SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (10%–4%): Headache, dizziness, rhinitis. Occasional (3%–1%): Asthenia insomnia, nervousness, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, dyspepsia, edema, EKG changes, pharyngitis, cough, arthralgia, myalgia. Rare (Less Than 1%): Syncope, hypotension, arrhythmias.
trabectedin
tra-bek-te-din
(Yondelis)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Alkylating agent. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of unresectable or metastatic liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma in pts who have received a prior anthracycline-containing regimen.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity reaction, anaphylactic reaction to trabectedin. Cautions: Baseline anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia; chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, hepatic impairment, hepatitis; renal impairment; history of DVT, pulmonary embolism; recent MI, cardiomyopathy, HF. Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers, strong CYP3A inhibitors not recommended.
ACTION
Binds to guanine residues in the minor groove of DNA, leading to cell cycle disruption and cellular death. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Widely distributed. Metabolized in liver. Protein binding: 97%. Eliminated in feces (58%), urine (6%). Hemodialysis not expected to enhance elimination. Half-life: 175 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Avoid pregnancy; may cause fetal harm/malformations. Female pts of reproductive potential should use effective contraception during treatment and up to 2 mos after discontinuation. Breastfeeding not recommended. Males: Male pts with female partners of reproductive potential should use barrier methods, abstinence during treatment and up to 5 mos after discontinuation. May impair fertility in both females and males. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Safety and efficacy not established.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Strong CYP3A inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenobarbital, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effect. Strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, ketoconazole, ritonavir) may increase concentration/effects. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effect. FOOD: Grapefruit products may increase concentration/effect. LAB VALUES: May decrease Hgb, Hct, platelets, neutrophils, RBCs; serum albumin, phosphate. May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, bilirubin, CPK, creatinine. May reduce diagnostic effect of Coccidioides immitis skin test.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Powder for Reconstitution: 1 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Contents are hazardous; use cytotoxic precautions during handling and disposal. • Reconstitute with 20 ml Sterile Water for Injection for final concentration of 0.05 mg/ml. • Shake until fully dissolved. • Visually inspect solution for particulate matter or discoloration. Solution should appear clear, colorless to pale brownish-yellow in color. Discard if solution is discolored or particles are observed. • Dilute in 500 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W bag. • See manufacturer guidelines for materials/containers that are compatible with diluted solution.
Infusion Guidelines • Premedicate with dexamethasone 20 mg IV (or appropriate corticosteroid) 30 mins prior to each infusion. • Infuse diluted solution immediately after reconstitution. • Use an inline, 0.2-micron polyethersulfone filter. • Infuse via dedicated central venous line using an infusion pump.
Rate of Administration • Infuse over 24 hrs.
Storage • Refrigerate unused vials. • Diluted solution must be administered within 30 hrs of reconstitution.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix or infuse with other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Liposarcoma, Leiomyosarcoma
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 1.5 mg/m2 once q3wks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
CrCl greater than or equal to 30 ml/min: No dose adjustment.
CrCl greater less than 30 ml/min or end-stage renal disease: Not specified; use caution.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate impairment: 0.9 mg/m2 once q3wks. Severe impairment: Not recommended.
Dose Reduction for Normal Hepatic Function or Mild Hepatic Impairment
Initial dose: 1.5 mg/m2 once q3wks. First dose reduction: 1.2 mg/m2 once q3wks. Second dose reduction: 1 mg/m2 once q3wks.
Dose Reduction for Moderate Hepatic Impairment
Initial dose: 0.9 mg/m2 once q3wks. First dose reduction: 0.6 mg/m2 once q3wks. Second dose reduction: 0.3 mg/m2 once q3wks.
Hepatotoxicity
Serum ALT/AST greater than 2.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN): Delay next dose for up to 3 wks.
Alkaline phosphatase greater than 2.5 times ULN; serum ALT/AST greater than 5 times ULN; total serum bilirubin greater than ULN: Delay next dose for up to 3 wks, then resume at reduced dose level.
Hematologic Toxicity
Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) less than 1,500/mm3: Delay next dose for up to 3 wks.
ANC less than 1,000/mm3 with fever or infection; ANC less than 500/mm3 lasting more than 5 days: Delay next dose for up to 3 wks, then resume at reduced dose level.
Platelet count less than 100,000/mm3: Delay next dose for up to 3 wks.
Platelet count less than 25,000/mm3: Delay next dose for up to 3 wks, then resume at reduced dose level.
Nonhematologic Toxicity
CPK greater than 2.5 times ULN: Delay next dose for up to 3 wks.
CPK greater than 5 times ULN: Delay next dose for up to 3 wks, then resume at reduced dose level.
Decreased LVEF less than lower limit of normal or clinical evidence of cardiomyopathy: Delay next dose for up to 3 wks.
Decreased LVEF with an absolute decrease of 10% or more from baseline and less than lower limit of normal, or clinical evidence of cardiomyopathy: Delay next dose for up to 3 wks, then resume at reduced dose level.
Any other grade 3 or 4 reaction: Delay next dose for up to 3 wks, then resume at reduced dose level.
