Solutions
-
k = 6
If −4 is a solution, then you know that (x + 4) must be one of the factors of the quadratic equation. The other factor is (x + ?). You know that the product of 4 and ? must be equal to 8; thus, the other factor is (x + 2). You know that the sum of 4 and 2 must be equal to k. Therefore, k = 6.
- (A)
If the solutions to the equation are 8 and −4, the factored form of the equation is:
(x − 8)(x + 4) = 0
Distributed, this equals: x2 − 4x − 32 = 0.
-
y = {−4, −6}
Simplify and factor to solve.
16 − y2 = 10(4 + y)
16 − y2 = 40 + 10y
y2 + 10y + 24 = 0
(y + 4)(y + 6) = 0y + 4 = 0
y = −4OR y + 6 = 0
y = −6Notice that it is possible to factor the left side of the equation first: 16 − y2 = (4 + y)(4 − y). However, doing so is potentially dangerous: You may decide to then divide both sides of the equation by (4 + y). You cannot do this, because it is possible that (4 + y) equals 0 (and, in fact, for one solution of the equation, it does).
-
x = {−3, 3}

-
x = {15, −2}

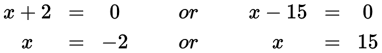
-
s = 7
The area of the square = s2. The perimeter of the square = 4s:
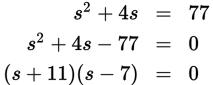

-
t = 2
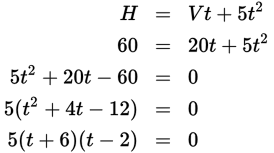
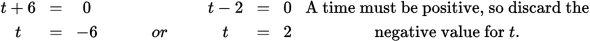
-
2
Use FOIL to simplify this product:

-
19
Factor both quadratic equations. Then use the greatest possible values of x and y to find the maximum value of the sum x + y:
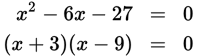
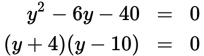
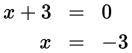
or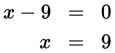
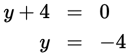
or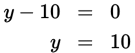
The maximum possible value of x + y = 9 + 10 = 19.
-
x = {1, 9}
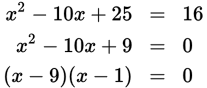

or
-
(D)
First, factor the equation in the common information:
x2 − 2x − 15 = 0 → (x − 5)(x + 3) = 0
x = 5 or x = −3x2 − 2x − 15 = 0
Quantity A Quantity B x = 5 or –3 1 The value of x could be greater than or less than 1. The relationship cannot be determined.
-
(C)
First, factor the equation in the common information:
x2 − 12x + 36 = 0 → (x − 6)(x − 6) = 0
x = 6x2 – 12x + 36 = 0 Quantity A Quantity B x = 6 6 The two quantities are equal.
-
(A)
Expand the expressions in both columns:
xy>0 Quantity A Quantity B 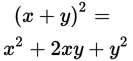
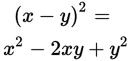
Now subtract x2 + y2 from both columns:
xy>0 Quantity A Quantity B 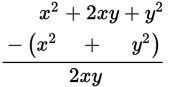
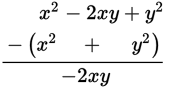
Because xy is positive, Quantity A will be positive, regardless of the values of x and y. Similarly, Quantity B will always be negative, regardless of the values of x and y.
Quantity A is greater.