Introduction
1 Thomas Vought, Ryan Bergstrom, Michael Dulin and Mitchell Stimers, ‘The Spatial Distribution of the Seven Deadly Sins by County Within the United States’ (poster presented at the Annual Meeting of the Association of American Geographers, Las Vegas, NV, 2009).
2 S. Gregory the Great, Morals on the Book of Job (London: F. & J. Rivington, 590/1847).
3 Rebecca DeYoung, Glittering Vices (Grand Rapids, MI: Baker Publishing Group, 2009).
4 William Sinnott-Armstrong, ed., Moral Psychology, vol. 1, The Evolution of Morality (Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2008).
5 William Hoverd and Chris Sibley, ‘Immoral Bodies: The Implicit Association Between Moral Discourse and the Body’, Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion 46 (2007): 391–403.
6 S. Gregory the Great, Morals on the Book of Job.
Chapter 1: Lust
1 Cindy M. Meston and David M. Buss, ‘Why Humans Have Sex’, Archives of Sexual Behavior 36 (2007): 477–507.
2 D. Amen, ‘Bedtime Stories’, Men’s Health 19, no. 2 (2005): 152.
3 ‘Cosmo’s Sex Trick Hall of Fame’, Cosmopolitan 238, no. 6 (2005): 118.
4 David M. Buss, ‘Sex Differences in Human Mate Preferences: Evolutionary Hypotheses Tested in 37 Cultures’, Behavioral and Brain Sciences 12 (1989): 1–49; David M. Buss, The Evolution of Desire: Strategies of Human Mating (New York: Basic Books, 1994); David M. Buss and David R. Schmitt, ‘Sexual Strategies Theory: An Evolutionary Perspective on Human Mating’, Psychological Review 100 (1993): 204–32; Boguslaw Pawlowski and Slawomir Koziel, ‘The Impact of Traits Offered in Personal Advertisements on Response Rates’, Evolution and Human Behavior 23 (2002): 139–49.
5 Buss, The Evolution of Desire.
6 Jeffrey A. Hall, Namkee Park, Hayeon Song and Michael J. Cody, ‘Strategic Misrepresentation in Online Dating: The Effects of Gender, Self-Monitoring and Personality Traits’, Journal of Social and Personal Relationships 27 (2010): 117–35.
7 James R. Roney, ‘Effects of Visual Exposure to the Opposite Sex: Cognitive Aspects of Mate Attraction in Human Males’, Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 29 (March 2003): 393–404.
8 Bruce J. Ellis and Donald Symons, ‘Sex Differences in Sexual Fantasy: An Evolutionary Psychological Approach’, Journal of Sex Research 27 (November 1990): 527–55.
9 Antonio Zadra, ‘Sex Dreams: What Do Men and Women Dream About?’ Sleep 20 (2007): A376.
10 Russell D. Clark III and Elaine Hatfield, ‘Gender Differences in Receptivity to Sexual Offers’, Journal of Psychology and Human Sexuality 2 (1989): 39–55.
11 Buss, The Evolution of Desire.
12 Meston and Buss, ‘Why Humans Have Sex.’
13 Willibrord Weijmar Schultz, Pek van Andel, Ida Sabelis and Eduard Mooyaart, ‘Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Male and Female Genitals During Coitus and Female Sexual Arousal’, British Medical Journal 319 (1999): 1596–600.
14 Omri Gillath, Mario Mikulincer, Gurit E. Birnbaum and Phillip R. Shaver, ‘Does Subliminal Exposure to Sexual Stimuli have the Same Effects on Men and Women?’ Journal of Sex Research 44 (2007): 111–21.
15 Jon K. Maner, Douglas T. Kenrick, D. Vaughn Becker, Theresa E. Robertson, Brian Hofer, Steven L. Neuberg, Andrew W. Delton, Jonathan Butner and Mark Schaller, ‘Functional Projection: How Fundamental Social Motives can bias Interpersonal Perception’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 88 (2005): 63–78.
16 Walter Stephan, Ellen Berscheid and Elaine Walster, ‘Sexual Arousal and Heterosexual Perception’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 20 (1971): 93–101; Jon K. Maner, Matthew T. Gailliot, D. Aaron Rouby and Saul L. Miller, ‘Can’t Take My Eyes Off You: Attentional Adhesion to Mates and Rivals’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 93 (2007): 389–401.
17 Gregory J. Madden and Warren K. Bickel, Impulsivity: The Behavioral and Neurological Science of Discounting (Washington, DC: American Psychological Association, 2010).
18 Bram van den Bergh, Siegfried Dewitte and Luk Warlop, ‘Bikinis Instigate Generalized Impatience in Intertemporal Choice’, Journal of Consumer Research 35 (June 2008): 85–97.
19 Ibid.
20 Richard E. Nisbett, Kaiping Peng, Incheol Choi and Ara Norenzayan, ‘Culture and Systems of Thought: Holistic Versus Analytic Cognition’, Psychological Review 108 (2001): 291–310.
21 Jens Förster, Amina Özelsel and Kai Epstude, ‘How Love and Lust Change People’s Perception of Relationship Partners’, Journal of Experimental Social Psychology 46 (2010): 237–46.
22 Jens Förster, Kai Epstude and Amina Özelsel, ‘Why Love Has Wings and Sex Has Not: How Remindersof Love and Sex Influence Creative and Analytic Thinking’, Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 35 (2009): 1479–90.
23 Omri Gillath, ‘Neural and Cognitive Correlates of Exposure to Sex’ (talk presented at the 22nd annual meeting of the Association for Psychological Science, Boston, MA, May 2010).
24 Brad J. Bushman, ‘Violence and Sex in Television Programs Do Not Sell Products in Advertisements’, Psychological Science 16 (2005): 702–8.
25 Anemone Cerridwen and Dean Keith Simonton, ‘Sex Doesn’t Sell – Nor Impress! Content, Box Office, Critics and Awards in Mainstream Cinema’, Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity and the Arts 3 (2009): 200–10.
