CHAPTER 10 Muscular System: Gross Anatomy
317
quite limited as to how much weight can be lifted and how highit can be lifted. For example, consider what happens when thechild on one end of the seesaw is much larger than the child onthe other end.
Class II Lever
(a)
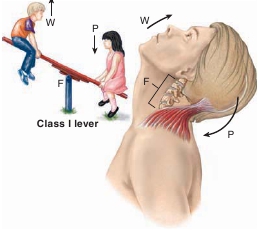
Class I:
The fulcrum (
F
) is located between the weight (
W
) and thepull (
P
), or force. The pull is directed downward, and the weight, on theopposite side of the fulcrum, is lifted. In the body, the fulcrum extendsthrough several cervical vertebrae.
In a
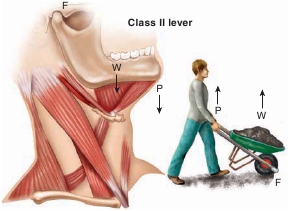
class II lever system,
the weight is located between thefulcrum and the pull (figure 10.2
b
). An example is a wheelbar-row; the wheel is the fulcrum, and the person lifting on the han-dles provides the pull. The weight, or load, carried in thewheelbarrow is placed between the wheel and the operator. In thebody, there are relatively few examples of class II levers. Depress-ing the mandible when you open your mouth is one example.Another is your entire body when doing push-ups—your toes arethe fulcrum, your body is the weight, and your arms provide thepull (force).
Class III Lever
In a
class III lever system,
the most common type in thebody, the pull is between the fulcrum and the weight(figure 10.2
c
). An example is a person using a shovel. The handplaced on the part of the handle closest to the blade provides thepull to lift the weight, such as a shovelful of dirt, and the handplaced near the end of the handle acts as the fulcrum. In thebody, the action of the biceps brachii muscle (force) pulling onthe radius (lever) to flex the elbow (fulcrum) and elevate thehand (weight) is a class III lever. This type of lever system doesnot allow as great a weight to be lifted, but it can be lifted agreater distance.
Muscle Anatomy
(b)
Class II:
The weight (
W
) is located between the fulcrum (
F
) and thepull (
P
), or force. The upward pull lifts the weight. The movement of themandible is easier to compare to a wheelbarrow if the head is consideredupside down.
An overview of the superficial skeletal muscles appears infigure 10.3. Muscles of the head and neck, trunk, and limbs aredescribed in the following sections.

F
example of each.
6.
Using the terms
fulcrum, lever,
and
force,
explain howcontraction of a muscle results in movement.
7.
Describe the three classes of levers, and give an exampleof each type in the body.
(c)
Class III:
The pull (
P
), or force, is located between the fulcrum (
F
) andthe weight (
W
). The upward pull lifts the weight.
FIGURE 10.2
Classes of Levers