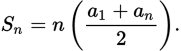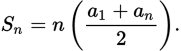
An arithmetic sequence is a sequence such as 5, 8, 11, 14, 17, . . . in which the difference between any two consecutive terms is the same. In this sequence, the difference is 3 (8 – 5 = 3; 11 – 8 = 3; 14 – 11 = 3, . . .). An easy way to find the nth term of such a sequence is to start with the first term and add the common difference n – 1 times. Here, the 5th term is 17, which can be obtained by taking the first term, 5, and adding the common difference, 3, four times: 5 + 4(3) = 17. In the same way, the 100th term is 5 + 99(3) = 5 + 297 = 302.
Key Fact Q2
If a1, a2, a3, . . . is an arithmetic sequence whose common difference is d, then an = a1 + (n – 1)d.
Key Fact Q3
If Sn represents the sum of the first n terms of the arithmetic sequence a1, a2, a3, . . ., then Sn is equal to n times the average of a1 and an: