Solutions
-
54 ft
You know that one side of the yard is 40 feet long, so call this the length. You also know that the area of the yard is 280 square feet. To determine the perimeter, you must know the width of the yard:
A = l × w
280 = 40w
w = 280 ÷ 40 = 7 feetFrank fences the two 7-foot sides and one of the 40-foot sides. Therefore, he needs 40 + 2(7) = 54 feet of fence.
-
6 inches
The perimeter of a pentagon is the sum of its five sides: x + x + x + 3x + 3x = 9x. If x is
 of an inch, the perimeter is
of an inch, the perimeter is
 , or 6 inches.
, or 6 inches. -
35 in2
If E is the midpoint of AD, then AE = ED. Set x as the length of each AE and ED. You can determine the length of x by using what you know about the area of triangle ABE:

Therefore, the length of AD is 2x, or 10.
Because AD is parallel to BC, the shape ABCD is a trapezoid.
To find the area of the trapezoid, use the formula:

-
$1,700
To find the surface area of a rectangular solid, sum the individual areas of all six faces:
Each Both Top and Bottom: 5 × 4 = 20 → 2 × 20 = 40 Side 1: 5 × 2.5 = 12.5 → 2 × 12.5 = 25 Side 2: 4 × 2.5 = 10 → 2 × 10 = 20 40 + 25 + 20 = 85 ft2 Covering the entire tank will cost 85 × $20, which equals $1,700.
-
7
The area of a triangle is equal to half the base times the height. Therefore, you can write the following relationship:

-
90 ft2
The area of the carpet is equal to l × w, or 36 ft2. Set up a percent table or a proportion to find the area of the whole living room floor:

Cross-multiply to solve. 
-
4 ft
Set up equations to represent the area and perimeter of the flower bed:
A = l × w P = 2(l + w) Then, substitute the known values for the variables A and P:
44 = l × w 30 = 2(l + w) Solve the two equations using the substitution method:

Substitute this expression for l in the second equation.
Solve the first equation for l.
Solving the quadratic equation yields two solutions: 4 and 11. Because you are looking only for the length of the shorter side, the answer is 4. Alternatively, you can arrive at the correct solution by picking numbers. What length and width add up to 15 (half of the perimeter) and multiply to produce 44 (the area)? Some experimentation will demonstrate that the longer side must be 11 and the shorter side must be 4.
-

If the length of the parking lot is 2x and the width is x, you can set up a fraction to represent the ratio of the perimeter to the area as follows:

-
144 m2
The volume of a rectangular solid equals (length) × (width) × (height). If you know that the length and width are both 4 meters long, you can substitute values into the formulas as shown:
112 = 4 × 4 × h
h = 7To find the surface area of a rectangular solid, sum the individual areas of all six faces:
Each Both Top and Bottom: 4 × 4 = 16 → 2 × 16 = 32 Side 1: 4 × 7 = 28 → 2 × 28 = 56 Side 2: 4 × 7 = 28 → 2 × 28 = 56 32 + 56 + 56 = 144 m2 -
20 hours
The volume of the pool is (length) × (width) × (height), or 30 × 10 × 2 = 600 cubic meters. Use a standard work equation, RT = W, where W represents the total work of 600 m3:
0.5t = 600
t = 1,200 minutes
Convert this time to hours by dividing by 60: 1,200 ÷ 60 = 20 hours. -

To find the surface area of a cube, find the area of one face, and multiply that by 6: 6(52) = 150.
To find the volume of a cube, cube its edge length: 53 = 125.
The ratio of the cube’s surface area to its volume, therefore, is
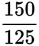 ,
which simplifies to
,
which simplifies to
 .
. -

First, assign the variable x to the length of one side of cube A. Then the length of one side of cube B is 3x. The volume of cube A is x3. The volume of cube B is (3x)3, or 27x3.
Therefore, the ratio of the volume of cube A to cube B is
 , or
, or
 . You can also pick a number for the length of a side of cube A and solve accordingly.
. You can also pick a number for the length of a side of cube A and solve accordingly. -

The area of the frame and the area of the picture sum to the total area of the image, which is 62, or 36. Therefore, the area of the frame and the picture are each equal to half of 36, or 18. Because EFGH is a square, the length of EF is
 , or
, or
 .
. -
400 cm2
The quadrilateral with maximum area for a given perimeter is a square, which has four equal sides. Therefore, the square that has a perimeter of 80 centimeters has sides of length 20 centimeters each. Because the area of a square is the side length squared, the area = (20 cm)(20 cm) = 400 cm2.
-
160 ft
The quadrilateral with minimum perimeter for a given area is a square. Because the area of a square is the side length squared, you can solve the equation x2 = 1,600 ft2 for the side length x, yielding x = 40 ft. The perimeter, which is four times the side length, is (4)(40 ft) = 160 ft.
-
20 m2
If one side of the parallelogram is 2 meters long, then the opposite side must also be 2 meters long. You can solve for the unknown sides, which are equal in length, by writing an equation for the perimeter: 24 = 2(2) + 2x, with x as the unknown side. Solving, you get x = 10 meters. The parallelogram with these dimensions and maximum area is a rectangle with 2-meter and 10-meter sides. Thus, the maximum possible area of the figure is (2 m)(10 m) = 20 m2.
-
28 square units
A triangle with two given sides has maximum area if these two sides are placed at right angles to each other. For this triangle, one of the given sides can be considered the base, and the other side can be considered the height (because they meet at a right angle). Thus, plug these sides into the formula
 .
. -
200 square units
You can think of a right triangle as half of a rectangle. Constructing this right triangle with legs adding to 40 is equivalent to constructing the rectangle with a perimeter of 80. Because the area of the triangle is half that of the rectangle, you can use the previously mentioned technique for maximizing the area of a rectangle: of all rectangles with a given perimeter, the square has the greatest area. Likewise, of all right triangles with a given perimeter, the isosceles right triangle (a 45–45–90 triangle) has the greatest area. The desired rectangle is thus a 20 by 20 square, and the right triangle has an area of
 units.
units.
-
(C)
The surface area of a cube is 6 times e2, where e is the length of each edge (that is, the surface area is the number of faces times the area of each face). Apply this formula to Quantity A:
Quantity A Quantity B The surface area, in square inches, of a cube with edges of length 6 = 6 × (6 × 6) The volume, in cubic inches, of a cube with edges of length 6 The volume of a cube is e3, where e is the length of each edge. Apply this formula to Quantity B:
Quantity A Quantity B 6 × (6 × 6) The volume, in cubic inches, of a cube with edges of length 6
= 6 × 6 × 6It is not generally the case that the volume of a cube in cubic units is equal to the surface area of the cube in square inches; they are only equal when the edge of the cube is of length 6. In this case, the two quantities are equal.
-
(B)
The volume of a cube is e3, where e is the length of each edge. Apply this formula to each quantity:
Quantity A Quantity B The total volume of 3 cubes with edges of length 2 = 3 × 23 = 24 The total volume of 2 cubes with edges of length 3 = 2 × 33 = 54 Therefore, Quantity B is greater.
-
(A)
A rectangular solid has three pairs of opposing equal faces, each pair representing two of the dimensions of the solid (length × width; length × height; height × width). The total surface area of a rectangular solid is the sum of the surface areas of those three pairs of opposing sides.
According to the diagram, the dimensions of each rod must be 1 × 1 × 6. So the surface area of one such rod is:
2(1 × 1) + 2(1 × 6) + 2(1 × 6) = 26 or 2[(1 × 1) + (1 × 6) + (1 × 6)] = 26
That is, one rod has a total surface area of 26, and four times this surface area is 4 × 26 = 104.
Quantity A Quantity B Four times the surface area of just one of the identical rectangular rods = 104 The surface area of the large rectangular solid above The large rectangular solid has a total surface area of: 2(3 × 3) + 2(3 × 6) + 2(3 × 6), or 90.
Quantity A Quantity B 104 The surface area of the large rectangular solid above = 90 Therefore, Quantity A is greater.