Riders on White Horses
By early November, winter is already spreading its dark cloak over the landscape. What better time to send the children parading through the streets with pretty lights? In Germany’s Protestant north, this can happen anytime during the autumn. In the Catholic south, lantern processions are centered around the larger observance of St. Martin’s Day on November 11. There, the Christmas season is ushered in by the figure of St. Martin himself, riding into town on a white horse, his costume put together by the aldermen’s wives in approximation of a Roman soldier, complete with helmet, horsehair crest, and scarlet cape. According to his legend, St. Martin surrendered half his cloak to a shivering beggar who turned out to be Jesus himself.
In the German saying “St. Martin comes riding on a white horse,” the horse is the embodiment of the first snowfall. While the figure of the saint disappeared from pageants in the north, the horse did not. The Schimmel, or “white horse,” consisted of one to four men under a white sheet, holding a hollow, carved head on a pole. A pot of live coals might be placed inside the head, making the mouth and eyes glow red. When the Schimmel had a rider, the whole thing was called a Schimmelreiter and thus became a kind of hobby horse.
Sun, Moon, and Stars
Protestant or Catholic, Martinmas lanterns are supposed to represent the light of the Christian faith, but the tiny flames are also late expressions of the bonfires that once marked winter-nights, the ancient pagan New Year at the end of October. In the old days, if you wanted to send a small child out after dark to sing and beg for sweets, you had to provide him or her with a reliable, not readily flammable or breakable, light source. Such a lantern could be made from a turnip or a Kürbis, a smaller, ruddier version of the American pumpkin. The lanterns were carved with frightening faces, for who knew what other creatures might be about in the frosty autumn night? Better for the children to carry their own goblins’ faces, so that when the light shone out of them it would send the real goblins scuttling back into the hedgerows. And just to be on the safe side, the children themselves might dress as ghosts or other unearthly spirits.
Among farm children, both Protestant and Catholic, these customs survived into the twentieth century, while in the cities, children starting carrying Chinese paper lanterns. Today, you can buy a paper lantern ready-made for the occasion, the face decorated with the sun, moon, or stars celebrated in the old, slightly mournful folk songs that accompany the processions. Schoolchildren often make their own paper lanterns out of papier-mâché or black paper and cellophane. When the odd flare-up occurs, the lantern is simply dropped and stamped out on the cobbles.
 Craft: Martinmas Lantern
Craft: Martinmas Lantern
The following craft features Scherenschnitte, a German folk art in which figures, plants, animals, and fairy-tale scenes are cut from a single sheet of paper. Scherenschnitte artists work in both black and white paper—Hans Christian Andersen was famous for his spontaneous cuttings in white—but for this project, black provides the most dramatic effect. If you use the template in this book, you should first double it in size.
Tools and materials:
1 sheet black paper, 9" x 12" or larger (Poster board is too thick, but construction paper will do.)
Tracing paper
Bristol board or thin cardboard
Clear tape
Glue
Scissors
X-Acto or other craft knife
Hole punch
Tea light
2 shish kebab skewers
Loop of thin wire
Long stick or dowel for carrying lantern

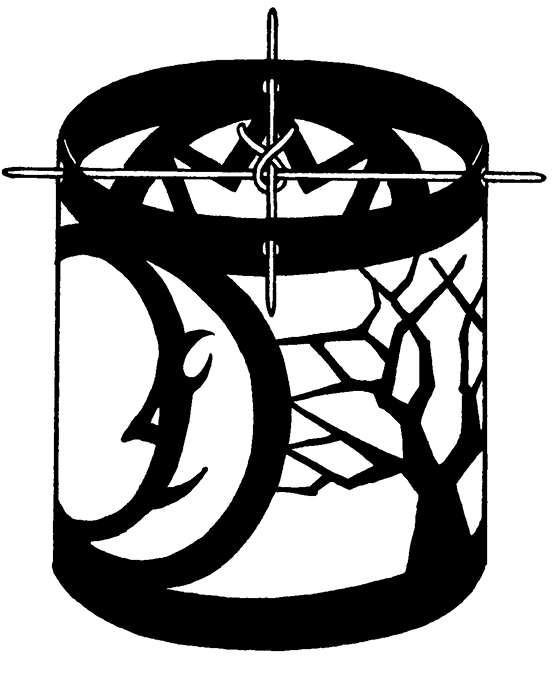
Lay the template sketch on the black paper; tape securely in place at the edges; and cut out all the white spaces with your knife. Take your time, but if you do slip up, you can make repairs with tape or glue when you mount the piece on the tracing paper.