Permanent Discontinuation
Permanently discontinue for persistent adverse effects requiring a delay of treatment for more than 3 wks; continued adverse effects after reducing dose to 1 mg/m2 in pts with normal hepatic function, or 0.3 mg/m2 in pts with preexisting moderate hepatic impairment; severe hepatic dysfunction with bilirubin 2 times ULN, and ALT/AST 3 times ULN, and alkaline phosphatase less than 2 times ULN in prior treatment cycle in pts with baseline normal hepatic function; exacerbation of hepatic dysfunction in pts with preexisting moderate hepatic impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (75%–25%): Nausea, fatigue, asthenia, malaise, vomiting, decreased appetite, constipation, diarrhea, peripheral edema, dyspnea, headache. Occasional (15%–11%): Insomnia, arthralgia, myalgia, paresthesia.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia is an expected response to therapy. Life-threatening, sometimes fatal, neutropenic sepsis (3% of pts) may occur. Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia (43% of pts), febrile neutropenia (5% of pts) were reported. Fatal rhabdomyolysis, muscular toxicity may result in renal failure. CPK elevation occurred in 32% of pts; grade 3 or 4 CPK elevation occurred in 6% of pts. Hepatotoxicity, including hepatic failure, may occur. LFT elevation occurred in 70%–90% of pts. Cardiomyopathy including decreased ejection fraction, diastolic dysfunction, HF, right ventricular dysfunction reported in 6% of pts; grade 3 or 4 cardiomyopathy reported in 4% of pts. Drug extravasation may result in tissue necrosis requiring debridement. Other adverse effects may include phlebitis (15% of pts), pulmonary embolism (less than 10% of pts), hypersensitivity reaction.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain ANC, CBC, CPK, BMP, LFT; vital signs prior to each dose and periodically thereafter. Obtain baseline echocardiogram to assess LVEF. Verify placement of central venous line. Receive full medication history. Assess nutritional status. Question history of DVT, pulmonary embolism, cardiac disease, recent MI; renal/hepatic impairment; prior hypersensitivity reaction. Screen for active infection. Offer emotional support.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor ANC, CBC for anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia; CPK, serum creatinine for rhabdomyolysis, renal failure; LFT for hepatotoxicity; BMP for electrolyte imbalance (esp. in pts with diarrhea, vomiting, malnutrition); vital signs. Assess LVEF by echocardiogram at 2- to 3-mo intervals (or more frequently in pts with cardiomyopathy). Diligently screen for infections, sepsis. Monitor for DVT (leg or arm pain/swelling), rhabdomyolysis (decreased urinary output, amber-colored urine, fatigue, muscle pain/weakness), pulmonary embolism (sudden chest pain, dyspnea, hypoxia, tachycardia), HF (dyspnea, fatigue, palpitations, edema, exercise intolerance); hypersensitivity reaction; side effects of dexamethasone (e.g., hyperglycemia, weight loss, decreased appetite). Monitor I&Os. Monitor daily pattern bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Treatment may depress your immune system and reduce your ability to fight infection. Report symptoms of infection such as body aches, chills, cough, fatigue, fever. Avoid those with active infection. • Blood levels, echocardiograms will be routinely monitored. • Life-threatening events such as heart failure (shortness of breath, fast or slow heart rate, exercise intolerance, swelling of the ankles or legs), liver injury or failure (abdominal pain, easy bruising, clay-colored stools, dark-amber urine, fatigue, loss of appetite, yellowing of skin or eyes), muscle toxicity (muscle pain/weakness, kidney failure), blood clots in lungs (difficulty breathing, fast heart rate, chest pain). • Avoid pregnancy. Female pts of childbearing potential should use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 2 mos after last dose. Do not breastfeed. Male pts with female partners of reproductive potential should use condoms during sexual activity for at least 5 mos after last dose. • Treatment may impair fertility. • Avoid grapefruit products, herbal supplements. • Do not receive live vaccines.
*traMADol
tram-a-dol
(Apo-Tramadol  , ConZip, Synapryn FusePaq, Ultram, Ultram ER)
, ConZip, Synapryn FusePaq, Ultram, Ultram ER)
Do not confuse tramadol with tapentadol, Toradol, Trandate or Ultram with Ultracet.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Ultracet: tramadol/acetaminophen (a non-narcotic analgesic): 37.5 mg/325 mg.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Centrally acting synthetic opioid analgesic. CLINICAL: Analgesic.
USES
Immediate-Release: Management of moderate to moderately severe pain. Extended-Release: Around-the-clock management of moderate to moderately severe pain for extended period.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tramadol, opioids. (Additional) Ultram, Ultram ER: Acute alcohol intoxication, concurrent use of centrally acting analgesics, hypnotics, opioids, psychotropic drugs, hypersensitivity to opioids. (Additional) ConZip, Severe/acute bronchial asthma, hypercapnia, significant respiratory depression. Caution: CNS depression, anoxia, advanced hepatic cirrhosis, respiratory depression, elevated ICP, history of seizures or risk for seizures, hepatic/renal impairment, treatment of acute abdominal conditions, opioid-dependent pts, head injury, myxedema, hypothyroidism, hypoadrenalism, pregnancy. Avoid use in pts who are suicidal or addiction prone, emotionally disturbed, depressed, heavy alcohol users, elderly, debilitated pts.
ACTION
Binds to mu-opioid receptors, inhibits reuptake of norepinephrine, serotonin, inhibiting ascending and descending pain pathways. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces pain.
PHARMACOKINETICS
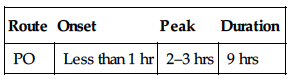
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | Less than 1 hr | 2–3 hrs | 9 hrs |
Rapidly, almost completely absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 20%. Metabolized in liver (reduced in pts with advanced cirrhosis). Primarily excreted in urine. Minimally removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 6–7 hrs (increased in renal/hepatic failure).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Crosses placenta. Distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related renal impairment may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Alcohol, other CNS depressants (e.g., lorazepam, morphine, zolpidem) may increase CNS depression. Carbamazepine decreases concentration/effects. CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g., paroxetine), CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin), triptans, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, doxepin) may increase risk of seizures, risk of serotonin syndrome. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression. St. John’s wort may increase risk of serotonin syndrome. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum creatinine, ALT, AST. May decrease Hgb. May cause proteinuria.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets (Immediate-Release) (Ultram): 50 mg. Capsule (Variable-Release): ConZip: 100 mg (25 mg immediate/75 mg extended), 200 mg (50 mg immediate/150 mg extended), 300 mg (50 mg immediate/250 mg extended). Suspension, Oral (Synapryn FusePaq): 10 mg/ml.
 Tablets (Extended-Release) (Ultram ER): 100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg.
Tablets (Extended-Release) (Ultram ER): 100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to meals but consistently with or without meals. • Extended-Release: Swallow whole; do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Moderate to Moderately Severe Pain
PO (Immediate-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 50–100 mg q4–6h. Maximum: 400 mg/day for pts 75 yrs and younger; 300 mg/day for pts older than 75 yrs.
PO (Extended-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 100 mg once daily. Titrate q5days. Maximum: 300 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Immediate-Release: For pts with CrCl less than 30 ml/min, increase dosing interval to q12h. Maximum: 200 mg/day. Do not use extended-release.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Immediate-Release: Cirrhosis: Dosage is decreased to 50 mg q12h. Do not use extended-release with severe hepatic impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (25%–15%): Dizziness, vertigo, nausea, constipation, headache, drowsiness. Occasional (10%–5%): Vomiting, pruritus, CNS stimulation (e.g., nervousness, anxiety, agitation, tremor, euphoria, mood swings, hallucinations), asthenia, diaphoresis, dyspepsia, dry mouth, diarrhea. Rare (less than 5%): Malaise, vasodilation, anorexia, flatulence, rash, blurred vision, urinary retention/frequency, menopausal symptoms.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Seizures reported in pts receiving tramadol within recommended dosage range. May have prolonged duration of action, cumulative effect in pts with hepatic/renal impairment, serotonin syndrome (agitation, hallucinations, tachycardia, hyperreflexia).
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess onset, type, location, duration of pain. Assess drug history, esp. carbamazepine, analgesics, CNS depressants, MAOIs. Review past medical history, esp. epilepsy, seizures. Assess renal function, LFT.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor pulse, B/P, renal/hepatic function. Assist with ambulation if dizziness, vertigo occurs. Dry crackers, cola may relieve nausea. Palpate bladder for urinary retention. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Sips of water may relieve dry mouth. Assess for clinical improvement, record onset of relief of pain.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• May cause dependence. • Avoid alcohol, OTC medications (analgesics, sedatives). • May cause drowsiness, dizziness, blurred vision. • Avoid tasks requiring alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Report severe constipation, difficulty breathing, excessive sedation, seizures, muscle weakness, tremors, chest pain, palpitations.
trametinib
tra-me-ti-nib
(Mekinist)
Do not confuse trametinib with imatinib or tipifarnib.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Kinase inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Used as a single agent or in combination with dabrafenib for treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600L mutations, as detected by FDA-approved test. Single-agent regimen is not indicated in pts who have received prior BRAF-inhibitor therapy.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to trametinib. Cautions: Cardiac/pulmonary impairment, preexisting diabetes or diabetes.
ACTION
Inhibits mitogen-activated extracellular kinase (MEK), Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits tumor cell growth, causing apoptosis.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 97.4%. Peak plasma concentration: 1.5 hrs. Metabolized in liver. Excreted in feces (80%), urine (20%). Half-life: 3.9–4.8 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Avoid pregnancy. May cause fetal harm. Must use effective nonhormonal contraception during treatment and for at least 4 wks after discontinuation (intrauterine device, barrier methods). Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Must either discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue treatment. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: May have increased risk of adverse effects, skin lesions, primary malignancies. Males: May decrease sperm count.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: May decrease levels/effect of aripiprazole, ibrutinib, saxagliptin, simeprevir. HERBAL: None known. FOOD: High-fat meals may decrease absorption/effect. LAB VALUES: SINGLE REGIMEN: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST. May decrease serum albumin; Hgb, Hct. COMBINATION REGIMEN: May increase serum alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, bilirubin, calcium, creatinine, glucose, GGT, potassium. May decrease Hgb, Hct, leukocytes, lymphocytes, neutrophils, platelets; serum albumin, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 0.5 mg, 2 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Administer at least 1 hr before or 2 hrs after meal.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Melanoma
PO: ADULTS/ELDERLY: 2 mg once daily (either as a single agent or in combination with dabrafenib). Continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
Dose Reduction Schedule
Trametinib Regimen: FIRST DOSE REDUCTION: 1.5 mg once daily. SECOND DOSE REDUCTION: 1 mg once daily. Discontinue if unable to tolerate 1-mg dose.
Dabrafenib Combination Regimen: FIRST DOSE REDUCTION: 100 mg twice daily. SECOND DOSE REDUCTION: 75 mg twice daily.
THIRD DOSE REDUCTION: 50 mg twice daily. Discontinue if unable to tolerate 50-mg dose.
Dose Modification
Based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) grading 1–4.
Cardiac: ASYMPTOMATIC DECREASE IN LEFT VENTRICULAR EJECTION FRACTION (LVEF) GREATER THAN 10% FROM BASELINE: Withhold trametinib up to 4 wks. If LVEF improved, resume at lower dose level. Discontinue if not improved. Do not modify dabrafenib dose. SYMPTOMATIC HF OR DECREASE IN LVEF GREATER THAN 20% FROM BASELINE: Discontinue trametinib. Withhold dabrafenib until improved, then resume at lower dose level.
CUTANEOUS EVENTS: INTOLERABLE GRADE 2 SKIN TOXICITY OR GRADE 3–4 TOXICITY: Withhold both regimens for up to 3 wks. If improved, resume both at lower dose level. Discontinue both regimens if not improved. FEBRILE EVENTS: FEVER OF 101.3ºF–104ºF: Do not modify trametinib dose. Withhold dabrafenib until fever resolved, then resume at either same dose or lower dose level.
FEVER GREATER THAN 104ºF OR FEVER COMPLICATED BY DEYDRATION, HYPOTENSION, RENAL FAILURE: Withhold trametinib until resolved, then resume at either same dose or lower dose level. Withhold dabrafenib until resolved, then resume at either lower dose level or discontinue.
New Primary Malignancies: CUTANEOUS: No changes required for either regimen. NONCUTANEOUS: Do not change trametinib dose. Discontinue dabrafenib in pts who develop RAS mutation-positive malignancies.
Nonspecific Adverse Reactions: INTOLERABLE GRADE 2 OR ANY GRADE 3: Withhold both regimens until resolved to grade 0–1, then resume at lower dose level. Discontinue both regimens if not improved. FIRST OCCURRENCE OF ANY GRADE 4 REACTIONS: Withhold both regimens until resolved to grade 0–1, then resume at lower dose level or discontinue.
Ocular Toxicities: GRADE 2–3 RETINAL PIGMENT EPITHELIAL DETACHMENTS: Withhold trametinib up to 3 wks. If improved to grade 0–1, resume at lower dose level. Discontinue if not improved. Do not modify dabrafenib. RETINAL VEIN OCCLUSION: Discontinue trametinib. Do not modify dabrafenib.
UVEITIS OR IRITIS: Do not modify trametinib. Withhold dabrafenib for up to 6 wks. If improved to grade 0–1, then resume at same dose level. Discontinue if not improved.
Pulmonary: INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE: Discontinue trametinib. Do not modify dabrafenib.
Venous Thromboembolism: UNCOMPLICATED (DVT) OR (PE): Withhold trametinib for up to 3 wks. If improved to grade 0–1, then resume at lower dose level. Discontinue if not improved. Do not modify dabrafenib. LIFE-THREATENING PE: Discontinue both regimens.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Single Regimen:
Frequent (57%–32%): Rash, diarrhea, lymphedema, peripheral edema. Occasional (19%–10%): Dermatitis acneiform, hypertension, stomatitis, mouth ulceration, mucosal ulceration, abdominal pain, dry skin, pruritus, paronychia, folliculitis, cellulitis, dizziness, dysgeusia, blurred vision, dry eye.
Combination Regimen:
Frequent (71%–40%): Pyrexia, chills, fatigue, rash, nausea, vomiting. Occasional (36%–11%): Diarrhea, abdominal pain, peripheral edema, headache, cough, arthralgia, night sweats, myalgia, constipation, decreased appetite, back pain, dry skin, insomnia, dermatitis acneiform, dizziness, muscle spasm, extremity pain, actinic keratosis, erythema, oral/throat pain, urinary tract infection, pruritus, dry mouth, dehydration.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Primary malignancies including basal or squamous cell carcinoma, keratoacanthoma, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, glioblastoma (brain cancer) reported. DVT, PE reported in 9% of pts. May increase cell proliferation of wild-type BRAF melanoma or new malignant melanomas. Serious, sometimes fatal intracranial or gastric bleeding occurred in 5% of pts. Other hemorrhagic events may include conjunctival/gingival/rectal/hemorrhoidal/vaginal bleeding; epistaxis (nosebleed), melena (bloody stools). Cardiomyopathy, HF, decreased LVEF reported in 7%–9% of pts. Ocular toxicities such as retinal vein occlusion, retinal detachment, vision loss, glaucoma, uveitis, iritis reported. Cough, dyspnea, hypoxia, pleural effusion, infiltrates may indicate interstitial lung disease. Serious febrile reactions may lead to renal failure, severe dehydration, hypotension, rigors. Skin toxicities including palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (PPES), papilloma have occurred. Hyperglycemia reported in 2%–5% of pts. Other effects may include hypertension, rhabdomyolysis. May prolong QT interval of cardiac cycle.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Obtain baseline CBC, serum metabolic panel (with LFT), magnesium, phosphate, ionized calcium, capillary glucose level, vital signs. Obtain BRAF V600E mutation history, negative pregnancy status, ophthalmologic exam with visual acuity, echocardiogram, EKG before initiating treatment. Assess skin for moles, lesions, papillomas. Question current breastfeeding status. Receive full medication history including herbal products. Question any history as listed in PRECAUTIONS.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Offer emotional support. Monitor CBC, serum electrolytes, capillary blood glucose, stool characteristics routinely. Monitor for signs of hyperglycemia (thirst, polyuria, confusion, dehydration). Assess skin for new lesions, toxicities every 2 mos during treatment and at least 6 mos after discontinuation. Obtain LVEF by echocardiogram 1 mo after initiation, then every 2–3 mos; ophthalmologic exam with any vision changes. Immediately report any altered mental status, bleeding events, vision changes, eye pain/swelling/infection, fever, urinary changes. Screen for bleeding of any kind. If dyspnea or leg swelling occurs, contact physician and initiate appropriate medical therapy (may require oxygen therapy, EKG, or radiologic test to rule out DVT, PE, or ILD).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Blood work, cardiac function tests, eye exams will be performed routinely. • Treatment may lead to heart failure, vision changes, lung complications, difficulty breathing, fever, skin toxicities (such as severe rash, peeling), high blood pressure, severe diarrhea. • Report bloody stools/urine, heavy menstruation, or nosebleeds. • Do not breastfeed. • Avoid pregnancy; nonhormonal contraception should be used during treatment and up to 4 wks after treatment. • Take medication at least 1 hr before or at least 2 hrs after meal (food reduces absorption). • Report any increased urination, thirst, confusion (may indicate high blood sugar); chest pain, eye pain, fever, leg swelling, new skin moles or lesions, vision changes. • Minimize sunlight exposure. • Males may experience a decreased sperm count. • Report any newly prescribed medications.
trastuzumab 

tras-too-zoo-mab
(Herceptin)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Anaphylactic reaction, infusion reaction, acute respiratory distress syndrome have been associated with fatalities. Reduction in left ventricular ejection fraction, severe heart failure may result in thrombus formation, stroke, cardiac death. Exposure during pregnancy may result in pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal malformations, neonatal death.
Anaphylactic reaction, infusion reaction, acute respiratory distress syndrome have been associated with fatalities. Reduction in left ventricular ejection fraction, severe heart failure may result in thrombus formation, stroke, cardiac death. Exposure during pregnancy may result in pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal malformations, neonatal death.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Monoclonal antibody. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Treatment of HER2 overexpressing breast cancer (adjuvant), metastatic breast cancer, metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (in pts without prior treatment). OFF-LABEL: Treatment of HER2–positive metastatic breast cancer in pts who have not received prior anti-HER2 therapy or in pts whose cancer has progressed on prior trastuzumab therapy (in combination with lapatinib).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to trastuzumab. Cautions: Preexisting cardiac disease or dysfunction, preexisting pulmonary disease or extensive pulmonary tumor involvement, preganancy.
ACTION
Binds to HER2 protein, overexpressed in 25%–30% of primary breast cancers, inhibiting proliferation of tumor cells. Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits growth of tumor cells, mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Half-life: 11–23 days.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Age-related cardiac dysfunction may require dosage adjustment.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution: 440 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
 IV
IV
Reconstitution • Reconstitute with 20 ml Bacteriostatic Water for Injection to yield concentration of 21 mg/ml. • Add calculated dose to 250 ml 0.9% NaCl (do not use D5W). • Gently mix contents in bag.
Rate of Administration • Do not give IV push or bolus. • Give loading dose (4 mg/kg) over 90 min. Give maintenance infusion (2 mg/kg) over 30 min.
Storage • Refrigerate. • Reconstituted solution appears colorless to pale yellow. • Reconstituted solution in vial is stable for 28 days if refrigerated after reconstitution with Bacteriostatic Water for Injection (if using Sterile Water for Injection without preservative, use immediately; discard unused portions). • Solution diluted in 250 ml 0.9% NaCl stable for 24 hrs if refrigerated.
 IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
IV INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not mix with D5W or any other medications.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Breast Cancer (Adjuvant)
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (with concurrent paclitaxel or docetaxel): Initially, 4 mg/kg as 90-min infusion, then 2 mg/kg wkly as 30-min infusion for 12 wks followed 1 wk later (when concurrent chemotherapy completed) by 6 mg/kg infusion over 30–90 min q3wks for total therapy duration of 52 wks. (with docetaxel/carboplatin): Initially, 4 mg/kg as 90-min infusion, then 2 mg/kg wkly as 30-min infusion for a total of 18 wks, followed 1 wk later (when concurrent chemotherapy completed) by 6 mg/kg infused over 30–90 min q3wks for total therapy duration of 52 wks (follow multimodality chemotherapy): Initially, 8 mg/kg over 90 min, then 6 mg/kg over 30–90 min q3wks for total of 52 wks.
Breast Cancer (Metastatic)
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Either as single agent or in combination with paclitaxel): Initially, 4 mg/kg as 90-min infusion, then 2 mg/kg as 30-min infusion wkly until disease progression.
Gastric Cancer
IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: (In combination with cisplatin and either capecitabine or fluorouracil for 6 cycles, then as monotherapy): Initially, 8 mg/kg over 90 min, then 6 mg/kg over 30–90 min q3wks until disease progression.
