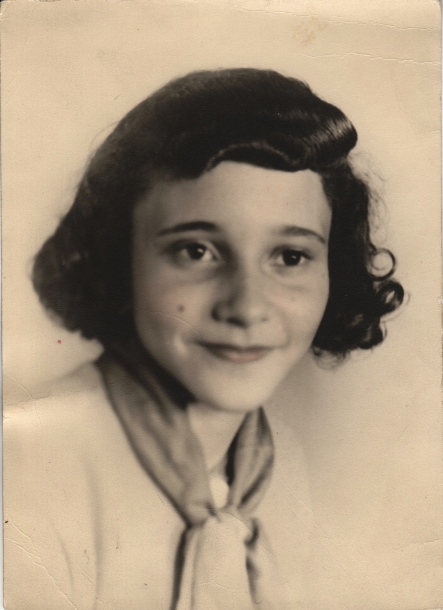
A twelve-year-old Hamilton in 1948, when she was in the seventh grade.
Virginia Hamilton (1934–2002) was the author of forty-one books for young readers and their older allies, including M.C. Higgins, the Great, which won the National Book Award, the Newbery Medal, and the Boston Globe-Horn Book Award, three of the most prestigious awards in youth literature. Hamilton’s many successful titles earned her numerous other awards, including the international Hans Christian Andersen Award, which honors authors who have made exceptional contributions to children’s literature, the Coretta Scott King Award, and a MacArthur Fellowship, or “Genius Award.”
Virginia Esther Hamilton was born in 1934 outside the college town of Yellow Springs, Ohio. She was the youngest of five children born to Kenneth James and Etta Belle Perry Hamilton. Her grandfather on her mother’s side, a man named Levi Perry, had been brought to the area as an infant probably through the Underground Railroad shortly before the Civil War. Hamilton grew up amid a large extended family in picturesque farmlands and forests. She loved her home and would end up spending much of her adult life in the area.
Hamilton excelled as a student and graduated at the top of her high school class, winning a full scholarship to Antioch College in Yellow Springs. Hamilton transferred to Ohio State University in nearby Columbus, Ohio, in order to study literature and creative writing. In 1958, she moved to New York City in hopes of publishing her fiction. During her early years in New York, she supported herself with jobs as an accountant, a museum receptionist, and even a nightclub singer. She took additional writing courses at the New School for Social Research and continued to meet other writers, including the poet Arnold Adoff, whom she married in 1960. The couple had two children, daughter Leigh in 1963 and son Jaime in 1967. In 1969, the family moved to Yellow Springs and built a new home on the old Perry-Hamilton farm. Here, Virginia and Arnold were able to devote more time to writing books.
Hamilton’s first published novel, Zeely, was published in 1967. Zeely was an instant success, winning a Nancy Bloch Award and earning recognition as an American Library Association Notable Children’s Book. After returning to Yellow Springs with her young family, Hamilton began to write and publish a book nearly every year. Though most of her writing targeted young adults or children, she experimented in a wide range of styles and genres. Her second book, The House of Dies Drear (1968), is a haunting mystery that won the Edgar Allan Poe Award. The Planet of Junior Brown (1971) and Sweet Whispers, Brother Rush (1982) rely on elements of fantasy and science fiction. Many of her titles focus on the importance of family, including M.C. Higgins, the Great (1974) and Cousins (1990). Much of Hamilton’s work explores African American history, such as her fictionalized account Anthony Burns: The Defeat and Triumph of a Fugitive Slave (1988).
Hamilton passed away in 2002 after a long battle with breast cancer. She is survived by her husband Arnold Adoff and their two children.
For further information, please visit Hamilton’s updated and comprehensive website: www.virginiahamilton.com
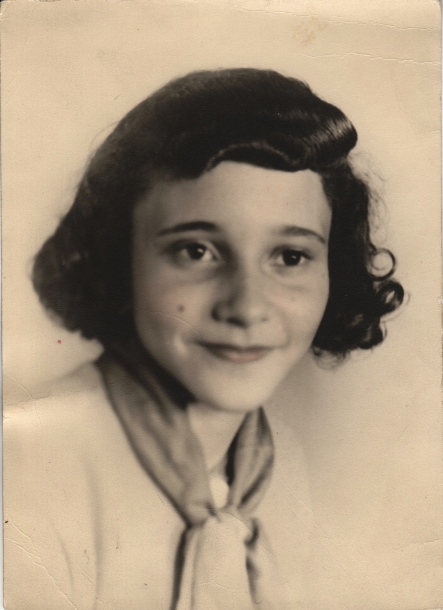
A twelve-year-old Hamilton in 1948, when she was in the seventh grade.

Hamilton at a New York City club while she was a student at Antioch College in the mid-1950s. She often performed as a folk and jazz vocalist in clubs and larger venues.
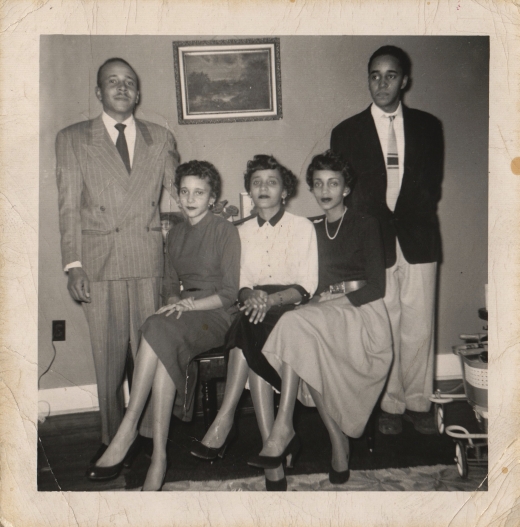

Hamilton with her brothers, Buster and Bill, and sisters, Barbara and Nina, around 1954.