Answers and Explanations
Practice Test
- D
Hepat/o means liver. Stomach (A) is gastr/o, intestine (B) is enter/o, pancreas (C) is pancreat/o, gallbladder (E) is cholecyst/o.
- C
Defense mechanisms assist us with circumstances that are difficult for the mind to cope with. Grief (A) is a process that people experience during a time of loss. The unconscious mind (B) is the term Freud used to describe repressed thoughts and feelings. Freud defined the ego (D) as the conscious mind containing our thoughts and feelings. Maslow defined self-actualization (E) as the attainment of the peak of one’s capabilities in life.
- B
The optic nerve carries visual stimulation to the brain. The vestibular cochlear nerve deals with hearing (A). The olfactory nerve carries stimulation for smell to the brain (C). The nerve pathway for taste (D) is the lingual nerve. Touch (E) is carried by pressure receptors in the skin.
- C
Medical assistants are expected to comply with rules and regulations that protect individual health information. Unless your coworker has a legitimate reason in the course of care or treatment, the patient record is off limits, and you need to make sure the information remains confidential and secure in your office setting. None of the other actions supports your obligation in regard to patient privacy.
- A
The DASH diet lowers blood pressure significantly. The BRAT diet is for diarrhea (B). The bland diet is used with digestive disorders (C). Antioxidant diets help prevent cancer (E). High protein diets assist with muscle strength (D).
- B
A deposition is sworn testimony given outside of the courtroom. A subpoena (A) is a legal directive to come to court to testify. Standard of care (C) refers to the expectation that a level of care will be given that is equal to what a reasonable, prudent person with the same training would offer. Evidence (D) is proof submitted supporting a plaintiff. A verdict (E) is the final decision.
- C
Intent has nothing to do with malpractice or negligence. Negligence occurs when a heath care provider has a duty toward a patient, is derelict in performing that duty and damages occur directly because of it. When all four D’s are present, negligence exists.
- D
The ability to recognize and categorize objects by size and weight is part of the period of concrete operations. Children ages 7 to 11 are normally in this stage of cognitive development. Self-actualization (E) is not one of Piaget’s stages.
- D
Poly- means many. Semi- (A) means half, macro- (B) means large, pseudo- (C) means false, and dia- (E) means through.
- C
Begin by dividing the word into word parts: myel/o/mening/o/cele. Cele means herniation. Myel/o means bone marrow or spinal cord. Mening/o means meninges or covering on the brain and spinal cord. When we look over the options, we want one close to “herniation of the spinal cord and meninges.”
- D
Potassium is the correct answer. Calcium (A) is found in dairy products, sardines, and canned salmon. Vitamin C (B) and vitamin K (C) are vitamins, not minerals. Iron (E) is found in red meats, dried fruit, and organ meat.
- C
There are four types of body tissue: epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscular.
- E
All of the following are true except (E). A patient owns the information in the chart and may request to have it disclosed and the physician cannot refuse (A). Having a power of attorney for health care gives all the powers normally given to a patient to the designee (B). Any member of the health care team can release information without permission if another person is in imminent, life-threatening danger (D). For example, the patient who storms out of the office brandishing a knife saying that he is going to kill his girlfriend. The last answer is incorrect because the mentally ill do not lose any rights and even if a person is not in touch with reality; they are entitled to confidentiality unless the guardian or power of attorney signs a release of information.
- C
This patient is experiencing the anger stage of grieving. Kübler-Ross pointed out in her study of terminally ill patients that anger is often displaced on health professionals and that the anger should not be taken personally. In this response, you are supporting the patient’s feelings and acknowledging his issue. None of the other responses would be appropriate to this patient’s remark.
- E
There is electrical interference from within the room. This type of interference results from any extraneous electrical source, such as lights or computers, and also from excessive current running through the walls. There will be even, sharp peaks on the tracing. When electrodes are too tight (A) or not attached completely (C), the result is a wandering baseline, in which the tracing does not continue in a straight line across the graph paper. Incorrect placement of the electrodes (B) produces artifacts in the tracing that can mimic serious conditions such as ischemia or gross arrhythmia. If the patient moves in any way (D), interference referred to as “somatic tremors” occurs, and uneven, rounded peaks will appear on the tracing.
- E
Orrhaphy means sewing or stitching. Phlebo means vein. Venostenosis (A) means narrowing of veins. Phlebosclerosis (B) means hardening of veins. Vasoplasty (C) means surgical repair of vessel. Venopexy (D) means surgical repair of veins.
- E
Threatening him with calling security should be your last and least preferred strategy for managing the patient’s anger. It is reasonable to attempt to defuse Mr. Hall’s anger and offer him empathy (C) and a sincere apology (A) even when you are not responsible for the delay. By lowering your own voice (B), he is likely to follow your lead and lower his. In some instances, service recovery with an unhappy patient can occur if you offer a small and tangible token of apology for a problem or delay in service (D).
- E
Vitamin K is the clotting vitamin. Vitamin A (A) is used for skin and night vision. Vitamin B6 (B) and B12 (C) have a role in the nervous system. Vitamin C (D) assists with immunity.
- E
The mighty mitochondria is responsible for the production of energy in the cell. The Golgi body (B) transports mucous. The endoplasmic reticulum (C) transports ribosomes. The nucleus (D) is the “command center” and responsible for DNA production in the cell. Lysosomes (A) are the waste-removing organelles in the cell.
- C
Onc is a word root that means tumor. Onc/o (A) is incorrect because it is a combining form. Because it is a suffix, -oma (B) is incorrect. Carcin (E) and carcin/o (D) deal with cancer.
- D
Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic theories held that people experienced problems because of repressed memories and thoughts from childhood. Kübler-Ross (A) is associated with the grieving process. Maslow (E) developed the hierarchy of needs, and Piaget (B) and Erickson (C) are developmental theorists.
- B
Defendants are not held liable for damages when contributory risk is the defense because the patient was in part responsible for the injury. In assumed risk (A), the patient willingly accepts the risk. In comparative risk (C), both the plaintiff and defendant are assigned a portion of the responsibility for the injury. A technical defense (D) is based on a point of law being violated. An intervening cause (E) is an extraneous variable that came into existence altering the course of events.
- D
Start by looking for a suffix meaning infestation of stones: lithiasis. Either choice (C) or choice (D) will be correct. Chole means gall and lithiasis means infestation of stones. Together they mean infestation of gallstones making (D) the correct choice. Cholecystolithiasis (C) means infestation of gallbladder stones which is close but not the best answer. Cholecystitis (A) means inflammation of the gallbladder. Cholecystosis (B) means a condition of the gall bladder. Cholecystectomy is a surgical removal of the gallbladder.
- A
By rewarding the child for losing weight, the medical assistant is reinforcing the behavior of weight loss.
- B
Vitamin C is the only water-soluble vitamin listed. Excess is excreted from the body in the urine. Vitamins A, D, K, and E are fat-soluble and can build up to a toxin level in the body.
- D
A comparative defense assigns portions of the responsibility for damages to both plaintiff and defendant. A technical defense (A) is based on errors in the legal system. Denial (B) is not an affirmative defense. Contributory defense (C) means a defendant cannot be found guilty of negligence if the patient is in any part responsible. Assumed risk (E) is when the patient willingly takes on a risk.
- C
The senses are part of the nervous system because they pick up information and deliver it to the brain for a response.
- D
The stage described in this question is the sensorimotor stage. In this stage, from birth until about age two, children learn what they take in from hearing, touching, smelling, and seeing. They have limited motor skills.
- D
The patella is the kneecap of the leg.
- C
ARDS is the abbreviation for adult respiratory distress syndrome. SOB is an abbreviation for shortness of breath. COPD is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. These are all respiratory diseases and should be handled by a physician who specializes in respiratory disease, a pulmonologist. A nephrologist (A) is a physician who specializes in kidney disease. A gastroenterologist (B) treats gastrointestinal diseases. A cardiologist (D) treats the heart and cardiac diseases. A hospitalist (E) sees persons who are inpatients in the hospital.
- A
The Uniform Anatomical Gift Act allows those over 18 years of age to make decisions about disposal of their body or body parts for medical education, research, or transplantation. A living will (B) authorizes the continuation or withdrawal of life support if the person is too sick to voice an opinion. A power of attorney for health care (C) is the designation of another person to serve as agent in making all decisions, including surgical or life-threatening decisions, when the patient is unable to voice an opinion. ERISA (D) is a federal act designed to protect retirement fund and pensions. Res ipsa loquitor (E) is a circumstance where the responsibility for a situation is grossly obvious.
- C
In the word hematuria, -uria is the suffix meaning condition of urine. The prefix hemat- means blood. Uremia (B) is not correct. Remember, you begin translating at the back of the word. Uremia is a condition of the blood.
- B
Sudoriferous glands produce perspiration. Ceruminous glands (A) produce earwax. Parathyroid glands (C) are endocrine glands imbedded in the thyroid gland. Sebaceous glands (D) produce sebum to moisturize the skin and scalp. Adrenal glands (E) produce glucocorticosteroids that involve immunity.
- C
Thrombocytes are called platelets. They are the initial patch to prevent blood loss when a vessel is injured. Erythrocytes (A) carry oxygen and nutrients. Leukocytes (B) fight invaders/infection. Neutrophils (D) and eosinophils (E) are specific types of white blood cells.
- C
Showing photos of a surgery without patient consent is an intentional tort. Intentional torts include assault, battery, slander, libel, invasion of privacy, fraud, and false imprisonment. Showing photos without permission (C) is invasion of privacy. Giving the wrong medication (A) is misfeasance, improperly cleaning a surgical site (B) is misfeasance, not drawing an ordered lab (D) is nonfeasance and suturing a laceration (E) is malfeasance. These are all unintentional torts.
- C
Meta- (C) means beyond. Mal- (A) means bad, ambi- (B) means both, retro- (D) means behind, and multi- (E) means many.
- C
Subpoena duces tecum means “come and bring records.” Respondeat superior (A) involves the responsibility of the employer for the employee’s actions. Res ipsa loquitur (B) translates literally to mean “the thing speaks for itself.” It is used when an error is grossly obvious and blame is directed at one person. Res judicata (D) means “a matter decided by judgment.” Caveat emptor (E) means “buyer beware” and has nothing to do with law.
- C
Food, water, oxygen, and shelter are fundamental needs that must be met before this mother can attend to the safety and security needs of her child. The other stages are all higher-ranking items on Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. The mother would be more likely to attend to the instruction if she had food available.
- C
Most pathogenic organisms are aerobic, meaning that they require oxygen to survive. An example of an aerobe is Streptococcus, which causes strep throat. Pathogens that are able to thrive with minimal or no oxygen are anaerobes (D); one example is tetanus. Microorganisms (A) are microscopic living creatures and can be pathogenic or nonpathogenic, aerobic or anaerobic. Spores (B) are encapsulated, inactive bacteria that are difficult to destroy. Protists (E) are a varied group of mostly single-celled microorganisms; some are pathogenic (such as Plasmodium falciparum, which causes malaria) and others are nonpathogenic (such as algae).
- D
The suffix -ity means condition.
- C
The physician can terminate care of a patient if the patient is noncompliant with treatment (B), misses appointments (D), does not pay her bills (A), or sees another physician (E). However, abusive language (C) is insufficient cause to break a contract.
- B
Prefixes come at the beginning of a word. That eliminates -para (C) and -oma (D). Meta (E) means beyond, peri- (A) means around and para- (B) means near.
- D
A bone broken into pieces is a comminuted fracture. A compound (A) or open (E) fracture has broken the skin. A pathological fracture (B) is the secondary result of another disease. An impacted fracture (C) is the jamming of one bone into another.
- B
Dark green, orange, and yellow vegetables are high in antioxidants. Liver and organ meats (A) are high in iron. Citrus fruit (C) is high in vitamin C. Root vegetables (D) have no special significance. Dairy products (E) are rich in vitamin D and calcium.
- A
A transverse plane cuts through the body parallel to the horizon. A sagittal cut (B) goes through the midline. A frontal (C) or coronal (D) plane divides the body into a front and back half. The midsagittal (E) plane divides the body into right and left halves.
- B
IBS is the abbreviation for irritable bowel syndrome. PUD is the abbreviation for peptic ulcer disease. Pyloric stenosis involves the stomach and small intestine. These diseases would be treated by a physician who specializes in the stomach and intestine and disease of the gastrointestinal tract: a gastroenterologist.
- C
Digestion begins in the mouth with the breakdown of carbohydrates by amylase.
- D
Torts are crimes against another person or property. Misdemeanors (B) are crimes against the state punishable by incarceration in jail for less than a year. Felonies (A) are serious crimes, such as burglary, that are punished by incarceration in prison for more than a year. Treason (C) is a crime against the state and negligence (E) occurs when a professional is derelict in performing a duty and damages occur directly because of it.
- B
Hemorrhoid is spelled correctly.
- B
The pancreas is a digestive organ and is located in the abdominal cavity. The thoracic cavity (A) holds the lungs and heart. The pelvic cavity (C) holds the organs of reproduction and some of the organs related to the urinary system. The spinal cavity (D) contains the spinal cord and the cranial cavity (E) contains the cranium.
- D
Minors cannot make their own health care decisions unless it involves reproductive care, substance abuse, or psychiatric treatment. The only exceptions are when the minor is emancipated by marriage, is self-supporting, or is enlisted in the military. Elderly persons who have not been designated as incompetent or have no guardian may make their own medical choices despite confusion.
- C
PO (from the Latin per os), meaning “by mouth,” is not a parenteral route of medication administration. Parenteral refers to the introduction of a substance into the body via a route other than the alimentary canal (digestive tract). Intravenous, or IV, administration (A) is infusion into the vein; IM, or intramuscular (B), is injection into the muscle; subQ, or subcutaneous (D), is injection under the skin; intradermal (E) is injection just under the epidermis, or outer layer of skin.
- A
Menstruation is the correct spelling. None of the other answer choices is misspelled.
- D
A banana is low in sodium. High-sodium foods are processed items like packaged cheese and salty items like chips, pretzels, and snack foods. Pickled and smoked items like ham are high in sodium.
- D
The SA node is the pacemaker of the heart. The impulse travels to the AV node (B) where it slows. It separates at the bundle of His (A) and travels down the left or right bundle branches (C). The impulse travels to the purkinje fibers (E) that are imbedded in the walls of the atria, causing them to contract.
- C
The medical chart has four purposes. It is a research tool, a communication tool among health team members, legal record, and record of personal health.
- A
The length of time after an event in which a person can file a lawsuit is called statute of limitations. Doctrine of informed consent (B) means making certain the patient is aware of all details about any procedure, alternative choices, potential complications and side effects, consequences of refusing treatment, etc. Mandatory reporting (C) refers to the obligation of medical assistants to report child or elder abuse. HIPAA (D) refers to regulations for confidentiality in reporting health information. COBRA (E) refers to federal regulations regarding continuation of health insurance after leaving a job.
- C
Laboratory results are protected health information that should only be given directly to the patient. Leaving the information on an answering machine is a violation of patient confidentiality. None of the other items is as effective as asking her to call the office back.
- E
Either -dynia or -algia is the suffix meaning pain. That means the correct choice is either (C) or (E). Chrondr/o means cartilage and oste/o means bone. This makes the correct choice osteodynia (E). Chondromalacia (A) is softening of cartilage. Osteochrondritis (B) is inflammation of bone and cartilage. Chrondralgia (C) is pain in cartilage. Osteolysis (D) is destruction of bone.
- D
Cauliflower is not a source of calcium. Milk, sardines, canned salmon, and cheese are rich in calcium.
- E
AC (from the Latin ante cibum) means “before a meal.” The abbreviation PC (D) (post cibum) indicates “after meals.” NPO (A) (nil per os) means “nothing by mouth” and is used when a patient should have nothing to eat or drink prior to a test, exam, or procedure. NOS (B) stands for “not otherwise specified” and is used to code encounters. PRN (C) (pro re nata) means “as needed.”
- C
In civil cases, only a preponderance of evidence is sufficient to prove guilt. In criminal cases, there must be overwhelming evidence beyond a reasonable doubt.
- D
Fluoride is added to water and toothpaste to prevent dental decay (cavities). Calcium (A) builds bones and teeth. Potassium (B) keeps heart contraction regular. Iron (C) prevents anemia and iodine (E) prevents goiters.
- C
Type O can donate to all blood types and is called the universal donor. Type A (A) can donate to type A or type AB. Type B (B) can donate to type B or type AB. Type AB (D) can donate to only AB blood type. ABO (E) refers to the overall blood typing group and is not an actual blood type.
- C
The household equivalent of 10 mL is 2 teaspoons. One teaspoon equals approximately 5 mL; it is also equivalent to 60 drops (E)—too little of the medication. A half-teaspoon (B) equals approximately 2.5 mL—too little of the medication. There are 3 teaspoons or 15 mL in a tablespoon, so 2 tablespoons (D) equals 30 mL—too much of the medication. A half-pint (A) equals 8 ounces, which is equivalent to 240 mL—too much of the medication.
- A
The abbreviation PERRLA refers to eyes and stands for “pupils equal, round, and reactive to light and accommodation.” It indicates that the pupils are normal; it has no bearing on physical exam results for the ears (B), throat (C), heart (D), or abdomen (E). The eye examination may involve using a penlight or flashlight to observe the dilation and constriction of the pupil.
- B
Prostrate is not a medical term. The correct term is prostate.
- E
Arteries are thick, elastic, and carry blood away from the heart. Veins are thin, fragile, and return blood to the heart.
- B
The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates at the back of the head and inserts into the sternum. A severe spasm prevents moving or turning of the head. The gastocnemius (A) is a calf muscle that often spasms and give the patient a “charley horse.” The rectus abdominus (C) is the “six pack” muscle of the abdomen. The deltoid (D) is the muscle of the upper arm that we use for injection. The sartorius (E) involves the “tailor muscle.” Sitting on the floor, putting the soles of the feet together, and pressing down on the knees stretches the sartorius.
- E
The Fair Debt Collection Act is a regulation to protect debtors from collectors calling at work, leaving incriminating messages, or calling at inconvenient hours to harass the debtor. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (A) allows persons to see their credit record and the information given to potential lenders. The Equal Credit Opportunity Act (B) prohibits discrimination against extending credit based on race, sex, gender, religion, or marital status. The Consumer Protection Act of 1971 (C) protects the patient’s finances by regulating the lending of funds. Fair Labor Standards Act (D) regulates the minimum wage and controls the number of hours worked.
- E
Tendons join muscle to bone. Ligaments (A) join bone to bone. Perisoteum (B) is the protective covering on the outside of a long bone. Cartilage (C) is a semi-hard, fibrous connective tissue. The meninges (D) are a three-layer covering over the brain and spinal cord.
- D
The suffix -para means only live births. The prefix multi- means many.
- A
Only schedule II drugs must be ordered in writing on a triplicate form, signed by the physician, filled within a time limit, and no refills given. Schedule IV drugs are frequently abused (D), but have a lower potential for abuse. Drugs like Xanax, Ativan, and Valium are in this category. They must be locked in a secure place (E), but they can be called in over the phone (C) and may be refilled up to five times in six months (B) if the doctor thinks this appropriate.
- C
The umbilical or gastric region surrounds the navel. The epigastric region (B) is above the navel. The suprapubic region (A) is below the navel and above the pubic bone. The hypochondriac regions (D) are in the area of the false ribs. The lumbar regions (E) are in the lower back.
- A
The ego is the part of the conscious mind that contains our thoughts and behaviors.
- B
Menstrual flow is menorrhea. That means the correct choice is (B), (C), or (D). The prefix for without is a- or an-. That makes amenorrhea (B) correct. Nullipara (A) would be translated as no live births. Oligomenorrhea (C) translates to scanty menstrual flow. Dysmenorrhea (D) means painful menstruation. Nulligravida (E) means no pregnancies.
- B
Eggs are not eaten by a lacto-vegetarian. Lacto-vegetarians eat only plant-based items and dairy foods such as milk and cheese.
- A
The Patient Self-Determination Act allows patients to control their own lives and make informed decisions about what medical care they do or do not want. The Consumer Protection Act of 1971 (B) protects the patient’s finances by regulating the lending of funds. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 (C) prohibits discrimination based on race, religion, color, sex, or national origin. The HIPAA Act (D) is recent legislation to protect individual health information. The Americans with Disabilities Act (E) protects those with physical, mental, or emotional handicaps from discrimination.
- B
A subdural hematoma is a bleed under the layers of tissue covering the brain, but the bleeding does not go into the brain itself. An intracerebral hematoma (C) is bleeding into the brain tissue itself. A concussion (A) is a head injury in which the brain has a temporary injury (bruising and bleeding) due to a blow. Epilepsy (D) is irregular electrical activity of the brain that may result in seizure. Hydrocephalus (E) is an increase in fluid pressure because ventricles in the brain do not drain properly.
- C
K is the abbreviation for potassium.
- B
Pain and weight loss are advanced symptoms of cancer. Early warning symptoms allow treatment and increase survival rates. The seven early warning symptoms are: a sore that does not heal, a lump or mass, unexplained bleeding, a mole that has changed shape or color, chronic cough or hoarseness, change in bowel or bladder habits, and persistent indigestion.
- A
ADHD is the abbreviation for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. PTSD is the abbreviation for post-traumatic stress disorder. Bipolar disorder is a mental illness. Stress, attention disorders, and mental illness are treated by a psychiatrist.
- D
The duties of the public health department include recording of vital statistics such as births, deaths, communicable diseases, animal bites, gunshot and knife wounds, epidemic control, and research. Medicare is managed by the federal government and Medicaid is managed by the state.
- D
The T wave indicates the relaxation of the ventricles. The P wave (A) shows the contraction of the atria, and the QRS complex (C) indicates the contraction of the ventricles and the relaxation of the atria. A U wave (E) is not always seen on an EKG and may indicate hypokalemia. The Q wave (B) is a componenet of the QRS complex, showing the depolarization of the ventricles of the heart.
- D
Carcinogenic means pertaining to the formation of cancer. The suffix -ic means pertaining to, carcin/o means cancer, and gen/ means formation. Formation of tumors (A) would be oncogenesis. Pertaining to tumors (B) would be a reference to abnormal growths. The study of tumors (E) is oncology.
- A
Multiple sclerosis involves the appearance of bare spots on the myelin sheath (demyelization of the axon). Myasthenia gravis (B) involves extreme fatigue of muscles with the slightest exertion. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (C) is a progressive degeneration of voluntary motor neurons. Cerebral palsy (D) is a disorder of balance and movement often caused by anoxia during the birth process. Parkinson’s disease (E) is a disease of dopamine deficiency that affects gait. It often is accompanied by “pill-rolling” movements of the fingers.
