risk of hypertensive crisis. Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, nortriptyline) may increase cardiovascular effects. HERBAL: Ephedra, yohimbe may cause CNS stimulation. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease serum potassium. May increase serum glucose.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 1 mg/ml. Tablets: 2.5 mg, 5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
• May administer undiluted, direct IV over 5–10 min or continuous infusion diluted in D5W or 0.9% NaCl.
SQ
• Do not use if solution appears discolored. • Inject subcutaneously into lateral deltoid region.
PO
• Give without regard to food (give with food if GI upset occurs). • Tablets may be crushed.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Bronchospasm
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 15 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 2.5–5 mg 3 times/day. Maintenance: 2.5–5 mg 3 times/day q6h while awake. Maximum: 15 mg/day. CHILDREN 12–14 YRS: 2.5 mg 3 times/day. Maximum: 7.5 mg/day. CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 12 YRS: Initially, 0.05 mg/kg/dose q8h. May increase up to 0.15 mg/kg/dose. Maximum: 5 mg/24 hr.
SQ: ADULTS, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 0.25 mg. Repeat in 15–30 min for 3 doses. Total dose of 0.75 mg should not be exceeded. CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 12 YRS: 0.005–0.01 mg/kg/dose to a maximum of 0.4 mg/dose q15–20min for 3 doses. May repeat q2–6h as needed.
Preterm Labor
◀ ALERT ▶ IV form should be used with caution in pregnancy; do not administer for longer than 48–72 hrs.
IV: ADULTS: Acute: 2.5–10 mcg/min. May increase gradually q15–20min up to 17.5–30 mcg/min. SQ: 0.25 mg q20min–3 hrs.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (38%–23%): Tremor, anxiety. Occasional (11%–10%): Drowsiness, headache, nausea, heartburn, dizziness. Rare (3%–1%): Flushing, asthenia, oropharyngeal dryness, irritation (with inhalation therapy).
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Too-frequent or excessive use may lead to decreased drug effectiveness and/or severe, paradoxical bronchoconstriction. Excessive sympathomimetic stimulation may cause palpitations, extrasystoles, tachycardia, chest pain, slight increase in B/P followed by a substantial decrease, chills, diaphoresis, skin blanching.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Bronchospasm: Offer emotional support (high incidence of anxiety due to difficulty in breathing, sympathomimetic response to drug). Preterm labor: Assess baseline maternal pulse, B/P, frequency and duration of contractions, fetal heart rate. Question history of cardiac arrhythmias, narrow-angle glaucoma, hypertension, seizures.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Bronchospasm: Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respiration; quality, rate of pulse. Assess lung sounds for rhonchi, wheezing, rales. Monitor ABGs. Observe lips, fingernails for cyanosis. Observe for clavicular retractions, hand tremor. Evaluate for clinical improvement (quieter, slower respirations, relaxed facial expression, cessation of clavicular retractions). Preterm labor: Monitor for frequency, duration, strength of contractions. Diligently monitor maternal and fetal heart rate.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report persistent palpitations, chest pain, muscle tremor, dizziness, headache, flushing, breathing difficulties. • May cause nervousness, anxiety, shakiness. • Avoid excessive use of caffeine derivatives (chocolate, coffee, tea, cola, cocoa).
Teriflunomide
ter-i-floo-noe-myde
(Aubagio)
Do not confuse teriflunomide with leflunomide.
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May result in major birth defects. Pregnancy must be excluded before initiating therapy, and must be avoided during treatment or prior to completion of an accelerated elimination procedure. Severe hepatic injury may occur. Do not initiate with acute/chronic liver disease or ALT greater than 2 times upper limit of normal.
May result in major birth defects. Pregnancy must be excluded before initiating therapy, and must be avoided during treatment or prior to completion of an accelerated elimination procedure. Severe hepatic injury may occur. Do not initiate with acute/chronic liver disease or ALT greater than 2 times upper limit of normal.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor, immunomodulatory agent. CLINICAL: Multiple sclerosis agent.
USES
Treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to teriflunomide. Pregnant women or women of childbearing potential who are not using reliable contraception, severe hepatic impairment, concurrent use of leflunomide. Cautions: Concomitant neurotoxic medications, diabetes, pulmonary disease, severe immunodeficiency or bone marrow dysplasia, history of significant hematologic abnormalities, uncontrolled infection, history of new/recurrent infections, pts older than 60 yrs.
ACTION
Inhibits pyrimidine synthesis, exhibiting anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative properties. Therapeutic Effect: May slow progression of multiple sclerosis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed following PO administration. Peak concentration: 1–4 h. Protein binding: greater than 99%. Metabolized by hydrolysis. Eliminated in urine (23%), feces (38%). Half-life: 18–19 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May produce embryo-fetal toxicity. Pregnancy contraindicated. Avoid breastfeeding. Detected in human semen. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs of age. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May increase concentration/effects of CYP2C8 substrates (e.g., repaglinide, paclitaxel, pioglitazone, or rosiglitazone), oral contraceptives. May decrease concentration/effects of warfarin, CYP1A2 substrates (e.g., duloxetine, tizanidine). HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum potassium, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin. May decrease WBCs, neutrophil count.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 7 mg, 14 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Multiple Sclerosis
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 7 mg or 14 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Contraindicated.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (19%–6%): Headache, diarrhea, nausea, alopecia, paresthesia, upper abdominal pain. Occasional (4%–3%): Hypertension, oral herpes, anxiety, hypertension, toothache, musculoskeletal pain. Rare (2%–1%): Seasonal allergy, sciatica, burning sensation, carpal tunnel syndrome, blurred vision, acne, pruritus, myalgia, abdominal distention, conjunctivitis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Influenza occurs in 12% of pts, upper respiratory infection with sinusitis, bronchitis, in 9%. Cystitis, sinusitis, viral gastroenteritis may occur. Neutropenia, leukopenia occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Because of high potential for birth defects/fetal death, female pts must avoid pregnancy. Obtain baseline PPD for latent TB. Obtain CBC, hepatic function test results prior to treatment, and for 6 mos thereafter. Obtain baseline pregnancy test. Assess limitations for activities of daily living due to multiple sclerosis.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for signs/symptoms of infection. Treatment should not be initiated if pt has active infection; discontinuation of treatment must be considered. If drug-induced hepatic impairment, peripheral neuropathy, severe skin reaction occur, discontinue medication, begin accelerated elimination procedure (cholestyramine or charcoal for 11 days).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Women of childbearing potential must be counseled regarding fetal risk, use of reliable contraceptives confirmed, possibility of pregnancy excluded. • May take without regard to food.
teriparatide
ter-i-par-a-tide
(Forteo)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk of osteosarcoma; risk dependent on dose and duration.
Increased risk of osteosarcoma; risk dependent on dose and duration.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Parathyroid hormone. CLINICAL: Osteoporosis agent.
USES
Treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who are at increased risk for fractures. Treatment of men with primary or hypogonadal osteoporosis who are at high risk for fractures. High-risk pts include those with a history of osteoporotic fractures, who have failed previous osteoporosis therapy, or were intolerant of previous osteoporosis therapy. Treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in men and women.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to teriparatide. Cautions: Conditions that increase risk of osteosarcoma (e.g., Paget’s disease, unexplained elevations of alkaline phosphatase level, open epiphyses, prior skeletal radiation therapy, implant therapy), hypercalcemia, hypercalcemic disorders (e.g., hyperparathyroidism), bone metastases, history of skeletal malignancies, metabolic bone diseases other than osteoporosis, cardiac disease, renal/hepatic impairment, pts at risk for orthostasis, active or recent urolithiasis.
ACTION
Stimulates osteoblast function. Increases calcium absorption from GI tract/renal tubular reabsorption. Therapeutic Effect: Increases bone mineral density, bone mass/strength, reduces osteoporosis-related fractures.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Extensively absorbed following SQ injection. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 1 hr.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum calcium (transient), uric acid.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 250 mcg/ml (2.4 ml) delivers 20 mcg/dose.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
SQ
• Refrigerate, but minimize time out of refrigerator. Do not freeze; discard if frozen. • Administer into thigh, abdominal wall.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Osteoporosis
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20 mcg once daily into thigh, abdominal wall.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Leg cramps, nausea, dizziness, headache, orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Angina pectoris has been reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Check urinary, serum calcium, ionized calcium levels, serum parathyroid hormone levels.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor bone mineral density, urinary/serum calcium levels, serum parathyroid hormone levels. Observe for symptoms of hypercalcemia. Monitor B/P for hypotension, pulse for tachycardia.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Go from lying to standing slowly. • Report persistent symptoms of hypercalcemia (nausea, vomiting, constipation, lethargy, asthenia).
Testosterone

tes-tos-te-rone
(Andriol
![]() , Androderm, AndroGel Pump, Andropository
, Androderm, AndroGel Pump, Andropository
![]() , Aveed, Axiron, Delatestryl, Depotest
, Aveed, Axiron, Delatestryl, Depotest
![]() , Depo-Testosterone, Everone
, Depo-Testosterone, Everone
![]() , FIRST-Testosterone, FIRST-Testosterone MC, Fortesta, Natesto, Striant, Testim, Testopel, Vogelxo Pump)
, FIRST-Testosterone, FIRST-Testosterone MC, Fortesta, Natesto, Striant, Testim, Testopel, Vogelxo Pump)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Virilization in children and women may occur following secondary exposure to testosterone gel. Aveed: Serious pulmonary oil microembolism reaction and anaphylaxis reported during or immediately after administration.
Virilization in children and women may occur following secondary exposure to testosterone gel. Aveed: Serious pulmonary oil microembolism reaction and anaphylaxis reported during or immediately after administration.
Do not confuse testosterone with testolactone, Testoderm with Estraderm.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
USES
Androgen replacement therapy in treatment of delayed male puberty, male hypogonadism (congenital or acquired), inoperable female breast cancer pts who are 1–5 yrs postmenopausal.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to testosterone. Breastfeeding, pregnant or who may become pregnant, prostate or breast cancer in males. Depo-Testosterone: Severe cardiac hepatic/renal disease. Cautions: Renal/hepatic/cardiac dysfunction, pts with history of MI or CAD; conditions influenced by edema (e.g., seizure disorder, migraines).
ACTION
Promotes growth, development of male sex organs, maintains secondary sex characteristics in androgen-deficient males. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves androgen deficiency.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed after IM administration. Protein binding: 98%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 10–100 min.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Contraindicated during lactation. Children: Safety and efficacy not established; use with caution. Elderly: May increase risk of hyperplasia, stimulate growth of occult prostate carcinoma.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease serum glucose, requiring insulin adjustments. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase Hgb, Hct, LDL, serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, calcium, potassium, sodium, AST. May decrease HDL.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Cream (First Testosterone, MC): 2%. Ointment (First Testosterone): 2% Gel, Topical (AndroGel, Testim): 1%, 1.62%. (Vogelxo): 50-mg packet or tube, 12.5 mg/actuation metered dose pump. (Fortesta): 10 mg/actuation. Injection (Cypionate [Depo-Testosterone]): 100 mg/ml, 200 mg/ml. (Enanthate [Delatestryl]): 200 mg/ml. (Aveed [undecanoate]): 750 mg/3 ml. Mucoadhesive, for Buccal Application (Striant): 30 mg. Nasal Gel (Natesto): 5.5 mg/actuation. Pellet, for Subcutaneous Implantation (Testopel): 75 mg. Solution (Metered Dose Pump [Axiron]): 30 mg/activation. Transdermal System (Androderm): 2 mg/day or 4 mg/day.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
IM
• Give deep in gluteal muscle. • Do not give IV. • Warming or shaking redissolves crystals that may form in long-acting preparations. • Wet needle of syringe may cause solution to become cloudy; this does not affect potency.
