Solutions
-
(A)
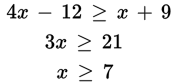
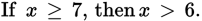
- (A)
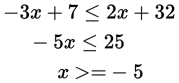
When you divide by a negative number, you must reverse the direction of the inequality symbol. - (C)
If G2 < G, then G must be positive (because G2 will never be negative), and G must be less than 1, because otherwise, G2 > G. Thus, 0 < G < 1. You can eliminate choices (D) and (E) because they violate the condition that G be positive. Then test choice (A): 1 is not less than 1, so you can eliminate (A). Choice (B) is greater than 1, so only choice (C) satisfies the inequality.
- (C)
If |A| > 19, then A > 19 OR A < −19. The only answer choice that does not satisfy either of these inequalities is choice (C), 18.
- (A)
If A is positive, B3 must be negative. Therefore, B must be negative. If A is positive and B is negative, the product AB must be negative.
-
(D)
To evaluate the absolute value, set up two equations and isolate x:
+ (2x − 5) ≤ 7
2x − 5 ≤ 7
2x ≤ 12
x ≤ 6and −(2x − 5) ≤ 7
−2x + 5 ≤ 7
−2x ≤ 2
x ≥ −1
Combine the information from the two equations:
|2x − 5| ≤ 7 Quantity A Quantity B −1 ≤ x ≤ 6 3 There are possible values of x greater than and less than 3. The relationship cannot be determined.
-
(D)
To find the minimum and maximum values of xy, test the boundaries of x and y:
x y xy Min 1 Min −2 (1) × (−2) = −2 Min 1 Max 1 (1) × (1) = 1 Max 5 Min −2 (5) × (−2) = −10 Max 5 Max 1 (5) × (1) = 5 Combine the information from the chart to show the range of xy:
1 ≤ x ≤ 5 and 1 ≥ y ≥ −2 Quantity A Quantity B −10 ≤ xy ≤ 5 −10 Quantity A can be either greater than or equal to −10. The relationship cannot be determined.
-
(C)
Plug in 4 for x in Quantity A.
x = 4 Quantity A Quantity B |2 − x| =
|2 − (4)| = |−2| = 22 The two quantities are equal.