There are several different ways to stop, start, or restart Splunk. The easiest way to restart Splunk is to do it from the web interface, as demonstrated in the preceding section. The web interface, however, only allows you to restart your Splunk instance. It does not offer any other control options.
The most flexible way to control Splunk is by using the CLI. Using the CLI is an essential skill for Splunk administrators.
In the console or Command Prompt, type in the following command and hit Enter on your keyboard:
Windows: C:> cd C:Splunk\bin
Linux: cd /$SPLUNK_HOME/bin
While in the $SPLUNK_HOME/bin directory, issue the following command to restart Splunk:
Windows: C:Splunk\bin>splunk restart
Linux: [user@server bin]$ ./splunk restart
After issuing this command, splunkd will go through its restart process. Here are the other basic parameters that you can pass to the Splunk application to control Splunk:
Windows:
- splunk status: Tells you whether splunkd is running or not
- splunk stop: Stops splunkd and all its processes
- splunk start: Starts splunkd and all its processes
- splunk restart: Restarts splunkd and all its processes
Linux:
- ./splunk status: Tells you whether splunkd is running or not
- ./splunk stop: Stops splunkd and all its processes
- ./splunk start: Starts splunkd and all its processes
- ./splunk restart: Restarts splunkd and all its processes
Doing this from a CLI gives the added benefit of verbose messages. A verbose message is a message with a lot of information in it. Such messages can be useful for making sure the system is working correctly or troubleshooting any errors.
A successful restart of splunkd generally has the following output (elements of which may vary):

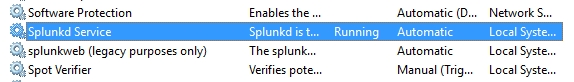
In Windows, you can also control Splunk through the Splunkd Service, as shown in the following screenshot. The d in the service name, denoting daemon, means a background process. Note that the second service, splunkweb, is not running. Do not try to start splunkweb as it is deprecated and is there only for legacy purposes. The Splunk-running web application is now bundled in Splunkd Service: