Docker Toolbox has been available for developers for a few years. It precedes the newer tools such as Docker for Mac and Docker for Windows. The toolbox allows a user to work very elegantly with containers on any Mac or Windows computer. Containers must run on a Linux host. Neither Windows or Mac can run containers natively. Thus, we need to run a Linux VM on our laptop, where we can then run our containers. Docker Toolbox installs VirtualBox on our laptop, which is used to run the Linux VMs we need.
Let's use docker-machine to set up our environment. Firstly, we list all Docker-ready VMs we have currently defined on our system. If you have just installed Docker Toolbox, you should see the following output:

The IP address used might be different in your case, but it will be definitely in the 192.168.0.0/24 range. We can also see that the VM has Docker version 18.04.0-ce installed.
If, for some reason, you don't have a default VM or you have accidentally deleted it, you can create it using the following command:
$ docker-machine create --driver virtualbox default
The output you should see looks as follows:

To see how to connect your Docker client to the Docker Engine running on this virtual machine, run the following command:
$ docker-machine env default
Once we have our VM called default ready, we can try to SSH into it:
$ docker-machine ssh default
When executing the preceding command, we are greeted by a boot2docker welcome message.
Type docker --version in the Command Prompt as follows:
docker@default:~$ docker --version
Docker version 17.12.1-ce, build 7390fc6
Now, let's try to run a container:
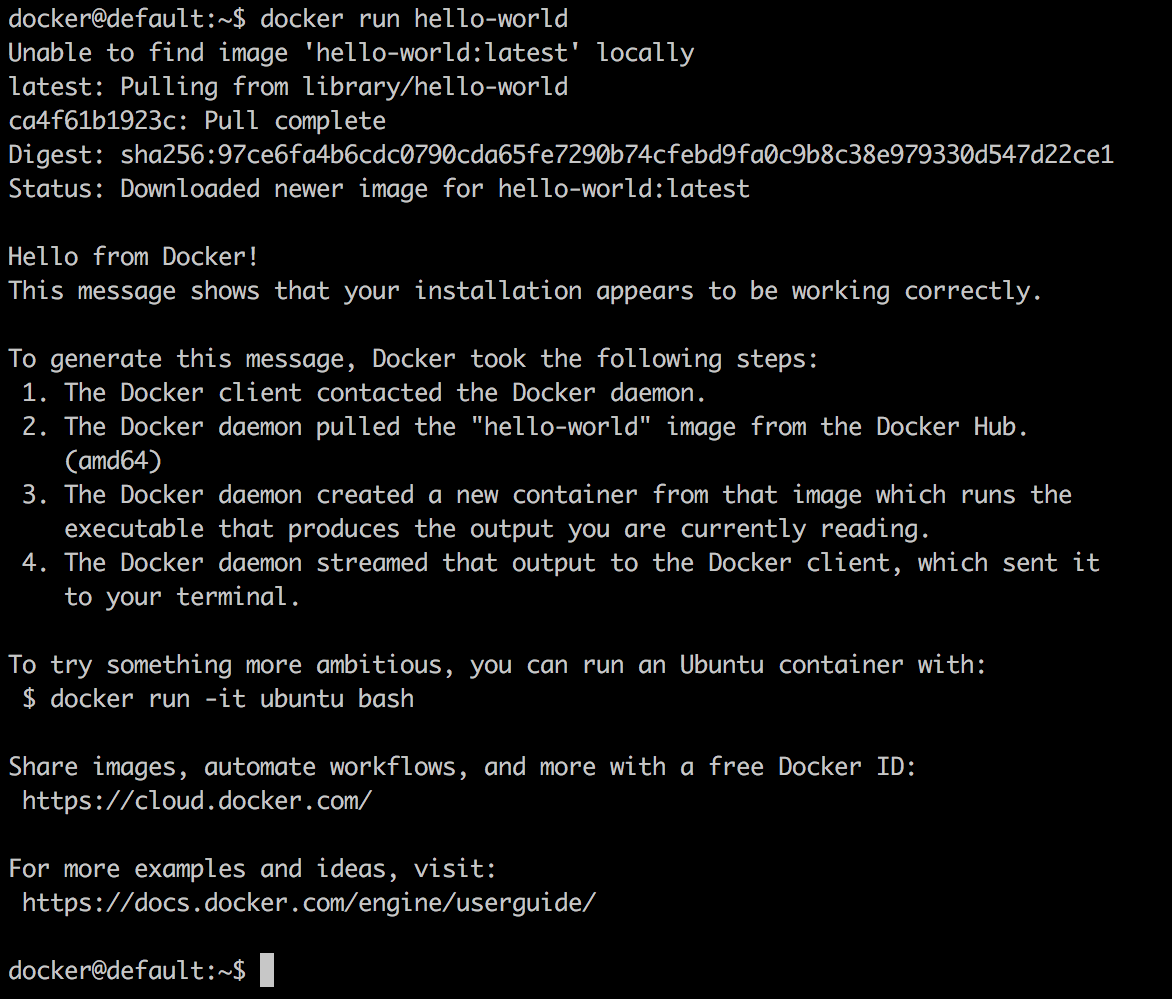
docker@default:~$ docker run hello-world
This will produce the following output: