Regional adoption
This section marks which society first adopted a key innovation within each of the 11 major world regions – East Asia, Southeast Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, Southwest Asia, Europe, North Africa, sub-Saharan Africa, North America, South America and Oceania – beginning with the first overall to develop the technology.
Adoption of bureaucracy by world region
(Refers to the adoption of full-time administrative specialists)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Bronze Age Susa |
Southwest Asia |
early 4th millennium BCE |
Pre-dynastic Egypt |
North Africa |
mid-4th millennium BCE |
Indus Valley, urban period |
South Asia |
late 3rd millennium BCE |
Minoan Crete |
Europe |
early 2nd millennium BCE |
Shang dynasty |
East Asia |
late 2nd millennium BCE |
Baiyue kingdoms |
Southeast Asia |
4th century BCE |
Kangju Federation |
Central Asia |
2nd century BCE |
Teotihuacan |
North America |
3rd century CE |
Peru, late intermediate period |
South America |
13th century CE |
Ashanti Empire |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
18th century CE |
Colonial period Papua New Guinea, Orokaiva peoples |
Oceania |
18th century CE |
Adoption of state postal service by world region
(Refers to the adoption of dedicated communications infrastructure)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Achaemenid Empire |
Southwest Asia |
6th century BCE |
Qin Empire |
East Asia |
4th century BCE |
Mauryan Empire |
South Asia |
4th century BCE |
Ptolemaic kingdom |
North Africa |
3rd century BCE |
Roman Principate |
Europe |
1st century BCE |
Mongolian Empire |
Central Asia |