- D
(A), (B), (C), and (E) correctly describe reasons for erythema (redness of the skin). Bile problems (D) would likely result in jaundice (yellowing of the skin and mucus membranes).
- A
Begin by dividing the word into parts and look at the ending.
(A) electr/o/cardi/o/graphy
(B) electr/o/cardi/o/graph
(C) electr/o/cardi/o/gram
(D) ech/o/cardi/o/gram
(E) ech/o/cardi/o/graphy
Only two endings mean “the process of using an instrument to record data.”
(A) electr/o/cardi/o/graphy
(E) ech/o/cardi/o/graphy
When we look at the beginning of the word, only electrocardiography (A) involves electrical activity. Echocardiography (E) involves reflected sound (ech/o/cardi/o/graphy). Looking at the entire word, electrocardiography does mean “the process of using an instrument to record data of the electrical activity in the heart.”
- D
Battery is illegal touching. It is an intentional tort. Assault is the mere threat of illegal touching.
- B
A vesicle is a papule with clear fluid; for example, a blister or chicken pox lesion. A pustule (A) is a papule filled with white or yellow pus. A macule (C) is a flat lesion and although visible, it cannot be felt. A nevus (D) is a mole. A nodule (E) is a large, hard knot or tumor.
- C
One of these abbreviations does not belong with the others. Start by figuring out the meaning of each. TAH is total abdominal hysterectomy. LMP is last menstrual period. LOC is level of consciousness. PID is pelvic inflammatory disease. STD is sexually transmitted disease. The one that does not seem to fall under the area of women’s health where a gynecologist would specialize is the LOC (C).
- B
The person accused of a crime is the defendant. The plaintiff (A) offers a complaint. The jury (C) is a group of peers who try a case. Bench (D) refers to a judge trying a case. An agent (E) is someone representing another, such as the medical assistant representing the physician.
- E
Gout (E) is an accumulation of uric acid crystals in joints. Bursitis (A) is an enlarged sac between joints that fills with fluid to provide extra protection to the joint. Arthritis (B) is inflammation of a joint causing pain and stiffness. Kyphosis (C) is an exaggerated curvature to the thoracic spine. Scoliosis (D) is a deviation of the spine to the side.
- D
Reciprocity allows a person licensed in one state to practice in another. Revocation is canceling a license to practice.
- C
Recognizing the word parts help us to know what body area is involved. Translating the end first, -ism is a condition. The beginning of the word is crypt/o, which means hidden, and the middle of the word is orchid/o or testicles. Cryptorchidism is a condition of hidden testicles. Balanitis is inflammation of the glans penis. Hematuria is a condition of blood in the urine. These conditions would be treated by a doctor who specializes in male reproductive organs and urinary problems, a urologist.
- D
Respiration would increase under the effect of the sympathetic nervous system as the body prepares for “fight or flight.” Muscles require glucose and oxygen for energy.
- B
A contract can be written or oral. All contracts involve a good or service for a consideration that is accepted by two parties of legal capacity.
- E
CABG is coronary artery bypass graft and an EKG is an electrocardiogram. Both would involve the heart and require the services of a physician who specializes in the heart, a cardiologist.
- E
Negligence (A) is failure to perform at the reasonable standard of care. Defamation of character (C) is malicious misrepresentation of facts to harm another. Slander (B) is defamation of character through spoken words and libel (D) is defamation of character through written words.
- C
The scenario described in the question is an example of bargaining. In this state of the grief process, patients seek to negotiate with a higher power and resolve their illness.
- E
Coordination of benefits is undertaken when the patient has more than one insurance plan: After the primary carrier has made payment based on its plan, the secondary carrier determines its own amount of payment based on the balance. Capitation (A) means that the insurance carrier pays a set fee per patient regardless of degree of injury or illness. Coinsurance (B) requires the insured patient to pay for portion of a medical bill, while the insurance carrier pays the remainder. A third-party payment (C) is one made by an insurance carrier, government-funded program, or other payer that is not the patient. In assignment of benefits (D), a patient authorizes the health insurance carrier to make payment for a covered procedure directly to his/her health-care provider rather than to himself/herself.
- C
Posting is the process of copying or recording an amount from one record, such as a journal, onto another record, such as a ledger or from a day sheet onto a ledger card. A ledger (A) is a record of charges, payments, and adjustments for individual patients or families. A superbill (B) is a combination charge slip, statement, and insurance reporting form. A trial balance (D) is a method of checking the accuracy of accounts. It should be done once a month. Deducting (E) refers to when money is subtracted or deducted from an employee pay to cover taxes, insurance, and possible other expenses.
- D
The goal of using wave is to keep the office on track. To determine how many patients to be seen in an hour, divide the hour by the length of the average visit.
- A
Inspecting and releasing means ensuring that the appropriate people have taken action on a document. Before the document is filed, a release mark should be noted on it.
- A
“Tickler file” and “reminder file” are two names for the file that holds work that has to be completed. A supplemental file (B) is a file that holds papers that are needed in addition to main papers. A retained file (C) may be a file that retains or holds specific information. An inactive file (D) holds paperwork from patients that are no longer part of the medical practice. An active file (E) may hold information on patients that are currently using the medical office.
- B
The HITECH Act of 2009 does not dictate any single electronic health record (EHR) software system, and many software and hardware vendors have entered the market for EHRs. The act establishes financial incentives for EHR adoption (A) to promote the goal of improving Americans’ health (D), and it requires health care providers to demonstrate “meaningful use” of EHRs (C). As of 2013, 78 percent of U.S. physicians had adopted an EHR system (E).
- C
Withholding is the amount of salary held out of payroll checks for the purpose of paying government taxes or for employees’ benefits. To determine the amount of money to be withheld from each paycheck, each new employee must complete a W-4 (A). The Federal Unemployment Tax Act (B) requires employers to pay a percentage of each employee’s income, up to a specified dollar amount, to fund an account used to pay employees who have been laid off. All employees file an annual tax return (D). FICA (E) governs the Social Security system.
- C
In block format the salutation is followed by a colon.
- B
A common concern among clinical providers is that the simultaneous entry of patient information during an examination places a barrier between themselves and the patient. Often the computer station is across the room from the exam table and the clinician has their back turned to the patient as they are talking. While some clinicians do not like keyboarding aspects the communication issue is the most common issue being raised.
- C
The standard size business envelope is No. 10, 4
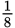 inches by 9
inches by 9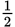 inches.
inches. - C
Account aging is the method of identifying how long an account is overdue. Collecting the receivable on time (A) is the best way to keep accounts accurate but this is not always feasible. Account aging is necessary in all physician offices regardless of size (B). Account aging shows how the account is aging; it does not allow the account to be written off (D and E).
- C
Open-hours scheduling is when patients come at their own convenience. Modified-wave (A) can be used in different ways. One way is to schedule in 15-minute slots, regardless of appointment type. Double-booking (B) is used when two patients are scheduled at the same time. Cluster scheduling (D) groups similar appointments together during the day. Time-specified scheduling (E) assumes a steady stream of patients all day long.
- A
Scheduling these appointments at the beginning of the hour will allow time for catching up. The less time-consuming appointments can be given 10-minute time slots. Ten-minute time slots (B) may not be enough for all patients. Scheduling these appointments at the end of the hour (C) will not allow the doctor to catch up. Scheduling an appointment at the same time as another patient’s 10-minute slot (D) will not give the time needed for the appointment. Ten-minute appointments (E) would be used for follow-up care.
- C
For the tickler file to be most effective, it has to be checked frequently; so all paperwork is quickly put in patients’ charts. A tickler file is kept in a folder (A), but it still has to be checked frequently. If the tickler file is locked in a secure area (B), it may not get checked as needed. Tickler files should be cleaned out every week, not left in weekly files (D). Keeping the tickler file in a separate area of the office (E) may cause it to be overlooked.
- C
Under managed care, in which a copayment is part of the plan, patients are expected to pay at each visit. By collecting payment before the provider sees the patient, the medical office enhances its ability to collect the expected copayment. Asking the patient how they want to pay (C) implies that payment is expected now. Deferring payment to checkout time (A) and asking the patient for information (D) suggest that payment is not expected now; these practices are not encouraged. Suggesting that the patient send in the payment (B) conveys the idea that it is the patient’s choice to pay or not pay. It is not the provider’s job to tell a patient how much they owe (E).
- E
All aspects of the flow and provision of care in a practice office or health care setting will be part of a well-integrated electronic management system. This includes not only the clinical systems but billing and scheduling aspects as well.
- A
A spreadsheet is a worksheet that is used to see many types of information at once. Hardware (B) refers to a computer’s physical components. A patient list (C) is created by the medical office. A cover letter (D) is used to send to introduce you or the medical office to the reader. A work grid (E) shows what time employees are in.
- D
The U.S. Postal Service defines first-class mail as all items weighing 13 ounces or less.
- D
Written communication, such as letters, memos, and email, must take into consideration legal and ethical issues. Body language (A) is useful when speaking directly to someone, but cannot be viewed in written communication. The speed of the document (B) has no bearing on the written communication. Formatting (C) is important in written communication, but is not as important as legal and ethical issues. Grammar (E) is important in written communication, but is not as important as legal and ethical issues.
- D
A double-entry system is a bookkeeping system. When the practice charges for a medical service, the patient’s account is debited and the appropriate account for the practice is credited. All the other options are commonly used models for managed care organizations.
- D
The federal government implemented a “meaningful use” program that reimbursed medical offices for some costs related to implementation of EHRs.
- A
A key strategy to secure a computer network is the use of password protected log-ons. In this way, only approved staff members can access health records in a particular locaton. A single sign-on could be used by any individual; it would defeat the purpose of the system to only allow access to physician providers and it would be a logistical problem to keep the computer station out of the patient care and office areas of the facility.
- E
Always consult the physician when determining the policy and procedures of an office. Talking to fellow employees (A) will not determine what the physician wants for the office. Choosing a color of the manual (B) would not be the first step in preparing the manual. Deciding on the format (C) can be done after the wishes of the physician are established. Buying paper for the manual (D) would not be the first step.
- A
Leaving gaps in a doctor’s schedule will cause the doctor and staff to have excess time that could be used for patients. Overbooking (B) occurs when more patients are scheduled than open appointment slots. Clustering (C) is grouping similar appointments together during the day. Wave scheduling (D) is scheduling a set number of patients per hour, all of whom will arrive at the top of the hour. Advance scheduling (E) is scheduling appointments weeks or months in advance.
- B
In the alphabetical filing system, the patient’s last name is unit 1, first name is unit 2, and middle name (or initial) is unit 3. Hyphenated names are treated as one unit.
- A
Documenting the no-show information is necessary because the medical chart, whether in hard copy or electronic format, is a legal document. This information is important for the health of the patient. Doctors’ offices can request payment for missed appointments, but patients should be notified of this practice when they first become a patient (B). Refusing to reschedule an appointment is not good customer relations (C). Rescheduling is a good idea while the patient is on the phone, but telling the patient that they have to confirm is not good customer relations (D). Erasing an appointment is not an option (E). The appointment record must be treated as a legal document.
- C
Documentation of a referral has to go into a patient’s medical chart.
- B
Trial balance is a method used to check the accuracy of accounts. A daily summary (A) is used to record charges and payments in the physician’s office. An accounting system (C) is used to record, classify, and summarize financial transactions. Accrual accounting (D) is recording income when it is earned and expenses when they are incurred. Bookkeeping (E) is the recording of the accounting processes. Bookkeeping records income, charges, and disbursements.
- B
A new patient does not need to provide information regarding income. All of the other information is required.
- C
For the office to run smoothly, all employees must read the policy and procedures manual. All employees can help write the manual (A), but all old and new employees must read the manual. Knowing where the manual is kept is a great idea (B), but it needs to be read also. It is not necessary to give patients a copy of the manual (D). It is not necessary for each employee to have a personal copy of the manual (E).
- B
Physicians do not accept all insurance. The database would contain the names of the insurance that the physician accepts. Since the physician usually does not accept all insurance, all insurance would not be listed (A). The database would contain all the insurance that physician accepts, not just Medicare and Medicaid (C). Only the insurance carriers that the physician accepts would be entered, not the most popular ones (D). The medical insurance that a physician offers his employees (E) would not be entered into the patient database.
- A
All checks and cash should be deposited on a daily basis so that no money is lying around the office. It is easier to keep track of the money in a bank account.
- A
Open-hours scheduling is the system in which patients arrive at their own convenience with the understanding that they will be seen on a first-come, first-seen basis, unless it is an emergency.
- D
The individual cannot choose which doctor he or she goes to. When a report is made to the employer, the employer directs the individual where to go for treatment. This may or may not be the individual’s primary care physician. The other four choices (A, B, C, and E) are true statements about workers’ compensation.
- A
SOAP is a standard method of documentation used in medical records. It stands for Subjective, Objective, Assessment, and Plan.
- A
When a word is unclear during transcription, leave a blank space and write a note to the physician specifying the location of the space in the document. The medical assistant should never guess while transcribing dictation (B). The medical assistant should continue transcribing the rest of the dictation and wait to ask the physician about the confusing word (C). The medical assistant should never reword sections of dictation without first consulting the physician (D). It is better to leave a blank space rather than an “X” (E).
- D
Using cycle billing, all accounts are divided alphabetically into groups, with each group billed at a different time. No billing cycle is completed every fourth month (A). This can be done by computer (B), but a medical assistant has to go into the computer to divide the bills alphabetically. A monthly billing system is mailed out by the 25th of the month in order to receive payment on the 1st of the month (C and E).
- B
Software is a set of instructions, or a program, that tells the computer what to do. Portable hardware (A) is not a term used for computers. Input devices (C) are used to enter data into the computer. A palmtop computer (D) is very light and the size of your palm. The system unit of many newer desktop models is housed in a tower case (E).
- D
An appointment request is information that can be sent through email. This information is not confidential. Diagnosis (A) is confidential information and should not be sent by email. Lab test results (B) also are confidential and cannot be sent by email. Follow-up information (C) should not be discussed by email. The physician should speak with the patient directly. A list of medications (E) can tell a reader why the patient has seen the physician, so this information is confidential.
- D
The medical assistant should repeat the patient’s name and phone number back to the caller to reduce errors.
- E
The policy and procedures manual is the most important communication tool for all employees in a medical office. A tickler file (A) is used to keep track of papers that have to be filed. A patient’s medical records (B) are never used as a communication tool. Data entry (C) is used to store raw facts in the doctor’s office. The appointment book (D) is used to keep track of appointments.
- C
It is important to update the policies and procedures on a yearly basis.
- B
Organizing the key points before you write up a rough draft will help put your thoughts in order. It allows you to make sure that all the information is included. To just start writing without any thought as to what has to be included (A) will cause you to make many mistakes and will reflect poorly on you. Once you begin writing the rough draft, using language that is easy to understand (C) improves the communication. Anyone reading will know what the subject is. Composing a rough draft (D) would be the next step after organizing your thoughts. Choosing a letter format (E) would be done when you are ready to write.
- E
CPT codes are based on the level of service provided. When the code is manipulated to a higher level, or upcoded, it dishonestly claims a higher level of payment due. Dirty claims (A) are those with mistakes or omissions; they must be corrected and resubmitted to be paid. An EOB, or Explanation of Benefits (B), is the statement an insurance carrier provides to patients to explain the outcome of medical payment requests. Bundling (C) refers to an insurance carrier’s combining two or more CPT codes under one, usually less costly, “umbrella” code. Superbilling (D) is preparing the patient encounter form, also called a superbill or charge slip.
- A
For the medical assistant to schedule the proper procedure with the right specialist, he must have the exact procedure to be performed. Though finding out what would be a good time to schedule an appointment for the patient (B), it is not necessary. The patient could not schedule the appointment herself (C), as she would not have all the appropriate information. Determining the day and time the procedure must be performed (D) is not necessary. Determining who will be with the patient at the time of the procedure before making an appointment is not necessary (E).
- A
Coding is the basis for information on the claim form. A claim (B) is a demand for payment. Subrogation (C) is the right of an insurer to collect monies. A superbill (D) is the bill the patient receives from the physician at the time of service delineating the visit, tests, diagnosis, charges, and when to return. A charge slip form (E) is used to record services supplied, and charges and payments for those services; it functions as a billing form for insurance reimbursement.
- E
Individuals age 65 and older who are retired and receive Social Security benefits qualify for Medicare, as do those retired from the railroad or civil service. The minimum age for the general population is 65, not 62 (D). Children of veterans who died of service-related disabilities (A) qualify for medical coverage through the Civilian Health and Medical Program of the Department of Veterans Affairs (CHAMPVA). There is no age restriction to Medicare for blind individuals (B), and the finically indigent (C) are eligible for Medicaid benefits, not Medicare.
- D
Time-specified is the type of scheduling that is recognized by the regular time intervals in the appointment schedule.
- A
Patients never have the ability to change medical information that has been documented by a provider. On the other hand, patients are empowered to actively participate in their care by being informed through information available in a portal or PHR (C). They can also request or make appointments (B) and send/receive messages to/from their provider (D). With electronic documentation and scheduling, reminders are easy to relay through the portal or PHR (E).
- C
Authorized newsletters and periodicals ship via second-class mail. Third-class (A), also known as bulk mail (D), includes books, catalogs, and other printed material weighing less than 16 ounces. First-class (B) includes correspondence, billing statements, and other letters weighing 13 ounces or less. Priority mail (E) may be used for items weighing more than 13 ounces. It allows them to arrive more quickly.
- C
A debit is an amount usually representing things acquired for the intended use or benefit of a business. A debit is also called a charge; debits are incurred when the practice pays for something, such as medical supplies. The total (A) is the entire amount owed, collected, or accrued on the daily summary. You would subtract (B) or remove an amount from the total when a payment is made. The subtotal (D) is the amount before taxes are added. The balance (E) is the amount owed after payments are deducted and taxes added.
- C
Email has to be short and to the point. Email is set up to be read quickly. Additional background information can be communicated later (A). Writing in italic can be harder to read. Not all email systems pick up formatting such as bold, italics, and color (B), so the recipient may not see it. Writing in capitals is equivalent to shouting in an email and may be harder to read (B). It is more professional to use capital letters in email just as you would in a business letter (E).
- B
Double booking is commonly used in scheduling appointments when the patients only need to see the physician for a short time.
- C
HMO insurance requires a referral to see a specialist. The primary care physician must create the referral for insurance purposes.
- A
Computers have many uses in the medical office, but a main one is scheduling appointments. Interpreting lab results (B) is the responsibility of the provider and is based on reference ranges that may be included in the computerized documentation of results. Diagnosing patients (C) is the physician’s job. The medical assistant or physician takes the vital signs of a patient (D). Most medical offices still use paper files, and a member of the office staff would be responsible for locating them (E).
- B
The size of the medical practice always determines which billing cycle is used. The size of the practice, rather than the number of physicians (A), determines the billing cycle. The type of medicine that the physicians practice (C) is not a factor. The amount of employees who do the billing (D) does not matter. The physician will prefer a billing cycle that fits the practice size (E).
- A
Accounts payable refers to all money owed by the practice to other businesses. Accounts receivable (B) is the money owed to the practice. Charges (C) are the items billed to patients; debits (D) is an accounting term used to describe money paid out by the practice; and owner’s equity (E) is the profit made after taxes and expenses.
- E
HCFA-1500 is the “universal” claim form accepted by most insurance carriers. If left blank, this form contains no sensitive patient or medical office information and can be disposed of without shredding. The appointment list (A), patient lab results (C), patient referral, and patient insurance card (D) should all be shredded before disposal to maintain confidentiality.
- A
When a practice has flexible office hours, it stays open at unusual hours on certain days in addition to normal business hours. This occurs most frequently in group practices.
- A
The problem-oriented medical record is used to document a patient’s information according to the problem the patient is having.
- A
Petty cash in a physician’s office is used to pay for minor things needed by the staff. Paying an invoice for supplies ordered (B) would not come out of petty cash. Petty cash would not have a large amount of money in it. The electric bill (C) would be paid with the monthly bills and taken out of the medical office account. The petty cash would be available to authorized employees to use (D). Petty cash should be used not only in an emergency but also as needed (E).
- A
It is necessary to date-stamp each piece of mail when it is opened so the mail can be answered or addressed in a timely manner. Putting the mail aside until the patients are gone for the day (B) is a way for mail to get lost. The mail should be given to the physician immediately (C), but after it has been stamped with the current date. It is not the job of the medical assistant to read the physician’s mail (D). The mail should be delivered immediately to the physician after being stamped, not set aside to be delivered later (E).
- E
An outguide can be used to identify who has a document or record. It can be plastic or paper and is available in a variety of colors.
- B
Rescheduling the appointment while the patient is on the telephone will save both the medical assistant and the patient time. Saying “thank you” is polite (A), but it is best to ask the patient if he would like to reschedule. Asking the patient to call back to reschedule an appointment (C) is not an effective way to run an office. Appointments are important (D) but there are times when an emergency does come up. The physician cannot make a patient keep an appointment (E).
- D
A database is a collection of records created and stored on a computer. A scanner (E) is used to scan documents to forward in email. The Internet (B) is an electronic communication network. The cursor (C) is a symbol used to mark one’s place on the computer screen. “Hard copy” means any printed material.
- A
The main circuit board is the motherboard, which controls the other components in the system. A flash drive (B) is used to copy and transfer information. The hard disk drive (C) is where information is stored permanently for later retrieval. The operating system (D) is the main software system that the computer uses. Memory (E) is information stored for later use.
- C
Copayments are collected when the patient checks in to see the physician, unless other arrangements have been made prior to the appointment. Collecting a copayment after the patient sees the physician (A) is not ideal because the patient may be able to leave without paying. Bills are only sent out if the patient has an outstanding balance (B). Patients do not need to pay in advance before coming to the medical office (D). The patient should not pay while in the exam room (E).
- C
Registered mail is the most secure service offered by the post office. Registered mail provides insurance coverage for valuable items and is controlled from the point of mailing to the point of delivery. Certified mail (A) offers a guarantee that the item has been mailed and received by the correct party by requiring the mail carrier to obtain a signature on delivery. Insured mail (B) is for any piece of domestic mail for damage or loss. First-class mail (D) is classification by the weight of 13 ounces or less. Priority (E) is the classification for mail that weighs 70 pounds or less.
- B
Promoting Interoperability (PI) is the result of an overhaul of the meaningful use program. There are four main objectives of PI: e-prescribing, health information exchange, provider-to-patient exchange, and a public health and clinical data exchange.
- C
A higher level of specificity is documented due to the move from a maximum of 5 digits to 7 digits and a database of more codes. The coding system changed for all providers as it relates to the classification of diseases, illnesses, and injuries, not just to hospitals (A). ICD-10 was developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), not the American Medical Association (B). The system is NOT optional (D); it is mandatory. ICD-10 does not remove responsibility for coding from medical assistants (E); to the contrary, medical assistants must be familiar with the system to complete documentation and medical record information for office patients.
- A
The beginning of the day would be the best time to schedule. If the patient is late, it will not disrupt the end of the day’s schedule. Middle of the day (B) would disrupt the afternoon schedule. Right after lunch (C) could cause the afternoon to back up. Never scheduling a patient (D) is not appropriate and does not support a customer service approach. Scheduling the patient at the end of the day (E) could delay closing the office on time.
- E
Wave scheduling works best in large facilities where there are enough personnel to give service to several patients at once.
- C
In the cycle billing system, all accounts are divided alphabetically into groups, and each group billed at a different time. Past due (A) is when services are rendered and a balance is owed but has not been paid in the past 30 days. Account aging (B) is a method used to determine how long an account is overdue. Wave scheduling (D) is a method of scheduling appointments and is not related to billing. Monthly billing (E) is the method that sends all bills out at the same time each month, usually around the 25th of the month.
- C
If the medical office has contracted with a repair service to fix office machines whenever necessary, the medical assistant should renew the agreement annually.
- D
The World Health Organization developed the International Classification of Disease system for use in describing and tracking diseases across the globe. (A) is incorrect; HCFA was the former name of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid, a branch of the U.S. government that is accountable for oversight of Medicare and Medicaid entitlement programs. (B) is incorrect, as it is the professional association for U.S. physicians. (C) is incorrect, as it is the professional organization for Medical Record and Health Information experts. (E) is incorrect, as it is the branch of the U.S. government that oversees taxation.
- D
Bookkeeping is the actual daily recording of the accounts or transactions of the business and is the major part of the accounting process. A day sheet (A) is used to list or post each day’s charges, payments, credits, and adjustments: the daily financial transactions. Charges (B) are the fees for services rendered. Accounts receivable (C) is the amount owed to a business for services or goods supplied. A pegboard system (E) consists of day sheets, ledger cards, charge slips, and receipt forms.
- B
Software is not one of the physical components of a computer.
- D
Medical assistants who monitor care, facilitate referrals, and serve as a point of contact for the patient are acting in the role of patient navigator. In this role, the medical assistant is responsible for providing information to patients and fostering empowerment so patients make decisions that are their best interest. A medical assistant can serve as the liaison between the provider and other members of the health care team, and is often the one to actively communicate with the patient.
- A
Although the practice is increasingly uncommon, patients may still pay with cash for services rendered. Documentation of the payment in the accounting record is important for balancing funds and accurately reflecting the patient payment on their account, and providing a receipt is important for the patient to have a record of the transaction (A). Cash should never be refused (B). Deposits should be made on a daily basis, not weekly (D), and deposit slips are typically completed at the end of the day (C). Petty cash is used for small office expenses and not to make change for payment of services (E).
- A
CMS-1500 (A) is the claim form accepted by most insurance carriers. This form is prepared using words and CPT codes for procedures performed and ICD-10-CM codes for diagnoses. A ledger (B) is a record of charges, payments, and adjustments. Subrogation (C) is the right of an insurer to collect monies. HCFA Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) is used by Medicare as a supplement to the CPT codes (D). A superbill (E) is the bill the patient receives from the physician at the time of service delineating the visit, tests, diagnosis, charges, and when to return.
- B
Asking the purpose of the visit is a way to control the schedule. You can accurately schedule appointments so that patients are not waiting to be seen.
- B
The ICD-10-CM system is intended to improve the specificity and efficiency of medical coding and billing. (A) is incorrect because it is not a rationale for implementing the new system. (C) is true, but simply adding more codes was not a major intent of this transition. (D) is also technically true, but it is not a major intent of the implementation of this system. (E) is incorrect and does not apply to the use of the new coding system.
- C
CMS-1500 is the claim form accepted by most insurance carriers. This form is prepared using words and CPT codes for procedures performed and ICD-9-CM codes for diagnoses. A claim register (A) is a diary or register of claims submitted to each insurance carrier. When payment is received, the date and amount of payment is entered in the register. A superbill (B) is the bill the patient receives from the physician at the time of service delineating the visit, tests, diagnoses, charges, and when to return. A diagnosis code (D) is the numerical designation for a specific illness, injury, or disease. Modifiers (E) are two-digit numerical codes that indicate unusual procedural services.
- E
The correct answer is (E), medical information. (A) includes facts about the patient, such as name, address, and date of birth. Health history (B) is part of the medical record in the patient’s chart, as is (C), chief complaint. DRG (D) refers to the diagnostic related group assigned to the Medicare patient for an inpatient stay and is used for Medicare billing.
- A
Codes are expanded to seven digits. (B) is incorrect, as the codes are indexed in alphabetical order. (C) is incorrect because the anatomic site is included in the digits of the code. (D) is incorrect because the codes include both numbers and an alphabetical character. (E) is incorrect, as the E and V codes were eliminated under ICD-10.
- E
Gynecology is not a section in the Current Procedural Terminology book. The seven sections are: 1. Evaluation and Management, 2. Anesthesia, 3. Surgery, 4. Radiology, Nuclear Medicine, and Diagnostic Ultrasound, 5. Pathology, 6. Laboratory, and 7. Medicine.
- B
Items that are sent via registered mail, certified mail, or overnight mail have top priority. The next level of priority includes personal or confidential mail (D), and the following level includes priority mail (A), airmail (E), and first-class mail (C).
- E
Only authorized employees can take money from petty cash. An authorized person should be in charge of purchasing because too many different people ordering can cause confusion (A). All receipts of goods need to be recorded so a record of the goods can be kept (B). It is best to purchase goods of high quality at the lowest possible price (C). All shipments received need to be checked against the packing slip to ensure that supplies ordered were received (D).
- D
Once the overdue account has reached 90 days, it is considered serious.
- C
The way to properly correct any written error in the medical record is to draw a single line through the error and make the correction above the error. This method is used so the error can be seen in this legal record.
- B
A voucher check contains a detachable voucher form. The voucher portion is used to itemize the purpose of the check, deductions, or other information. A bank draft (A) is a check written by a bank against its funds in another bank. A limited check (C) is issued on a special check form that displays a preprinted maximum dollar amount for which the check can be written. A certified check (D) is written on the payer’s own check form and verified by the bank with an official stamp. A cashier’s check (E) is written using the bank’s own check form and signed by a bank representative.
- B
It is very difficult to get payment from a patient who does not want to pay. Such a patient may have a reason for believing that a payment does not have to be made. A patient who has forgotten to pay (A) can be reminded by receiving a payment statement or a telephone call. A person having financial hardship (C) may not be able to pay the entire amount but is often willing to make small payments to clear the debt. A patient who has no insurance (D) can be put on a monthly payment plan. Most patients who owe money will pay their bills (E).
- E
Monthly billing is the method that sends all bills out at the same time each month, usually around the 25th of the month. Past due is when services are rendered and a balance is owed but has not been paid past 30 days (A). Account aging is a method used to determine how long an account is overdue (B). In the cycle billing system, all accounts are divided alphabetically into groups, and each group billed at a different time (C). Wave scheduling is a method of scheduling appointments and is not related to billing (D).
- D
Each appointment day should have times allotted for emergency appointments. Wave scheduling (A), where several patients are scheduled for the top of the hour, is based on the idea that some patients will be late and other patients require more time with the doctor. When double booking (B), more than one patient is scheduled at the same appointment time. Open-hours scheduling (C) is the system in which patients arrive at their own convenience with the understanding that they will be seen on a first-come, first-seen basis, unless it is an emergency. Physicians who see pharmaceutical representatives often block out certain times and days when they can be seen.
- D
A file drawer is labeled on the outside so it is easy to locate the correct file. If the drawer is labeled inside the drawer (A), it would be difficult to locate the correct drawer. The side of the drawer (B) would be difficult to see. A tickler file (C) is a reminder file for active documents. Keeping the drawers listed in the office database would not be helpful. The drawer itself needs to be labeled so files can be located quickly (E).
- B
The correct answer is hospitals. The emergency room (A) is only a component of a hospital, so this answer option is incorrect. Physicians’ offices (C) continue to use CPT and HCPCS codes for their services; they do not use not ICD-10-PCS codes exclusively, so this option is incorrect. ICD-10-PCS codes are not used in pharmacies (D). ICD-10-PCS codes apply exclusively to inpatient hospitals; they are not used in psychiatric long-term care homes.
- A
Minutes are the official record of a professional meeting. They include the date, time, location, and topic of the meeting, as well as those attending, those absent, topics discussed, and time of adjournment. The agenda (B) lists the order in which business is to be conducted during a meeting. Bylaws (C) are the rules established to provide guidance as to the structure and business practices of a company. An itinerary (D) is a list of travel information. A resolution (E) is an order of business or action taken by the governing body of an organization.
- E
The address of the office should not be included in a job description. All other items should be part of a job description.
- A
An inventory of equipment should be taken at least once a year.
- A
Conditioning is the first step in the filing process. It is followed by releasing, indexing, sorting, and storing.
- A
Sterilization means that all organisms have been removed from an object by either gas or chemical sterilization or by autoclave. Disinfection is removal of all pathogens (B). Removal of debris with soap and water is called sanitization (C). Boiling (D) does not sterilize, and ultrasonic cleaning (E) is a method of sanitization for delicate instruments.
- B
Disposable thermometers become inaccurate after their expiration dates. As the thermometers have not been used before, sterilization and probe covers are not required.
- B
Personal opinion of the medical staff is not to be placed in the patient’s chart. Only facts are to be documented. Direct quotations from the patient may be included and quotation marks used to specify these quotes (D). Medication history (E) would be documented to give information about past medications that have been used and the effect of those medications. This includes medication allergies. Legal history (C) and patient report of drug use (A) are included, as this information is used to assess risk of disease.
- B
Mensuration is the process of measuring something. Auscultation (A) involves listening, as in evaluation of the bowel sounds using a stethoscope. Palpation (C) and percussion (D) both use touch; palpation would be using the hands to feel the temperature of the skin and percussion is tapping in order to hear different sounds. Observation (E) is visually evaluating the patient.
- D
Commonly called the SST (serum separator tubes), the red/gray tubes and the gold Hemogard closure tubes contain a clot activator and separation gel. After inverting the tube five times, the clot activator shortens the time required for the formation of a clot. The separation gel in the bottom of the tube changes viscosity and will migrate up and form a barrier between the serum and blood cells. One minute (A) may seem like a familiar number during the routine phlebotomy procedure because of the typical time restraint associated with tourniquet application. Five minutes (B) is associated with an accelerated clotting time seen with the use of the yellow/gray stopper tubes or orange Hemogard closure tubes. These tubes contain thrombin, which is activated after the filled tube is inverted eight times. These tubes are used for stat serum chemistry testing. Fifteen minutes (C) is the customary time for centrifuging a serum separator tube. Sixty minutes (E) is the normal amount of time for a blood sample to clot in a tube that contains no additive. Red stopper tubes are then centrifuged to yield a separated sample of serum from blood cells.
- C
The vastus lateralis is the preferred site for an infant who is not yet walking. The gluteus muscles are not well developed until the child is walking (A). The deltoid (B) is too small and underdeveloped in the infant. The injection is to be given in the muscle so the subcutaneous route is not acceptable (D).
- B
Have ready a speculum for visualization and a water-soluble lubricant. You would not need to dilate the cervix in order to do the procedure (A). A suture removal tray would not be needed for a vaginal exam (C). Sterile gloves are not necessary for the routine procedure (E). The Hemoccult card (D) would only be necessary if the physician is also doing a rectal exam.
