Companies today, especially corporations, have strict guidelines on how and where to deploy solutions. The first question that should be answered is which type of deployment will be needed, since it will greatly influence our solution architecture.
Usually, we can split possible deployments into four categories:
- A public cloud platform is accessible and open to the public, to individuals or organizations, and is owned by a company that sells cloud computing services. In the case of public platforms, the question of the security of personal data is raised. Apps from different users are often located on the same servers, storage systems, and networks. Public clouds reduce security risks and costs by providing a variable infrastructure. They make the temporary leased infrastructure of the organization. If the public cloud is implemented with a performance-oriented focus, the security and location of other applications launched on the cloud should not create problems with the cloud architecture and end users.
One of the benefits of public clouds is that they can be much larger than private clouds. Public clouds offer the ability to increase or decrease the leased part of the cloud, and shift responsibilities, if unplanned risks arise, from the organization to service providers. Public cloud components can also be under the exclusive use of only one user, making a private data center. However, incorporating images of virtual machines into the public cloud does not provide insight into the cloud infrastructure, while leasing data centers gives users greater insights into the infrastructure itself. Then, users can manage not only virtual machine images but also servers, storage systems, network devices, and network topologies. Creating a private virtual data center with components in the same object reduces the problem of having a multitude of different data locations, because the upload speed is much larger when connecting objects within the same cloud. This kind of offering usually utilizes a pay-per-usage model.
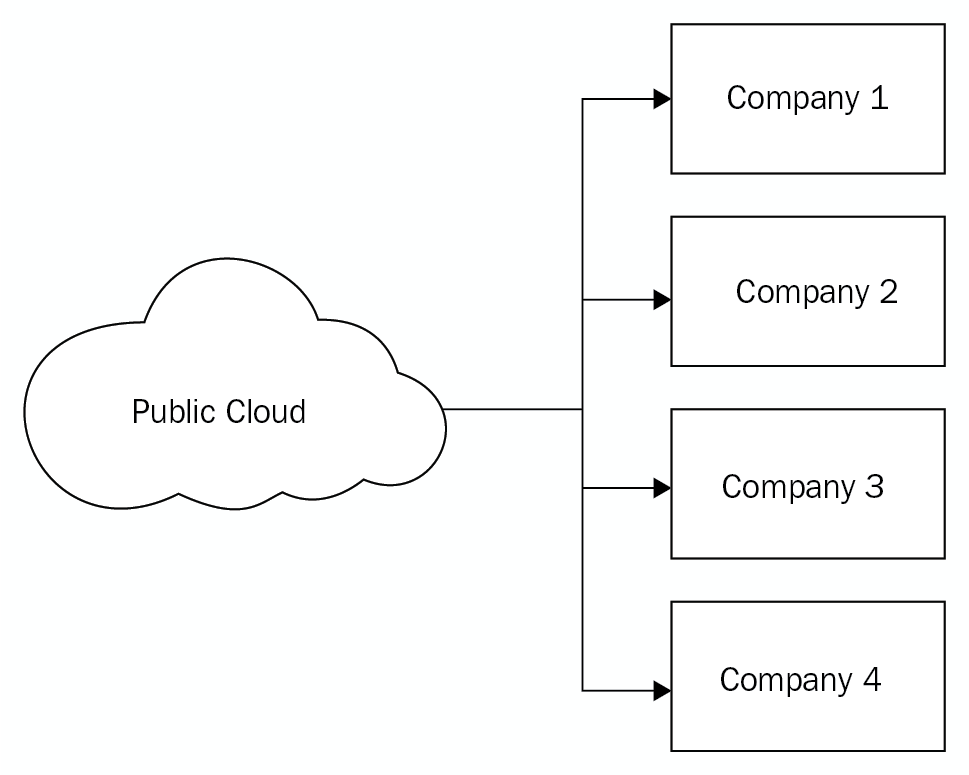
The following diagram outlines how public clouds are utilized. All four companies are connecting to the same cloud, but each of the companies are sandboxed, so that there are no interactions between the data or processes of each company:
- A Private Cloud is available to one organization only. It can be managed by the organization itself, or by someone else. Organizations use private clouds when they need or want more data control than they can get by using public clouds. Private clouds are designed solely for the use of a single client, giving them the highest degree of data control and the highest level of security for the data on the cloud. The organization has the infrastructure, and has control over the distribution of applications on its own infrastructure. Private clouds can also be deployed within the organizational data center. IT service companies, or service providers, build and manage private clouds. Organizations that have a private cloud can install programs, apps, store data, and can manage the cloud structure. Private clouds also provide companies with a high level of control over the use of cloud resources.
The following diagram outlines how private clouds are utilized. Company PCs are connected to the cloud, and consume the cloud's resources. Only PCs that are a part of that company can access the private cloud's resources:

- Managed services demand that the business should outsource certain processes and systems. The goal of managed services is for the company to attain up-to-date technology, have access to skills, and address problems associated with value, quality of service, and risk, because the IT infrastructure elements of the many small and medium businesses (SMB) and enormous companies are migrating to the cloud, with managed services providers (MSPs) facing the challenge of cloud computing more and more. A variety of MSPs are providing in-house cloud services, or are acting as brokers with cloud services suppliers. The absence of information and experience in cloud computing, rather than the companies, reluctance, seems to be the main obstacle for the companies making transition.
The purpose of managed services is to enable companies to always have the latest technology, and the know-how associated with it, without the investment in the hardware or people required to run the service. Companies providing this service are called MSPs. MSPs can manage in-house systems and processes, cloud-based systems, or a combination of both. Usually, MSPs also take care of communication with the cloud provider. MSPs remediate the main problem with the adoption of cloud-based solutions—a lack of knowledge and experience—since the company is purchasing this service from the MSP.
The following diagram outlines how the managed services model is utilized. The company consumes cloud resources, and it is on premise infrastructure as a service. All maintenance and configuration are outsourced to the managing company:

- On premise is a traditional method employed for the running of enterprise software, which means that the company owns and runs the software on its own servers.
The following diagram outlines how the on premise model is utilized. The company is managing all of its infrastructure and PCs:

These categories are not exclusive, and usually, for best results, they can be combined and we can use a hybrid approach to solution architecture.
- Hybrid clouds can also be used to manage large planned loads. While private clouds can be used to perform periodic tasks that simply divide same workloads between on premise and public clouds, hybrid clouds encounter the complexity of determining how to distribute public and private cloud applications. In addition to this problem, you must also take into account the relationship between data and resource processing. If the data is small, or the application does not remember the condition, the hybrid cloud may be a better solution than copying a large amount of data into a public cloud (where simple processing is performed).