26 Vladas Griskevicius, Noah J. Goldstein, Chad R. Mortensen, Robert B. Cialdini and Douglas T. Kenrick, ‘Going Along Versus Going Alone: When Fundamental Motives Facilitate Strategic (Non)Conformity’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 91 (2006): 281–94.
27 Vladas Griskevicius, Joshua M. Tybur, Jill M. Sundie, Robert B. Cialdini, Geoffrey F. Miller and Douglas T. Kenrick, ‘Blatant Benevolence and Conspicuous Consumption: When Romantic Motives Elicit Strategic Costly Signals’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 93 (2007): 85–102.
28 Ibid.
29 Omri Gillath, Mario Mikulincer, Gurit E. Birnbaum and Phillip R. Shaver, ‘When Sex Primes Love: Subliminal Sexual Priming Motivates Relationship Goal Pursuit’, Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 34 (2008): 1057–69.
30 Ibid.
31 Dan Ariely and George Loewenstein, ‘The Heat of the Moment: The Effect of Sexual Arousal on Sexual Decision Making’, Journal of Behavioral Decision Making 19 (2006): 87–98.
32 Richard Ronay and William von Hippel, ‘The Presence of an Attractive Woman Elevates Testosterone and Physical Risk Taking in Young Men’, Social Psychological and Personality Science 1 (January 2010): 57–64.
33 Geoffrey F. Miller, ‘Sexual Selection for Moral Virtues’, Quarterly Review of Biology 82 (2007): 97–125.
34 David M. Buss and Michael Barnes, ‘Preferences in Human Mate Selection’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 50 (1986): 559–70.
35 Vladas Griskevicius, Robert B. Cialdini and Douglas T. Kenrick, ‘Peacocks, Picasso and Parental Investment: The Effects of Romantic Motives on Creativity’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 91 (2006): 63–76.
36 Miller, ‘Sexual Selection for Moral Virtues’.
37 Griskevicius et al., ‘Blatant Benevolence and Conspicuous Consumption’.
38 Catechism of the Catholic Church (Homebush, NSW: St Pauls, 1994).
Chapter 2: Gluttony
1 P. Rozin, C. Fischler, S. Imada, A. Sarubin and A. Wrzesniewski, ‘Attitudes to Food and the Role of Food in Life in the USA, Japan, Flemish Belgium and France: Possible Implications for the Diet-Health Debate’, Appetite 33 (1999): 163–80; Paul Rozin, ‘The Meaning of Food in Our Lives: A Cross-Cultural Perspective on Eating and Well-Being’, Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior 37 (2005): S107-S112.
2 National Center for Health Statistics, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: Data Tables, retrieved 31 December 2010, www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/databriefs/adultweight.pdf; Paul Rozin, Kimberly Kabnick, Erin Pete, Claude Fischler and Christy Shields, ‘The Ecology of Eating: Smaller Portion Sizes in France than in the United States Help Explain the French Paradox’, Psychological Science 14 (September 2003): 450–4.
3 Susan E. Hill, ‘The Ooze of Gluttony: Attitudes Towards Food, Eating and Excess in the Middle Ages’, in The Seven Deadly Sins: From Communities to Individuals, ed. Richard Newhauser (The Netherlands: Koninklijke Brill NV, 2007).
4 Richard I. Stein and Carol J. Nemeroff, ‘Moral Overtones of Food: Judgments of Others Based on What They Eat’, Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 21 (May 1995): 480–90.
5 Ibid.
6 Sarah-Jeanne Salvy, Julie C. Bowker, Lauren A. Nitecki, Melissa A. Kluczynski, Lisa J. Germeroth and James N. Roemmich, ‘Impact of Simulated Ostracism on Overweight and Normal-Weight Youths’ Motivation to Eat and Food Intake’, Appetite 56 (February 2011): 39–45.
7 Brian Wansink, ‘Can Package Size Accelerate Usage Volume?’ Journal of Marketing 60 (July 1996): 1–14; Brian Wansink and Junyong Kim, ‘Bad Popcorn in Big Buckets: Portion Size Can Influence Intake as Much as Taste’, Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior 37 (2005): 242–45.
8 Brian Wansink, ‘Environmental Factors That Increase the Food Intake and Consumption Volume of Unknowing Consumers’, Annual Review of Nutrition 24 (2004): 455–79.
9 Brian Wansink, James E. Painter and Jill North, ‘Bottomless Bowls: Why Visual Cues of Portion Size May Influence Intake’, Obesity Research 13 (2005): 93–100.
10 Brian Wansink and Koert Van Ittersum, ‘Bottoms Up! The Influence of Elongation On Pouring and Consumption Volume’, Journal of Consumer Research 30 (2003): 455–63.
11 For more on the ice cream study, see Brian Wansink, Koert van Ittersum and James E. Painter, ‘Ice Cream Illusions: Bowls, Spoons and Self-Served Portion Sizes’, American Journal of Preventive Medicine 31 (2006): 240–3; on office sweets consumption, see B. Wansink, J. E. Painter and Y-K. Lee, ‘The Office Candy Dish: Proximity’s Influence on Estimated and Actual Consumption’, International Journal of Obesity 30 (2006): 871–5; on M&M colors, see Barbara E. Kahn and Brian Wansink, ‘The Influence of Assortment Structure on Perceived Variety and Consumption Quantities’, Journal of Consumer Research 30 (2004): 519–33.
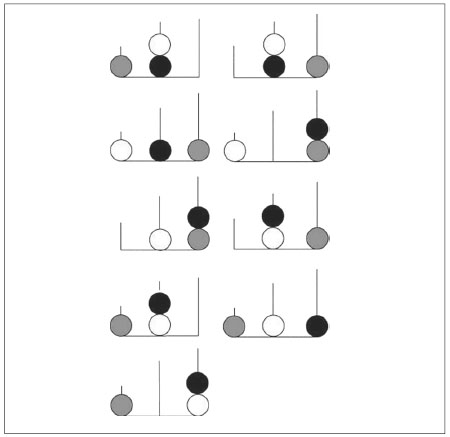
13 Michael W. Green and Peter J. Rogers, ‘Impairments in Working Memory Associated with Spontaneous Dieting Behaviour’, Psychological Medicine 28 (1998): 1063–70. (See diagram)
14 Ibid.
15 Matthew T. Gailliot, ‘Unlocking the Energy Dynamics of Executive Functioning’, Perspectives on Psychological Science 3 (2008): 245–63.
16 Matthew T. Gailliot, Roy F. Baumeister, C. Nathan DeWall, Jon K. Maner, E. Ashby Plant, Dianne M. Tice, Lauren E. Brewer and Brandon J. Schmeichel, ‘Self-Control Relies on Glucose as a Limited Energy Source: Willpower is More Than a Metaphor’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 92 (2007): 325–36.
17 Matthew T. Gailliot and Roy F. Baumeister, ‘The Physiology of Willpower: Linking Blood Glucose to Self-Control’, Personality and Social Psychology Review 11 (2007): 303–27; Gailliot, ‘Unlocking the Energy Dynamics of Executive Functioning’.
18 Matthew T. Gailliot, B. Michelle Peruche, E. Ashby Plant and Roy F. Baumeister, ‘Stereotypes and Prejudice in the Blood: Sucrose Drinks Reduce Prejudice and Stereotyping’, Journal of Experimental Social Psychology 45 (2009): 288–90.
19 Barbara Briers, Mario Pandelaere, Siegfried Dewitte and Luk Warlop, ‘Hungry for Money: The Desire for Caloric Resources Increases the Desire for Financial Resources and Vice Versa’, Psychological Science 17 (2006): 939–43.
20 Hans C. Breiter, Itzhak Aharon, Daniel Kahneman, Anders Dale and Peter Shizgal, ‘Functional Imaging of Neural Responses to Expectancy and Experience of Monetary Gains and Losses’, Neuron 30 (May 2001): 619–39; John P. O’Doherty, Ralf Diechmann, Hugo D. Critchley and Raymond J. Dolan, ‘Neural Responses During Anticipation of a Primary Taste Reward’, Neuron 33, no. 28 (2001): 815–26, 2002.
21 Briers et al., ‘Hungry for Money’.
22 The impact of labels was reported in Brian Wansink, Koert van Ittersum and James E. Painter, ‘How Diet and Health Labels Influence Taste and Satiation’, Journal of Food Science 69 (2004): S340-S346; the preferences for wine and chocolate cake were discussed in Brian Wansink, Mindless Eating: Why We Eat More Than We Think (New York: Bantam Dell, 2007).
23 Akshay R. Rao and Kent B. Monroe, ‘The Effect of Price, Brand Name and Store Name on Buyers’ Perceptions of Product Quality: An Integrative Review’, Journal of Marketing Research 26 (August 1989): 351–7.
24 Hilke Plassmann, John O’Doherty, Baba Shiv and Antonio Rangel, ‘Marketing Actions Can Modulate Neural Representations of Experienced Pleasantness’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 105 (January 2008): 1050–54.
25 Aner Sela, Jonah Berger and Wendy Liu, ‘Variety, Vice and Virtue: How Assortment Size Influences Option Choice’, Journal of Consumer Research 35 (April 2009): 941–51.
26 Sheena S. Iyengar and Mark R. Lepper, ‘When Choice Is Demotivating: Can One Desire Too Much of a Good Thing?’ Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 79 (2000): 995–1006.
27 Dan Ariely and Jonathan Levav, ‘Sequential Choice in Group Settings: Taking the Road Less Traveled and Less Enjoyed’, Journal of Consumer Research 27 (December 2000): 279–90.
28 Rozin et al., ‘Attitudes to Food and the Role of Food in Life’.
29 Rozin et al., ‘The Ecology of Eating’.
30 Ibid.
31 Wansink, Mindless Eating.
32 Richard Wrangham, Catching Fire: How Cooking Made Us Human (London: Profile Books, 2009).
33 Matthew W. Gillman, Sheryl L. Rifas-Shiman, A. Lindsay Frazier, Helaine R. H. Rockett, Carlos A. Camargo Jr., Alison E. Field, Catherine S. Berkey and Graham A. Colditz, ‘Family Dinner and Diet Quality Among Older Children and Adolescents’, Archives of Family Medicine 9 (March 2000): 235–40.
34 Oxford English Dictionary Online, s.v. ‘companion, n/1’, retrieved 1 January 2011, www.oed.com:80/Entry/37402.
Chapter 3: Greed
1 ‘Memorable Quotes for Wall Street’, Internet Movie Database, www.imdb.com/title/tt0094291/quotes, retrieved 4 January 2011.
2 Betsey Stevenson and Justin Wolfers, ‘Economic Growth and Subjective Well-Being: Reassessing the Easterlin Paradox’, Brookings Papers on Economic Activity (Spring 2008): 1–87.
3 Ibid., 65–7.
4 Aristotle, ‘The Politics’, in Aristotle: The Politics and the Constitution of Athens, ed. S. Everson and trans. J. Barnes (Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, 1996), 9–207, 185, 197.
5 Leaf Van Boven and Thomas Gilovich, ‘To Do or to Have? That is the Question’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 85 (2003): 1193–202.
6 Ibid.
7 Daniel Gilbert, Stumbling on Happiness (London: Harper Perennial, 2006).
8 Ibid.
9 Ed Diener and Robert Biswas-Diener, Happiness: Unlocking the Mysteries of Psychological Wealth (Malden, MA: Blackwell, 2008).
10 Ibid.
11 Ed Diener and Martin Seligman, ‘Beyond Money: Toward an Economy of Well-Being’, Psychological Science in the Public Interest 5 (2004): 1–31.
12 Diener and Biswas-Diener, Happiness (ibid.).
13 Ibid.
14 Thomas Gilovich, Robert Vallone and Amos Tversky, ‘The Hot Hand in Basketball: On the Misperception of Random Sequences’, Cognitive Psychology 17 (1985): 295–314.
15 Todd McFall, Charles Knoeber and Walter Thurman, ‘Contests, Grand Prizes and the Hot Hand’, Journal of Sports Economics 10 (2009): 236–55.
16 Douglas Jenkins Jr., Atul Mitra, Nina Gupta and Jason Shaw, ‘Are Financial Incentives Related to Performance? A Meta-analytic Review of Empirical Research’, Journal of Applied Psychology 83 (1998): 777–87.
17 Edward L. Deci, ‘Effects of Externally Mediated Rewards on Intrinsic Motivation’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 18 (1971): 105–15.
18 Philip Tetlock, Orie Kristel, Beth Elson, Melanie Green and Jennifer Lerner, ‘The Psychology of the Unthinkable: Taboo Trade-offs, Forbidden Base Rates and Heretical Counterfactuals’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 78 (2000): 853–70.
19 Dan Ariely, Predictably Irrational (London: Harper-Collins, 2008).
20 Uri Gneezy and Aldo Rustichini, ‘Pay Enough or Don’t Pay at All’, Quarterly Journal of Economics (August 2000): 791–810.
21 Kathleen Vohs, Nicole Mead and Miranda Goode, ‘Psychological Consequences of Money’, Science 314 (2006): 1154–56.
23 Kathleen Vohs, Nicole Mead and Miranda Goode, ‘Merely Activating the Concept of Money Changes Personal and Interpersonal Behavior’, Current Directions in Psychological Science 17 (2008): 209.
24 Xinyue Zhou, Kathleen Vohs and Roy Baumeister, ‘The Symbolic Power of Money: Reminders of Money Alter Social Distress and Physical Pain’, Psychological Science 20 (2009): 700–6.
25 Ibid.
26 Kathleen Vohs, ‘Small Reminders of Money Elicit Big Changes in Behavior’ (keynote address at 39th Annual Conference of the Society of Australasian Social Psychologists, Melbourne, Australia, 2009).
27 Kathleen Vohs, Nicole Mead and Miranda Goode, ‘Psychological Consequences of Money’, Science 314 (2006): 1154–6.
28 Stephen Lea and Paul Webley, ‘Money as Tool, Money as Drug: The Biological Psychology of a Strong Incentive’, Behavioral and Brain Sciences 29 (2006): 161–209.
Chapter 4: Sloth
1 Oxford English Dictionary Online, s.v. ‘sloth’, retrieved 29 December 2010, www.oed.com:80/Entry/182099.
2 Robert E. Sinkewicz, Evagrius of Pontus: The Greek Ascetic Corpus (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2006), 99.
3 Max Weber, The Protestant Ethic and the ‘Spirit’ of Capitalism and Other Writings (New York: Penguin Books, 2002).
4 Bertrand Russell, In Praise of Idleness (London: Allen & Unwin, 1935), 12.
5 Robert Louis Stevenson, ‘An Apology for Idlers’, 1876, retrieved from essays.quotidiana.org/stevenson/apology_for_idlers/.
6 Sheldon Cohen, William J. Doyle, Cuneyt M. Alper, Denise Janicki-Deverts and Ronald B. Turner, ‘Sleep Habits and Susceptibility to the Common Cold’, Archives of Internal Medicine 169 (2009): 62–7.
7 Matthew P. Walker and Robert Stickgold, ‘Sleep, Memory and Plasticity’, Annual Review of Psychology 57 (2006): 139–66.
8 Jessica D. Payne, Daniel L. Schacter, Ruth E. Propper, Li-Wen Huang, Erin J. Wamsley, Matthew A. Tucker, Matthew P. Walker and Robert Stickgold, ‘The Role of Sleep in False Memory Formation’, Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 92 (2009): 327–34.
9 Ibid.
10 Jessica D. Payne and Elizabeth A. Kensinger, ‘Sleep’s Role in the Consolidation of Emotional Episodic Memories’, Current Directions in Psychological Science 19 (2010): 290–5.
11 Walker and Stickgold, ‘Sleep, Memory and Plasticity.’
12 Ullrich Wagner, Steffen Gais, Hilde Haider, Rolf Verleger and Jan Born, ‘Sleep Inspires Insight’, Nature 427 (2004): 352–5.
13 Denise J. Cai, Sarnoff A. Mednick, Elizabeth M. Harrison, Jennifer C. Kanady and Sara C. Mednick, ‘REM, not Incubation, Improves Creativity by Priming Associative Networks’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106 (2009): 10130–34.
14 Erin J. Wamsley, Matthew Tucker, Jessica D. Payne, Joseph A. Benavides and Robert Stickgold, ‘Dreaming of a Learning Task is Associated with Enhanced Sleep-Dependent Memory Consolidation’, Current Biology 20 (2010): 850–5.
15 Ibid.
16 Jonathan Schooler, Erik Reichle and David Halpern, ‘Zoning Out While Reading: Evidence for Dissociations Between Experience and Metaconsciousness’, in Thinking and Seeing: Visual Metacognition in Adults and Children, ed. Daniel Levin (Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2004), 203–26.
17 Eric Klinger and Miles Cox, ‘Dimensions of Thought Flow in Everyday Life’, Imagination, Cognition and Personality 7 (1987–1988): 105–28.
18 Deborah F. Greenwald and David W. Harder, ‘Fantasies, Coping Behavior and Psychopathology’, Journal of Clinical Psychology 59 (October 2003): 1089–95.
19 John Kounios, Jennifer L. Frymiare, Edward M. Bowden, Jessica I. Fleck, Karuna Subramaniam, Todd B. Parrish and Mark Jung-Beeman, ‘The Prepared Mind: Neural Activity Prior to Problem Presentation Predicts Subsequent Solution by Sudden Insight’, Psychological Science 17 (2006): 882–90.
20 Kalina Christoff, Alan M. Gordon, Jonathan Smallwood, Rachelle Smith and Jonathan W. Schooler, ‘Experience Sampling during MRI Reveals Default Network and Executive System Contributions to Mind Wandering’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106 (2009): 8719–24.