13th century CE |
Peru, Spanish colonial period |
South America |
16th century CE |
Ayutthaya kingdom |
Southeast Asia |
16th century CE |
Mississippi Valley, French colonial period |
North America |
17th century CE |
Innovation remained absent until modern period or evidence is unavailable for these regions |
Sub-Saharan Africa Oceania |
Adoption of a formalised law code by world region
(Refers to the adoption of a formal code of rules/procedures, usually but not always written)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Ur Kingdom dynasty III |
Southwest Asia |
late 3rd millennium BCE |
Old Kingdom Egypt |
North Africa |
early 2nd millennium BCE |
Minoan Crete |
Europe |
8th century BCE |
State of Chu |
East Asia |
5th century BCE |
Mauryan Empire |
South Asia |
4th century BCE |
Greco-Bactrian kingdom |
Central Asia |
3rd century BCE |
Funan kingdom |
Southeast Asia |
3rd century CE |
Wagadu kingdom of Ghana |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
11th century CE |
Killke period Inca |
South America |
13th century CE |
Aztec Empire |
North America |
15th century CE |
Kingdom of Hawaii, post-Kamehameha period |
Oceania |
19th century CE |
Adoption of calendars by world region
(Refers to the adoption of a formalised written system for marking time/seasons)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Early Bronze Age Susa |
Southwest Asia |
early 4th millennium BCE |
Early Dynastic Egypt |
North Africa |
late 4th millennium BCE |
China, Erlitou culture |
East Asia |
early 2nd millennium BCE |
Minoan Crete |
Europe |
mid-2nd millennium BCE |
Basin of Mexico, late classic period |
North America |
6th century BCE |
Mauryan Empire |
South Asia |
4th century BCE |
Baiyue kingdoms |
Southeast Asia |
3rd century BCE |
Greco-Bactrian kingdom |
Central Asia |
3rd century BCE |
Wagadu kingdom of Ghana |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
11th century CE |
Peru, Spanish colonial period |
South America |
16th century CE |
Innovation remained absent until modern period or evidence is unavailable for this region |
Oceania |
Adoption of scientific literature by world region
(Refers to the adoption of writing concerning mathematics, natural sciences or social sciences)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Early Bronze Age Susa |
Southwest Asia |
early 4th millennium BCE |
Early Dynastic Egypt |
North Africa |
late 4th millennium BCE |
Western Zhou dynasty |
East Asia |
late 2nd millennium BCE |
Roman Republic |
Europe |
6th century BCE |
Mauryan Empire |
South Asia |
4th century BCE |
Baiyue kingdoms |
Southeast Asia |
3rd century BCE |
Greco-Bactrian kingdom |
Central Asia |
3rd century BCE |
Mayan period Mesoamerica |
North America |
8th century CE |
Songhai Empire |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
16th century CE |
Kingdom of Hawaii, post-Kamehameha period |
Oceania |
19th century CE |
Innovation remained absent until modern period or evidence is unavailable for this region |
South America |
Adoption of fiction writing by world region
(Refers to the adoption of written fiction literature, including prose)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Old Kingdom Egypt |
North Africa |
mid-3rd millennium BCE |
Akkadian Empire |
Southwest Asia |
late 3rd millennium BCE |
Western Zhou dynasty |
East Asia |
late 2nd millennium BCE |
Roman Republic |
Europe |
6th century BCE |
Mauryan Empire |
South Asia |
4th century BCE |
Baiyue kingdoms |
Southeast Asia |
3rd century BCE |
Greco-Bactrian kingdom |
Central Asia |
3rd century BCE |
Wagadu kingdom of Ghana |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
11th century CE |
Peru, Spanish colonial period |
South America |
16th century CE |
Mississippi Valley, French colonial period |
North America |
17th century CE |
Innovation remained absent until modern period or evidence is unavailable for this region |
Oceania |
Adoption of monogamy by world region
(Refers to the adoption of monogamy as widely practised, either by law or custom)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Ur Kingdom city-state III |
Southwest Asia |
late 3rd millennium BCE |
New Kingdom Egypt |
North Africa |
mid-2nd millennium BCE |
Oaxaca Valley, Rosario culture |
North America |
8th century BCE |
Roman kingdom |
Europe |
8th century BCE |
Ganga Valley, Mahajanapada era |
South Asia |
7th century BCE |
Kalingga kingdom |
Southeast Asia |
6th century CE |
Colombia, Tairona peoples |
South America |
11th century CE |
Innovation remained absent until Central Asia modern period or evidence is East Asia unavailable for these regions Oceania |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
Adoption of rule by god-kings by world region
(Refers to the adoption of the idea that rulers are living gods, either by formal declaration or widespread belief)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Naqada period Egypt |
North Africa |
mid-4th millennium BCE |
