This chapter includes samples of the pretest materials typically supplied to applicants, a sample test and an answer key to the test.


Study the following materials prior to taking this exam. These materials will be provided to you in the pretest materials from the city. You may study these as much as you like prior to the exam, but you will not be allowed to refer to them during the exam. Learn to associate each drawing with its label so as to apply the correct information.
Directions: Read and understand the following law enforcement-related terms and definitions and then be prepared to use this information on the actual exam to answer a series of questions.
VOCABULARY TERMS

Learn the details of the drawings provided below and the information provided with each drawing. Be sure to remember the caption for each drawing because the pictures will not be on the exam, and you will be asked to answer questions about each drawing.
Pay attention to the details of the drawing, including numbers, dates, signs, and other details.
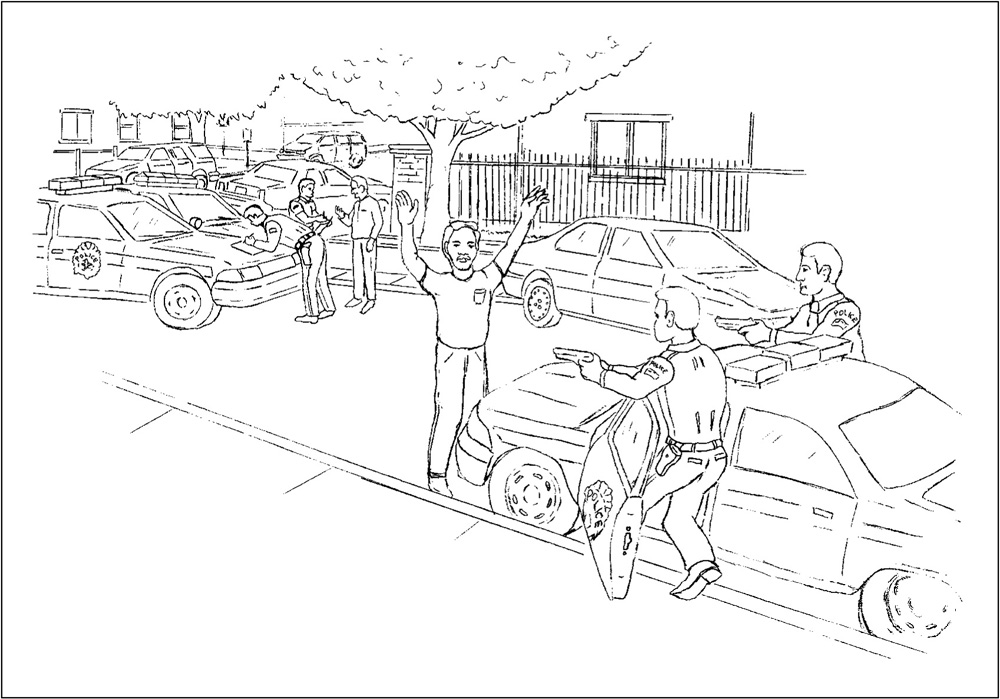
FELONY CAR STOP
Officers had lawfully stopped the vehicle on the street for failing to signal a lane change. Upon approaching the vehicle after it was stopped, officers saw evidence of a serious crime lying in plain view on the back seat. Officers seized the evidence and arrested the two occupants of the vehicle. One of the occupants attempted to flee on foot but was quickly apprehended by officers. Upon arresting the driver of the vehicle police are able to lawfully search the vehicle.
FORCED CAR STOP
A high speed chase between a suspect in a drive-by shooting and state police down State Highway 50 ended when a law enforcement officer was able to use his car to force the suspect off the side of the road. Although the crash seriously damaged a patrol car and the suspect’s car, there were no serious injuries. The single occupant of the pick-up truck was taken into custody. Traffic on Highway 50 was backed up for several hours.
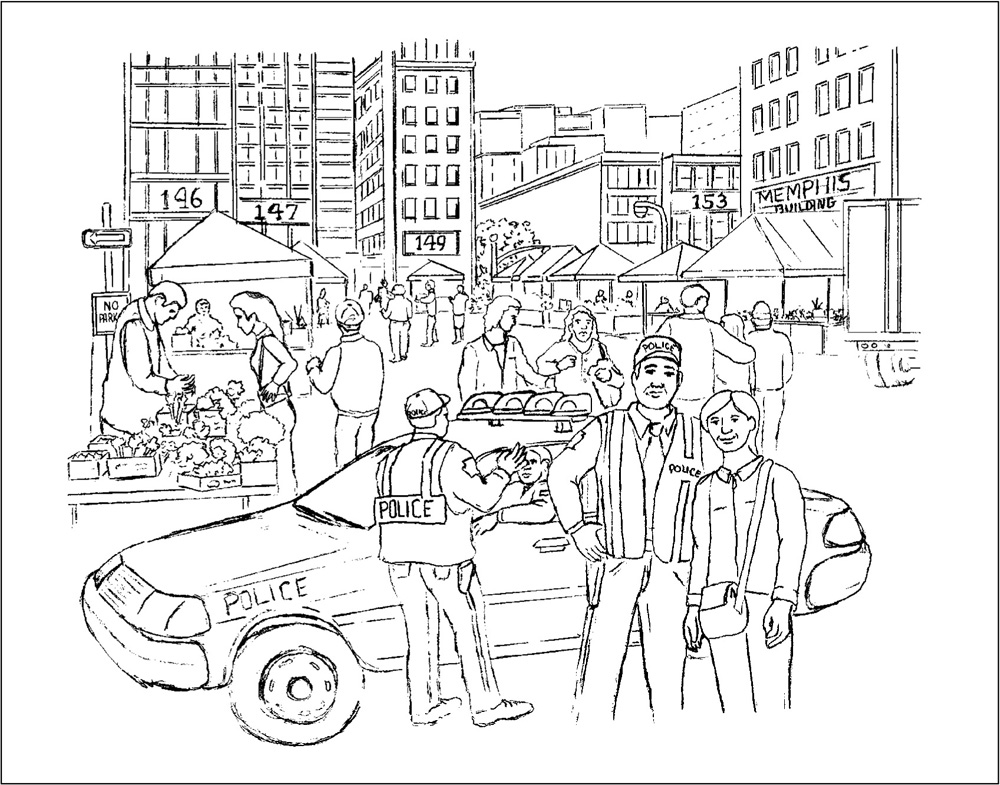

