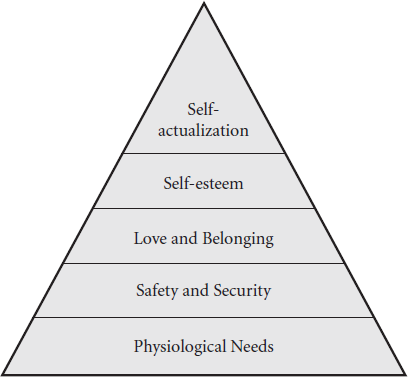
Maslow, an American psychologist, is considered the founder of humanist psychology. Maslow followed Freud’s psychoanalytic model and viewed his work as an extension rather than a replacement for other theory. Maslow is best known for his hierarchy of human needs. Maslow believed that human behavior was motivated by a series of hierarchical needs ranging from basic physiological survival to self-actualization.
The following chart displays a graphic of the levels of human need in Maslow’s hierarchy. Maslow believed that having basic survival and physiologic needs unmet prevented individuals from addressing safety needs and issues. In turn, safety needs for security, stability, and protection must be met before people can deal with love and belonging needs in social relationships. Once social relationship needs are met, the person can focus on developing self-esteem through achievements and accomplishments. Once all of the levels of need are met, the individual seeks self-actualization, which is attainment of peak performance living. This person has met and accomplished what he is best suited for in life, and is reaping the rewards of living.
Maslow recognized that life circumstances create situations that move people between stages. You will need to recognize what life realities and needs your patients face as you assist in your office practice. It will be important to assist patients who are struggling with basic physical needs or safety needs by referring them to social service agencies or other human service organizations in your community. Being aware of where a patient is on this hierarchy will help guide your interventions and communication to be more effective.
