| If You See... | Write: | Not: | ||
| “A is half the size of B.” | ✔ |
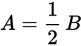
|
✘ |
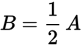
|
| “A is 5 less than B.” | ✔ | A = B − 5 | ✘ | A = 5 − B |
| “A is less than B.” | ✔ | A < B | ✘ | A > B |
| “Jane bought twice as many apples as bananas.” | ✔ | A = 2B | ✘ | 2A = B |
For the last example in the table, you might think the following:
“Jane bought twice as many apples as bananas. More apples than bananas. Say she buys five bananas. She buys twice as many apples—that’s 10 apples. Makes sense. So the equation is Apples equals two times Bananas, or A = 2B, not the other way around.”
These numbers do not have to satisfy any other conditions of the problem. Use these “quick picks” only to test the form of your translation.
| If You See... | Write | Not | ||
| “P is X percent of Q.” | ✔ |
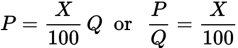
|
✘ |
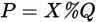
|
| (Cannot be manipulated.) | ||||
| If You See... | Write | Not | |||
|
✔ |
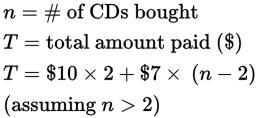
|
✘ |

|
Always pay attention to the meaning of the sentence you are translating. If necessary, take a few extra seconds to make sure you’ve set up the algebra correctly.