460
PART 3 Integration and Control Systems
Diseases
and
Disorders
TABLE 13.6
CNS and Cranial Nerves
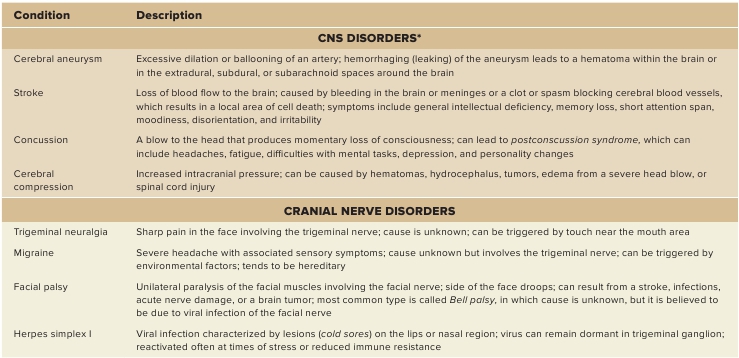
* For more CNS disorders, see Diseases and Disorders tables in chapters 12 and 14.
Reflexes Involving Cranial Nerves
Reflexes integrated within the spinal cord were discussed inchapter 12. Many of the body’s functions, especially those involvedin maintaining homeostasis, involve reflexes that are integratedwithin the brain. Some of these reflexes, such as those involvedin controlling heart rate (see chapter 20), blood pressure (seechapter 21), and respiration (see chapter 23), are integrated in thebrainstem and many involve cranial nerve X (vagus nerve).Many of the brainstem reflexes are associated with cranialnerve function. In general, these reflexes involve sensory inputfrom the cranial nerves or spinal cord and the motor output of thecranial nerves.Turning the eyes toward a flash of light, a sudden noise, ora touch on the skin is an example of a brainstem reflex. Movingthe eyes to track a moving object is another complex brainstemreflex. Some of the sensory neurons from cranial nerve VIIIform a reflex arc with neurons of cranial nerves V and VII,which send axons to muscles of the middle ear and dampen theeffects of very loud, sustained noises on delicate inner ear struc-tures (see chapter 15). Reflexes that occur during chewing allowthe jaws to react to foods of various hardness and protect theteeth from breaking on very hard foods. Both the sensory andmotor components of the reflex arc are carried by cranial nerveV. Reflexes involving input through cranial nerve V and output
through cranial nerve XII move the tongue to position foodbetween the teeth for chewing and then move the tongue out ofthe way, so that it is not bitten.

ASSESS
YOUR PROGRESS
25.
What are the three major functions of the cranialnerves?
26.
Which cranial nerves are sensory only? With what sense iseach of these associated?
27.
Name the cranial nerves that are somatic motor andproprioceptive only. What muscles or groups of musclesdoes each nerve supply? What is proprioception?
28.
What cranial nerve provides the sensory cutaneousinnervation of the face? How is this nerve important indentistry? Name the muscles that would not function ifthis nerve were damaged.
29.
Which four cranial nerves have a parasympatheticfunction? Describe the functions of each of thesenerves.
30.
Which cranial nerve leaves the head and neck region?
31.
Give an example of reflex integration by cranialnerves.