Internal storage is yet another way of storing data in Android Apps, usually in the file directory under /data/data/<app name>.
The following code shows how the internal storage is used to store the private key of an application, which it is used to store and send credit card and SSN numbers of a user:
String publicKeyFilename = "public.key";
String privateKeyFilename = "private.key";
try{
GenerateRSAKeys generateRSAKeys = new GenerateRSAKeys();
Security.addProvider(new org.bouncycastle.jce.provider.BouncyCastleProvider());
// Generate public & private keys
KeyPairGenerator generator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA", "BC");
//create base64 handler
BASE64Encoder b64 = new BASE64Encoder();
//Create random number
SecureRandom rand = secureRandom();
generator.initialize(2048, rand);
//generate key pair
KeyPair keyPair = generator.generateKeyPair();
Key publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
Key privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = openFileOutput(publicKeyFilename, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
fos.write(b64.encode(publicKey.getEncoded()));
fos.close();
fos = openFileOutput(privateKeyFilename, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
fos.write(b64.encode(privateKey.getEncoded()));
fos.close();
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
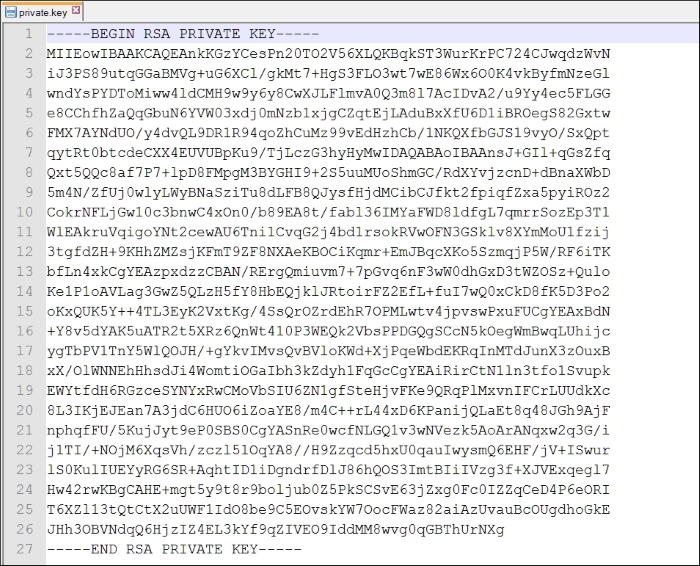
}As we can see in the previous screenshot, the private key is being stored insecurely in the private.key file under files.
Let's open up Droid Explorer (or use adb pull command) and copy the private key from the device to the machine and open it up in a text editor: