Check Your Skills Answer Key
-
x2 + 13x + 36
(x + 4)(x + 9) (x + 4)(x + 9) F – multiply the first term in each parentheses: x × x = x2. (x + 4)(x + 9) O – multiply the outer term in each: x × 9 = 9x. (x + 4)(x + 9) I – multiply the inner term in each: 4 × x = 4x. (x + 4)(x + 9) L – multiply the last term in each: 4 × 9 = 36. x2 + 9x + 4x + 36 → x2 + 13x + 36 -
y2 − 3y − 18
(y + 3)(y − 6) (y + 3)( y − 6) F – multiply the first term in each parentheses: y × y = y2. (y + 3)(y − 6) O – multiply the outer term in each: y × −6 = −6y. (y + 3)(y − 6) I – multiply the inner term in each: 3 × y = 3y. (y + 3)(y − 6) L – multiply the last term in each: 3 × −6 = −18. y2 − 6y + 3y − 18 → y2 − 3y − 18 -
x2 + 10x + 21
(x + 7)(3 + x) (x + 7)(3 + x) F – multiply the first term in each parentheses: x × 3 = 3x. (x + 7)(3 + x) O – multiply the outer term in each: x × x = x2. (x + 7)(3 + x) I – multiply the inner term in each: 7 × 3 = 21. (x + 7)(3 + x) L – multiply the last term in each: 7 × x = 7x. 3x + x2 + 21 + 7x → x2 + 10x + 21
-
4 + 8t 4(1 + 2t) Factor out a 4. -
5x + 25y 5(x + 5y) Factor out a 5. -
2x2 + 16x3 2x2(1 + 8x) Factor out a 2x2.
-
x = 2 OR 1
(x − 2)(x − 1) = 0 (x − 2) = 0 → x = 2 Remove the parentheses and solve for x. OR (x − 1) = 0 → x = 1 Remove the parentheses and solve for x. -
x = −4 OR −5
(x + 4)(x + 5) = 0 (x + 4) = 0 → x = −4 Remove the parentheses and solve for x. OR (x + 5) = 0 → x = −5 Remove the parentheses and solve for x. -
y = 3 OR −6
(y − 3)(y + 6) = 0 (y − 3) = 0 → y = 3 Remove the parentheses and solve for y. OR (y + 6) = 0 → y = −6 Remove the parentheses and solve for y.
-
(x + 3)(x + 11)
x2 + 14x + 33

The numbers 1 and 33 and 3 and 11 multiply to 33, and the numbers 3 and 11 sum to 14 (x + 3)(x + 11)
-
(x − 5)(x − 9)
x2 − 14x + 45

The numbers 1 and 45, 3 and 15, and 5 and 9 multiply to 45. The numbers 5 and 9 sum to 14. (x − 5)(x − 9)
-
(x + 6)(x − 3)
x2 + 3x − 18

The numbers 1 and 18, 2 and 9, and 3 and 6 multiply to 18. The difference of 3 and 6 is 3. The middle term is positive, so the greater of the two numbers (6) is positive.
(x + 6)(x − 3)
-
(x + 6)(x − 11)
x2 − 5x − 66

The numbers 1 and 66, 2 and 33, 3 and 22, and 6 and 11 multiply to 66. The difference of 6 and 11 is 5.
(x + 6)(x − 11)
-
x = 1 OR 2
x2 − 3x + 2 = 0

The numbers 1 and 2 multiply to 2 and add to 3.
(x − 1)(x − 2) = 0
-
x = 5 OR −7
x2 + 2x − 35 = 0
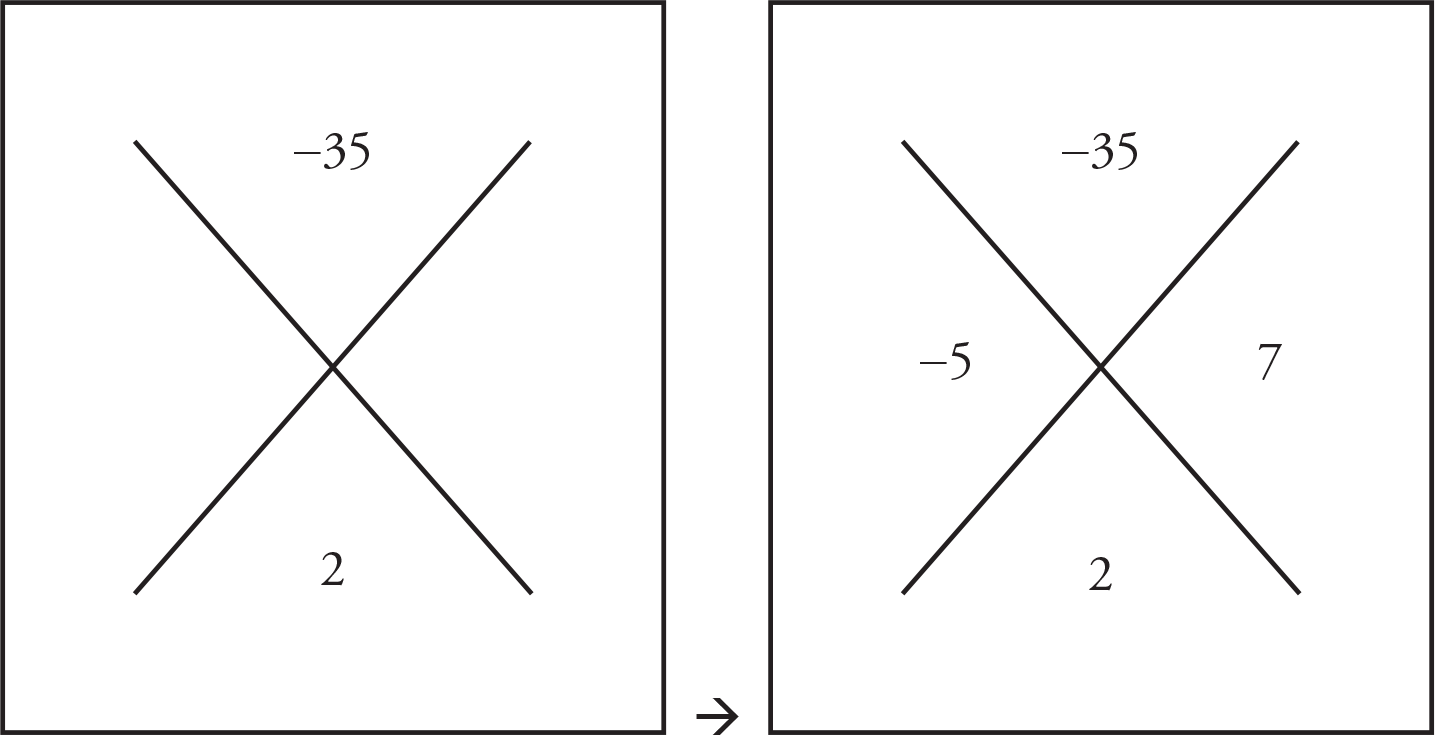
The numbers 5 and 7 multiply to 35 and their difference is 2. The middle term is positive, so the greater of the two numbers, 7, is positive. Thus, (x − 5)(x + 7) = 0.
-
x = 2 OR 13
x2 − 15x = −26
x2 − 15x + 26 = 0 Add 26 to both sides so that the expression equals 0.

The numbers 2 and 13 multiply to 26 and sum to 15.
(x − 2)(x − 13) = 0
-
2


-
x = 5
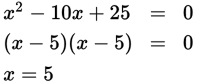
-
x = −1, 2; x ≠ 4

The numerator is 0 if either (x + 1) or (x − 2) is 0. Thus, x = −1 or x = 2. However, x ≠ 4 because x = 4 would make the fraction undefined.
-
(2a + b)2 = 0
4a2 + 4ab + b2 = 0 → (2a)2 + 2(2a)(b) + b2 = 0 → (2a + b)(2a + b) = 0
-
(x + 11y)2 = 0
x2 + 22xy + 121y2 = 0 → x2 + 2x(11y) + (11y)2 = 0 → (x + 11y)(x + 11y) = 0