Practice Test 1
Click here to download a PDF of Practice Test 1.
PRACTICE SAT SUBJECT TEST IN CHEMISTRY–TEST 1
You are about to take the first of three practice SAT Subject Tests in Chemistry. The bubble sheet can be found near the back of the book; feel free to tear it out for use. (Just don’t lose it!)
After answering questions 1–23, which constitute Part A, you’ll be directed to answer questions 101–116, which constitute Part B. Then you will begin again at question 24. Questions 24–70 constitute Part C.
When you’re ready to score yourself, refer to the answer key and scoring instructions on this page and this page. Full explanations regarding the correct answers to all questions start on this page.
SAT SUBJECT TEST IN CHEMISTRY
MATERIAL IN THE FOLLOWING TABLE MAY BE USEFUL IN ANSWERING THE QUESTIONS IN THIS EXAMINATION.
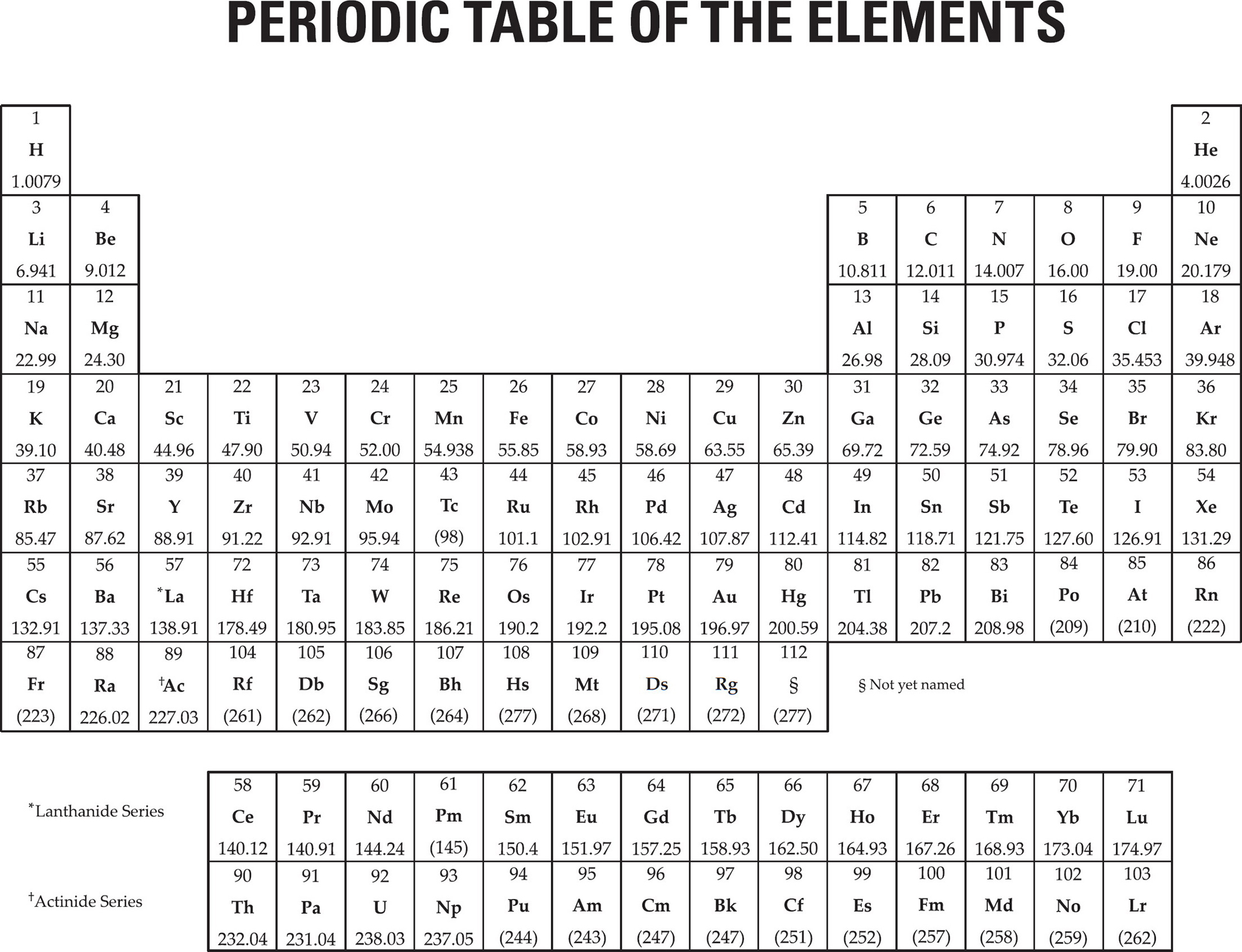
SAT SUBJECT TEST IN CHEMISTRY—TEST 1
Note: For all questions involving solutions and/or chemical equations, assume that the system is in pure water unless otherwise stated.
Part A
Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered statements or questions immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement or answers each question, and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set.
Questions 1-4 refer to the following.
(A) Thermometer
(B) Conductivity tester
(C) Volumetric flask
(D) Buret
(E) Graduated cylinder
1. May be used in combination with a calorimeter to compare the specific heats of two substances
2. Is used to measure the volume of a solid by water displacement
3. Useful for adding small quantities of acid into a base
4. Is considered infinitely precise at a specific volume
Questions 5-9 refer to the following.
(A) Nucleic acids
(B) Proteins
(C) Carbohydrates
(D) Lipids
(E) Electrolytes
5. Always amphoteric in nature
6. Found as both straight-chained and branched polymers
7. Deoxyribose in DNA nucleotides belongs to this family of biologically important molecules
8. Always ionic in nature
9. Tend not to be water soluble, and aggregate into droplets or molecular bilayers
Questions 10-13 refer to the following.
(A) Ag+ + Br− → AgBr
(B) 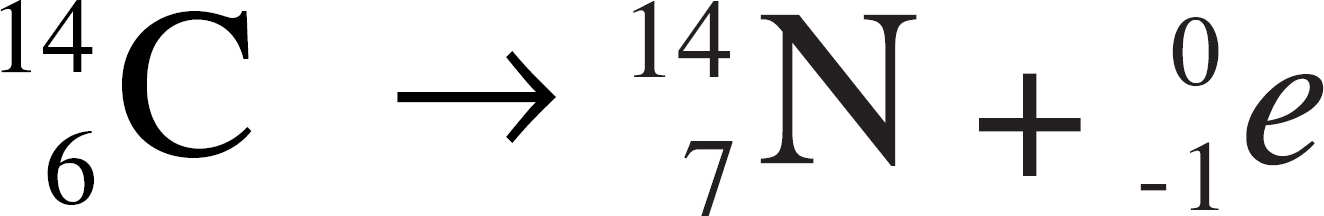
(C) 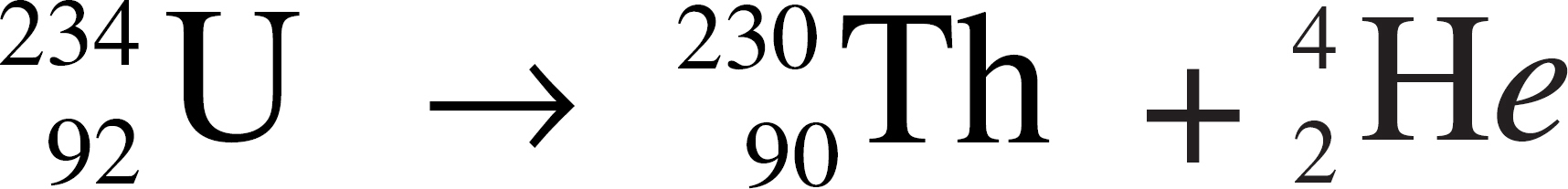
(D) 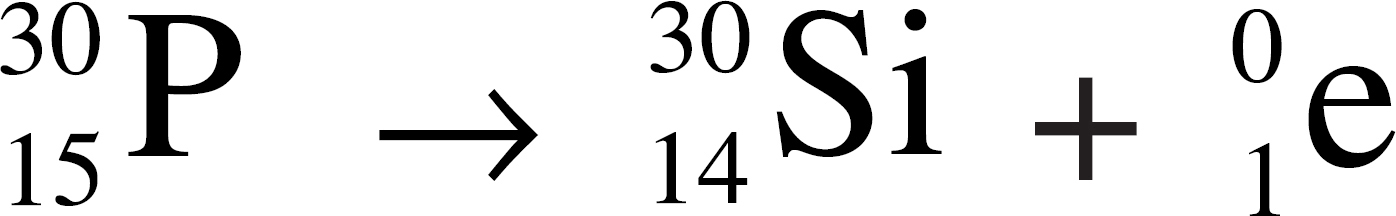
(E) 2HgO → 2Hg + O2
10. Represents the decomposition of a compound into its constituent elements
11. Represents alpha decay
12. Represents an oxidation-reduction reaction
13. Causes the neutron-to-proton ratio in a nucleus to be lowered
Questions 14-16 refer to the following.
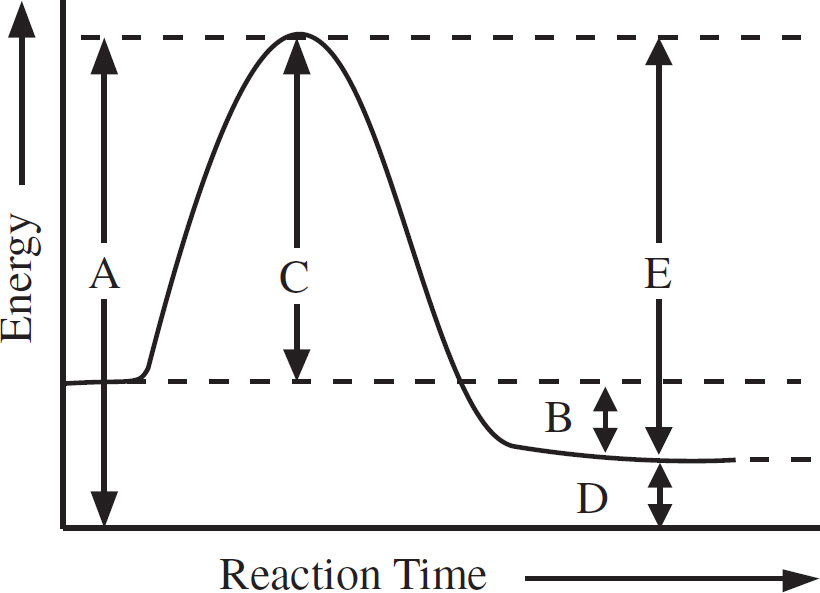
14. Is the activation energy of the reverse reaction
15. Is the enthalpy change of the forward reaction
16. Represents energy of the activated complex
Questions 17-20 refer to the following.
(A) Hydrogen bonding
(B) Ionic bonding
(C) Metallic bonding
(D) Nonpolar covalent bonding
(E) Polar covalent bonding
17. Holds a sample of barium iodide, BaI2, together
18. Allows solids to conduct electricity
19. Attracts atoms of hydrogen to each other in an H2 molecule
20. Responsible for relatively low vapor pressure of water
Questions 21-23 refer to the following.
(A) Iron(III) chloride, FeCl3(s)
(B) Iodine, I2(s)
(C) Sodium hydroxide, NaOH(s)
(D) Sucrose, C12H22O11(s)
(E) Graphite, C(s)
21. Gives off a purplish vapor as it sublimes
22. Can conduct electricity in the solid state
23. Its dissolution in water is highly exothermic
PLEASE GO TO THE SPECIAL SECTION LABELED CHEMISTRY AT THE LOWER RIGHT-HAND CORNER OF THE ANSWER SHEET YOU ARE WORKING ON AND ANSWER QUESTIONS 101–116 ACCORDING TO THE FOLLOWING DIRECTIONS.
Part B
Directions: Each question below consists of two statements, I in the left-hand column and II in the right-hand column. For each question, determine whether statement I is true or false and whether statement II is true or false, and fill in the corresponding T or F ovals on your answer sheet. Fill in oval CE only if statement II is a correct explanation of statement I.
|
EXAMPLES: |
||
|
I |
II |
|
|
EX 1. H2SO4 is a strong acid |
BECAUSE | H2SO4 contains sulfur |
|
EX 2. An atom of oxygen is electrically neutral |
BECAUSE | an oxygen atom contains an equal number of protons and electrons. |
|
SAMPLE ANSWERS |
||
|
||
|
I |
II |
|
|
101. Carbon is a nonmetal |
BECAUSE | carbon atoms can bond with each other. |
|
102. Two isotopes of the same element have the same mass number |
BECAUSE | isotopes have the same number of protons. |
|
103. The density of a sample of water is doubled by doubling its mass |
BECAUSE | compared to a gas, the molecules in a liquid are relatively far apart. |
|
104. Sodium and cesium exhibit similar chemical properties |
BECAUSE | their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. |
|
105. An endothermic reaction can be spontaneous |
BECAUSE | both enthalpy and entropy changes affect the value of a reaction’s Gibbs free energy change. |
|
106. The 4s orbital fills before the 3d orbitals |
BECAUSE | subshells fill in order from lower to higher energy. |
|
107. Calcium acts as a reducing agent when it reacts with bromine |
BECAUSE | mass is conserved in a chemical reaction. |
|
108. If an acid is added to pure water, it increases the water’s pH |
BECAUSE | adding an acid to water raises the hydrogen ion concentration in the water. |
|
109. Covalent bonds must be broken for a liquid to boil |
BECAUSE | heat must be released for a liquid to change into a gas. |
|
110. Alpha particles can be detected using a Geiger counter |
BECAUSE | all radioactive elements are highly chemically reactive. |
|
111. As ice absorbs heat and begins to melt, its temperature remains constant |
BECAUSE | the absorbed heat is consumed by the breaking of intermolecular interactions. |
|
112. When a solute is added to pure water, the vapor pressure of the water will decrease |
BECAUSE | all solutes dissociate into positive and negative ions. |
|
113. The rate of a reaction is accelerated by increasing temperature |
BECAUSE | a large equilibrium constant favors the formation of product. |
|
114. Hydrofluoric acid, HF(aq), is a weaker electrolyte than hydrochloric acid, HCl(aq), |
BECAUSE | fluorine has a lower electronegativity than chlorine. |
|
115. A nonpolar molecule can have polar bonds |
BECAUSE | polar bonds can be symmetrically arranged in a molecule so that there are no net poles. |
RETURN TO THE SECTION OF YOUR ANSWER SHEET YOU STARTED FOR CHEMISTRY AND ANSWER QUESTIONS 24–70.
Part C
Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each case and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet.
24. What is the number of protons and neutrons in an atom with mass number 89 and atomic number 39 ?
(A) 50 protons and 50 neutrons
(B) 50 protons and 39 neutrons
(C) 39 protons and 89 neutrons
(D) 39 protons and 50 neutrons
(E) 39 protons and 39 neutrons
C4H10(g) +…O2(g) →…CO2(g) +…H2O(l)
25. When the above equation is balanced using the lowest whole-number terms, the coefficient of CO2 is
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 8
(D) 10
(E) 13
26. Which of the following is closest in mass to a proton?
(A) Alpha particle
(B) Positron
(C) Neutron
(D) Electron
(E) Hydrogen molecule
27. What is the approximate percentage composition by mass of the element oxygen in the compound HClO4 ?
(A) 16%
(B) 32%
(C) 50%
(D) 64%
(E) 75%
28. If two atoms that differ in electronegativity combine by chemical reaction and share electrons, the bond that joins them will be
(A) metallic
(B) ionic
(C) a hydrogen bond
(D) nonpolar covalent
(E) polar covalent
29. When the temperature of a 20-gram sample of water is increased from 10°C to 30°C, the heat transferred to the water is
(A) 600 calories
(B) 400 calories
(C) 200 calories
(D) 30 calories
(E) 20 calories
30. What is the oxidation state of chromium, Cr, in the compound potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7 ?
(A) +1
(B) +2
(C) +3
(D) +6
(E) +12
31. An aqueous solution with pH 5 at 25°C has a hydroxide ion (OH–) concentration of
(A) 1 ×10–11 molar
(B) 1 ×10–9 molar
(C) 1 ×10–7 molar
(D) 1 ×10–5 molar
(E) 1 ×10–3 molar
2H2O(g) → 2H2(g) + O2(g)
32. The volume of water vapor required to produce 44.8 liters of oxygen by the above reaction is
(A) 11.2 liters
(B) 22.4 liters
(C) 44.8 liters
(D) 89.6 liters
(E) 100.0 liters
33. When 190 grams of MgCl2 are dissolved in water and the resulting solution is 500 milliliters in volume, what is the molar concentration of MgCl2 in the solution?
