Discrete Practice Answers
- B
Using the Pythagorean theorem, calculate the magnitude of the man’s displacement:
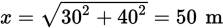
His total distance traveled is equal to 30 + 40 = 70 m. Therefore, the difference between these two is 20 m.
- A
The average force on the rocket equals its mass times the average acceleration; the average acceleration equals the change in velocity divided by the time over which the change occurs. So, the change in velocity equals the average force times the time divided by the mass:
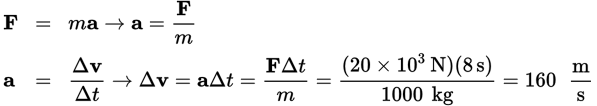
(B) represents the new velocity of the rocket, not its change in velocity. (C) and (D) neglect dividing by the mass of the rocket.
- C
The magnitude of the average acceleration is the change in velocity divided by the time. The velocity changes by
 because the car comes to rest. The time, in hours, is
because the car comes to rest. The time, in hours, is
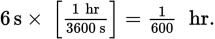 The average acceleration is then
The average acceleration is then
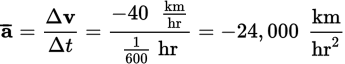
This question asked for the magnitude of this acceleration, which is
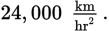
- A
The forces on the elevator are the tension upward and the weight downward, so the net force on the elevator is the difference between the two. For the elevator to accelerate upwards, the tension in the cable will have to be greater than the maximum weight so that there is a net force directed upwards. - A
Each object experiences an acceleration of 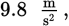 which means that each object’s velocity changes by
which means that each object’s velocity changes by
 each second. Therefore, both objects experience the same change in velocity over the
2-second period of
each second. Therefore, both objects experience the same change in velocity over the
2-second period of
 However, this question asks for the change in speed. The first object starts with
a velocity of
However, this question asks for the change in speed. The first object starts with
a velocity of
 and ends with a velocity of
and ends with a velocity of
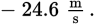 This represents a change in speed of
This represents a change in speed of
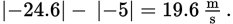 The second object starts with a velocity of
The second object starts with a velocity of
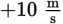 and ends with a velocity of
and ends with a velocity of
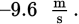 This represents a change in speed of
This represents a change in speed of
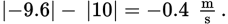 Therefore, the second object has a much smaller change in speed than the first. This
is because the force acting on the object was from the opposite direction
of the object’s
motion in the initial conditions.
Therefore, the second object has a much smaller change in speed than the first. This
is because the force acting on the object was from the opposite direction
of the object’s
motion in the initial conditions.
- A
The firefighter’s acceleration is always directed downward, whereas his velocity starts out horizontal and gradually rotates downwards as his downward velocity increases. Therefore, as time progresses, the angle between his velocity and acceleration decreases, which means that the maximum angle occurs at the instant he jumps. - B
The static force of friction acts parallel to the plane and is in the opposite direction from the parallel component of gravity in this setup. Because the wagon is in equilibrium, these two forces are equal in magnitude. Remember that gravity is often split into components in inclined plane problems. Rather than splitting into x- and y-components, however, it is more convenient to split the gravity vector into parallel and perpendicular components. The parallel component of gravity is given by the expression mg sin θ. Plugging in the values from the question, both the parallel component of gravity and static force of friction must be equal to 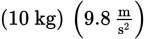 (sin 30°) = 49 N.
(sin 30°) = 49 N.
- C
In SI units, mass is measured in kilograms (kg), velocity in meters per second 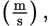 and time in seconds (s). The newton is a derived unit, and is not considered to be
a base unit of the SI system. A newton is equal to a
and time in seconds (s). The newton is a derived unit, and is not considered to be
a base unit of the SI system. A newton is equal to a
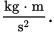
- B
The force of friction on an object sliding down an incline equals the coefficient of friction times the normal force. The normal force is equal in magnitude to the perpendicular component of gravity, which is given by mg cos θ. As θ increases, cos θ decreases. Therefore, the normal force and frictional force decrease as the angle of the incline increases. - D
A vector is characterized by both magnitude and direction. From the given answer choices, all are vectors except for distance. Distance is a scalar because it has only a numerical value and lacks direction. - B
In order for the seesaw to be balanced, the torque due to the girl (τg) must be exactly counteracted by the torque due to her father (τf). In other words, the magnitudes of these torques must be equal (τg = τf):
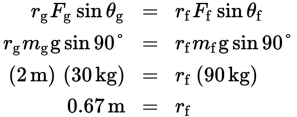
Because r represents the distance of each person from the fulcrum, the father must sit 67 cm from the fulcrum.
- B
This is a projectile motion question. The horizontal component of the jumper’s velocity will remain
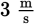 throughout the jump. The vertical component of his velocity starts at
throughout the jump. The vertical component of his velocity starts at
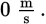 After 0.5 seconds, it will be:
After 0.5 seconds, it will be:
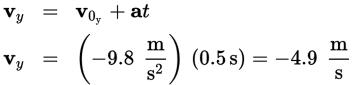
To get the overall velocity, consider the horizontal and vertical velocities using vector analysis and find the resultant. Doing so gives
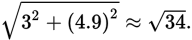 This magnitude (speed) is just a bit under 6, which matches most closely to
(B).
This magnitude (speed) is just a bit under 6, which matches most closely to
(B).
- C
We only need to analyze the motion in the vertical dimension to answer this question. If both the rock and ball began with no vertical velocity, they would reach the ground at the same time. However, because the rock begins with an upward component of velocity, it will take time to reach a maximum height before falling back toward the ground. Functionally, the rock’s free fall thus starts higher and later than the ball’s. The rock will necessarily hit the ground after the ball. - C
Because the question stem indicates that centrifugal force is reactionary and acts outwardly away from the center of rotation, we can draw the conclusion that it is a reaction to the centripetal force. According to Newton’s third law, these forces must have equal magnitude and opposite directions (antiparallel). - B
The presence of friction does not change the impact of Newton’s laws. A net force must still be applied to cause motion. This net force is not necessarily equal to an applied force, as friction and gravity also act on the object; thus, statement I is eliminated. Static friction opposes the movement of stationary objects, and is necessarily greater than the force of kinetic friction; thus, statement II is correct. Statement III is false because the normal force is related to mass, and friction is related to the normal force.