When your picture is all cut out, coat the back with glue and mount it on the tracing paper. Smooth the piece gently with your hands to make sure all the fine details are stuck firmly to the tracing paper.
When the glue is dry, bend your work of art into a cylinder—tracing paper on the inside—and carefully close the seam with a strip of clear, strong tape. It will look best if the tape is on the inside of the cylinder.
To make the right-size base, trace the bottom of the cylinder on a piece of Bristol board. Cut out the circle, leaving a ½-inch margin all around. Cut slits all around to make tabs. Fold the tabs up, dab each tab with glue, and slide the base into the bottom of the lantern cylinder.
Glue or tape a tea light into the lantern base. When the first candle has burnt out, you can drop a new one into the same holder. But before you strike the match, punch four equidistant holes in the upper border of your lantern. These are for the shish kebab skewers to pass through.
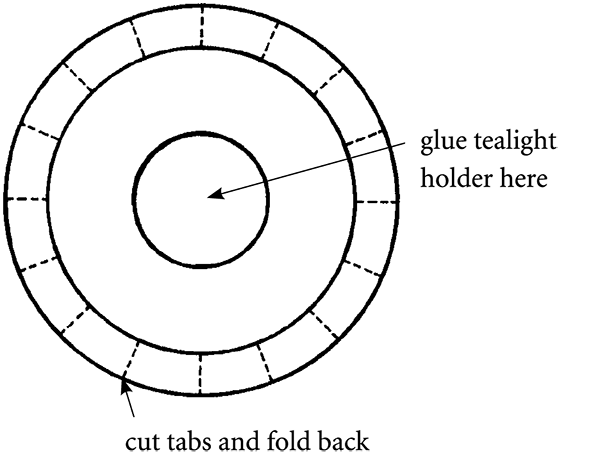
Now light the candle. If your lantern is tall, you will probably want to use a fireplace match. Slide the skewers through the holes and through the wire loop, being careful not to burn yourself as the heat rises up from the candle flame. Hook your carrying stick through the loop, and you’re ready to set off into the dark streets.

Martinmas Treats
Although there is no mention of wolves in the legend of St. Martin, the Martinmas snows once brought out wolves in the form of the Pelzmarten, men dressed up in shaggy furs. Rather than eat the children, they threw apples to the good ones and beat the bad ones with a whip or rod. The tradition dates back to the fifteenth century at least and may be even older than the “Furry Nicks” we’ll meet on St. Nicholas’ Eve.
There is no mention of horns in St. Martin’s legend either, but they, too, have become a part of his day. Pastries known as Martinshoernchen, or “little Martinmas horns,” may represent the hunting horn that once belonged to the god Woden. Then again, the crescent shape might represent the moon, which can be seen bobbing in the alleys along with the sun and stars at this time of year. In bygone days, St. Martin himself was believed to enter the house on the eve of his feast day. Once inside, he turned the jug of water left out for him into wine, depositing a little horn-shaped pastry beside it when he left.
 Recipe: Martinmas Horns
Recipe: Martinmas Horns
There is no one definitive recipe for Martinshoernchen. Some call for a yeast dough; others, like this one, call for a short pastry dough. To this day, Martinshoernchen, which are not overly sweet, are eaten as breakfast buns in the fall.
Ingredients for the dough:
2 sticks (one cup) unsalted butter, softened
¾ cup sour cream
1 egg yolk
2 Tablespoons sugar
2½ cups flour
For the filling:
1 small jar (8 oz.) apricot jam
About 3½ oz. marzipan—i.e., half a box Odense or other brand “almond candy dough”
Pinch cinnamon
For the glaze:
1 egg white
In a large bowl, mix all of the dough ingredients, adding the flour a little at a time. When the flour has all been worked in, form the dough into a ball. It will be sticky. Wrap the ball lightly in plastic wrap and refrigerate several hours or overnight.
Cut the chilled dough into four quarters. Work with one quarter at a time, leaving the rest wrapped up in the refrigerator. Roll out the dough on wax paper until it’s about 1⁄8 inch thick or as thin as you can get it. Cut into circles with a cup or large glass.
Place the circles on a greased cookie sheet or one lined with baking parchment. Spread each one sparingly with apricot jam and sprinkle with a little cinnamon. Place a pinch of marzipan at the edge of the circle of dough, then roll the circle up with the marzipan inside. Bend the roll into a crescent or “horn,” pinching the tips.
Brush horns with egg white and bake at 350°F for 20–25 minutes or until lightly browned.
The Wild Rider
The image of St. Martin as a Roman soldier never really took hold in the Anglo-Saxon realm, where another older rider on a white horse appeared in the woods at this time of year. He was known as the Wild Rider, Wild Huntsman, Hakelbarend, or simply Grim. His mount, like the cloudy November sky, was aeppelfealo, or “apple gray”—what later speakers of English would call “dappled.” He wore a swirling cloak of blue or black homespun felted against the elements, much rougher stuff than that worn by the German Martin. Of course, none dared to touch the cloak’s greasy edge as the Rider thundered past; if they knew what was good for them, they ran for cover. Those who were foolish enough to look him in the face saw that he kept half his own face covered by a floppy-brimmed hat or hood, hiding the eye that was not an eye at all but a dark, empty socket.
Before the sixth century, this ghostly huntsman would have been openly acknowledged as Woden, god of magic and the dead, retriever of the runes, of poetry and the mead that inspires it. Even after he had lost his divine status, he was treated with deference. Those living in and around the forest would have known which tracks he preferred and scrupulously avoided them when he was abroad. The lonely yeoman surprised in the woods by the croaking of ravens and the pounding of hooves knew to hide behind a shelter of nine boards or, if that were not possible, to throw himself face down on the ground and wait until the spectral hunting party had passed. Most importantly, he must not answer their hunting cry or try to engage them in conversation lest he become one of their number.
From November on through the Twelve Nights of Christmas,12 it was wise to stay out of barns that had opposite doors, for these were the ones through which the Wild Hunt was most likely to pass. This makes perfect sense when we take into account the fact that Woden’s hunting party was comprised not of the recently dead but of the long, predominantly heathen dead. A long hall with a door at each end was the construction with which these spirits were most familiar, for this was the blueprint the Angles and Saxons had brought with them from the lowlands of northern Germany. Back in the old country, the Wild Hunt left gifts behind when it passed through such houses.
Quite often, the Wild Hunt was not seen, only heard, leading some to speculate that the phenomenon was nothing more than a flock of migratory birds crying out of a cloud as they passed overhead. Even when it was “seen,” the witnesses might have been observing only what the stories had led them to expect. In other words, just because it wasn’t there didn’t mean you couldn’t see it, or be grievously harmed by it. If you failed to take the proper precautions you might be struck blind, mad, or even dead upon the passing of the Wild Rider and his ghostly retinue. At the very least, you could expect to spend several weeks in bed, recovering from the trauma.