(A) 2.0 M
(B) 4.0 M
(C) 8.0 M
(D) 12.0 M
(E) 16.0 M
34. When a fixed amount of gas has its Kelvin temperature doubled and its pressure doubled, the new volume of the gas is
(A) four times greater than its original volume
(B) twice its original volume
(C) unchanged
(D) one-half its original volume
(E) one-fourth its original volume
35. In 12.4 hours, a 100 gram sample of an element decays so that its mass is 25 grams. What is the approximate half-life of this radioactive substance?
(A) 1.6 hours
(B) 3.1 hours
(C) 6.2 hours
(D) 24.8 hours
(E) 49.6 hours
36. In the equation Q → 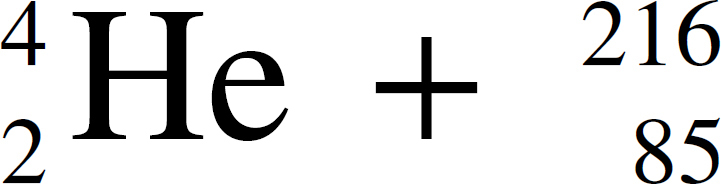 At, the species represented by Q is
At, the species represented by Q is
(A) 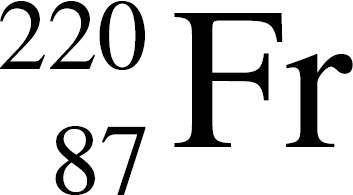
(B) 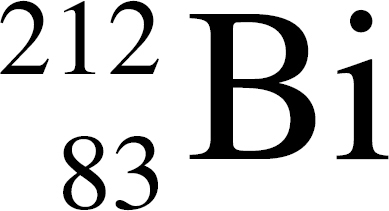
(C) 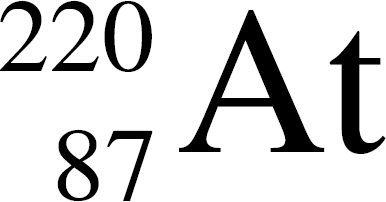
(D) 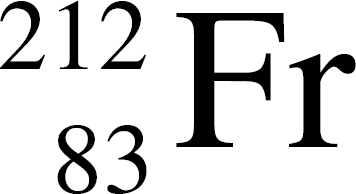
(E) 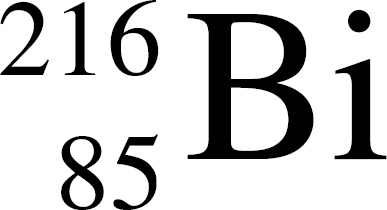
37. A compound with a molecular weight of 56 amu has an empirical formula of CH2. What is its molecular formula?
(A) C2H2
(B) C2H4
(C) C4H8
(D) C4H10
(E) C6H12
38. The change in heat energy for a reaction is best expressed as a change in
(A) enthalpy
(B) absolute temperature
(C) specific heat
(D) entropy
(E) kinetic energy
…NF3(g)+…H2O(g) →…HF(g)+…NO(g)+…NO2(g)
39. When the equation for the reaction above is balanced, how many moles of NF3 would be required to react completely with 6 moles of H2O ?
(A) 0.5 mole
(B) 1 mole
(C) 2 moles
(D) 3 moles
(E) 4 moles
40. Which characteristic is associated with bases?
(A) React with metal to produce hydrogen gas
(B) Donate an unshared electron pair
(C) Always contain the hydroxide ion in their structure
(D) Taste sour
(E) Formed by the reaction of a nonmetal oxide and water
41. An element has the following properties: shiny, brittle, poor electrical conductivity, and high melting point. This element can be best classified as a(n)
(A) alkali metal
(B) halogen
(C) metalloid
(D) transition metal
(E) noble gas
42. Which of the following forward processes produces a decrease in entropy?
I. H2O(g) → H2O(l)
II. Fe2+ (aq) + S2– (aq) → FeS(s)
III. 2SO3(g) ⇋ 2SO2(g) + O2(g)
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) I and II only
(D) II and III only
(E) I, II, and III
43. Which of the following will raise the boiling point of a sample of water?
(A) Heat the water
(B) Mix gasoline into the water
(C) Bring the water sample to a higher altitude
(D) Place the water sample on a magnetic stirrer
(E) Dissolve table sugar into the water
44. Elements H and J lie in the same period. If the atoms of H are smaller than the atoms of J, then compared to atoms of J, atoms of H are most likely to
(A) exist in a greater number of isotopes
(B) exist in a lesser number of isotopes
(C) exist in a greater number of oxidation states
(D) have a greater positive charge in their nuclei
(E) have a lesser positive charge in their nuclei
…Al(s) +…O2(g) →…Al2O3(s)
45. When the equation representing the reaction shown above is completed and balanced and all coefficients are reduced to lowest whole-number terms, the coefficient of O2(g) is
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 6
46. Which of the following solids has a brilliant blue color?
(A) Ca(OH)2
(B) KCl
(C) NaBr
(D) Fe2O3
(E) CuSO4
47. Twenty-five percent of element X exists as 210X and 75 percent of it exists as 214X. What is the atomic weight of element X in amu?
(A) 85
(B) 211
(C) 212
(D) 213
(E) 214
48. A 600-milliliter container holds 2 moles of O2(g), 3 moles of H2(g), and 1 mole of He(g). Total pressure within the container is 760 torr. What is the partial pressure of O2?
