Now, we will discuss a simple program where we ask the user to enter two numbers and the program returns the sum of two numbers. For now, we are going to pretend that the user always provides a valid input.
In Python, user input to a Python program can be provided using the input() function (https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#input):
var = input("Enter the first number: ")
In the preceding example, we are making use of the input() function to seek the user's input of the number. The input() function takes the prompt ("Enter the first number: ") as an argument and returns the user input. In this example, the user input is stored in the variable, var. In order to add two numbers, we make use of the input() function to request user to provide two numbers as input:
var1 = input("Enter the first number: ")
var2 = input("Enter the second number: ")
total = int(var1) + int(var2)
print("The sum is %d" % total)
We are making use of the input() function to seek user input on two numbers. In this case, the user number is stored in var1 and var2, respectively.
The user input is a string. We need to convert them into integers before adding them. We can convert a string to an integer using the int() function (https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#int).
The int() function takes the string as an argument and returns the converted integer. The converted integers are added and stored in the variable, total. The preceding example is available for download along with this chapter as input_function.py.
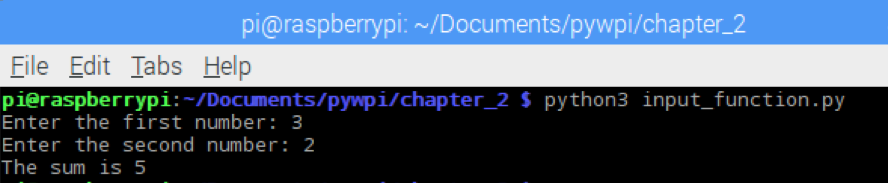
The following snapshot shows the program output: