Chapter 4
Formulas & Functions
Plug In Formulas
The most basic GRE formula problems provide you with a formula and ask you to solve for one of the variables in the formula by plugging in given values for the other variables. For example:
The formula for determining an individual’s comedic aptitude, C, on a given day is defined as
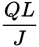 , where J represents the number of jokes told, Q represents the overall joke quality on a scale of 1 to 10, and L represents the number of individual laughs generated. If Nicole told 12 jokes, generated 18 laughs, and earned a comedic aptitude of 10.5, what was the overall quality of her jokes?
, where J represents the number of jokes told, Q represents the overall joke quality on a scale of 1 to 10, and L represents the number of individual laughs generated. If Nicole told 12 jokes, generated 18 laughs, and earned a comedic aptitude of 10.5, what was the overall quality of her jokes?
Solving this problem involves plugging the given values into the formula to solve for the unknown variable Q:
The quality of Nicole’s jokes was rated a 7.
Notice that you will typically have to do some rearrangement after plugging in the numbers, to isolate the desired unknown. The actual computations are not complex. What makes formula problems tricky is the unfamiliarity of the given formula, which may seem to come from “out of the blue.” Do not be intimidated. Simply write the equation down, plug in the numbers carefully, and solve for the required unknown. Alternatively, you can rearrange the original equation to solve for the unknown before plugging in the numbers. Either order works fine.
Be sure to write the formula as a part of an equation. For instance, do not just write “ ” on your paper. Rather, write “
” on your paper. Rather, write “ .” Look for language such as “is defined as” to identify what equals what.
.” Look for language such as “is defined as” to identify what equals what.
-
The baking time in minutes for a certain cake is defined as
 , where V is the volume of the cake in inches cubed, T is the oven temperature in degrees Fahrenheit, and k is a constant. If the
baking time was 30 minutes at 350 degrees Fahrenheit for a cake with a volume of 150 cubic inches, what is the value of constant k?
, where V is the volume of the cake in inches cubed, T is the oven temperature in degrees Fahrenheit, and k is a constant. If the
baking time was 30 minutes at 350 degrees Fahrenheit for a cake with a volume of 150 cubic inches, what is the value of constant k?
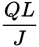 , where J represents the number of jokes told, Q represents the overall joke quality on a scale of 1 to 10, and L represents the number of individual laughs generated. If Nicole told 12 jokes, generated 18 laughs, and earned a comedic aptitude of 10.5, what was the overall quality of her jokes?
, where J represents the number of jokes told, Q represents the overall joke quality on a scale of 1 to 10, and L represents the number of individual laughs generated. If Nicole told 12 jokes, generated 18 laughs, and earned a comedic aptitude of 10.5, what was the overall quality of her jokes? 

 ” on your paper. Rather, write “
” on your paper. Rather, write “ .” Look for language such as “is defined as” to identify what equals what.
.” Look for language such as “is defined as” to identify what equals what. , where V is the volume of the cake in inches cubed, T is the oven temperature in degrees Fahrenheit, and k is a constant. If the
baking time was 30 minutes at 350 degrees Fahrenheit for a cake with a volume of 150 cubic inches, what is the value of constant k?
, where V is the volume of the cake in inches cubed, T is the oven temperature in degrees Fahrenheit, and k is a constant. If the
baking time was 30 minutes at 350 degrees Fahrenheit for a cake with a volume of 150 cubic inches, what is the value of constant k?