(A) 127 torr
(B) 253 torr
(C) 380 torr
(D) 507 torr
(E) 760 torr
Fe(OH)3(s) ⇋ Fe3+(aq) + 3OH–(aq)
49. The ionic solid Fe(OH)3 is added to water and dissociates into its component ions, as shown above. The solubility product expression for the saturated solution is
(A) Ksp = [Fe3+] [OH–]
(B) Ksp = [Fe3+] [3OH–]
(C) Ksp = [Fe3+] [3OH–]3
(D) Ksp = [Fe3+] [OH–]3
(E) Ksp =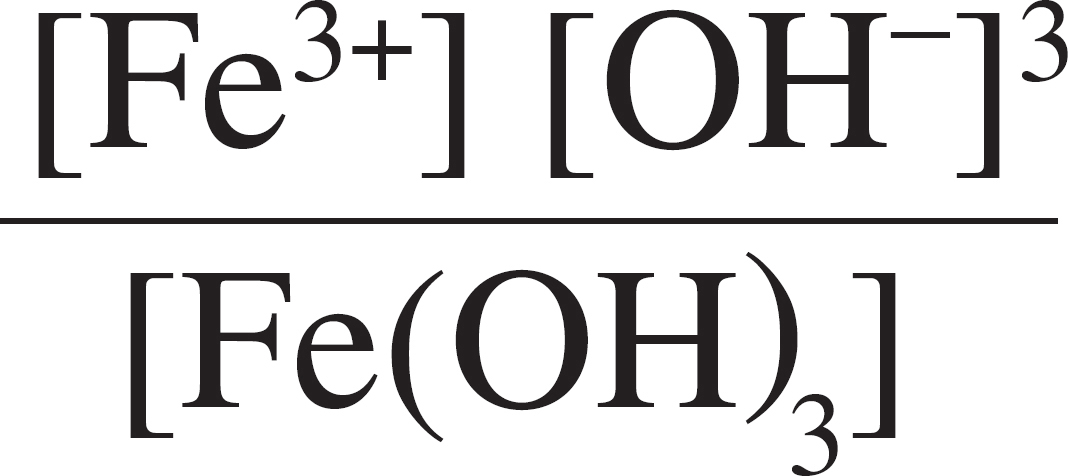
50. Which of the following electron configurations represents an atom of magnesium in an excited state?
(A) 1s22s22p6
(B) 1s22s22p63s2
(C) 1s22s22p53s23p2
(D) 1s22s22p63s13p1
(E) 1s22s22p63s13p2
51. All of the following when added to water will produce an electrolytic solution EXCEPT
(A) N2(g)
(B) HCl(g)
(C) KOH(s)
(D) NaI(s)
(E) CaCl2(s)
NH3 (aq) + H2CO3(aq) ⇋ NH4+(aq) + HCO3–(aq)
52. In the reaction represented above, NH4+ acts as a(n)
(A) indicator
(B) hydrate
(C) acid
(D) base
(E) salt
53. Which species has the ground state electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p6 ?
