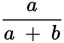 and
and
 :
:Although weighted averages differ from traditional averages, they are still averages, meaning that their values will still fall between the values being averaged (or between the highest and lowest of those values, if there are more than two).
A weighted average of only two values will fall closer to whichever value is weighted more heavily. For instance, if a drink is made by mixing 2 shots of a liquor containing 15% alcohol with 3 shots of a liquor containing 20% alcohol, then the alcohol content of the mixed drink will be closer to 20% than to 15%.
For example, take the weighted average of 20 and 30, with weights
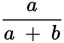 and
and
 :
:
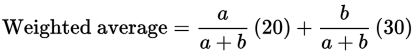
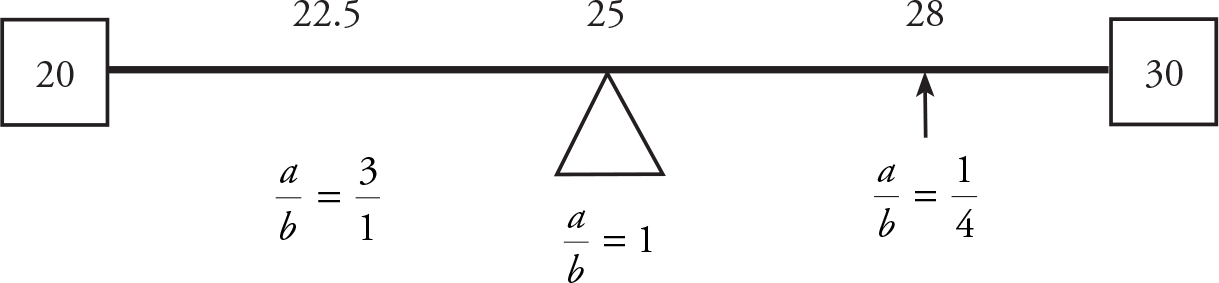
The weighted average will always be between 20 and 30, as long as a and b are both positive (and on the GRE, they always have been). A number line between 20 and 30 can help you visualize where the weighted average will fall:

If, for example, you’re told that the ratio of a to b is 3 to 1, then you know that the average will fall somewhere between 20 and 25, and you also know that it is possible to calculate the specific value:
A stock portfolio is comprised of Stock A, whose annual gain was 10%, and Stock B, whose annual gain was 20%. If the stock portfolio gained 14% overall, does it contain more shares of Stock A or Stock B?
2/3 of the aliens on Planet X are Zorgs, whose average IQ is 120. The rest are Weebs, whose average IQ is 180. What is the average IQ of all the aliens on Planet X?