6
Recovery stroke.
The heads of the myosin moleculesreturn to their resting position (
small, dark blue arrow
), andenergy is stored in the heads of the myosin molecules. IfCa
2+
is still attached to troponin, cross-bridge formation andmovement are repeated (return to step 2). This cycle occursmany times during a muscle contraction. Not allcross-bridges form and release simultaneously.
P
2
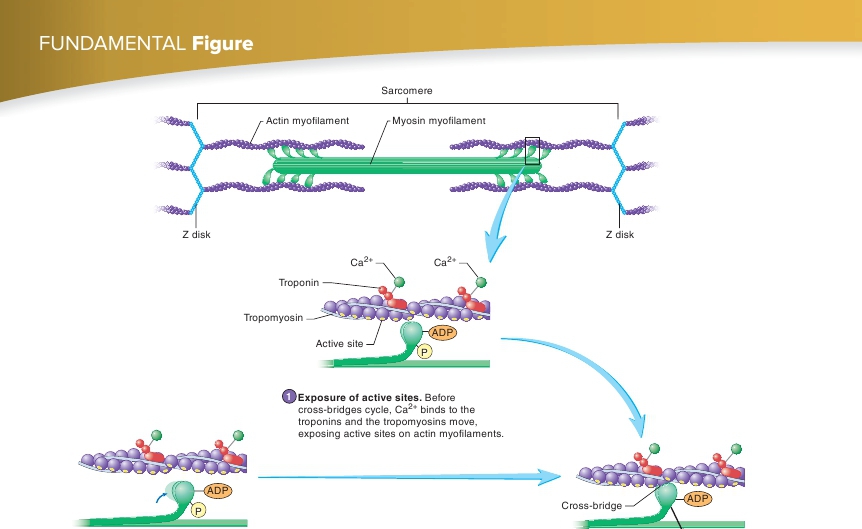
Cross-bridge formation.
The myosin heads bind to theexposed active sites on the actin myofilaments to formcross-bridges, and phosphates are released from themyosin heads.

5
Hydrolysis of ATP.
The myosin ATPase portion of themyosin heads break down ATP into ADP and phosphate (P),which remain attached to the myosin heads.
arrow
),causing the actin myofilaments to slide past the myosinmyofilaments (
dark blue arrow
), and ADP molecules arereleased from the myosin heads (
black arrow
).
4
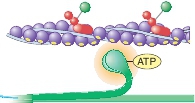
Cross-bridge release.
An ATP molecule binds to each ofthe myosin heads, causing them to detach from the actin.

PROCESS FIGURE 9.15
Breakdown of ATP and Cross-Bridge Movement During Muscle Contraction
286