Check Your Skills Answer Key
-
5
There are five digits in 99,999. Although there are only 9’s, the 9 takes up five digit places (ten-thousands, thousands, hundreds, tens, and ones).
-
Tenths place
In the number 4,472.1023, the 1 is in the tenths place.
-
0.000652
Move the decimal to the left when you multiply by 10 raised to a negative power. In this case, move the decimal to the left two places:
0.0652 × 10-2 = 0.000652
-
264,000,000
Move the decimal to the right when dividing by 10 raised to a negative power. In this case, move the decimal to the right six places. Notice that dividing by 10 raised to a negative power has exactly the same effect as multiplying by 10 raised to the positive version of that power:
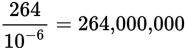
-
a, b, c
- a = 2.34
- b = 23.4
- c = 23,400
-
4
With large numbers, you can effectively ignore the smaller digits:
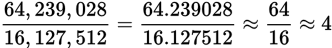
Note that it is not good enough to focus on just the first digits in the numerator and denominator. That would give you
 , or 6, which is not accurate enough.
, or 6, which is not accurate enough.
-
67.3768

-
2.816

-
108
Trade decimal places. Change 0.00018 to 18 by moving the decimal to the right five places. To compensate, move the decimal of 600,000 to the left five places, making it 6. The multiplication problem is now:
18 × 6 = 108
-
117.4
Be sure to move the decimal so that you are dividing by whole numbers—and be sure to move the decimal the same direction and number of places in both the dividend and the divisor:
85.702 ÷ 0.73 → 8,570.2 ÷ 73.
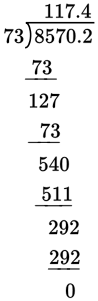

-
Terminating: a.; Repeating: b., c.; Non-Repeating: d.
The fraction
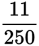 has a denominator with a prime factorization of 2 × 5 × 5 × 5. Because this only includes 2’s and 5’s, the decimal form of the fraction will terminate. To be precise,
has a denominator with a prime factorization of 2 × 5 × 5 × 5. Because this only includes 2’s and 5’s, the decimal form of the fraction will terminate. To be precise,
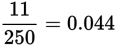 .
.In
 , 393 is not divisible by 7, and 7 is a prime (but not a 2 or a 5). Thus, the decimal will repeat infinitely:
, 393 is not divisible by 7, and 7 is a prime (but not a 2 or a 5). Thus, the decimal will repeat infinitely: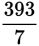 =
=
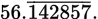
In
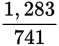 , the prime factorization of the denominator is 741 = 3 × 13 × 19. Because this includes primes other than 2 and 5 and is fully reduced, and because the numerator and denominator are both integers, the decimal will repeat infinitely (eventually!).
, the prime factorization of the denominator is 741 = 3 × 13 × 19. Because this includes primes other than 2 and 5 and is fully reduced, and because the numerator and denominator are both integers, the decimal will repeat infinitely (eventually!).In
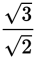 , both the numerator and denominator are what are known as irrational numbers. This means they are decimals that never exhibit a repeating pattern and therefore cannot be expressed as fractions with integers.
, both the numerator and denominator are what are known as irrational numbers. This means they are decimals that never exhibit a repeating pattern and therefore cannot be expressed as fractions with integers.
-
8
Focus only on the units digit of each step of the problem:
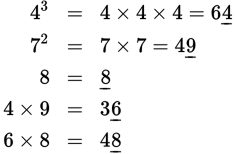
-
7
Because you are dealing with only the units digit of the product, you can ignore the tens digit of 13 (1) and focus only on 33: 3 × 3 × 3 = 27.
-
5
For higher exponents in units digit problems, try to find a pattern as you raise the base to higher powers:
51 = 5
52 = 25
53 = 125
Notice that the units digit is always 5. This is because 5 × 5 = 25.
Therefore, 1537 → 537 = 5 × 5 × 5 × … = 25 × 5 × … → …5.