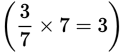 , so there are eight French majors (5 + 3 = 8). In this scenario, Quantity A is greater.
, so there are eight French majors (5 + 3 = 8). In this scenario, Quantity A is greater.Don’t confuse a ratio with actual numbers of objects. For instance, if you know that a store carries red shirts and white shirts in a 2 to 3 ratio, the store may have five total shirts (two red and three white), 10 total shirts (four red and six white), 500 total shirts (200 red and 300 white), and so on. What is known is that there are fewer red shirts than white shirts and that the total number of shirts must be a multiple of 5.
Adding real numbers of objects to a ratio isn’t very helpful without some real numbers of objects to begin with. For example, if a store carries red shirts and white shirts in a 2 to 3 ratio, what effect does adding three red shirts have? Well, if the store had five total shirts (two red and three white), adding three red shirts changes the ratio to 5 to 3 (five red and three white). But if you started with 500 total shirts (200 red and 300 white), adding three red shirts doesn’t change the ratio very much at all; it’s now 203 to 300. Try an example:
| A university contains French majors and Spanish majors in a 5 to 7 ratio. |
|
| Quantity A | Quantity B |
| The number of French majors if 10 French majors transfer into the university and no other students leave, join, or change majors |
The number of French majors if 3/7 of the Spanish majors switch to French |
Try to prove (D). Start by constructing two scenarios for “A university contains French majors and Spanish majors in a 5 to 7 ratio.” For the first scenario, use the smallest possible values: five French majors and seven Spanish majors. For the second scenario, use much larger (but still easy to work with) numbers: 500 French majors and 700 Spanish majors.
Evaluate the first scenario. For the first scenario (five French majors and seven Spanish majors), Quantity A gives us 15 French majors (5 + 10 = 15). In Quantity B, three Spanish majors switch to French
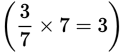 , so there are eight French majors (5 + 3 = 8). In this scenario, Quantity A is greater.
, so there are eight French majors (5 + 3 = 8). In this scenario, Quantity A is greater.
Now, evaluate the second scenario (500 French majors and 700 Spanish majors). Quantity A gives you 510 French majors (500 + 10 = 510). In Quantity B, 300 Spanish majors switch to French
 , so there are 800 total French majors. In this scenario, Quantity B is greater. The correct answer is (D).
, so there are 800 total French majors. In this scenario, Quantity B is greater. The correct answer is (D).