CHAPTER 21 Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation
745
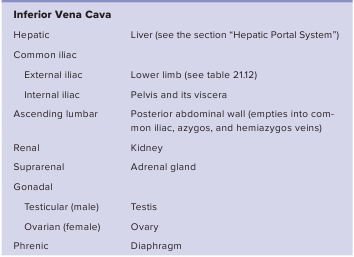
kidneys, and adrenal glands are the only abdominal organs outsidethe pelvis that drain directly into the inferior vena cava. The
internal iliac veins
drain the pelvis and join the
external iliacveins
from the lower limbs to form the
common iliac veins,
whichunite to form the inferior vena cava. The major abdominal andpelvic veins are listed in table 21.10 and illustrated in figure 21.26;also see figure 21.28.
TABLE 21.10
Veins Draining the Abdomen andPelvis (figures 21.26 and 21.28)

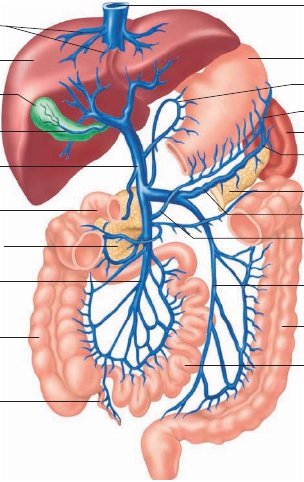
Hepatic Portal System
The
hepatic
(he-pat′ik; relating to the liver)
portal system
(figures 21.27 and 21.28; table 21.11) carries blood drained fromcapillaries within most of the abdominal viscera, such as the stomach,intestines, and spleen, to a series of dilated capillaries, called sinu-soids, in the liver. This system delivers nutrients and othersubstances absorbed from the stomach or small intestine to theliver (see chapter 24).The
hepatic portal vein,
the largest vein of the system, isformed by the union of the
superior mesenteric vein,
which drainsthe small intestine, and the
splenic vein,
which drains the spleen.The splenic vein receives blood from the
inferior mesenteric vein,
Inferior vena cava
Hepatic veins
Liver
Gallbladder
Cysticvein
Hepaticportal vein
Duodenum
Stomach
Gastric veins
Gastroomental veins
Spleen
Splenic vein withpancreatic branches
Tail of pancreas
Splenic vein
Gastroomental veins
Head of pancreas
Superiormesenteric vein
Inferior mesenteric vein
Descending colon
Ascending colon
Small intestine
Appendix
FIGURE 21.27
Veins of the Hepatic Portal System
The hepatic portal system begins as capillary beds in the stomach, pancreas, spleen, small intestine, and large intestine. The veins of the hepatic portal sys-tem converge on the hepatic portal vein, which carries blood to a series of capillaries (sinusoids) in the liver. Hepatic veins carry blood from capillaries in theliver to the inferior vena cava (also see figure 21.26).