(A) Sulfide ion, S2–
(B) Bromide ion, Br–
(C) Neon atom, Ne
(D) Chromium ion, Cr3+
(E) Potassium atom, K
54. Which of the following species is amphoteric?
(A) Na3PO4
(B) HSO4–
(C) KOH
(D) HNO3
(E) C2O2–4
55. An ideal gas has a volume of 10 liters at 20˚°C and a pressure of 750 mmHg. Which of the following expressions is needed to determine the volume of the same amount of gas at STP?
(A) 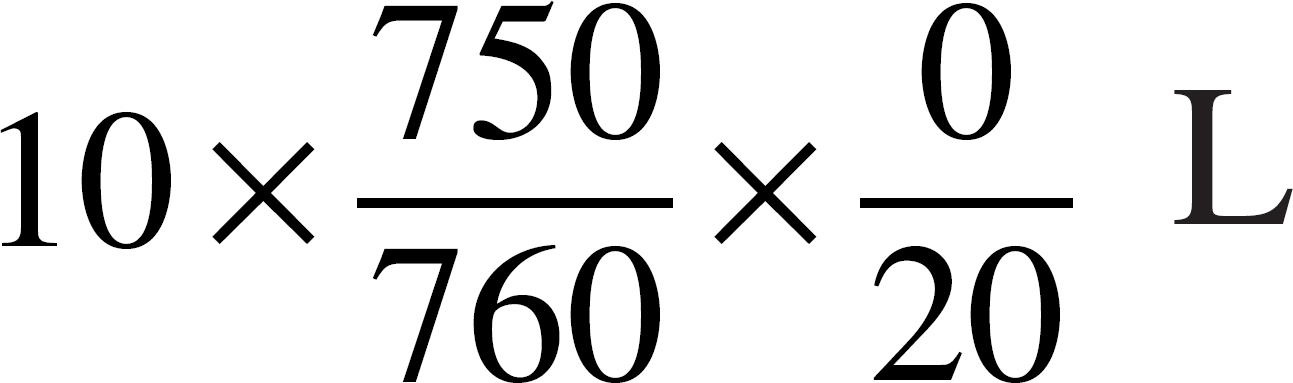
(B) 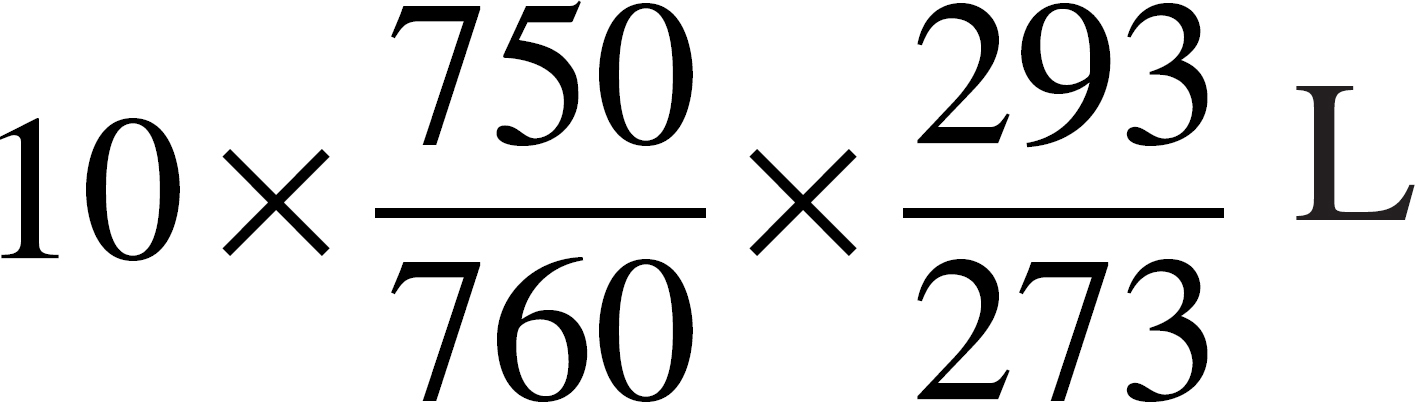
(C) 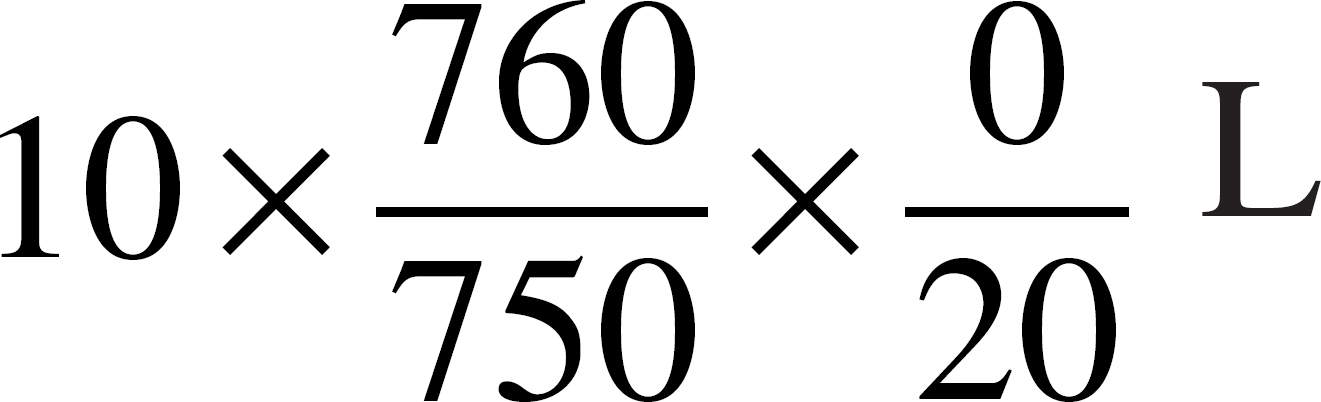
(D) 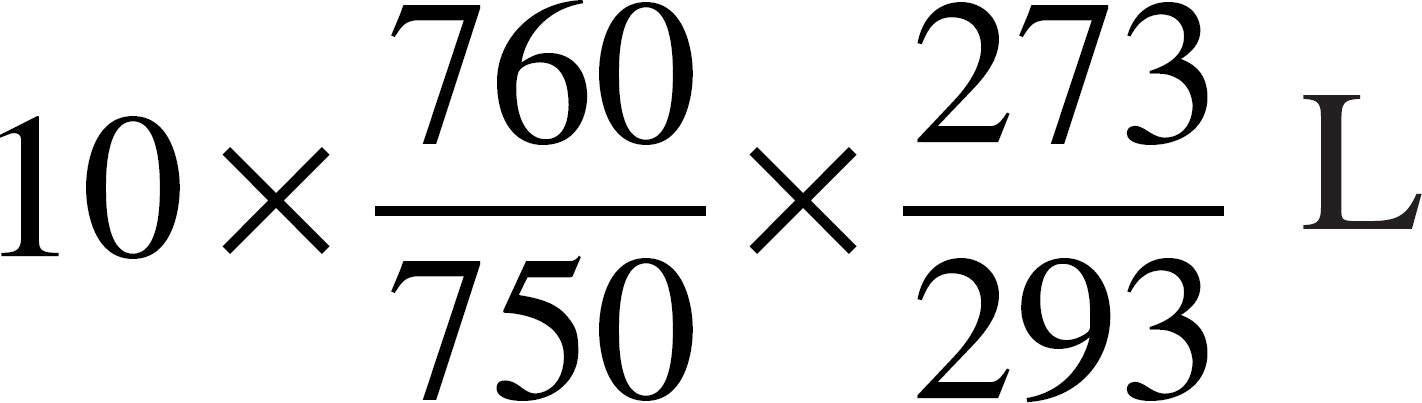
(E) 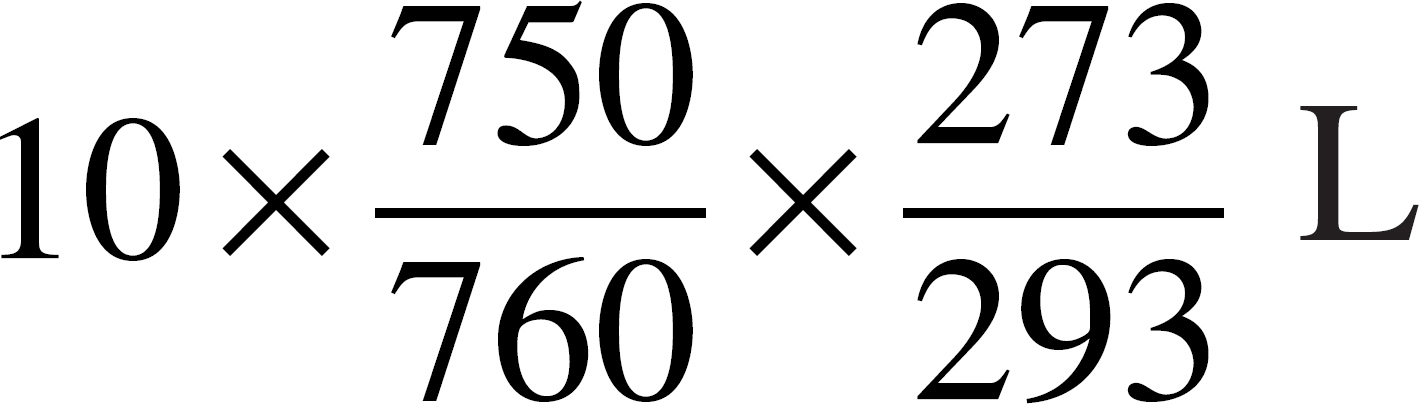
Questions 56-57 pertain to the phase diagram for substance Z below.
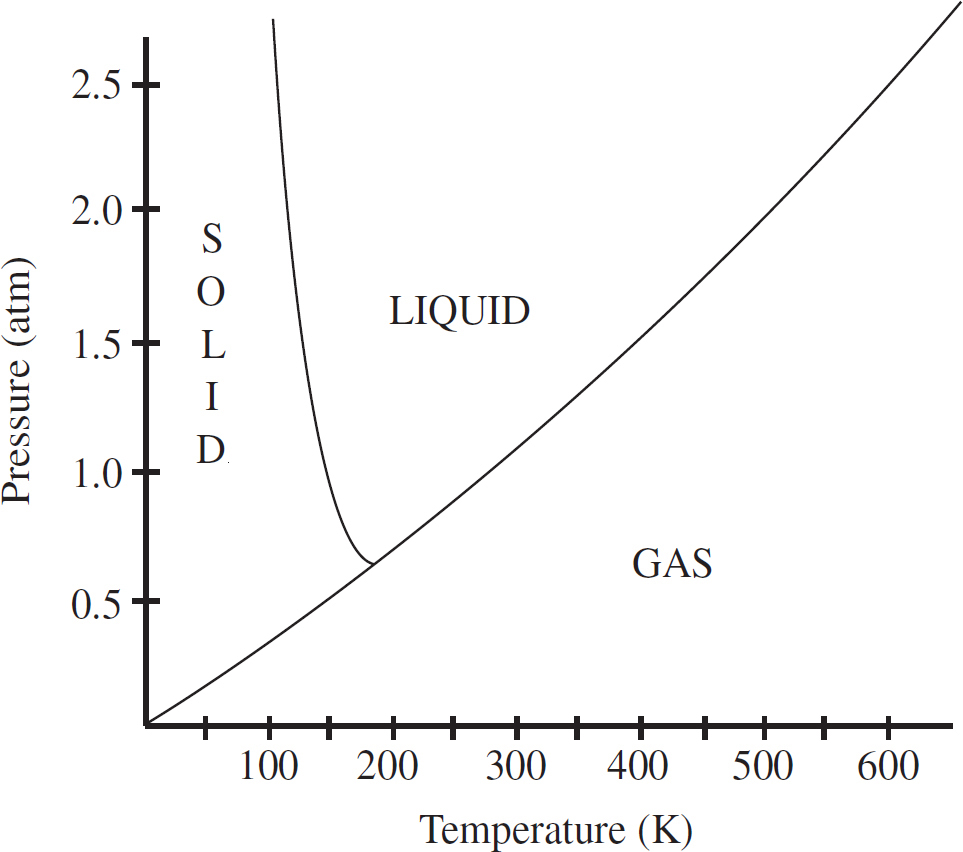
56. Substance Z is at 0.5 atm and 200 K. If the pressure on substance Z is steadily increased and its temperature is kept constant, what phase change will eventually occur?
(A) Condensation
(B) Freezing
(C) Melting
(D) Sublimation
(E) Vaporization
57. The normal boiling point of substance Z is closest to
(A) 100 K
(B) 200 K
(C) 300 K
(D) 400 K
(E) 500 K
58. The shape of a PCl3 molecule is described as
(A) bent
(B) trigonal pyramidal
(C) linear
(D) trigonal planar
(E) tetrahedral
59. What volume of 0.4 M Ba(OH)2 (aq) is needed to exactly neutralize 100 milliliters of 0.2 M HBr(aq) ?
(A) 25 mL
(B) 50 mL
(C) 100 mL
(D) 200 mL
(E) 400 mL
60. Which of the following is true regarding the aqueous dissociation of HCN, Ka = 4.9 × 10–10 at 25°C?
I. At equilibrium, [H+] = [CN–]
II. At equilibrium, [H+] > [HCN]
III. HCN(aq) is a strong acid.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) I and II only
(D) II and III only
(E) I, II, and III
61. Which of the following atoms has the largest second ionization energy?
(A) Silicon, Si
(B) Calcium, Ca
(C) Chlorine, Cl
(D) Iron, Fe
(E) Sodium, Na
Question 62 refers to the overall reaction and half-reactions with standard reduction potentials below.
