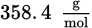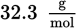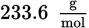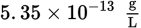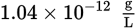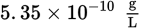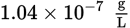Discrete Practice Questions
-
An aqueous solution was prepared by mixing 70 g of an unknown nondissociating solute into 100 g of water. The solution has a boiling point of 101.0°C. What is the molar mass of the solute? (Note:
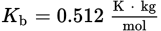 )
) -
-
Which phases of solvent and solute can form a solution?
- Solid solvent, gaseous solute
- Solid solvent, solid solute
- Gaseous solvent, gaseous solute
- I and II only
- I and III only
- II and III only
- I, II, and III
-
Two organic liquids, pictured in the figure below, are combined to form a solution. Based on their structures, will the solution closely obey Raoult’s law?

- Yes; the liquids differ due to the additional methyl group on toluene and, therefore, will not deviate from Raoult’s law.
- Yes; the liquids are very similar and, therefore, will not deviate from Raoult’s law.
- No; the liquids differ due to the additional methyl group on toluene and, therefore, will deviate from Raoult’s law.
- No; the liquids both contain benzene rings, which will interact with each other and cause deviation from Raoult’s law.
-
Which of the following explanations best describes the mechanism by which solute particles affect the melting point of ice?
- Melting point is elevated because the kinetic energy of the substance increases.
- Melting point is elevated because the kinetic energy of the substance decreases.
- Melting point is depressed because solute particles interfere with lattice formation.
- Melting point is depressed because solute particles enhance lattice formation.
-
The process of formation of a salt solution can be better understood by breaking the process into three steps:
- Breaking the solute into its individual components
- Making room for the solute in the solvent by overcoming intermolecular forces in the solvent
- Allowing solute–solvent interactions to occur to form the solution
Which of the following correctly lists the enthalpy changes for these three steps, respectively?
- Endothermic, exothermic, endothermic
- Exothermic, endothermic, endothermic
- Exothermic, exothermic, endothermic
- Endothermic, endothermic, exothermic
-
The entropy change when a solution forms can be expressed by the term ΔS°soln. When water molecules become ordered around an ion as it dissolves, the ordering would be expected to make a negative contribution to ΔS°soln. An ion that has more charge density will have a greater hydration effect, or ordering of water molecules. Based on this information, which of the following compounds will have the most negative contribution to ΔS°soln?
- KCl
- CsI
- CaS
- NaCl
-
When ammonia, NH3, is used as a solvent, it can form complex ions. For example, dissolving AgCl in NH3 will result in the complex ion [Ag(NH3)]2+. What effect would the formation of complex ions have on the solubility of a compound like AgCl in NH3?
- The solubility of AgCl will increase because complex ion formation will cause more ions to exist in solution, which interact with AgCl to cause it to dissociate.
- The solubility of AgCl will increase because complex ion formation will consume Ag+ ions and cause the equilibrium to shift away from solid AgCl.
- The solubility of AgCl will decrease because Ag+ ions are in complexes, and the Ag+ ions that are not complexed will associate with Cl− to form solid AgCl.
- The solubility of AgCl will decrease because complex ion formation will consume Ag+ ions and cause the equilibrium to shift toward the solid AgCl.
-
One hundred grams of sucrose are dissolved in a cup of hot water at 80°C. The cup of water contains 300.00 mL of water. What is the percent composition by mass of sugar in the resulting solution? (Note: Sucrose = C12H22O11, density of water at
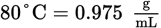 )
)- 25.0%
- 25.5%
- 33.3%
- 34.2%
-
Which of the following combinations of liquids would be expected to have a vapor pressure higher than the vapor pressure that would be predicted by Raoult’s law?
- Ethanol and hexane
- Acetone and water
- Isopropanol and methanol
- Nitric acid and water
-
The salt KCl is dissolved in a beaker. To an observer holding the beaker, the solution begins to feel colder as the KCl dissolves. From this observation, one could conclude that:
- ΔS°soln is large enough to overcome the unfavorable ΔH°soln.
- KCl is mostly insoluble in water.
- ΔS°soln must be negative when KCl dissolves.
- boiling point depression will occur in this solution.
-
Which of the following will cause the greatest increase in the boiling point of water when it is dissolved in 1.00 kg H2O?
- 0.4 mol calcium sulfate
- 0.5 mol iron(III) nitrate
- 1.0 mol acetic acid
- 1.0 mol sucrose
-
Reverse osmosis is a process that allows fresh water to be obtained by using pressure to force an impure water source through a semi-permeable membrane that only allows water molecules to pass. What is the minimum pressure that would be required to purify seawater at 25°C that has a total osmolarity of 1,000 mOsm/L?
- 23.5 atm
- 24.5 atm
- 24,000 atm
- 24,500 atm
-
Lead is a toxic element that can cause many symptoms, including mental retardation in children. If a body of water is polluted with lead ions at 200 ppb (parts per billion), what is the concentration of lead expressed as molarity? (Note: The density of water is
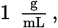 and ppb = grams per 109 grams of solution)
and ppb = grams per 109 grams of solution)- 9.7 × 10−10 M Pb2+
- 9.7 × 10−7 M Pb2+
- 6.2 × 10−7 M Pb2+
- 6.2 × 10−6 M Pb2+
-
A saturated solution of cobalt(III) hydroxide (Ksp = 1.6 × 10−44) is added to a saturated solution of thallium(III) hydroxide (Ksp = 6.3 × 10−46). What is likely to occur?
- Both cobalt(III) hydroxide and thallium(III) hydroxide remain stable in solution.
- Cobalt(III) hydroxide precipitates and thallium(III) hydroxide remains stable in solution.
- Thallium(III) hydroxide precipitates and cobalt(III) hydroxide remains stable in solution.
- Both thallium(III) hydroxide and cobalt(III) hydroxide precipitate.
-
The following equilibrium exists when AgBr (Ksp = 5.35 × 10−13) is in solution:
AgBr (s) ⇌ Ag+ (aq) + Br− (aq)What is the solubility of AgBr in a solution of 0.0010 M NaBr?
-