Dosage Adjustment in Cardiotoxicity
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) 16% or greater decrease from baseline WNL (within normal limits) or LVEF below normal limits and 10% or greater decrease from baseline: Hold treatment for 4 wks. Repeat LVEF q4wks. Resume therapy if LVEF returns to normal limits in 4–8 wks and remains at 15% or less decrease from baseline.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (Greater Than 20%): Pain, asthenia, fever, chills, headache, abdominal pain, back pain, infection, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, cough, dyspnea. Occasional (15%–5%): Tachycardia, HF, flu-like symptoms, anorexia, edema, bone pain, arthralgia, insomnia, dizziness, paresthesia, depression, rhinitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis. Rare (Less Than 5%): Allergic reaction, anemia, leukopenia, neuropathy, herpes simplex.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Cardiomyopathy, ventricular dysfunction, HF occur rarely. Pancytopenia may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Evaluate left ventricular function. Obtain baseline echocardiogram, EKG, multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan. Obtain CBC at baseline and at regular intervals during therapy.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Frequently monitor for deteriorating cardiac function. Assess for asthenia (loss of strength, energy). Assist with ambulation if asthenia occurs. Monitor for fever, chills, abdominal pain, back pain. Offer antiemetics if nausea, vomiting occur. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not have immunizations without physician’s approval (lowers resistance). • Avoid contact with those who have recently taken oral polio vaccine. • Avoid crowds, those with infection.
*traZODone
traz-o-done
(Apo-Trazodone  , Novo-Trazodone
, Novo-Trazodone  , Oleptro)
, Oleptro)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, young adults 18–24 yrs with major depressive disorder, other psychiatric disorders.
Do not confuse trazodone with tramadol or ziprasidone.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Serotonin reuptake inhibitor. CLINICAL: Antidepressant.
USES
Treatment of depression. OFF-LABEL: Insomnia.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to trazodone. Use of MAOIs (concurrently or within 14 days of discontinuing trazodone or MAOI); initiation in pt receiving linezolid or methylene blue. Cautions: Cardiac disease, arrhythmias, cerebrovascular disease, hepatic/renal impairment, pts at high risk of suicide. Conditions predisposing to priapism (e.g., sickle cell anemia); concurrent use of antihypertensives; history of seizure disorder or conditions predisposing to seizures (e.g., alcoholism); elderly.
ACTION
Blocks reuptake of serotonin at neuronal presynaptic membranes, increasing its availability at postsynaptic receptor sites. Therapeutic Effect: Relieves depression.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 85%–95%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Unknown if removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 5–9 hrs (increased in elderly).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Drug crosses placenta; minimally distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established in pts younger than 6 yrs. Elderly: More likely to experience sedative, hypotensive effects; lower dosage recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, ketoconazole) increase concentration/effects. May increase concentration of digoxin, phenytoin. HERBAL: Gotu kola, kava kava, St. John’s wort, valerian may increase CNS depression and serotonin syndrome. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May decrease WBC, neutrophil counts.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets: 50 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg.
 Tablets: (Extended-Release [Oleptro]): 150 mg, 300 mg.
Tablets: (Extended-Release [Oleptro]): 150 mg, 300 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give shortly after snack, meal (reduces risk of dizziness). • Tablets may be crushed. • Do not crush or divide extended-release tablets. Give whole or break in half along score line. • Best taken at bedtime.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Therapeutic effect may take up to 6 wks to occur.
Depression
PO: ADULTS:(Immediate-Release): Initially, 150 mg/day in 3 equally divided doses. Increase by 50 mg/day at 3- to 4-day intervals until therapeutic response is achieved. Maximum: 600 mg/day (inpatients); 400 mg/day (outpatients). ELDERLY: Initially, 25–50 mg at bedtime. May increase by 25–50 mg every 3–7 days. Range: 75–150 mg/day. Tablets (Extended-Release): ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 150 mg once daily. May increase by 75 mg q3days. Maximum: 375 mg/day. ADOLESCENTS 13–18 YRS: (Immediate-Release):Initially, 25–50 mg/day. May increase to 100–150 mg/day in divided doses. CHILDREN 6–12 YRS: (Immediate-Release):Initially, 1.5–2 mg/kg/day in divided doses. May increase gradually q3–4 days to 6 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Use caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (9%–3%): Drowsiness, dry mouth, light-headedness, dizziness, headache, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting. Occasional (3%–1%): Nervousness, fatigue, constipation, myalgia/arthralgia, mild hypotension. Rare: Photosensitivity reaction.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Priapism, altered libido, retrograde ejaculation, impotence occur rarely. Appears to be less cardiotoxic than other antidepressants, although arrhythmias may occur in pts with preexisting cardiac disease.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess mental status, mood, behavior. For pts on long-term therapy, serum hepatic/renal function tests, blood counts should be performed periodically. Elderly are more likely to experience sedative, hypotensive effects.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for suicidal ideation (esp. at beginning of therapy or dosage change). Assess appearance, behavior, speech pattern, level of interest, mood. Monitor WBC, neutrophil count, hepatic enzymes. Assist with ambulation if dizziness, light-headedness occurs.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Immediately discontinue medication, consult physician if priapism occurs. • May take after meal, snack. • May take at bedtime if drowsiness occurs. • Change positions slowly to avoid hypotensive effect. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Tolerance to sedative, anticholinergic effects usually develops during early therapy. • Photosensitivity to sun may occur. • Dry mouth may be relieved by sugarless gum, sips of water. • Report visual disturbances, worsening depression, suicidal ideation, unusual changes in behavior. • Do not abruptly discontinue medication. • Avoid alcohol.
tretinoin 
tret-i-noyn
(Atralin, Avita, Refissa, Rejuva-A  , Renova, Retin-A, Retin-A Micro, Tretin X, Vesanoid
, Renova, Retin-A, Retin-A Micro, Tretin X, Vesanoid  )
)
 BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT  High risk for teratogenicity; major fetal abnormalities, spontaneous abortions. Pts with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) are at severe risk for reactions (fever, dyspnea, acute respiratory distress syndrome [pulmonary infiltrates, pleural effusions, pericardial effusions]), edema, hepatic, renal, and/or multiorgan failure; 40% develop leukocytosis.
High risk for teratogenicity; major fetal abnormalities, spontaneous abortions. Pts with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) are at severe risk for reactions (fever, dyspnea, acute respiratory distress syndrome [pulmonary infiltrates, pleural effusions, pericardial effusions]), edema, hepatic, renal, and/or multiorgan failure; 40% develop leukocytosis.
Do not confuse tretinoin with isotretinoin, phenytoin, or triamcinolone.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
With octyl methoxycinnamate and oxybenzone, moisturizers, and SPF-12, a sunscreen (Retin-A Regimen Kit).
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Retinoid. CLINICAL: Antiacne, transdermal, antineoplastic.
USES
Topical: Treatment of acne vulgaris, photodamaged skin. PO: Induction of remission in pts with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). OFF-LABEL (PO): Maintenance therapy in APL, combination therapy (arsenic trioxide) for remission induction in APL. Topical: Some skin cancers.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tretinoin. Sensitivity to parabens (used as preservative in gelatin capsule). Extreme Caution: Topical: Eczema, sun exposure. Cautions: Topical: Those with considerable sun exposure in their occupation, hypersensitivity to sun. PO: Elevated serum cholesterol/triglycerides, concurrent use of antifibrinolytic agents.
ACTION
Antiacne: Decreases cohesiveness of follicular epithelial cells. Increases turnover of follicular epithelial cells. Therapeutic Effect: Causes expulsion of blackheads. Bacterial skin counts are not altered. Transdermal: Exerts effects on growth/differentiation of epithelial cells. Therapeutic Effect: Alleviates fine wrinkles, hyperpigmentation. Antineoplastic: Induces maturation, decreases proliferation of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cells. Therapeutic Effect: Repopulation of bone marrow, and peripheral blood with normal hematopoietic cells.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Topical: Minimally absorbed. PO: Well absorbed following PO administration. Protein binding: greater than 95%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Half-life: 0.5–2 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Topical: Use during pregnancy only if clearly necessary. Unknown if distributed in breast milk. PO: Teratogenic, embryotoxic effect. Children/Elderly: Safety and efficacy not established.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: TOPICAL: Retinoids (e.g., acitretin, oral tretinoin) may increase drying, irritative effects. PO: Tetracyclines may increase risk of pseudotumor cerebri, intracranial hypertension. Aminocaproic acid may increase risk of thrombotic complications. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., phenobarbital, rifampin) may decrease concentration/effects. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) may increase concentration, risk of toxicity. HERBAL: St. John’s wort may decrease concentration/effects. Dong quai, St. John’s wort may increase photosensitization. Vitamin A supplementation may increase vitamin A toxicity. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: PO: Leukocytosis occurs commonly (40%). May elevate serum hepatic function tests, cholesterol, triglycerides.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Cream: 0.02% (Renova), 0.025% (Avita, Retin-A, Tretin X), 0.05% (Refissa, Retin-A, Tretin X), 0.1% (Retin-A). Gel: 0.01% (Retin-A, Tretin X), 0.025% (Avita, Retin-A, Tretin X), 0.04% (Retin-A Micro), 0.1% (Retin-A Micro).
 Capsules: (Vesanoid): 10 mg.
Capsules: (Vesanoid): 10 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Do not crush/break capsule. • Administer with a meal.
Topical
• Thoroughly cleanse area before applying tretinoin. • Lightly cover only affected area. Liquid may be applied with fingertip, gauze, cotton; do not rub onto unaffected skin. • Keep medication away from eyes, mouth, angles of nose, mucous membranes. • Wash hands immediately after application.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Acne
Topical: ADULTS, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: Apply once daily at bedtime or in the evening.
Remission Induction in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL)
PO: ADULTS: 45 mg/m2/day given as 2–3 evenly divided doses until complete remission is documented. Discontinue therapy 30 days after complete remission or after 90 days of treatment, whichever comes first.
Remission Maintenance in APL
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 45 mg/m2/day in 2 divided doses for 15 days q3mos for 2 yrs. CHILDREN: 25 mg/m2/day in 2 divided doses for 15 days q3mos for 2 yrs.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Topical: Temporary change in pigmentation, photosensitivity. Local inflammatory reactions (peeling, dry skin, stinging, erythema, pruritus) are to be expected and are reversible with discontinuation of tretinoin. Frequent: PO (87%–54%): Headache, fever, dry skin/oral mucosa, bone pain, nausea, vomiting, rash. Occasional: PO (26%–6%): Mucositis, earache or feeling of fullness in ears, flushing, pruritus, diaphoresis, visual disturbances, hypotension/hypertension, dizziness, anxiety, insomnia, alopecia, skin changes. Rare (Less Than 6%): Altered visual acuity, temporary hearing loss.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
PO: Retinoic acid syndrome (fever, dyspnea, weight gain, abnormal chest auscultatory findings [pulmonary infiltrates, pleural/pericardial effusions], episodic hypotension) occurs commonly (25%), as does leukocytosis (40%). Syndrome generally occurs during first month of therapy (sometimes after first dose). High-dose steroids (dexamethasone 10 mg IV) at first suspicion of syndrome reduce morbidity, mortality. Pseudotumor cerebri may be noted, esp. in children (headache, nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances). Topical: Possible tumorigenic potential when combined with ultraviolet radiation.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
PO: Inform women of childbearing potential of risk to fetus if pregnancy occurs. Instruct on need for use of 2 reliable forms of contraceptives concurrently during therapy and for 1 mo after discontinuation of therapy, even in infertile women. Pregnancy test should be obtained within 1 wk before institution of therapy. Obtain initial serum LFT, cholesterol, triglyceride levels.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
PO: Monitor LFT, hematologic, coagulation profiles, cholesterol, triglycerides. Monitor for signs/symptoms of pseudotumor cerebri in children.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Topical: Avoid exposure to sunlight, tanning beds; use sunscreens, protective clothing. • Protect affected areas from wind, cold. • If skin is already sunburned, do not use drug until fully healed. • Keep tretinoin away from eyes, mouth, angles of nose, mucous membranes. • Do not use medicated, drying, abrasive soaps; wash face no more than 2–3 times/day with gentle soap. • Avoid use of preparations containing alcohol, menthol, spice, lime (e.g., shaving lotions, astringents, perfume). • Mild redness, peeling are expected; decrease frequency or discontinue medication if excessive reaction occurs. • Nonmedicated cosmetics may be used; however, cosmetics must be removed before tretinoin application. • Improvement noted during first 24 wks of therapy. • Antiacne: Therapeutic results noted in 2–3 wks; optimal results in 6 wks. Oral: • Avoid tasks requiring motor skills, alertness until response to drug is established. • Avoid alcohol. • Avoid exposure to sunlight, tanning beds. • Report persistent vomiting, diarrhea, unusual bleeding/bruising, acute abdominal pain, vision changes, or if pregnancy is suspected.
triamcinolone hexacetonide
(Aristospan)
Do not confuse Nasacort with Nasalcrom.
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Myco-II, Mycolog II, Myco-Triacet: triamcinolone/nystatin (an antifungal): 0.1%/100,000 units/g.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Adrenocortical steroid. CLINICAL: Anti-inflammatory.
USES
Nasal inhalation: Management of seasonal, perennial rhinitis in adults and children 2 yrs and older. (OTC): Relief of hay fever, other upper respiratory allergies. Intra-articular: Acute gouty arthritis, bursitis, tenosynovitis, epicondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, synovitis of osteoarthritis. Intralesional: Alopecia areata, discoid lupus erythematosus, keloids, lichen plaques, psoriatic plaques. Topical: Relief of inflammation, pruritus associated with corticoid-responsive dermatoses.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to triamcinolone. Systemic fungal infections, cerebral malaria, serious infections. IM: Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Topical: Local fungal, viral, bacterial infections. Cautions: Administration of live virus vaccines, following acute MI, elderly, hepatic impairment, myasthenia gravis, pts at risk for osteoporosis/seizures/GI disease, history of tuberculosis (may reactivate disease), hypothyroidism, cirrhosis, HF, hypertension, renal insufficiency, diabetes, cardiovascular disease. Prolonged therapy should be discontinued slowly.
ACTION
Inhibits accumulation of inflammatory cells at inflammation sites, phagocytosis, lysosomal enzyme release, synthesis/release of mediators of inflammation. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents/suppresses cell-mediated immune reactions. Decreases/prevents tissue response to inflammatory process.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Amphotericin, diuretics may worsen hypokalemia. May increase risk of digoxin toxicity (due to hypokalemia). May decrease effects of insulin, oral hypoglycemics. CYP3A inducers (e.g., phenytoin, rifampin) may decrease effects. May reduce response to vaccines due to inhibition of antibody response. HERBAL: Echinacea may decrease effects. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum glucose, lipid, amylase, sodium. May decrease serum calcium, potassium, thyroxine.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Cream: 0.025%, 0.1%. Injection, Suspension (Kenalog-10): 10 mg/ml. (Kenalog-40): 40 mg/ml. Ointment: 0.025%, 0.1%, 0.5%. Paste, Oral, Topical: 0.1%. Suspension, Spray Nasal Inhalation (Nasacort AQ): 55 mcg/inhalation.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
Topical
• Gently cleanse area before application. • Use occlusive dressings only as ordered. • Apply sparingly, rub into area thoroughly.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Triamcinolone Hexacetonide
Intralesional: Up to 0.5 mg/square inch. Range: 2–48 mg.
Intra-articular: Average dose: 2–20 mg q3–4 wks.
Triamcinolone Acetonide
Intra-articular: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially: 2–20 mg/day. Doses can be adjusted between 20–80 mg as needed.
Rhinitis
Note: Discontinue if symptomatic relief not observed within 3 wks (1 wk of OTC use). Intranasal: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: Initially, 220 mcg/day as 2 sprays in each nostril once daily. CHILDREN 6–11 YRS: Initially, 110 mcg/day as 1 spray in each nostril once daily. May increase to 2 sprays in each nostril once daily. CHILDREN 2–5 YRS: 110 mcg/day as 1 spray in each nostril once daily.
Usual Topical Dosage
Topical: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN: 2–3 times/day. May give 1–2 times/day or as intermittent therapy.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent: Insomnia, dry mouth, heartburn, nervousness, abdominal distention, diaphoresis, acne, mood swings, increased appetite, facial flushing, delayed wound healing, increased susceptibility to infection, diarrhea, constipation. Occasional: Headache, edema, change in skin color, frequent urination. Rare: Tachycardia, allergic reaction (rash, urticaria), altered mental status, hallucinations, depression. Topical: Allergic contact dermatitis.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Long-term therapy: Muscle wasting (arms, legs), osteoporosis, spontaneous fractures, amenorrhea, cataracts, glaucoma, peptic ulcer, HF. Abrupt withdrawal following long-term therapy: Anorexia, nausea, fever, headache, arthralgia, rebound inflammation, fatigue, weakness, lethargy, dizziness, orthostatic hypotension. Anaphylaxis occurs rarely with parenteral administration. Sudden discontinuation may be fatal. Blindness has occurred rarely after intralesional injection around face, head.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Question for hypersensitivity to any corticosteroids. Obtain baselines for height, weight, B/P, serum glucose, electrolytes.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Oral inhalation, intranasal: Check mucous membranes for signs of fungal infection. Monitor growth in children. Monitor B/P.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report if condition being treated persists or worsens. • Avoid exposure to chickenpox or measles. • Avoid alcohol. • Inhalation: Do not take for acute asthma attack. • Rinse mouth to decrease risk of mouth soreness. • Report oropharyngeal lesions or soreness (stomatitis). • Nasal: Report unusual cough/spasm, persistent nasal bleeding, burning, infection.
trimethoprim
trye-meth-oh-prim
(Apo-Trimethoprim  , Primsol)
, Primsol)
FIXED-COMBINATION(S)
Bactrim, Septra: trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (a sulfonamide): 16 mg/80 mg/ml (injection), 40 mg/200 mg/5 ml (suspension), 80 mg/400 mg, 160 mg/800 mg (tablets).
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Folate antagonist. CLINICAL: Antibacterial.
USES
Treatment of UTI caused by susceptible strains of E. coli, P. mirabilis, K. pneumoniae. Treatment of acute otitis media due to H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae. OFF-LABEL: Treatment of pneumonia caused by Pneumocystis jiroveci (in combination with dapsone).
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to trimethoprim. Megaloblastic anemia due to folic acid deficiency. Cautions: Renal/hepatic impairment, pts with folic acid deficiency, elderly.
ACTION
Inhibits folic acid reduction to tetrahydrofolate, inhibiting microbial growth. Therapeutic Effect: Bacteriostatic.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Rapidly, completely absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 42%–46%. Widely distributed, including to CSF. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Moderately removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 8–10 hrs (increased in renal impairment, newborns; decreased in children).
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Drug readily crosses placenta; is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted. May increase incidence of thrombocytopenia.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Folate antagonists (e.g., methotrexate) may increase risk of megaloblastic anemia. May increase concentration, side effects of phenytoin. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May increase serum BUN, bilirubin, creatinine, ALT, AST.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Oral Solution (Primsol): 50 mg/5 ml. Tablets: 100 mg.
Administration/Hadling
PO
• Space doses evenly to maintain constant therapeutic level. • Give with milk or food.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
UTI
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 100 mg q12h or 200 mg once daily for 10–14 days. CHILDREN YOUNGER THAN 12 YRS: 4–6 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses for 10 days.
Otitis Media
PO: CHILDREN, 6 MOS AND OLDER: 10 mg/kg/day in divided doses q12h for 10 days. Maximum: 400 mg/day.
Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia (PCP)
ADULTS, ELDERLY, CHILDREN 12 YRS AND OLDER: 15–20 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses for 21 days in combination with dapsone.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage and frequency are modified based on creatinine clearance.
