W
warfarin 

war-far-in
(Apo-Warfarin ![]() , Coumadin, Jantoven, Novo-Warfarin
, Coumadin, Jantoven, Novo-Warfarin ![]() )
)
![]() BLACK BOX ALERT
BLACK BOX ALERT ![]() May cause major or fatal bleeding. Risk factors include history of GI bleeding, hypertension, cerebrovascular disease, heart disease, malignancy, trauma, anemia, renal insufficiency, age 65 yrs and older, high anticoagulation factor (INR greater than 4). Consider cardiac/hepatic function, age, nutritional status, concurrent medications, risk of bleeding when dosing warfarin. Genetic variations have been identified as factors associated with dosage and bleeding risk. Genotyping tests are available.
May cause major or fatal bleeding. Risk factors include history of GI bleeding, hypertension, cerebrovascular disease, heart disease, malignancy, trauma, anemia, renal insufficiency, age 65 yrs and older, high anticoagulation factor (INR greater than 4). Consider cardiac/hepatic function, age, nutritional status, concurrent medications, risk of bleeding when dosing warfarin. Genetic variations have been identified as factors associated with dosage and bleeding risk. Genotyping tests are available.
Do not confuse Coumadin with Kemadrin, or Jantoven with Janumet or Januvia.
♦ CLASSIFICATION
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: Coumarin derivative. CLINICAL: Anticoagulant.
USES
Prophylaxis, treatment of thromboembolic disorders and embolic complications arising from atrial fibrillation or valve replacement. Risk reduction of systemic embolism following MI (e.g., recurrent MI, stroke). OFF-LABEL: Adjunct treatment in transient ischemic attacks.
PRECAUTIONS
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to warfarin. Hemorrhagic tendencies (e.g., cerebral aneurysms, bleeding from GI tract), recent or potential surgery of eye or CNS, neurosurgical procedures, open wounds, severe uncontrolled or malignant hypertension, spinal puncture procedures, uncontrolled bleeding, ulcers, unreliable or noncompliant pts, unsupervised pts, blood dyscrasias, pericarditis or pericardial effusion, pregnancy (except in women with mechanical heart valves at high risk for thromboembolism), bacterial endocarditis, threatened abortion. Major regional lumbar block anesthesia or traumatic surgery, eclampsia/preeclampsia. Cautions: Active tuberculosis, acute infection, diabetes, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and deep vein thrombosis, pts at risk for hemorrhage, moderate to severe renal impairment, moderate to severe hypertension, thyroid disease, polycythemia vera, vasculitis, open wound, menstruating and postpartum women, indwelling catheters, trauma, prolonged dietary deficiencies, disruption of GI normal flora, history of peptic ulcer disease, protein C deficiency, elderly.
ACTION
Interferes with hepatic synthesis of vitamin K–dependent clotting factors, resulting in depletion of coagulation factors II, VII, IX, X. Therapeutic Effect: Prevents further extension of formed existing clot; prevents new clot formation, secondary thromboembolic complications.
PHARMACOKINETICS
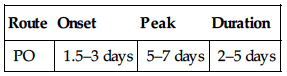
| Route | Onset | Peak | Duration |
| PO | 1.5–3 days | 5–7 days | 2–5 days |
Well absorbed from GI tract. Protein binding: 99%. Metabolized in liver. Primarily excreted in urine. Not removed by hemodialysis. Half-life: 20–60 hrs.
 LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
LIFESPAN CONSIDERATIONS
Pregnancy/Lactation: Contraindicated in pregnancy (fetal, neonatal hemorrhage, intrauterine death). Crosses placenta; distributed in breast milk. Children: More susceptible to effect. Elderly: Increased risk of hemorrhage; lower dosage recommended.
INTERACTIONS
DRUG: Amiodarone, azole antifungals, cimetidine, disulfiram, fluvoxamine, sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, levothyroxine, metronidazole, NSAIDs, omeprazole, platelet aggregation inhibitors (e.g., clopidogrel), salicylates (e.g., aspirin), thrombolytic agents (e.g., alteplase), thyroid hormones may increase effect. Griseofulvin, hepatic enzyme inducers (e.g., rifampin), vitamin K may decrease effects. Alcohol may enhance anticoagulant effect. HERBAL: Cat’s claw, dong quai, evening primrose, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo biloba, ginseng possess antiplatelet activity, may increase risk of bleeding. Ginseng, St. John’s wort may decrease effect. FOOD: None known. LAB VALUES: None known.
AVAILABILITY (Rx)
Tablets (Coumadin, Jantoven): 1 mg, 2 mg, 2.5 mg, 3 mg, 4 mg, 5 mg, 6 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg.
ADMINISTRATION/HANDLING
PO
• Give without regard to food. Give with food if GI upset occurs. • Give at same time each day.
INDICATIONS/ROUTES/DOSAGE
◀ ALERT ▶ Initial dosing must be individualized.
Anticoagulant
PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 2–5 mg/daily for 2 days OR 5–10 mg daily for 1–2 days, adjusting the dose based on INR results. Usual maintenance dose: 2–10 mg/day, but may vary outside these guidelines. CHILDREN: Initially, 0.05–0.2 mg/kg/day. Maximum: 10 mg. Maintenance: Adjust based on INR.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment. Closely monitor INR.
SIDE EFFECTS
Occasional: GI distress (nausea, anorexia, abdominal cramps, diarrhea). Rare: Hypersensitivity reaction (dermatitis, urticaria), esp. in those sensitive to aspirin.
ADVERSE EFFECTS/TOXIC REACTIONS
Bleeding complications ranging from local ecchymoses to major hemorrhage may occur. Antidote: Vitamin K. Amount based on INR, significance of bleeding. Range: 2.5–10 mg given orally or slow IV infusion (see Appendix J for dosage). Hepatotoxicity, blood dyscrasias, necrosis, vasculitis, local thrombosis occur rarely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Cross-check dose with coworker. Obtain CBC, PT/INR before administration and daily following therapy initiation. When stabilized, follow with INR determination q4–6wks. Obtain genotyping prior to initiating therapy if available.
INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Monitor INR diligently. Assess CBC for anemia; urine/stool for occult blood. Be alert to complaints of abdominal/back pain, severe headache, confusion, seizures, hemiparesis, aphasia (may be sign of hemorrhage). Decrease in B/P, increase in pulse rate may be sign of hemorrhage. Question for increase in amount of menstrual discharge. Assess peripheral pulses; skin for ecchymoses, petechiae. Check for excessive bleeding from minor cuts, scratches. Assess gums for erythema, gingival bleeding.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Take medication at same time each day. • Blood levels will be monitored routinely. • Do not take, discontinue any other medication except on advice of physician. • Avoid alcohol, aspirin, drastic dietary changes. • Consult with physician before surgery, dental work. • Urine may become red-orange. • Avoid, minimize significant bodily trauma. • Report bleeding, bruising, red or brown urine, black stools. • Use electric razor, soft toothbrush to prevent bleeding. • Report coffee-ground vomitus, blood-tinged mucus from cough. • Do not use any OTC medication without physician approval (may interfere with platelet aggregation). • Seek immediate medical attention for stroke–like symptoms (confusion, difficulty speaking, headache, one-sided weakness); bloody stool or urine.