Buccal
(Striant): • Apply to gum area (above incisor tooth). • Hold firmly in place for 30 sec to ensure adhesion. Instruct pt to not chew or swallow. • Not affected by food, toothbrushing, gum, chewing, alcoholic beverages. • Remove before placing new system.
Transdermal
(Androderm): • Apply to clean, dry area on skin on back, abdomen, upper arms, thighs. • Do not apply to bony prominences (e.g., shoulder) or oily, damaged, irritated skin. Do not apply to scrotum. • Rotate application site with 7-day interval to same site.
Transdermal Gel
(AndroGel, Testim, Vogelxo): • Apply (morning preferred) to clean, dry, intact skin of shoulder, upper arms (AndroGel 1% may also be applied to abdomen). • Upon opening packet(s), squeeze entire contents into palm of hand, immediately apply to application site. • Allow to dry. • Do not apply to genitals. (Fortesta): Apply to skin of front and inner thighs.
Topical Solution
(Axiron): • Apply using applicator to axilla at same time each morning. • Avoid washing site for 2 hrs after application.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Male Hypogonadism
IM: ADULTS: 50–400 mg q2–4wks or 75–100 mg/wk or 150–200 mg q2wks. (Aveed):750 mg at initiation, 4 wks and q10 wks thereafter. ADOLESCENTS: Initiation of pubertal growth: 25–75 mg q3–4wks, titrate q6–9mos to 100–150 mg. Duration: 3–4yrs. Maintenance Virilizing Dose: 100 mg/m2/dose twice monthly.
SQ: (Pellets): ADULTS: 150–450 mg q3–6mos.
Topical Gel: (Fortesta): 40 mg once daily in morning. Range: 10–70 mg. (Vogelxo):50 mg once daily (one tube or one packet or 4 pump actuations).
Topical Solution: (Axiron): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 60 mg once daily (1 pump activation of 30 mg to each axilla). Range: 30–120 mg.
Transdermal Patch: (Androderm): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Start therapy with 4 mg/day patch applied at night. Apply patch to abdomen, back, thighs, upper arms. Dose adjustment based on testosterone levels.
Transdermal Gel: (AndroGel): ADULTS, ELDERLY: (AndroGel 1%): Initial dose of 5 g delivers 50 mg testosterone and is applied once daily to abdomen, shoulders, upper arms. May increase to 7.5 g, then to 10 g, if necessary. (AndroGel 1.62%): Initial dose of 40.5 mg applied once daily in the morning to shoulder and upper arms. May increase to 81 mg. Further adjustments based on testosterone levels.
Transdermal Gel: (Testim): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initial dose of 5 g delivers 50 mg testosterone and is applied once daily to the shoulders, upper arms. May increase to 10 g (100 mg testosterone).
Buccal: (Striant): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 30 mg q12h.
Nasal Gel: (Natesto):ADULTS ELDERLY: 11 mg (2 actuations, 1 per each nostril) 3 times/day.
Delayed Male Puberty
IM: (Cypionate or enanthate):ADOLESCENTS: 50–200 mg q2–4wks for limited duration.
SQ: (Pellets): ADULTS: 150–450 mg q3–6mos.
Breast Carcinoma
IM: (Testosterone Cypionate, Testosterone Ethanate):ADULTS: 200–400 mg q2–4wks.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Gynecomastia, acne. Females: Hirsutism, amenorrhea, other menstrual irregularities; deepening of voice; clitoral enlargement (may not be reversible when drug is discontinued). Occasional: Edema, nausea, insomnia, oligospermia, priapism, male-pattern baldness, bladder irritability, hypercalcemia (in immobilized pts, those with breast cancer), hypercholesterolemia, inflammation/pain at IM injection site. Transdermal: Pruritus, erythema, skin irritation. Rare: Polycythemia (with high dosage), hypersensitivity.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Peliosis hepatitis (presence of blood-filled cysts in parenchyma of liver), hepatic neoplasms, hepatocellular carcinoma have been associated with prolonged high-dose therapy. Anaphylactic reactions occur rarely. Venous thromboembolism (e.g., DVT, PE) reported.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Establish baseline weight, B/P, Hgb, Hct. Check serum hepatic function, electrolytes, cholesterol. Wrist X-rays may be ordered to determine bone maturation in children.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Weigh daily, report wkly gain of more than 5 lb; evaluate for edema. Monitor I&O. Monitor B/P. Assess serum electrolytes, cholesterol, Hgb, Hct (periodically for high dosage), LFT, radiologic exam of wrist, hand (when using in prepubertal children). With breast cancer or immobility, check for hypercalcemia (lethargy, muscle weakness, confusion, irritability). Ensure adequate intake of protein, calories. Assess for virilization. Monitor sleep patterns. Check injection site for redness, swelling, pain.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Regular visits to physician and monitoring tests are necessary. • Do not take any other medication without consulting physician. • Maintain diet high in protein, calories. • Food may be better tolerated in small, frequent feedings. • Weigh daily, report 5 lb/wk gain. • Report nausea, vomiting, acne, pedal edema. • Females: Promptly report menstrual irregularities, hoarseness, deepening of voice. • Males: Report frequent erections, difficulty urinating, gynecomastia.
tetracycline
tet-ra-sye-kleen
(Apo-Tetra
![]() , Nu-Tetra
, Nu-Tetra
![]() )
)
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Pylera: tetracycline/bismuth/metronidazole (an anti-infective): 125 mg/140 mg/125 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Tetracycline. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of susceptible infections due to Rickettsiae, M. pneumoniae, C. trachomatis, C. psittaci, H. ducreyi, Yersinia pestis, Francisella tularensis, Vibrio cholerae, Brucella spp.; treatment of susceptible infections due to gram-negative organisms including inflammatory acne vulgaris, Lyme disease, mycoplasma disease, Legionella, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, chlamydial infection in pts with gonorrhea. Part of multidrug regimen of H. pylori eradication to reduce risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tetracycline. Cautions: Sun, ultraviolet light exposure (severe photosensitivity reaction). Renal, hepatic impairment. Avoid use during tooth development (children 8 yrs or younger). Do not use during pregnancy.
ACTION
Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to ribosomes. Therapeutic Effect: Bacteriostatic.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 30%–60%. Widely distributed. Excreted in urine; eliminated in feces through biliary system. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 6–11 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Readily crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Avoid use in women during last half of pregnancy. Children: Not recommended in pts 8 yrs or younger; may cause permanent staining of teeth, enamel hypoplasia, decreased linear skeletal growth rate. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of oral contraceptives. Antacids, calcium or iron supplements, laxatives containing magnesium may form nonabsorbable, undigestible complexes. HERBAL: Dong quai, St. John’s wort may increase risk of photosensitivity. FOOD: Dairy products inhibit absorption. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, alkaline phosphatase, amylase, bilirubin, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 250 mg, 500 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give with full glass of water 1 hr before or 2 hrs after meals. • Avoid antacids, dairy products within 3 hrs of tetracycline.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Space doses evenly around the clock.
Usual Dosage
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 250–500 mg q6–12h. CHILDREN OLDER THAN 8 YRS: 25–50 mg/kg/day in 4 divided doses.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage interval is modified based on creatinine clearance.
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 50–80 ml/min | Usual dose q8–12h |
| 10–49 ml/min | Usual dose q12–24h |
| Less than 10 ml/min | Usual dose q24h |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Dizziness, light-headedness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, photosensitivity (may be severe). Occasional: Pigmentation of skin or mucous membranes, anal/genital pruritus, stomatitis, discoloration of teeth.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Superinfection (esp. fungal), anaphylaxis, elevated intracranial pressure (ICP) may occur. Bulging fontanelles occur rarely in infants.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for history of allergies, esp. tetracyclines, sulfite.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess skin for rash. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Monitor food intake, tolerance. Be alert for superinfection (diarrhea, stomatitis, anal/genital pruritus). Monitor B/P, level of consciousness (potential for elevated ICP).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Continue antibiotic for full length of treatment. • Space doses evenly. • Take oral doses on empty stomach (1 hr before or 2 hrs after food, beverages). • Avoid antacids, dairy products within 3 hrs of tetracycline. • Drink full glass of water with capsules; avoid bedtime doses. • Report diarrhea, rash, other new symptoms. • Protect skin from sun, ultraviolet light exposure. • Consult physician before taking any other medication. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established (may cause dizziness, light-headedness).
thiamine (vitamin B1)
thy-a-min
(Betaxin
![]() )
)
Do not confuse thiamine with Thorazine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Water-soluble vitamin. CLINICAL: Vitamin B complex.
USES
Prevention/treatment of thiamine deficiency (e.g., beriberi, Wernicke’s encephalopathy syndrome, peripheral neuritis associated with pellagra, alcoholic pts with altered sensorium), metabolic disorders.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to thiamine. Cautions: Wernicke’s encephalopathy.
ACTION
Combines with adenosine triphosphate in liver, kidneys, leukocytes to form thiamine diphosphate, a coenzyme necessary for carbohydrate metabolism. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents, reverses thiamine deficiency.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly and completely absorbed from GI tract, primarily in duodenum, after IM administration. Widely distributed. Primarily excreted in urine.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Children/Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY
Injection Solution (Vitamin B1): 100 mg/ml. Tablets (OTC): 50 mg, 100 mg, 250 mg, 500 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ V, IM administration used only in acutely ill or those unresponsive to PO route (GI malabsorption syndrome). IM route preferred to IV use. Give by IV push, or add to most IV solutions and give as infusion.
PO
• May take without regard to food.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
None known.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Famotidine (Pepcid), multivitamins, folic acid magnesium.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Dietary Supplement
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1–2 mg/day. CHILDREN: 0.5–1 mg/day. INFANTS: 0.3–0.5 mg/day.
Thiamine Deficiency (Beriberi)
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–30 mg/dose IM or IV 3 times/day (if critically ill), then 5–30 mg/day orally, as a single dose or in 3 divided doses, for 1 mo. CHILDREN: 10–25 mg IM or IV (if critically ill) or 10–50 mg/dose orally every day for 2 wks, then 5–10 mg/day for 1 mo.
Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome
IV, IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 100 mg/day for several days, then PO: 50–100 mg/day.
Metabolic Disorders
PO: ADULTS: 10–20 mg/day.
Wernicke’s Encephalopathy
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 100 mg then IV/IM: 50–100 mg/day until consuming a regular, balanced diet.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Pain, induration, tenderness at IM injection site.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
IV administration may result in rare, severe hypersensitivity reaction marked by feeling of warmth, pruritus, urticaria, weakness, diaphoresis, nausea, restlessness, tightness in throat, angioedema, cyanosis, pulmonary edema, GI tract bleeding, cardiovascular collapse.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for clinical improvement (improved sense of well-being, weight gain). Observe for reversal of deficiency symptoms (neurologic: altered mental status, peripheral neuropathy, hyporeflexia, nystagmus, ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, muscle weakness; cardiac: venous hypertension, bounding arterial pulse, tachycardia, edema).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Discomfort may occur with IM injection. • Foods rich in thiamine include pork, organ meats, whole grain and enriched cereals, legumes, nuts, seeds, yeast, wheat germ, rice bran. • Urine may appear bright yellow.
*tiaGABine
tye-a-ga-been
(Gabitril)
Do not confuse tiagabine with tizanidine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Anticonvulsant. CLINICAL: Anticonvulsant.