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| Greater than 30 ml/min | No change |
| 15–30 ml/min | 50 mg q12h or 100 mg once daily |
| Less than 15 ml/min | Avoid use |
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, decreased appetite, abdominal cramps, headache. Rare: Hypersensitivity reaction (pruritus, rash), methemoglobinemia (bluish fingernails, lips, skin; fever; pale skin; sore throat; asthenia, photosensitivity.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, anaphylaxis occur rarely. Hematologic toxicity (thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, leukopenia, megaloblastic anemia) more likely to occur in elderly, debilitated, alcoholics, those with renal impairment or receiving prolonged high dosage.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess hematology baseline reports, serum renal function tests.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Assess skin for rash. Evaluate food tolerance. Monitor serum hematology reports, renal function, LFT. Check for developing signs of hematologic toxicity (pallor, fever, sore throat, malaise, bleeding/bruising).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Space doses evenly. • Complete full length of therapy (10–14 days). • May take on empty stomach or with food if stomach upset occurs. • Avoid sun, ultraviolet light; use sunscreen, wear protective clothing. • Immediately report pallor, fatigue, sore throat, bruising/bleeding, discoloration of skin, fever, rash.
triptorelin
trip-toe-rel-in
(Trelstar, Trelstar Depot, Trelstar LA)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogue. CLINICAL: Antineoplastic.
USES
Palliative treatment of advanced prostate cancer.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to triptorelin, luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH), LHRH agonists, pregnancy. Cautions: None known.
ACTION
Through a negative feedback mechanism, inhibits gonadotropin hormone secretion. Circulating levels of luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), testosterone, estradiol rise initially, then subside with continued therapy. Therapeutic Effect: Suppresses growth of abnormal prostate tissue.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: No age-related precautions noted.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: None significant. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: May alter serum pituitary-gonadal function test results. May cause transient increase in serum testosterone, usually during first wk of treatment.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Trelstar Depot): 3.75 mg. Injection, Powder for Reconstitution (Trelstar LA): 11.25 mg, 22.5 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
IM
• Reconstitute with 2 ml Sterile Water for Injection. • Administer into large muscle mass, esp. gluteus muscle, alternating injection sites.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Prostate Cancer
IM: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 3.75 mg once q4wks, 11.25 mg q12 wks, or 22.5 mg q24 wks.
IM (Trelstar LA): ADULTS, ELDERLY: 11.25 mg q12wks, 22.5 mg q24wks.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (Greater Than 5%): Hot flashes, skeletal pain, headache, impotence. Occasional (5%–2%): Insomnia, vomiting, leg pain, fatigue. Rare (Less Than 2%): Dizziness, emotional lability, diarrhea, urinary retention, UTI, anemia, pruritus.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Bladder outlet obstruction, skeletal pain, hematuria, spinal cord compression with weakness, paralysis of lower extremities may occur.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Obtain serum testosterone, prostate-specific antigen (PSA), prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) levels periodically during therapy. Serum testosterone, PAP levels should increase during first wk of therapy. Testosterone level then should decrease to baseline level or less within 2 wks, PAP level within 4 wks. Monitor pt closely for worsening signs and symptoms of prostatic cancer, esp. during first wk of therapy (due to transient increase in testosterone).
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Do not miss monthly injections. • May experience increased skeletal pain, blood in urine, urinary retention initially (subsides within 1 wk). • Hot flashes may occur. • Report tachycardia, persistent nausea or vomiting, numbness of arms/legs, pain/swelling of breasts, difficulty breathing, infection at injection site.
trospium
tro-spee-um
(Trosec  )
)
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Anticholinergic. CLINICAL: Antispasmotic.
USES
Treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, urinary frequency.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to trospium. Gastric retention, uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma, urinary retention. Cautions: Decreased GI motility, renal/hepatic impairment, obstructive GI disorders, ulcerative colitis, intestinal atony, myasthenia gravis, controlled narrow-angle glaucoma, bladder flow obstruction, Alzheimer’s disease, hot weather/exercise, elderly.
ACTION
Antagonizes effect of acetylcholine on muscarinic receptors, producing parasympatholytic action. Therapeutic Effect: Reduces smooth muscle tone in bladder.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Minimally absorbed after PO administration. Protein binding: 50%–85%. Distributed in plasma. Excreted in feces (82%), urine (6%). Half-life: 20 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Unknown if drug crosses placenta or is distributed in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established. Elderly: Higher incidence of dry mouth, constipation, dyspepsia, UTI, urinary retention in pts 75 yrs and older.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Other anticholinergic agents increase severity, frequency of side effects, may alter absorption of other drugs due to anticholinergic effects on GI motility. Morphine, procainamide, tenofovir, vancomycin may increase concentration. HERBAL: None significant. FOOD: High-fat meals may reduce absorption. LAB VALUES: None significant.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
 Tablets (Sanctura): 20 mg.
Tablets (Sanctura): 20 mg.  Capsules, Extended-Release (Sanctura XR): 60 mg.
Capsules, Extended-Release (Sanctura XR): 60 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Store at room temperature. • Give at least 1 hr before meals or on an empty stomach. • Do not break, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets or extended-release capsules; swallow whole. • Administer tablets at bedtime, capsules in morning with full glass of water, 1 hr before eating.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
Overactive Bladder
PO: ADULTS: (Immediate-Release):20 mg twice daily. ELDERLY 75 YRS AND OLDER: 20 mg once daily at bedtime. (Extended-Release): 60 mg once daily.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
For pts with CrCl less than 30 ml/min, immediate-release dosage reduced to 20 mg once daily at bedtime. Extended-release not recommended.
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Mild impairment: No dose adjustment. Moderate to severe impairment: Use with caution.
SIDE EFFECTS
Frequent (20%): Dry mouth. Occasional (10%–4%): Constipation, headache. Rare (Less Than 2%): Fatigue, upper abdominal pain, dyspepsia (heartburn, indigestion, epigastric pain), flatulence, dry eyes, urinary retention.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Overdose may result in severe anticholinergic effects, characterized by nervousness, restlessness, nausea, vomiting, confusion, diaphoresis, facial flushing, hypertension, hypotension, respiratory depression, irritability, lacrimation. Supraventricular tachycardia and hallucinations occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Assess for presence of dysuria, urinary urgency, frequency, incontinence.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor for symptomatic relief. Monitor I&O; palpate bladder for retention. Monitor daily pattern of bowel activity, stool consistency. Dry mouth may be relieved by sips of tepid water.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Report nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, increased salivary secretions, palpitations, severe abdominal pain. • Swallow tablets, extended-release capsules whole.
![]() IV
IV