Indexes are where Splunk Enterprise stores all the data it has processed. It is essentially a collection of databases that are, by default, located at $SPLUNK_HOME/var/lib/splunk. Before data can be searched, it needs to be indexed—a process we describe here.
There are two ways to create an index, through the Splunk user interface or by creating an indexes.conf file. You will be shown here how to create an index using the Splunk portal, but you should realize that when you do that, it simply generates an indexes.conf file.
You will be creating an index called winlogs to store a sample Windows perfmon log. To do this, take the following steps:
- In the Splunk navigation bar, go to Settings.
- In the Data section, click on Indexes, which will take you to the Indexes page.
- Click on the New Index button in the upper-right corner.
- Fill out the information for this new index as seen in the following screenshots, carefully going through steps 1 to 6. You will need to scroll down in the window to complete all the steps.
The following screenshot displays the first three steps to be followed:

The next screenshot indicates step 4 and step 5 to be followed:
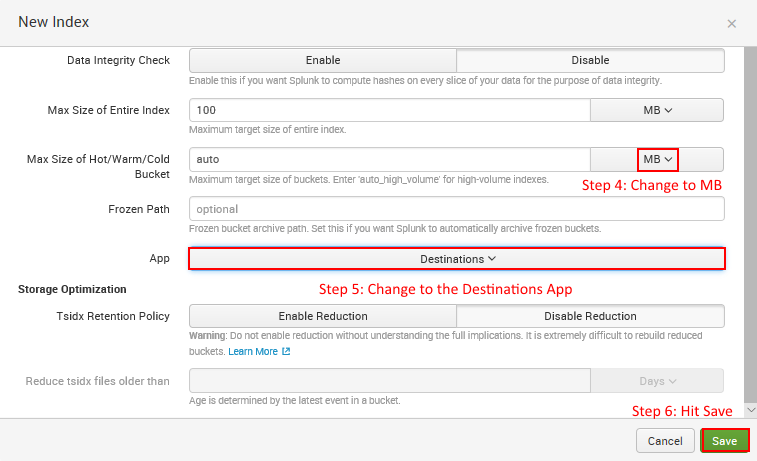
- Be sure to Save when you are done.
You will now see the new index in the list as shown here:

The preceding steps have created a new indexes.conf file.
Now go ahead and inspect this file. In Windows this can be done through Notepad. In Linux, you can use a visual text editor such as Notepad++ to connect to your Linux server or, at the command line, use vi.
The specific indexes.conf to open will be found in $SPLUNK_HOMEetcappsdestinationslocal. Specifying the destinations app for the index is what placed the indexes.conf file below the destinations directory.
Every index has specific settings of its own. Here is how your index looks when automatically configured by the portal. In production environments, this is how Splunk administrators manage indexes:
[winlogs] coldPath = $SPLUNK_DBwinlogscolddb
enableDataIntegrityControl = 0
enableTsidxReduction = 0 homePath = $SPLUNK_DBwinlogsdb maxTotalDataSizeMB = 100 thawedPath = $SPLUNK_DBwinlogsthaweddb
The complete indexes.conf documentation can be found at http://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/admin/indexesconf.