- C
The goal of emergency treatment is to stop the burning in the skin. By cooling the area, the heat is dissipated. A cool cloth will also decrease pain. Care needs to be taken to not break the blisters (B) and to maintain the skin integrity to prevent infection (D). A bandage, if necessary, should be applied loosely (A). The physician may order silver sulfadiazine cream, which has bacteriostatic properties after the burn has been assessed (E).
- B
Prone position, which is lying flat on the abdomen, would offer the best access to the spine. Knee-chest (A) is used for proctologic exams. Supine (C) is lying flat on the back. Lithotomy (D) is used for vaginal exams and Pap tests. Trendelenburg (E) is the shock position with the legs positioned higher than the heart. It is used in patients who have a low blood pressure or feel faint.
- C
By providing a quiet and private area, the patient will feel comfortable sharing information with the medical assistant. Questions should be asked in person so that answers can be clarified (A). If a form is given to the patient to fill out, it should be followed up with a personal review of the information. You should not pressure the patient to answer any questions that they do not want to but can reassure them that their answers will be confidential (E). The physician may have additional questions to ask the patient but you should not leave history items for the physician to address unless the patient requests this (D).
- C
When circulating substances such as glucose rise to an unhealthy level, the body will attempt to expel the excess via the kidneys. The renal threshold of glucose is 160–180 mg/dl. Glucose found in the urine can be associated with diabetes mellitus or pancreatic pathology. Supernatant (A) is the clear upper portion of a urine specimen that is poured off before staining the remainder for visualization under the microscope. Refractive index (B) is the method in which specific gravity is measured by the refractometer. The refractometer measures the refraction of light through sediment in the liquid. Micturition (D) is the act of voiding or emptying the bladder. After assessing the volume of a 24-hour timed urine specimen, a well-mixed portion called aliquot (E) is removed for testing. The remainder of the specimen is stored or discarded.
- B
Coumadin is an anticoagulant and causes thinning of the blood. The blood levels must be monitored to ensure there is no abnormal bleeding due to overmedication.
- C
A fomite is an object that can harbor pathogens such as the exam table, blood pressure cuff, or stethoscope. Disinfection is the method that is used to remove pathogens from the surface of objects (B). A vector is an animal or insect that can transmit disease (A). Ultrasonic sanitization is the method of sanitization that is used on objects that cannot be scrubbed with soap and water (E).
- D
You should first look for the universal sign of choking: the placement of hands at the throat. You will ask the patient if he is able to speak and will not intervene if the patient is able to speak or cough. If his airway is obstructed, you should place your hands around the victim from behind and make a fist with the thumb side of the first in the space below the ribcage and above the navel. Quick, upward thrusts are made until the object is removed. The patient should not be placed on the floor while he conscious (B). There is no need to check the pulse prior to trying to remove the airway obstruction while the patient is still conscious (C). Checking for a foreign body in the patient’s mouth would be inappropriate at this time (A).
- D
The Ishihara test is used to test colorblindness. Myopia (A) is nearsightedness. Hyperopia (B) is farsightedness. Presbyopia (C) refers to changes in the vision as the eye ages and brings about the need for reading glasses (E).
- E
You must start over again preparing the sterile field. Any instruments that are in the sterile field must be sanitized and re-sterilized before use. Once the nonsterile item is on the sterile field, the field is contaminated and should be redone.
- C
Sanitization is the process of using soap and water scrubbing to remove blood and tissue from medical instruments. Asepsis (A) is the absence of disease. Disinfection (B) is the process of removing pathogens from objects. Sterilization (D) is the absence of all living forms from objects. Boiling (E) is a method of disinfection but cannot kill spores.
- B
The 1-minute time limit was set forth by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (formerly NCCLS). Leaving the tourniquet on longer than 60 seconds may change the hemoconcentration of certain substances due to the passage of plasma into tissues. Thirty seconds (A) may be considered a safe amount of time but usually does not allow enough time to complete the venipuncture. The remaining choices exceed a safe and effective time limit to have a tourniquet tied in place.
- E
The correct answer is (E), all of the above. (D) is incorrect, as (A), (B), and (C) are all important considerations if a disaster or disease outbreak occurs.
- A
This information is found in the social history. This section may also include sexual history, drug use, recreational activities, and present family status. The chief complaint (B) is where you will find the reason for the patient coming to see the doctor this visit. The review of systems (C) is data that is collected as each of the body systems is reviewed and evaluated. Medical history (D) will include the past medical history and immunization history. Family history (E) is the medical status of the patient’s family and any genetic or familial illnesses.
- D
Hydrochlorothizide is a diuretic. Cipro (E) and amoxicillin (A) are both antibiotics. Robitussin (C) is an antitussive. Albuterol (B) is a bronchodilator.
- A
The condenser is found within the diaphragm of the microscope and is responsible for collecting and concentrating light rays onto the object on the slide. The stage is responsible for holding and moving the slide (B). The iris is responsible for controlling the amount of light focused on the object (C). The coarse and fine adjustments will bring the object into focus (D). Water evaporation (E) is not a function of the microscope.
- C
Disturbance in vision, headache, difficulty in speaking or understanding spoken words, and weakness on one side of the body are all signs of neurological problems. Referred pain from a heart attack can be experienced in the back, shoulder, arms, jaw, and abdomen.
- E
The yellow-stoppered tube contains sodium polyanetholesulfonate and is used for blood cultures. When a yellow-stoppered tube is among the tubes to be used in a blood draw, it is always drawn first, so the other four choices (A, B, C, and D) are incorrect. The purpose of the order of draw is to prevent mixing and potential contamination of additives.
- D
Waived tests have been approved by the FDA for home use or are simple lab exams and procedures that have insignificant risk of error. Pregnancy tests are low complexity tests that can be performed in a clinical laboratory or by a patient at home. Microscopic examination of urine (A) is considered a moderate-complexity test that requires laboratory equipment such as the centrifuge, microscope, specialized stain, and urine specimen slides. Gram staining (B) is a moderate-complexity test. Blood chemistry (C) is a moderate-complexity test. Pap smear (E) is considered a high-complexity test.
- C
The normal respiratory rate for an adult is 12 to 20 breaths per minute.
- C
The first thing that you should do is check to make sure the autoclave process was successful by checking the indicator tape or strips in bags. The packs should be marked before being put in the autoclave (D). Placing the newly sterilized packs under the older ones (A) and discarding outdated packs (B) are things to be done, but not until you are sure that the packs have been sterilized. Once a pack is sterilized, it is sterile for 28 days, as long as it remains intact.
- E
Prozac is used to treat depression. Lanoxin (A) is a cardiotonic medication. Lasix (B) is a diuretic. Potassium chloride (C) is frequently prescribed in addition to Lasix, which can deplete the potassium in the body. Lisinopril (D) is a medication given to control blood pressure.
- C
It is very important for the medical assistant to be prepared for an office emergency by reviewing the office policies about emergencies and making sure that she is familiar with all the available equipment that might be used in an emergency. The medical assistant must do this when she is new to an area and not rely on more experienced staff or emergency services to respond to situations (B). While it is a good idea to make a phone list and to keep policies in an area where they can be reached easily (E), this does not replace the need to be familiar with policies and emergency equipment.
- C
Tubular gauze is a bandage that is placed over areas that are hard to bandage. Bandages hold dressings in place, maintain even pressure, support, and protect a wound from contamination or further injury. All other examples are dressings.
- E
Sensitivity testing involves the use of the disc-diffusion method. Commercially prepared discs with known concentrations of various antibiotics are dropped on the surface of a solid culture medium in the Petri plate inoculated with the pathogen. If the pathogen is “sensitive” to an antibiotic, there is a clear or kill zone without bacterial growth around the disc. Blood agar (A) is a common additive to Petri dishes serving as a culture medium. Culturing (B) involves inoculating the specimen on a Petri dish or other growth medium and incubating at favorable temperatures that allow for optimal growth. Morphology (C) is the study of a microorganism’s shape. Liquid culture medium (D) can be utilized to keep a specimen alive until it reaches the lab or can be processed.
- D
A “blind” weight is done when you do not want the patient to know exactly what their weight is. This may be done if the patient is anorexic or overly concerned about weight gain during pregnancy so that the patient will not decrease their intake due to an increase in weight according to the scale. It is inappropriate not to record a weight in the chart (A) or to ask a patient to weigh himself at home and not weigh them at the office (B). Patients who are in danger of rapid weight gain due to fluid retention may be asked to weigh themselves at home and report weight gain of more than two pounds in one day to prevent complications of their disease.
- B
Each practice should evaluate its unique patient population and specialty areas of practice to determine which forms of patient emergencies are most likely to occur during office hours. Directing very sick patients to the emergency room (ER) (A) is not always a proper use of ER services. A physician may not always be available in the medical office (C), so this answer is also incorrect. While having a first aid kit (D) is helpful, it may not meet the needs of more critical emergency situations—such as cardiac arrest—that can occur in a medical office. Poison control contact information (E) is also effective only in a certain type of emergency and is not the correct answer.
- D
Choice (D), sending patients to the emergency room, would NOT be an approach used by medical practice offices during a large-scale act of bioterrorism, and the practice office should be able to make this diagnosis. (A) is incorrect, as offices would be in communication with local public health offices in this situation. (B) is incorrect, as offices should provide vaccines or immunizations, as needed. (C) is incorrect, as offices should know what signs and symptoms of diseases to look for to properly respond in a bioterrorism attack. (E) is incorrect, as offices would need to ensure patient and staff safety by proper infection control and hazardous waste disposal during a bioterrorism occurrence.
- B
The Snellen test is used to screen for visual acuity. The eye chart is read by the patient from a distance of 20 feet and the results are compared to the normal findings of 20/20 vision. An accucheck will give blood sugar results (A). Ability to hear vibratory sound is called the Rinne test (C). Ability to distinguish color is measured by the Ishihara test (E).
- B
The occluded airway would receive the first priority, as the body is unable to go without available oxygen for more than a few minutes before brain damage will occur. It will always be the priority situation when there is a medical problem.
- B
The medical assistant must make sure that the patient understands the procedure that will be done and has had her questions about the procedure answered before signing the consent. The medical assistant can then have the patient sign the form and witness the signature (D). If the patient has not had the benefits and risks (A) and any alternative treatments available (E) explained or has further questions (C), the medical assistant must refer the patient back to the physician and have the patient sign the consent after this is done.
- D
Littauer scissors are fashioned with a hook to make it easier to pick up the suture and cut it. Bandage scissors (E) are fashioned in order to cut clothing and dressings without cutting skin. Mayo scissors (B) are a type of operating scissors. A Senn retractor (C) is used to hold back tissue in an incision and a Kelly hemostat (A) is used to clamp and hold tissue.
- D
The medical assistant would want to wear gloves when cleaning up the spill, but they would not need to be sterile gloves (E). It is appropriate to clean up the spill with a disposable paper towel and to place the paper towel in the biohazardous waste as it is unclear what the spill is. It is not appropriate to ask the patient what the spill is (A). It should be placed in the biohazard garbage, as it is unclear as to what the spill is. It should not be left for someone else to clean up (C) but would be appropriate for you to disinfect the area of the floor, or ask a housekeeper to do this if one is available after the spill is cleaned up. (B) fails to mention the use of gloves in the cleanup of an unknown liquid. It may be a bodily fluid and thus biohazardous.
- C
Antibiotic treatment is not used for viral infections unless there is a secondary bacterial infection. The viral infection can be spread in a number of ways, including droplets (A). It may resolve quickly or can last for the lifetime of the patient (B). Tuberculosis is caused by a bacterial infection (D). While vaccinations are available for some viruses, they are not for all (E).
- B
Generic and brand name medications must have the same active ingredients. Drug doses are calculated based on a body weight of 150 pounds (A). The effect will be increased or decreased if the weight is more or less than 150 pounds. The elderly and the young may be more sensitive to medication than adults are (D). The difference in the fat-to-muscle ratio of body composition between males and females (C) may make a difference in drug action.
- D
Autoclaved items are considered sterile for 28 days. After that time, they must not be used and must be re-sterilized. They must be repackaged in the appropriate manner in order to make sure that the sterilization cycle has been effective.
- E
Symptoms of insulin shock or low blood sugar is sudden and symptoms include diaphoresis, tremulousness, confusion, hunger, and tachycardia. Hyperglycemia or diabetic coma come on slowly and cause lethargy, thirst, rapid and weak pulse, and a fruity or acetone odor to the breath.
- A
The correct answer is (A). The best way to prepare for a patient emergency is to have an emergency plan and protocol in the office. (B) is incorrect, as practices regularly treat seriously ill patients. (C) is incorrect, as many offices are not located near hospital emergency rooms. (D) is incorrect, as it is not practical to disperse patients in the office during the emergency. (E) is incorrect, because it is useful only for a narrow range of patient emergency situations, such as cardiac arrest.
- C
The medical assistant should take a careful allergy history from the patient so that the possibility of an allergic reaction can be minimized. The medical assistant would not administer a test dose (A). While medication used in the past is useful for information, the same medication may not be appropriate for this procedure (B). The patient will not be sedated or put to sleep for a minor procedure, so a person to drive would not be necessary for that reason (D).
- A
The knee-chest position is used for proctologic exams and sigmoidoscopy. The patient is positioned on his knees with the chest on the exam table. The patient is on the exam table on his knees, in a bowing position with the chest down, leaning on his elbows or hands. Vaginal exams are usually performed in the lithotomy position (B). Exams of the chest and the upper torso are best accomplished in the Fowler’s position (C). This position is also used for patients who have difficulty breathing (D). Trendelenburg position is used for patients that have hypotension (E).
- B
Lithotomy is the standard position for a vaginal exam. Sims position (C) is on the left side and usually used for rectal exams. Prone (A) is lying face down. Both Fowler’s (D) and semi-Fowler’s (E) position the patient in the sitting position with the head up and are frequently used to aid respiratory effort.
- C
According to sequence represented by CAB (which stands for “circulation, airway, breathing”), the first step of cardiopulmonary resuscitation is to check for the pulse. The carotid pulse is the most commonly accessed in emergency situations (C). In the event the patient has a pulse but no respiration, a blocked airway is possible, and repositioning the head may open the airway and allow the patient to breathe (E). Attempting to open and look in the mouth for an obstruction is not recommended (D), as the obstruction may be too far back to view and retrieve, and the rescuer could be injured if the patient clamps the teeth together. Rescue breaths are never administered before compressions (A). Although moving the patient as one unit is important for patients who have experienced trauma (B), the first step is to assess for circulation. If breathing is still absent, rescue breathing should continue until either respirations are restored, help arrives, or you become too tired to continue. The pulse should be checked periodically; if it is absent, perform 30 compressions per every 2 breaths administered.
- B
Sterile packs that have been damaged in any way must be discarded or unwrapped and re-sterilized. They can be damaged by water, dropping them onto the floor, or any break in the packaging. Sterile packs are good for 28 days. Packs that will expire the earliest should be used first. Sterile packs may be sealed in plastic to extend the time that they may be used, but this must be done at the time of sterilization and not when they are due to be re-sterilized. The sterile packs are considered sterile until they are opened for use or contaminated in some way.
- A
Placing sutures is the one procedure listed that must be performed with sterile gloves in a normal situation. All other scenarios necessitate the use of non-sterile exam gloves and are not sterile procedures.
- B
The normal range for specific gravity of urine is between 1.003 and 1.030. Most urine samples fall between the range of 1.010 and 1.025 making (B) the correct choice. The specific gravity of distilled water is 1.000 (A). Specific gravity measurements above 1.030 (C, D, and E) exceed the normal range and may indicate severe UTI, dehydration (associated with fever or prolonged vomiting and diarrhea), congestive heart failure, adrenal dysfunction, or hepatic disease.
- B
Capillary or micropipettes are small glass or plastic tubes designed to hold a measured amount of blood. These tubes are used primarily for hematocrit determination. The tube is placed at the edge of the blood droplet and fills through capillary action. Microcollection (A) or microtainer tubes are small plastic tubes that have a wider opening that allows blood to flow quickly into the tube. These tubes have different-colored tops that correspond to the additives they contain. Reagent tubes (C) are a distracter. There is no such item. Serum separator tubes (D) are tubes utilized for the vacuum method of venipuncture. Evacuated glass tubes (E) are used for venipuncture if a large sample of blood is needed.
- C
Aricept is administered for mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease, which you would not expect to be ordered for a 52-year-old patient. Premarin (A) and Provera (B) are female hormones. Calcium citrate (D) and multivitamins (E) may be ordered to prevent bone loss and vitamin deficiency.
- B
Bleach and water mixed in a 1:10 solution makes a cheap and very effective disinfectant solution.
- C
The tuning fork is used to screen for hearing acuity and bone conduction of sound and results and can lead to further testing for the patient. The tuning fork is struck on the palm of the hand of the practitioner, which causes it to vibrate. The tuning fork emits a low frequency sound and vibration that can be felt and heard by the patient. An otoscope (A) is used to examine the inside of the ear canal. The ophthalmoscope (B) is used to look at the structure of the eye. The Snellen test (D) measures visual acuity. The reflex hammer (E) is used for neurological testing of reflexes.
- D
When performing the CCMS or midvoid specimen collection, females should clean the urinary meatus from front to back to avoid contaminating the area. The most common urinary contaminant is E. coli from the anal opening. Students often misread this choice. Removing the undergarments (A) allows for freedom of movement and accessibility of the area. The patient should not touch the inside of the container (B) to avoid contamination of the specimen. Female patients should continue to hold the labia apart (C) ensuring that the cleansed area does not become contaminated during urination. Touching the specimen container (E) leads to contamination and erroneous test results.
- B
You should suspect a problem with the patient’s blood glucose. By giving a form of glucose, you may fix the immediate problem. Even if the blood glucose is high, it will not do any damage and if the blood glucose is low, the patient will improve. Once glucose is given, you should immediately draw a blood sugar or do an accucheck (C). This will confirm the blood sugar. It would not be appropriate to spend time questioning the patient if he is confused and disoriented (E). The vital signs would be checked after these steps would be taken (A). If the patient is conscious, it would not be appropriate to check for respirations (D).
- B
You would not expect to do a lung biopsy in the office as a minor procedure. Minor procedures are done for superficial lesions, cyst removal, suture of lacerations, and incision and drainage of superficial wounds. These procedures have little chance of major complications.
- A
The sounds that are heard when the blood pressure is being auscultated using a stethoscope and a sphygmomanometer are called the Korotkoff sounds. Rinne (B) is the name of a test of hearing. The Snellen (C), Jeager (E), and Isahara (D) tests are all names of eye exams.
- B
The popliteal pulse is located behind the knee and most easily located by bending the knee and palpating in the crease behind the knee joint. The radial pulse is located on the thumb side of the wrist (A). The dorsalis pedis is located on the dorsal surface of the foot (C). The apical pulse is located at the apex of the heart (D). The femoral pulse is located in the inner aspect of the leg at the groin (E).
- C
While all of these things are important, hand washing is the single most effective thing that you can do to prevent the spread of infectious material. Hand washing can be accomplished with soap and water or with an alcohol-based hand sanitizer. Good hand wash practices will prevent the spread of pathogens between patients.
- B
First-voided morning urine specimens contain the greatest concentration of certain substances. This specimen is utilized for pregnancy testing, nitrite and protein determination, bacterial culture, and microscopic examination.
Most urinalysis is performed on freshly voided random (A) urine samples collected in clean containers. A clean-catch midstream specimen (C) may be collected if a bacterial infection is suspected. An untainted specimen is needed for urine culture. The only other method of collection for a noncontaminated specimen is through catheterization. A 24-hour specimen (D) is utilized for quantitative chemical analysis such as hormone levels. Second-voided specimens (E) are usually collected to test for glucose levels.
- D
The object should be assessed prior to the lift so you have a plan and can ask for help if you are unable to lift it alone. You should not try to lift an object if you have any doubts about its size or your ability. You should always bend at the knees and keep the back straight with the load close to the body. Never lift a heavy object that is located above your base of support. It is always better to ask for assistance or use assistive equipment to prevent injury to yourself.
- E
The soiled paper should be gathered inward and away from clothing to prevent contamination of clothing. The exam table must be cleaned with disinfectant prior to pulling down the unused paper. Gloves should be changed between cleaning the table and pulling down the unused paper to prevent recontamination of the clean area.
- C
The brachial artery is the preferred pulse site in the infant. If circulation is limited, the peripheral pulses such as the radial (B) or temporal (E) may not be palpable. The body fat composition of the infant may make it difficult to find the carotid (A) and femoral (D) pulses. The brachial artery is easily accessible as it is located in the inner aspect of the upper arm.
- B
Lipitor’s generic name is altorvastatin calcium. Atenolol (A) is the generic for Tenormin. Plavix is the trade name for clopidogrel bisulfate (C) and furosemide (D) is the generic for Lasix. Amlodipine (E) is the generic name for Norvasc.
- A
It is normal for a person to be confused and very drowsy after a seizure. Usually there is no problem with the airway (D) after the seizure unless the patient has vomited. If this occurs, rolling the patient to the side will usually take care of this. You would expect the pulse rate and blood pressure to be elevated (C) due to the muscle activity. Immediate transfer to the hospital (E) should not be necessary unless the patient has never had a seizure, has repeated seizures, or does not regain consciousness.
- B
Fowler’s position is sitting upright and is the most appropriate for patients who have respiratory problems. Trendelenberg’s position (A) is the head lower than the rest of the body and is used most frequently for hypotension or shock. Lithotomy position (C) is used for vaginal examination. Dorsal recumbent (D) is lying on the back with legs bent and up on the same level as the body. Prone (E) is lying flat on the abdomen.
- C
The hepatic vein is a large, deep vessel responsible for draining the digestive tract and liver. The median cubital vein (A) is the most common vein utilized for venipuncture. This vessel serves as a connection between the cephalic and the basilic veins and is less likely to roll. The brachial vein (B) is located on the medial aspect of the upper arm and may be utilized for venipuncture. The cephalic vein (D) is located on the lateral aspect of the arm and is a good choice for phlebotomy. The basilic vein (E) extends from the median basilic vein up the inside of the arm. This vessel tends to roll and the medial assistant must anchor it well.
- C
A nonsterile person who enters the room but does not approach the sterile field will not interfere with the sterile field in a minor procedure. Members of the sterile team should have their hair pulled back (B) and should avoid talking over the sterile field (A). Once a nonsterile item is added to the field, it is considered contaminated (D). A tear in the glove must be changed immediately in order to prevent contamination of the sterile field (E).
- C
The primary function of draping is to preserve the privacy and dignity of the patient. Draping is done differently for different exams (E) but the patient should be adequately covered no matter what the position is. Draping material may be helpful in keeping the undressed patient comfortable (B) but if the patient is cold, the room temperature should be adjusted. While convenience of the medical staff is important (A and D), it is not the primary reason for draping.