Minoan Crete |
Europe |
early 2nd millennium BCE |
Qin Empire |
East Asia |
4th century BCE |
Seleucid kingdom |
Southwest Asia |
3rd century BCE |
Greco-Bactrian kingdom |
Central Asia |
3rd century BCE |
Satavahana Empire |
South Asia |
2nd century BCE |
Kofun kingdom |
East Asia |
3rd century CE |
Killke period Inca |
South America |
11th century CE |
Innovation remained absent until modern period or evidence is unavailable for these regions |
North America Sub-Saharan Africa Oceania |
Adoption of firearms by world region
(Refers to the adoption of hand-held gunpowder devices, such as muskets, pistols and rifles)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Yuan dynasty |
East Asia |
13th century CE |
Valois kingdom |
Europe |
14th century CE |
Ottoman Empire |
Southwest Asia |
15th century CE |
Ottoman Empire |
North Africa |
15th century CE |
Mamluk sultanate |
North Africa |
15th century CE |
Delhi sultanate |
South Asia |
15th century CE |
Mataram kingdom |
Southeast Asia |
16th century CE |
Oneota Mississippi Valley peoples |
North America |
16th century CE |
Spanish Empire |
South America |
16th century CE |
Khanate of Bukhara |
Central Asia |
17th century CE |
Ashanti kingdom |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
18th century CE |
Kamehameha’s kingdom Hawaii |
Oceania |
18th century CE |
Adoption of paper currency by world region
(Refers to the adoption of paper money as legal tender)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Western Han Empire |
East Asia |
3rd century BCE |
Delhi sultanate |
South Asia |
13th century CE |
Ilkhanate |
Central Asia |
13th century CE |
Papal States |
Europe |
17th century CE |
Mississippi Valley, French colonial period |
North America |
18th century CE |
Peru, Spanish colonial period |
South America |
18th century CE |
Rattanakosin kingdom |
Southeast Asia |
19th century CE |
Brooke Raj, colonial Borneo |
Oceania |
19th century CE |
Ottoman Empire |
Southwest Asia |
19th century CE |
Ottoman Empire |
North Africa |
19th century CE |
Innovation remained absent until modern period or evidence is unavailable for this region |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
Adoption of Irrigation systems by world region
(Refers to the adoption and widespread use of any hydraulic infrastructure, such as large reservoirs, cisterns, canals and aqueducts)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Naqada period Egypt |
North Africa |
early 4th millennium BCE |
Chalcolithic period Pakistan |
South Asia |
early 4th millennium BCE |
Bronze Age Susa |
Southwest Asia |
early 4th millennium BCE |
Sarazm peoples |
Central Asia |
mid-4th millennium BCE |
France, Beaker culture |
Europe |
late 4th millennium BCE |
Shang dynasty |
East Asia |
late 2nd millennium BCE |
Baiyue kingdoms |
Southeast Asia |
4th century BCE |
Peru, formative period culture |
South America |
3rd century CE |
Oaxaca, Monte Albán period |
North America |
4th century CE |
Jenné-jenno culture |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
5th century CE |
Big Island Hawaii, pre-unification period |
Oceania |
13th century CE |
Adoption of state-wide provision of drinking water by world region
(Refers to the adoption of publicly accessible sources of drinking water, such as public fountains, reservoirs and wells)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Indus Valley, urban period |