USES
Adjunctive therapy for treatment of partial seizures in adults and children 12 yrs or older.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tiagabine. Cautions: Hepatic impairment. Pts at risk for suicidal behavior/thoughts.
ACTION
Enhances activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits seizures.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 96%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily eliminated in feces. Half-life: 2–5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May produce teratogenic effects. Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 12 yrs. Elderly: Age-related hepatic impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin may increase clearance. May alter effects of valproic acid. HERBAL: Evening primrose may decrease seizure threshold. St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 2 mg, 4 mg, 12 mg, 16 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• Give with food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Pts not taking enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Lower doses required, slower titration may be needed.
Partial Seizures
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Pts receiving enzyme-inducing AED regimens): Initially, 4 mg once daily. May increase by 4–8 mg/day at wkly intervals. Maintenance: 32–56 mg/day. CHILDREN 12–18 YRS: Initially, 4 mg once daily for 1 wk. May increase by 4 mg in 2 divided doses for 1 wk, then may increase by 4–8 mg at wkly intervals thereafter. Maximum: 32 mg/day in 2–4 divided doses.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (34%–20%): Dizziness, asthenia (loss of strength, energy), drowsiness, nervousness, confusion, headache, infection, tremor. Occasional: Nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, impaired concentration.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose characterized by agitation, confusion, hostility, weakness. Full recovery occurs within 24 hrs of discontinuation.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Review history of seizure disorder (intensity, frequency, duration, LOC). Observe frequently for recurrence of seizure activity. Initiate seizure precautions.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
For pts on long-term therapy, serum hepatic/renal function tests, CBC should be performed periodically. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Assess for clinical improvement (decrease in intensity, frequency of seizures). Monitor for depression, unusual behavior, suicidal ideation or thoughts.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Go from lying to standing slowly. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol. • Report worsening seizure activity, thoughts of suicide, increased depression.
ticagrelor
tye-ka-grel-or
(Brilinta)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause significant, sometimes fatal bleeding. Do not use with active bleeding or history of intracranial bleeding. Do not initiate in pts planning urgent coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. Discontinue at least 5 days prior to any surgery. Suspect bleeding in any pt who is hypotensive and has had recent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), CABG, or other surgical procedures. If possible, manage bleeding without discontinuing therapy to decrease risk of cardiovascular events. Aspirin maintenance doses greater than 100 mg/day may reduce effectiveness and should be strictly avoided.
May cause significant, sometimes fatal bleeding. Do not use with active bleeding or history of intracranial bleeding. Do not initiate in pts planning urgent coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. Discontinue at least 5 days prior to any surgery. Suspect bleeding in any pt who is hypotensive and has had recent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), CABG, or other surgical procedures. If possible, manage bleeding without discontinuing therapy to decrease risk of cardiovascular events. Aspirin maintenance doses greater than 100 mg/day may reduce effectiveness and should be strictly avoided.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: P2Y12 platelet aggregation inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiplatelet.
USES
Reduce rate of cardiovascular death, MI, stroke in pts with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) or history of MI. Reduce rate of stent thrombosis in pts who have been stented for treatment of ACS.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ticagrelor. History of intracranial hemorrhage, active pathologic bleeding, severe hepatic impairment. Cautions: Moderate hepatic impairment, renal impairment, history of hyperuricemia or gouty arthritis. Pts at increased risk of bradycardia, concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers, elderly. (Recommend holding dose 5 days before planned surgery if applicable.) Pts with risk factors for bleeding (e.g., trauma, peptic ulcer disease).
ACTION
Reversibly inhibits platelet P2Y12 ADP receptor to prevent signal transduction and platelet activation. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces platelet aggregation.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in feces (58%), urine (26%). Half-life: 7–9 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Must either discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue drug therapy. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Aspirin greater than 100 mg/day may decrease effectiveness. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., atazanavir, clarithromycin, ketoconazole, nefazodone, ritonavir, saquinavir) may increase concentration/effects. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, dexamethasone, phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effects. Anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelets, NSAIDs may increase risk of bleeding. May increase concentration of digoxin, simvastatin, lovastatin. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease effectiveness. Fenugreek, feverfew, flaxseed, garlic, ginger, ginkgo biloba, ginseng, omega-3, red clover with anticoagulant/antiplatelet activity may increase risk of bleeding. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase potential for bleeding. LAB VALUES: May increase serum uric acid, creatinine.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 60 mg, 90 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals. • May be crushed, mixed with water, and drunk immediately (refill glass with water, stir and drink contents).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Acute Coronary Syndrome
PO: ADULTS: Initially, 180 mg once, then 90 mg twice daily. Give with aspirin 325 mg once (loading dose), then maintain with aspirin 75–100 mg daily. Continue for up to 12 mos, then decrease dose to 60 mg twice daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate impairment: Use caution. Severe impairment: Avoid use.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (13%–7%): Dyspnea, headache. Rare (5%–3%): Cough, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, back pain, fatigue.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Life-threatening events including intracranial bleeding, epistaxis, intrapericardial bleeding with cardiac tamponade, hypovolemic shock requiring vasopressive support, or blood transfusion reported. Pts with history of sick sinus syndrome, second- or third-degree AV block, bradycardic syncope have increased risk of bradycardia. May induce episodes of atrial fibrillation, hypotension, hypertension. Gynecomastia reported in less than 1% of men.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain CBC, serum chemistries, renal function, LFT. Question for history of bleeding, stomach ulcers, colon polyps, head trauma, cardiac arrhythmias, unstable angina, recent MI, hepatic impairment, hypertension, stroke. Receive full medication history including herbal products. Question for history of COPD, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, asthma, exertional dyspnea.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Routinely screen for bleeding. Assess skin for bruising, hematoma. Monitor renal function, uric acid, digoxin levels if applicable. Report hematuria, epistaxis, coffee-ground emesis, black/tarry stools. Monitor EKG for chest pain, shortness of breath, syncope.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• It may take longer to stop bleeding during therapy. • Do not vigorously blow nose. • Use soft toothbrush, electric razor to decrease risk of bleeding. • Immediately report bloody stool, urine, or nosebleeds. • Report all newly prescribed medications. • Inform physician of any planned dental procedures or surgeries.
tigecycline
tye-gee-sye-kleen
(Tygacil)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Use reserved where alternative treatments not appropriate.
Use reserved where alternative treatments not appropriate.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Glycylcycline. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of susceptible infections due to E. coli, E. faecalis, S. aureus, S. agalactiae, S. anginosus group (includes S. anginosus, S. intermedius, S. constellatus), S. pyogenes, B. fragilis, Citrobacter freundii, E. cloacae, K. oxytoca, K. pneumoniae, B. thetaiotaomicron, B. uniformis, B. vulgatus, C. perfringens, Peptostreptococcus micros including complicated skin/skin structure infections, complicated intra-abdominal infections, community-acquired bacterial pneumonia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tigecycline. Cautions: Hypersensitivity to tetracyclines, pregnancy, hepatic impairment, monotherapy for pts with intestinal perforation. Do not use for diabetic foot infections, healthcare-acquired pneumonia, or ventilator-associated pneumonia.
ACTION
Inhibits protein synthesis by binding to ribosomal receptor sites of bacterial cell wall. Therapeutic Effect: Bacteriostatic effect.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Extensive tissue distribution, minimally metabolized. Eliminated by biliary/fecal route (59%), urine (33%). Protein binding: 71%–89%. Half-life: Single dose: 27 hrs; following multiple doses: 42 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. May be distributed in breast milk. Permanent discoloration of the teeth (brown-gray) may occur if used during tooth development. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 18 yrs. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease effects of oral contraceptives may be decreased. May increase concentration of warfarin; increase bleeding time. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, amylase, BUN, bilirubin, glucose, LDH, ALT, AST. May decrease Hgb, WBCs, thrombocytes, serum potassium, protein.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Tygacil): 50-mg vial.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Add 5.3 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W to each 50-mg vial. • Swirl gently to dissolve. • Resulting solution is 10 mg/ml. • Immediately withdraw 5 ml reconstituted solution and add to 100 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W bag for infusion (final concentration should not exceed 1 mg/ml).
Rate of Administration • Administer over 30–60 min every 12 hrs. • May be given through a dedicated line or piggyback. If same line is used for sequential infusion of several different drugs, line should be flushed before and after infusion of tigecycline with either 0.9% NaCl or D5W.
Storage • Reconstituted solution is stable for up to 6 hrs at room temperature or up to 24 hrs if refrigerated. • Reconstituted solution appears yellow to red-orange. • Discard if solution is discolored (green, black) or precipitate forms.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B, methylprednisolone, voriconazole.
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amikacin, azithromycin, aztreonam, cefepime, ceftazidime, ciprofloxacin, doripenem, ertapenem, fluconazole, gentamicin, linezolid, piperacillin-tazobactam, potassium chloride, telavancin, tobramycin, vancomycin.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Systemic Infections
IV: ADULTS OVER 18 YRS, ELDERLY: Initially, 100 mg, followed by 50 mg every 12 hrs for 5–14 days.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment in mild to moderate impairment.
Dosage in Severe Hepatic Impairment
IV: ADULTS OVER 18 YRS, ELDERLY: Initially, 100 mg, followed by 25 mg every 12 hrs.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (29%–13%): Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. Occasional (7%–4%): Headache, hypertension, dizziness, increased cough, delayed healing. Rare (3%–2%): Peripheral edema, pruritus, constipation, dyspepsia, asthenia (loss of strength, energy), hypotension, phlebitis, insomnia, rash, diaphoresis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Dyspnea, abscess, pseudomembranous colitis (abdominal cramps, severe watery diarrhea, fever) ranging from mild to life-threatening may result from altered bacterial balance in GI tract.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, hepatic function test. Question for history of allergies, esp. tetracyclines, before therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Be alert for superinfection: fever, anal/genital pruritus, oral mucosal changes (ulceration, pain, erythema). Nausea, vomiting may be controlled by antiemetics.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report diarrhea, rash, mouth soreness, other new symptoms.
tiotropium

tye-oh-trope-ee-yum
(Spiriva HandiHaler, Spiriva Respimat)
Do not confuse Spiriva with Inspra, or tiotropium with ipratropium.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Stiolto Respimat: tiotropium/olodaterol (a bronchodilator): 2.5 mcg/2.5 mcg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Anticholinergic. CLINICAL: Bronchodilator.
USES
Long-term maintenance treatment of bronchospasm associated with COPD, including chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and for reducing COPD exacerbations. Maintenance treatment of asthma in pts 12 yrs and older.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tiotropium. History of hypersensitivity to ipratropium. Cautions: Narrow-angle glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, bladder neck obstruction, moderate to severe renal impairment, history of hypersensitivity to atropine, myasthenia gravis.
ACTION
Binds to recombinant human muscarinic receptors at smooth muscle, resulting in long-acting bronchial smooth muscle relaxation. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves bronchospasm.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Binds extensively to tissue. Protein binding: 72%. Metabolized by oxidation. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 5–6 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Higher frequency of dry mouth, constipation, UTI noted with increasing age.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Concurrent administration with anticholinergics (e.g., ipratropium) may increase adverse effects. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Inhalation Spray (Spiriva Respimat): 1.25 mcg/actuation, 2.5 mcg/actuation.
Powder for Inhalation (Spiriva): 18 mcg/capsule (in blister packs).
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Inhalation (Spiriva)
• Open dustcap of HandiHaler by pulling it upward, then open mouthpiece. • Place capsule in center chamber and firmly close mouthpiece until a click is heard, leaving the dustcap open. • Hold HandiHaler device with mouthpiece upward, press piercing button completely in once, and release. • Instruct pt to breathe out completely before breathing in slowly and deeply but at rate sufficient to hear the capsule vibrate. • Have pt hold breath as long as it is comfortable until exhaling slowly. • Instruct pt to repeat once again to ensure full dose is received.
Spiriva Respimat • Refer to manufacturer’s pt instructions.
Storage • Store at room temperature. Do not expose capsules to extreme temperature, moisture. • Do not store capsules in HandiHaler device. • Use immediately once foil is peeled back or removed.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
COPD (Maintenance Treatment, Reduction of COPD Exacerbations)
Inhalation:(Spiriva):ADULTS, ELDERLY: 18 mcg (1 capsule)/day via HandiHaler inhalation device. (Spiriva Respimat): 2 inhalation (2.5 mg/inhalation) once daily.
Asthma
Inhalation: (Spiriva Respimat): ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 2 inhalations of 1.25 mcg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl 50 ml/min or less: Use caution in moderate to severe impairment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (16%–6%): Dry mouth, sinusitis, pharyngitis, dyspepsia, UTI, rhinitis. Occasional (5%–4%): Abdominal pain, peripheral edema, constipation, epistaxis, vomiting, myalgia, rash, oral candidiasis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Angina pectoris, depression, flu-like symptoms, glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Offer emotional support (high incidence of anxiety due to difficulty in breathing, sympathomimetic response to drug). Auscultate lung sounds.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respiration; quality, rate of pulse. Assess lung sounds for rhonchi, wheezing, rales. Monitor ABGs. Observe for clavicular retractions, hand tremor. Evaluate for clinical improvement (quieter, slower respirations, relaxed facial expression, cessation of clavicular retractions).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Increase fluid intake (decreases lung secretion viscosity). • Do not use more than 1 capsule for inhalation at any one time. • Rinsing mouth with water immediately after inhalation may prevent mouth/throat dryness, thrush. • Avoid excessive use of caffeine derivatives (chocolate, coffee, tea, cola, cocoa). • Report eye pain/discomfort, blurred vision, visual halos.
tipiracil/trifluridine
trye-flure-i-deen/tye-pir-a-sil
(Lonsurf)
Do not confuse trifluridine with floxuridine, or tipiracil with tipifarnib or Pipracil.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Nucleoside metabolic inhibitor/thymidine phosphorylase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of pts with metastatic colorectal cancer who have been previously treated with fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin-, and irinotecan-based chemotherapy, an anti–vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) biological therapy, and if RAS wild-type, an anti–epidermal growth factor (EGFR) therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to trifluridine or tipiracil. Cautions: Baseline anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia; active infection, pts at increased risk of infection (e.g., diabetes, indwelling catheters), pts with high tumor burden. History of pulmonary embolism.
ACTION
Trifluridine interferes with DNA synthesis and cell proliferation of cancer cells. Tipiracil increases exposure of trifluridine by inhibiting metabolism via thymidine phosphorylase. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed. Metabolized by thymidine phosphorylase (not metabolized in liver). Protein binding: trifluridine: 96%; tipiracil: 8%. Peak plasma concentration: 2 hrs. Eliminated primarily in urine (50%). Half-life: trifluridine: 1.4 hrs (2.1 hrs at steady state); tipiracil: 2.1 hrs (2.4 hrs at steady state).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Avoid pregnancy; may cause fetal harm. Female pts of reproductive potential must use effective contraception during treatment. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Must either discontinue drug or discontinue breastfeeding. Males: Due to risk of potential exposure, male pts must use condoms during sexual activity during treatment and up to 3 mos after discontinuation. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May have increased risk of neutropenia, thrombocytopenia.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Not specified (no formal studies have been conducted). HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: Expected to decrease Hct, Hgb, platelets, neutrophils, RBC, WBC.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Fixed-Dose Combination Tablets: trifluridine/tipiracil: 15 mg/6.14 mg, 20 mg/8.19 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give within 1 hr of completion of morning and evening meals. Do not give on empty stomach.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Do not initiate the cycle until ANC is 1,500/mm3 or greater; febrile neutropenia is resolved; platelet count is 75,000/mm3 or greater; grade 3 or 4 nonhematologic toxicity is resolved to grade 1 or 0.
Colorectal Cancer
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Dose based on trifluridine component) 35 mg/m2 (rounded to nearest 5-mg increment) twice daily on days 1–5 and days 8–12 of 28-day cycle. Continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Maximum: 80 mg/dose (based on trifluridine component).
Dose Modification
Based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE).
Hematological/Nonhematologic Toxicity
Interrupt treatment for ANC less than 500/mm3; febrile neutropenia; platelet count less than 50,000/mm3; grade 3 or 4 nonhematologic toxicity. Do not restart until ANC is 1,500/mm3 or greater; febrile neutropenia is resolved; platelet count is 75,000/mm3 or greater; grade 3 or 4 nonhematologic toxicity is resolved to grade 1 or 0 (except grade 3 nausea and/or vomiting controlled by antiemetic therapy; grade 3 diarrhea responsive to antidiarrheal medication). Once resolved, resume at decreased incremental dose of 5 mg/m2 from previous dose. A maximum of 3 dose reductions is allowed to dosage minimum of 20 mg/m2 twice daily. Do not increase dose after it has been reduced.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: No dose adjustment. Severe impairment: Not studied; use caution.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment: Not studied; use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (52%–19%): Asthenia, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite, vomiting, abdominal pain, pyrexia. Occasional (8%–7%): Stomatitis, dysgeusia, alopecia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Severe and/or life-threatening myelosuppression including anemia (77% of pts), grade 3 anemia (18% of pts), neutropenia (67% of pts), grade 3 or 4 neutropenia (27% and 11% of pts), thrombocytopenia (42% of pts), grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia (5% and 1% of pts), febrile neutropenia (3.8% of pts) may occur. Infectious processes including nasopharyngitis, urinary tract infection reported in 2%–4% of pts. Pulmonary embolism occurred in 2% of pts. Interstitial lung disease occurs rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC and screen for anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia. Obtain vital signs. Verify pregnancy status before start of each cycle. Screen for active infection; history of pulmonary embolism. Assess hydration status. Question pt’s usual stool characteristics (color, frequency, consistency).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Follow proper handling and disposal procedures for cytotoxic drugs. Monitor ANC, CBC on day 15 of each cycle. If any grade 3 or 4 hematologic toxicity occurs, repeat ANC, CBC more frequently. If chest pain, dyspnea, tachycardia occurs, provide supplemental O2 and obtain radiologic testing to rule out pulmonary embolism. Diligently monitor for infection. Monitor daily stool pattern, consistency. Encourage PO intake. Monitor for bleeding if thrombocytopenia occurs.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Blood levels will be monitored regularly. • Treatment may cause fetal harm. Female pts of childbearing potential should use effective contraception during treatment. Immediately report suspected pregnancy. Do not breastfeed. • Male pts must use condoms during sexual activity. • Immediately report chest pain, difficult breathing, fast heart rate, rapid breathing; may indicate life-threatening blood clot in the lungs. • Report symptoms of bone marrow suppression or infection such as bruising easily, chills, cough, dizziness, fainting, fever, shortness of breath, weakness, or burning with urination. • Avoid crowds; those with active infection. • Take within 1 hr of breakfast and evening meal. • Drink plenty of fluids. • Report diarrhea, nausea, vomiting that is not controlled by antinausea, antidiarrheal medication. • Report bleeding of any kind.
tipranavir
tye-pran-a-veer
(Aptivus)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause hepatitis (including fatalities), hepatic dysfunction. Intracranial hemorrhage has occurred (in combination with ritonavir).
May cause hepatitis (including fatalities), hepatic dysfunction. Intracranial hemorrhage has occurred (in combination with ritonavir).
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Protease inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antiretroviral.
USES
Treatment of HIV infection in combination with ritonavir and other antiretroviral agents (limited to highly treatment experienced or multi–protease inhibitor resistant pts).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tipranavir. Moderate to severe hepatic impairment, medications dependent on CYP3A for clearance, concurrent use of tipranavir/ritonavir with strong CYP3A inducers: alfuzosin, amiodarone, bepridil, dihydroergotamine, ergonovine, ergotamine, flecainide, lovastatin, methylergonovine, midazolam (oral), propafenone, quinidine, rifampin, sildenafil (pulmonary arterial hypertension), simvastatin, St. John’s wort, triazolam. Cautions: Hemophilia, known sulfonamide allergy, mild hepatic impairment, pts at increased risk for bleeding from trauma, surgery, concurrent antiplatelet/anticoagulant therapy.
ACTION
Binds to HIV-1 protease activity sites. Inhibits cleavage of viral protein precursors into functional proteins necessary for infectious HIV. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents formation of mature infectious viral cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Incompletely absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 98%–99%. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated in feces (82%), urine (4%). Half-life: 6 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related hepatic impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May interfere with metabolism of amiodarone, bepridil, ergotamine, midazolam, oral contraceptives. Carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin may decrease concentration. May increase concentration of colchicine, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy including rhabdomyolysis. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may lead to loss of virologic response, potential resistance to tipranavir. FOOD: High-fat meals may increase bioavailability. LAB VALUES: May increase serum cholesterol, triglycerides, amylase, ALT, AST. May decrease WBC count.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 250 mg. Oral Solution: 100 mg/ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May take without regard to food. When taken with ritonavir tablets, must be taken with meals. • Store unopened bottles of capsules in refrigerator. • Do not freeze/refrigerate oral solution. • Once bottle is opened, capsules may be stored at room temperature for 60 days. Use oral solution within 60 days after opening.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Must be taken with ritonavir.
HIV Infection
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 500 mg administered with 200 mg of ritonavir twice daily. CHILDREN 2–18 YRS: 14 mg/kg with 6 mg/kg ritonavir twice daily. Maximum: 500 mg with 200 mg ritonavir twice daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: Use caution. Moderate to severe impairment: Contraindicated.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (11%): Diarrhea. Occasional (7%–2%): Nausea, fever, fatigue, headache, depression, vomiting, abdominal pain, weakness, rash. Rare (Less Than 2%): Abdominal distention, anorexia, flatulence, dizziness, insomnia, myalgia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Bronchitis occurs in 3% of pts. Anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, diabetes mellitus, hepatic failure, hepatitis, peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline LFT before beginning therapy and at periodic intervals during therapy. Offer emotional support. Obtain full medication history and screen for interactions.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Closely monitor for evidence of GI discomfort. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Assess skin for evidence of rash. Monitor serum chemistry tests for marked laboratory abnormalities, particularly hepatic profile, CD4 cell count, HIV RNA plasma levels. Assess for opportunistic infections (onset of fever, oral mucosa changes, cough, other respiratory symptoms).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Eat small, frequent meals to offset nausea, vomiting. • Continue therapy for full length of treatment. • Doses should be evenly spaced. • Tipranavir is not a cure for HIV infection, nor does it reduce risk of transmission to others. • Pt may continue to experience illnesses, including opportunistic infections. • Diarrhea can be controlled with OTC medication.
*tiZANidine
tye-zan-i-deen
(Apo-Tizanidine
![]() , Zanaflex)
, Zanaflex)
Do not confuse tizanidine with tiagabine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Skeletal muscle relaxant. CLINICAL: Antispastic.