OUTDOOR MARKET
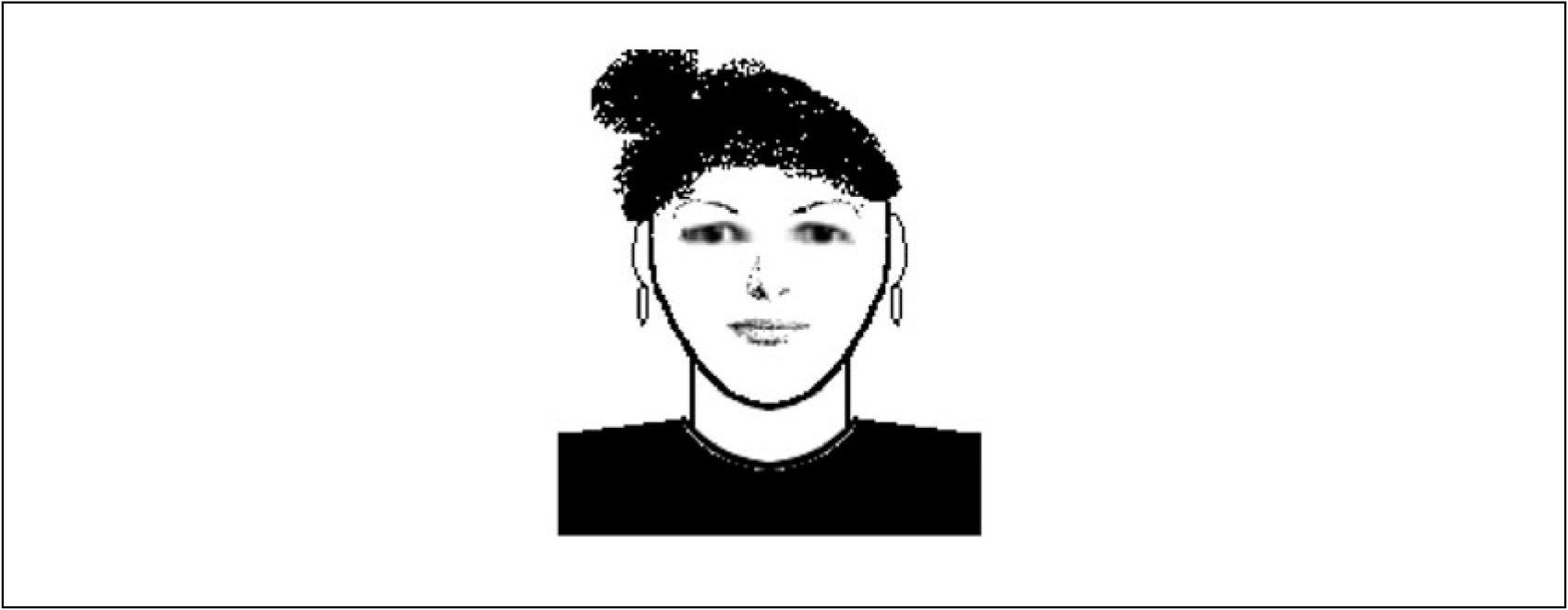

SUSPECT No. 1

SUSPECT No. 2


SUSPECT No. 3

SUSPECT No. 4

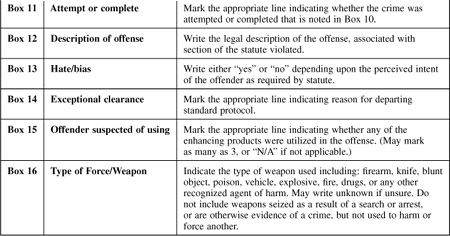
General Rules for Completing the STANDARD OFFENSE REPORT Form
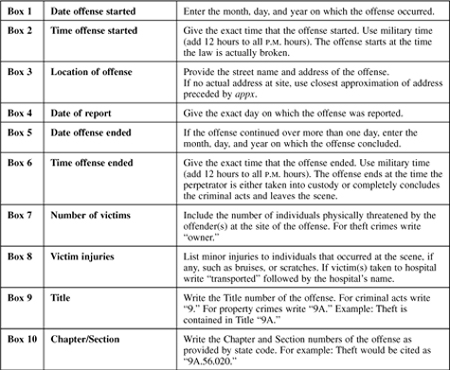
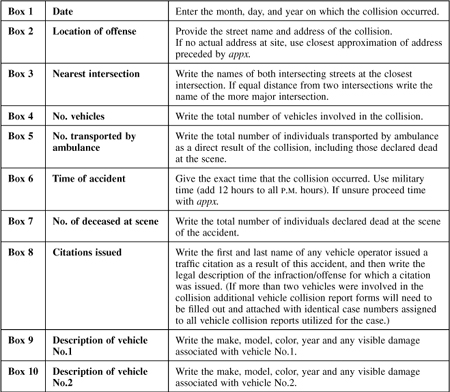
General Rules for Completing the VEHICLE COLLISION REPORT Form

One of the duties of law enforcement officers is traffic enforcement. Generally, when an officer sees a violation of the traffic laws the officer has probable cause to stop the vehicle. Probable cause to stop the vehicle arises out of the officer’s knowledge that an infraction of the traffic laws has occurred and a belief that the infraction was caused by the driver of the vehicle seen violating the law. Probable cause requires a clear link between an illegal act and an individual. For example, when an officer sees a vehicle speeding, the officer has a clear link between the driver of the vehicle and the violation of the law.
Upon stopping a vehicle for a traffic infraction the officer must use extreme care when approaching the occupants of the vehicle. Although the majority of traffic stops result in an irritated driver leaving with a citation, there is always a possibility that a driver will react to the stop with violence. The reason for the violence could be merely that the driver is emotionally out of control. It could also be something more serious: an individual who is transporting evidence of criminal activity in his/her vehicle or an individual on the run from the law.
The Fourth Amendment to the Constitution of the United States requires that law enforcement only conduct a search after obtaining a warrant from the local magistrate. However, the United States Supreme Court has developed several exceptions to that rule. Each of these exceptions to the warrant requirement will still require that the officer establish probable cause to justify the search.
Law enforcement who merely suspect that a vehicle contains evidence of criminal activity are limited in their options for searching the vehicle. Reasonable suspicion is a lower standard of proof than probable cause. It requires more than a “gut feeling” or a “hunch.” Reasonable suspicion requires that an officer be able to clearly articulate his/her reasons for being suspicious. For example, an officer could support being reasonably suspicious if he stops a vehicle transporting two teenage males at 3A.M. through a neighborhood several miles from the address shown on the driver’s license, soon after several reports of burglaries were reported in the neighborhood. Although nothing concrete links the occupants to the burglaries the officer can explain why he is suspicious of them.
Reasonable suspicion that criminal activity is afoot will only support asking the occupants of the vehicle to provide identification and a general explanation of their actions or reason for being in the location where they were stopped. This low-level questioning is known as a stop or a Terry stop. Additionally, if the officer reasonably believes that an individual presents a threat of danger, the officer may conduct a frisk of the individual. A frisk is a limited pat down of the exterior of an individual’s clothing to feel for weapons. A frisk is not to be used as justification for a thorough search of the individual.
If a law enforcement officer has a reasonable suspicion that a vehicle contains evidence of criminal activity, but has not established probable cause to support his belief that evidence of criminal activity will be found in the vehicle, the officer may ask the driver of the vehicle for permission to search the vehicle. If another occupant of the vehicle is the owner of the vehicle, however, that is the individual who must give permission to search. Individuals are not required to give their consent to search, but law enforcement is not required to advise them of their right to refuse. If an individual refuses to consent to the search, their refusal does not create probable cause to believe that the vehicle contains evidence of criminal activity. When an individual refuses to consent to a search, law enforcement must generally release the individual and their vehicle without further delay.
Probable cause to support a search of the vehicle requires something to clearly link the vehicle to a criminal act beyond a traffic infraction. Sometimes, as an officer approaches a vehicle that the officer has stopped for a traffic infraction, the officer will see evidence of a criminal act lying out in plain view. For example, an officer may see a clear bag of a green botanical substance or an object used for self-administering illegal substances (drug paraphernalia) lying on the dashboard of the vehicle. Or, an officer may smell an odor of marijuana (plain smell). Upon seeing what appears to be evidence of criminal activity in plain view, the officer has a clear link between the occupant(s) of the vehicle and criminal activity. The officer has probable cause to believe that the vehicle contains evidence of criminal activity and may search the vehicle. While plain view is not a search, evidence left in plain view will establish the probable cause necessary to support a vehicle search. A vehicle search is one of the exceptions to the warrant clause.
Another exception to the warrant clause is the search incident to arrest. Whenever an officer has lawfully placed an individual under arrest, the officer may conduct a contemporaneous search of the individual’s wingspan. The term wingspan is not defined to be the length that the arrested individual’s arms can reach. The term is defined to be the individual’s immediate surroundings. When an individual is taken from a car and placed under arrest, their wingspan includes the entire passenger portion of the vehicle. Most searches of vehicles arise out of this exception to the warrant clause.
A final exception to the warrant clause that is applicable to vehicle searches is a search based on exigent (emergency) circumstances. If an officer has reason to believe that an individual is in serious danger or is placing others in serious danger, the officer may act to prevent that serious harm. For example, if an officer is given reliable information that a vehicle is transporting a bomb, the officer may stop the vehicle and may take the action necessary to locate and disarm the bomb.
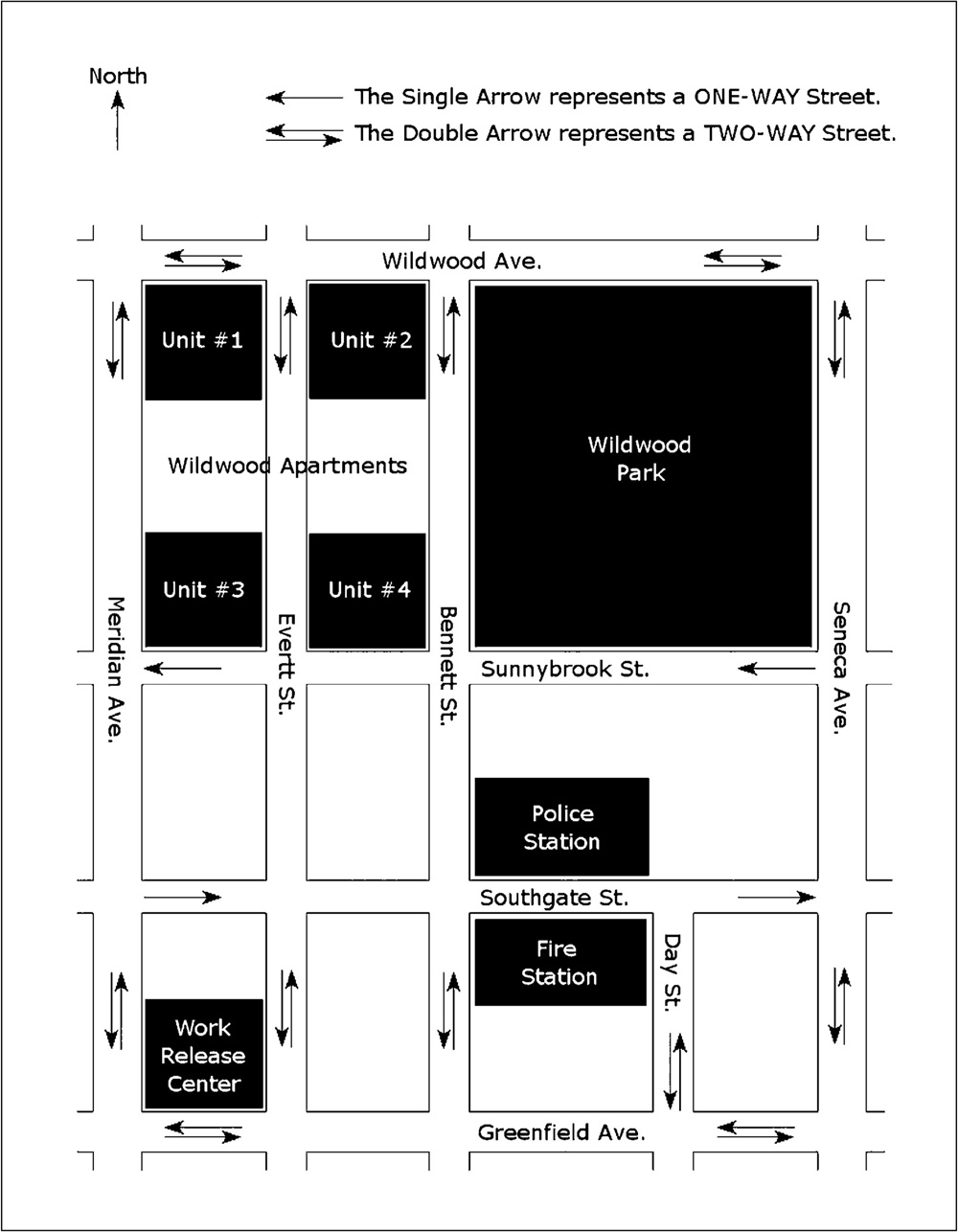
MAP OF CENTRAL CITY 1
MAP OF OFFICE BUILDING 1
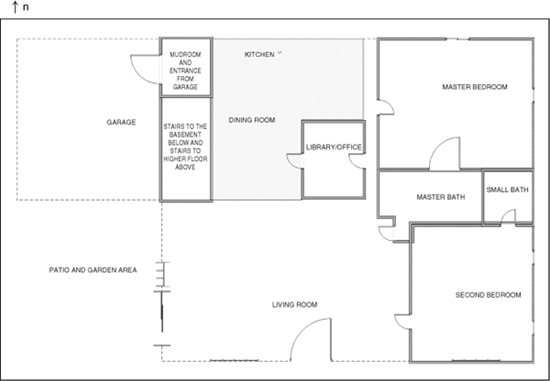
MAP OF HOME 1
RULE 1: There are four kinds of sentences.

RULE 2: The subject of a sentence is the part that is doing something or is being discussed. The predicate of the sentence is the part that is describing the subject.

RULE 3: A sentence fragment is a phrase that is not a complete sentence. A runon sentence is two or more sentences run together without appropriate punctuation marks.
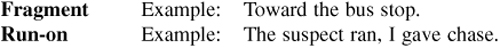
RULE 4: A noun is a person, place, or thing. A proper noun is the name of a person, place or thing.
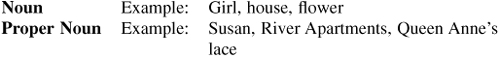
RULE 5: A verb is a word that shows action or existence. Verbs and linking verbs (is, are, seem, etc . . .) should agree in number with the subject.
RULE 6: A pronoun is used in place of a noun.
Note: Pronouns will show ownership without an apostrophe
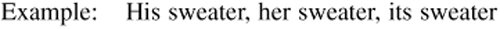
RULE 7: Verb tense denotes the time the action in the sentence occurred.

RULE 8: An adjective is a word used to describe a noun or pronoun. It should usually answer the questions: “How many?” “What kind?” or “Which one?”

RULE 9: An apostrophe may be used to:
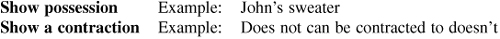
RULE 10: Each sentence should begin with a capital letter, end with an appropriate punctuation mark, and use commas to separate phrases.

Note: This test contains 140 multiple-choice questions, divided into seven sections. In each section the questions are numbered 1–20. Mark your answers on the answer sheet provided. The following pages present samples of the pretest materials typically supplied to applicants, a sample test, and an answer key to the test.
Use the information provided in the pretest materials to answer the following questions. You may not refer to any pretest materials or notes during the exam.
1. The offender claimed that he committed the assault but that he was acting in self-defense. The offender is:
(A) Insane
(B) Claiming a justification
(C) Incompetent
(D) Claiming an alibi
2. The police detective is called to the scene of a homicide but told nothing else by dispatch. Which of the following statements can the detective infer is true before reaching the scene?
(A) The victim is dead.
(B) The perpetrator acted with premeditation.
(C) The perpetrator was committing a serious felony when the homicide occurred.
(D) The perpetrator was angry at the time the homicide occurred.
3. A police officer is told to assist in gathering all physical evidence at a crime scene. He looks around the area but does not see anything that looks like evidence of a crime. Has he completed his duty?
(A) Yes. Physical evidence must be visually identifiable.
(B) Yes. Physical evidence is evidence associated with the victim.
(C) No. Physical evidence is evidence associated with the perpetrator.
(D) No. Physical evidence includes items that are not clearly visible such as latent fingerprints.
4. The Police Manual states that all officers must report questions or concerns about other officers through the official chain of command. Officer Martin has seen his partner remove evidence from a crime scene without logging it in as required. Officer Martin should _____.
(A) Report his concerns to his union representative.
(B) Talk with his partner, unofficially, to try to find out what is going on.
(C) Report his concerns to his direct supervisor.
(D) Send an anonymous note to the Chief of Police.
5. Sergeant Martin identified Exhibit 4 as a necktie found in the bedroom of the Smith residence. When Martin testified that the evidence tag on Exhibit 4 indicated that another officer had processed the evidence, defense counsel objected based on foundation for the _____________ and the State withdrew the exhibit. However, Detective Ferris later identified the evidence tag on Exhibit 4, testifying that Martin gave him the evidence and he tagged it and sent it to the State Patrol Lab thus resolving the earlier issue.
The appropriate term to fill in the blank above is:
(A) Latent fingerprint
(B) Physical evidence
(C) Chain of custody
(D) Discretion
6. Officer Martin had authority to enforce the criminal laws of both the state and his city, as both the state and his city have enacted criminal ______.
(A) Laws
(B) Codes
(C) Jurisdictions
(D) Venues
7. State law and departmental policy states that “offender’s vehicles could be impounded at the direction of law enforcement present at the scene.” Both state law and departmental policy were defining the scope of _______ applicable to vehicle impoundment.
(A) A warrant
(B) Physical evidence
(C) Chain of custody
(D) Officer discretion
8. The offender is legally incompetent. This means that the offender:
(A) Is incapable of assisting in his own defense.
(B) Has a legal justification for his actions.
(C) Was legally insane at the time he committed the offense.
(D) Is unable to afford legal counsel.
9. Professor Martinez taught a course about human sexuality at the local community college. A female student signed a complaint against Professor Martinez alleging that she distributed obscene literature to the class. Professor Martinez will likely not be charged with any offense because the law concerning obscene materials excludes “those persons or entities having scientific, educational, or similar reason for possessing such materials.” This law gives Professor Martinez _________ for possessing and disseminating the information to her students.
(A) Lack of mens rea so she cannot be held accountable
(B) Discretion
(C) A legally recognized justification
(D) A right to distribute obscene material whenever she likes
10. Officer Martin found a latent fingerprint. This means she found a fingerprint ___.
(A) After the investigation officially concluded
(B) That is invisible to the naked eye
(C) That was left by a member of the investigative team
(D) That was unidentifiable due to significant residue and deposits
11. John wanted to try out his new sports car to see how fast it would go. After dark he went out to a stretch of paved road that was seldom used and put the gas pedal to the floorboard. After a few seconds the vehicle had exceeded the speed limit and was about to go into a blind curve. Before John could slow his car, another vehicle came around the turn and the two vehicles collided causing the driver in the other car severe injuries. Before deciding whether to charge John with a crime, the officer gathered as much information about John’s actions in order to determine John’s _________.
(A) Authority
(B) Discretion
(C) Competency
(D) Mens rea.
12. After investigation, Officer Martin determined that the facts showed that John’s behavior was reckless. This means that John:
(A) Could not have known that speeding down a dark road could cause serious harm to others.
(B) Was less at fault for the accident than the other driver.
(C) Knew there was a substantial risk that speeding down a dark road could cause serious harm to others.
(D) Was a juvenile.
13. Dominic went into a store to rob it while his brother Louis waited in the car. Louis’ job was to keep the car running so that Dominic would be able to escape the scene of the robbery as fast as possible. Carl was sitting on a bench down the street with a cell phone ready to call Dominic as soon as he heard sirens in the area. Who was/were the accomplice(s)?
(A) Carl and Dominic
(B) Dominic and Louis
(C) Louis and Carl
(D) Dominic
14. Dominic went into a store to rob it while his brother Louis waited in the car. Louis’ job was to keep the car running so that Dominic would be able to escape the scene of the robbery as fast as possible. Carl was sitting on a bench down the street with a cell phone ready to call Dominic as soon as he heard sirens in the area. Who was/were the perpetrator(s)?
(A) Carl and Dominic
(B) Dominic and Louis
(C) Louis
(D) Dominic
15. Officer Peterson was through investigating a homicide in Edwardsville. He needed to file his case with the appropriate court. He knows that only state courts have jurisdiction to hear homicide cases, but he doesn’t like the state court judges in his area. Officer Peterson decides to file his case in the state court located in a large metropolitan area on the other side of the state, outside the geographical area of the state court for Edwardsville. Will the state court in the metropolitan area be able to accept this case?
(A) Yes, as long as a court has jurisdiction it may accept the case.
(B) Yes, a police officer has discretion to file his case in any court of competent jurisdiction.
(C) No, a court must have both jurisdiction and venue.
(D) Yes, each case has its own individual venue.
16. Officer Peterson tells his supervisor that he is acting on a warrant. From this information alone, what can the supervisor determine that Officer Peterson is doing?
(A) He is serving an arrest warrant.
(B) He is serving a bench warrant.
(C) He is serving a search warrant.
(D) The supervisor needs more information.
17. Which of the following defenses to a crime is NOT a justification?
(A) Self-defense
(B) Defense of others
(C) Insanity
(D) Defense of property
18. Officer Smith found an empty whiskey bottle on the back floorboard of Petra’s car after Petra’s vehicle is involved in an accident. Officer Smith believes that Petra is under the influence of alcohol. The whiskey bottle should be considered physical evidence because _______.
(A) it used to contain an alcoholic beverage
(B) it can establish a link between Petra and the use of alcohol
(C) it can establish a chain of custody between Petra and the alcohol
(D) it can establish that Petra used discretion to drink an alcoholic beverage
19. Officer Peterson drafts and signs an arrest warrant and gets ready to serve it. His supervisor stops him and tells him the warrant is not valid. What is the primary problem with Officer Peterson’s arrest warrant?
(A) Officer Peterson, a law enforcement officer, has no authority to arrest.
(B) Officer Peterson, a law enforcement officer, has no authority to sign an arrest warrant.
(C) Officer Peterson, a law enforcement officer, has no authority to serve warrants.
(D) Officer Peterson, a law enforcement officer, has no authority to request an arrest warrant.
20. Greg sees a man waving a knife at a small child in a parked car. Greg grabs a baseball bat and breaks the driver’s side window of the car. Before the man in the vehicle can react Greg takes his knife away. When the police arrive the man in the vehicle asks them to charge Greg with criminal destruction of property. After hearing the facts, the police decline to arrest Greg because _______.
(A) Greg obtained physical evidence of a crime for them.
(B) Greg is a hero.
(C) Greg was not the perpetrator of the more serious crime.
(D) Greg had a lawful justification to support his actions.
STOP. THIS IS THE END OF SECTION 1.
Use the drawings provided in the pretest materials to answer the following questions. You may not refer to any pretest materials or notes during the exam.
The following questions are in reference to the drawing labeled “FELONY CAR STOP,” which was provided in the pretest materials.
1. How many people were under arrest?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
2. How many police officers were on the scene?
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 6
(D) 8
3. Where was the arrest taking place?
(A) In a parking lot
(B) On the side of the highway
(C) On a residential street
(D) At the police station
4. Why was the arrest occurring?
(A) Suspicion that the driver had committed a traffic offense.
(B) Suspicion that the driver had attempted to evade and elude officers.
(C) Suspicion that the driver was under the influence of intoxicants.
(D) Suspicion that the driver and occupants were involved in a serious crime.
5. What grounds did the police use to justify the lawful search of the vehicle?
(A) Search incident to arrest
(B) Plain view
(C) Traffic stop
(D) Search of a motor vehicle
The following questions are in reference to the drawing labeled “FORCED CAR STOP,” which was provided in the pretest materials.
6. How many vehicles were involved in the collision?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
7. What roadway did the collision occur upon?
(A) Highway 80
(B) Market Street
(C) Highway 50
(D) Memphis Avenue
8. What type of vehicle was the suspect driving?
(A) Sedan
(B) Jeep
(C) Van
(D) Pick-up
9. What information was provided on the roadway sign shown in the drawing?
(A) Highway 80 exit
(B) Market Street exit
(C) Welcome to Central City
(D) Speed limit 45
10. What criminal act was the driver suspected of committing just prior to the onset of the high-speed chase?
(A) Kidnapping
(B) Traffic offenses
(C) Drive-by shooting
(D) Assault of a law enforcement officer
11. The suspect’s vehicle was eventually pinned between a patrol car and a _______.
(A) Guard rail
(B) Second patrol car
(C) Semi truck
(D) The vehicle was not pinned
12. How many patrol cars were visible in the drawing?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
13. What number was shown on the roadside mile marker?
(A) 234
(B) 187
(C) 546
(D) 53
The following questions are in reference to the drawing labeled “OUTDOOR MARKET” which was provided in the pretest materials.
14. How many police officers are shown in the drawing?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
15. What type of items are available at the outdoor market?
(A) Clothing
(B) Crafts
(C) Vegetables
(D) Paintings
16. Based on the apparel of the shoppers, what is the weather?
(A) Cold
(B) Hot
(C) Raining
(D) Snowing
17. How many people are shown being arrested?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) None
18. The type of buildings shown surrounding the outdoor market are:
(A) Generally 1 story high
(B) Generally 2–3 stories high
(C) Generally 4 or more stories high
(D) Too varied to categorize
19. The sign on the building on the right side of the photo says:
(A) Restaurant
(B) Memphis Building
(C) Outdoor Market Square
(D) Stark Street Diner
20. The addresses shown on the buildings reveal what pattern?
(A) The buildings are numbered sequentially with odd numbers.
(B) The buildings are numbered sequentially with even numbers.
(C) The buildings are numbered sequentially with both odd and even numbers.
(D) The buildings are not numbered sequentially.
STOP. THIS IS THE END OF SECTION 2.
Use the information provided in the pretest materials to answer the following questions. You may not refer to any pretest materials or notes during the exam.

1. This man is wanted for:
(A) Rape
(B) Murder
(C) Drug manufacturing
(D) Aggravated assault
2. Which of the following statements is NOT true about this suspect?
(A) He is 194 lbs.
(B) He has a snake tattoo on his bicep.
(C) He is 5 ft 6 in tall.
(D) He has no known aliases.
3. What is this man’s age?
(A) 19
(B) 24
(C) 29
(D) 34
4. Which of the following is TRUE about this suspect?
(A) His last name is Norris.
(B) His last name is North.
(C) His last name is Norton.
(D) His last name is Northern.
5. Which of the following is TRUE about this suspect?
(A) He may pretend to not speak English to avoid answering questions.
(B) He may pretend not to understand an Italian interpreter by speaking Spanish.
(C) He may pretend not to understand a Spanish interpreter by speaking Italian.
(D) All of the above.

6. This woman is wanted for:
(A) Rape
(B) Murder
(C) Drug manufacturing
(D) Aggravated assault
7. Which of the following statements is NOT true about this suspect?
(A) She is 151 lbs.
(B) She has an alias.
(C) She is 5 ft 4 in tall.
(D) She is Hispanic.
8. What is this woman’s age?
(A) 19
(B) 24
(C) 29
(D) 34
9. Which of the following is TRUE about this suspect?
(A) Her first name is Alicia.
(B) Her first name is Alice.
(C) Her first name is Alexandra.
(D) Her first name is Amelia.
10. Which of the following is TRUE about this suspect?
(A) She may pretend to not speak English to avoid answering questions.
(B) She may pretend not to understand an Italian interpreter by speaking Spanish.
(C) She may pretend not to understand a Spanish interpreter by speaking Italian.
(D) All of the above.
11. This woman is wanted for:
(A) Bank robbery
(B) Murder
(C) Drug manufacturing
(D) Aggravated assault
12. Which of the following statements is NOT true about this suspect?
(A) She is 151 lbs.
(B) She has an alias.
(C) She is Hispanic.
(D) All of the above.
(A) 19
(B) 23
(C) 29
(D) 34
14. Which of the following is TRUE about this suspect?
(A) She has a butterfly tattoo on her ankle.
(B) She has a pierced lip.
(C) She has a butterfly tattoo on her wrist.
(D) She has a pierced eyebrow.
15. Which of the following is TRUE about this suspect?
(A) She may pretend to not speak English to avoid answering questions.
(B) The extent of her linguistic abilities is not known.
(C) Her strong accent implies that she speaks at least one other language.
(D) All of the above.

16. This woman is wanted for:
(A) Bank robbery
(B) Kidnapping
(C) Drug manufacturing
(D) Aggravated assault
17. Which of the following statements is NOT true about this suspect?
(A) She is 121 lbs.
(B) She has an alias.
(C) She is 5 ft 7 in tall.
(D) She is Hispanic.
(A) 19
(B) 24
(C) 29
(D) 34
19. Which of the following is TRUE about this suspect?
(A) Her first name is Peggy.
(B) Her first name is Patty.
(C) Her first name is Paige.
(D) Her first name is Piper.
20. Which of the following is TRUE about this suspect?
(A) She is a mother.
(B) She is known to carry weapons.
(C) She is traveling with three children.
(D) All of the above.
STOP. THIS IS THE END OF SECTION 3.
Use the information provided in the pretest materials to answer the following questions. You may not refer to any pretest materials or notes during the exam.
INCIDENT
On September 29, 2006, at approximately 6 P.M. Eric Jackson walked into the Super-Mart, located at 12122 E. Seneca Street. Jackson proceeded to walk through the store, and then loaded a $179 television-video cassette recorder combo into a shopping cart, removed the security tag, and pushed the cart out the front door. Two security guards observed him leaving the store with the television-video cassette recorder at 6:15 P.M., followed him into the parking lot, and confronted him. Jackson abandoned the shopping cart beside a late model maroon Buick and started to run away, but suddenly turned back. One of the guards grabbed Jackson’s arm. Jackson punched the guard in the nose, attempted to hit the second guard in the arm, and ran away. The guards were unable to catch him, but a police officer positioned his car in Jackson’s path and arrested him at approximately 6:22 P.M. The crime of robbery, 9A.56.190, was complete when Jackson left the store. No weapons or intoxicating substances were indicated or found at the scene. No ambulance was called.
1. What entry should be made in box 2?
(A) 1800 hours
(B) 1900 hours
(C) 1815 hours
(D) 1922 hours
2. What entry should be made in box 7?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
3. What entry should be made in box 8?
(A) Injury to arm
(B) Injury to nose/face
(C) Injury to television-video recorder
(D) No injury noted
4. What line should be marked in box 15?
(A) Drugs/narcotics
(B) Alcohol
(C) Computer equipment
(D) N/A
5. What entry should be made in box 16?
(A) Knife
(B) Blunt object
(C) Vehicle
(D) None
On August 2, 2006, at approximately 10:13 A.M., a Central City police officer stopped Jason Goodman, age 42, for making an illegal left turn at the 1300 block of Washington Streets. The officer asked Goodman for his driver’s license, vehicle registration, and insurance information. Mr. Goodman said he did not have his wallet with him, but he provided the vehicle registration for his pickup truck. He also gave his name, address, and date of birth. The officer conducted a driver’s check through the local police database and learned that Goodman’s out of state driver’s license had been suspended. The officer also smelled an odor of alcoholic beverage coming from Goodman’s vehicle. The officer arrested Goodman for driving while his license was suspended, handcuffed him, searched him, and placed him in the back of his patrol car at 10:27 A.M.
A second officer arrived. Pursuant to city police procedure, the officers conducted an inventory search before impounding Goodman’s truck. One of the officers began the inventory on the driver side, seeing nothing on the driver’s seat, he reached under the front seat and felt a satchel directly under the driver’s seat. The Officer pulled the satchel out from under the seat, unzipped the top, main portion and saw what appeared to be a gun holster. The Officer removed this object from the backpack and found a black 9mm pistol in the holster. The pistol was unloaded, but a fully loaded magazine for the pistol was found in the satchel. Goodman was also charged under CR 9.41.050 for transporting a weapon without a license.
6. What line should be marked in box 14?
(A) Juvenile
(B) Probation revoked
(C) Victim refused to prosecute
(D) No line should be marked
7. What line should be marked in box 11?
(A) Attempt
(B) Complete
(C) Both lines should be marked
(D) Neither line should be marked
8. Although the officer noted many details possibly associated with offenses, Goodman was actually charged with how many offenses according to the report?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
9. Which of the following is the correct response to put in box 9 associated with the offense of transporting a weapon without a license?
(A) CR
(B) 9.41
(C) 9
(D) 9.41.050
10. What entry should be made in box 6?
(A) 10:13 hours
(B) 10:27 hours
(C) 10:30 A.M.
(D) Unknown at this time
On the afternoon of October 1, 2005, at approximately 4:00 P.M., a two-vehicle accident occurred in Central City. Vehicle No.1. a green Toyota Corolla driven by Harry Dillon collided with a parked Chevrolet minivan occupied by two people. A Central City Police Department code enforcement officer (CEO) on bike patrol saw Dillon staggering toward his car parked in front of 155 James Street, approximately 200 feet west of the intersection of Central and James, just prior to the accident. The CEO noticed that although the day was clear and warm with no wind, Dillon was having trouble with his balance and co-ordination. As Dillon entered his car, the CEO called dispatch to inform the police that he believed he was witnessing an intoxicated driver getting into a vehicle. The collision occurred while the CEO was still on the radio. Dillon backed into vehicle No.2, a Chevrolet minivan parked behind the Corolla. The minivan sustained a severely damaged front end. The Toyota’s back end was also seriously damaged causing the trunk to open. Two clear bags containing a white powdered substance were clearly visible in the trunk. Following on-scene testing both bags were seized as evidence, and Dillon was arrested and charged with various traffic offenses and criminal offenses. (See case No. CR 100600343.)
The driver of the Chevrolet minivan was injured and was taken to hospital via ambulance. Her two-year-old son was uninjured. Dillon was uninjured, but was transported by police vehicle for blood testing.
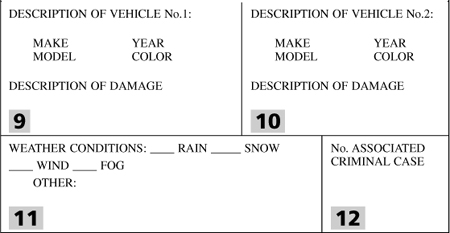
11. What entry should be made in box 2?
(A) 155 James Street
(B) 200 W. James Street
(C) 200 W. Central
(D) Unknown at this time
12. What lines/entry should be made in box 11?
(A) Wind
(B) Fog
(C) Clear visibility/no wind
(D) Warm day
13. What entry should be made in box No.10?
(A) Damaged front end
(B) Damaged back end
(C) No visible damage
(D) Undetermined amount of damage
14. What entry should be made in box 5?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
15. What entry should be made in box 12?
(A) CR 343
(B) CR 100600343
(C) CR 1006
(D) CR 100600334
On the evening of May 3, 2006, at approximately 7 P.M. Stacy Moore was driving herself and her husband, Trey Moore, home after attending church on Lincoln Avenue. En route to their home, the Moores had an altercation with the driver of another vehicle, Caleb Lewis. The altercation began when Lewis started tailgating the Moores and flashing his headlights. In response, Stephanie Moore slowed down and pumped her brakes, attempting unsuccessfully to get Lewis to drive around her car, a 2001 convertible yellow Volkswagen. As they approached a stoplight, Lewis pulled alongside the Moores’ car and he and the passenger in his car exchanged words with Tracy Moore. The verbal altercation then ended and Stephanie Moore proceeded to drive away. At about the 2000 block of E. Lincoln, Lewis passed their car and slammed on his brakes causing the Moore vehicle to collide with the rear of the vehicle driven by Lewis, a 1991 White Ford Explorer. Lewis then left the scene but was apprehended on May 5, 2006, in an incident detailed in case No. CR 100601253. The Moore vehicle spun out of control through the intersection of Lincoln and Jefferson, hit a telephone pole, and rolled over. It came to rest in the eastbound lanes of Lincoln Avenue where other drivers rendered aide and called for assistance. Stacy Moore was seriously injured and was transported to Mercy Hospital. Trey Moore died at the scene. Lewis was charged with Manslaughter, 9A.32.060, in the criminal case associated with this traffic incident, No. CR 100601214. Weather was not a factor in this accident.

16. What entry should be made in box 5?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
17. What entry should be made in box 7?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
18. According to the report, which driver was issued a traffic citation at the scene?
(A) Stephanie Moore
(B) No one
(C) Caleb Lewis
(D) Trey Moore
19. Which of the following information should be marked in box 11?
(A) Information not provided
(B) Snow
(C) Other
(D) Rain
20. What entry should be made in box 12?
(A) No. CR 100601253
(B) No. CR 9A.32.060
(C) No. CR 100601214
(D) N/A
STOP. THIS IS THE END OF SECTION 4.
The questions below are based on the information from the VEHICLE SEARCHES article provided in the pretest materials and on information provided in the incidents presented below.
INCIDENT 1
At approximately 1600 hours, Officer Patterson was patrolling in his squad car in a quiet residential neighborhood when he noticed a small white vehicle spin out and squeal its tires while making a turn. Officer Patterson had been patrolling the neighborhood because of several reports of drag racing in the area over the last several days. Officer Patterson stopped the car for violation of the traffic code. When he approached the vehicle he noticed that the driver was a male in his late teens. Officer Patterson asked the driver for his driver’s license, proof of insurance, and registration. He then asked the driver why he had spun his tires. The driver answered he “was just being dumb.” As the driver was answering the question Officer Patterson could smell an odor of an alcoholic beverage emanating from the driver’s breath. Officer Patterson asked the driver to step out of his vehicle in order to perform field sobriety tests. The driver refused to conduct the tests. The driver was placed under arrest for suspicion of driving under the influence of alcohol.
1. Officer Patterson’s probable cause to stop the small white vehicle was ____
(A) The vehicle was in an enforcement zone.
(B) The officer suspected the driver was driving under the influence.
(C) The vehicle had been seen by the officer committing a traffic infraction.
(D) The officer knew the driver and knew he was advertising his desire to drag race.
2. When Officer Patterson approached the vehicle he knew that he should use extreme care because ______
(A) The officer knew the driver and knew he was dangerous.
(B) It is common knowledge that drag racers are violent.
(C) The traffic infraction was very serious and the driver knew he would go to jail.
(D) There is always a possibility that a driver will react to a stop with violence.
3. After asking the driver of the vehicle for his standard documents, Officer Patterson asked the driver why he had committed the traffic infraction. What illegal act did Officer Patterson have reasonable suspicion to believe was occurring in addition to the traffic violation?
(A) Driving under the influence
(B) Drag racing
(C) Possession of a stolen vehicle
(D) Both (A) and (B)
4. Which of the following statements would NOT support Officer Patterson’s reasonable suspicion to believe that criminal activity was occurring beyond the traffic infraction?
(A) Time of day
(B) Recent reports from residents about drag racing in the neighborhood
(C) The age of the driver
(D) Squealing of tires in a quiet residential neighborhood
5. When Officer Patterson stopped the vehicle should he have frisked the driver?
(A) Yes, because a driver frisk is standard procedure.
(B) Only if the officer had a reasonable belief that the driver presented a threat to his safety.
(C) Yes, because it may have yielded additional evidence about criminal activity.
(D) Only if the officer had probable cause to believe that an individual has evidence of criminal activity on his person.
6. Of the following possibilities, which answer is the MOST LIKELY reason that Officer Patterson did not ask the driver of the vehicle for consent to search his vehicle?
(A) The driver did not own the vehicle.
(B) The officer was waiting for an opportunity to arrest the driver.
(C) The officer did not have a suspicion that the vehicle contained evidence of crime.
(D) The officer was trying to catch the driver off-guard so that he would admit to additional crimes.
7. What evidence supported Officer Patterson’s probable cause to arrest the driver?
(A) Poor driving.
(B) The smell of alcoholic beverage on driver’s breath and test refusal.
(C) Poor driving and the smell of alcoholic beverage on driver’s breath.
(D) There was no probable cause to arrest the driver.
8. If Officer Patterson searched the vehicle, what exception to the warrant requirement supported the search?
(A) Search incident to arrest.
(B) Vehicle search.
(C) Consent search.
(D) Exigent circumstances.
9. “Exigent” means _______.
(A) Exceptional
(B) Extraordinary
(C) Emergency
(D) Extraneous evidence
10. The size of an individual’s wingspan is ________.
(A) Six feet, the average length of an adult males reach.
(B) The actual length that an individual’s arms can reach.
(C) The individual’s immediate surroundings.
(D) The area that the arresting officer believes that an individual could reach into and secure a weapon.
INCIDENT 2
Officer Spencer was on patrol on a residential arterial roadway at approximately 11 P.M. when he noticed a green sports car traveling toward him. A stop sign and a streetlight were located between his vehicle and the approaching vehicle. No other vehicles were in sight. Officer Spencer watched the vehicle approach the stop sign and come to a complete stop. The vehicle remained stopped at the stop sign until Officer Spencer’s car had not only reached the stop sign, but had stopped at the stop sign, waited 30 seconds, and then proceeded through the stop sign. Officer Spencer watched the vehicle in his rear view mirror for approximately 15 more seconds before he saw the vehicle cross the intersection and proceed down the roadway. Officer Spencer turned around and followed the vehicle. He noticed that it crossed the center lane on three occasions within a two-block distance. Officer Spencer activated his emergency lights to signal the driver to pull over to the side of the road. As the vehicle was pulling over Officer Spencer saw the back-up lights activate and as his window was down he was also able to hear the transmission gears grinding. Officer Spencer ascertained that the driver had put the vehicle in park as it was still moving onto the shoulder of the roadway. When Officer Spencer approached the driver’s side window he detected a strong odor of an alcoholic beverage emanating from within the vehicle. He asked the female driver for her driver’s license. She claimed that she did not have it in her possession. He saw a cell phone lying on the seat next to her with its face light on. He asked her where she had been, and she replied that she had been across town with friends. He asked her where she was going, and she replied that she was going home. He asked her where she lived and she gave him an address for a street that he had seen her drive past.
11. Officer Spencer’s probable cause to stop the vehicle was ____.
(A) The vehicle was in an enforcement zone.
(B) He suspected the driver was driving under the influence.
(C) The vehicle had been seen by the officer committing a traffic infraction.
(D) The driver of the vehicle seemed to be trying to avoid Officer Spencer’s notice.
12. What action did Officer Spencer have only reasonable suspicion to believe was occurring?
(A) Driving under the influence
(B) Drag racing
(C) Possession of a stolen vehicle
(D) Driving without a valid driver’s license
13. Which of the following statements would NOT support Officer Spencer’s reasonable suspicion to believe that criminal activity was occurring beyond the traffic infraction?
(A) The vehicle sat for a prolonged period at an intersection where no other traffic prevented it from moving.
(B) The vehicle was a sports car.
(C) The vehicle crossed the center lane of the roadway more than once.
(D) The vehicle’s driver had put the vehicle in park as it was still moving onto the shoulder of the roadway causing an audible grinding of the transmission’s gears.
14. If Officer Spencer had reasonable suspicion to believe that a crime beyond mere traffic infractions was occurring, what additional authority did he have?
(A) The authority to arrest the suspect.
(B) The authority to search the suspect.
(C) The authority to search the suspect’s vehicle.
(D) The authority to ask the suspect who they were and what they were doing in the area.
15. If Officer Spencer had asked the driver for consent to search the vehicle and she had refused to give consent, _______.
(A) Her refusal would support probable cause to search.
(B) Her refusal would be grounds for arrest.
(C) She has the right to refuse and Officer Spencer could not take any further action.
(D) She could be kept at the scene until she gave her consent to search.
16. After approaching the driver and evaluating the interior of the vehicle, Officer Spencer suspected that _______.
(A) The driver of the vehicle was not comfortable driving her car.
(B) The driver of the vehicle was not familiar with her surroundings.
(C) The driver of the vehicle was trying to hide evidence of criminal acts.
(D) The driver of the vehicle was talking on her cell phone while driving.
17. The evidence that least supports charging the driver of this vehicle with driving under the influence is:
(A) The odor of alcoholic beverage.
(B) The cell phone in view and recently used.
(C) Crossing the center lane of the roadway.
(D) Sitting too long at an intersection when no other cars were in the area.
18. Recognizing an odor as evidence of a criminal act is called ______.
(A) Plain view
(B) Plain smell
(C) Odor identification
(D) None of the above
19. Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE concerning “reasonable suspicion”?
(A) Reasonable suspicion is a lower standard of proof than probable cause.
(B) Reasonable suspicion requires that an officer be able to clearly articulate his/her reasons for being suspicious.
(C) Reasonable suspicion requires a clear link between an individual and a crime.
(D) Reasonable suspicion requires more than a “gut feeling” or a “hunch.”
20. Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE concerning “probable cause” to stop a vehicle involved in a traffic infraction?
(A) Probable cause requires a clear link between the illegal act and an individual.
(B) Probable cause to stop a vehicle is only necessary to justify a subsequent search.
(C) Probable cause to stop a vehicle arises out of the officer’s knowledge that the infraction was caused by the driver of the vehicle seen violating the law.
(D) Probable cause to stop a vehicle arises out of the officer’s knowledge that an infraction of the traffic laws has occurred.
STOP. THIS IS THE END OF SECTION 5.
Use the information provided in the pretest materials to answer the following questions. You may not refer to any pretest materials or notes during the exam.
TO ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS UTILIZE INFORMATION PROVIDED IN THE DRAWING LABELED “MAP OF CENTRAL CITY.”
1. Police receive a call that a burglary is in progress at the Northeast corner of Everett St. and Wildwood Ave. If police are able to travel directly from the police station of the reported site of the burglary which direction will they need to go?
(A) Northeast
(B) Southeast
(C) Southwest
(D) Northwest
2. Which direction of travel is permitted on Sunnybrook Street?
(A) Vehicles may travel both directions.
(B) Vehicles may only travel west.
(C) Vehicles may only travel east.
(D) Vehicles may only travel north.
3. Which direction of travel is permitted on Everett Street?
(A) Vehicles may travel both directions.
(B) Vehicles may only travel west.
(C) Vehicles may only travel east.
(D) Vehicles may only travel north.
4. Which two streets only permit one-way travel?
(A) Wildwood and Everett
(B) Seneca and Sunnybrook
(C) Southgate and Sunnybrook
(D) Wildwood and Seneca
5. A police cruiser is headed south at the intersection of Wildwood and Everett. Which street will he turn east on to reach the police station?
(A) Day Street
(B) Seneca Ave
(C) Meridian Ave
(D) Southgate St
6. Which street is the only one-way street abutting Wildwood Park?
(A) Seneca Ave
(B) Southgate St
(C) Sunnybrook St
(D) Southhampton Rd
7. Which direction must police travel from the police station to reach the Work Release Center?
(A) Southeast
(B) South
(C) Southwest
(D) Northeast
8. Police receive a report of a domestic incident on Everett Street in front of Unit No. 1 of the Wildwood Apartment Complex. If police are able to travel directly from the police station of the reported site of the incident which general direction will they need to go?
(A) Northeast
(B) North
(C) Northwest
(D) Southwest
9. Which building is the police station located nearest to?
(A) Work release center
(B) Fire station
(C) Unit No. 3 of Wildwood Apartment Complex
(D) Unit No. 4 of Wildwood Apartment Complex
10. The police station is located on the _______ corner of Bennett St and Southgate.
(A) Northeast
(B) North
(C) Northwest
(D) Southwest
TO ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS UTILIZE INFORMATION PROVIDED IN THE DRAWING LABELED “MAP OF OFFICE BUILDING.”
Police receive a call that an armed man has entered an office building and is currently barricaded inside the conference room. Civilians are still inside the building seeking the best shelter they can find. Study this diagram so that when you arrive on the scene, you will understand the layout of the bank. You will be asked to recall the information shown here without the use of this diagram.
11. How many offices are located in the building?
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 7
12. If all of the offices are currently occupied as well as the reception desk, what is the minimum number of civilians currently working in this building?
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 7
13. If the suspect exits through the door of the conference room, which exterior door would he be closest to?
(A) North
(B) West
(C) East
(D) South
14. If the suspect exits through the window of the conference room which side of the building will he be on?
(A) North
(B) West
(C) East
(D) South
15. In which corner of the building was the largest office located?
(A) Northwest
(B) Northeast
(C) Southwest
(D) Southeast
16. Judging by the thickness of the walls, which room will provide the greatest safety to the civilians inside?
(A) Conference room
(B) Manager’s office
(C) Restrooms
(D) Reception area
17. If it seems advisable to evacuate the building, through which door will you recommend that civilians exit the building?
(A) North
(B) West
(C) East
(D) South
TO ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS UTILIZE INFORMATION PROVIDED IN THE DRAWING LABELED “MAP OF HOUSE.”
Police receive a call that a distraught man has barricaded himself inside his home and is holding his wife and infant daughter hostage. You do not know where inside the building the wife and baby are being located. Study this diagram so that when you arrive on the scene, you will understand the layout of the house. You will be asked to recall the information shown here without the use of this diagram.
18. How many levels are in this home?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
19. In addition to the sliding glass door that leads to the patio, how many exterior doors to this home are you aware of?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
20. How many enclosed rooms (rooms that can be closed off from other areas of the house) are located on the main floor?
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 6
(D) 8
STOP. THIS IS THE END OF SECTION 6.
Use the information provided in the pretest materials to answer the following questions. You may not refer to any pretest materials or notes during the exam.
1. Which of the following is grammatically CORRECT?
(A) Stop right now.
(B) Stop right now!
(C) Stop right now?
(D) Stop, right now!
2. Which of the following is grammatically CORRECT?
(A) Officer Pete are running.
(B) Officer Pete be running.
(C) Officer Pete is running.
(D) Officer Pete were running.
3. Which of the following is grammatically INCORRECT?
(A) Officer John ran to the bus stop.
(B) Officer John, grasping his radio, ran to the bus stop.
(C) Officer John grasping his radio at the bus stop.
(D) Officer John, grasping his radio and weapon belt, ran to the bus stop as fast as he had ever run in his life.
4. Which of the following is CORRECT?
(A) It’s cold outside.
(B) Its cold outside.
(C) Iss cold outside.
(D) Its’ cold outside
5. Which of the following is NOT a noun?
(A) John
(B) San Francisco
(C) Rock
(D) Run
6. Which of the following is a VERB?
(A) John
(B) San Francisco
(C) Rock
(D) Run
7. Which of the following is CORRECT?
(A) I approached the passenger, Thad Rose, he had had a few beers also.
(B) I approached the passenger, Thad Rose, he had had a few beers, also.
(C) I approached the passenger Thad Rose he had had a few beers also.
(D) I approached the passenger, Thad Rose. He had had a few beers also.
8. Which is NOT a sentence fragment?
(A) Running to catch the suspect.
(B) Every time I looked at the suspect.
(C) When I searched the suspect.
(D) I completed the arrest of the suspect.
9. Which sentence is CORRECT?
(A) John is a criminal.
(B) John is a criminal
(C) john is a criminal.
(D) john is a criminal
10. Which sentence uses verb tense correctly?
(A) Officer John stopped the vehicle and walks toward the occupant.
(B) Officer John stopped the vehicle and walked toward the occupant.
(C) Officer John stops the vehicle and walked toward the occupant.
(D) Officer John was stopping the vehicle and walks toward the occupant.
11. Which of the following uses a pronoun in place of the subject?
(A) He ran away from Officer John.
(B) Paul ran away from Officer John.
(C) The dog ran away from Officer John.
(D) The little boy ran away from Officer John.
12. Which of the following sentences is CORRECT?
(A) I will do the paperwork yesterday.
(B) I did the paperwork later today.
(C) I did the paperwork yesterday.
(D) I did the paperwork tomorrow.
13. Which of the following sentences is CORRECT?
(A) We had reports of drag racers from past days.
(B) We had received reports of drag racers in the past few days.
(C) We had received reports of drag racers in the past days.
(D) We had reports of drag racers in past few days.
14. Which of the following is an exclamatory sentence?
(A) Pull your car over to the side of the road!
(B) Will you please pull your car over to the side of the road?
(C) After you pass this next vehicle, pull your car over to the side of the road.
(D) Pull your car over to the side of the road.
15. Which sentence is CORRECT?
(A) That sweater is hers.
(B) That sweater is her’s.
(C) That sweater is hers’.
(D) That sweater is her’s’.
16. Which sentence is CORRECT?
(A) I then took Mr. Young to the county jail, after further testing, Mr. Young tested above the legal limit for breath alcohol level.
(B) I then took Mr. Young, to the county jail, after further testing, Mr. Young tested, above the legal limit, for breath alcohol level.
(C) I then took Mr. Young to the county jail. After further testing, Mr. Young tested above the legal limit for breath alcohol level.
(D) I then took Mr. Young to the county jail after further testing. Mr. Young tested above the legal limit for breath alcohol level.
17. Which sentence is CORRECT?
(A) This house is there’s.
(B) This house is their’s.
(C) This is house is theirs.
(D) This is house is theres.
18. Which sentence is CORRECT?
(A) Is this your sweater?
(B) Is this you’re sweater?
(C) Is this youre sweater?
(D) Is this your’ sweater?
19. Read the following sentence and identify the subject. Officer John is careful to use correct grammar when writing police reports.
(A) Officer John
(B) grammar
(C) police reports
(D) writing
20. Read the following sentence and identify the verb. Officer John is careful to use correct grammar when writing police reports.
(A) Is
(B) Use
(C) Writing
(D) Reports
STOP. THIS IS THE END OF PRACTICE TEST 1.
Section 1: Vocabulary
1. B
2. A
3. D
4. C
5. C
6. B
7. D
8. A
9. C
10. B
11. D
12. C
13. C
14. D
15. C
16. D
17. C
18. B
19. B
20. D
Section 2: Ability to Observe and Recall
1. B
2. B
3. C
4. D
5. B
6. B
7. C
8. D
9. B
10. C
11. A
12. B
13. D
14. C
15. C
16. A
17. D
18. C
19. B
20. A
Section 3: Ability to Observe and Report Information
1. D
2. B
3. B
4. C
5. D
6. C
7. A
8. A
9. B
10. A
11. A
12. D
13. B
14. A
15. D
16. B
17. D
18. D
19. C
20. D
Section 4: Ability to Write Reports and Complete Forms
1. C
2. B
3. B
4. D
5. D
6. D
7. B
8. A
9. D
10. B
11. A
12. C
13. A
14. A
15. B
16. B
17. A
18. B
19. A
20. C
Section 5: Applying Learned Material
1. C
2. D
3. D
4. A
5. B
6. C
7. B
8. A
9. C
10. C
11. C
12. A
13. B
14. D
15. C
16. D
17. B
18. B
19. C
20. B
Section 6: Map Reading
1. D
2. B
3. A
4. C
5. D
6. C
7. C
8. C
9. B
10. D
11. D
12. D
13. B
14. B
15. B
16. C
17. C
18. C
19. C
20. C
Section 7: Grammar And Usage
1. D
2. C
3. C
4. A
5. D
6. D
7. D
8. D
9. A
10. B
11. A
12. C
13. B
14. A
15. A
16. C
17. C
18. A
19. A
20. A