390
PART 3 Integration and Control Systems
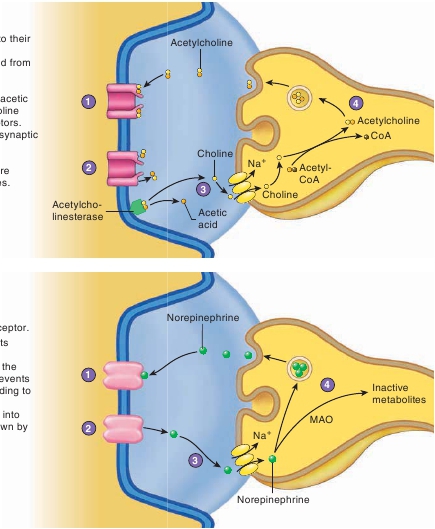
1
Acetylcholine molecules bindreceptors.
2
Acetylcholine molecules unbindtheir receptors.
3
Acetylcholinesterase splitsacetylcholine into choline andacid, which prevents acetylcholinefrom again binding to its receptors.Choline is taken up by the presynapticterminal.
4
Choline is used to make newacetylcholine molecules that arepackaged into synaptic vesicles.
(a)
1
Norepinephrine binds to its receptor.
2
Norepinephrine unbinds fromreceptor.
3
Norepinephrine is taken up bypresynaptic terminal, which preventsnorepinephrine from again bindingits receptor.
4
Norepinephrine is repackagedsynaptic vesicles or broken downmonoamine oxidase (MAO).
(b)
PROCESS FIGURE 11.19
Removal of Neurotransmitters from the Synaptic Cleft
(
a
) In some synapses, neurotransmitters are broken down by enzymes and recycled into the presynaptic terminal. (
b
) In other synapses, neurotransmitters aretaken up whole into the presynaptic terminal.
Predict 9
Is an action potential transmitted faster between cells connected by anelectrical synapse or by a chemical synapse? Explain.
Neurotransmitter Removal
The interaction between a neurotransmitter and a receptor representsan equilibrium:
Neurotransmitter + Receptor
Neurotransmitter – Receptor complex
When the neurotransmitter concentration in the synaptic cleft is high,many of the receptor molecules have neurotransmitter moleculesbound to them; when the neurotransmitter concentration declines, theneurotransmitter molecules diffuse away from the receptor molecules.Neurotransmitters have short-term effects on postsynapticmembranes because the neurotransmitter is rapidly destroyed orremoved from the synaptic cleft. For example, in the neuromuscularjunction (see chapter 9), the neurotransmitter acetylcholine is broken
down by the enzyme
acetylcholinesterase
(as′e-til-k ō -lin-es′ter- ā s)to acetic acid and choline (figure 11.19
a
). Choline is then transportedback into the presynaptic terminal and combines with acetyl-CoA tore-form acetylcholine. Acetyl-CoA is synthesized by mitochondriaas foods are metabolized to produce ATP (see chapter 25). Aceticacid can be absorbed from the synaptic cleft into the presynapticterminal, or it can diffuse out of the synaptic cleft and be taken up bya variety of cells. Acetic acid can be used to synthesize acetyl-CoA.When the neurotransmitter norepinephrine is released into thesynaptic cleft, most of it is transported back into the presynapticterminal, where it is repackaged into synaptic vesicles for later use(figure 11.19
b
). The enzyme
monoamine oxidase
(
MAO;
mon-ō -am′ ī n ok′si-d ā s) breaks down some of the norepinephrine.Diffusion of neurotransmitter molecules away from the syn-apse and into the extracellular fluid also limits the length of timethe neurotransmitter molecules remain bound to their receptors.Norepinephrine in the circulation is taken up primarily by liverand kidney cells, where the enzymes monoamine oxidase and