- B
The correct level for the arm to be is at or near heart level. The cuff must be the correct fit for the patient’s arm. Markings are on the cuff for minimum and maximum arm size. If the fit is not correct, you will not receive an accurate reading. Normally you cannot hear any sound when the stethoscope is placed on the brachial artery. The cuff should be positioned so that the artery marking is at the brachial artery. The air should be released slowly so you do not miss the beginning sounds.
- B
Anaphylactic shock is due to a severe allergic reaction and a massive immune response by the body. It causes difficulty breathing and swelling of the respiratory tract. There can also be cardiovascular symptoms such as hypotension and cardiovascular collapse. It can be fatal. An asthma attack (E) will cause difficulty breathing but is a chronic condition usually controlled by medication. Cardiogenic shock (D) is caused by inability of the cardiac system to pump enough blood to supply the body and does not cause swelling of the respiratory system. A myocardial infarction (A) is a heart attack. Obstructive airway disease (C) is a chronic condition of the respiratory system.
- C
Induration is an indication of TB exposure but not necessarily disease; follow-up testing is necessary for diagnosis. The other four choices (A, B, D, and E) are all true statements regarding tuberculin testing.
- C
The reagent strips should be held horizontally to avoid chemical reagents from each testing pad from mixing. This may cause aberrant color changes and give questionable results. Holding the testing strips vertically will also allow urine to drip onto the medical assistant’s hand. Recapping the testing strip bottle quickly (A) helps preserve the integrity of the testing strips. The testing strips are sensitive to light, heat, and moisture. Touching the testing the strips with your fingers (B) may influence the effectiveness of the chemical reagents, giving false results. The testing strips need complete immersion into the urine sample (D). Discolored strips should be discarded (E). Multistix strip results are determined by assessing color changes to the reagent pads when in contact with urine.
- C
Zoloft is from the antidepressant category, which is used to treat depression. All of the other choices are antianxiety medications, although they are used for depression in certain cases.
- E
Ordinarily a speculum would not be needed for a simple cyst removal. The scalpel (A) would be used to cut the skin. The Senn retractor (C) would be used to pull the skin back after the incision is made. The needle holder (B) would be used to suture the incision after the surgery is done and the dressing forceps (D) would be used to apply the dressing after the procedure is done.
- E
By asking open-ended questions, you allow the patient to answer fully and you may get more information that will in turn make the interview go more quickly. If you appear to be in a hurry (D), the patient may not offer important information. Yes and no answers (A) will not allow the patient to answer fully. Not all elderly are hard of hearing (C) nor do they need family to answer questions for them (B). This can offend the patient, which will affect the amount of information that you get from them.
- D
Human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG) is produced by the placenta and presents in the urine during pregnancy. After implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterus, the hCG levels in serum double every few days. This occurs for about 7 weeks and then begins to decline. Pregnancy tests can detect the presence of hCG as early as 1 week after implantation or 4 to 5 days before a missed menstrual period. Human growth hormone (B) is released by the anterior pituitary gland. The purpose of this hormone is to stimulate musculoskeletal growth. Antidiuretic hormone (A) is released from the posterior pituitary gland. The hormone acts to control the body’s fluid balance. Heterphile antibody (C) is released into bloodstream in a patient with infectious mononucleosis and can be detected within 6 to 10 days of illness in an individual. Phenylketonuria (E) is an inherited condition in which a baby lacks phenylalanine, an essential enzyme necessary to metabolize amino acids.
- D
Supine is lying on the back, and patients who have fainted should be assisted to a recumbent back-lying position (D). Prone (A) is lying face downward. Trendelenburg (B) positioning places the patient’s head lower than the body and raises the lower extremities. Although still used some with shock to raise the blood pressure, recent evidence shows that this position does not increase cardiac output. Lithotomy position (C) is usually used for vaginal exams. Fowler’s position (E) raises the head at a 90-degree angle and is used to ease respiratory problems.
- B
The correct dosage is 250 mg. It is calculated by dividing the 75-lb. weight of the child by the 150-lb. weight of the adult (which would be 1/2), and then multiplying 1/2 by the 500-mg dosage.
- B
While all of these factors could influence the tracing, the status of the patient is the first variable that should be checked to make sure that there is not a significant problem.
- D
For a surgical hand wash, you would hold your fingers higher than your elbows so that water runs off the elbow area instead of the hands. This is opposite of the way that you do with a medical hand wash (B). A 60-second wash (A) would be appropriate for aseptic technique, not surgical technique. You must dry your hands with a sterile towel (C). Ideally you will have foot controls for the water but if you do not, you should turn off the water with the sterile towel after you have dried your hands and do not touch the faucet with your bare hands (E).
- C
Lyme disease is a bacterial disease that initially causes a rash with a characteristic bull’s eye and flu symptoms. If the symptoms are mild, the infection may be missed and not treated with antibiotic therapy. It then continues as a chronic infection and affects the musculoskeletal and nervous systems.
- C
Application of ice to the area would be the first treatment, along with rest and elevation of the ankle. Exercise (B) is inappropriate as it might cause further injury at the time of the injury. Massage (D) would also be inappropriate at this time for the same reason. Ice (C) will decrease the circulation to the area, which will decrease bleeding into damaged tissues. The ice will also decrease pain. It should only be applied in 20-minute intervals to prevent cold injury to the tissues. Heat is applied only after 48 hours has passed after the injury (A). Application of an air cast (E) may be appropriate after the assessment is done but not as an initial treatment.
- B
Nitrites occur in urine when bacteria convert or reduce nitrates to nitrites. A sufficient amount of incubation time in the bladder must pass for this conversion to take place. A positive reagent strip test may indicate the presence of a bacterial urinary tract infection. Escherichia coli bacterium is the most common cause of UTIs and can reduce nitrate to nitrite. Glucose (A) present in a urine sample would signify the body’s inability to process carbohydrates. Ketones (C) are by-products of fat metabolism in the body and include three types: beta hydroxybutyric, acetoacetic acid, and acetone. Ketosis occurs when fat is used for energy and the muscles cannot handle the accumulation of ketones. The ketones will accrue in the body tissues and fluids. Ketonuria is observed with diabetes mellitus, low-carbohydrate diets, excessive vomiting, and starvation. Bilirubin (D) is a bile pigment not normally found in urine. Bilirubinuria is an indication of liver disease and can result from gallstones, hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Urine becomes yellow-brown or greenish and foam appears when shaken. Protein (E) should not be detected in the urine. Proteinuria is one of the first signs of renal disease. Protein excretion in high amount can be caused by unusually high stress or strenuous exercise.
- B
Palpation is using the fingers to feel the pulse. Usually the radial artery is used in the adult patient for a routine pulse rate. A stethoscope (A) would be used in a young child or infant. The temporal pulse is located in the temporal area of the skull (C). The carotid pulse is located in the side of the neck and usually used in emergencies and to evaluate the effectiveness of CPR (D). The femoral pulse is located in the groin (E).
- A
By placing the indicator strips in the bags and packs and using autoclave tape to secure packs, the medical assistant will be able to make sure that the instruments are sterile and ready to use in a sterile procedure. It is not necessary to open a pack and check it (C). The time needed to make sure that a pack is sterile is dependent upon the manufacturers’ instructions and the material that you are sterilizing (B). It is not appropriate to leave an open area in the pack (D). You should not remove the packs from the autoclave until the drying cycle is over (E). Moisture will encourage the migration of pathogens.
- B
Supine positioning requires the patient to lie on his back. Prone (A) requires the patient to lie face down. Oblique (C) positioning has the patient at an angle to the radiogram. Lateral (D) imaging is taking the picture from the side of the patient. Posteroanterior (E) allows the x-ray beam to penetrate the patient from back to front.
- B
A level less than 200 mg/dl is desirable. Cholesterol is necessary in the body for several reasons. A level of 0 mg/dl (A) would be detrimental to the body. Levels 200–239 mg/dl are considered borderline high (C). Levels of 240 mg/dl and above are considered high (D and E).
- A
Surgical asepsis is removing all organisms prior to entering the body. This is done by using sterile technique and sterile instruments in a procedure. Medical asepsis (C) is disposing of organisms after they leave the body, as in the correct disposal of biohazardous waste. Sterilization (B) is the removal of all organisms from objects, not people. Sanitization (E) is the removal of debris from objects. Personal protective equipment or PPE are items such as gloves, masks, gowns, and eye protection (D).
- C
Equipment that serves as protection for health care workers is called personal protective equipment. This includes gowns, gloves, face masks, eye protection, shields, and hair and shoe covers.
- A
An elastic or ACE wrap is an example of bandaging. The function of bandaging in this case would be to provide even pressure and support to the ankle by applying a bandage made of elastic cloth.
- B
A 15-degree angle is optimal for placing the needle in the center of the selected vein. A 5-degree angle (A) is utilized when seating the needle during placement of a butterfly-winged infusion device. A 30-degree angle (C) is too much for venipuncture. This angle may cause the needle to go through the vein by puncturing the posterior wall resulting in a hematoma. A 45-degree angle (D) is utilized for subcutaneous injections. A 90-degree angle (E) is utilized during an intramuscular injection.
- A
Staphylo- is a Greek term that denotes “bunch of grapes.” Staphylococci are round bacteria that grow in grapelike clusters. Neisseria meningitidis (B) is a gram-negative bacterium. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (C) has a straight, curved, or branched rod shape and requires an acid-fast stain. Escherichia coli (D) is a gram-negative bacillus. Streptococcus pneumoniae (E) is a gram-positive bacterium, but this species grows in chains.
- A
A scraping of the superficial layer of skin is called an abrasion. An avulsion (B) is a flap of skin that is forcibly torn or separated. A laceration (C) is a jagged or irregular tear of the tissues due to trauma. An incision (D) is a clean cut with a sharp object. A contusion (E) is an injury involving bleeding into the tissues without breaking the skin.
- B
You should wash the skin with an antiseptic soap in a circular manner from the inside to the outside, not going back once you have moved further out. Up and down (A) is inappropriate direction. You would not use alcohol (C) or a disinfectant solution (E), and sterile gloves (D) are not necessary for this procedure.
- C
Venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) and rapid plasma regain (RPR) are both serological tests that detect syphilis. Hepatitis (A) detection utilizes a serological test. Mononucleosis (B) testing detects the heterophil antibody within 6 to 10 days of the disease. Rheumatoid arthritis (D) can be detected by testing for rheumatoid factor. Systemic lupus (E) diagnosis requires antinucleotide antibody.
- E
If a tear is noted, the assistant needs to replace the gloves. Putting tape over the tear (A) will not restore sterility. Continuing the procedure (D) is an unlikely option since most procedures require two hands. Involving a coworker (C) is unnecessary in a routine procedure. Alerting the physician (B) may not be needed if the physician is present for the procedure.
- E
Hemoglobin is measured by weight and is expressed in grams per deciliter (g/dl). A spirometer (A) is a device used to measure lung capacity by tracking the volume and flow of exhaled air. The specific gravity of urine (B) is part of the physical examination of urine. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, or ESR (C), measures the time it takes for red blood cells to settle in a specimen and is expressed in millimeters per hour (mm/hr); elevated times are associated with inflammatory processes. Hematocrit (D) is measured after centrifuging a specimen and is expressed as a percentage of red blood cells in a specimen; normal adult hematocrit values are 36–55 percent.