But there was also the possibility that you would be swept up, carried over the treetops, and deposited in a strange land. In the mid-nineteenth century, a Norwegian farm boy claimed to have been briefly taken up by the Oskorei,13 as the Wild Hunt was sometimes known in Norway. None the worse for it, he lived to a great age, but all he could ever say of his adventure was that he had been taken to a place of splendor. Interestingly, the famous, feral Green Children of medieval East Anglia claimed to hail from “St. Martin’s Land,” where it was always twilight, the grass was always green, and the natives apparently ate only beans. According to a twelfth-century chronicler of wonders, the green-skinned children, a boy and a girl, had strayed into the village of St. Mary’s of the Wolf-Pittes, now Woolpit, by accident, through a fissure in the earth. Was St. Martin’s Land the same realm to which the Norwegian boy had been transported? Unfortunately, there is no one now living who can tell us.
“Blacker Than Pitch”
Another rider on a white horse, St. Nicholas, was of a kindlier bent. Sinterklaas, as he is known to the Dutch, starts rambling around the countryside in mid-November, well in advance of his feast day of December 6. Like Woden, Sinterklaas is old and bearded, but instead of the floppy hat, he wears a bishop’s mitre. More importantly, he never goes anywhere without his sidekick, Zwarte Piet or “Black Peter,” whose job it is to stuff naughty children in his sack and carry them off to Spain. (In the staunchly Protestant Netherlands of the sixteenth century, a trip to sunny Catholic Spain was akin to a sojourn in Purgatory.)
In the Netherlands, Black Peter is St. Nicholas’s sole attendant. Dressed in brightly colored cap or turban, his puffed sleeves peeking out from the fashionable slashings in his velvet jacket, Black Peter resembles a Moorish page boy of sixteenth-century Spain. Today, few children are afraid of this colorfully anachronistic figure. Rather than terror, he provides the comic relief to the bishop’s solemn visit. Still, there can be no doubt that Black Peter has sprung from the same ageless bloodline as brasher devils like Čert and Krampus (whom we’ll meet in the next chapter) and perhaps even Snorri Sturluson’s pitch-black elves.
While he resembles the medieval stereotype of “the Moor,” Piet’s Spanish/Moorish identity has been laid over one of those dark winter spirits who were already known to emerge from the forest in the wake of the Wild Rider. And Dutch children might tell you that there is another more obvious explanation for the page’s dark face: it is Black Peter’s job to go up and down the sooty chimneys to fill the children’s shoes so that St. Nicholas won’t soil his costly bishop’s robes.
 Recipe: Bishop’s Wine
Recipe: Bishop’s Wine
Bisschopswijn, or bishop’s wine, is drunk by the grown-ups on the feast day of St. Nicholas, Bishop of Myra, but it could just as easily have been named for St. Martin, Bishop of Tours, on whose day new wine was drunk with the Martinmas goose. Bishop’s wine is just one variation of the mulled, spiced wine that is ladled out under the twinkling lights of northern Europe’s outdoor Christmas markets.
Ingredients:
1 bottle cheap, dry red wine
1⁄3 cup vanilla sugar (This is white sugar in which a vanilla bean or two have resided for at least a few days.)
1 slice fresh ginger or chunk of candied ginger
1 star anise
1 cinnamon stick
6 cardamom pods
6 allspice berries
10 cloves
1 orange, sliced
Pour the wine and vanilla sugar into a large pot. Tie up the spices in a piece of cheesecloth and add to pot. Heat to simmering, stirring occasionally with a wooden spoon. Keep simmering but not boiling for about half an hour. Remove spices and float orange slices on top just before serving.
12. This was the season in which the Wild Hunt was most commonly perceived, but the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle reports that in 1127, reliable witnesses (read “monks”) in the area of Stamford both heard and saw the phantom hunting party go by with their black hounds and horses after February 6. The change in color is probably the result of Woden’s transformation from deity to demon.
13. Oskorei comes from an Old Norse word meaning “terror,” but the Norwegians had plenty of other names for this phenomenon, including Asgardsrei, indicating that it issued from Asgard, the abode of the Norse sky gods, and Jolorei, or “Yule Host.” When the witch Lussi rode at its head, it was called the Lussiferd.