21 Malia F. Mason, Michael I. Norton, John D. Van Horn, Daniel M. Wegner, Scott T. Grafton and C. Neil Macrae, ‘Wandering Minds: The Default Network and Stimulus-Independent Thought’, Science 315 (2007): 393–5.
22 Jackie Andrade, ‘What Does Doodling Do?’ Applied Cognitive Psychology 24 (2010): 100–6.
23 K. Anders Ericsson, Ralf T. Krampe and Clemens Tesch-Romer, ‘The Role of Deliberate Practice in the Acquisition of Expert Performance’, Psychological Review 100 (1993): 363–406; Malcolm Gladwell, Outliers: The Story of Success (New York: Little, Brown/Hachette Book Group, 2008).
24 Nicholas O. Rule and Nalini Ambady, ‘The Face of Success: Inferences from Chief Executive Officers’ Appearance Predict Company Profits’, Psychological Science 19 (2008): 109–11.
25 Timothy D. Wilson and Jonathan W. Schooler, ‘Thinking Too Much: Introspection Can Reduce the Quality of Preferences and Decisions’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 60 (1991): 181–92.
26 Ap Dijksterhuis, Rick. B. van Baaren, Karin C. A. Bongers, Maarten W. Bos, Matthijs L. van Leeuwen and Andries van der Leij, ‘The Rational Unconscious: Conscious Versus Unconscious Thought in Complex Consumer Choice’ in Social Psychology of Consumer Behavior, ed. Michaela Wanke (New York: Psychology Press, 2009), 468–77.
27 Ibid.
28 Ap Dijksterhuis and Loran F. Nordgren, ‘A Theory of Unconscious Thought’, Perspectives on Psychological Science 1 (2006): 95–109.
29 Ben R. Newell, Kwan Yao Wong, Jeremy C. H. Cheung and Tim Rakow, ‘Think, Blink or Sleep on It? The Impact of Modes of Thought on Complex Decision Making’, Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 62 (2009): 707–32; John W. Payne, Adriana Samper, James R. Bettman and Mary Frances Luce, ‘Boundary Conditions on Unconscious Thought in Complex Decision Making’, Psychological Science 19 (2008): 1118–23.
30 Dijksterhuis et al., ‘The Rational Unconscious’ (ibid.).
31 Jaap Ham, Kees van den Bos and Evert A. Van Doorn, ‘Lady Justice Thinks Unconsciously: Unconscious Thought Can Lead to More Accurate Justice Judgments’, Social Cognition 27 (2009): 509–21.
32 John A. Bargh, Mark Chen and Lara Burrows, ‘Automaticity of Social Behavior: Direct Effects of Trait Construct and Stereotype Activation on Action’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 71 (1996): 230–44.
33 Rob Gray and Russ Branaghan, ‘Changing Driver Behavior Through Unconscious Stereotype Activation’, in Proceedings of the Fifth International Driving Symposium on Human Factors in Driver Assessment, Training and Vehicle Design (2009).
34 Robert Levine, A Geography of Time (New York: Basic Books, 1997).
35 Ibid.
36 Robert V. Levine, Karen Lynch, Kunitate Miyake and Marty Lucia, ‘The Type A City: Coronary Heart Disease and the Pace of Life’, Journal of Behavioral Medicine 12 (1989): 509–24.
37 Robert V. Levine, Stephen Reysen and Ellen Ganz, ‘The Kindness of Strangers Revisited: A Comparison of 24 US Cities’, Social Indicators Research 85 (2008): 461–81.
38 Ibid.
39 John M. Darley and C. Daniel Batson, ‘From Jerusalem to Jericho: A Study of Situational and Dispositional Variables in Helping Behavior’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 27 (1973): 100–8.
40 Ibid., 101.
41 Ibid., 102.
42 Stanley Milgram, ‘The Experience of Living in Cities’, Science 167 (March 1970): 1461–8.
43 Ibid.
Chapter 5: Anger
1 Oxford English Dictionary Online, s.v. ‘violence, n’, retrieved 29 December 2010, www.oed.com:80/Entry/223638.
2 Joel R. Davitz, The Language of Emotion (New York: Academic Press, 1969).
3 Jill Lobbestael, Arnoud Arntz and Reinout W. Wiers, ‘How to Push Someone’s Buttons: A Comparison of Four Anger-Induction Methods’, Cognition and Emotion 22 (2008): 353–73.
4 The first estimate is from Howard Kassinove, Denis G. Sukhodolsky, Sergei V. Tsytsarev and Svetlana Solovyova, ‘Self-Reported Anger Episodes in Russia and America’, Journal of Social Behavior and Personality 12 (1997); 301–24; the second from H. Meltzer, ‘Students’ Adjustments in Anger’, Journal of Social Psychology 4 (August 1933): 285–309.
5 Evidence of cardiovascular problems is reported in Janice E. Williams, Catherine C. Paton, Ilene C. Siegler, Marsha L. Eigenbrodt, F. Javier Nieto and Herman A. Tyroler, ‘Anger Proneness Predicts Coronary Heart Disease Risk: Prospective Analysis from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study’, Circulation 101 (May 2000): 2034–9; Patricia P. Chang, Daniel E. Ford, Lucy A. Meoni, Nae-Yuh Wang and Michael J. Klag, ‘Anger in Young Men and Subsequent Premature Cardiovascular Disease: The Precursors Study’, Archives of Internal Medicine 162 (2002): 901–6. Other risk factors are noted in Jerry L. Deffenbacher, Maureen E. Huff, Rebekah S. Lynch, Eugene R. Oetting and Natalie F. Salvatore, ‘Characteristics and Treatment of High-Anger Drivers’, Journal of Counseling Psychology 47 (2000): 5–17.
6 Mario Mikulincer, ‘Reactance and Helplessness Following Exposure to Unsolvable Problems: The Effects of Attributional Style’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 54 (1988): 679–86.
7 Michael Cosio, ‘Soda Pop Vending Machine Injuries’, Journal of the American Medical Association 260 (1988): 2697–9.
8 Charles S. Carver and Eddie Harmon-Jones, ‘Anger is an Approach-Related Effect: Evidence and Implications’, Psychological Bulletin 135 (2009): 183–204.
9 Ibid.
10 Maya Tamir, Christopher Mitchell and James J. Gross, ‘Hedonic and Instrumental Motives in Anger Regulation’, Psychological Science 19 (2008): 324–8.
11 Brett Q. Ford, Maya Tamir, Tad T. Brunyé, William R. Shirer, Caroline R. Mahoney and Holly A. Taylor, ‘Keeping Your Eyes on the Prize: Anger and Visual Attention to Threats and Rewards’, Psychological Science 21 (2010): 1098–105.
12 John Cassian, The Institutes of the Coenobia and the Remedies for the Eight Principal Vices, trans. Boniface Ramsey, OP, in Ancient Christian Writers, vol. 58 (Mahwah, NJ: Newman Press, 2000).
13 Norbert Schwarz and Gerald L. Clore, ‘Mood, Misattribution and Judgments of Well-Being: Informative and Directive Functions of Affective States’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 45 (1983): 513–23.
14 Jennifer S. Lerner and Dacher Keltner, ‘Fear, Anger and Risk’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 81 (2001): 146–59.
15 Maia J. Young, Larissa Z. Tiedens, Heajung Jung and Ming-Hong Tsai, ‘Mad Enough to See the Other Side: Anger and the Search for Disconfirming Information’, Cognition and Emotion 25 (2011) 110–21.
16 Ibid.
17 Wesley G. Moons and Diane M. Mackie, ‘Thinking Straight While Seeing Red: The Influence of Anger on Information Processing’, Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 33 (2007): 706–20.
18 Joseph Henrich, Steven J. Heine and Ara Norenzayan, ‘The Weirdest People in the World’, Behavioral and Brain Sciences 33 (2010): 61–83.
19 Jonathan Haidt, ‘The New Synthesis in Moral Psychology’, Science 316 (2007): 998–1002; Jonathan Haidt and Jesse Graham, ‘When Morality Opposes Justice: Conservatives Have Moral Intuitions That Liberals May Not Recognize’, Social Justice Research 20 (March 2007): 98–116.
20 Haidt and Graham, ibid. (2).
21 Henrich, Heine and Norenzayan, ‘The Weirdest People in the World’ (ibid.).
22 Jonathan Haidt, ‘The Emotional Dog and Its Rational Tail: A Social Intuitionist Approach to Moral Judgment’, Psychological Review 108 (2001): 814–34; Paul Rozin, Laura Lowery, Sumio Imada and Jonathan Haidt, ‘The CAD Triad Hypothesis: A Mapping Between Three Moral Emotions (Contempt, Anger, Disgust) and Three Moral Codes (Community, Autonomy, Divinity)’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 76 (1999): 574–86.
23 Roberto Gutierrez and Roger Giner-Sorolla, ‘Anger, Disgust and Presumption of Harm as Reactions to Taboo-Breaking Behaviors’, Emotion 7 (2007): 853–68.
24 Joydeep Srivastava, Francine Espinoza, and Alexander Fedorikhin, ‘Coupling and Decoupling of Unfairness and Anger in Ultimatum Bargaining’, Journal of Behavioral Decision Making 22 (2009): 475–89.
25 Larissa Z. Tiedens, ‘Anger and Advancement Versus Sadness and Subjugation: The Effect of Negative Emotion Expressions of Social Status Conferral’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 80 (2001): 86–94.
26 Ibid.
27 Ibid.
28 Adam Nagourney, ‘Calling Senator Clinton “Angry,” G.O.P. Chairman Attacks’, New York Times, 5 February 2006, A16.
29 Maureen Dowd, ‘Who’s Hormonal? Hillary or Dick?’, New York Times, 8 February 2006, A21.
30 Victoria L. Brescoll and Eric Luis Uhlmann, ‘Can an Angry Woman Get Ahead? Status Conferral, Gender and Expression of Emotion in the Workplace’, Psychological Science 19 (2008): 268–75.
31 Gerben A. van Kleef, Carsten K. W. De Dreu and Antony S. R. Manstead, ‘The Interpersonal Effects of Anger and Happiness in Negotiations’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 86 (2004): 57–76.
32 Marwan Sinaceur and Larissa Z. Tiedens, ‘Get Mad and Get More Than Even: When and Why Anger Expression Is Effective in Negotiations’, Journal of Experimental Social Psychology 42 (2006): 314–22.
33 Gerben A. van Kleef and Stéphane Côté, ‘Expressing Anger in Conflict: When it Helps and When it Hurts’, Journal of Applied Psychology 92 (2007): 1557–69.
34 Hajo Adam, Aiwa Shirako and William W. Maddux, ‘Cultural Variance in the Interpersonal Effects of Anger in Negotiations’, Psychological Science 21 (2010): 882–9.
35 James R. Averill, ‘Studies on Anger and Aggression: Implications for Theories of Emotion’, American Psychologist 38 (November 1983): 1145–60; Kassinove et al., ‘Self-Reported Anger Episodes in Russia and America.’ Howard Kassinove, Denis G. Sukhodolsky, Sergei V. Tsytsarev and Svetlana Solovyova, ‘Self-Reported Anger Episodes in Russia and America’, Journal of Social Behavior and Personality 12 (997): 301–24.
36 Kassinove et al., ‘Self-Reported Anger Episodes in Russia and America’ (ibid.); Raymond Chip Tafrate, Howard Kassinove and Louis Dundin, ‘Anger Episodes in High- and Low-Trait-Anger Community Adults’, Journal of Clinical Psychology 58 (2002): 1573–90.
37 Kassinove et al., ‘Self-Reported Anger Episodes in Russia and America’ (ibid.).
38 Tafrate, Kassinove and Dundin, ‘Anger Episodes in High- and Low-Trait-Anger Community Adults’ (ibid.).
39 Mary Gordon, ‘Anger’, in Deadly Sins, ed. Thomas Pynchon (New York: William Morrow, 1993).
Chapter 6: Envy
1 W. Gerrod Parrott and Richard H. Smith, ‘Distinguishing the Experiences of Envy and Jealousy’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 64 (1993): 906–20.