2H2O(l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g)
ΔH° = + 572 kJ/mol
62. Given the enthalpy change for the above reaction, what would the enthalpy change for
H2(g) + ½O2(g) → H2O(l) ?
(A) – 286 kJ/mol
(B) + 286 kJ/mol
(C) – 1044 kJ/mol
(D) + 1044 kJ/mol
(E) + 572 kJ/mol
63. The reaction of zinc metal, Zn, and hydrochloric acid, HCl, produces which of the following?
I. H2(g)
II. Cl2(g)
III. Zn2+(aq)
(A) II only
(B) III only
(C) I and II only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, II, and III
Questions 64-65 refer to the following reaction.
2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) ⇋ 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(g) + heat
64. For the above reaction, the equilibrium concentration of SO2(g) can be increased by
(A) adding neon gas
(B) increasing the temperature
(C) adding a catalyst
(D) increasing the concentration of H2O(g)
(E) increasing the concentration of O2(g)
65. Which of the following is increased by decreasing the volume of the reaction system?
I. Rate of reaction
II. Equilibrium concentration of reactants
III. Value of Keq
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) I and II only
(D) II and III only
(E) I, II, and III
Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) ⇋ 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
66. When 3 moles of Fe2O3 are allowed to completely react with 56 grams of CO according to the above equation, approximately how many moles of iron, Fe, are produced?
(A) 0.7
(B) 1.3
(C) 2.0
(D) 2.7
(E) 6.0
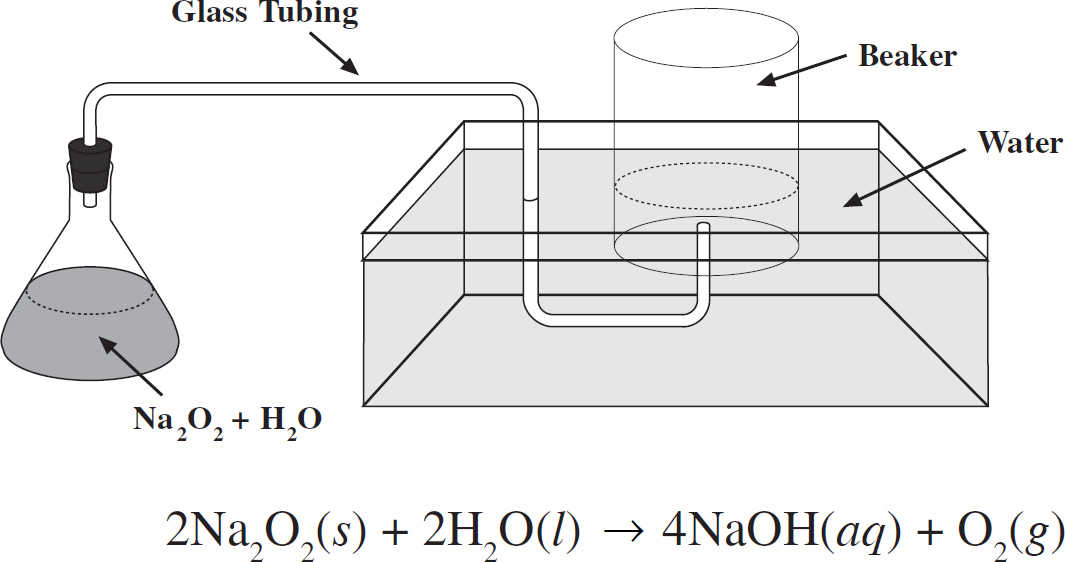
67. Sodium peroxide, Na2O2, and water react in the flask at 25°C according to the equation and in the diagram above. If water levels are equal inside and outside the beaker, then the gas pressure inside the beaker is equal to the
(A) pressure of oxygen gas collected
(B) vapor pressure of water at 25°C
(C) sum of pressure of oxygen gas collected and atmospheric pressure
(D) sum of vapor pressure of water at 25°C and atmospheric pressure
(E) sum of pressure of oxygen gas collected and vapor pressure of water at 25°C
68. Which of the following molecules has the strongest carbon-to-carbon bond?
(A) C2H2
(B) C2H4
(C) C2H6
(D) C3H8
(E) C4H10
N2O4(g) ⇋ 2NO2(g)
The following concentration data were gathered for the above reaction at 5 minute intervals from the start of an experiment:
| Time After Start of Experiment | [N2O4] | [NO2] |
| 0 min (start) | 0.00 M | 0.50 M |
| 5 min | 0.10 M | 0.33 M |
| 10 min | 0.20 M | 0.20 M |
| 15 min | 0.25 M | 0.15 M |
| 20 min | 0.28 M | 0.13 M |
| 25 min | 0.28 M | 0.13 M |
69. If the experiment was carried out in a closed system at constant temperature, then during which time interval (from the start of the experiment) did the reaction most likely achieve equilibrium?
(A) 0 min (start) to 5 min
(B) 5 min to 10 min
(C) 10 min to 15 min
(D) 15 min to 20 min
(E) 20 min to 25 min
70. The emission spectrum of an element can be created when atoms of that element are
(A) reacted with a different atom to form a new molecule
(B) fired from a machine into a patch of metal foil
(C) change phase
(D) exposed to an outside energy source
(E) cooled to extremely low temperatures
STOP
If you finish before time is called, you may check your work on this section only. Do not turn to any other section in the test.