USES
Acute and intermittent management of muscle spasticity (spasms, stiffness, rigidity), spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injury.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tizanidine. Concurrent use with strong CYP1A2 inhibitors. Cautions: Renal/hepatic disease, pts at risk for severe hypotensive effects, cardiac disease, psychiatric disorders, elderly.
ACTION
Increases presynaptic inhibition of spinal motor neurons mediated by alpha2-adrenergic agonists, reducing facilitation to postsynaptic motor neurons. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces muscle spasticity.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 2 hrs.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g,. lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase CNS depressant effects. Antiarrhythmics (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol), cimetidine, oral contraceptives, acyclovir may increase risk of bradycardia, hypotension, or CNS depression. Strong CYP1A2 inhibitors (e.g., ciprofloxacin, fluvoxamine) may increase concentration/adverse effects (contraindicated). HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. Black cohosh, hawthorn, periwinkle may increase hypotensive effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules: 2 mg, 4 mg, 6 mg. Tablets: 2 mg, 4 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Capsules may be opened and sprinkled on food. • May give without regard to food. • Administration should be consistent and not switched between giving with or without food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Muscle spasticity
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 2 mg 3 times/day at 6- to 8-hr intervals as needed. Can be gradually increased in 2- to 4-mg increments with a minimum of 1–4 days between dosage increases. Maximum: 36 mg/24 hrs in divided doses.
Discontinuation of Therapy: Gradually taper dose by 2–4 mg daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
May require dose reduction/less frequent dosing. CrCl less than 25 ml/min: Reduce dose by 50%. If higher doses needed, increase dose instead of frequency.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use if possible. If used, monitor for adverse effects (e.g., hypotension).
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (49%–41%): Dry mouth, drowsiness, asthenia. Occasional (16%–4%): Dizziness, UTI, constipation. Rare (3%): Nervousness, amblyopia, pharyngitis, rhinitis, vomiting, urinary frequency.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Hypotension may be associated with bradycardia, orthostatic hypotension, and, rarely, syncope. Risk of hypotension increases as dosage increases; hypotension is noted within 1 hr after administration.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Record onset, type, location, duration of muscular spasm. Check for immobility, stiffness, swelling. Obtain LFT.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation at all times. For those on long-term therapy, serum hepatic/renal function tests should be performed periodically. Evaluate for therapeutic response (decreased intensity of skeletal muscle pain/tenderness, improved mobility, decrease in spasticity). Go from lying to standing slowly.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Avoid sudden changes in posture. • May cause hypotension, sedation, impaired coordination. • Avoid alcohol.
tobramycin
toe-bra-mye-sin
(TOBI, Tobrex)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause neurotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity. Ototoxicity usually is irreversible. Increased risk of neuromuscular blockade, including respiratory paralysis, particularly when given after anesthesia or muscle relaxants. May cause fetal harm.
May cause neurotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity. Ototoxicity usually is irreversible. Increased risk of neuromuscular blockade, including respiratory paralysis, particularly when given after anesthesia or muscle relaxants. May cause fetal harm.
Do not confuse tobramycin with vancomycin, or Tobrex with TobraDex.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
TobraDex: tobramycin/dexamethasone (a steroid): 0.3%/0.1% per ml or per g. Zylet: tobramycin/loteprednol: 0.3%/0.5%.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Aminoglycoside. CLINICAL: Antibiotic.
USES
Treatment of susceptible infections due to P. aeruginosa, other gram-negative organisms including skin/skin structure, bone, joint, respiratory tract infections; postop, burn, intra-abdominal infections; complicated UTI; septicemia; meningitis. Ophthalmic: Superficial eye infections: blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, corneal ulcers. Inhalation: Bronchopulmonary infections (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) in pts with cystic fibrosis.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tobramycin, other aminoglycosides (cross-sensitivity) and their components. Cautions: Renal impairment, preexisting auditory or vestibular impairment, conditions that depress neuromuscular transmission, Parkinson’s disease, myasthenia gravis, hypocalcemia, preganancy, elderly.
ACTION
Irreversibly binds to protein on bacterial ribosomes. Therapeutic Effect: Interferes with protein synthesis of susceptible microorganisms.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapid, complete absorption after IM administration. Protein binding: less than 30%. Widely distributed (does not cross blood-brain barrier; low concentrations in CSF). Excreted unchanged in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2–4 hrs (increased in renal impairment, neonates; decreased in cystic fibrosis, febrile or burn pts).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Drug readily crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. May cause fetal nephrotoxicity. Ophthalmic form should not be used in breastfeeding mothers and only when specifically indicated in pregnancy. Children: Immature renal function in neonates, premature infants may increase risk of toxicity. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may increase risk of toxicity; dosage adjustment recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Nephrotoxic medications (e.g., NSAIDs, IV contrast, lisinopril, furosemide), ototoxic medications (e.g., bumetanide, furosemide) may increase risk of nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity. Neuromuscular blockers (e.g., cisatracurium, vercuronium) may increase neuromuscular blockade. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, bilirubin, creatinine, alkaline phosphatase, LDH, ALT, AST. May decrease serum calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium. Therapeutic peak serum level: 5–20 mcg/ml; therapeutic trough serum level: 0.5–2 mcg/ml. Toxic peak serum level: greater than 20 mcg/ml; toxic trough serum level: greater than 2 mcg/ml.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Infusion, Premix: 60 mg/50 ml, 80 mg/100 ml. Inhalation Powder (TOBI Podhaler): 28 mg in a capsule. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 1.2 g. Injection, Solution: 10 mg/ml, 40 mg/ml. Ointment, Ophthalmic (Tobrex): 0.3%. Solution, Nebulization (TOBI): 60 mg/ml. Solution, Ophthalmic (Tobrex): 0.3%.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Coordinate peak and trough lab draws with administration times.
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Dilute with 50–100 ml D5W or 0.9% NaCl. Amount of diluent for infants, children depends on individual need.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 30–60 min.
Storage • Store vials at room temperature. • Solutions may be discolored by light or air (does not affect potency). • Reconstituted solution stable for 24 hrs at room temperature or 96 hrs if refrigerated.
IM
• To minimize discomfort, give deep IM slowly. • Less painful if injected into gluteus maximus rather than lateral aspect of thigh.
Inhalation
• Refrigerate. • May store at room temperature up to 28 days after removing from refrigerator. • Do not use if cloudy or contains particulates. • Podhaler: • Pt must not swallow capsules. • Doses should be as close as possible to 12 hrs apart and not less than 6 hrs apart. • Use Podhaler device supplied.
Ophthalmic
• Place gloved finger on lower eyelid, pull out until pocket is formed between eye and lower lid. • Place correct number of drops (¼–½ inch ointment) into pocket. • Solution: Apply digital pressure to lacrimal sac for 1–2 min (minimizes drainage into nose/throat, reducing risk of systemic effects). • Ointment: Instruct pt to close eye for 1–2 min, rolling eyeball (increases contact area of drug to eye). • Remove excess solution/ointment around eye.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Amphotericin B complex (Abelcet, AmBisome, Amphotec), heparin, indomethacin (Indocin), piperacillin-tazobactam (Zosyn), propofol (Diprivan), sargramostim (Leukine, Prokine).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Amiodarone (Cordarone), calcium gluconate, cefepime, ceftaroline, ceftazidime, dexmedetomidine (Precedex), diltiazem (Cardizem), furosemide (Lasix), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), insulin, linezolid (Zyvox), magnesium sulfate, midazolam (Versed), morphine, nicardipine (Cardene), tigecycline (Tygacil).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Space parenteral doses evenly around the clock. Dosage based on ideal body weight. Peak, trough levels determined periodically to maintain desired serum concentrations (minimizes risk of toxicity). Recommended peak level: 4–10 mcg/ml; trough level: 0.5–2 mcg/ml.
Usual Parenteral Dosage
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 3–7.5 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses. Once-daily dosing: 4–7 mg/kg every 24 hrs. CHILDREN 5 YRS AND OLDER: 2–2.5 mg/kg/dose q8h. CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 5 YRS: 2.5 mg/kg/dose q8h. NEONATES LESS THAN 1 KG (14 DAYS OR YOUNGER): 5 mg/kg/dose q48h; (15–28 DAYS): 4–5 mg/kg/dose q24–48hrs. 1–2 KG (7 DAYS OR YOUNGER): 5 mg/kg/dose q48h; (8–28 DAYS): 4–5 mg/kg/dose q24–48hrs. GREATER THAN 2 KG (7 DAYS OR YOUNGER): 4 mg/kg q24h; (8–28 DAYS): 4 mg/kg q12–24hrs.
Usual Ophthalmic Dosage
Ophthalmic Ointment: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 2 MOS AND OLDER: Apply ½ inch to conjunctiva q8–12h (q3–4h for severe infections).
Ophthalmic Solution: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 2 MOS AND OLDER: 1–2 drops in affected eye q4h (2 drops/hr for severe infections).
Usual Inhalation Dosage (Cystic Fibrosis)
Inhalation High Dose: ADULTS, CHILDREN 6 YRS AND OLDER: 300 mg q12h 28 days on, 28 days off. Podhaler: Four 28-mg capsules twice daily for 28 days followed by 28 days off.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage and frequency modified based on degree of renal impairment, serum drug concentration. After loading dose of 1–2 mg/kg, maintenance dose and frequency are based on serum creatinine levels, creatinine clearance.
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosing Interval |
| 41–60 ml/min | q12h |
| 21–40 ml/min | q24h |
| 10–20 ml/min | q48h |
| Less than 10 ml/min | q72h |
| Hemodialysis | Loading dose 2–3 mg/kg then 1–2 mg/kg q48–72h |
| Continuous renal replacement therapy | Loading dose 2–3 mg/kg then 1–2.5 mg/kg q24–48h |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: IM: Pain, induration. IV: Phlebitis, thrombophlebitis. Topical: Hypersensitivity reaction (fever, pruritus, rash, urticaria). Ophthalmic: Tearing, itching, redness, eyelid swelling. Rare: Hypotension, nausea, vomiting.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Nephrotoxicity (acute kidney injury, acute tubular necrosis, renal failure) may be reversible if drug is stopped at first sign of symptoms. Irreversible ototoxicity (dizziness, ringing/roaring in ears, hearing loss), neurotoxicity (headache, dizziness, lethargy, tremor, visual disturbances) occur occasionally. Risk increases with higher dosages or prolonged therapy or if solution is applied directly to mucosa. Superinfections, particularly fungal infections, may result from bacterial imbalance with any administration route. Anaphylaxis may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Dehydration must be treated before beginning parenteral therapy. Question for history of allergies, esp. aminoglycosides, sulfite (and parabens for topical, ophthalmic routes). Establish baseline for hearing acuity. Obtain baseline lab tests, esp. renal function.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor I&O (maintain hydration), urinalysis, renal function. Monitor results of peak/trough blood tests. Therapeutic serum level: peak: 5–20 mcg/ml; trough: 0.5–2 mcg/ml. Toxic serum level: peak: greater than 20 mcg/ml; trough: greater than 2 mcg/ml. Be alert to ototoxic, neurotoxic symptoms. Evaluate IV site for phlebitis (heat, pain, red streaking over vein). Assess for rash. Be alert for superinfection, particularly anal/genital pruritus, changes of oral mucosa, diarrhea. When treating pts with neuromuscular disorders, assess respiratory response carefully. Ophthalmic: Assess for redness, swelling, itching, tearing.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report any hearing, visual, balance, urinary problems, even after therapy is completed. • Ophthalmic: Blurred vision, tearing may occur briefly after application. • Report persistent tearing, redness, irritation.
tocilizumab
toe-si-liz-oo-mab
(Actemra)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Tuberculosis, serious, invasive fungal infections, other opportunistic infections have occurred. Test for tuberculosis prior to and during treatment, regardless of initial result.