South Asia |
mid-3rd millennium BCE |
Bronze Age Canaanite city-states |
Southwest Asia |
late 3rd millennium BCE |
Iron Age Crete |
Europe |
early 1st millennium BCE |
Achaemenid Empire |
Central Asia |
6th century BCE |
Wei State, Warring States period |
East Asia |
5th century BCE |
Egypt, inter-occupation period |
North Africa |
5th century BCE |
Oaxaca, Monte Albán period |
North America |
4th century BCE |
Funan kingdom |
Southeast Asia |
3rd century CE |
Wari Empire |
South America |
7th century CE |
Hawaiian kingdom |
Oceania |
19th century CE |
Innovation remained absent until modern period or evidence is unavailable for this region |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
Adoption of public markets by world region
(Refers to the adoption of publicly accessible open spaces for commerce, congregation and information exchange)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Old Kingdom Egypt |
North Africa |
3rd millennium BCE |
Awan dynasty Elam |
Southwest Asia |
3rd millennium BCE |
Minoan Crete |
Europe |
2nd millennium BCE |
Kingdom of Wu, Warring States period |
East Asia |
8th century BCE |
Achaemenid Empire |
Central Asia |
6th century BCE |
Indo-Greek kingdom |
South Asia |
2nd century BCE |
Jenné-jenno culture |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
5th century CE |
Angkor kingdom |
Southeast Asia |
9th century CE |
Tairona cultures, Colombia |
South America |
11th century CE |
Mississippi Valley, French colonial period |
North America |
17th century CE |
Papua New Guinea, British colonial period |