2 Leon Festinger, ‘A Theory of Social Comparison Processes’, Human Relations 7 (1954): 117–40.
3 Francis Bacon, ‘Of Envy’, The Essays (London: Penguin Group, 1985), 83–7.
4 Daniel T. Gilbert, Kathryn A. Morris and R. Brian Giesler, ‘When Comparisons Arise’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 69 (1995): 227–36.
5 Lisa G. Aspinwall and Shelley E. Taylor, ‘Effects of Social Comparison Direction, Threat, and Self-Esteem on Affect, Self-Evaluation, and Expected Success’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 64 (1993): 708–22.
6 Ladd Wheeler, ‘Motivation as a Determinant of Upward Comparison’, Supplement 1, Journal of Experimental Social Psychology (1966): 27–31.
7 Penelope Lockwood and Ziva Kunda, ‘Superstars and Me: Predicting the Impact of Role Models on the Self, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 73 (1997): 91–103.
8 George Loewenstein, ‘Anticipation and the Valuation of Delayed Consumption’, Economic Journal 97 (September 1987): 666–84.
9 Ibid.
10 Richard H. Smith and Sung Hee Kim, ‘Comprehending Envy’, Psychological Bulletin 133 (2007): 46–64.
11 Camille S. Johnson and Diederik A. Stapel, ‘No Pain, No Gain: The Conditions Under Which Upward Comparisons Lead to Better Performance’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 92 (2007): 1051–67.
12 Hart Blanton, Bram P. Buunk, Frederick X. Gibbons and Hans Kuyper, ‘When Better-Than-Others Compare Upward: Choice of Comparison and Comparative Evaluation as Independent Predictors of Academic Performance’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 76 (1999): 420–30.
13 John J. Seta, ‘The Impact of Comparison Processes on Coactors’ Task Performance’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 42 (1982): 281–91; David M. Marx and Jasmin S. Roman, ‘Female Role Models: Protecting Women’s Math Test Performance’, Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 28 (2002): 1183–93.
14 Naomi Mandel, Petia K. Petrova and Robert B. Cialdini, ‘Images of Success and the Preference for Luxury Brands’, Journal of Consumer Psychology 16 (2006): 57–69.
15 Lockwood and Kunda, ‘Superstars and Me.’
16 Ibid.
17 Timothy D. Wilson, Thalia Wheatley, Jonathan M. Meyers, Daniel T. Gilbert and Danny Axsom, ‘Focalism: A Source of Durability Bias in Affective Forecasting’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 78 (2000): 821–36.
18 Philip Brickman, Dan Coates and Ronnie Janoff-Bulman, ‘Lottery Winners and Accident Victims: is Happiness Relative?’ Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 36 (1978): 917–27.
19 Richard E. Lucas and Andrew E. Clark, ‘Do People Really Adapt to Marriage?’ Journal of Happiness Studies 7 (2006): 405–26; Richard E. Lucas, Andrew E. Clark, Yannis Georgellis and Ed Diener, ‘Reexamining Adaptation and the Set Point Model of Happiness: Reactions to Changes in Marital Status’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 84 (2003): 527–39.
20 Jaime L. Kurtz, Timothy D. Wilson and Daniel T. Gilbert, ‘Quantity Versus Uncertainty: When Winning One Prize is Better Than Winning Two’, Journal of Experimental Social Psychology 43 (2007): 979–85.
21 Timothy Wilson, Jay Meyers and Daniel Gilbert, “How Happy Was I, Anyway?” A Retrospective Impact Bias’, Social Cognition 21 (2003): 407–32.
22 Timothy Wilson, David Centerbar, Deborah Kermer and Daniel Gilbert, ‘The Pleasures of Uncertainty: Prolonging Positive Moods in Ways People Do Not Anticipate’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 88 (2005): 5–21.
23 Douglas H. Wedell and Allen Parducci, ‘The Category Effect in Social Judgment: Experimental Ratings of Happiness’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 55 (1988): 341–56.
24 Christopher K. Hsee, Reid Hastie and Jingqiu Chen, ‘Hedonomics: Bridging Decision Research with Happiness Research’, Perspectives on Psychological Science 3 (2008): 224–43.
25 Christopher K. Hsee, Yang Yang, Naihe Li and Luxi Shen, ‘Wealth, Warmth, and Well-Being: Whether Happiness Is Relative or Absolute Depends on Whether It Is About Money, Acquisition, or Consumption’, Journal of Marketing Research 46 (2009): 396–409.
26 Ibid.
Chapter 7: Pride
1 Stanford M. Lyman, The Seven Deadly Sins: Society and Evil, rev. ed. (Dix Hills, NY: General Hall, 1989), 136; Michael Eric Dyson, Pride: The Seven Deadly Sins (New York: Oxford University Press, 2006); Matthew Baasten, Pride According to Pope Gregory the Great: A Study of the Moralia (Lewiston, NY: Edwin Mellen Press, 1986).
2 Jessica L. Tracy and Richard W. Robins, ‘The Psychological Structure of Pride: A Tale of Two Facets’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 92 (2007): 506–25.
3 Aristotle, The Ethics of Aristotle: The Nicomachean Ethics (New York: Viking, 1955).
4 Tracy and Robins, ‘The Psychological Structure of Pride’ (ibid.).
5 Martin Amis, The Moronic Inferno (London: Jonathan Cape, 1986), 105.
6 Gore Vidal, ‘Pride’, in Deadly Sins, ed. Thomas Pynchon (New York: William Morrow, 1993), 67.
7 Jessica L. Tracy, Azim F. Shariff and Joey T. Cheng, ‘A Naturalist’s View of Pride’, Emotion Review 2 (April 2010): 163–77.
8 Roy F. Baumeister, Jennifer D. Campbell, Joachim I. Krueger and Kathleen D. Vohs, ‘Does High Self-Esteem Cause Better Performance, Interpersonal Success, Happiness or Healthier Lifestyles?’ Psychological Science in the Public Interest 4 (May 2003): 1–44.