Tuberculosis, serious, invasive fungal infections, other opportunistic infections have occurred. Test for tuberculosis prior to and during treatment, regardless of initial result.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Interleukin (IL)-6 receptor inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antirheumatic arthritis agent.
USES
Treatment of moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis in adults who had inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Treatment of active systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SJIA) in pts 2 yrs of age and older. Treatment of active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (PJIA) in pts 2 yrs and older.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tocilizumab. Cautions: Platelet count 100,000/mm3 or less, ANC less than 2,000/mm3, ALT, AST greater than 1.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN) prior to treatment. Do not administer to pts with active infection. Preexisting or recent-onset CNS demyelinating disorders, including multiple sclerosis; pts with chronic or recurrent infection or who have been exposed to tuberculosis; hematologic cytopenia, hepatic impairment, elderly, pts at increased risk of GI perforation. Avoid live vaccinations.
ACTION
Binds to IL-6 receptors, inhibiting signals of proinflammatory cytokines. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits/slows structural joint damage, improves physical function.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Distributed in steady state of plasma and tissue compartments. Undergoes biphasic elimination from circulation. Half-life: 11–13 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Cautious use due to increased risk of serious infections, malignancy.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Anakinra, abatacept, corticosteroids, methotrexate may increase risk of infection. Live vaccines not recommended. May decrease effects of lovastatin, simvastatin, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, warfarin. HERBAL: Echinacea may alter levels/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum ALT, AST, lipids. May decrease platelets, neutrophils.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection Solution: 20 mg/ml (80 mg/4 ml, 200 mg/10 ml, 400 mg/20 ml). Syringe for Subcutaneous Administration: 162 mg/0.9 ml.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Do not infuse IV push or bolus.
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Dilute in 100 ml 0.9% NaCl (50 ml 0.9% NaCl for SJIA pts weighing less than 30 kg). • Prior to mixing, withdraw and discard volume of NaCl equal to volume of patient-dosed solution. • Invert bag to avoid foaming. • Inject solution and dilute for mixture that equals 50 ml or 100 ml in NaCl bag.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 1 hr.
Storage • Refrigerate vials; do not freeze. • Diluted solutions may be stored for 24 hrs at room temperature or refrigerated. • Protect from light until time of use. • Solution appears colorless. Discard solution if appears cloudy, discolored, or contains particulate.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Note: Do not infuse concomitantly in same IV line with other drugs. Do not begin if ANC less than 2,000/mm3, platelets less than 100,000/mm3, or ALT or AST more than 1.5 times ULN.
Moderate to Severely Active Rheumatoid Arthritis
IV Infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 4 mg/kg every 4 wks initially. May increase to 8 mg/kg every 4 wks. Maximum: 800 mg per dose.
SQ: ADULTS, ELDERLY (100 KG OR GREATER): 162 mg/wk. (LESS THAN 100 KG): 162 mg every other wk. May increase to every wk based on clinical response.
Dosage Modification
Hepatic enzyme levels greater than ULN.
| Lab Value | Recommendation |
| 1−3 times ULN | Dose modify concomitant DMARDs or reduce dose to 4 mg/kg until ALT, AST normalized |
| Greater than 3−5 times ULN | Interrupt treatment until ALT, AST less than 3 times ULN, then follow guidelines for 1−3 times ULN |
| Greater than 5 times ULN | Discontinue treatment |
SJIA
IV: CHILDREN MORE THAN 30 KG: 8 mg/kg q2wks. CHILDREN 30 KG OR LESS: 12 mg/kg q2wks.
PJIA
IV: CHILDREN MORE THAN 30 KG: 8 mg/kg q4wks. CHILDREN 30 KG OR LESS: 10 mg/kg q4wks.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment: Use caution (not studied).
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional (8%–6%): Upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, headache, hypertension. Rare (5%–3%): Infusion reaction, dizziness, bronchitis, rash, oral ulceration.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Up to 48% of pts experience elevated ALT, AST. Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia occur in 4% of pts. Serious infections, including sepsis, pneumonia, tuberculosis, invasive fungal infections, hepatitis B have occurred. Anaphylactic reaction, rash, pruritus, urticaria, bronchospasm, swelling, dyspnea occur in less than 0.2% of pts; hypersensitivity reactions (hypertension, headaches, flushing) occur more frequently. Increased risk of lymphoma, melanoma. New onset or exacerbation of CNS demyelinating disorders, including multiple sclerosis. Risk of gastric perforation with concomitant use of NSAIDs, corticosteroids.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Evaluate pt for active tuberculosis and test for latent infection prior to initiating treatment and periodically during therapy. Induration of 5 mm or greater with tuberculin skin testing should be considered a positive test result when assessing for latent tuberculosis. Antifungal therapy should be considered for pts who reside or travel to regions where mycoses are endemic. Do not initiate therapy during an active infection. Viral reactivation can occur in cases of herpes zoster, HIV. Assess baseline lab results (hepatic enzymes, cholesterol, triglycerides, platelets, neutrophils) q4–8wks during treatment. Pts should report history of diverticulitis, weakened immune system, HIV, hepatic disease, GI bleeding, hemoptysis, diarrhea, weight loss, cancer, prior cancer treatment, use of NSAIDs, glucocorticosteroids.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor hepatitis B carriers during and several months following therapy. If reactivation occurs, consider interrupting treatment. Monitor pts for signs/symptoms of tuberculosis regardless of baseline PPD. Discontinue treatment if pt develops acute infection, opportunistic infection, or sepsis and initiate appropriate antimicrobial therapy. Monitor warfarin, theophylline, cyclosporine levels for therapeutic ranges. Modify, interrupt, or discontinue treatment if ALT, AST is 1–5 times ULN.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Inform pt that therapy may lower immune system response. • Detail any concomitant immunosuppressive therapy, methotrexate. • Report any history of HIV, fungal infections, hepatitis B, multiple sclerosis, hemoptysis, tuberculosis, or close relatives with active tuberculosis. • Report any travel plans to possible endemic areas. • Report signs/symptoms of stomach pain to evaluate risk of gastric perforation or history of taking NSAIDs, corticosteroids, methotrexate. • Pt will need blood levels drawn q4–8wks during treatment along with routine tuberculosis screening. • Seek immediate medical attention if adverse reaction occurs. • Do not receive live vaccines during therapy. • Notify physician if pregnant or planning on becoming pregnant. • During treatment, report any signs of liver problems, such as stomach pains, yellowing of skin/eyes, dark-amber urine, clay-colored or bloody stools, fatigue, reduced appetite, coffee ground emesis. • Pt must adhere to strict dosing schedule. • Decreased platelet count may lead to risk of bleeding.
tofacitinib
toe-fa-sye-ti-nib
(Xeljanz, Xeljanz XR)
Do not confuse tofacitinib with tipifarnib or Xeljanz with Xeloda.
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Increased risk for developing bacterial, viral, invasive fungal, other opportunistic infections including tuberculosis, cryptococcosis, pneumocystosis that may lead to hospitalization or death; infections often occurred in combination with other immunosuppressants (methotrexate, corticosteroids). Test for latent tuberculosis prior to treatment and during treatment, regardless of initial result. Malignancies including lymphoma, nonmelanoma skin cancer reported. Increased rate of Epstein-Barr virus–associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder observed in renal transplant pts who are treated with tofacitinib and other immunosuppressive therapy drugs.
Increased risk for developing bacterial, viral, invasive fungal, other opportunistic infections including tuberculosis, cryptococcosis, pneumocystosis that may lead to hospitalization or death; infections often occurred in combination with other immunosuppressants (methotrexate, corticosteroids). Test for latent tuberculosis prior to treatment and during treatment, regardless of initial result. Malignancies including lymphoma, nonmelanoma skin cancer reported. Increased rate of Epstein-Barr virus–associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder observed in renal transplant pts who are treated with tofacitinib and other immunosuppressive therapy drugs.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. CLINICAL: Anti-rheumatic agent.
USES
Treatment of adult pts with moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis with previous inadequate response or intolerance to methotrexate. May be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate or other nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Do not use in combination with other biologic DMARDs or with potent immunosuppressants (e.g., azathioprine, cyclosporine).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tofacitinib. Cautions: Pts exposed to TB, history of serious opportunistic infections, conditions that predispose to infections (e.g., diabetes), pts at risk for GI perforation (e.g., diverticulitis), pts who resided or traveled in areas where TB is endemic, moderate to severe renal impairment, elderly, hepatic impairment, history of anemia, hyperlipidemia, hepatitis, Asian ancestry, pts with history of interstitial lung disease, heart rate less than 60 bpm, conduction abnormalities, ischemic heart disease, HF.
ACTION
Inhibits JAK enzymes which are involved in stimulating hematopoiesis and immune cell functioning. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces inflammation, tenderness, swelling of joints; slows or prevents progressive joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: 40%. Peak concentration: 30–60 min. Metabolized in liver. Eliminated primarily in urine. Half-life: 3 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Not recommended in nursing mothers. Must either discontinue drug or discontinue breastfeeding. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Increased risk for serious infections, malignancy.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May alter effects of live virus vaccines. Immunosuppressants (e.g., azathioprine, cyclosporine) may increase risk for added immunosuppression, infection. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole), CYP2C19 inhibitors (e.g., fluconazole) may increase concentration/effects. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin) may decrease concentration/effects. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase ALT, AST, bilirubin, lipids, creatinine. May decrease Hgb, neutrophils, lymphocytes.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets, Film-Coated: (Xeljanz): 5 mg. (Xeljanz XR): 11 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. • Do not cut, split, crush, or chew XR tablet.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Do not initiate treatment in pts with baseline active infection (systemic/localized), severe hepatic impairment, lymphocytes less than 500/mm3, ANC less than 1,000/mm3, Hgb less than 9 g/dL.
Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid arthritis
PO: ADULTS/ELDERLY: (Xeljanz): 5 mg twice daily. (Xeljanz XR): 11 mg once daily.
Dose Modification
Reduce to 5 mg once daily for any of the following: moderate to severe renal impairment, moderate hepatic impairment, concurrent use of potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, concurrent use of one or more moderate CYP3A4 or potent CYP2C19 inhibitors.
Lymphopenia
Interrupt treatment until lymphocytes greater than or equal to 500/mm3. Discontinue if lymphocytes less than 500/mm3 after repeat testing.
Neutropenia
Interrupt treatment until neutrophils greater than 1,000/mm3. Discontinue if neutrophils less than 500/mm3 after repeat testing.
Anemia
Interrupt treatment until Hgb greater than or equal to 9 g/dL or baseline Hgb decreases less than or equal to 2 g/dL after repeat testing.
Hepatotoxicity
Interrupt treatment until diagnosis of drug-induced hepatic injury has been excluded.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment: 5 mg once daily.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate impairment: 5 mg once daily. Severe impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Rare (4%–2%): Upper respiratory tract infection, diarrhea, nasopharyngitis, headache, hypertension.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Neutropenia, lymphopenia may increase risk for infection. Serious infections may include aspergillosis, BK virus, cellulitis, coccidioidomycosis, cryptococcus, cytomegalovirus, esophageal candidiasis, histoplasmosis, invasive fungal infections, listeriosis, pneumocystosis, pneumonia, tuberculosis, UTI, sepsis. Increased risk for various malignancies. May induce viral reactivation of hepatitis B or C virus infection, herpes zoster, HIV. Epstein-Barr virus–associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder reported in 2% of pts with renal transplant. Increased risk for GI perforation.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain vital signs, CBC, BMP, LFT, lipid panel, urine pregnancy test results. Evaluate for active tuberculosis (TB) and test for latent infection prior to and during treatment. Induration of 5 mm or greater with purified protein derivative (PPD) is considered positive result when assessing for latent TB. Question possibility of pregnancy or breastfeeding. Screen for history/comorbidities. Obtain full medication history including vitamins, herbal products.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Obtain CBC every 4–8 wks, then every 3 mos, lipid panel 4–8 wks after initiation; hepatic function panel if hepatic impairment suspected. Monitor for TB regardless of baseline PPD. Consider discontinuation if pt develops acute infection, opportunistic infection, sepsis; initiate appropriate antimicrobial therapy. Immediately report any hemorrhaging, melena, abdominal pain, hemoptysis (may indicate GI perforation).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Routinely monitor blood levels. • Therapy will lower immune system response. • Do not receive live virus vaccines. • Other immunosuppressant drugs may increase risk for infection. • Expect routine TB screening. • Fever, cough, burning with urination, body aches, chills, skin changes may indicate infection. • Report history of HIV, recent infections, hepatitis B or C, TB or close relatives who have active TB. • Report any travel plans to possible endemic areas. • Notify physician if pregnant or planning pregnancy. • Do not breast-feed. • Immediately report bleeding of any kind. • Yellowing of skin or eyes, right upper quadrant abdominal pain, bruising, clay-colored stool, dark urine may indicate liver problem. • Avoid grapefruit products.
tolterodine
tol-ter-oh-deen
(Detrol, Detrol LA, Unidet
![]() )
)
Do not confuse Detrol with Ditropan, or tolterodine with fesoterodine.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Muscarinic receptor antagonist. CLINICAL: Antispasmodic.
USES
Treatment of overactive bladder in pts with symptoms of urinary frequency, urgency, incontinence.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tolterodine or fesoterodine. Gastric retention, uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma, urinary retention. Cautions: Renal impairment, clinically significant bladder outflow obstruction (risk of urinary retention), GI obstructive disorders (e.g., pyloric stenosis [risk of gastric retention]), treated narrow-angle glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, prolonged QT interval (congenital/medications, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia), hepatic impairment, elderly.
ACTION
Antagonist of muscarinic receptors mediating urinary bladder contraction. Increases residual urine volume, reduces detrusor muscle pressure. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases urinary frequency, urgency.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Immediate-release form rapidly, well absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 96%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: Immediate-release: 2–10 hrs. Extended-release: 7–18 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, erythromycin, ketoconazole) may increase concentration. Fluoxetine may inhibit drug metabolism. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None known.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets (Detrol): 1 mg, 2 mg.
![]() Capsules (Extended-Release [Detrol LA]): 2 mg, 4 mg.
Capsules (Extended-Release [Detrol LA]): 2 mg, 4 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• May give without regard to food. • Give extended-release capsules whole; do not break, crush, or open.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Overactive Bladder
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY (IMMEDIATE-RELEASE): 1–2 mg twice daily (WITH CYP3A4 INHIBITORS): 1 mg twice daily. (EXTENDED-RELEASE): 2–4 mg once daily. (WITH CYP3A4 INHIBITORS): 2 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Mild to moderate impairment: (IMMEDIATE-RELEASE): 1 mg twice daily. Use caution. (EXTENDED-RELEASE): 2 mg once daily. Use caution. Severe impairment: Not recommended.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (40%): Dry mouth. Occasional (11%–4%): Headache, dizziness, fatigue, constipation, dyspepsia, upper respiratory tract infection, UTI, dry eyes, abnormal vision (accommodation problems), nausea, diarrhea. Rare (3%): Drowsiness, chest/back pain, arthralgia, rash, weight gain, dry skin.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose can result in severe anticholinergic effects, including abdominal cramps, facial warmth, excessive salivation/lacrimation, diaphoresis, pallor, urinary urgency, blurred vision, prolonged QT interval.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess degree of overactive bladder (urinary urgency, frequency, incontinence). Question history as listed in Precautions.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs. Question for visual changes. Monitor incontinence, postvoid residuals.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• May cause blurred vision, dry eyes/mouth, constipation. • Report any confusion, altered mental status. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established.
tolvaptan
tol-vap-tan
(Samsca)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Osmotic demyelination (dysphagia, lethargy, slurred speech or inability to speak, seizures, coma, death) may occur with too-rapid correction of hyponatremia; slow rate of correction is essential. Should be initiated and reinitiated only in a hospital where serum sodium is monitored closely.
Osmotic demyelination (dysphagia, lethargy, slurred speech or inability to speak, seizures, coma, death) may occur with too-rapid correction of hyponatremia; slow rate of correction is essential. Should be initiated and reinitiated only in a hospital where serum sodium is monitored closely.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Vasopressin antagonist. CLINICAL: Hyponatremia adjunct.
USES
Treatment of symptomatic hypervolemic or euvolemic hyponatremia resistant to correction with fluid restriction, including pts with HF, cirrhosis, and syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tolvaptan. Hypovolemic hyponatremia, concurrent use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir), pts with urgent need to raise sodium level, inability to sense or respond to thirst, pts who are anuric. Cautions: Hyperkalemia, concurrent use of medications that increase serum potassium, GI bleeding in pts with cirrhosis, dehydration, hypovolemia, concurrent use with hypertonic saline.
ACTION
Promotes excretion of free water (without loss of serum electrolytes), resulting in net fluid loss, increased urine output, decreased urine osmolarity and increase in serum sodium concentration. Therapeutic Effect: Restores normal serum sodium levels.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Readily absorbed following oral administration. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 99%. Eliminated in feces. Half-life: 5 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Systemic exposure to fetus likely. Potential for decreased neonatal viability, delayed growth/development. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, diltiazem, fluconazole, ketoconazole, nefazodone, saquinavir, verapamil) may increase concentration, effects. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifabutin, rifampin) may decrease concentration. Cyclosporine may increase concentration. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase absorption, concentration. LAB VALUES: May increase serum potassium, magnesium. May alter serum glucose.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 15 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
• Give without regard to meals.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Usual Dosage
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 15 mg once daily. Increase dose to 30 mg once daily, after at least 24 hrs (maximum: 60 mg once daily), to achieve desired level of serum sodium.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Not recommended with CrCl less than 10 ml/min.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (16%–13%): Thirst, dry mouth. Occasional (11%–4%): Increase in urine output/urgency, asthenia, nausea, constipation, hyperglycemia, anorexia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Dysphagia, lethargy, slurred speech or inability to speak, affective changes, spastic quadriparesis, seizures, coma, death may occur with too-rapid correction of hyponatremia.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Initiate only in hospital setting with serum sodium monitoring. Obtain baseline CBC, BMP, LFT, renal function test. Assess for increased pulse rate, poor skin turgor, nausea, diarrhea (signs of hyponatremia).
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
During initiation and titration, frequently monitor for changes in serum electrolytes and volume. Avoid fluid restriction during first 24 hrs of therapy. Monitor for improvement in signs/symptoms of hyponatremia, hypernatremia (flushing, edema, restlessness, dry mucous membranes, fever).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Continue ingesting fluids in response to thirst. • Report urinary changes, loss of strength, unusual fatigue. • Report immediately symptoms of osmotic demyelination (e.g., trouble speaking/swallowing, confusion, mood changes, trouble controlling body movements, seizures).
topiramate
toe-peer-a-mate
(Apo-Topiramate
![]() , Qudexy XR, Topamax, Topamax Sprinkle, Trokendi XR)
, Qudexy XR, Topamax, Topamax Sprinkle, Trokendi XR)
Do not confuse Topamax or topiramate with Tegretol, Tegretol XR, or Toprol XL.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Anticonvulsant.
USES
Monotherapy for treatment of partial-onset or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in pts 2 yrs and older (immediate-release, Qudexy XR) or 10 yrs and older (Trokendi XR). Adjunctive therapy for partial-onset, primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures or seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in pts 2 yrs and older (immediate-release, Qudexy XR) or 6 yrs and older (Trokendi XR). Prevention of migraine headache (immediate-release only). OFF-LABEL: Neuropathic pain, diabetic neuropathy, prophylaxis of cluster headaches, infantile spasms.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to topiramate. (Extended-Release): Recent alcohol use (within 6 hrs prior to or after); pts with metabolic acidosis who are taking metformin. Cautions: Hepatic/renal impairment, elderly, pts who are high risk for suicide, respiratory impairment, pts with congenital metabolism dysfunction or decreased mitochondrial activity. During strenuous exercise, exposure to high environmental temperature, concomitant use of medications with anticholinergic activity.
ACTION
Blocks neuronal sodium channels, enhances GABA activity; antagonizes glutamate receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Decreases seizure activity.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 15%–41%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted unchanged in urine. Removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 21 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: No age-related precautions noted in pts older than 2 yrs. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g., lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase CNS depression. Carbamazepine, phenytoin, valproic acid may decrease concentration/effects. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may increase risk of kidney stone formation and severity of metabolic acidosis. May decrease effectiveness of oral contraceptives. HERBAL: Evening primrose may decrease seizure threshold. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May reduce serum bicarbonate, increase ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Capsules (Sprinkle): 15 mg, 25 mg.
![]() Tablets: (Topamax, Topiragen) 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg.
Tablets: (Topamax, Topiragen) 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg.
![]() Capsules, Extended-Release (Trokendi XR): 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg. Qudexy XR: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg.
Capsules, Extended-Release (Trokendi XR): 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg. Qudexy XR: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets (bitter taste). • Give without regard to meals. • Sprinkle capsules may be swallowed whole or contents sprinkled on teaspoonful of soft food and swallowed immediately; do not chew. • Trokendi XR: • Give whole. Do not sprinkle on food, chew, or crush. Qudexy XR: Swallow whole; may open and sprinkle on spoonful of soft food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Adjunctive Treatment of Partial-Onset Seizures, Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome (LGS), Tonic-Clonic Seizures
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 17 YRS AND OLDER: (Immediate-Release):Initially, 25 mg once or twice daily for 1 wk. May increase by 25–50 mg/day at wkly intervals. Usual maintenance dose: 100–200 mg twice daily (partial-onset) or 200 mg 2 times/day (primary tonic-clonic). Maximum: 1,600 mg/day. CHILDREN 2–16 YRS: Initially, 1–3 mg/kg/day to maximum of 25 mg at night for 1 wk. May increase by 1–3 mg/kg/day at wkly intervals given in 2 divided doses. Maintenance: 5–9 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses. ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Extended-Release): Initially, 25–50 mg/day. Increase by 25–50 mg/day at wkly intervals, up to 400 mg/day. CHILDREN 2 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 25 mg (based on range of 1–3 mg/kg) once daily at bedtime for 1 wk. Increase dose by 1–3 mg/kg at 1–2 wk intervals up to 5–9 mg/kg once daily.
Monotherapy with Partial-Onset, Tonic-Clonic Seizures
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 10 YRS AND OLDER: (Immediate-Release):Initially, 25 mg twice daily. Increase at wkly intervals up to 400 mg/day according to the following schedule: Wk 1, 25 mg twice daily. Wk 2, 50 mg twice daily. Wk 3, 75 mg twice daily. Wk 4, 100 mg twice daily. Wk 5, 150 mg twice daily. Wk 6, 200 mg twice daily. CHILDREN 2–9 YRS: Initially, 25 mg/day. Then 25 mg 2 times/day wk 2; then increase by 25–50 mg/day at wkly intervals up to minimum dose. (see table below) ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 10 YRS OR OLDER: (Extended-Release): (Qudexy XR, Trokendi XR): Initially, 50 mg once daily. Increase by 50 mg/day at wkly intervals for first 4 wks, then by 100 mg/day for wks 5 and 6, up to 400 mg/day. CHILDREN 2–9 YRS: (Qudexy XR only): Initially, 25 mg once daily in evening. May increase to 50 mg once daily in wk 2, then 25–50 mg/day at wkly intervals over 5–7 wks up to minimum daily dose (32 KG OR MORE): 250 mg; (12–31 KG): 200 mg; (11 KG OR LESS): 150 mg. Maximum daily dose: (38 KG OR MORE): 300 mg; (23–38 KG): 350 mg; (12–22 KG): 300 mg; (11 KG OR LESS): 250 mg.
| Wgt. | Minimum | Maximum |
| 11 kg or less | 150 mg/day in 2 divided doses | 250 mg/day in 2 divided doses |
| 12–22 kg | 200 mg/day in 2 divided doses | 300 mg/day in 2 divided doses |
| 23–31 kg | 200 mg/day in 2 divided doses | 350 mg/day in 2 divided doses |
| 32–38 kg | 250 mg/day in 2 divided doses | 350 mg/day in 2 divided doses |
| 39 or more kg | 250 mg/day in 2 divided doses | 400 mg/day in 2 divided doses |
Migraine Prevention
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS and OLDER: Initially, 25 mg/day. May increase by 25 mg/day at 7-day intervals up to a total daily dose of 100 mg/day in 2 divided doses.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Reduce drug dosage by 50% and titrate more slowly in pts who have CrCl less than 70 ml/min.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Use with caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (30%–10%): Drowsiness, dizziness, ataxia, nervousness, nystagmus, diplopia, paresthesia, nausea, tremor. Occasional (9%–3%): Confusion, breast pain, dysmenorrhea, dyspepsia, depression, asthenia, pharyngitis, weight loss, anorexia, rash, musculoskeletal pain, abdominal pain, difficulty with coordination, sinusitis, agitation, flu-like symptoms. Rare (3%–2%): Mood disturbances (e.g., irritability, depression), dry mouth, aggressive behavior, impaired heat regulation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Psychomotor slowing, impaired concentration, language problems (esp. word-finding difficulties), memory disturbances occur occasionally. Metabolic acidosis, suicidal ideation occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Seizures: Review history of seizure disorder (intensity, frequency, duration, level of consciousness). Initiate seizure precautions. Provide quiet, dark environment. Question for sensitivity to topiramate, pregnancy, use of other anticonvulsant medication (esp. carbamazepine, valproic acid, phenytoin). Migraine: Assess pain location, duration, intensity. Assess renal function.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Observe frequently for recurrence of seizure activity. Assess for clinical improvement (decrease in intensity/frequency of seizures). Monitor renal function tests, LFT. Assist with ambulation if dizziness occurs.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established (may cause dizziness, drowsiness, impaired concentration). • Drowsiness usually diminishes with continued therapy. • Avoid use of alcohol, other CNS depressants. • Do not abruptly discontinue drug (may precipitate seizures). • Strict maintenance of drug therapy is essential for seizure control. • Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets (bitter taste). • Maintain adequate fluid intake (decreases risk of renal stone formation). • Report blurred vision, eye pain. • Report suicidal ideation, depression, unusual behavior. • Use caution with activities that may increase core temperature (exposure to extreme heat, dehydration). • Instruct pt to use alternative/additional means of contraception (topiramate decreases effectiveness of oral contraceptives).
topotecan

toe-poe-tee-kan
(Hycamtin)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. Potent immunosuppressant; severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count [ANC] less than 500 cells/mm3) occurs in 60% of pts. Do not administer with baseline neutrophils less than 1,500/mm3 and platelets less than 100,000/mm3.
Must be administered by personnel trained in administration/handling of chemotherapeutic agents. Potent immunosuppressant; severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count [ANC] less than 500 cells/mm3) occurs in 60% of pts. Do not administer with baseline neutrophils less than 1,500/mm3 and platelets less than 100,000/mm3.
Do not confuse Hycamtin with Hycomine, Mycamine, or topotecan with irinotecan.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: DNA topoisomerase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of metastatic ovarian cancer, relapsed or refractory small cell lung cancer, recurrent or resistant cervical cancer (in combination with cisplatin). OFF-LABEL: Treatment of central nervous system lesions/lymphoma, Ewing’s sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, neuroblastoma, acute myeloid leukemia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to topotecan. Baseline neutrophil count less than 1,500 cells/mm3 and platelet count less than 100,000/mm3, severe myelosuppression. Cautions: Mild myelosuppression, renal impairment, breastfeeding, pregnancy, elderly. Pts at risk for developing interstitial lung disease (e.g., lung cancer, pulmonary fibrosis).
ACTION
Interacts with topoisomerase I, an enzyme that relieves torsional strain in DNA by inducing reversible single-strand breaks. Prevents religation of DNA strand, resulting in damage to double-strand DNA, cell death. Therapeutic Effect: Produces cytotoxic effect.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Hydrolyzed to active form after IV administration. Protein binding: 35%. Excreted in urine. Half-life: 2–3 hrs (increased in renal impairment).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: May cause fetal harm. Avoid pregnancy; breastfeeding not recommended. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Live virus vaccines may potentiate virus replication, increase vaccine side effects, decrease pt’s antibody response to vaccine. Other bone marrow depressants may increase risk of myelosuppression. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease effectiveness. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum bilirubin, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase. May decrease RBC, leukocyte, neutrophil, platelet counts, Hgb, Hct.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 4 mg (single-dose vial). Injection, Solution: 1 mg/ml (4 ml).
![]() Capsule: 0.25 mg, 1 mg.
Capsule: 0.25 mg, 1 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
◀ ALERT ▶ Because topotecan may be carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic, handle drug with extreme care during preparation/administration.
PO
• May take with or without food. • Swallow whole; do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide capsule. • Do not take replacement dose if vomiting occurs.
![]() IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute each 4-mg vial (lyophilized powder) with 4 ml Sterile Water for Injection. • Further dilute with 50–100 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W.
Rate of Administration • Administer as IV infusion over 30 min. • Extravasation associated with only mild local reactions (erythema, ecchymosis).
Storage • Store vials (lyophilized powder) at room temperature; refrigerate diluted solution. Diluted solution for infusion stable for 24 hrs at room temperature.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Dexamethasone (Decadron), 5-fluorouracil, mitomycin (Mutamycin).
 IV COMPATIBILITIES
IV COMPATIBILITIES
Carboplatin (Paraplatin), cisplatin (Platinol AQ), cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), doxorubicin (Adriamycin), etoposide (VePesid), gemcitabine (Gemzar), granisetron (Kytril), ondansetron (Zofran), paclitaxel (Taxol), palonosetron (Aloxi), vincristine (Oncovin).
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Do not give topotecan if baseline neutrophil count is less than 1,500 cells/mm3 and platelet count is less than 100,000/mm3. For retreatment, neutrophils should be greater than 1,000/mm3, platelets greater than 100,000/mm3, and Hgb 9 g/dL or greater.
Ovarian Carcinoma, Small Cell Lung Cancer
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1.5 mg/m2/day over 30 min for 5 consecutive days, beginning on day 1 of 21-day course. Minimum of 4 courses recommended. If severe neutropenia (neutrophil count less than 1,500/mm3) occurs during treatment, reduce dose for subsequent courses by 0.25 mg/m2 or administer filgrastim (G-CSF) no sooner than 24 hrs after last dose of topotecan.
PO (Small Cell Lung Cancer): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 2.3 mg/m2/day for 5 days; repeat q21days (dose rounded to nearest 0.25 mg). For severe neutropenia or prolonged neutropenia, platelets less than 25,000/mm3, recovery from grade 3 or 4 diarrhea: Reduce dose by 0.4 mg/m2/day for subsequent cycles.
Cervical Cancer
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.75 mg/m2/day for 3 days (followed by cisplatin 50 mg/m2 on day 1 only). Repeat q21days (baseline neutrophil count greater than 1,500/mm3 and platelet count greater than 100,000/mm3). For severe febrile neutropenia (neutrophils less than 1,000/mm3 with temperature of 38°C) or platelet count less than 25,000/mm3: Reduce dose to 0.6 mg/m2/day for subsequent cycles. If necessary, further decrease dose to 0.45 mg/m2/day.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
IV: No dosage adjustment is necessary in pts with mild renal impairment (CrCl 40–60 ml/min). For moderate renal impairment (CrCl 20–39 ml/min), give 0.75 mg/m2.
PO: CrCl 30–49 ml/min: 1.5 mg/m2/day. May increase by 0.4 mg/m2/day following first cycle if no GI/hematologic toxicities occur. CrCl less than 30 ml/min: Decrease dose to 0.6 mg/m2/day. May increase by 0.4 mg/m2/day following first cycle if no GI/hematologic toxicities occur.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (77%–21%): Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, total alopecia, headache, dyspnea. Occasional (9%–3%): Paresthesia, constipation, abdominal pain. Rare: Anorexia, malaise, arthralgia, asthenia, myalgia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count [ANC] less than 500 cells/mm3) occurs in 60% of pts (develops at median of 11 days after day 1 of initial therapy). Thrombocytopenia (platelet count less than 25,000/mm3) occurs in 26% of pts. Severe anemia (RBC count less than 8 g/dL) occurs in 40% of pts (develops at median of 15 days after day 1 of initial therapy).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Offer emotional support. Assess CBC with differential before each dose. Myelosuppression may precipitate life-threatening hemorrhage, infection, anemia. If platelet count drops, minimize trauma to pt (e.g., IM injections, pt positioning). Premedicate with antiemetics on day of treatment, starting at least 30 min before administration.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess for bleeding, signs of infection, anemia. Monitor hydration status, I&O, serum electrolytes (diarrhea, vomiting are common side effects). Monitor CBC for evidence of myelosuppression. Monitor renal function, LFT. Assess response to medication; provide interventions (e.g., small, frequent meals; antiemetics for nausea/vomiting). Question for complaints of headache. Assess breathing pattern for evidence of dyspnea.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Hair loss is reversible but new hair may have different color, texture. • Diarrhea may cause dehydration, electrolyte depletion. • Antiemetic and antidiarrheal medications may reduce side effects. • Notify physician if diarrhea, vomiting, persistent fever, bruising/bleeding, yellowing of eyes/skin occur. • Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (drug lowers resistance). • Avoid contact with those who have recently received live virus vaccine.
torsemide
tore-se-myde
(Demadex)
Do not confuse torsemide with furosemide.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Loop diuretic. CLINICAL: Antihypertensive, diuretic.
USES
Treatment of hypertension either alone or in combination with other antihypertensives. Edema associated with HF, hepatic/renal impairment.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to torsemide. Anuria, other sulfonylureas. Cautions: Pts with cirrhosis, hypotension, hypokalemia.
ACTION
Enhances excretion of sodium, chloride, potassium, water at ascending limb of loop of Henle. Reduces plasma, extracellular fluid volume. Therapeutic Effect: Produces diuresis; lowers B/P.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO, IV (diuresis) | 30–60 min | 1–2 hrs | 6–8 hrs |
Rapidly, well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 97%–99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 2–4 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.