Oceania |
19th century CE |
Adoption of state-run libraries by world region
(Refers to the adoption of publicly built infrastructure for holding and disseminating knowledge)
Society |
Region |
Approx. time of adoption |
Early Dynastic Egypt |
North Africa |
early 3rd millennium BCE |
Shang dynasty |
East Asia |
late 2nd millennium BCE |
Neo-Assyrian Empire |
Southwest Asia |
early 1st millennium BCE |
Roman kingdom |
Europe |
8th century BCE |
Seleucid Empire |
Central Asia |
3rd century BCE |
Kushan Empire |
South Asia |
1st century CE |
Funan kingdom |
Southeast Asia |
3rd century CE |
Jenné-jenno culture |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
13th century CE |
Innovation remained absent until modern period or evidence is North unavailable for these regions |
America South America Oceania |
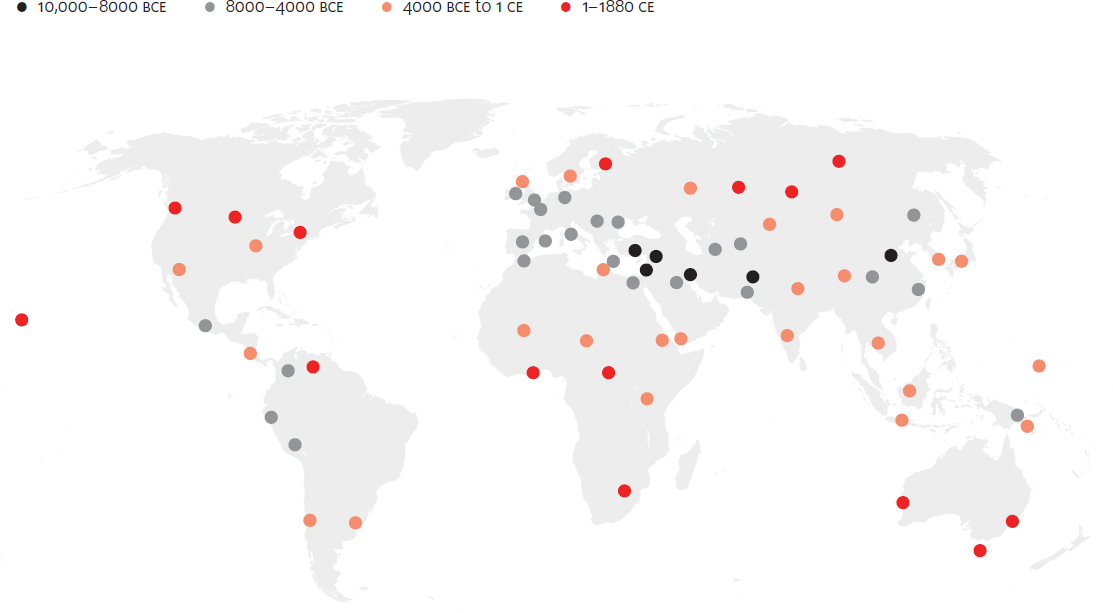
Spread of agriculture, 10,000 BCE to 1880 CE
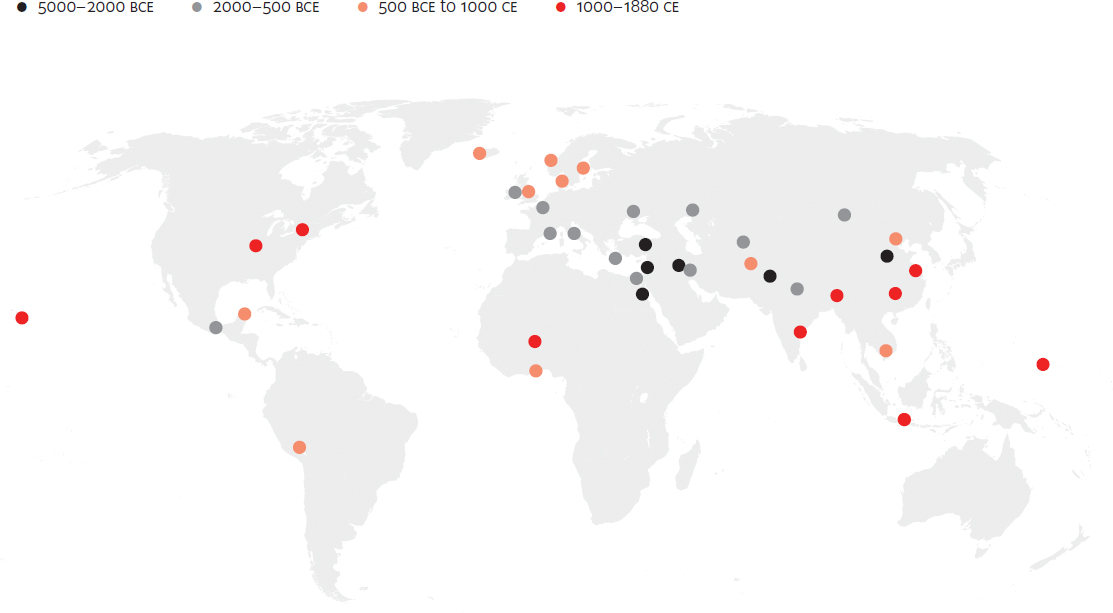
Spread of human sacrifice, 5000 BCE to 1880 CE
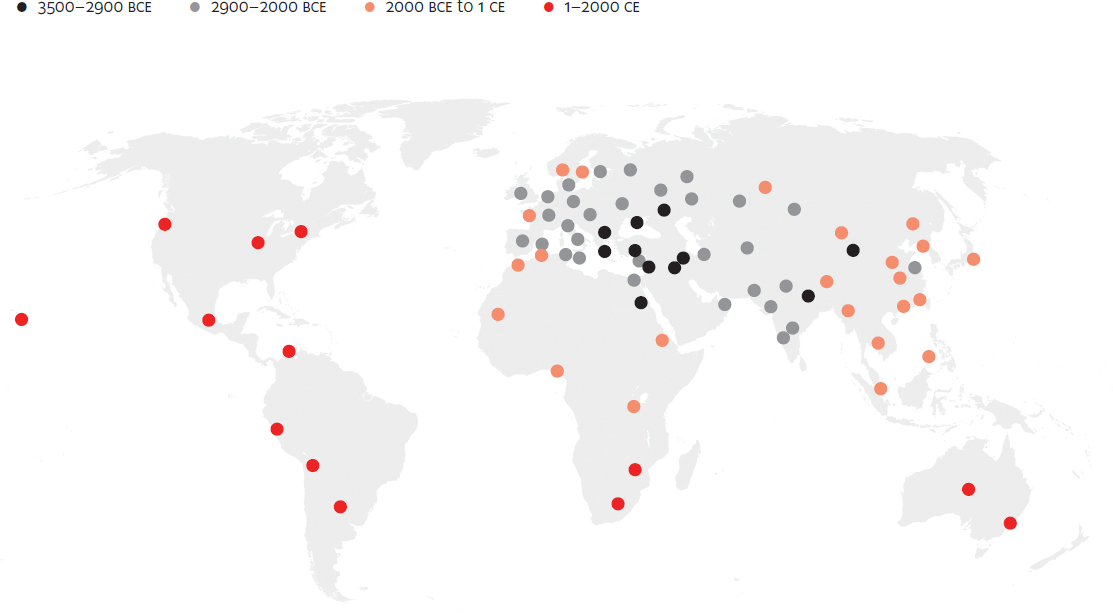
Spread of bronze, 3500 BCE to 2000 CE
Spread of writing, 3200 BCE to 1920 CE
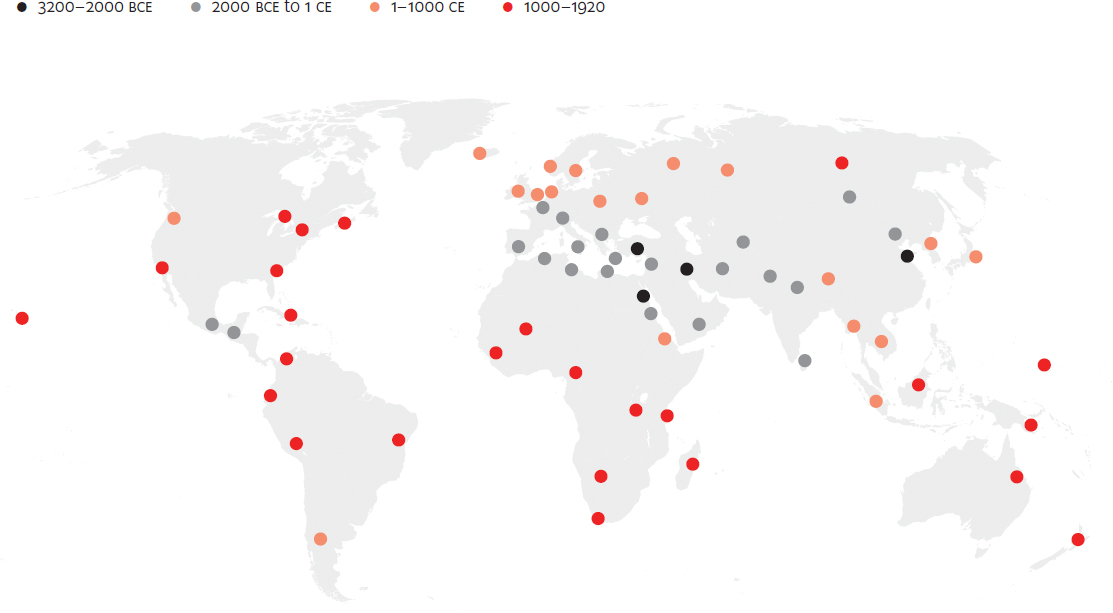
Spread of moralising religion, 2100 BCE to 1900 CE
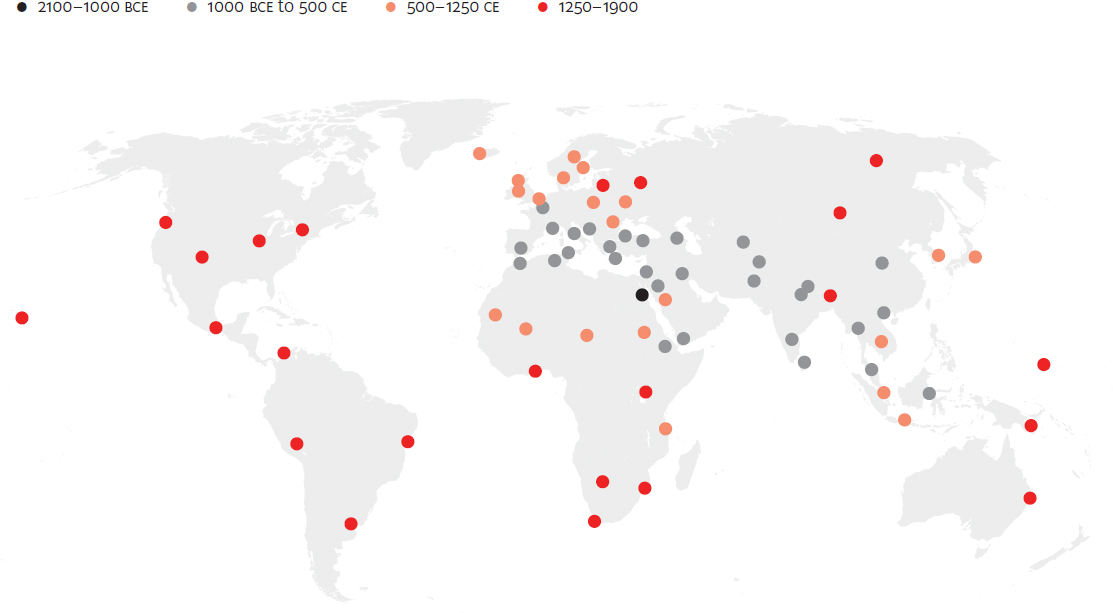
Spread of chariots, 2000 BCE to 1780 CE
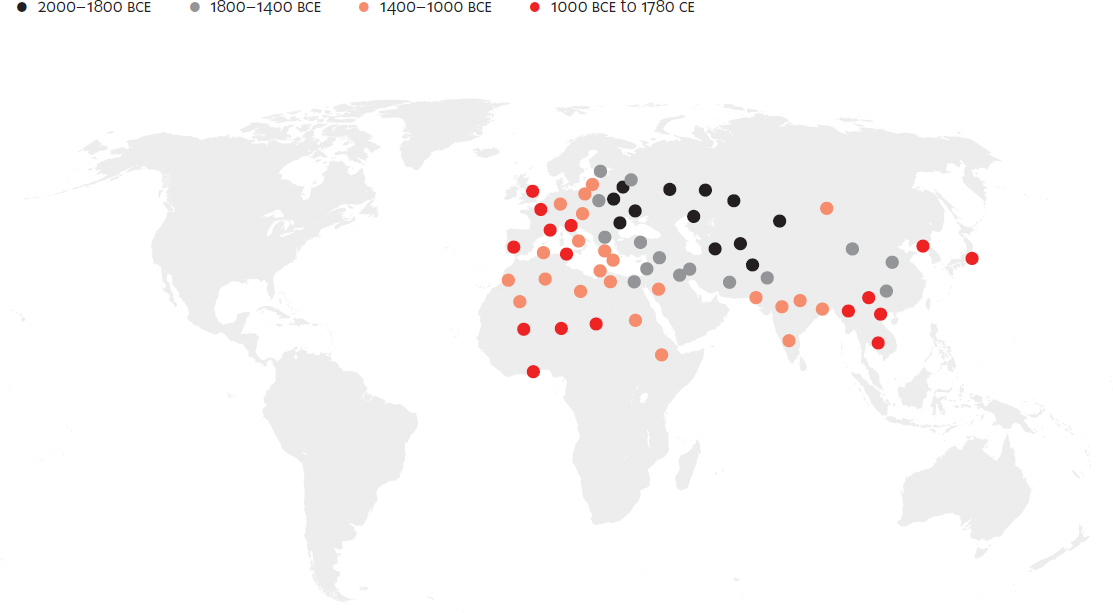
Spread of iron, 1400 BCE to 1870 CE
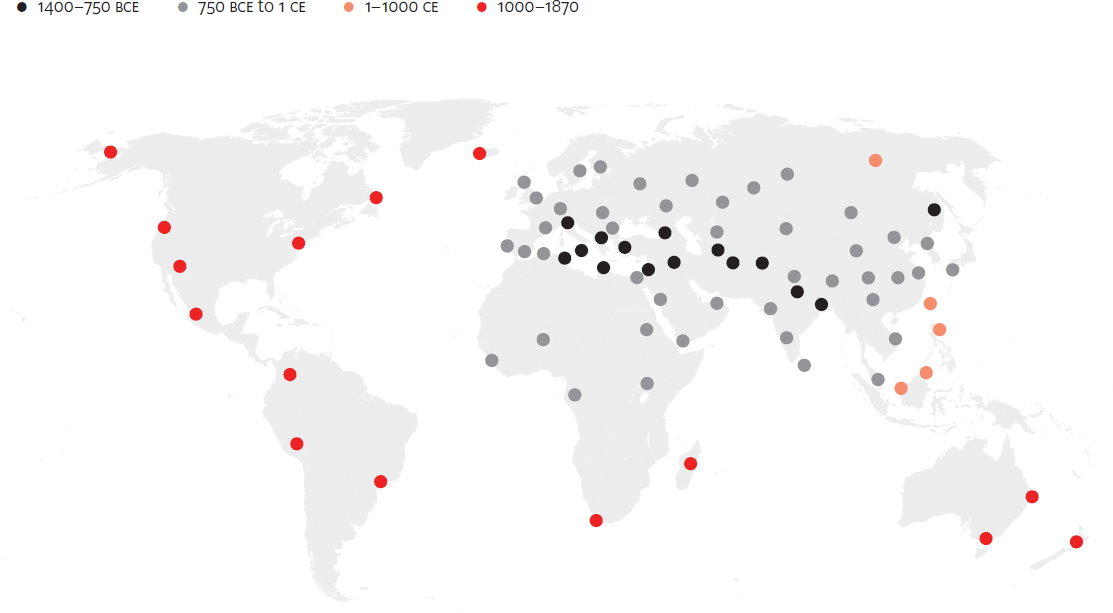
Spread of cavalry, 1000 BCE to 1870 CE
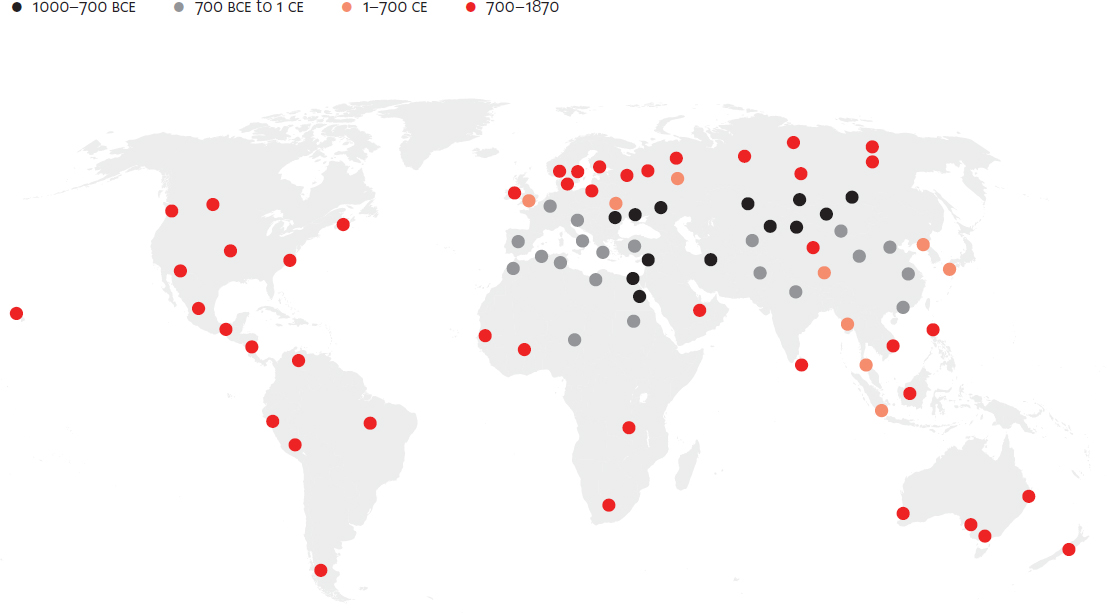
Spread of coinage, 600 BCE to 1900 CE
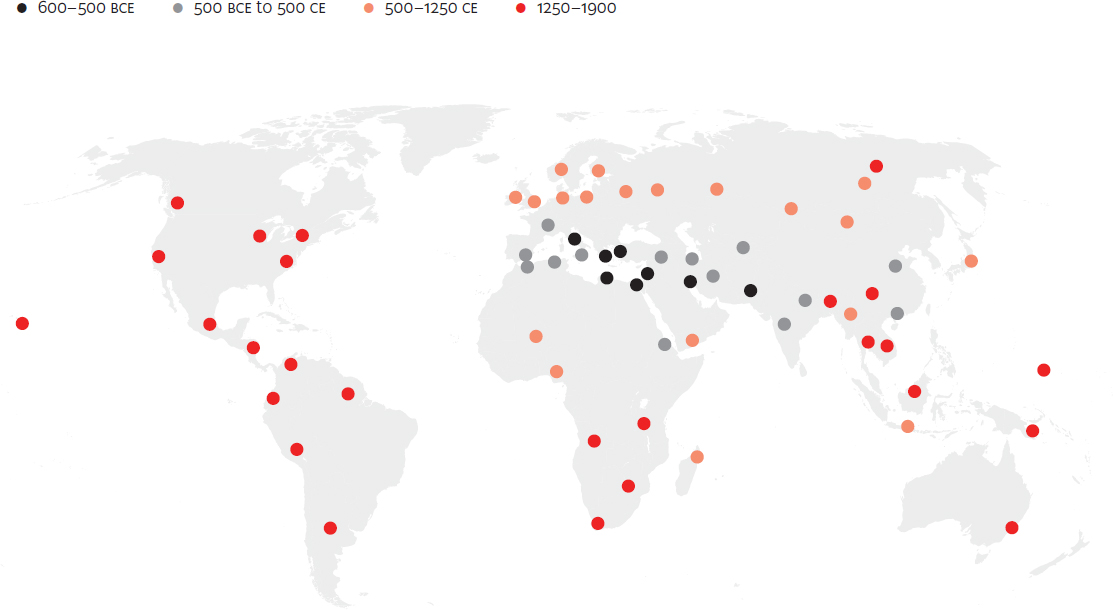
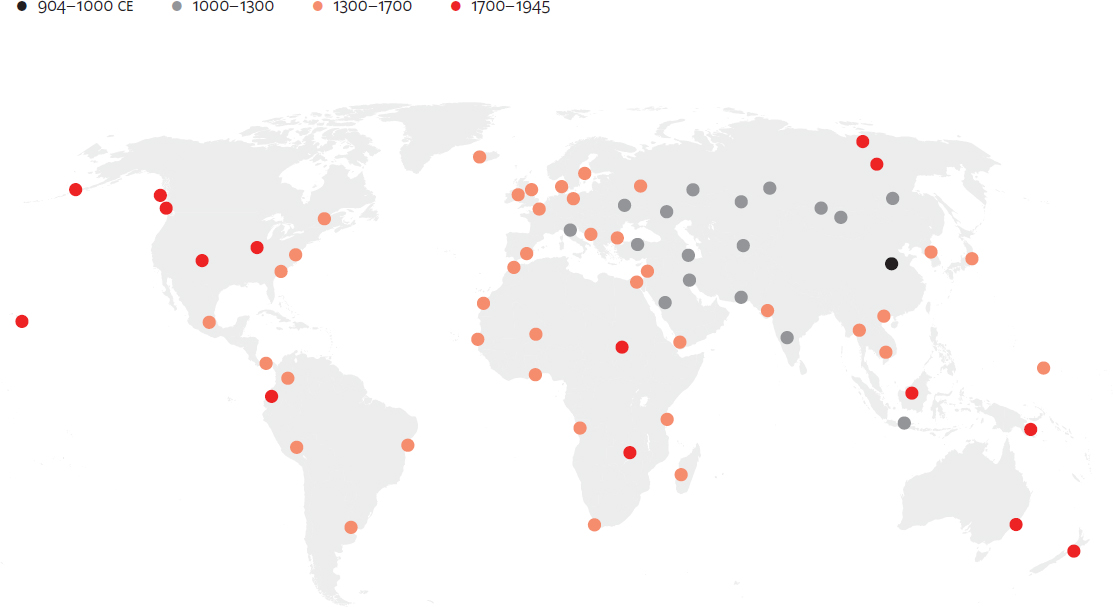
Spread of gunpowder, 904-1945 CE