9 Lisa A. Williams and David DeSteno, ‘Pride and Perseverance: The Motivational Role of Pride’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 94 (2008): 1007–17.
10 Willem Verbeke, Frank Belschak and Richard P. Bagozzi, ‘The Adaptive Consequences of Pride in Personal Selling’, Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 32 (2004): 386–402.
11 Mary M. Herrald and Joe Tomaka, ‘Patterns of Emotion-Specific Appraisal, Coping and Cardiovascular Reactivity During an Ongoing Emotional Episode’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 83 (2002): 434–50.
12 Lisa A. Williams and David DeSteno, ‘Pride: Adaptive Social Emotion or Seventh Sin?’ Psychological Science 20 (2009): 284–8.
13 Ibid.
14 Jessica L. Tracy, Joey T. Cheng, Richard W. Robins and Kali H. Trzesniewski, ‘Authentic and Hubristic Pride: The Affective Core of Self-Esteem and Narcissism’, Self and Identity 8 (2009): 196–213.
15 MacArthur Foundation Research Network on Successful Midlife Development, Midlife in the United States: A National Study of Health and Well-Being (1994–1995).
16 Daniel Hart and M. Kyle Matsuba, ‘The Development of Pride and Moral Life’, in The Self-Conscious Emotions: Theory and Research, eds. Jessica L. Tracy, Richard W. Robins and June Price Tangney (New York: Guilford Press, 2007), 114–33.
17 Robert B. Cialdini, Richard J. Borden, Avril Thorne, Marcus Randall Walker, Stephen Freeman and Lloyd Reynolds Sloan, ‘Basking in Reflected Glory: Three (Football) Field Studies’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 34 (1976): 366–75.
18 Chris B. Miller, ‘Yes We Did! Basking in Reflected Glory and Cutting Off Reflected Failure in the 2008 Presidential Election’, Analyses of Social Issues and Public Policy 9 (2009): 283–96.
19 Tracy et al., ‘Authentic and Hubristic Pride’ (ibid.).
20 Claire E. Ashton-James and Jessica L. Tracy, ‘Pride and Prejudice: How Feelings About the Self, Influence Judgments of Others’, manuscript submitted for publication.
21 W. Keith Campbell and Laura E. Buffardi, ‘The Lure of the Noisy Ego: Narcissism as a Social Trap’, in Quieting the Ego: Psychological Benefits of Transcending Egotism, eds. J. Bauer and H. Wayment (Washington, DC: American Psychological Association, 2008), 23–32.
22 Ibid.
23 Ibid.
24 Jessica L. Tracy and David Matsumoto, ‘The Spontaneous Expression of Pride and Shame: Evidence for Biologically Innate Nonverbal Displays’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105 (2008): 11655–60.
25 Jessica L. Tracy and Richard W. Robins, ‘Show Your Pride: Evidence for a Discrete Emotion Expression’, Psychological Science 15 (2004): 194–7; Jessica L. Tracy, Richard W. Robins and Kristin H. Lagattuta, ‘Can Children Recognize the Pride Expression?’, Emotion 5 (2005): 251–7; Jessica L. Tracy and Richard W. Robins, ‘The Nonverbal Expression of Pride: Evidence for Cross-Cultural Recognition’, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 94 (2008): 516–30.
26 Michael D. Ruel, ‘Vanity Tax: How New Jersey has Opened Pandora’s Box by Elevating its Moral Judgment About Cosmetic Surgery Without Consideration of Fair Health Care Policy’, Journal of Legal Medicine 28 (2007): 119–34.
27 David J. Berri, Rob Simmons, Jennifer Van Gilder and Lisle O’Neill, ‘What Does It Mean to Find the Face of the Franchise? Physical Attractiveness and the Evaluation of Athletic Performance’ (paper presented at Western Economic Association International 85th Annual Conference, Portland, 29 June to 3 July 2010).
28 Vicki Ritts, Miles L. Patterson and Mark E. Tubbs, ‘Expectations, Impressions, and Judgments of Physically Attractive Students: A Review’, Review of Educational Research 62 (1992): 413–26.
29 Daniel S. Hamermesh and Jeff E. Biddle, ‘Beauty and the Labor Market’, American Economic Review 84 (2004): 1174–94.
30 Ibid.
31 Naci Mocan and Erdal Tekin, ‘Ugly Criminals’, Review of Economics and Statistics 92 (2010): 15–30.
32 Judith Langlois, Lisa Kalakanis, Adam Rubenstein, Andrea Larson, Monica Hallam and Monica Smoot, ‘Maxims or Myths of Beauty? A Meta-Analytic and Theoretical Review’, Psychological Bulletin 126 (2000): 390–423.
33 Ibid.; Stephen West and Jan Brown, ‘Physical Attractiveness, the Severity of the Emergency and Helping: A Field Experiment and Interpersonal Simulation’, Journal of Experimental Social Psychology 11 (1975): 531–8.
34 Michael T. French, Philip K. Robins, Jenny F. Homer and Lauren M. Tapsell, ‘Effects of Physical Attractiveness, Personality, and Grooming on Academic Performance in High School’, Labor Economics 16 (2009): 373–82.
35 Sam Gosling, Snoop: What Your Stuff Says About You (London: Profile Books, 2008).
36 Ibid.
37 Monroe Lefkowitz, Robert R. Blake and Jane Srygley Mouton, ‘Status Factors in Pedestrian Violation of Traffic Signals’, Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology 51 (November 1955): 704–6.
38 Christopher Hitchens, Hitch-22: A Memoir (New York: Twelve/Hachette Book Group, 2010).
Conclusion
1 Andy Ridgway, ‘The Human Brain: Hardwired to Sin’, BBC Focus 212 (2010).
2 Nicola Gori, ‘The New Forms of Social Sin’, L’Osservatore Romano, 9 March 2008.
3 Craig Brown, ‘Out with the Old Deadly Sins, in with the New’, Scotsman, 7 February 2005.