Chapter 25
The average (or the arithmetic mean) of a list of numbers is given by the following formula (also known as “the average formula”):
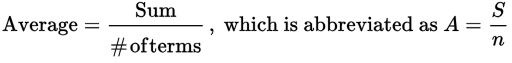
The sum, S, refers to the sum of all the terms in the list.
The number, n, refers to the number of terms that are in the list.
The average, A, refers to the average value (arithmetic mean) of the terms in the list.
The language in an average problem will often refer to an “arithmetic mean.” However, occasionally the concept is implied. “The cost per employee, if equally shared, is $20” means that the average cost per employee is $20.
A commonly used variation of the Average formula is:
Average × # of terms = Sum, or A × n = S
This formula has the same basic form as the Rate × Time = Distance (RTD) equation that you reviewed in Chapter 23, so it lends itself readily to the same kind of table you would use for RTD problems.
Every GRE problem dealing with averages can be solved with the average formula. If you are asked to use or find the average of a list of numbers, you should not generally concentrate on the individual terms of the list. As you can see from the formulas above, all that matters is the sum of the terms—which often can be found even if the individual terms cannot be determined.